History of East Asia
Encyclopedia
Prehistory
In East AsiaEast Asia
East Asia or Eastern Asia is a subregion of Asia that can be defined in either geographical or cultural terms...
, the Neolithic
Neolithic
The Neolithic Age, Era, or Period, or New Stone Age, was a period in the development of human technology, beginning about 9500 BC in some parts of the Middle East, and later in other parts of the world. It is traditionally considered as the last part of the Stone Age...
period may have begun as early as 7500 BC. The earliest evidence suggests the existence of the Pengtoushan culture
Pengtoushan culture
The Pengtoushan culture , dating 7500–6100 BCE, was a Neolithic culture centered primarily around the central Yangtze River region in northwestern Hunan, China. It was roughly contemporaneous with its northern neighbor, the Peiligang culture...
in northern Hunan
Hunan
' is a province of South-Central China, located to the south of the middle reaches of the Yangtze River and south of Lake Dongting...
province from about 7500 BC to 6100 BC and of the Peiligang culture
Peiligang culture
The Peiligang culture is a name given by archaeologists to a group of Neolithic communities in the Yi-Luo river basin in Henan Province, China. The culture existed from 7000 BC to 5000 BC. Over 70 sites have been identified with the Peiligang culture. The culture is named after the site discovered...
in Henan
Henan
Henan , is a province of the People's Republic of China, located in the central part of the country. Its one-character abbreviation is "豫" , named after Yuzhou , a Han Dynasty state that included parts of Henan...
province around from about 7000 BC to 5000 BC.
The Jeulmun pottery period
Jeulmun pottery period
The Jeulmun Pottery Period is an archaeological era in Korean prehistory that dates to approximately 8000-1500 BC.. It is named after the decorated pottery vessels that form a large part of the pottery assemblage consistently over the above period, especially 4000-2000 BC. Jeulmun means...
is sometimes labeled the "Korean Neolithic", but since intensive agriculture and evidence of European-style 'Neolithic' lifestyle is sparse at best, such terminology is misleading. The Jeulmun was a period of hunting, gathering, and small-scale cultivation of plants. Archaeologists sometimes refer to this life-style pattern as 'broad-spectrum hunting-and-gathering
Hunter-gatherer
A hunter-gatherer or forage society is one in which most or all food is obtained from wild plants and animals, in contrast to agricultural societies which rely mainly on domesticated species. Hunting and gathering was the ancestral subsistence mode of Homo, and all modern humans were...
'.
The Jōmon period
Jomon period
The is the time in Japanese prehistory from about 14,000 BC to 300 BC.The term jōmon means "cord-patterned" in Japanese. This refers to the pottery style characteristic of the Jōmon culture, and which has markings made using sticks with cords wrapped around them...
is a similar era in prehistoric Japan, with some characteristics of both Neolithic and Mesolithic
Mesolithic
The Mesolithic is an archaeological concept used to refer to certain groups of archaeological cultures defined as falling between the Paleolithic and the Neolithic....
culture.
The history of East Asia is highly focused on territories within the Chinese sphere of influence where the majority of East Asian cultures and technologies originated from.
Xia, Shang and Zhou
Even though archaeological evidence has been found at ErlitouErlitou culture
The Erlitou culture is a name given by archaeologists to an Early Bronze Age urban society that existed in China from 2000 BCE to 1500 BCE. The culture was named after the site discovered at Erlitou in Yanshi, Henan Province...
that indicate the Xia Dynasty
Xia Dynasty
The Xia Dynasty is the first dynasty in China to be described in ancient historical chronicles such as Bamboo Annals, Classic of History and Records of the Grand Historian. The Xia Dynasty was established by the legendary Yu the Great after Shun, the last of the Five Emperors gave his throne to him...
existed from about 2100 BC to 1800 BC, they are not usually considered a true dynasty. The first universally accepted true Chinese dynasty was the Bronze Age Shang Dynasty
Shang Dynasty
The Shang Dynasty or Yin Dynasty was, according to traditional sources, the second Chinese dynasty, after the Xia. They ruled in the northeastern regions of the area known as "China proper" in the Yellow River valley...
, 1766-1050 BC. One of their most important accomplishments was the invention of writing
Writing
Writing is the representation of language in a textual medium through the use of a set of signs or symbols . It is distinguished from illustration, such as cave drawing and painting, and non-symbolic preservation of language via non-textual media, such as magnetic tape audio.Writing most likely...
. In fact, before it was discovered that Chinese pharmacists were selling oracle bone
Oracle bone
Oracle bones are pieces of bone normally from ox scapula or turtle plastron which were used for divination chiefly during the late Shang Dynasty. The bones were first inscribed with divination in oracle bone script by using a bronze pin, and then heated until crack lines appeared in which the...
s from Shang times, the Shang Dynasty was considered a myth. Eventually, Shang rule deteriorated. The last Shang ruler, King Zhou
King Zhou of Shang
Emperor Xin of Shang was the last king of the Shang Dynasty. He was later given the pejorative posthumous name Zhòu . He is also called Zhou Xin or King Zhou . He may also be referred to by adding "Shang" in front of any of his names...
was a cruel corrupt despot. Meanwhile, the Zhou
Zhou Dynasty
The Zhou Dynasty was a Chinese dynasty that followed the Shang Dynasty and preceded the Qin Dynasty. Although the Zhou Dynasty lasted longer than any other dynasty in Chinese history, the actual political and military control of China by the Ji family lasted only until 771 BC, a period known as...
, a Shang vassal, grew strong. In 1122 BC, King Wu of Zhou launched an attack on the Shang capital, and the Shang Dynasty collapsed.
There was not much difference between the Zhou and Shang Dynasties, as the Zhou adopted much of Shang lifestyle. To justify their rule, the Zhou introduced the Mandate of Heaven
Mandate of Heaven
The Mandate of Heaven is a traditional Chinese philosophical concept concerning the legitimacy of rulers. It is similar to the European concept of the divine right of kings, in that both sought to legitimaze rule from divine approval; however, unlike the divine right of kings, the Mandate of...
. This stated that the ruler ruled by divine right, but if he is overthrown, that meant he had lost the divine right to the victor. The first part of the Zhou Dynasty is called the Western Zhou. In 771 BC, the Zhou were forced east by northern barbarians. This marked the beginning of Eastern Zhou. During this period, the Zhou king lost power, and many small kingdoms sprang up. This period, known as the Spring and Autumn Period, was when great philosophers of China, such as Confucius
Confucius
Confucius , literally "Master Kong", was a Chinese thinker and social philosopher of the Spring and Autumn Period....
, Laozi
Laozi
Laozi was a mystic philosopher of ancient China, best known as the author of the Tao Te Ching . His association with the Tao Te Ching has led him to be traditionally considered the founder of Taoism...
, and Mozi
Mozi
Mozi |Lat.]] as Micius, ca. 470 BC – ca. 391 BC), original name Mo Di , was a Chinese philosopher during the Hundred Schools of Thought period . Born in Tengzhou, Shandong Province, China, he founded the school of Mohism, and argued strongly against Confucianism and Daoism...
lived. This flourishing of philosophy is called the Hundred Schools of Thought
Hundred Schools of Thought
The Hundred Schools of Thought were philosophers and schools that flourished from 770 to 221 BC during the Spring and Autumn period and the Warring States period , an era of great cultural and intellectual expansion in China...
. Confucianism
Confucianism
Confucianism is a Chinese ethical and philosophical system developed from the teachings of the Chinese philosopher Confucius . Confucianism originated as an "ethical-sociopolitical teaching" during the Spring and Autumn Period, but later developed metaphysical and cosmological elements in the Han...
, Daoism
Taoism
Taoism refers to a philosophical or religious tradition in which the basic concept is to establish harmony with the Tao , which is the mechanism of everything that exists...
, and Mohism
Mohism
Mohism or Moism was a Chinese philosophy developed by the followers of Mozi , 470 BC–c.391 BC...
all have their roots during this period. The Warring States Period
Warring States Period
The Warring States Period , also known as the Era of Warring States, or the Warring Kingdoms period, covers the Iron Age period from about 475 BC to the reunification of China under the Qin Dynasty in 221 BC...
began when the smaller states have all been annexed, and only seven large states remained: Qi
Qi (state)
Qi was a powerful state during the Spring and Autumn Period and Period of the Warring States in ancient China. Its capital was Linzi, now part of the modern day city of Zibo in Shandong Province....
, Chu
Chu (state)
The State of Chu was a Zhou Dynasty vassal state in present-day central and southern China during the Spring and Autumn period and Warring States Period . Its ruling house had the surname Nai , and clan name Yan , later evolved to surname Mi , and clan name Xiong...
, Yan
Yan (state)
Yān was a state during the Western Zhou, Spring and Autumn and Warring States Periods of Chinese history. Its capital was Ji...
, Han
Han (state)
Han was a kingdom during the Warring States Period in China, located in modern-day Shanxi and Henan. Not to be confused with South Korea which shares the same character....
, Zhao
Zhao (state)
Zhao was a significant Chinese state during the Warring States Period, along with six others...
, Wei
Wei (state)
The State of Wei was a Zhou Dynasty vassal state during the Warring States Period of Chinese history. Its territory lay between the states of Qin and Qi and included parts of modern day Henan, Hebei, Shanxi and Shandong...
, Qin
Qin (state)
The State of Qin was a Chinese feudal state that existed during the Spring and Autumn and Warring States Periods of Chinese history...
.
Confucianism
ConfucianismConfucianism
Confucianism is a Chinese ethical and philosophical system developed from the teachings of the Chinese philosopher Confucius . Confucianism originated as an "ethical-sociopolitical teaching" during the Spring and Autumn Period, but later developed metaphysical and cosmological elements in the Han...
, a more elaborate form of ancestor worship, was a major influence on East Asian history. It originated in northern China in the 5th century BC and was based on the Zhou Dynasty social system, including ancestor worship. Confucianism showed a strong adherence toward existing hierarchy and respect for the authorities: aged, ancestor and political authority considered authentic by blood.
Debated during the Warring States Period
Warring States Period
The Warring States Period , also known as the Era of Warring States, or the Warring Kingdoms period, covers the Iron Age period from about 475 BC to the reunification of China under the Qin Dynasty in 221 BC...
and forbidden during the short-lived Qin Dynasty
Qin Dynasty
The Qin Dynasty was the first imperial dynasty of China, lasting from 221 to 207 BC. The Qin state derived its name from its heartland of Qin, in modern-day Shaanxi. The strength of the Qin state was greatly increased by the legalist reforms of Shang Yang in the 4th century BC, during the Warring...
, Confucianism was chosen by Emperor Wu of Han
Emperor Wu of Han
Emperor Wu of Han , , personal name Liu Che , was the seventh emperor of the Han Dynasty of China, ruling from 141 BC to 87 BC. Emperor Wu is best remembered for the vast territorial expansion that occurred under his reign, as well as the strong and centralized Confucian state he organized...
for use as a political system
Political system
A political system is a system of politics and government. It is usually compared to the legal system, economic system, cultural system, and other social systems...
to govern the Chinese state. Despite its loss of influence during the Tang Dynasty
Tang Dynasty
The Tang Dynasty was an imperial dynasty of China preceded by the Sui Dynasty and followed by the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms Period. It was founded by the Li family, who seized power during the decline and collapse of the Sui Empire...
, Confucianist doctrine remained a mainstream Chinese orthodoxy for two millennia until the 20th century, when it was attacked by radical Chinese thinkers as a vanguard of a pre-modern system and an obstacle to China's modernization
Modernization
In the social sciences, modernization or modernisation refers to a model of an evolutionary transition from a 'pre-modern' or 'traditional' to a 'modern' society. The teleology of modernization is described in social evolutionism theories, existing as a template that has been generally followed by...
, eventually culminating in its repression during the Cultural Revolution
Cultural Revolution
The Great Proletarian Cultural Revolution, commonly known as the Cultural Revolution , was a socio-political movement that took place in the People's Republic of China from 1966 through 1976...
in the People's Republic of China. After the end of the Cultural Revolution, Confucianism was revived in mainland China
Mainland China
Mainland China, the Chinese mainland or simply the mainland, is a geopolitical term that refers to the area under the jurisdiction of the People's Republic of China . According to the Taipei-based Mainland Affairs Council, the term excludes the PRC Special Administrative Regions of Hong Kong and...
, and both interest in and debate about Confucianism have surged.
The culture
Culture
Culture is a term that has many different inter-related meanings. For example, in 1952, Alfred Kroeber and Clyde Kluckhohn compiled a list of 164 definitions of "culture" in Culture: A Critical Review of Concepts and Definitions...
s most strongly influenced by Confucianism include those of China
Culture of China
Chinese culture is one of the world's oldest and most complex. The area in which the culture is dominant covers a large geographical region in eastern Asia with customs and traditions varying greatly between towns, cities and provinces...
, Korea
Culture of Korea
The current political separation of North and South Korea has resulted in divergence in modern Korean cultures; nevertheless, the traditional culture of Korea is historically shared by both states.-Dance:...
, and Vietnam
Culture of Vietnam
The Culture of Vietnam, an agricultural civilization based on the cultivation of wet rice, is one of the oldest in East Asia; the ancient Bronze age Dong Son culture is considered to be one of its most important progenitors...
. Korean Confucianism
Korean Confucianism
Korean Confucianism is the form of Confucianism developed in Korea. One of the most substantial influences in Korean intellectual history was the introduction of Confucian thought as part of the cultural influence from China...
is one of the most substantial influences in Korean intellectual history was introduced through the cultural exchange
Culture of China
Chinese culture is one of the world's oldest and most complex. The area in which the culture is dominant covers a large geographical region in eastern Asia with customs and traditions varying greatly between towns, cities and provinces...
with China. On the other hand, while Confucianism was introduced as both a philosophy and as a ritual tradition in Japan
Culture of Japan
The culture of Japan has evolved greatly over the millennia, from the country's prehistoric Jōmon period to its contemporary hybrid culture, which combines influences from Asia, Europe and North America...
, the latter did not become popular in Japan.
Taoism
The third major religion of East Asia is TaoismTaoism
Taoism refers to a philosophical or religious tradition in which the basic concept is to establish harmony with the Tao , which is the mechanism of everything that exists...
. In China, it affected Buddhism and develop the thought of void which would later ripe as Zen Buddhism. Also, Taoism combined with the rural and vulgar religious feelings and developed its pantheon. Taoism is still widely practiced in mainland China, Hong Kong and Taiwan. Fengshui, fortune telling related to location and colors, is one of derivatives of Taoism.
Taoism was introduced to Korea from China during the Three Kingdoms period, and remains a minor but significant element of Korean thought. Although Taoism did not overshadow Buddhism or Confucianism, it permeated through all strata of the Korean populace, integrating with its native animism as well as with Buddhist and Confucian institutions, temples, and ceremonies.
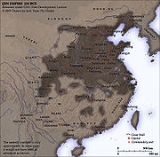
Qin Dynasty
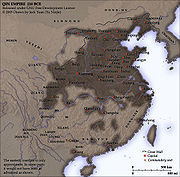
Qin Dynasty
The Qin Dynasty was the first imperial dynasty of China, lasting from 221 to 207 BC. The Qin state derived its name from its heartland of Qin, in modern-day Shaanxi. The strength of the Qin state was greatly increased by the legalist reforms of Shang Yang in the 4th century BC, during the Warring...
. Its ruler, Qin Shi Huang
Qin Shi Huang
Qin Shi Huang , personal name Ying Zheng , was king of the Chinese State of Qin from 246 BC to 221 BC during the Warring States Period. He became the first emperor of a unified China in 221 BC...
, implemented the Legalist
Legalism (Chinese philosophy)
In Chinese history, Legalism was one of the main philosophic currents during the Warring States Period, although the term itself was invented in the Han Dynasty and thus does not refer to an organized 'school' of thought....
system of rule, which was used to rule the former Qin state. All other schools of philosophy were forbidden. Beginning in 213 BC, all books from the Hundred Schools of Thought (except Legalism) were burned
Burning of books and burying of scholars
Burning of the books and burying of the scholars is a phrase that refers to a policy and a sequence of events in the Qin Dynasty of Ancient China, between the period of 213 and 206 BC. During these events, the Hundred Schools of Thought were pruned; legalism survived...
. More than 460 scholars were also buried alive
Burning of books and burying of scholars
Burning of the books and burying of the scholars is a phrase that refers to a policy and a sequence of events in the Qin Dynasty of Ancient China, between the period of 213 and 206 BC. During these events, the Hundred Schools of Thought were pruned; legalism survived...
. He also standardized writing, currency
Chinese currency
The Renminbi is the official currency of the People's Republic of China . It is the legal tender in mainland China, but not in Hong Kong and Macau. It is abbreviated as RMB, and the units for the Renminbi are the Yuan , Jiao , and Fen : 1 Yuan = 10 Jiao = 100 Fen. Fen have almost disappeared, so...
, and Chinese units of measurement
Chinese units of measurement
Chinese units of measurement are the customary and traditional units of measure used in China. In the People's Republic of China, the units were re-standardised during the late 20th century to make them approximate SI units. Many of the units were formerly based on the number 16 instead of 10...
. Qin Shi Huang also reduced the power of the nobility. To defend against barbarian tribes from the north, Qin Shi Huang ordered the old walls of Yan, Zhao, and Qin to be connected. This formed the Great Wall of China
Great Wall of China
The Great Wall of China is a series of stone and earthen fortifications in northern China, built originally to protect the northern borders of the Chinese Empire against intrusions by various nomadic groups...
. In addition to that, he also built luxurious palaces and a huge tomb
Terracotta Army
The Terracotta Army or the "Terra Cotta Warriors and Horses", is a collection of terracotta sculptures depicting the armies of Qin Shi Huang, the first Emperor of China...
for himself. These massive construction projects exhausted resources and labor. Only four years after Qin Shi Huang's death, revolts and territorial uprisings overthrew the Qin Dynasty.
Han Dynasty

Han Dynasty
The Han Dynasty was the second imperial dynasty of China, preceded by the Qin Dynasty and succeeded by the Three Kingdoms . It was founded by the rebel leader Liu Bang, known posthumously as Emperor Gaozu of Han. It was briefly interrupted by the Xin Dynasty of the former regent Wang Mang...
began when Liu Bang defeated the Qin army and other rebel leaders in 206 BC. He established the Han capital at Chang'an
Chang'an
Chang'an is an ancient capital of more than ten dynasties in Chinese history, today known as Xi'an. Chang'an literally means "Perpetual Peace" in Classical Chinese. During the short-lived Xin Dynasty, the city was renamed "Constant Peace" ; yet after its fall in AD 23, the old name was restored...
. The Han Dynasty was renowned for its cultural, technological, and military advances. China's most famous historian, Sima Qian
Sima Qian
Sima Qian was a Prefect of the Grand Scribes of the Han Dynasty. He is regarded as the father of Chinese historiography for his highly praised work, Records of the Grand Historian , a "Jizhuanti"-style general history of China, covering more than two thousand years from the Yellow Emperor to...
, lived during this dynasty. Paper and Porcelain were also invented in the Han Dynasty. A civil examination system was initiated. One of the greatest emperors in Chinese history was Emperor Wu Di
Emperor Wu of Han
Emperor Wu of Han , , personal name Liu Che , was the seventh emperor of the Han Dynasty of China, ruling from 141 BC to 87 BC. Emperor Wu is best remembered for the vast territorial expansion that occurred under his reign, as well as the strong and centralized Confucian state he organized...
. He sent Zhang Qian
Zhang Qian
Zhang Qian was an imperial envoy to the world outside of China in the 2nd century BCE, during the time of the Han Dynasty...
to find allies against the Xiongnu
Xiongnu
The Xiongnu were ancient nomadic-based people that formed a state or confederation north of the agriculture-based empire of the Han Dynasty. Most of the information on the Xiongnu comes from Chinese sources...
. Zhang Qian did not succeed, but he brought back accurate information about Central Asia. Emperor Wu Di immediately sent envoys to Central Asian countries, and set up Chinese settlements as far as the Tarim Basin
Tarim Basin
The Tarim Basin is a large endorheic basin occupying an area of about . It is located in the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region in China's far west. Its northern boundary is the Tian Shan mountain range and its southern is the Kunlun Mountains on the northern edge of the Tibetan Plateau. The...
. Eventually, the Silk Road
Silk Road
The Silk Road or Silk Route refers to a historical network of interlinking trade routes across the Afro-Eurasian landmass that connected East, South, and Western Asia with the Mediterranean and European world, as well as parts of North and East Africa...
was formed. By 22 BC, as taxation rose, revolts broke out across the country. The regent Wang Mang
Wang Mang
Wang Mang , courtesy name Jujun , was a Han Dynasty official who seized the throne from the Liu family and founded the Xin Dynasty , ruling AD 9–23. The Han dynasty was restored after his overthrow and his rule marks the separation between the Western Han Dynasty and Eastern Han Dynasty...
seized control of the government and ruled until AD 23. Floods, famines, and invasions from the Xiongnu all contributed to Wang Mang's downfall. In AD 23, the Chimei
Chimei
Chimei refers, as an umbrella term, to one of the two major agrarian rebellion movements against Wang Mang's Xin Dynasty, initially active in the modern Shandong and northern Jiangsu regions, that eventually led to Wang Mang's downfall by draining his resources, allowing the leader of the other...
overthrew and executed Wang Mang. The Eastern Han began when Liu Xiu
Emperor Guangwu of Han
Emperor Guangwu , born Liu Xiu, was an emperor of the Chinese Han Dynasty, restorer of the dynasty in AD 25 and thus founder of the Later Han or Eastern Han...
became Emperor Guangwu of Han. In AD 50, the Eastern Han allied itself with some Xiongnu tribes. 40 years later, it attacked the Northern Xiongnu, which was so successful it triggered Xiongnu migrations all the way to Europe. However, the Eastern Han soon had the same problems that the Western Han had suffered. Taxes increased, and many wealthy landowners managed to get out of paying taxes. In AD 184, the Yellow Turban Rebellion
Yellow Turban Rebellion
The Yellow Turban Rebellion, also translated as Yellow Scarves Rebellion, was a peasant revolt that broke out in 184 AD in China during the reign of Emperor Ling of the Han Dynasty...
broke out. Even though the Han military quickly crushed the uprising, it weakened the Han Dynasty considerably. In AD 220, the Han empire collapsed into the Three Kingdoms
Three Kingdoms
The Three Kingdoms period was a period in Chinese history, part of an era of disunity called the "Six Dynasties" following immediately the loss of de facto power of the Han Dynasty rulers. In a strict academic sense it refers to the period between the foundation of the state of Wei in 220 and the...
.
Early Imperial China
Early Imperial China begins in the Iron Age with the unification of China by the Qin dynasty in 221 BC. It ended five centuries of feudal warfare, similar to that of Western Europe, that plagued the Eastern Zhou dynasty. The short-lived Qin introduced centralized government under the absolute...
are typically associated with the unification of China in 221 BC under the First Emperor Qin Shi Huangdi.
Silk Road
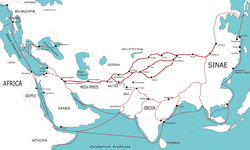
Silk Road
The Silk Road or Silk Route refers to a historical network of interlinking trade routes across the Afro-Eurasian landmass that connected East, South, and Western Asia with the Mediterranean and European world, as well as parts of North and East Africa...
, which connected China, India, the Middle East and Europe. Hinduism
Hinduism
Hinduism is the predominant and indigenous religious tradition of the Indian Subcontinent. Hinduism is known to its followers as , amongst many other expressions...
and Buddhism
Buddhism
Buddhism is a religion and philosophy encompassing a variety of traditions, beliefs and practices, largely based on teachings attributed to Siddhartha Gautama, commonly known as the Buddha . The Buddha lived and taught in the northeastern Indian subcontinent some time between the 6th and 4th...
, which both began in India, were important influences on South and East Asia. Christianity
Christianity
Christianity is a monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus as presented in canonical gospels and other New Testament writings...
, Nestorianism
Nestorianism
Nestorianism is a Christological doctrine advanced by Nestorius, Patriarch of Constantinople from 428–431. The doctrine, which was informed by Nestorius's studies under Theodore of Mopsuestia at the School of Antioch, emphasizes the disunion between the human and divine natures of Jesus...
in particular, came to China via the Silk Road. While it had a significant presence in the Central Asia, it did not gain any significance in China and East Asia until modern missionaries from Europe and North America arrived in the 19th century. On the contrary, the Silk Road passed Chinese products and inventions by the Mongols
Mongols
Mongols ) are a Central-East Asian ethnic group that lives mainly in the countries of Mongolia, China, and Russia. In China, ethnic Mongols can be found mainly in the central north region of China such as Inner Mongolia...
to the Western regions, including paper
Paper
Paper is a thin material mainly used for writing upon, printing upon, drawing or for packaging. It is produced by pressing together moist fibers, typically cellulose pulp derived from wood, rags or grasses, and drying them into flexible sheets....
: papermaking
Papermaking
Papermaking is the process of making paper, a substance which is used universally today for writing and packaging.In papermaking a dilute suspension of fibres in water is drained through a screen, so that a mat of randomly interwoven fibres is laid down. Water is removed from this mat of fibres by...
originated in China and is considered one of Four Great Inventions. It gained notoriety in the Middle East after the Battle of Talas
Battle of Talas
The Battle of Talas in 751 AD was an especially notable conflict between the Arab Abbasid Caliphate and the Chinese Tang Dynasty for control not only of the Syr Darya region, but even more...
between the Arabs and the Chinese Tang Dynasty
Tang Dynasty
The Tang Dynasty was an imperial dynasty of China preceded by the Sui Dynasty and followed by the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms Period. It was founded by the Li family, who seized power during the decline and collapse of the Sui Empire...
in 751.
The Silk Road was also a pathway for intruders, namely the Turkic-Mongol peoples of Central Asia. One of the main concerns of the foreign affairs of the Chinese dynasties was how to defeat these "nomadic barbarians". The Great Wall, begun in the 2nd century BC by the Qin dynasty, was one such attempt to deter invasions from the nomadic groups of Central Asia who were almost Mongol tribes.
Three Kingdoms Period
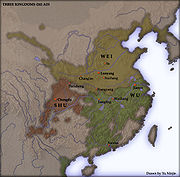
Three Kingdoms
The Three Kingdoms period was a period in Chinese history, part of an era of disunity called the "Six Dynasties" following immediately the loss of de facto power of the Han Dynasty rulers. In a strict academic sense it refers to the period between the foundation of the state of Wei in 220 and the...
consisted of the kingdom of Wei
Cao Wei
Cao Wei was one of the states that competed for control of China during the Three Kingdoms period. With the capital at Luoyang, the state was established by Cao Pi in 220, based upon the foundations that his father Cao Cao laid...
, Shu
Shu Han
Shu Han was one of the three states competing for control of China during the Three Kingdoms period, after the fall of the Han Dynasty. The state was based on areas around Sichuan, which was then known as Shu...
, and Wu
Eastern Wu
Eastern Wu, also known as Sun Wu, was one the three states competing for control of China during the Three Kingdoms period after the fall of the Han Dynasty. It was based in the Jiangnan region of China...
. It began when the ruler of Wei, Cao Cao
Cao Cao
Cao Cao was a warlord and the penultimate chancellor of the Eastern Han Dynasty who rose to great power during the dynasty's final years. As one of the central figures of the Three Kingdoms period, he laid the foundations for what was to become the state of Cao Wei and was posthumously titled...
, was defeated by Liu Bei
Liu Bei
Liu Bei , also known as Liu Xuande, was a warlord, military general and later the founding emperor of the state of Shu Han during the Three Kingdoms era of Chinese history...
and Sun Quan
Sun Quan
Sun Quan , son of Sun Jian, formally Emperor Da of Wu, was the founder of Eastern Wu during the Three Kingdoms period of Chinese history. He ruled from 222 to 229 as King of Wu and from 229 to 252 as Emperor of Wu....
at the Battle of Red Cliffs
Battle of Red Cliffs
The Battle of Red Cliffs, otherwise known as the Battle of Chibi, was a decisive battle at the end of the Han Dynasty, immediately prior to the Three Kingdoms period of Chinese history. It was fought in the winter of 208/9 AD between the allied forces of the southern warlords Liu Bei and Sun Quan...
. After Cao Cao's death in AD 220, his son Cao Pi became emperor of Wei. Liu Bei and Sun Quan declared themselves emperor of Shu and Wu respectively. Many famous personages in Chinese history were born during this period, including Hua Tuo
Hua Tuo
Hua Tuo was an ancient Chinese physician who lived during the late Han Dynasty and Three Kingdoms era of Chinese history. The Records of Three Kingdoms and Book of Later Han record Hua as the first person in China to use anesthesia during surgery. He used a general anesthetic combining wine with a...
and the great military strategist Zhuge Liang
Zhuge Liang
Zhuge Liang was a chancellor of the state of Shu Han during the Three Kingdoms period of Chinese history. He is often recognised as the greatest and most accomplished strategist of his era....
. Buddhism
Buddhism
Buddhism is a religion and philosophy encompassing a variety of traditions, beliefs and practices, largely based on teachings attributed to Siddhartha Gautama, commonly known as the Buddha . The Buddha lived and taught in the northeastern Indian subcontinent some time between the 6th and 4th...
, which was introduced during the Han Dynasty, also became popular in this period. Two years after Wei conquered Shu
Conquest of Shu by Wei
The conquest of Shu by Wei was a military campaign launched by the state of Cao Wei against its rival Shu Han in 263 during the Three Kingdoms period of Chinese history. The campaign culminated in the fall of Shu and the tripartite equilibrium maintained in China for over 40 years since the end of...
in AD 263, Sima Yan, Wei's Imperial Chancellor, overthrew Wei and started the Western Jin Dynasty. The conquest of Wu by the Western Jin Dynasty ended the Three Kingdoms period, and China was unified again. However, the Western Jin did not last long. Following the death of Sima Yan, the War of the Eight Princes
War of the Eight Princes
The War of the Eight Princes or Rebellion of the Eight Kings or Rebellion of the Eight Princes was a civil war for power among princes and dukes of the Chinese Jin Dynasty from AD 291 to AD 306. It was fought mostly in northern China and devastated the country, later triggering the Wu Hu ravaging...
began. This war weakened the Jin Dynasty, and it soon fell to the kingdom of Han Zhao. This ushered in the Sixteen Kingdoms
Sixteen Kingdoms
The Sixteen Kingdoms, or less commonly the Sixteen States, were a collection of numerous short-lived sovereign states in China proper and its neighboring areas from 304 to 439 AD after the retreat of the Jin Dynasty to South China and before the establishment of the Northern Dynasties...
.
Southern and Northern Dynasties
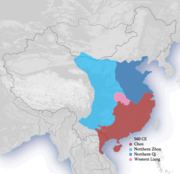
Northern Wei
The Northern Wei Dynasty , also known as the Tuoba Wei , Later Wei , or Yuan Wei , was a dynasty which ruled northern China from 386 to 534 . It has been described as "part of an era of political turbulence and intense social and cultural change"...
was established by the Tuoba
Tuoba
Tuoba, or Tabgach, were a clan of Xianbei people of ancient China.-Xianbei Tuoba:Tuoba was a clan of the Xianbei people in the early centuries of the 1st millennium AD. They established the State of Dai from 310 to 376 AD, and the Northern Wei Dynasty from 386 to 536 AD...
clan of the Xianbei
Xianbei
The Xianbei were a significant Mongolic nomadic people residing in Manchuria, Inner Mongolia and eastern Mongolia. The title “Khan” was first used among the Xianbei.-Origins:...
people in AD 386, when they united the northern part of China. During the Northern Wei, Buddhism flourished, and became an important tool for the emperors of the Northern Wei, since they were believed to be living incarnation
Incarnation
Incarnation literally means embodied in flesh or taking on flesh. It refers to the conception and birth of a sentient creature who is the material manifestation of an entity, god or force whose original nature is immaterial....
s of Buddha
Buddha
In Buddhism, buddhahood is the state of perfect enlightenment attained by a buddha .In Buddhism, the term buddha usually refers to one who has become enlightened...
. Soon, the Northern Wei was divided into the Eastern Wei
Eastern Wei
The Eastern Wei Dynasty followed the disintegration of the Northern Wei, and ruled northern China from 534 to 550.In 534 Gao Huan, the potentate of the eastern half of what was Northern Wei territory following the disintegration of the Northern Wei dynasty installed Yuan Shanjian a descendant of...
and Western Wei
Western Wei
The Western Wei Dynasty followed the disintegration of the Northern Wei, and ruled northern China from 535 to 556.After the Xianbei general Yuwen Tai killed the Northern Wei emperor Yuan Xiu, he installed Yuan Baoju as emperor of Western Wei while Yuwen Tai would remain as the virtual ruler...
. These were followed by the Northern Zhou
Northern Zhou
The Northern Zhou Dynasty followed the Western Wei, and ruled northern China from 557 to 581. It was overthrown by the Sui Dynasty.Northern Zhou's basis of power was established by Yuwen Tai, who was paramount general of Western Wei, following the split of Northern Wei into Western Wei and...
and Northern Qi
Northern Qi
The Northern Qi Dynasty was one of the Northern dynasties of Chinese history and ruled northern China from 550 to 577.-History:The Chinese state of Northern Qi was the successor state of the Chinese/Xianbei state of Eastern Wei and was founded by Emperor Wenxuan...
. In the south, the dynasties were much less stable than the Northern Dynasties. The four dynasties
Southern dynasties
The Southern dynasties comprise the Liu Song, Southern Qi, Liang Dynasty and Chen Dynasty, whose capital were at Jiankang , and Emperor Yuan of Liang, as well as the later Western Liang emperors , also set their...
were weakened by conflicts between the ruling families.
Buddhism
BuddhismBuddhism
Buddhism is a religion and philosophy encompassing a variety of traditions, beliefs and practices, largely based on teachings attributed to Siddhartha Gautama, commonly known as the Buddha . The Buddha lived and taught in the northeastern Indian subcontinent some time between the 6th and 4th...
, also one of the major religions in East Asia, was introduced into China during the Han dynasty
Han Dynasty
The Han Dynasty was the second imperial dynasty of China, preceded by the Qin Dynasty and succeeded by the Three Kingdoms . It was founded by the rebel leader Liu Bang, known posthumously as Emperor Gaozu of Han. It was briefly interrupted by the Xin Dynasty of the former regent Wang Mang...
from India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
in the 1st century BC. Buddhism was originally introduced to Korea from China in 372, and eventually arrived in Japan around the turn of the 6th century.
For a long time Buddhism remained a foreign religion with a few believers in China, mainly taught by immigrant Indian teachers. During the Tang dynasty
Tang Dynasty
The Tang Dynasty was an imperial dynasty of China preceded by the Sui Dynasty and followed by the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms Period. It was founded by the Li family, who seized power during the decline and collapse of the Sui Empire...
, a fair amount of translations from Sanskrit into Chinese were done by Chinese priests, and Buddhism became one of the major religions of the Chinese along with the other two indigenous religions.
In Korea, Buddhism was not seen to conflict with the rites of nature worship; it was allowed to blend in with Shamanism. Thus, the mountains that were believed to be the residence of spirits in pre-Buddhist times became the sites of Buddhist temples. Though Buddhism initially enjoyed wide acceptance, even being supported as the state ideology during the Goguryeo
Goguryeo
Goguryeo or Koguryŏ was an ancient Korean kingdom located in present day northern and central parts of the Korean Peninsula, southern Manchuria, and southern Russian Maritime province....
, Silla
Silla
Silla was one of the Three Kingdoms of Korea, and one of the longest sustained dynasties in...
, Baekje
Baekje
Baekje or Paekche was a kingdom located in southwest Korea. It was one of the Three Kingdoms of Korea, together with Goguryeo and Silla....
, Balhae
Balhae
Balhae was a Manchurian kingdom established after the fall of Goguryeo. After Goguryeo's capital and southern territories fell to Unified Silla, Dae Jo-yeong, a Mohe general, whose father was Dae Jung-sang, established Jin , later called Balhae.Balhae occupied southern parts of Manchuria and...
, and Goryeo
Goryeo
The Goryeo Dynasty or Koryŏ was a Korean dynasty established in 918 by Emperor Taejo. Korea gets its name from this kingdom which came to be pronounced Korea. It united the Later Three Kingdoms in 936 and ruled most of the Korean peninsula until it was removed by the Joseon dynasty in 1392...
periods, Buddhism in Korea suffered extreme repression during the Joseon Dynasty
Joseon Dynasty
Joseon , was a Korean state founded by Taejo Yi Seong-gye that lasted for approximately five centuries. It was founded in the aftermath of the overthrow of the Goryeo at what is today the city of Kaesong. Early on, Korea was retitled and the capital was relocated to modern-day Seoul...
.
In Japan, Buddhism and Shinto
Shinto
or Shintoism, also kami-no-michi, is the indigenous spirituality of Japan and the Japanese people. It is a set of practices, to be carried out diligently, to establish a connection between present day Japan and its ancient past. Shinto practices were first recorded and codified in the written...
were combined by a theological theory "Ryōbushintō", which says Shinto deities are avatars of various Buddhist entities, including Buddhas and Bodhisattvas. This became the mainstream notion of Japanese religion. In fact until the Meiji government declared their separation in the mid 19th Century, many Japanese people believed that Buddhism and Shinto were one religion.
In Mongolia, Buddhism was flowered into Nomadic land for three times during the Hunnu (1-3 centuries BC), Mongol Empire (13-14 centuries), Manchu Empire (16-19 centuries) from Tibet in last 2000 years. It was mixed in with Tengeriism and Shamanism.
Sui Dynasty
In AD 581, Yang Jian overthrew the Northern Zhou, and established the Sui DynastySui Dynasty
The Sui Dynasty was a powerful, but short-lived Imperial Chinese dynasty. Preceded by the Southern and Northern Dynasties, it ended nearly four centuries of division between rival regimes. It was followed by the Tang Dynasty....
. Later, Yang Jian, who became Sui Wendi
Emperor Wen of Sui
Emperor Wen of Sui — personal name Yang Jian , Xianbei name Puliuru Jian , nickname Naluoyan — was the founder and first emperor of China's Sui Dynasty . He was a hard-working administrator and a micromanager. As a Buddhist, he encouraged the spread of Buddhism through the state...
, conquered the Chen Dynasty
Chen Dynasty
The Chen Dynasty , also known as the Southern Chen Dynasty, was the fourth and last of the Southern dynasties in China, eventually destroyed by the Sui Dynasty....
, and united China. However, this dynasty was short-lived. Sui Wendi's successor, Sui Yangdi
Emperor Yang of Sui
Emperor Yang of Sui , personal name Yang Guang , alternative name Ying , nickname Amo , known as Emperor Ming during the brief reign of his grandson Yang Tong), was the second son of Emperor Wen of Sui, and the second emperor of China's Sui Dynasty.Emperor Yang's original name was Yang Ying, but...
, expanded the Grand Canal, and launched four disastrous wars
Goguryeo-Sui Wars
The Goguryeo–Sui Wars were a series of campaigns launched by the Sui Dynasty of China against the Goguryeo of Korea between 598 and 614. It resulted in the defeat of Sui and contributed to the eventual downfall of the dynasty in 618.-Background:...
against the Goguryeo
Goguryeo
Goguryeo or Koguryŏ was an ancient Korean kingdom located in present day northern and central parts of the Korean Peninsula, southern Manchuria, and southern Russian Maritime province....
. These projects depleted the resources and the workforce of the Sui. In AD 618, Sui Yangdi was murdered. Li Yuan
Emperor Gaozu of Tang
Emperor Gāozǔ of Táng , born Lǐ Yuān , courtesy name Shūdé , was the founder of the Tang Dynasty of China, and the first emperor of this dynasty from 618 to 626. Under the Sui dynasty, Li Yuan was the governor in the area of modern-day Shanxi, and was based in Taiyuan.In 615, Li Yuan was assigned...
, the former governor of Taiyuan
Taiyuan
Taiyuan is the capital and largest city of Shanxi province in North China. At the 2010 census, it had a total population of 4,201,591 inhabitants on 6959 km² whom 3,212,500 are urban on 1,460 km². The name of the city literally means "Great Plains", referring to the location where the Fen River...
, declared himself the emperor, and founded the Tang Dynasty
Tang Dynasty
The Tang Dynasty was an imperial dynasty of China preceded by the Sui Dynasty and followed by the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms Period. It was founded by the Li family, who seized power during the decline and collapse of the Sui Empire...
.
Three Kingdoms of Korea
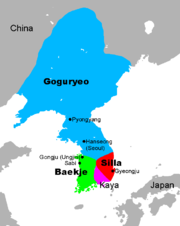
Baekje
Baekje or Paekche was a kingdom located in southwest Korea. It was one of the Three Kingdoms of Korea, together with Goguryeo and Silla....
, Silla
Silla
Silla was one of the Three Kingdoms of Korea, and one of the longest sustained dynasties in...
and Goguryeo
Goguryeo
Goguryeo or Koguryŏ was an ancient Korean kingdom located in present day northern and central parts of the Korean Peninsula, southern Manchuria, and southern Russian Maritime province....
. Although they shared a similar language and culture, these three kingdoms constantly fought with each other for control of the peninsula. Furthermore, Goguryeo had been engaged in constant wars with the Chinese. This included the Goguryeo-Sui Wars
Goguryeo-Sui Wars
The Goguryeo–Sui Wars were a series of campaigns launched by the Sui Dynasty of China against the Goguryeo of Korea between 598 and 614. It resulted in the defeat of Sui and contributed to the eventual downfall of the dynasty in 618.-Background:...
, where the Kingdom of Goguryeo managed to repel the invading forces of the Sui Dynasty
Sui Dynasty
The Sui Dynasty was a powerful, but short-lived Imperial Chinese dynasty. Preceded by the Southern and Northern Dynasties, it ended nearly four centuries of division between rival regimes. It was followed by the Tang Dynasty....
.
As the Kingdom of Silla conquered nearby city-states, they gained access to the Yellow Sea
Yellow Sea
The Yellow Sea is the name given to the northern part of the East China Sea, which is a marginal sea of the Pacific Ocean. It is located between mainland China and the Korean Peninsula. Its name comes from the sand particles from Gobi Desert sand storms that turn the surface of the water golden...
, making direct contact with the Tang Dynasty
Tang Dynasty
The Tang Dynasty was an imperial dynasty of China preceded by the Sui Dynasty and followed by the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms Period. It was founded by the Li family, who seized power during the decline and collapse of the Sui Empire...
possible. The Tang Dynasty teamed up with Silla and formed a strategy to invade Goguryeo. Since Goguryeo had been able to repel earlier Chinese invasions from the North, perhaps Gorguryeo would fall if it were attacked by Silla from the south at the same time. However, in order to do this, the Tang-Silla alliance had to eliminate Goguryeo's nominal ally Baekje and secure a base of operations in southern Korea for a second front.
In 660, the coalition troops of Silla and Tang of China attacked Baekje, resulting in the annexation of Baekje by Silla. Together, Silla and Tang effectively eliminated Baekje when they captured the capital of Sabi, as well as Baekje's last king, Uija, and most of the royal family.
However, Yamato
Yamato period
The is the period of Japanese history when the Japanese Imperial court ruled from modern-day Nara Prefecture, then known as Yamato Province.While conventionally assigned to the period 250–710 , the actual start of Yamato rule is disputed...
Japan and Baekje had been long-standing and very close allies. In 663, Baekje revival forces and a Japanese naval fleet convened in southern Baekje to confront the Silla forces in the Battle of Baekgang
Battle of Baekgang
The Battle of Baekgang, also known as Battle of Baekgang-gu or by the Japanese name Battle of Hakusukinoe , was a battle between Baekje restoration forces and their ally, Yamato Japan, against the allied forces of Silla and the Tang Dynasty of ancient China...
. The Tang dynasty also sent 7,000 soldiers and 170 ships. After five naval confrontations that took place in August 663 at Baekgang, considered the lower reaches of Tongjin river, the Silla-Tang forces emerged victorious.
The Silla-Tang forces turned their attention to Goguryeo. Although Goguryeo had repelled the Sui Dynasty a century earlier, attacks by the Tang Dynasty from the west proved too formidable. The Silla-Tang alliance emerged victorious in the Goguryeo-Tang Wars
Goguryeo-Tang Wars
The Goguryeo–Tang Wars occurred in the 7th century between Korean Goguryeo and an allied Chinese Tang Dynasty and Silla. Exhausted from numerous attacks by China, Goguryeo finally succumbed to a two front attack by Tang and Silla...
. Silla thus unified most of the Korean peninsula in 668.
But the kingdom's reliance on China's Tang Dynasty had its price. Silla had to forcibly resist the imposition of Chinese rule over the entire peninsula. Silla then fought for nearly a decade to expel Chinese forces to finally establish a unified kingdom as far north as modern Pyongyang
Pyongyang
Pyongyang is the capital of the Democratic People's Republic of Korea, commonly known as North Korea, and the largest city in the country. Pyongyang is located on the Taedong River and, according to preliminary results from the 2008 population census, has a population of 3,255,388. The city was...
.
Silla'a unification of Korea was short lived. The northern region of the defunct Goguryeo state later reemerged as Balhae
Balhae
Balhae was a Manchurian kingdom established after the fall of Goguryeo. After Goguryeo's capital and southern territories fell to Unified Silla, Dae Jo-yeong, a Mohe general, whose father was Dae Jung-sang, established Jin , later called Balhae.Balhae occupied southern parts of Manchuria and...
, due to the leadership of former Goguryeo General Dae Joyeong.
Civil service
A government system supported by a large class of Confucian literatiScholar-bureaucrats
Scholar-officials or Scholar-bureaucrats were civil servants appointed by the emperor of China to perform day-to-day governance from the Sui Dynasty to the end of the Qing Dynasty in 1912, China's last imperial dynasty. These officials mostly came from the well-educated men known as the...
selected through civil service examinations was perfected under Tang rule. This competitive procedure was designed to draw the best talents into government. But perhaps an even greater consideration for the Tang rulers, aware that imperial dependence on powerful aristocratic families and warlords would have destabilizing consequences, was to create a body of career officials having no autonomous territorial or functional power base. As it turned out, these scholar-officials acquired status in their local communities, family ties, and shared values that connected them to the imperial court. From Tang times until the closing days of the Qing Dynasty
Qing Dynasty
The Qing Dynasty was the last dynasty of China, ruling from 1644 to 1912 with a brief, abortive restoration in 1917. It was preceded by the Ming Dynasty and followed by the Republic of China....
in 1911, scholar officials functioned often as intermediaries between the grassroots level and the government. This model of government had an influence on Korea and Japan.
Printing press

History of typography in East Asia
The history of printing in East Asia refers to the use of woodblock printing and movable type printing by East Asian artisans. The former existed in Tang China as early as the 7th century, and the latter in Song China by the 11th century. Use of woodblock printing quickly spread to other East Asian...
was invented in China around 1040 AD by Pi Sheng (990-1051) (spelled Bi Sheng in the Pinyin
Pinyin
Pinyin is the official system to transcribe Chinese characters into the Roman alphabet in China, Malaysia, Singapore and Taiwan. It is also often used to teach Mandarin Chinese and spell Chinese names in foreign publications and used as an input method to enter Chinese characters into...
system). Pi Sheng's type was made of baked clay. As described by the Chinese scholar Shen Kuo
Shen Kuo
Shen Kuo or Shen Gua , style name Cunzhong and pseudonym Mengqi Weng , was a polymathic Chinese scientist and statesman of the Song Dynasty...
(1031–1095)
The world's first metal-based movable type
Movable type
Movable type is the system of printing and typography that uses movable components to reproduce the elements of a document ....
printing press
Printing press
A printing press is a device for applying pressure to an inked surface resting upon a print medium , thereby transferring the ink...
was invented in Korea
Korea
Korea ) is an East Asian geographic region that is currently divided into two separate sovereign states — North Korea and South Korea. Located on the Korean Peninsula, Korea is bordered by the People's Republic of China to the northwest, Russia to the northeast, and is separated from Japan to the...
in 1234. That was 210 years before Johannes Gutenberg from Germany did.
Jikji
Jikji
Jikji is the abbreviated title of a Korean Buddhist document, whose title can be translated "Anthology of Great Buddhist Priests' Zen Teachings". Printed during the Goryeo Dynasty in 1377, it is the world's oldest extant movable metal print book...
is the world's oldest extant movable metal print book. it was published in Heungdeok Temple in 1377, 78 years prior to Johannes Gutenberg's "42-Line Bible" printed during the years 1452-1455.
Invasions from Central Asia. Altaic and Mongols
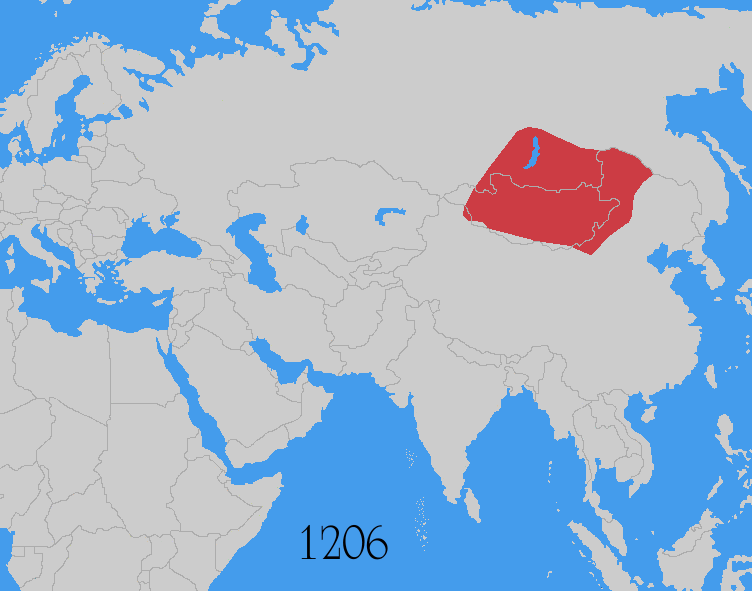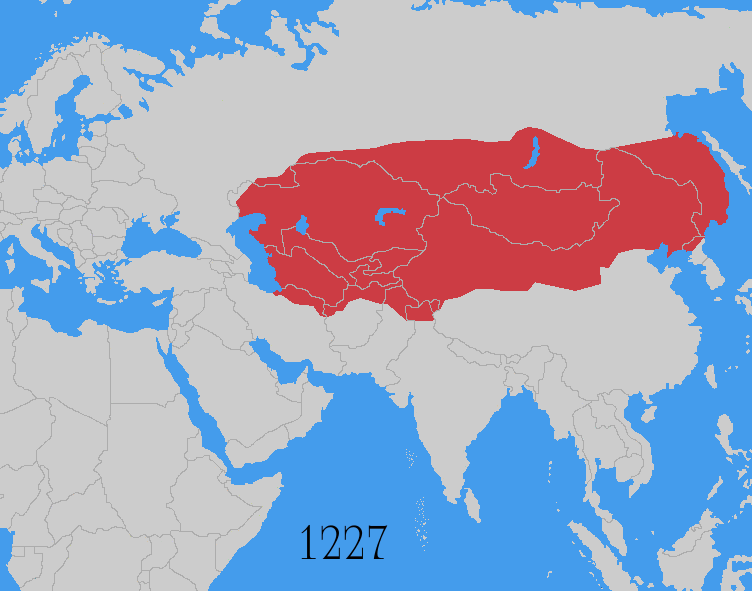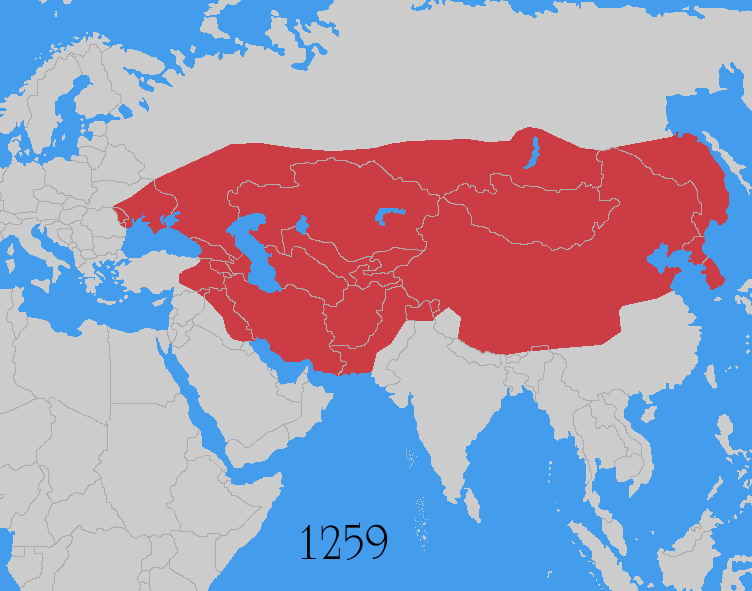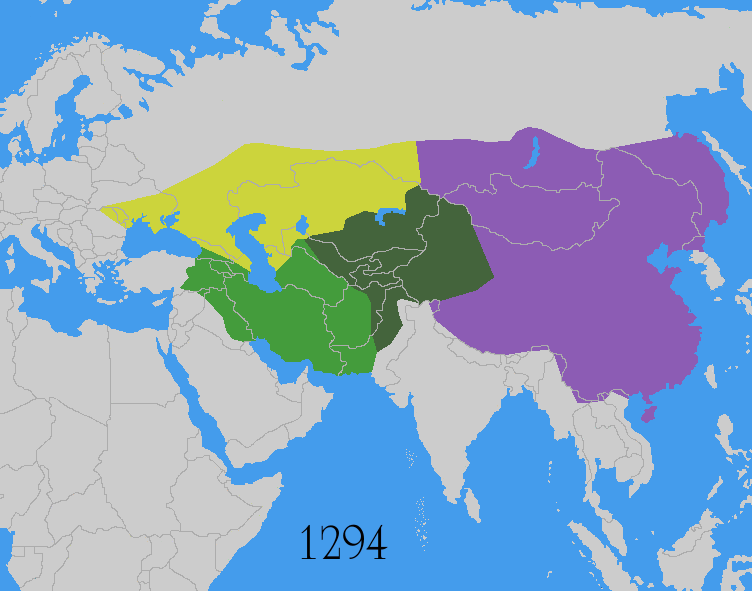
- The Goryeo-Khitan WarsGoryeo-Khitan WarsThe Goryeo-Khitan Wars were a series of 10th- and 11th-century invasions of Korea's Goryeo Dynasty by the Khitan Liao Dynasty near the present-day border between China and North Korea. It resulted in the defeat of Liao Dynasty.-Background:...
of the 10th and 11th century. - The Mongol invasions of KoreaMongol invasions of KoreaThe Mongol invasions of Korea consisted of a series of campaigns by the Mongol Empire against Korea, then known as Goryeo, from 1231 to 1270...
between 1231 to 1259. - The Mongol invasions of JapanMongol invasions of JapanThe ' of 1274 and 1281 were major military efforts undertaken by Kublai Khan to conquer the Japanese islands after the submission of Goryeo to vassaldom. Despite their ultimate failure, the invasion attempts are of macrohistorical importance, because they set a limit on Mongol expansion, and rank...
of 1274 and 1281. - The Mongol invasions of VietnamMongol invasions of VietnamMongol invasions of Vietnam or Mongol-Vietnamese War refer to the three times that the Mongol Empire and its chief khanate the Yuan Dynasty invaded Đại Việt during the Trần Dynasty and the Kingdom of Champa: in 1257–1258, 1284–1285, and 1287–1288. The Mongols were defeated by Đại...
in 1257, 1285 and 1287 AD.
Gunpowder
Most sources credit the discovery of gunpowder to Chinese alchemistsAlchemy
Alchemy is an influential philosophical tradition whose early practitioners’ claims to profound powers were known from antiquity. The defining objectives of alchemy are varied; these include the creation of the fabled philosopher's stone possessing powers including the capability of turning base...
in the 9th century searching for an elixir of immortality
Elixir of life
The elixir of life, also known as the elixir of immortality and sometimes equated with the philosopher's stone, is a legendary potion, or drink, that grants the drinker eternal life and or eternal youth. Many practitioners of alchemy pursued it. The elixir of life was also said to be able to create...
. The discovery of gunpowder was probably the product of centuries of alchemical experimentation. Saltpetre was known to the Chinese by the mid-1st century AD and there is strong evidence of the use of saltpetre and sulfur in various largely medicine combinations. A Chinese alchemical text from 492 noted that saltpeter gave off a purple flame when ignited, providing for the first time a practical and reliable means of distinguishing it from other inorganic salts, making it possible to evaluate and compare purification techniques. By most accounts, the earliest Arabic and Latin
Latin
Latin is an Italic language originally spoken in Latium and Ancient Rome. It, along with most European languages, is a descendant of the ancient Proto-Indo-European language. Although it is considered a dead language, a number of scholars and members of the Christian clergy speak it fluently, and...
descriptions of the purification of saltpeter do not appear until the 13th century.
The first reference to gunpowder is probably a passage in the Zhenyuan miaodao yaolüe, a Taoism text tentatively dated to the mid-9th century:
Some have heated together sulfurSulfurSulfur or sulphur is the chemical element with atomic number 16. In the periodic table it is represented by the symbol S. It is an abundant, multivalent non-metal. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with chemical formula S8. Elemental sulfur is a bright yellow...
, realgarRealgarRealgar, α-As4S4, is an arsenic sulfide mineral, also known as "ruby sulphur" or "ruby of arsenic". It is a soft, sectile mineral occurring in monoclinic crystals, or in granular, compact, or powdery form, often in association with the related mineral, orpiment . It is orange-red in colour, melts...
and saltpeterPotassium nitratePotassium nitrate is a chemical compound with the formula KNO3. It is an ionic salt of potassium ions K+ and nitrate ions NO3−.It occurs as a mineral niter and is a natural solid source of nitrogen. Its common names include saltpetre , from medieval Latin sal petræ: "stone salt" or possibly "Salt...
with honeyHoneyHoney is a sweet food made by bees using nectar from flowers. The variety produced by honey bees is the one most commonly referred to and is the type of honey collected by beekeepers and consumed by humans...
; smoke and flames result, so that their hands and faces have been burnt, and even the whole house where they were working burned down.
The earliest surviving recipes for gunpowder can be found in the Chinese military
Military
A military is an organization authorized by its greater society to use lethal force, usually including use of weapons, in defending its country by combating actual or perceived threats. The military may have additional functions of use to its greater society, such as advancing a political agenda e.g...
treatise Wujing zongyao
Wujing Zongyao
The Wujing Zongyao was a Chinese military compendium written in 1044 AD, during the Northern Song Dynasty. Its authors were the prominent scholars Zeng Gongliang , Ding Du , and Yang Weide , whose writing influenced many later Chinese military writers. The book covered a wide range of subjects,...
of 1044 AD, which contains three: two for use in incendiary bombs to be thrown by siege engine
Siege engine
A siege engine is a device that is designed to break or circumvent city walls and other fortifications in siege warfare. Some have been operated close to the fortifications, while others have been used to attack from a distance. From antiquity, siege engines were constructed largely of wood and...
s and one intended as fuel for poison smoke bomb
Smoke bomb
A smoke bomb is a firework designed to produce smoke upon ignition. Smoke bombs are useful to military units, airsoft games, paintball games, self defense and pranks...
s. The formulas in the Wujing zongyao range from 27 to 50 percent nitrate. Experimenting with different levels of saltpetre content eventually produced bomb
Bomb
A bomb is any of a range of explosive weapons that only rely on the exothermic reaction of an explosive material to provide an extremely sudden and violent release of energy...
s, grenade
Grenade
A grenade is a small explosive device that is projected a safe distance away by its user. Soldiers called grenadiers specialize in the use of grenades. The term hand grenade refers any grenade designed to be hand thrown. Grenade Launchers are firearms designed to fire explosive projectile grenades...
s, and land mine
Land mine
A land mine is usually a weight-triggered explosive device which is intended to damage a target—either human or inanimate—by means of a blast and/or fragment impact....
s, in addition to giving fire arrow
Fire Arrow
Fire arrows are an early form of gun powder rocket which were attached to a stick. The Chinese are credited with the first use of fire arrows in a military application, they may have developed fire arrows from their use of fireworks.- Design :...
s a new lease on life. By the end of the 12th century, there were cast iron
Cast iron
Cast iron is derived from pig iron, and while it usually refers to gray iron, it also identifies a large group of ferrous alloys which solidify with a eutectic. The color of a fractured surface can be used to identify an alloy. White cast iron is named after its white surface when fractured, due...
grenades filled with gunpowder formulations capable of bursting through their metal containers. The 14th century Huolongjing
Huolongjing
The Huolongjing is a 14th century military treatise that was compiled and edited by Jiao Yu and Liu Ji of the early Ming Dynasty in China...
contains gunpowder recipes with nitrate levels ranging from 12 to 91 percent, six of which approach the theoretical composition for maximal explosive force.
In China, the 13th century saw the beginnings of rocket
Rocket
A rocket is a missile, spacecraft, aircraft or other vehicle which obtains thrust from a rocket engine. In all rockets, the exhaust is formed entirely from propellants carried within the rocket before use. Rocket engines work by action and reaction...
ry and the manufacture of the oldest gun still in existence, a descendant of the earlier fire-lance, a gunpowder-fueled flamethrower
Flamethrower
A flamethrower is a mechanical device designed to project a long controllable stream of fire.Some flamethrowers project a stream of ignited flammable liquid; some project a long gas flame. Most military flamethrowers use liquids, but commercial flamethrowers tend to use high-pressure propane and...
that could shoot shrapnel along with fire. The Huolongjing text of the 14th century also describes hollow, gunpowder-packed exploding cannonballs
Round shot
Round shot is a solid projectile without explosive charge, fired from a cannon. As the name implies, round shot is spherical; its diameter is slightly less than the bore of the gun it is fired from.Round shot was made in early times from dressed stone, but by the 17th century, from iron...
.

Mongols
Mongols ) are a Central-East Asian ethnic group that lives mainly in the countries of Mongolia, China, and Russia. In China, ethnic Mongols can be found mainly in the central north region of China such as Inner Mongolia...
to the rest of the world, starting with Europe and the Islamic world. The Arabs acquired knowledge of saltpetre—which they called "Chinese snow" (thalj al-Sīn) —around 1240 and, soon afterward, of gunpowder; they also learned of fireworks ("Chinese flowers") and rockets ("Chinese arrows"). Historian Ahmad Y. al-Hassan argues—contra the general notion—that the Chinese technology passed through Arabic alchemy and chemistry before the 13th century. Gunpowder arrived in India by the mid-14th century, but could have been introduced by the Mongols
Mongols
Mongols ) are a Central-East Asian ethnic group that lives mainly in the countries of Mongolia, China, and Russia. In China, ethnic Mongols can be found mainly in the central north region of China such as Inner Mongolia...
perhaps as early as the mid-13th century.
16th century to 1945
- The growth of European Imperialism in AsiaImperialism in AsiaImperialism in Asia traces its roots back to the late 15th century with a series of voyages that sought a sea passage to India in the hope of establishing direct trade between Europe and Asia in spices. Before 1500 European economies were largely self-sufficient, only supplemented by minor trade...
, starting with the rise of global trade routes. - The Haw warsHaw warsThe Haw Wars , so called in Thai, were fought against Chinese quasi-military forces invading parts of Tonkin and Thailand between the years 1865 and 1890.-Invasion of the flags:...
between the years 1865 and 1890. - The FirstFirst Opium WarThe First Anglo-Chinese War , known popularly as the First Opium War or simply the Opium War, was fought between the United Kingdom and the Qing Dynasty of China over their conflicting viewpoints on diplomatic relations, trade, and the administration of justice...
and Second Opium WarSecond Opium WarThe Second Opium War, the Second Anglo-Chinese War, the Second China War, the Arrow War, or the Anglo-French expedition to China, was a war pitting the British Empire and the Second French Empire against the Qing Dynasty of China, lasting from 1856 to 1860...
s in the mid 19th century (1840–1843 and 1856-1860 respectively). - The Sino-French WarSino-French WarThe Sino–French War was a limited conflict fought between August 1884 and April 1885 to decide whether France should replace China in control of Tonkin . As the French achieved their war aims, they are usually considered to have won the war...
from September 1884 to June 1885. - The First Sino-Japanese WarFirst Sino-Japanese WarThe First Sino-Japanese War was fought between Qing Dynasty China and Meiji Japan, primarily over control of Korea...
occurred between 1894 and 1895, primarily over control of the country Korea. - The Russo-Japanese WarRusso-Japanese WarThe Russo-Japanese War was "the first great war of the 20th century." It grew out of rival imperial ambitions of the Russian Empire and Japanese Empire over Manchuria and Korea...
from February 10, 1904 – September 5, 1905. - The Second Sino-Japanese WarSecond Sino-Japanese WarThe Second Sino-Japanese War was a military conflict fought primarily between the Republic of China and the Empire of Japan. From 1937 to 1941, China fought Japan with some economic help from Germany , the Soviet Union and the United States...
occurred between 1931 (proceeding in earnest in 1937) and 1945, from 1941 on as part of World War IIWorld War IIWorld War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
.
See also
Histories for East Asia are listed by area in alphabetical order:- History of ChinaHistory of ChinaChinese civilization originated in various regional centers along both the Yellow River and the Yangtze River valleys in the Neolithic era, but the Yellow River is said to be the Cradle of Chinese Civilization. With thousands of years of continuous history, China is one of the world's oldest...
- History of Hong KongHistory of Hong KongHong Kong began as a coastal island geographically located off the southern coast of China. While pockets of settlements had taken place in the region with archaeological findings dating back thousands of years, regular written records were not made...
- History of JapanHistory of JapanThe history of Japan encompasses the history of the islands of Japan and the Japanese people, spanning the ancient history of the region to the modern history of Japan as a nation state. Following the last ice age, around 12,000 BC, the rich ecosystem of the Japanese Archipelago fostered human...
- History of KoreaHistory of KoreaThe Korean Peninsula was inhabited from the Lower Paleolithic about 400,000-500,000 years ago. Archeological evidence indicates that the presence of modern humans in northeast Asia dates to 39,000 years ago. The earliest known Korean pottery dates to around 8000 BC, and the Neolithic period began...
- History of MacauHistory of MacauMacau is a Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China. It was administered by Portugal for 442 years, first as a trading post, however self administration was not achieved until the 1840's, it was subsequently turned as a Portuguese territory, until its handover to China in...
- History of MongoliaHistory of MongoliaThe area of what is now Mongolia has been ruled by various nomadic empires, including the Xiongnu, the Xianbei, the Nirun, the Gökturks, and others. The Mongol Empire was founded by Genghis Khan in 1206. After the collapse of the Yuan Dynasty in 1368, the Mongols returned to their earlier patterns...
- History of Russian Far EastRussian Far EastRussian Far East is a term that refers to the Russian part of the Far East, i.e., extreme east parts of Russia, between Lake Baikal in Eastern Siberia and the Pacific Ocean...
- History of Ryukyu Islands
- History of SiberiaHistory of SiberiaThe early history of Siberia is greatly influenced by the sophisticated nomadic civilizations of the Scythians and Xiongnu , both flourishing before the Christian era. The steppes of South Siberia saw a succession of nomadic empires, including the Turkic Empire and the Mongol Empire...
- History of TibetHistory of TibetTibetan history, as it has been recorded, is particularly focused on the history of Buddhism in Tibet. This is partly due to the pivotal role this religion has played in the development of Tibetan, Mongol, and Manchu cultures, and partly because almost all native historians of the country were...
- History of TaiwanHistory of TaiwanTaiwan was first populated by Negrito, and then Austronesian people. It was colonized by the Dutch in the 17th century, followed by an influx of Han Chinese including Hakka immigrants from areas of Fujian and Guangdong of mainland China, across the Taiwan Strait...
- History of VietnamHistory of VietnamThe history of Vietnam covers a period of more than 2,700 years. By far Vietnam's most important historical international relationship has been with China. Vietnam's prehistory includes a legend about a kingdom known as Van Lang that included what is now China's Guangxi Autonomous Region and...
- History of VladivostokHistory of VladivostokThe history of Vladivostok can roughly be divided into the history of the territory where Vladivostok is located and into the history of the city per se.- Influences :...

