
Lateral consonant
Encyclopedia
A lateral is an el-like consonant
, in which airstream
proceeds along the sides of the tongue, but is blocked by the tongue from going through the middle of the mouth.
Most commonly the tip of the tongue makes contact with the upper teeth (see dental consonant) or the upper gum (the alveolar ridge) just behind the teeth (see alveolar consonant
). The most common laterals are approximants and belong to the class of liquids
, though lateral fricatives
and affricates
are common in some parts of the world.
The labial fricatives [f v] often—perhaps usually—have lateral airflow, as the lip blocks the airflow in the center, but they are nonetheless not considered lateral consonants because no language makes a distinction between the two possibilities. Plosives are never lateral, and the distinction is meaningless for nasal consonant
s and consonants articulated in the throat.
s. One, found before vowels as in lady or fly, is called clear l, pronounced as the alveolar lateral approximant
[l] with a "neutral" position of the body of the tongue. The other variant, so-called dark l found before consonants or word-finally, as in bold or tell, is pronounced as the velarized alveolar lateral approximant
[ɫ] with the tongue assuming a spoon-like shape with its back part raised, which gives the sound a [w]- or [ʟ]-like resonance. In some languages, like Albanian
, those two sounds are different phonemes. East Slavic languages
contrast [ɫ] and [lʲ] but do not have a plain [l].
In many British accents (e.g. Cockney), dark [ɫ] may undergo vocalization
through the reduction and loss of contact between the tip of the tongue and the alveolar ridge, becoming a rounded back vowel or glide. This process turns tell into something like [tɛɰ]. A similar process happened during the development of many languages, including Brazilian Portuguese
, Old French
, and Polish
, in all three of these resulting in [ɰ] or [w], whence Modern French sauce as compared with Spanish
salsa, or Polish Wisła as compared with English Vistula
.
In central and Venice dialects of Vèneto
, intervocalic /l/ has turned into a semivocalic [e̯], so that the written word ła bała is pronounced [abae̯a]. The orthography uses the letter ł to represent this phoneme (not that it doesn't specifically represent the [e̯] sound, it represents the phoneme which in some dialects is [e̯] and in some [l]).
Many aboriginal Australian languages have a series of three or four lateral approximants, as do various dialects of Irish
. Rarer lateral consonants include the retroflex laterals that can be found in most Indic languages and in some Swedish dialects
, and the voiceless alveolar lateral fricative
/ɬ/, found in many Native North American languages
, Welsh
and Zulu
. In Adyghe
and some Athabaskan languages
like Hän
both voiceless and voiced alveolar lateral fricatives occur, but there is no approximant. Many of these languages also have lateral affricates. Some languages have palatal or velar voiceless lateral fricatives or affricates, such as Dahalo
and Zulu
but the IPA has no symbols for these sounds. However, appropriate symbols are easy to make by adding a lateral-fricative belt to the symbol for the corresponding lateral approximant (see below). Failing that, a devoicing diacritic is added to the approximant.
Nearly all languages with such lateral obstruents also have the approximant. However, there are a number of exceptions, many of them located in the Pacific Northwest
area. For example, Tlingit
has /tɬ, tɬʰ, tɬʼ, ɬ, ɬʼ/ but no /l/. Other examples from the same area include Nuu-chah-nulth
and Kutenai
, and elsewhere, Chukchi
and Kabardian
.
Tibetan
has a voiceless lateral approximant, usually romanized as lh, as in the name Lhasa
.
Pashto
has a retroflex lateral flap
.
There are a large number of lateral click consonant
s; seventeen occur in !Xóõ.
Lateral trills are possible (but occur in no known language). It is also possible to articulate uvular laterals, but they are also too hard to pronounce to occur as a phoneme in any known language.
, palatal
, and velar
(the latter two only known from affricates):
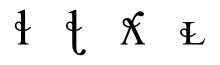 The symbol for the alveolar lateral flap [ɺ] is the basis for the expected symbol for the retroflex lateral flap
The symbol for the alveolar lateral flap [ɺ] is the basis for the expected symbol for the retroflex lateral flap
:
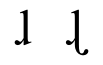 Such symbols are rare, but are becoming more common now that font-editing software has become accessible. The letter for the voiceless retroflex lateral fricative
Such symbols are rare, but are becoming more common now that font-editing software has become accessible. The letter for the voiceless retroflex lateral fricative
was included in Unicode 6.0 as , with the annotation, voiceless lateral retroflex fricative, used to transcribe Toda
. Everson Mono
already has a glyph for this tentative code point. Note however that this is not sanctioned by the IPA
. There are no Unicode code points assigned for the other letters, except that "ɭ with belt" and "ɺ with retroflex hook" can be represented as composite characters (ɬ or ɺ, followed by ). Also note that although the Charis SIL
and Doulos SIL
fonts have those glyphs in the Private Use Area (PUA), PUA code points should not be used for data exchange.
Consonant
In articulatory phonetics, a consonant is a speech sound that is articulated with complete or partial closure of the vocal tract. Examples are , pronounced with the lips; , pronounced with the front of the tongue; , pronounced with the back of the tongue; , pronounced in the throat; and ,...
, in which airstream
Airstream mechanism
In phonetics, the airstream mechanism is the method by which airflow is created in the vocal tract. Along with phonation, it is one of two mandatory aspects of sound production; without these, there can be no speech sound....
proceeds along the sides of the tongue, but is blocked by the tongue from going through the middle of the mouth.
Most commonly the tip of the tongue makes contact with the upper teeth (see dental consonant) or the upper gum (the alveolar ridge) just behind the teeth (see alveolar consonant
Alveolar consonant
Alveolar consonants are articulated with the tongue against or close to the superior alveolar ridge, which is called that because it contains the alveoli of the superior teeth...
). The most common laterals are approximants and belong to the class of liquids
Liquid consonant
In phonetics, liquids or liquid consonants are a class of consonants consisting of lateral consonants together with rhotics.-Description:...
, though lateral fricatives
Fricative consonant
Fricatives are consonants produced by forcing air through a narrow channel made by placing two articulators close together. These may be the lower lip against the upper teeth, in the case of ; the back of the tongue against the soft palate, in the case of German , the final consonant of Bach; or...
and affricates
Affricate consonant
Affricates are consonants that begin as stops but release as a fricative rather than directly into the following vowel.- Samples :...
are common in some parts of the world.
The labial fricatives [f v] often—perhaps usually—have lateral airflow, as the lip blocks the airflow in the center, but they are nonetheless not considered lateral consonants because no language makes a distinction between the two possibilities. Plosives are never lateral, and the distinction is meaningless for nasal consonant
Nasal consonant
A nasal consonant is a type of consonant produced with a lowered velum in the mouth, allowing air to escape freely through the nose. Examples of nasal consonants in English are and , in words such as nose and mouth.- Definition :...
s and consonants articulated in the throat.
Examples
English has one lateral phoneme: the lateral approximant /l/, which in many accents has two allophoneAllophone
In phonology, an allophone is one of a set of multiple possible spoken sounds used to pronounce a single phoneme. For example, and are allophones for the phoneme in the English language...
s. One, found before vowels as in lady or fly, is called clear l, pronounced as the alveolar lateral approximant
Alveolar lateral approximant
The alveolar lateral approximant, also known as clear l, is a type of consonantal sound used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents dental, alveolar, and postalveolar lateral approximants is , and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is l.As a...
[l] with a "neutral" position of the body of the tongue. The other variant, so-called dark l found before consonants or word-finally, as in bold or tell, is pronounced as the velarized alveolar lateral approximant
Velarized alveolar lateral approximant
-See also:* Lateral consonant* Velarization* l-vocalization* Ł...
[ɫ] with the tongue assuming a spoon-like shape with its back part raised, which gives the sound a [w]- or [ʟ]-like resonance. In some languages, like Albanian
Albanian language
Albanian is an Indo-European language spoken by approximately 7.6 million people, primarily in Albania and Kosovo but also in other areas of the Balkans in which there is an Albanian population, including western Macedonia, southern Montenegro, southern Serbia and northwestern Greece...
, those two sounds are different phonemes. East Slavic languages
East Slavic languages
The East Slavic languages constitute one of three regional subgroups of Slavic languages, currently spoken in Eastern Europe. It is the group with the largest numbers of speakers, far out-numbering the Western and Southern Slavic groups. Current East Slavic languages are Belarusian, Russian,...
contrast [ɫ] and [lʲ] but do not have a plain [l].
In many British accents (e.g. Cockney), dark [ɫ] may undergo vocalization
L-vocalization
In linguistics, l-vocalization is a process by which an sound is replaced by a vowel or semivowel sound. This happens most often to velarized .-English:...
through the reduction and loss of contact between the tip of the tongue and the alveolar ridge, becoming a rounded back vowel or glide. This process turns tell into something like [tɛɰ]. A similar process happened during the development of many languages, including Brazilian Portuguese
Brazilian Portuguese
Brazilian Portuguese is a group of Portuguese dialects written and spoken by most of the 190 million inhabitants of Brazil and by a few million Brazilian emigrants, mainly in the United States, United Kingdom, Portugal, Canada, Japan and Paraguay....
, Old French
Old French
Old French was the Romance dialect continuum spoken in territories that span roughly the northern half of modern France and parts of modern Belgium and Switzerland from the 9th century to the 14th century...
, and Polish
Polish language
Polish is a language of the Lechitic subgroup of West Slavic languages, used throughout Poland and by Polish minorities in other countries...
, in all three of these resulting in [ɰ] or [w], whence Modern French sauce as compared with Spanish
Spanish language
Spanish , also known as Castilian , is a Romance language in the Ibero-Romance group that evolved from several languages and dialects in central-northern Iberia around the 9th century and gradually spread with the expansion of the Kingdom of Castile into central and southern Iberia during the...
salsa, or Polish Wisła as compared with English Vistula
Vistula
The Vistula is the longest and the most important river in Poland, at 1,047 km in length. The watershed area of the Vistula is , of which lies within Poland ....
.
In central and Venice dialects of Vèneto
Venetian language
Venetian or Venetan is a Romance language spoken as a native language by over two million people, mostly in the Veneto region of Italy, where of five million inhabitants almost all can understand it. It is sometimes spoken and often well understood outside Veneto, in Trentino, Friuli, Venezia...
, intervocalic /l/ has turned into a semivocalic [e̯], so that the written word ła bała is pronounced [abae̯a]. The orthography uses the letter ł to represent this phoneme (not that it doesn't specifically represent the [e̯] sound, it represents the phoneme which in some dialects is [e̯] and in some [l]).
Many aboriginal Australian languages have a series of three or four lateral approximants, as do various dialects of Irish
Irish language
Irish , also known as Irish Gaelic, is a Goidelic language of the Indo-European language family, originating in Ireland and historically spoken by the Irish people. Irish is now spoken as a first language by a minority of Irish people, as well as being a second language of a larger proportion of...
. Rarer lateral consonants include the retroflex laterals that can be found in most Indic languages and in some Swedish dialects
Swedish dialects
Swedish dialects can be categorized into Traditional Dialects and Modern Dialects .-Traditional dialects:...
, and the voiceless alveolar lateral fricative
Voiceless alveolar lateral fricative
The voiceless alveolar lateral fricative is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents voiceless dental, alveolar, and postalveolar fricatives is , and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is K...
/ɬ/, found in many Native North American languages
Indigenous languages of the Americas
Indigenous languages of the Americas are spoken by indigenous peoples from Alaska and Greenland to the southern tip of South America, encompassing the land masses which constitute the Americas. These indigenous languages consist of dozens of distinct language families as well as many language...
, Welsh
Welsh phonology
The phonology of Welsh is characterised by a number of sounds that do not occur in English and are typologically rare in European languages, such as the voiceless lateral fricative and voiceless nasal consonants...
and Zulu
Zulu language
Zulu is the language of the Zulu people with about 10 million speakers, the vast majority of whom live in South Africa. Zulu is the most widely spoken home language in South Africa as well as being understood by over 50% of the population...
. In Adyghe
Adyghe language
Adyghe language , also known as West Circassian , is one of the two official languages of the Republic of Adygea in the Russian Federation, the other being Russian. It is spoken by various tribes of the Adyghe people: Abzekh, Adamey, Bzhedugh; Hatukuay, Kemirgoy, Makhosh; Natekuay, Shapsigh; Zhane,...
and some Athabaskan languages
Athabaskan languages
Athabaskan or Athabascan is a large group of indigenous peoples of North America, located in two main Southern and Northern groups in western North America, and of their language family...
like Hän
Hän language
The Hän language is a Native American endangered language spoken in only two places: Eagle, Alaska and Dawson City, Yukon. There are only a few fluent speakers left , all of them elderly....
both voiceless and voiced alveolar lateral fricatives occur, but there is no approximant. Many of these languages also have lateral affricates. Some languages have palatal or velar voiceless lateral fricatives or affricates, such as Dahalo
Dahalo language
Dahalo is an endangered South Cushitic language spoken by at most 400 people on the Kenyan coast near the mouth of the Tana River. The Dahalo, former elephant hunters, are dispersed among Swahili and other Bantu peoples, with no villages of their own, and are bilingual in those languages...
and Zulu
Zulu language
Zulu is the language of the Zulu people with about 10 million speakers, the vast majority of whom live in South Africa. Zulu is the most widely spoken home language in South Africa as well as being understood by over 50% of the population...
but the IPA has no symbols for these sounds. However, appropriate symbols are easy to make by adding a lateral-fricative belt to the symbol for the corresponding lateral approximant (see below). Failing that, a devoicing diacritic is added to the approximant.
Nearly all languages with such lateral obstruents also have the approximant. However, there are a number of exceptions, many of them located in the Pacific Northwest
Pacific Northwest
The Pacific Northwest is a region in northwestern North America, bounded by the Pacific Ocean to the west and, loosely, by the Rocky Mountains on the east. Definitions of the region vary and there is no commonly agreed upon boundary, even among Pacific Northwesterners. A common concept of the...
area. For example, Tlingit
Tlingit language
The Tlingit language ) is spoken by the Tlingit people of Southeast Alaska and Western Canada. It is a branch of the Na-Dené language family. Tlingit is very endangered, with fewer than 140 native speakers still living, all of whom are bilingual or near-bilingual in English...
has /tɬ, tɬʰ, tɬʼ, ɬ, ɬʼ/ but no /l/. Other examples from the same area include Nuu-chah-nulth
Nuu-chah-nulth language
Nuu-chah-nulth is a Wakashan language spoken in the Pacific Northwest of North America, on the west coast of Vancouver Island from Barkley Sound to Quatsino Sound in British Columbia, by the Nuu-chah-nulth people...
and Kutenai
Kutenai language
The Kutenai language is named after and is spoken by some of the Kootenai Native American/First Nations people who are indigenous to the area of North America that is now Montana, Idaho, and British Columbia....
, and elsewhere, Chukchi
Chukchi language
The Chukchi language is a Palaeosiberian language spoken by Chukchi people in the easternmost extremity of Siberia, mainly in Chukotka Autonomous Okrug...
and Kabardian
Kabardian language
The Kabardian language, also known as East Circassian , is a Northwest Caucasian language, closely related to the Adyghe language. It is spoken mainly in the Russian republics of Kabardino-Balkaria and Karachay-Cherkessia and in Turkey and the Middle East...
.
Tibetan
Tibetan language
The Tibetan languages are a cluster of mutually-unintelligible Tibeto-Burman languages spoken primarily by Tibetan peoples who live across a wide area of eastern Central Asia bordering the Indian subcontinent, including the Tibetan Plateau and the northern Indian subcontinent in Baltistan, Ladakh,...
has a voiceless lateral approximant, usually romanized as lh, as in the name Lhasa
Lhasa
Lhasa is the administrative capital of the Tibet Autonomous Region in the People's Republic of China and the second most populous city on the Tibetan Plateau, after Xining. At an altitude of , Lhasa is one of the highest cities in the world...
.
Pashto
Pashto language
Pashto , known as Afghani in Persian and Pathani in Punjabi , is the native language of the indigenous Pashtun people or Afghan people who are found primarily between an area south of the Amu Darya in Afghanistan and...
has a retroflex lateral flap
Retroflex lateral flap
The retroflex lateral flap is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. It has no symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet, but an ad hoc symbol may be easily created .-Features:Features of the retroflex flap:...
.
There are a large number of lateral click consonant
Click consonant
Clicks are speech sounds found as consonants in many languages of southern Africa, and in three languages of East Africa. Examples of these sounds familiar to English speakers are the tsk! tsk! or tut-tut used to express disapproval or pity, the tchick! used to spur on a horse, and the...
s; seventeen occur in !Xóõ.
Lateral trills are possible (but occur in no known language). It is also possible to articulate uvular laterals, but they are also too hard to pronounce to occur as a phoneme in any known language.
Approximants
- Alveolar lateral approximantAlveolar lateral approximantThe alveolar lateral approximant, also known as clear l, is a type of consonantal sound used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents dental, alveolar, and postalveolar lateral approximants is , and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is l.As a...
[l] - Velarized alveolar lateral approximantVelarized alveolar lateral approximant-See also:* Lateral consonant* Velarization* l-vocalization* Ł...
[ɫ] - Retroflex lateral approximant [ɭ]
- Palatal lateral approximantPalatal lateral approximantThe palatal lateral approximant is a type of consonantal sound used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is , a rotated lowercase letter ⟨y⟩ , and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is L.-Features:Features of the palatal lateral...
[ʎ] - Velar lateral approximant [ʟ]
Fricatives
- Voiceless alveolar lateral fricativeVoiceless alveolar lateral fricativeThe voiceless alveolar lateral fricative is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents voiceless dental, alveolar, and postalveolar fricatives is , and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is K...
[ɬ] (in NavajoNavajo languageNavajo or Navaho is an Athabaskan language spoken in the southwestern United States. It is geographically and linguistically one of the Southern Athabaskan languages .Navajo has more speakers than any other Native American language north of the...
, WelshWelsh languageWelsh is a member of the Brythonic branch of the Celtic languages spoken natively in Wales, by some along the Welsh border in England, and in Y Wladfa...
) - Voiced alveolar lateral fricative [ɮ] (in MongolianMongolian languageThe Mongolian language is the official language of Mongolia and the best-known member of the Mongolic language family. The number of speakers across all its dialects may be 5.2 million, including the vast majority of the residents of Mongolia and many of the Mongolian residents of the Inner...
, TigakTigak languageTigak is an Austronesian language spoken by about 6,000 people in the Kavieng District of New Ireland Province, Papua New Guinea.The Tigak language area includes the provincial capital, Kavieng....
) - Voiceless retroflex lateral fricativeVoiceless retroflex lateral fricativeThe voiceless retroflex lateral fricative is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The IPA has no officially recognized symbol for this sound...
[ɬ̢] (or []) (in TodaToda languageToda is a Dravidian language well known for its many fricatives and trills. It is spoken by the Toda people, a population of about one thousand who live in the Nilgiri Hills of southern India.-Vowels:...
) - Voiceless palatal lateral fricativeVoiceless palatal lateral fricativeThe voiceless palatal lateral fricative is a type of consonantal sound, used in a few spoken languages.This is a rare sound. Dahalo has both a palatal lateral fricative and an affricate; Hadza has a series of affricates. In Bura is the realization of palatalized and contrasts with .The IPA has no...
[ʎ̥˔] (or []) (in DahaloDahalo languageDahalo is an endangered South Cushitic language spoken by at most 400 people on the Kenyan coast near the mouth of the Tana River. The Dahalo, former elephant hunters, are dispersed among Swahili and other Bantu peoples, with no villages of their own, and are bilingual in those languages...
) - Voiced velar lateral fricativeVoiced velar lateral fricativeThe voiced velar lateral fricative is a very rare speech sound that can be found in Archi, a Northeast Caucasian language of Dagestan, in which it is clearly a fricative, although further forward than velars in most languages, and might better be called prevelar...
[ʟ̝] (in ArchiArchi languageArchi is a Northeast Caucasian language spoken by the 1,200 Archis in the village of Archib, southern Dagestan, Russia and the six surrounding smaller villages...
) - Voiceless velar lateral fricativeVoiceless velar lateral fricativeThe voiceless velar lateral fricative is a very rare speech sound. As one element of an affricate, it is found for example in Zulu and Xhosa. However, a simple fricative has only been reported from a few languages in the Caucasus and New Guinea....
[ʟ̝̊] (or []) (in ArchiArchi languageArchi is a Northeast Caucasian language spoken by the 1,200 Archis in the village of Archib, southern Dagestan, Russia and the six surrounding smaller villages...
)
Affricates
- Voiceless alveolar lateral affricateVoiceless alveolar lateral affricateThe voiceless alveolar lateral affricate is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet is , and in Americanist phonetic notation it is .-Features:...
[tɬ] (in Navajo) - Ejective alveolar lateral affricateAlveolar lateral ejective affricateThe alveolar lateral ejective affricate is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is , and in Americanist phonetic notation it is ⟨ƛ’⟩ ....
[tɬʼ] (in Navajo) - Voiced alveolar lateral affricateVoiced alveolar lateral affricateThe voiced alveolar lateral affricate is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet is...
[dɮ] - Voiceless palatal lateral affricateVoiceless palatal lateral affricateThe voiceless palatal lateral affricate is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet is or .-Features:Features of the voiceless alveolar lateral affricate:-Occurrence:...
[cʎ̥] (or [c]) (in HadzaHadza languageHadza is a language isolate spoken by fewer than a thousand Hadza people along the shores of Lake Eyasi in Tanzania, the last full-time hunter-gatherers in Africa. Despite the small number of speakers, language use is vigorous, with most children learning it...
) - Ejective palatal lateral affricate [cʎ̥ʼ] (or [cʼ]) (in DahaloDahalo languageDahalo is an endangered South Cushitic language spoken by at most 400 people on the Kenyan coast near the mouth of the Tana River. The Dahalo, former elephant hunters, are dispersed among Swahili and other Bantu peoples, with no villages of their own, and are bilingual in those languages...
, Hadza) - Voiced velar lateral affricate [ɡʟ̝] (in LaghuuLaghuu languageLaghuu is a Loloish language spoken in northwestern Vietnam in a single village in Lao Cai Province.- Consonants :Laghuu has the following consonants.-Vowels:Laghuu has the following vowels.- Tones :Laghu has five tones:...
) - Voiceless velar lateral affricateVoiceless velar lateral affricateThe voiceless velar lateral affricate is an uncommon speech sound found as a phoneme in the Caucasus and as an allophone in several languages of eastern and southern Africa....
[kʟ̝̊] (or [k]) (in ArchiArchi languageArchi is a Northeast Caucasian language spoken by the 1,200 Archis in the village of Archib, southern Dagestan, Russia and the six surrounding smaller villages...
, and LaghuuLaghuu languageLaghuu is a Loloish language spoken in northwestern Vietnam in a single village in Lao Cai Province.- Consonants :Laghuu has the following consonants.-Vowels:Laghuu has the following vowels.- Tones :Laghu has five tones:...
) - Ejective velar lateral affricateEjective velar lateral affricateThe velar lateral ejective affricate is a rare type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is ....
[kʟ̝̊ʼ] (or [kʼ]) (in ArchiArchi languageArchi is a Northeast Caucasian language spoken by the 1,200 Archis in the village of Archib, southern Dagestan, Russia and the six surrounding smaller villages...
, Gǀwi, ZuluZulu languageZulu is the language of the Zulu people with about 10 million speakers, the vast majority of whom live in South Africa. Zulu is the most widely spoken home language in South Africa as well as being understood by over 50% of the population...
)
Flaps
- Alveolar lateral flap [ɺ] (in WayuuWayuu languageThe Wayuu language, or Goajiro , is spoken by 305,000 indigenous Wayuu people in northeastern Colombia and northwestern Venezuela on the Guajira Peninsula....
) - Retroflex lateral flapRetroflex lateral flapThe retroflex lateral flap is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. It has no symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet, but an ad hoc symbol may be easily created .-Features:Features of the retroflex flap:...
[ɺ̢] (or []) (in PashtoPashto languagePashto , known as Afghani in Persian and Pathani in Punjabi , is the native language of the indigenous Pashtun people or Afghan people who are found primarily between an area south of the Amu Darya in Afghanistan and...
, IwaidjaIwaidja languageIwaidja, in phonemic spelling Iwaja, is an Australian language with about 150 speakers in northernmost Australia. Historically from the base of the Cobourg Peninsula, it is now spoken on Croker Island...
) - Palatal lateral flapPalatal lateral flapThe palatal lateral flap is a rare type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. There is no symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound...
[ʎ̯] (in IwaidjaIwaidja languageIwaidja, in phonemic spelling Iwaja, is an Australian language with about 150 speakers in northernmost Australia. Historically from the base of the Cobourg Peninsula, it is now spoken on Croker Island...
)
Clicks
- Dental lateral clicks [ǁ̪], [ᶢǁ̪], [ᵑǁ̪], etc. (in Juu!Kung language!Kung or !Xun, also called Ju, is a dialect continuum spoken in Namibia, Botswana, and Angola by the !Kung people. Together with the ǂHoan language, it forms the Kx'a language family...
) - Alveolar lateral clicks [ǁ], [ᶢǁ], [ᵑǁ], etc. (in KhoisanKhoisan languagesThe Khoisan languages are the click languages of Africa which do not belong to other language families. They include languages indigenous to southern and eastern Africa, though some, such as the Khoi languages, appear to have moved to their current locations not long before the Bantu expansion...
and BantuBantu languagesThe Bantu languages constitute a traditional sub-branch of the Niger–Congo languages. There are about 250 Bantu languages by the criterion of mutual intelligibility, though the distinction between language and dialect is often unclear, and Ethnologue counts 535 languages...
)
Other symbols
The symbol for the voiceless alveolar lateral fricative [ɬ] forms the basis for the occasional ad hoc symbols for other voiceless lateral fricatives—retroflexVoiceless retroflex lateral fricative
The voiceless retroflex lateral fricative is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The IPA has no officially recognized symbol for this sound...
, palatal
Voiceless palatal lateral fricative
The voiceless palatal lateral fricative is a type of consonantal sound, used in a few spoken languages.This is a rare sound. Dahalo has both a palatal lateral fricative and an affricate; Hadza has a series of affricates. In Bura is the realization of palatalized and contrasts with .The IPA has no...
, and velar
Voiceless velar lateral fricative
The voiceless velar lateral fricative is a very rare speech sound. As one element of an affricate, it is found for example in Zulu and Xhosa. However, a simple fricative has only been reported from a few languages in the Caucasus and New Guinea....
(the latter two only known from affricates):
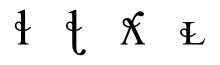
Retroflex lateral flap
The retroflex lateral flap is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. It has no symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet, but an ad hoc symbol may be easily created .-Features:Features of the retroflex flap:...
:
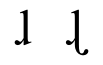
Voiceless retroflex lateral fricative
The voiceless retroflex lateral fricative is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The IPA has no officially recognized symbol for this sound...
was included in Unicode 6.0 as , with the annotation, voiceless lateral retroflex fricative, used to transcribe Toda
Toda language
Toda is a Dravidian language well known for its many fricatives and trills. It is spoken by the Toda people, a population of about one thousand who live in the Nilgiri Hills of southern India.-Vowels:...
. Everson Mono
Everson Mono
Everson Mono is a monospaced humanist sans serif Unicode font whose development by Michael Everson began in 1995. At first, Everson Mono was a collection of 8-bit fonts containing glyphs for tables in ISO/IEC 10646; at that time, it was not easy to edit cmaps to have true Unicode indices, and there...
already has a glyph for this tentative code point. Note however that this is not sanctioned by the IPA
International Phonetic Association
The International Phonetic Association is an organization that promotes the scientific study of phonetics and the various practical applications of that science. The IPA’s major contribution to phonetics is the International Phonetic Alphabet—a notational standard for the phonetic...
. There are no Unicode code points assigned for the other letters, except that "ɭ with belt" and "ɺ with retroflex hook" can be represented as composite characters (ɬ or ɺ, followed by ). Also note that although the Charis SIL
Charis SIL
Charis SIL is a glyphic serif typeface developed by SIL International. It is based on Bitstream Charter, one of the first fonts designed for laser printers...
and Doulos SIL
Doulos SIL
Doulos SIL is a serif typeface developed by SIL International, very similar to Times or Times New Roman. Unlike Times New Roman, Doulos only has a single face, Regular...
fonts have those glyphs in the Private Use Area (PUA), PUA code points should not be used for data exchange.

