
Greco-Iberian alphabet
Encyclopedia
.jpg)
Alphabet
An alphabet is a standard set of letters—basic written symbols or graphemes—each of which represents a phoneme in a spoken language, either as it exists now or as it was in the past. There are other systems, such as logographies, in which each character represents a word, morpheme, or semantic...
is a direct adaptation of an Ionic
Ionic Greek
Ionic Greek was a subdialect of the Attic–Ionic dialect group of Ancient Greek .-History:Ionic dialect appears to have spread originally from the Greek mainland across the Aegean at the time of the Dorian invasions, around the 11th Century B.C.By the end of the Greek Dark Ages in the 5th Century...
variant of a Greek alphabet
Greek alphabet
The Greek alphabet is the script that has been used to write the Greek language since at least 730 BC . The alphabet in its classical and modern form consists of 24 letters ordered in sequence from alpha to omega...
to the specifics of the Iberian language
Iberian language
The Iberian language was the language of a people identified by Greek and Roman sources who lived in the eastern and southeastern regions of the Iberian peninsula. The ancient Iberians can be identified as a rather nebulous local culture between the 7th and 1st century BC...
, thus this script is an alphabet and lacks the distinctive characteristic of the rest of paleohispanic scripts
Paleohispanic scripts
The Paleohispanic scripts are the writing systems created in the Iberian peninsula before the Latin alphabet became the dominant script...
that present signs with syllabic value, for the occlusives and signs with monophonemic value for the rest of consonants and vowels.
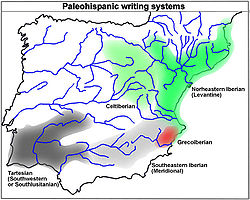
The inscriptions that use the Greco–Iberian alphabet had been found mainly in Alicante
Alicante
Alicante or Alacant is a city in Spain, the capital of the province of Alicante and of the comarca of Alacantí, in the south of the Valencian Community. It is also a historic Mediterranean port. The population of the city of Alicante proper was 334,418, estimated , ranking as the second-largest...
and Murcia
Murcia
-History:It is widely believed that Murcia's name is derived from the Latin words of Myrtea or Murtea, meaning land of Myrtle , although it may also be a derivation of the word Murtia, which would mean Murtius Village...
and the direction of the writing is left to right. The number of known Greco-Iberian inscriptions is small: fewer than two dozen ceramic
Ceramic
A ceramic is an inorganic, nonmetallic solid prepared by the action of heat and subsequent cooling. Ceramic materials may have a crystalline or partly crystalline structure, or may be amorphous...
inscriptions and a dozen lead
Lead
Lead is a main-group element in the carbon group with the symbol Pb and atomic number 82. Lead is a soft, malleable poor metal. It is also counted as one of the heavy metals. Metallic lead has a bluish-white color after being freshly cut, but it soon tarnishes to a dull grayish color when exposed...
plaques, among them the lead plaque from La Serreta (Alcoy, Alicante
Alicante
Alicante or Alacant is a city in Spain, the capital of the province of Alicante and of the comarca of Alacantí, in the south of the Valencian Community. It is also a historic Mediterranean port. The population of the city of Alicante proper was 334,418, estimated , ranking as the second-largest...
) and the lead plaque from El Cigarralejo (Mula, Murcia
Murcia
-History:It is widely believed that Murcia's name is derived from the Latin words of Myrtea or Murtea, meaning land of Myrtle , although it may also be a derivation of the word Murtia, which would mean Murtius Village...
). The archaeological context of the Greco-Iberian inscriptions seems to concentrate in the 4th century BC, but the paleographic characteristics of the model indicate that the adaptation may date from the 5th century BC.
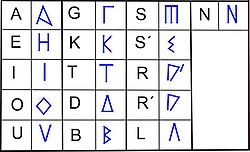
The Greco–Iberian alphabet contains 16 signs identical to the Greek signs, except for the sign corresponding to the second rhotic consonant
Rhotic consonant
In phonetics, rhotic consonants, also called tremulants or "R-like" sounds, are liquid consonants that are traditionally represented orthographically by symbols derived from the Greek letter rho, including "R, r" from the Roman alphabet and "Р, p" from the Cyrillic alphabet...
: five vowels, only one nasal
Nasal consonant
A nasal consonant is a type of consonant produced with a lowered velum in the mouth, allowing air to escape freely through the nose. Examples of nasal consonants in English are and , in words such as nose and mouth.- Definition :...
sign, one lateral
Lateral consonant
A lateral is an el-like consonant, in which airstream proceeds along the sides of the tongue, but is blocked by the tongue from going through the middle of the mouth....
, two sibilants, two rhotic
Rhotic
In linguistics, rhotic can refer to:* Rhotic consonant, such as the sound in red* R-colored vowel, such as the sound in Midwestern American English pronunciation of fur and before a consonant as in hard....
, three voiced
Voice (phonetics)
Voice or voicing is a term used in phonetics and phonology to characterize speech sounds, with sounds described as either voiceless or voiced. The term, however, is used to refer to two separate concepts. Voicing can refer to the articulatory process in which the vocal cords vibrate...
occlusives (labial
Labial consonant
Labial consonants are consonants in which one or both lips are the active articulator. This precludes linguolabials, in which the tip of the tongue reaches for the posterior side of the upper lip and which are considered coronals...
, dental and velar), but only two voiceless
Voiceless
In linguistics, voicelessness is the property of sounds being pronounced without the larynx vibrating. Phonologically, this is a type of phonation, which contrasts with other states of the larynx, but some object that the word "phonation" implies voicing, and that voicelessness is the lack of...
occlusives (dental and velar). To represent the second rhotic they add an additional stroke to rho
Rho
Rho is the 17th letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of 100. It is derived from Semitic resh "head"...
, they choose eta
ETA
ETA , an acronym for Euskadi Ta Askatasuna is an armed Basque nationalist and separatist organization. The group was founded in 1959 and has since evolved from a group promoting traditional Basque culture to a paramilitary group with the goal of gaining independence for the Greater Basque Country...
instead of epsilon
Epsilon
Epsilon is the fifth letter of the Greek alphabet, corresponding phonetically to a close-mid front unrounded vowel . In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 5. It was derived from the Phoenician letter He...
to represent e and they choose sampi
Sampi
Sampi is an archaic letter of the Greek alphabet. It was used in addition to the classical 24 letters of the alphabet to denote some type of a sibilant sound, probably or , in some eastern Ionic dialects of ancient Greek in the 6th and 5th centuries BC...
as the second sibilant.
See also
- Languages of SpainLanguages of SpainThe languages of Spain are the languages spoken or once spoken in Spain. Romance languages are the most widely spoken in Spain, of which Spanish is the country's official language...
- Languages of PortugalLanguages of PortugalThe languages of Portugal are the languages spoken or once spoken in the territory of the country of Portugal.-Modern:Portuguese is practically universal in Portugal, but there are some specificities.thumb|Portuguese dialects of Portugal...
- Iberian Romance languagesIberian Romance languagesThe Iberian Romance languages or Ibero-Romance languages are the Romance languages that developed on the Iberian Peninsula, an area consisting primarily of Spain, Portugal, and Andorra....
- Iberian languagesIberian languagesIberian languages is a generic term for the languages currently or formerly spoken in the Iberian Peninsula.- Pre-Roman languages :The following languages were spoken in the Iberian Peninsula before the Roman occupation and the spread of the Latin language.* Aquitanian * Proto-Basque* Tartessian*...
- Paleohispanic languagesPaleohispanic languagesThe Paleohispanic languages were the languages of the pre-Roman peoples of the Iberian Peninsula, excluding languages of foreign colonies, such as Greek in Emporion and Phoenician in Qart Hadast...
- Pre-Roman peoples of the Iberian PeninsulaPre-Roman peoples of the Iberian PeninsulaThis is a list of the Pre-Roman peoples of the Iberian peninsula .-Non-Indo-European:*Aquitanians**Aquitani**Autrigones - some consider them Celtic .**Caristii - some consider them Celtic ....

