
Glycoside hydrolase
Encyclopedia
Catalysis
Catalysis is the change in rate of a chemical reaction due to the participation of a substance called a catalyst. Unlike other reagents that participate in the chemical reaction, a catalyst is not consumed by the reaction itself. A catalyst may participate in multiple chemical transformations....
the hydrolysis
Hydrolysis
Hydrolysis is a chemical reaction during which molecules of water are split into hydrogen cations and hydroxide anions in the process of a chemical mechanism. It is the type of reaction that is used to break down certain polymers, especially those made by condensation polymerization...
of the glycosidic linkage to release smaller sugar
Sugar
Sugar is a class of edible crystalline carbohydrates, mainly sucrose, lactose, and fructose, characterized by a sweet flavor.Sucrose in its refined form primarily comes from sugar cane and sugar beet...
s. They are extremely common enzyme
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
s with roles in nature including degradation of biomass
Biomass
Biomass, as a renewable energy source, is biological material from living, or recently living organisms. As an energy source, biomass can either be used directly, or converted into other energy products such as biofuel....
such as cellulose
Cellulose
Cellulose is an organic compound with the formula , a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to over ten thousand β linked D-glucose units....
and hemicellulose
Hemicellulose
A hemicellulose is any of several heteropolymers , such as arabinoxylans, present along with cellulose in almost all plant cell walls. While cellulose is crystalline, strong, and resistant to hydrolysis, hemicellulose has a random, amorphous structure with little strength...
, in anti-bacterial defense strategies (e.g., lysozyme
Lysozyme
Lysozyme, also known as muramidase or N-acetylmuramide glycanhydrolase, are glycoside hydrolases, enzymes that damage bacterial cell walls by catalyzing hydrolysis of 1,4-beta-linkages between N-acetylmuramic acid and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine residues in a peptidoglycan and between...
), in pathogenesis
Pathogenesis
The pathogenesis of a disease is the mechanism by which the disease is caused. The term can also be used to describe the origin and development of the disease and whether it is acute, chronic or recurrent...
mechanisms (e.g., viral neuraminidase
Neuraminidase
Neuraminidase enzymes are glycoside hydrolase enzymes that cleave the glycosidic linkages of neuraminic acids. Neuraminidase enzymes are a large family, found in a range of organisms. The most commonly known neuraminidase is the viral neuraminidase, a drug target for the prevention of the spread...
s) and in normal cellular function (e.g., trimming mannosidase
Alpha-Mannosidase
alpha-Mannosidase is an enzyme involved in the cleavage of the alpha form of mannose.- Isozymes :Humans express the following three alpha-mannosidase isozymes:- Applications :...
s involved in N-linked glycoprotein biosynthesis
Biosynthesis
Biosynthesis is an enzyme-catalyzed process in cells of living organisms by which substrates are converted to more complex products. The biosynthesis process often consists of several enzymatic steps in which the product of one step is used as substrate in the following step...
). Together with glycosyltransferase
Glycosyltransferase
Glycosyltransferases are enzymes that act as a catalyst for the transfer of a monosaccharide unit from an activated nucleotide sugar to a glycosyl acceptor molecule, usually an alcohol....
s, glycosidases form the major catalytic machinery for the synthesis and breakage of glycosidic bonds.

Occurrence and importance
Glycoside hydrolases are found in essentially all domains of life. In prokaryotes, they are found both as intracellular and extracellular enzymes that are largely involved in nutrient acquisition. One of the important occurrences of glycoside hydrolases in bacteria is the enzyme beta-galactosidaseBeta-galactosidase
β-galactosidase, also called beta-gal or β-gal, is a hydrolase enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of β-galactosides into monosaccharides. Substrates of different β-galactosidases include ganglioside GM1, lactosylceramides, lactose, and various glycoproteins...
(LacZ), which is involved in regulation of expression of the lac operon
Lac operon
The lac operon is an operon required for the transport and metabolism of lactose in Escherichia coli and some other enteric bacteria. It consists of three adjacent structural genes, lacZ, lacY and lacA. The lac operon is regulated by several factors including the availability of glucose and of...
in E. coli. In higher organisms glycoside hydrolases are found within the endoplasmic reticulum
Endoplasmic reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum is an organelle of cells in eukaryotic organisms that forms an interconnected network of tubules, vesicles, and cisternae...
and Golgi apparatus
Golgi apparatus
The Golgi apparatus is an organelle found in most eukaryotic cells. It was identified in 1898 by the Italian physician Camillo Golgi, after whom the Golgi apparatus is named....
where they are involved in processing of N-linked glycoproteins, and in the lysozome as enzymes involved in the degradation of carbohydrate structures. Deficiency in specific lysozomal glycoside hydrolases can lead to a range of lysosomal storage disorders that result in developmental problems or death. Glycoside hydrolases are found in the intestinal tract and in saliva
Saliva
Saliva , referred to in various contexts as spit, spittle, drivel, drool, or slobber, is the watery substance produced in the mouths of humans and most other animals. Saliva is a component of oral fluid. In mammals, saliva is produced in and secreted from the three pairs of major salivary glands,...
where they degrade complex carbohydrates such as lactose
Lactose
Lactose is a disaccharide sugar that is found most notably in milk and is formed from galactose and glucose. Lactose makes up around 2~8% of milk , although the amount varies among species and individuals. It is extracted from sweet or sour whey. The name comes from or , the Latin word for milk,...
, starch
Starch
Starch or amylum is a carbohydrate consisting of a large number of glucose units joined together by glycosidic bonds. This polysaccharide is produced by all green plants as an energy store...
, sucrose
Sucrose
Sucrose is the organic compound commonly known as table sugar and sometimes called saccharose. A white, odorless, crystalline powder with a sweet taste, it is best known for its role in human nutrition. The molecule is a disaccharide composed of glucose and fructose with the molecular formula...
and trehalose
Trehalose
Trehalose, also known as mycose or tremalose, is a natural alpha-linked disaccharide formed by an α,α-1,1-glucoside bond between two α-glucose units. In 1832, H.A.L. Wiggers discovered trehalose in an ergot of rye, and in 1859 Marcellin Berthelot isolated it from trehala manna, a substance made...
. In the gut they are found as glycosylphosphatidyl anchored enzymes on endothelial cells. The enzyme lactase
Lactase
Lactase , a part of the β-galactosidase family of enzymes, is a glycoside hydrolase involved in the hydrolysis of the disaccharide lactose into constituent galactose and glucose monomers...
is required for degradation of the milk sugar lactose and is present at high levels in infants, but in most populations will decrease after weaning or during infancy, potentially leading to lactose intolerance
Lactose intolerance
Lactose intolerance, also called lactase deficiency or hypolactasia, is the inability to digest and metabolize lactose, a sugar found in milk...
in adulthood. The enzyme O-GlcNAcase is involved in removal of N-acetylglucoamine groups from serine and threonine residues in the cytoplasm and nucleus of the cell. The glycoside hydrolases are involved in the biosynthesis
Biosynthesis
Biosynthesis is an enzyme-catalyzed process in cells of living organisms by which substrates are converted to more complex products. The biosynthesis process often consists of several enzymatic steps in which the product of one step is used as substrate in the following step...
and degradation of glycogen
Glycogen
Glycogen is a molecule that serves as the secondary long-term energy storage in animal and fungal cells, with the primary energy stores being held in adipose tissue...
in the body.
Classification
Glycoside hydrolases are classified into EC 3.2.1 as enzymes catalyzing the hydrolysis of O- or S-glycosides. Glycoside hydrolases can also be classified according to the stereochemical outcome of the hydrolysis reaction: thus they can be classified as either retaining or inverting enzymes. Glycoside hydrolases can also be classified as exo or endo acting, dependent upon whether they act at the (usually non-reducing) end or in the middle, respectively, of an oligo/polysaccharide chain. Glycoside hydrolases may also be classified by sequence or structure based methods.Sequence-based classification
Sequence-based classifications are among the most powerful predictive method for suggesting function for newly sequenced enzymes for which function has not been biochemically demonstrated. A classification system for glycosyl hydrolases, based on sequence similarity, has led to the definition of more than 100 different families. This classification is available on the CAZy (CArbohydrate-Active EnZymes) web site. The database provides a series of regularly updated sequence based classification that allow reliable prediction of mechanism (retaining/inverting), active site residues and possible substrates. The online database is supported by CAZypedia, an online encyclopedia of carbohydrate active enzymes. Based on three dimensional structural similarities, the sequence-based families have been classified into 'clans' of related structure. Recent progress in glycosidase sequence analysis and 3D structure comparison has allowed the proposal of an extended hierarchical classification of the glycoside hydrolases.Inverting glycoside hydrolases
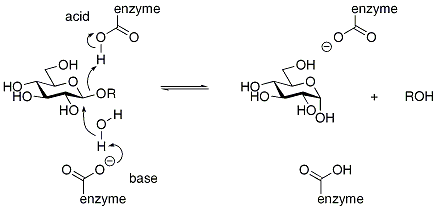
Inverting enzymes utilize two enzymic residues, typically carboxylate residues, that act as acidAcid
An acid is a substance which reacts with a base. Commonly, acids can be identified as tasting sour, reacting with metals such as calcium, and bases like sodium carbonate. Aqueous acids have a pH of less than 7, where an acid of lower pH is typically stronger, and turn blue litmus paper red...
and base
Base (chemistry)
For the term in genetics, see base A base in chemistry is a substance that can accept hydrogen ions or more generally, donate electron pairs. A soluble base is referred to as an alkali if it contains and releases hydroxide ions quantitatively...
respectively, as shown below for a β-glucosidase:
Retaining glycoside hydrolases
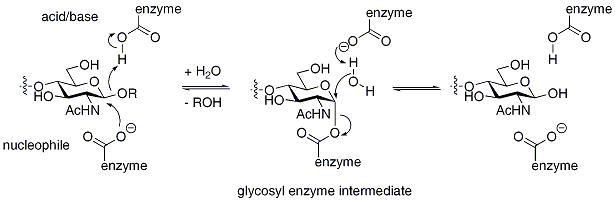
Retaining glycosidases operate through a two-step mechanism, with each step resulting in inversionWalden inversion
Walden inversion is the inversion of a chiral center in a molecule in a chemical reaction. Since a molecule can form two enantiomers around a chiral center, the Walden inversion converts the configuration of the molecule from one enantiomeric form to the other. For example, in a SN2 reaction,...
, for a net retention of stereochemistry. Again, two residues are involved, which are usually enzyme-borne carboxylates. One acts as a nucleophile
Nucleophile
A nucleophile is a species that donates an electron-pair to an electrophile to form a chemical bond in a reaction. All molecules or ions with a free pair of electrons can act as nucleophiles. Because nucleophiles donate electrons, they are by definition Lewis bases.Nucleophilic describes the...
and the other as an acid/base. In the first step the nucleophile attacks the anomer
Anomer
In carbohydrate chemistry, an anomer is a special type of epimer. It is one of two stereoisomers of a cyclic saccharide that differs only in its configuration at the hemiacetal or hemiketal carbon, also called the anomeric carbon. Anomerization is the process of conversion of one anomer to the other...
ic centre, resulting in the formation of a glycosyl enzyme intermediate, with acidic assistance provided by the acidic carboxylate. In the second step the now deprotoned acidic carboxylate acts as a base and assists a nucleophilic water to hydrolyze the glycosyl enzyme intermediate, giving the hydrolyzed product. The mechanism is illustrated below for hen egg white lysozyme
Lysozyme
Lysozyme, also known as muramidase or N-acetylmuramide glycanhydrolase, are glycoside hydrolases, enzymes that damage bacterial cell walls by catalyzing hydrolysis of 1,4-beta-linkages between N-acetylmuramic acid and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine residues in a peptidoglycan and between...
.
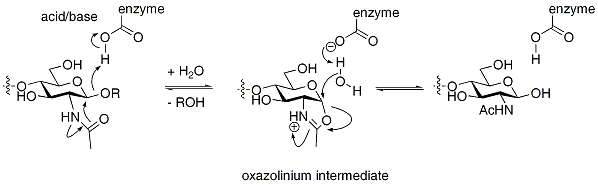
An alternative mechanism for hydrolysis with retention of stereochemistry can occur that proceeds through a nucleophilic residue that is bound to the substrate, rather than being attached to the enzyme. Such mechanisms are common for certain N-acetylhexosaminidases, which have an acetamido group capable of neighboring group participation to form an intermediate oxazoline or oxazolinium ion. Again, the mechanism proceeds in two steps through individual inversions to lead to a net retention of configuration.
Nomenclature and examples
Glycoside hydrolases are typically named after the substrate that they act upon. Thus glucosidases catalyze the hydrolysis of glucosides and xylanaseXylanase
Xylanase is the name given to a class of enzymes which degrade the linear polysaccharide beta-1,4-xylan into xylose, thus breaking down hemicellulose, one of the major components of plant cell walls....
s catalyze the cleavage of the xylose based homopolymer xylan. Other examples include lactase
Lactase
Lactase , a part of the β-galactosidase family of enzymes, is a glycoside hydrolase involved in the hydrolysis of the disaccharide lactose into constituent galactose and glucose monomers...
, amylase
Amylase
Amylase is an enzyme that catalyses the breakdown of starch into sugars. Amylase is present in human saliva, where it begins the chemical process of digestion. Food that contains much starch but little sugar, such as rice and potato, taste slightly sweet as they are chewed because amylase turns...
, chitinase
Chitinase
Chitinases are hydrolytic enzymes that break down glycosidic bonds in chitin. As chitin is a component of the cell walls of fungi and exoskeletal elements of some animals , chitinases are generally found in organisms that either need to reshape their own chitin or dissolve and digest the chitin of...
, sucrase
Sucrase
Sucrase is the name given to a number of enzymes that catalyze the hydrolysis of sucrose to fructose and glucose. The enzyme invertase, which occurs more commonly in plants, also hydrolyzes sucrose but by a different mechanism.-Physiology:...
, maltase
Maltase
Maltase is an enzyme that breaks down the disaccharide maltose. Maltase is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of the disaccharide maltose to the simple sugar glucose. This enzyme is found in plants, bacteria, and yeast. Then there is what is called Acid maltase deficiency...
, neuraminidase
Neuraminidase
Neuraminidase enzymes are glycoside hydrolase enzymes that cleave the glycosidic linkages of neuraminic acids. Neuraminidase enzymes are a large family, found in a range of organisms. The most commonly known neuraminidase is the viral neuraminidase, a drug target for the prevention of the spread...
, invertase
Invertase
Invertase is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of sucrose . The resulting mixture of fructose and glucose is called inverted sugar syrup. Related to invertases are sucrases. Invertases and sucrases hydrolyze sucrose to give the same mixture of glucose and fructose...
, hyaluronidase
Hyaluronidase
The hyaluronidases are a family of enzymes that degrade hyaluronic acid.In humans, there are six associated genes, including HYAL1, HYAL2, HYAL3, and PH-20/SPAM1.-Use as a drug:...
and lysozyme
Lysozyme
Lysozyme, also known as muramidase or N-acetylmuramide glycanhydrolase, are glycoside hydrolases, enzymes that damage bacterial cell walls by catalyzing hydrolysis of 1,4-beta-linkages between N-acetylmuramic acid and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine residues in a peptidoglycan and between...
.
Uses
Glycoside hydrolases have a variety of uses including degradation of plant materials (e.g., cellulases for degrading cellulose to glucose, which can be used for ethanolEthanol
Ethanol, also called ethyl alcohol, pure alcohol, grain alcohol, or drinking alcohol, is a volatile, flammable, colorless liquid. It is a psychoactive drug and one of the oldest recreational drugs. Best known as the type of alcohol found in alcoholic beverages, it is also used in thermometers, as a...
production), in the food industry
Food industry
The food production is a complex, global collective of diverse businesses that together supply much of the food energy consumed by the world population...
(invertase
Invertase
Invertase is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of sucrose . The resulting mixture of fructose and glucose is called inverted sugar syrup. Related to invertases are sucrases. Invertases and sucrases hydrolyze sucrose to give the same mixture of glucose and fructose...
for manufacture of invert sugar, amylase
Amylase
Amylase is an enzyme that catalyses the breakdown of starch into sugars. Amylase is present in human saliva, where it begins the chemical process of digestion. Food that contains much starch but little sugar, such as rice and potato, taste slightly sweet as they are chewed because amylase turns...
for production of maltodextrins), and in the paper and pulp industry (xylanase
Xylanase
Xylanase is the name given to a class of enzymes which degrade the linear polysaccharide beta-1,4-xylan into xylose, thus breaking down hemicellulose, one of the major components of plant cell walls....
s for removing hemicelluloses from paper pulp). Cellulases are added to detergents for the washing of cotton fabrics and assist in the maintenance of colours through removing microfibres that are raised from the surface of threads during wear.
In organic chemistry
Organic chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the scientific study of the structure, properties, composition, reactions, and preparation of carbon-based compounds, hydrocarbons, and their derivatives...
, glycoside hydrolases can be used as synthetic catalysts to form glycosidic bonds through either reverse hydrolysis (kinetic approach) where the equilibrium position is reversed; or by transglycosylation (kinetic approach) whereby retaining glycoside hydrolases can catalyze the transfer of a glycosyl moiety from an activated glycoside to an acceptor alcohol to afford a new glycoside.
Mutant glycoside hydrolases termed glycosynthases have been developed that can achieve the synthesis of glycosides in high yield from activated glycosyl donors such as glycosyl fluorides. Glycosynthases are typically formed from retaining glycoside hydrolases by site-directed mutagenesis of the enzymic nucleophile to some other less nucleophilic group, such as alanine or glycine. Another group of mutant glycoside hydrolases termed thioglycoligases can be formed by site-directed mutagenesis of the acid-base residue of a retaining glycoside hydrolase. Thioglycoligases catalyze the condensation of activated glycosides and various thiol containing acceptors.
Inhibitors
Many compounds are known that can act to inhibit the action of a glycoside hydrolase. Nitrogen-containing, 'sugar-shaped' heterocycles have been found in natureNatural product
A natural product is a chemical compound or substance produced by a living organism - found in nature that usually has a pharmacological or biological activity for use in pharmaceutical drug discovery and drug design...
, including deoxynojirimycin, swainsonine
Swainsonine
Swainsonine is an indolizine alkaloid. It is a potent inhibitor of Golgi alpha-mannosidase II, an immunomodulator, and a potential chemotherapy drug...
, australine and castanospermine
Castanospermine
Castanospermine is an indolizine alkaloid first isolated from the seeds of Castanospermum australe. It is a potent inhibitor of some glucosidase enzymes and has antiviral activity....
. From these natural templates many other inhibitors have been developed, including isofagomine and deoxygalactonojirimycin, and various unsaturated compounds such as PUGNAc. Inhibitors that are in clinical use include the anti-diabetic drug
Anti-diabetic drug
Anti-diabetic medications treat diabetes mellitus by lowering glucose levels in the blood. With the exceptions of insulin, exenatide, and pramlintide, all are administered orally and are thus also called oral hypoglycemic agents or oral antihyperglycemic agents...
s acarbose
Acarbose
Acarbose is an anti-diabetic drug used to treat type 2 diabetes mellitus and, in some countries, prediabetes. It is a generic sold in Europe and China as Glucobay , in North America as Precose , and in Canada as Prandase...
and miglitol, and the antiviral drug
Antiviral drug
Antiviral drugs are a class of medication used specifically for treating viral infections. Like antibiotics for bacteria, specific antivirals are used for specific viruses...
s oseltamivir
Oseltamivir
Oseltamivir INN , an antiviral drug, slows the spread of influenza virus between cells in the body by stopping the virus from chemically cutting ties with its host cell; median time to symptom alleviation is reduced by 0.5–1 day. The drug is sold under the trade name Tamiflu, and is taken orally...
and zanamivir. Some proteins have been found to act as glycoside hydrolase inhibitors.
See also
- Mucopolysaccharidoses
- Glucosidase
- LysozymeLysozymeLysozyme, also known as muramidase or N-acetylmuramide glycanhydrolase, are glycoside hydrolases, enzymes that damage bacterial cell walls by catalyzing hydrolysis of 1,4-beta-linkages between N-acetylmuramic acid and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine residues in a peptidoglycan and between...
- GlycosyltransferaseGlycosyltransferaseGlycosyltransferases are enzymes that act as a catalyst for the transfer of a monosaccharide unit from an activated nucleotide sugar to a glycosyl acceptor molecule, usually an alcohol....
- Glycoside hydrolase family 1
- Clans of glycoside hydrolases
- Hierarchical classification of the TIM-barrel type glycoside hydrolases

