
Grand Banks
Encyclopedia
Plateau
In geology and earth science, a plateau , also called a high plain or tableland, is an area of highland, usually consisting of relatively flat terrain. A highly eroded plateau is called a dissected plateau...
s southeast of Newfoundland on the North America
North America
North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas...
n continental shelf
Continental shelf
The continental shelf is the extended perimeter of each continent and associated coastal plain. Much of the shelf was exposed during glacial periods, but is now submerged under relatively shallow seas and gulfs, and was similarly submerged during other interglacial periods. The continental margin,...
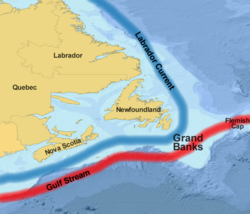
. These areas are relatively shallow, ranging from 80 to 330 ft (24.4 to 100.6 m) in depth. The cold Labrador Current
Labrador Current
The Labrador Current is a cold current in the North Atlantic Ocean which flows from the Arctic Ocean south along the coast of Labrador and passes around Newfoundland, continuing south along the east coast of Nova Scotia...
mixes with the warm waters of the Gulf Stream
Gulf Stream
The Gulf Stream, together with its northern extension towards Europe, the North Atlantic Drift, is a powerful, warm, and swift Atlantic ocean current that originates at the tip of Florida, and follows the eastern coastlines of the United States and Newfoundland before crossing the Atlantic Ocean...
here.
The mixing of these waters and the shape of the ocean bottom lifts nutrients to the surface. These conditions helped to create one of the richest fishing
Fishing
Fishing is the activity of trying to catch wild fish. Fish are normally caught in the wild. Techniques for catching fish include hand gathering, spearing, netting, angling and trapping....
grounds in the world. Fish
Fish
Fish are a paraphyletic group of organisms that consist of all gill-bearing aquatic vertebrate animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish, as well as various extinct related groups...
species include Atlantic cod
Atlantic cod
The Atlantic cod, Gadus morhua, is a well-known demersal food fish belonging to the family Gadidae. It is also commercially known as cod, codling or haberdine....
, sword fish, haddock
Haddock
The haddock , also known as the offshore hake, is a marine fish distributed on both sides of the North Atlantic. Haddock is a popular food fish and is widely fished commercially....
, and capelin
Capelin
The capelin or caplin, Mallotus villosus, is a small forage fish of the smelt family found in the Atlantic and Arctic oceans. In summer, it grazes on dense swarms of plankton at the edge of the ice shelf. Larger capelin also eat a great deal of krill and other crustaceans...
. Shellfish
Shellfish
Shellfish is a culinary and fisheries term for exoskeleton-bearing aquatic invertebrates used as food, including various species of molluscs, crustaceans, and echinoderms. Although most kinds of shellfish are harvested from saltwater environments, some kinds are found only in freshwater...
include scallop
Scallop
A scallop is a marine bivalve mollusk of the family Pectinidae. Scallops are a cosmopolitan family, found in all of the world's oceans. Many scallops are highly prized as a food source...
and lobster
Lobster
Clawed lobsters comprise a family of large marine crustaceans. Highly prized as seafood, lobsters are economically important, and are often one of the most profitable commodities in coastal areas they populate.Though several groups of crustaceans are known as lobsters, the clawed lobsters are most...
. The area also supports large colonies of sea birds such as Northern Gannet
Northern Gannet
The Northern Gannet is a seabird and is the largest member of the gannet family, Sulidae.- Description :Young birds are dark brown in their first year, and gradually acquire more white in subsequent seasons until they reach maturity after five years.Adults are long, weigh and have a wingspan...
s, shearwater
Shearwater
Shearwaters are medium-sized long-winged seabirds. There are more than 30 species of shearwaters, a few larger ones in the genus Calonectris and many smaller species in the genus Puffinus...
s, and sea ducks and various sea mammal
Mammal
Mammals are members of a class of air-breathing vertebrate animals characterised by the possession of endothermy, hair, three middle ear bones, and mammary glands functional in mothers with young...
s such as seals, dolphin
Dolphin
Dolphins are marine mammals that are closely related to whales and porpoises. There are almost forty species of dolphin in 17 genera. They vary in size from and , up to and . They are found worldwide, mostly in the shallower seas of the continental shelves, and are carnivores, mostly eating...
s, and whale
Whale
Whale is the common name for various marine mammals of the order Cetacea. The term whale sometimes refers to all cetaceans, but more often it excludes dolphins and porpoises, which belong to suborder Odontoceti . This suborder also includes the sperm whale, killer whale, pilot whale, and beluga...
s.
In addition to the effects on nutrients, the mixing of the cold and warm currents often causes fog
Fog
Fog is a collection of water droplets or ice crystals suspended in the air at or near the Earth's surface. While fog is a type of stratus cloud, the term "fog" is typically distinguished from the more generic term "cloud" in that fog is low-lying, and the moisture in the fog is often generated...
in the area. It is also noted for its proximity to the wreck of the RMS Titanic, and thus the launching point of Titanic shipwreck expeditions.
History
Several navigators, including BasqueBasque people
The Basques as an ethnic group, primarily inhabit an area traditionally known as the Basque Country , a region that is located around the western end of the Pyrenees on the coast of the Bay of Biscay and straddles parts of north-central Spain and south-western France.The Basques are known in the...
fishermen, are claimed to have fished these waters in the 15th century. In the 15th century some texts refer to a land called Bacalao
Bacalao
Bacallao was a phantom island depicted on several early 16th century maps and nautical charts. The name first appears on a chart in 1508, but there are earlier accounts of Bacalao...
, the land of the codfish, which is possibly Newfoundland. However, it was not until John Cabot
John Cabot
John Cabot was an Italian navigator and explorer whose 1497 discovery of parts of North America is commonly held to have been the first European encounter with the continent of North America since the Norse Vikings in the eleventh century...
reached the New World in 1497 that the existence of these fishing grounds became generally known in Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
. Ships from France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
, Spain
Spain
Spain , officially the Kingdom of Spain languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Spain's official name is as follows:;;;;;;), is a country and member state of the European Union located in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula...
, Portugal
Portugal
Portugal , officially the Portuguese Republic is a country situated in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula. Portugal is the westernmost country of Europe, and is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the West and South and by Spain to the North and East. The Atlantic archipelagos of the...
, and England
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Scotland to the north and Wales to the west; the Irish Sea is to the north west, the Celtic Sea to the south west, with the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south separating it from continental...
came to fish these waters. These fish stocks were also important for the early economies of eastern Canada
Canada
Canada is a North American country consisting of ten provinces and three territories. Located in the northern part of the continent, it extends from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west, and northward into the Arctic Ocean...
and New England
New England
New England is a region in the northeastern corner of the United States consisting of the six states of Maine, New Hampshire, Vermont, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, and Connecticut...
.
On 18 November 1929, a major earthquake
Earthquake
An earthquake is the result of a sudden release of energy in the Earth's crust that creates seismic waves. The seismicity, seismism or seismic activity of an area refers to the frequency, type and size of earthquakes experienced over a period of time...
(known as the 1929 Grand Banks earthquake
1929 Grand Banks earthquake
The 1929 Grand Banks earthquake, also called the Laurentian Slope earthquake and the South Shore Disaster, was a magnitude 7.2 earthquake that occurred on November 18, 1929 in the Atlantic Ocean off the south coast of Newfoundland in the Laurentian Slope Seismic Zone.The earthquake was centred on...
) on the southwestern part of the Grand Banks bordering the Laurentian Channel caused an underwater landslide which resulted in extensive damage to transatlantic cable
Transatlantic cable
Transatlantic cable may refer to:* Transatlantic telegraph cable* Transatlantic telephone cable* Other transatlantic submarine communications cable...
s and generated a rare Atlantic tsunami
Tsunami
A tsunami is a series of water waves caused by the displacement of a large volume of a body of water, typically an ocean or a large lake...
that struck the south coast of Newfoundland and eastern Cape Breton Island
Cape Breton Island
Cape Breton Island is an island on the Atlantic coast of North America. It likely corresponds to the word Breton, the French demonym for Brittany....
claiming 28 lives in the Burin Peninsula
Burin Peninsula
The Burin Peninsula is a Canadian peninsula located on the south coast of the island of Newfoundland in the province of Newfoundland and Labrador....
.
Technological advances in fishing such as large factory ship
Factory ship
A factory ship, also known as a fish processing vessel, is a large ocean-going vessel with extensive on-board facilities for processing and freezing caught fish...
s and sonar
Sonar
Sonar is a technique that uses sound propagation to navigate, communicate with or detect other vessels...
, as well as geopolitical disputes over territorial sea and exclusive economic zone
Exclusive Economic Zone
Under the law of the sea, an exclusive economic zone is a seazone over which a state has special rights over the exploration and use of marine resources, including production of energy from water and wind. It stretches from the seaward edge of the state's territorial sea out to 200 nautical...
(EEZ) boundaries, have led to overfishing
Overfishing
Overfishing occurs when fishing activities reduce fish stocks below an acceptable level. This can occur in any body of water from a pond to the oceans....
and a serious decline in the fish stock
Fish stock
Fish stocks are subpopulations of a particular species of fish, for which intrinsic parameters are the only significant factors in determining population dynamics, while extrinsic factors are considered to be insignificant.-The stock concept:All species have geographic limits to their...
s of the Grand Banks from around 1990. The fishery-based economy of Newfoundland and Labrador
Newfoundland and Labrador
Newfoundland and Labrador is the easternmost province of Canada. Situated in the country's Atlantic region, it incorporates the island of Newfoundland and mainland Labrador with a combined area of . As of April 2011, the province's estimated population is 508,400...
has been in a severe crisis since the 1990s.
Canada's EEZ currently occupies the majority of the Grand Banks except for the lucrative "nose" (eastern extremity, near the Flemish Cap
Flemish Cap
The Flemish Cap is an area of shallow waters in the north Atlantic Ocean centered roughly at 47° north, 45° west or about 350 miles east of St. John's, Newfoundland and Labrador....
) and "tail" (southern extremity) of the fishing bank. The Treaty of Paris (1783)
Treaty of Paris (1783)
The Treaty of Paris, signed on September 3, 1783, ended the American Revolutionary War between Great Britain on the one hand and the United States of America and its allies on the other. The other combatant nations, France, Spain and the Dutch Republic had separate agreements; for details of...
gave the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
shared rights to fish in these waters, but that section of the Treaty is no longer in force. The French territory Saint Pierre and Miquelon Exclusive Economic Zone occupies a pin-shaped section at the west edge of the Grand Banks, with the 22km radius head of the pin surrounding the islands and the needle heading south for 348km.
Research
Canada is currently performing the hydrographic and geological surveys necessary for claiming the entire continental shelf off eastern Canada, under the auspices of the latest United Nations Convention on the Law of the SeaUnited Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea
The United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea , also called the Law of the Sea Convention or the Law of the Sea treaty, is the international agreement that resulted from the third United Nations Conference on the Law of the Sea , which took place from 1973 through 1982...
. Once this aspect of UNCLOS is ratified, Canada will presumably control these remaining parts of Grand Banks which are outside of its EEZ jurisdiction.
Petroleum
Petroleum
Petroleum or crude oil is a naturally occurring, flammable liquid consisting of a complex mixture of hydrocarbons of various molecular weights and other liquid organic compounds, that are found in geologic formations beneath the Earth's surface. Petroleum is recovered mostly through oil drilling...
reserves have also been discovered and a number of oil fields are under development in this region, most notably the Hibernia, Terra Nova, and White Rose projects; the harsh environment on the Grand Banks also led to the Ocean Ranger
Ocean Ranger
Ocean Ranger was a semi-submersible mobile offshore drilling unit that sank in Canadian waters on 15 February 1982. It was drilling an exploration well in the Grand Banks area, east of St. John's, Newfoundland, for Mobil Oil of Canada, Ltd. with 84 crew members on board when it sank...
disaster.
Culture
Semi-fictional depictions of fishermen working on the Grand Banks can be found in Rudyard KiplingRudyard Kipling
Joseph Rudyard Kipling was an English poet, short-story writer, and novelist chiefly remembered for his celebration of British imperialism, tales and poems of British soldiers in India, and his tales for children. Kipling received the 1907 Nobel Prize for Literature...
's novel Captains Courageous
Captains Courageous
Captains Courageous is an 1897 novel, by Rudyard Kipling, that follows the adventures of fifteen-year-old Harvey Cheyne Jr., the arrogant and spoiled son of a railroad tycoon...
(1897) and in Sebastian Junger's non-fiction book The Perfect Storm (1997).
See also
- Banks doryBanks doryThe Banks dory, also known as the Grand Banks dory, is the most common variation of the family of boats known as dories. They were used as traditional fishing boats from the 1850s on the Grand Banks of Newfoundland. The Banks dory is a small, open, narrow, flat-bottomed and slab-sided boat with a...
- Collapse of the Northern Cod FisheryCollapse of the Northern Cod FisheryIn 1992 the Canadian government declared a moratorium on the Northern Cod fishery that, for the past 500 years, had largely shaped the lives and communities of Canada’s eastern coast...
- Continental shelfContinental shelfThe continental shelf is the extended perimeter of each continent and associated coastal plain. Much of the shelf was exposed during glacial periods, but is now submerged under relatively shallow seas and gulfs, and was similarly submerged during other interglacial periods. The continental margin,...
- Oil spillOil spillAn oil spill is the release of a liquid petroleum hydrocarbon into the environment, especially marine areas, due to human activity, and is a form of pollution. The term is mostly used to describe marine oil spills, where oil is released into the ocean or coastal waters...
- Turbot WarTurbot WarThe Turbot War of 1995 was an international fishing dispute between Canada, and Spain in which Canada stopped a Galician fishing trawler in international waters and arrested its crew...
- West Greenland CurrentWest Greenland CurrentThe West Greenland Current is a weak cold water current that flows to the north along the west coast of Greenland. The current results from the movement of water flowing around the southernmost point of Greenland caused by the East Greenland Current....
External links
- Overfishing:The Grand Banks and the Flemish Cap
- Government response to the standing committee on fisheries and oceans' tenth report
- Watch Cries from the Deep — a Jacques Cousteau documentary on the Grand Banks

