
History of Minnesota
Encyclopedia

Native Americans in the United States
Native Americans in the United States are the indigenous peoples in North America within the boundaries of the present-day continental United States, parts of Alaska, and the island state of Hawaii. They are composed of numerous, distinct tribes, states, and ethnic groups, many of which survive as...
residents, European exploration and settlement
European colonization of the Americas
The start of the European colonization of the Americas is typically dated to 1492. The first Europeans to reach the Americas were the Vikings during the 11th century, who established several colonies in Greenland and one short-lived settlement in present day Newfoundland...
, and the emergence of industries made possible by the state's natural resources. Minnesota
Minnesota
Minnesota is a U.S. state located in the Midwestern United States. The twelfth largest state of the U.S., it is the twenty-first most populous, with 5.3 million residents. Minnesota was carved out of the eastern half of the Minnesota Territory and admitted to the Union as the thirty-second state...
achieved prominence through fur trading, logging, and farming, and later through railroads, and iron mining. While those industries remain important, the state's economy is now driven by banking, computers, and health care.
The earliest known settlers followed herds of large game to the region during the last glacial period. They preceded the Anishinaabe
Anishinaabe
Anishinaabe or Anishinabe—or more properly Anishinaabeg or Anishinabek, which is the plural form of the word—is the autonym often used by the Odawa, Ojibwe, and Algonquin peoples. They all speak closely related Anishinaabemowin/Anishinaabe languages, of the Algonquian language family.The meaning...
, the Dakota
Sioux
The Sioux are Native American and First Nations people in North America. The term can refer to any ethnic group within the Great Sioux Nation or any of the nation's many language dialects...
, and other Native American inhabitants. Fur trade
Fur trade
The fur trade is a worldwide industry dealing in the acquisition and sale of animal fur. Since the establishment of world market for in the early modern period furs of boreal, polar and cold temperate mammalian animals have been the most valued...
rs from France arrived during the 17th century. Europeans, moving west during the 19th century, drove out most of the Native Americans. Fort Snelling, built to protect United States territorial interests, brought early settlers to the area. Early settlers used Saint Anthony Falls
Saint Anthony Falls
Saint Anthony Falls, or the Falls of Saint Anthony, located northeast of downtown Minneapolis, Minnesota, was the only natural major waterfall on the Upper Mississippi River. The natural falls was replaced by a concrete overflow spillway after it partially collapsed in 1869...
for powering sawmills in the area that became Minneapolis
Minneapolis, Minnesota
Minneapolis , nicknamed "City of Lakes" and the "Mill City," is the county seat of Hennepin County, the largest city in the U.S. state of Minnesota, and the 48th largest in the United States...
, while others settled downriver in the area that became Saint Paul
Saint Paul, Minnesota
Saint Paul is the capital and second-most populous city of the U.S. state of Minnesota. The city lies mostly on the east bank of the Mississippi River in the area surrounding its point of confluence with the Minnesota River, and adjoins Minneapolis, the state's largest city...
.
Minnesota became a part of the United States as Minnesota Territory
Minnesota Territory
The Territory of Minnesota was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from March 3, 1849, until May 11, 1858, when the eastern portion of the territory was admitted to the Union as the State of Minnesota.-History:...
in 1849, and became the 32nd U.S. state on May 11, 1858. After the upheaval of the American Civil War
American Civil War
The American Civil War was a civil war fought in the United States of America. In response to the election of Abraham Lincoln as President of the United States, 11 southern slave states declared their secession from the United States and formed the Confederate States of America ; the other 25...
and the Dakota War of 1862
Dakota War of 1862
The Dakota War of 1862, also known as the Sioux Uprising, was an armed conflict between the United States and several bands of the eastern Sioux. It began on August 17, 1862, along the Minnesota River in southwest Minnesota...
, the state's economy started to develop when natural resources were tapped for logging and farming. Railroads attracted immigrants, established the farm economy, and brought goods to market. The power provided by Saint Anthony Falls spurred the growth of Minneapolis, and the innovative milling methods gave it the title of the "milling capital of the world."
New industry came from iron ore, discovered in the north, mined relatively easily from open pits
Open-pit mining
Open-pit mining or opencast mining refers to a method of extracting rock or minerals from the earth by their removal from an open pit or borrow....
, and shipped to Great Lakes
Great Lakes
The Great Lakes are a collection of freshwater lakes located in northeastern North America, on the Canada – United States border. Consisting of Lakes Superior, Michigan, Huron, Erie, and Ontario, they form the largest group of freshwater lakes on Earth by total surface, coming in second by volume...
steel mills from the ports at Duluth
Duluth, Minnesota
Duluth is a port city in the U.S. state of Minnesota and is the county seat of Saint Louis County. The fourth largest city in Minnesota, Duluth had a total population of 86,265 in the 2010 census. Duluth is also the second largest city that is located on Lake Superior after Thunder Bay, Ontario,...
and Two Harbors
Two Harbors, Minnesota
As of the census of 2000, there were 3,613 people, 1,636 households, and 953 families residing in the city. The population density was 1,120.7 people per square mile . There were 1,631 housing units at an average density of 505.9 per square mile...
. Economic development and social changes led to an expanded role for state government and a population shift from rural areas to cities. The Great Depression
Great Depression
The Great Depression was a severe worldwide economic depression in the decade preceding World War II. The timing of the Great Depression varied across nations, but in most countries it started in about 1929 and lasted until the late 1930s or early 1940s...
brought layoffs in mining and tension in labor relations but New Deal
New Deal
The New Deal was a series of economic programs implemented in the United States between 1933 and 1936. They were passed by the U.S. Congress during the first term of President Franklin D. Roosevelt. The programs were Roosevelt's responses to the Great Depression, and focused on what historians call...
programs helped the state. After World War II, Minnesota became known for technology, fueled by early computer companies Sperry Rand, Control Data and Cray
Cray
Cray Inc. is an American supercomputer manufacturer based in Seattle, Washington. The company's predecessor, Cray Research, Inc. , was founded in 1972 by computer designer Seymour Cray. Seymour Cray went on to form the spin-off Cray Computer Corporation , in 1989, which went bankrupt in 1995,...
. The Twin Cities also became a regional center for the arts with cultural institutions such as the Guthrie Theater
Guthrie Theater
The Guthrie Theater is a center for theater performance, production, education, and professional training in Minneapolis, Minnesota. It is the result of the desire of Sir Tyrone Guthrie, Oliver Rea, and Peter Zeisler to create a resident acting company that would produce and perform the classics in...
, Minnesota Orchestra
Minnesota Orchestra
The Minnesota Orchestra is an American orchestra based in Minneapolis, Minnesota.Emil Oberhoffer founded the orchestra as the Minneapolis Symphony Orchestra in 1903, and it gave its first performance on November 5 of that year. In 1968 the orchestra changed to its name to the Minnesota Orchestra...
, and the Walker Art Center
Walker Art Center
The Walker Art Center is a contemporary art center in Minneapolis, Minnesota, United States. The Walker is considered one of the nation's "big five" museums for modern art along with the Museum of Modern Art, the San Francisco Museum of Modern Art, the Guggenheim Museum and the Hirshhorn...
.
Native American inhabitation

Browns Valley, Minnesota
As of the census of 2000, there were 690 people, 285 households, and 171 families residing in the city. The population density was 878.5 people per square mile . There were 317 housing units at an average density of 403.6 per square mile...
in 1933. "Browns Valley Man" was found with tools of the Clovis
Clovis point
Clovis points are the characteristically-fluted projectile points associated with the North American Clovis culture. They date to the Paleoindian period around 13,500 years ago. Clovis fluted points are named after the city of Clovis, New Mexico, where examples were first found in 1929.At the right...
and Folsom
Folsom point
Folsom points are a distinct form of chipped stone projectile points associated with the Folsom Tradition of North America. The style of toolmaking was named after Folsom, New Mexico where the first sample was found within the bone structure of a bison in 1927....
types. Some of the earliest evidence of a sustained presence in the area comes from a site known as Bradbury Brook
Bradbury Brook
Bradbury Brook is an archeological procurement area , located a few miles south of Mille Lacs Lake in east central Minnesota. Here Late Paleoindian inhabitants gathered cobbles of siltstone from a streambed or directly from glacial drift. A partially intact stone workshop at this site was dated to...
near Mille Lacs Lake
Mille Lacs Lake
Mille Lacs Lake is a lake in the U.S. state of Minnesota. It is located in the counties of Mille Lacs, Aitkin and Crow Wing, roughly 100 miles north of the Minneapolis-St. Paul metropolitan area....
which was used around 7500 BC. Subsequently, extensive trading networks developed in the region. The body of an early resident known as "Minnesota Woman
Minnesota Woman
"Minnesota Woman" is the name given to the skeletal remains of a woman believed to be at least 10,000 years old. The bones were found near Pelican Rapids, Minnesota on June 16, 1931, during construction on U.S. Route 59. The bones were brought to Dr...
" was discovered in 1931 in Otter Tail County
Otter Tail County, Minnesota
Otter Tail County is a county located in the U.S. state of Minnesota. As of 2010, the population was 57,303. Its county seat is Fergus Falls.-History:...
. Radiocarbon dating
Radiocarbon dating
Radiocarbon dating is a radiometric dating method that uses the naturally occurring radioisotope carbon-14 to estimate the age of carbon-bearing materials up to about 58,000 to 62,000 years. Raw, i.e. uncalibrated, radiocarbon ages are usually reported in radiocarbon years "Before Present" ,...
determined that she had come through the area in approximately 6600 BC. She had a conch shell from a snail species known as Busycon perversa
Busycon
Busycon is a genus of very large edible sea snails, marine gastropod mollusks in the family Buccinidae. These snails are commonly known in the United States as whelks or Busycon whelks....
, which had previously only been known to exist in Florida.

Lake Superior
Lake Superior is the largest of the five traditionally-demarcated Great Lakes of North America. It is bounded to the north by the Canadian province of Ontario and the U.S. state of Minnesota, and to the south by the U.S. states of Wisconsin and Michigan. It is the largest freshwater lake in the...
(in Minnesota and portions of what is now Michigan, Wisconsin, and Canada) were the first on the continent to begin making metal tools. Pieces of ore with high concentrations of copper were initially pounded into a rough shape, heated to reduce brittleness, pounded again to refine the shape, and reheated. Edges could be made sharp enough to be useful as knives or spear points.
Archaeological evidence of Native American settlements dates back to 3000 BC. The Jeffers Petroglyphs
Jeffers Petroglyphs
The Jeffers Petroglyphs site is an outcrop in southwestern Minnesota with pre-contact Native American petroglyphs. The petroglyphs are pecked into rock of the Red Rock Ridge, a -long Sioux quartzite outcrop that extends from Watonwan County, Minnesota to Brown County, Minnesota. The exposed...
site in southwest Minnesota contains carvings from the Late Archaic Period and from the 1750 BC – 900 BC time period. Pieces of pottery began to appear at short-lived settlements around 1000 BC. Around 700 BC, burial mounds were first created, and the practice continued until the arrival of Europeans, when 10,000 such mounds dotted the state.
The Hopewell culture
Hopewell culture
The Hopewell tradition is the term used to describe common aspects of the Native American culture that flourished along rivers in the northeastern and midwestern United States from 200 BCE to 500 CE. The Hopewell tradition was not a single culture or society, but a widely dispersed set of related...
is believed to have lived along the banks of the Mississippi River from 200 BC to about AD 400. By AD 800, wild rice
Wild rice
Wild rice is four species of grasses forming the genus Zizania, and the grain which can be harvested from them. The grain was historically gathered and eaten in both North America and China...
became a staple crop in the region, and corn farther to the south. Within a few hundred years, the Mississippian culture
Mississippian culture
The Mississippian culture was a mound-building Native American culture that flourished in what is now the Midwestern, Eastern, and Southeastern United States from approximately 800 CE to 1500 CE, varying regionally....
reached into the southeast portion of the state, and large villages were formed. The Dakota Native American culture may have descended from some of the peoples of the Mississippian culture.
When Europeans first started exploring Minnesota, the region was inhabited primarily by tribes of Dakota
Sioux
The Sioux are Native American and First Nations people in North America. The term can refer to any ethnic group within the Great Sioux Nation or any of the nation's many language dialects...
, with the Ojibwa
Ojibwa
The Ojibwe or Chippewa are among the largest groups of Native Americans–First Nations north of Mexico. They are divided between Canada and the United States. In Canada, they are the third-largest population among First Nations, surpassed only by Cree and Inuit...
(sometimes called Chippewa, or Anishinaabe) beginning to migrate westward into the state around 1700. The economy of these tribes was chiefly based on hunter-gatherer
Hunter-gatherer
A hunter-gatherer or forage society is one in which most or all food is obtained from wild plants and animals, in contrast to agricultural societies which rely mainly on domesticated species. Hunting and gathering was the ancestral subsistence mode of Homo, and all modern humans were...
activities. There was also a small group of Ho-Chunk
Ho-Chunk
The Ho-Chunk, also known as Winnebago, are a tribe of Native Americans, native to what is now Wisconsin and Illinois. There are two federally recognized Ho-Chunk tribes, the Ho-Chunk Nation of Wisconsin and Winnebago Tribe of Nebraska....
(Winnebago) Native Americans near Long Prairie
Long Prairie, Minnesota
At the 2000 census, there were 3,040 people, 1,229 households and 769 families residing in the city. The population density was 1,285.2 per square mile . There were 1,334 housing units at an average density of 564.0 per square mile...
, who later moved to a reservation in Blue Earth County
Blue Earth County, Minnesota
Blue Earth County is a county located in the U.S. state of Minnesota. As of 2010, the population was 64,013. Its county seat is Mankato.Blue Earth County is part of the Mankato–North Mankato Metropolitan Statistical Area.-Geography:...
in 1855.
European exploration

Kensington Runestone
The Kensington Runestone is a 200-pound slab of greywacke covered in runes on its face and side which, if genuine, would suggest that Scandinavian explorers reached the middle of North America in the 14th century. It was found in 1898 in the largely rural township of Solem, Douglas County,...
suggests that a group of Norse
Norsemen
Norsemen is used to refer to the group of people as a whole who spoke what is now called the Old Norse language belonging to the North Germanic branch of Indo-European languages, especially Norwegian, Icelandic, Faroese, Swedish and Danish in their earlier forms.The meaning of Norseman was "people...
explorers may have ventured as far inland as Minnesota as early as 1362. Though many consider it a hoax, recent geological examinations point toward a pre-19th century origin of the inscription.
It was a few more centuries before contact between Europeans and Native Americans of Minnesota could be confirmed. In the late 1650s, Pierre Esprit Radisson and Médard des Groseilliers
Médard des Groseilliers
Médard Chouart des Groseilliers was a French explorer and fur trader in Canada. He is often paired with his brother-in-law Pierre-Esprit Radisson who was about 20 years his junior...
were probably the first to meet Dakota Native Americans while following the southern shore of Lake Superior (which would become northern Wisconsin). The north shore was explored in the 1660s. Among the first to do this was Claude Allouez, a missionary on Madeline Island
Madeline Island
Madeline Island is an island of the U.S. state of Wisconsin located in Lake Superior approximately two miles northeast of Bayfield, Wisconsin, and connected to that town seasonally by a 20 minute ferry ride or an ice road. It is the largest of the Apostle Islands, although it is not included...
. He made an early map of the area in 1671.
Around this time, the Ojibwa Native Americans reached Minnesota as part of a westward migration. Having come from a region around Maine, they were experienced at dealing with European traders. They dealt in furs and possessed guns. Tensions rose between the Ojibwa and Dakota in the ensuing years.
In 1671, France signed a treaty with a number of tribes to allow trade. Shortly thereafter, French trader Daniel Greysolon, Sieur du Lhut
Daniel Greysolon, Sieur du Lhut
Daniel Greysolon, Sieur du Lhut was a French soldier and explorer who is the first European known to have visited the area where the city of Duluth, Minnesota is now located and the headwaters of the Mississippi River near Grand Rapids...
arrived in the area and began trading with the local tribes. Du Lhut explored the western area of Lake Superior, near his namesake, the city of Duluth, and areas south of there. He helped to arrange a peace agreement between the Dakota and Ojibwa tribes in 1679.

Louis Hennepin
Father Louis Hennepin, O.F.M. baptized Antoine, was a Catholic priest and missionary of the Franciscan Recollect order and an explorer of the interior of North America....
with companions Michel Aco
Michel Aco
Michel Aco was a French explorer who, along with René Robert Cavelier, Sieur de La Salle and Father Louis Hennepin, explored the Mississippi River. Aco became La Salle's lieutenant because of his knowledge of Native American languages and his abilities as an explorer...
and Antoine Auguelle
Antoine Auguelle
Antoine Auguelle Picard du Gay was a 17th century French explorer. Born at Amiens in Picardy, Auguelle along with Michel Aco accompanied Father Louis Hennepin during his exploration of the Upper Mississippi River...
(aka Picard Du Gay) headed north from the area of Illinois
Illinois
Illinois is the fifth-most populous state of the United States of America, and is often noted for being a microcosm of the entire country. With Chicago in the northeast, small industrial cities and great agricultural productivity in central and northern Illinois, and natural resources like coal,...
after coming into that area with an exploration party headed by René Robert Cavelier, Sieur de La Salle. They were captured by a Dakota tribe in 1680. While with the tribe, they came across and named the Falls of Saint Anthony
Saint Anthony Falls
Saint Anthony Falls, or the Falls of Saint Anthony, located northeast of downtown Minneapolis, Minnesota, was the only natural major waterfall on the Upper Mississippi River. The natural falls was replaced by a concrete overflow spillway after it partially collapsed in 1869...
. Soon, du Lhut negotiated to have Hennepin's party released from captivity. Hennepin returned to Europe and wrote a book, Description of Louisiana, published in 1683, about his travels where many portions (including the part about Saint Anthony Falls) were strongly embellished. As an example, he described the falls as being a drop of fifty or sixty feet, when they were really only about sixteen feet. Pierre-Charles Le Sueur
Pierre-Charles Le Sueur
Pierre-Charles Le Sueur was a French fur trader and explorer in North America, recognized as the first known European to explore the Minnesota River valley....
explored the Minnesota River
Minnesota River
The Minnesota River is a tributary of the Mississippi River, approximately 332 miles long, in the U.S. state of Minnesota. It drains a watershed of nearly , in Minnesota and about in South Dakota and Iowa....
to the Blue Earth
Blue Earth County, Minnesota
Blue Earth County is a county located in the U.S. state of Minnesota. As of 2010, the population was 64,013. Its county seat is Mankato.Blue Earth County is part of the Mankato–North Mankato Metropolitan Statistical Area.-Geography:...
area around 1700. He thought the blue earth was a source of copper, and he told stories about the possibility of mineral wealth, but there actually was no copper to be found.
Explorers searching for the fabled Northwest Passage
Northwest Passage
The Northwest Passage is a sea route through the Arctic Ocean, along the northern coast of North America via waterways amidst the Canadian Arctic Archipelago, connecting the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans...
and large inland seas in North America continued to pass through the state. In 1721, the French built Fort Beauharnois
Fort Beauharnois
Fort Beauharnois was a French fort built on the shores of Lake Pepin, a wide part of the upper Mississippi River, in 1727. The location chosen was on lowlands and the fort was rebuilt in 1730 on higher ground. It was the site of the first Roman Catholic chapel in Minnesota, which was dedicated to...
on Lake Pepin
Lake Pepin
Lake Pepin is a naturally occurring lake, and the widest naturally occurring part of the Mississippi River, located approximately 60 miles downstream from Saint Paul, Minnesota. It is a widening of the river on the border between Minnesota and Wisconsin. The formation of the lake was caused by the...
. In 1731, the Grand Portage trail was first traversed by a European, Pierre La Vérendrye
Pierre Gaultier de Varennes, sieur de La Vérendrye
Pierre Gaultier de Varennes, sieur de La Vérendrye was a French Canadian military officer, fur trader and explorer. In the 1730s he and his four sons opened up the area west of Lake Superior and thus began the process that added Western Canada to the original New France in the Saint Lawrence basin...
. He used a map written down on a piece of birch bark by Ochagach, an Assiniboine guide. The North West Company
North West Company
The North West Company was a fur trading business headquartered in Montreal from 1779 to 1821. It competed with increasing success against the Hudson's Bay Company in what was to become Western Canada...
, which traded in fur and competed with the Hudson's Bay Company
Hudson's Bay Company
The Hudson's Bay Company , abbreviated HBC, or "The Bay" is the oldest commercial corporation in North America and one of the oldest in the world. A fur trading business for much of its existence, today Hudson's Bay Company owns and operates retail stores throughout Canada...
, was established along the Grand Portage in 1783–1784.
Jonathan Carver
Jonathan Carver
Jonathan Carver was an American explorer and writer. He was born in Weymouth, Massachusetts and then moved with his family to Canterbury, Connecticut. He later married Abigail Robbins and became a shoemaker. He is believed to have had seven children.In 1755 Carver joined the colonial militia at...
, a shoemaker from Massachusetts, visited the area in 1767 as part of another expedition. He and the rest of the exploration party were only able to stay for a relatively short period, due to supply shortages. They headed back east to Fort Michilimackinac
Fort Michilimackinac
Fort Michilimackinac was an 18th century French, and later British, fort and trading post in the Great Lakes of North America. Built around 1715, it was located along the southern shore of the strategic Straits of Mackinac connecting Lake Huron and Lake Michigan, at the northern tip of the lower...
, where Carver wrote journals about the trip, though others would later claim the stories were largely plagiarized from others. The stories were published in 1778, but Carver died before the book earned him much money. Carver County
Carver County, Minnesota
As of the census of 2000, there were 70,205 people, 24,356 households, and 18,778 families residing in the county. The population density was 197 people per square mile . There were 24,883 housing units at an average density of 70 per square mile...
and Carver's Cave
Carver's Cave
Within Indian Mounds Park in St. Paul, Minnesota is a plaque memorializing Carver's Cave. The following is the exact text from the plaque:Repeated attempts were made by French and British Explorers to discover a northwest passage...
are named for him.
Until 1818 the Red River Valley was considered British and was subject to several colonization schemes, such as the Red River Colony
Red River Colony
The Red River Colony was a colonization project set up by Thomas Douglas, 5th Earl of Selkirk in 1811 on of land granted to him by the Hudson's Bay Company under what is referred to as the Selkirk Concession. The colony along the Red River of the North was never very successful...
. The boundary where the Red River crossed the 49th parallel was not marked until 1823, when Stephen H. Long conducted a survey expedition. When several hundred settlers abandoned the Red River Colony in the 1820s, they entered the United States by way of the Red River Valley, instead of moving to eastern Canada or returning to Europe. The region had been occupied by Métis
Métis people (Canada)
The Métis are one of the Aboriginal peoples in Canada who trace their descent to mixed First Nations parentage. The term was historically a catch-all describing the offspring of any such union, but within generations the culture syncretised into what is today a distinct aboriginal group, with...
people, the children of voyageurs and Native Americans, since the middle 17th century.
Several efforts were made to determine the source of the Mississippi River
Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the largest river system in North America. Flowing entirely in the United States, this river rises in western Minnesota and meanders slowly southwards for to the Mississippi River Delta at the Gulf of Mexico. With its many tributaries, the Mississippi's watershed drains...
. The true source was found in 1832, when Henry Schoolcraft
Henry Schoolcraft
Henry Rowe Schoolcraft was an American geographer, geologist, and ethnologist, noted for his early studies of Native American cultures, as well as for his 1832 discovery of the source of the Mississippi River. He married Jane Johnston, whose parents were Ojibwe and Scots-Irish...
was guided by a group of Ojibwa headed by Ozaawindib
Ozaawindib
Ozaawindib was an Ojibwa warrior who lived in the early 19th century and was described as an egwakwe —what a modern Ojibwa would describe as a niizh manidoowag...
("Yellow Head") to a lake in northern Minnesota. Schoolcraft named it Lake Itasca
Lake Itasca
Lake Itasca is a small glacial lake, approximately in area, in the Headwaters area of north central Minnesota. The lake is located in southeastern Clearwater County within Itasca State Park and it has an average depth of 20–35 feet , and is 1,475 ft above sea level.The Ojibwe name for...
, combining the Latin
Latin
Latin is an Italic language originally spoken in Latium and Ancient Rome. It, along with most European languages, is a descendant of the ancient Proto-Indo-European language. Although it is considered a dead language, a number of scholars and members of the Christian clergy speak it fluently, and...
words veritas ("truth") and caput ("head"). The native name for the lake was Omashkooz, meaning elk
Elk
The Elk is the large deer, also called Cervus canadensis or wapiti, of North America and eastern Asia.Elk may also refer to:Other antlered mammals:...
. Other explorers of the area include Zebulon Pike
Zebulon Pike
Zebulon Montgomery Pike Jr. was an American officer and explorer for whom Pikes Peak in Colorado is named. As a United States Army captain in 1806-1807, he led the Pike Expedition to explore and document the southern portion of the Louisiana Purchase and to find the headwaters of the Red River,...
in 1806, Major Stephen Long
Stephen Harriman Long
Stephen Harriman Long was a U.S. army explorer, topographical engineer, and railway engineer. As an inventor, he is noted for his developments in the design of steam locomotives. He was also one of the most prolific explorers of the early 1800s, although his career as an explorer was relatively...
in 1817, and George William Featherstonhaugh
George William Featherstonhaugh
George William Featherstonhaugh FRS was a British geologist and geographer who initiated the Albany and Schenectady Railroad and was a surveyor of the Louisiana Purchase for the US Government....
in 1835. Featherstonhaugh conducted a geological survey of the Minnesota River valley and wrote an account entitled A Canoe Voyage up the Minnay Sotor.
Joseph Nicollet
Joseph Nicollet
Joseph Nicolas Nicollet , also known as Jean-Nicolas Nicollet, was a French geographer and mathematician known for mapping the Upper Mississippi River basin during the 1830s....
scouted the area in the late 1830s, exploring and mapping the Upper Mississippi River basin, the St. Croix River, and the land between the Mississippi and Missouri Rivers. He and John C. Frémont
John C. Frémont
John Charles Frémont , was an American military officer, explorer, and the first candidate of the anti-slavery Republican Party for the office of President of the United States. During the 1840s, that era's penny press accorded Frémont the sobriquet The Pathfinder...
left their mark in the southwest of the state, carving their names in the pipestone
Catlinite
Catlinite is a type of argillite , usually brownish-red in color, which occurs in a matrix of Sioux quartzite. Because it is fine-grained and easily worked, it is prized by Native Americans for use in making sacred pipes such as calumets and chanunpas...
quarries near Winnewissa Falls (an area now part of Pipestone National Monument
Pipestone National Monument
Pipestone National Monument is located in southwestern Minnesota, just north of the city of Pipestone, Minnesota. It is located along the highways of U.S. Route 75, Minnesota State Highway 23 and Minnesota State Highway 30....
in Pipestone County
Pipestone County, Minnesota
As of the census of 2000, there were 9,895 people, 4,069 households, and 2,726 families residing in the county. The population density was 21 people per square mile . There were 4,434 housing units at an average density of 10 per square mile...
).
Henry Wadsworth Longfellow
Henry Wadsworth Longfellow
Henry Wadsworth Longfellow was an American poet and educator whose works include "Paul Revere's Ride", The Song of Hiawatha, and Evangeline...
never explored the state, but he did help to make it popular. He published The Song of Hiawatha
The Song of Hiawatha
The Song of Hiawatha is an 1855 epic poem, in trochaic tetrameter, by Henry Wadsworth Longfellow, featuring an Indian hero and loosely based on legends and ethnography of the Ojibwe and other Native American peoples contained in Algic Researches and additional writings of Henry Rowe Schoolcraft...
in 1855, which contains references to many regions in Minnesota. The story was based on Ojibwa legends carried back east by other explorers and traders (particularly those collected by Henry Rowe Schoolcraft).
Land acquisition
Treaty of Paris (1783)
The Treaty of Paris, signed on September 3, 1783, ended the American Revolutionary War between Great Britain on the one hand and the United States of America and its allies on the other. The other combatant nations, France, Spain and the Dutch Republic had separate agreements; for details of...
at the end of the American Revolution
American Revolution
The American Revolution was the political upheaval during the last half of the 18th century in which thirteen colonies in North America joined together to break free from the British Empire, combining to become the United States of America...
in 1783. This included what would become modern day Saint Paul but only part of Minneapolis, including the northeast, north-central and east-central portions of the state. The wording of the treaty in the Minnesota area depended on landmarks reported by fur traders, who erroneously reported an "Isle Phelipeaux" in Lake Superior, a "Long Lake" west of the island, and the belief that the Mississippi River ran well into modern Canada. Most of the state was purchased in 1803 from France as part of the Louisiana Purchase
Louisiana Purchase
The Louisiana Purchase was the acquisition by the United States of America of of France's claim to the territory of Louisiana in 1803. The U.S...
. Parts of northern Minnesota were considered to be in Rupert's Land
Rupert's Land
Rupert's Land, or Prince Rupert's Land, was a territory in British North America, consisting of the Hudson Bay drainage basin that was nominally owned by the Hudson's Bay Company for 200 years from 1670 to 1870, although numerous aboriginal groups lived in the same territory and disputed the...
. The exact definition of the boundary between Minnesota and British North America
British North America
British North America is a historical term. It consisted of the colonies and territories of the British Empire in continental North America after the end of the American Revolutionary War and the recognition of American independence in 1783.At the start of the Revolutionary War in 1775 the British...
was not addressed until the Anglo-American Convention of 1818, which set the U.S.–Canada border at the 49th parallel
49th parallel north
The 49th parallel north is a circle of latitude that is 49 degrees north of the Earth's equatorial plane. It crosses Europe, Asia, the Pacific Ocean, North America, and the Atlantic Ocean....
west of the Lake of the Woods
Lake of the Woods
Lake of the Woods is a lake occupying parts of the Canadian provinces of Ontario and Manitoba and the U.S. state of Minnesota. It separates a small land area of Minnesota from the rest of the United States. The Northwest Angle and the town of Angle Township can only be reached from the rest of...
(except for a small chunk of land now dubbed the Northwest Angle
Northwest Angle
The Northwest Angle, known simply as the Angle by locals, and coextensive with Angle Township, is a part of northern Lake of the Woods County, Minnesota, and is the only place in the United States outside Alaska that is north of the 49th parallel...
). Border disputes east of the Lake of the Woods continued until the Webster-Ashburton Treaty
Webster-Ashburton Treaty
The Webster–Ashburton Treaty, signed August 9, 1842, was a treaty resolving several border issues between the United States and the British North American colonies...
of 1842.
Throughout the first half of the 19th century, the northeastern portion of the state was a part of the Northwest Territory
Northwest Territory
The Territory Northwest of the River Ohio, more commonly known as the Northwest Territory, was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from July 13, 1787, until March 1, 1803, when the southeastern portion of the territory was admitted to the Union as the state of Ohio...
, then the Illinois Territory
Illinois Territory
The Territory of Illinois was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from March 1, 1809, until December 3, 1818, when the southern portion of the territory was admitted to the Union as the State of Illinois. The area was earlier known as "Illinois Country" while under...
, then the Michigan Territory
Michigan Territory
The Territory of Michigan was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from June 30, 1805, until January 26, 1837, when the final extent of the territory was admitted to the Union as the State of Michigan...
, and finally the Wisconsin Territory
Wisconsin Territory
The Territory of Wisconsin was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from July 3, 1836, until May 29, 1848, when an eastern portion of the territory was admitted to the Union as the State of Wisconsin...
. The western and southern areas of the state were not formally organized until 1838, when they became part of the Iowa Territory
Iowa Territory
The Territory of Iowa was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from July 4, 1838, until December 28, 1846, when the southeastern portion of the territory was admitted to the Union as the State of Iowa.-History:...
.
Fort Snelling and the establishment of Minneapolis and Saint Paul

Military history of the United States
The military history of the United States spans a period of over two centuries. During the course of those years, the United States evolved from a new nation fighting the British Empire for independence without a professional military , through a monumental American Civil War to the world's sole...
presence in the state. The land for the fort, at the confluence
Confluence (geography)
In geography, a confluence is the meeting of two or more bodies of water. It usually refers to the point where two streams flow together, merging into a single stream...
of the Minnesota and Mississippi rivers, was acquired in 1805 by Zebulon Pike
Zebulon Pike
Zebulon Montgomery Pike Jr. was an American officer and explorer for whom Pikes Peak in Colorado is named. As a United States Army captain in 1806-1807, he led the Pike Expedition to explore and document the southern portion of the Louisiana Purchase and to find the headwaters of the Red River,...
. When concerns mounted about the fur trade in the area, construction of the fort began in 1819. Construction was completed in 1825, and Colonel Josiah Snelling
Josiah Snelling
Colonel Josiah Snelling was the first commander of Fort Snelling, a fort located at the confluence of the Mississippi and Minnesota rivers in Minnesota. He was responsible for the initial design and construction of the fort, and he commanded it from 1820 through 1827. He had a reputation for...
and his officers and soldiers left their imprint on the area. One of the missions of the fort was to mediate disputes between the Ojibwa and the Dakota tribes. Lawrence Taliaferro
Lawrence Taliaferro
Lawrence Taliaferro was a United States Army officer best known for his service as an Indian agent at Fort Snelling, Minnesota from 1820 through 1839 and also as an individual who played a part in the saga of the famous African American slave Dred Scott.Taliaferro was born at Whitehall...
was an agent of the U.S. Bureau of Indian Affairs. He spent 20 years at the site, finally resigning in 1839.

Dred Scott v. Sandford
Dred Scott v. Sandford, , also known as the Dred Scott Decision, was a ruling by the U.S. Supreme Court that people of African descent brought into the United States and held as slaves were not protected by the Constitution and could never be U.S...
. Slaves Dred Scott and his wife were taken to the fort by their master, John Emerson. They lived at the fort and elsewhere in territories where slavery was prohibited. After Emerson's death, the Scotts argued that since they had lived in free territory, they were no longer slaves. Ultimately, the U.S. Supreme Court sided against the Scotts. Dred Scott Field, located just a short distance away in Bloomington
Bloomington, Minnesota
Bloomington is the fifth largest city in the U.S. state of Minnesota in Hennepin County. Located on the north bank of the Minnesota River above its confluence with the Mississippi River, Bloomington lies at the heart of the southern...
, is named in the memory of Fort Snelling's significance in one of the most important legal precedents in U.S. History.
By 1851, treaties between Native American tribes and the U.S. government had opened much of Minnesota to settlement, so Fort Snelling no longer was a frontier outpost. It served as a training center for soldiers during the American Civil War
American Civil War
The American Civil War was a civil war fought in the United States of America. In response to the election of Abraham Lincoln as President of the United States, 11 southern slave states declared their secession from the United States and formed the Confederate States of America ; the other 25...
and later as the headquarters for the Department of Dakota. A portion has been designated as Fort Snelling National Cemetery
Fort Snelling National Cemetery
Fort Snelling National Cemetery is a United States National Cemetery located in the city of Minneapolis in Hennepin County, Minnesota. It encompasses , and as of April 24, 2007 had 172,001 interments.- History :...
where over 160,000 are interred. During World War II, the fort served as a training center for nearly 300,000 inductees. After World War II, the fort was threatened with demolition due to the building of freeways Highway 5
Minnesota State Highway 5
Minnesota State Highway 5 is a highway in Minnesota, which runs from its intersection with State Highways 19 and 22 in Gaylord and continues east and northeast to its eastern terminus at its interchange with State Highway 36 and Washington County Road 5 in Stillwater...
and Highway 55
Minnesota State Highway 55
Minnesota State Highway 55 is a highway in west-central, central, and east-central Minnesota, which runs from the North Dakota state line near Tenney and continues east and southeast to its eastern terminus at its intersection with U.S...
, but citizens rallied to save it. Fort Snelling is now a historic site operated by the Minnesota Historical Society
Minnesota Historical Society
The Minnesota Historical Society is a private, non-profit educational and cultural institution dedicated to preserving the history of the U.S. state of Minnesota. It was founded by the territorial legislature in 1849, almost a decade before statehood. The Society is named in the Minnesota...
.
Fort Snelling was largely responsible for the establishment of the city of Minneapolis
Minneapolis, Minnesota
Minneapolis , nicknamed "City of Lakes" and the "Mill City," is the county seat of Hennepin County, the largest city in the U.S. state of Minnesota, and the 48th largest in the United States...
. In an effort to be self-sufficient, the soldiers of the fort built roads, planted crops, and built a grist mill and a sawmill at Saint Anthony Falls
Saint Anthony Falls
Saint Anthony Falls, or the Falls of Saint Anthony, located northeast of downtown Minneapolis, Minnesota, was the only natural major waterfall on the Upper Mississippi River. The natural falls was replaced by a concrete overflow spillway after it partially collapsed in 1869...
. Later, Franklin Steele came to Fort Snelling as the post sutler
Sutler
A sutler or victualer is a civilian merchant who sells provisions to an army in the field, in camp or in quarters. The sutler sold wares from the back of a wagon or a temporary tent, allowing them to travel along with an army or to remote military outposts...
(the operator of the general store), and established interests in lumbering and other activities. When the Ojibwa signed a treaty ceding lands in 1837, Steele staked a claim to land on the east side of the Mississippi River adjacent to Saint Anthony Falls. In 1848, he built a sawmill at the falls, and the community of Saint Anthony sprung up around the east side of the falls. Steele told one of his employees, John H. Stevens
John H. Stevens
John Harrington Stevens was the first authorized resident on the west bank of the Mississippi River in what would become Minneapolis, Minnesota. He was granted permission to occupy the site, then part of the Fort Snelling military reservation, in exchange for providing ferry service to St. Anthony...
, that land on the west side of the falls would make a good site for future mills. Since the land on the west side was still part of the military reservation, Stevens made a deal with Fort Snelling's commander. Stevens would provide free ferry service across the river in exchange for a tract of 160 acre (0.6474976 km²) at the head of the falls. Stevens received the claim and built a house, the first house in Minneapolis, in 1850. In 1854, Stevens platted the city of Minneapolis on the west bank. Later, in 1872, Minneapolis absorbed the city of Saint Anthony.
The city of Saint Paul, Minnesota
Saint Paul, Minnesota
Saint Paul is the capital and second-most populous city of the U.S. state of Minnesota. The city lies mostly on the east bank of the Mississippi River in the area surrounding its point of confluence with the Minnesota River, and adjoins Minneapolis, the state's largest city...
owes its existence to Fort Snelling. A group of squatters, mostly from the ill-fated Selkirk Colony in what is now the Canadian province of Manitoba
Manitoba
Manitoba is a Canadian prairie province with an area of . The province has over 110,000 lakes and has a largely continental climate because of its flat topography. Agriculture, mostly concentrated in the fertile southern and western parts of the province, is vital to the province's economy; other...
, established a camp near the fort. The commandant of Fort Snelling, Major Joseph Plympton, found their presence problematic because they were using timber and allowing their cattle and horses to graze around the fort. Plympton banned lumbering and the construction of any new buildings on the military reservation land. As a result, the squatters moved four miles downstream on the Mississippi River. They settled at a site known as Fountain Cave. This site was not quite far enough for the officers at the fort, so the squatters were forced out again. Pierre "Pig's Eye" Parrant
Pierre Parrant
Pierre “Pig’s Eye” Parrant is recognized as being the first person of European descent to live within the borders of what would eventually become the city of Saint Paul, Minnesota...
, a popular moonshine
Moonshine
Moonshine is an illegally produced distilled beverage...
r among the group, moved downriver and established a saloon, becoming the first European resident in the area that later became Saint Paul. The squatters named their settlement "Pig's Eye" after Parrant. The name was later changed to Lambert's Landing and then finally Saint Paul. However, the earliest name for the area comes from a Native American colony Im-in-i-ja Ska, meaning "White Rock" and referring to the limestone bluffs nearby.
Minneapolis and Saint Paul are collectively known as the "Twin Cities". The cities enjoyed a rivalry during their early years, with Saint Paul being the capital city and Minneapolis becoming prominent through industry. The term "Twin Cities" was coined around 1872, after a newspaper editorial suggested that Minneapolis could absorb Saint Paul. Residents decided that the cities needed a separate identity, so people coined the phrase "Dual Cities", which later evolved into "Twin Cities". Today, Minneapolis is the largest city in Minnesota, with a population of 382,618 in the 2000 census. Saint Paul is the second largest city, with a population of 287,151. Minneapolis and Saint Paul anchor a metropolitan area with a population of 2,968,806 as of 2000, with a total state population of 4,919,479.
Early European settlement and development

Henry Hastings Sibley
Henry Hastings Sibley was the first Governor of the U.S. state of Minnesota.-Early life and education:...
built the first stone house in the Minnesota Territory in Mendota
Mendota, Minnesota
Mendota is a city in Dakota County, Minnesota, United States. The name comes from the Dakota word for "where the waters meet." The population was 198 at the 2010 census.-History:...
in 1838, along with other limestone buildings used by the American Fur Company
American Fur Company
The American Fur Company was founded by John Jacob Astor in 1808. The company grew to monopolize the fur trade in the United States by 1830, and became one of the largest businesses in the country. The company was one the first great trusts in American business...
, which bought animal pelts at that location from 1825 to 1853. Another area of early economic development in Minnesota was the logging industry. Loggers found the white pine
Eastern White Pine
Pinus strobus, commonly known as the eastern white pine, is a large pine native to eastern North America, occurring from Newfoundland west to Minnesota and southeastern Manitoba, and south along the Appalachian Mountains to the northern edge of Georgia.It is occasionally known as simply white pine,...
especially valuable, and it was plentiful in the northeastern section of the state and in the St. Croix River
St. Croix River (Wisconsin-Minnesota)
The St. Croix River is a tributary of the Mississippi River, approximately long, in the U.S. states of Wisconsin and Minnesota. The lower of the river form the border between Wisconsin and Minnesota. The river is a National Scenic Riverway under the protection of the National Park Service. A...
valley. Before railroads, lumbermen relied mostly on river transportation to bring logs to market, which made Minnesota's timber resources attractive. Towns like Marine on St. Croix
Marine on St. Croix, Minnesota
Marine on St. Croix is a city in Washington County, Minnesota, United States. The population was 689 at the 2010 census.-Geography:According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of , of which, of it is land and of it is water. Minnesota State Highway 95 serves as a main...
and Stillwater
Stillwater, Minnesota
As of the census of 2000, there were 15,143 people, 5,797 households, and 4,115 families residing in the city. The population density was 2,340.0 people per square mile . There were 5,926 housing units at an average density of 915.7 per square mile...
became important lumber centers fed by the St. Croix River, while Winona
Winona, Minnesota
Winona is a city in and the county seat of Winona County, in the U.S. State of Minnesota. Located in picturesque bluff country on the Mississippi River, its most noticeable physical landmark is Sugar Loaf....
was supplied lumber by areas in southern Minnesota and along the Minnesota River. The unregulated logging practices of the time and a severe drought took their toll in 1894, when the Great Hinckley Fire
Great Hinckley Fire
The Great Hinckley Fire was a major conflagration on September 1, 1894, which burned an area of at least 810 km² , perhaps more than 1000 km², including the town of Hinckley, Minnesota. The fire killed hundreds, with the minimum number estimated at 418. However, some scholars believe the...
ravaged 480 square miles (1,243.2 km²) in the Hinckley
Hinckley, Minnesota
As of the census of 2000, there were 1,291 people, 551 households, and 332 families residing in the city. The population density was 454.3 people per square mile . There were 614 housing units at an average density of 216.0 per square mile...
and Sandstone
Sandstone, Minnesota
As of the census of 2000, there were 1,549 people, 580 households, and 359 families residing in the city. The population density was 292.5 people per square mile . There were 634 housing units at an average density of 119.7 per square mile...
areas of Pine County, killing over 400 residents. The combination of logging and drought struck again in the Baudette Fire of 1910
Baudette Fire of 1910
The Baudette Fire, also known as the Spooner-Baudette Fire, was a large wildfire that burned in Lake of the Woods County, Minnesota, including nearly all of the twin towns of Spooner and Baudette on October 7, 1910. In addition to Baudette, the fire also burned the villages of Graceton, Pitt,...
and the Cloquet Fire
1918 Cloquet Fire
The 1918 Cloquet fire was a massive fire in northern Minnesota in October, 1918 caused by sparks on the local railroads and dry conditions. The fire left much of western Carlton County devastated, mostly affecting Moose Lake, Cloquet, and Kettle River. Cloquet was hit the hardest by the fires...
of 1918.

Rum River
The Rum River is a slow, meandering channel that connects Minnesota's Mille Lacs Lake with the Mississippi River. It runs for through the farming communities of Onamia, Milaca, Princeton, Cambridge, and Isanti before ending at the Twin Cities suburb of Anoka, roughly 20 miles northwest of downtown...
. In 1848, businessman Franklin Steele built the first private sawmill on the Saint Anthony Falls, and more sawmills quickly followed. The oldest home still standing in Saint Anthony is the Ard Godfrey house, built in 1848, and lived in by Ard and Harriet Godfrey. The house of John H. Stevens
John Harrington Stevens House
The John Harrington Stevens House was the first authorized house on the west bank of the Mississippi River in what would become Minneapolis in the U.S. state of Minnesota. It was built in 1850 at Saint Anthony Falls by John H. Stevens on the site where the Minneapolis Post Office now sits...
, the first house on the west bank in Minneapolis, was moved several times, finally to Minnehaha Park in south Minneapolis in 1896.
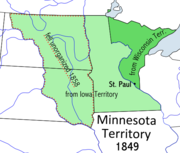
Minnesota Territory
Stephen A. DouglasStephen A. Douglas
Stephen Arnold Douglas was an American politician from the western state of Illinois, and was the Northern Democratic Party nominee for President in 1860. He lost to the Republican Party's candidate, Abraham Lincoln, whom he had defeated two years earlier in a Senate contest following a famed...
(D)
Democratic Party (United States)
The Democratic Party is one of two major contemporary political parties in the United States, along with the Republican Party. The party's socially liberal and progressive platform is largely considered center-left in the U.S. political spectrum. The party has the lengthiest record of continuous...
, the chair of the Senate Committee on Territories, drafted the bill authorizing Minnesota Territory. He had envisioned a future for the upper Mississippi valley, so he was motivated to keep the area from being carved up by neighboring territories. In 1846, he prevented Iowa from including Fort Snelling and Saint Anthony Falls within its northern border. In 1847, he kept the organizers of Wisconsin from including Saint Paul and Saint Anthony Falls. The Minnesota Territory
Minnesota Territory
The Territory of Minnesota was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from March 3, 1849, until May 11, 1858, when the eastern portion of the territory was admitted to the Union as the State of Minnesota.-History:...
was established from the lands remaining from Iowa Territory
Iowa Territory
The Territory of Iowa was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from July 4, 1838, until December 28, 1846, when the southeastern portion of the territory was admitted to the Union as the State of Iowa.-History:...
and Wisconsin Territory
Wisconsin Territory
The Territory of Wisconsin was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from July 3, 1836, until May 29, 1848, when an eastern portion of the territory was admitted to the Union as the State of Wisconsin...
on March 3, 1849. The Minnesota Territory extended far into what is now North Dakota and South Dakota, to the Missouri River
Missouri River
The Missouri River flows through the central United States, and is a tributary of the Mississippi River. It is the longest river in North America and drains the third largest area, though only the thirteenth largest by discharge. The Missouri's watershed encompasses most of the American Great...
. There was a dispute over the shape of the state to be carved out of Minnesota Territory. An alternate proposal that was only narrowly defeated would have made the 46th parallel the state's northern border and the Missouri River its western border, thus giving up the whole northern half of the state in exchange for the eastern half of what later became South Dakota.
With Alexander Ramsey
Alexander Ramsey
Alexander Ramsey was an American politician. He was born near Harrisburg, Pennsylvania.Alexander Ramsey was elected from Pennsylvania as a Whig to the U.S. House of Representatives and served in the 28th and 29th congresses from March 4, 1843 to March 4, 1847...
(W)
Whig Party (United States)
The Whig Party was a political party of the United States during the era of Jacksonian democracy. Considered integral to the Second Party System and operating from the early 1830s to the mid-1850s, the party was formed in opposition to the policies of President Andrew Jackson and his Democratic...
as the first governor of Minnesota Territory and Henry Hastings Sibley
Henry Hastings Sibley
Henry Hastings Sibley was the first Governor of the U.S. state of Minnesota.-Early life and education:...
(D)
Democratic Party (United States)
The Democratic Party is one of two major contemporary political parties in the United States, along with the Republican Party. The party's socially liberal and progressive platform is largely considered center-left in the U.S. political spectrum. The party has the lengthiest record of continuous...
as the territorial delegate to the United States Congress, the populations of Saint Paul and Saint Anthony swelled. Henry M. Rice (D), who replaced Sibley as the territorial delegate in 1853, worked in Congress to promote Minnesota interests. He lobbied for the construction of a railroad connecting Saint Paul and Lake Superior, with a link from Saint Paul to the Illinois Central
Illinois Central Railroad
The Illinois Central Railroad , sometimes called the Main Line of Mid-America, is a railroad in the central United States, with its primary routes connecting Chicago, Illinois with New Orleans, Louisiana and Birmingham, Alabama. A line also connected Chicago with Sioux City, Iowa...
.
Statehood
In December 1856, Rice brought forward two bills in Congress: an enabling actEnabling act
An enabling act is a piece of legislation by which a legislative body grants an entity which depends on it for authorization or legitimacy the power to take certain actions. For example, enabling acts often establish government agencies to carry out specific government policies in a modern nation...
that would allow Minnesota to form a state constitution, and a railroad land grant bill. Rice's enabling act defined a state containing both prairie and forest lands. The state was bounded on the south by Iowa, on the east by Wisconsin, on the north by Canada, and on the west by the Red River of the North
Red River of the North
The Red River is a North American river. Originating at the confluence of the Bois de Sioux and Otter Tail rivers in the United States, it flows northward through the Red River Valley and forms the border between the U.S. states of Minnesota and North Dakota before continuing into Manitoba, Canada...
and the Bois de Sioux River
Bois de Sioux River
The Bois de Sioux River drains Lake Traverse, the southernmost body of water in the Hudson Bay watershed of North America. It is a tributary of the Red River of the North and defines part of the western border of the U.S. state of Minnesota, and the eastern borders of North Dakota and South Dakota...
, Lake Traverse
Lake Traverse
Lake Traverse is the southernmost body of water in the Hudson Bay watershed of North America. It lies along the border between the U.S. states of Minnesota and South Dakota...
, Big Stone Lake
Big Stone Lake
Big Stone Lake is a long, narrow freshwater lake and reservoir forming the border between western Minnesota and northeastern South Dakota in the USA. The lake covers 12,610 acres of surface area, stretching 26 miles from end to end and averaging around 1 mile wide, and at an elevation of 965...
, and then a line extending due south to the Iowa border. Rice made this motion based on Minnesota's population growth.
At the time, tensions between the northern and the southern United States were growing, in a series of conflicts
Origins of the American Civil War
The main explanation for the origins of the American Civil War is slavery, especially Southern anger at the attempts by Northern antislavery political forces to block the expansion of slavery into the western territories...
that eventually resulted in the American Civil War. There was little debate in the United States House of Representatives
United States House of Representatives
The United States House of Representatives is one of the two Houses of the United States Congress, the bicameral legislature which also includes the Senate.The composition and powers of the House are established in Article One of the Constitution...
, but when Stephen A. Douglas
Stephen A. Douglas
Stephen Arnold Douglas was an American politician from the western state of Illinois, and was the Northern Democratic Party nominee for President in 1860. He lost to the Republican Party's candidate, Abraham Lincoln, whom he had defeated two years earlier in a Senate contest following a famed...
introduced the bill in the United States Senate
United States Senate
The United States Senate is the upper house of the bicameral legislature of the United States, and together with the United States House of Representatives comprises the United States Congress. The composition and powers of the Senate are established in Article One of the U.S. Constitution. Each...
, it caused a firestorm of debate. Northerners saw their chance to add two senators to the side of the free states, while Southerners were sure that they would lose power. Many senators offered polite arguments that the population was too sparse and that statehood was premature. Senator John Burton Thompson
John Burton Thompson
John Burton Thompson was a United States Representative and Senator from Kentucky.Born near Harrodsburg, Kentucky, Thompson completed preparatory studies and studied law. He was admitted to the bar and practiced in Harrodsburg, becoming the Commonwealth's Attorney...
of Kentucky, in particular, argued that new states would cost the government too much for roads, canals, forts, and lighthouses. Although Thompson and 21 other senators voted against statehood, the enabling act was passed on February 26, 1857.
After the enabling act was passed, territorial legislators had a difficult time writing a state constitution. A constitutional convention
Constitutional convention (political meeting)
A constitutional convention is now a gathering for the purpose of writing a new constitution or revising an existing constitution. A general constitutional convention is called to create the first constitution of a political unit or to entirely replace an existing constitution...
was assembled in July 1857, but Republicans and Democrats were deeply divided. In fact, they formed two separate constitutional conventions and drafted two separate constitutions. Eventually, the two groups formed a conference committee and worked out a common constitution. The divisions continued, though, because Republicans refused to sign a document that had Democratic signatures on it, and vice versa. One copy of the constitution was written on white paper and signed only by Republicans, while the other copy was written on blue-tinged paper and signed by Democrats. These copies were signed on August 29, 1857. An election was called on October 13, 1857, where Minnesota residents would vote to approve or disapprove the constitution. The constitution was approved by 30,055 voters, while 571 rejected it.
The state constitution was sent to the United States Congress
United States Congress
The United States Congress is the bicameral legislature of the federal government of the United States, consisting of the Senate and the House of Representatives. The Congress meets in the United States Capitol in Washington, D.C....
for ratification in December 1857. The approval process was drawn out for several months while Congress debated over issues that had stemmed from the Kansas-Nebraska Act
Kansas-Nebraska Act
The Kansas–Nebraska Act of 1854 created the territories of Kansas and Nebraska, opening new lands for settlement, and had the effect of repealing the Missouri Compromise of 1820 by allowing settlers in those territories to determine through Popular Sovereignty if they would allow slavery within...
. Southerners had been arguing that the next state should be pro-slavery, so when Kansas submitted the pro-slavery Lecompton Constitution
Lecompton Constitution
The Lecompton Constitution was the second of four proposed constitutions for the state of Kansas . The document was written in response to the anti-slavery position of the 1855 Topeka Constitution of James H. Lane and other free-state advocates...
, the Minnesota statehood bill was delayed. After that, Northerners feared that Minnesota's Democratic delegation would support slavery in Kansas. Finally, after the Kansas question was settled and after Congress decided how many representatives Minnesota would get in the House of Representatives, the bill passed. The eastern half of the Minnesota Territory, under the boundaries defined by Henry Mower Rice, became the country's 32nd state on May 11, 1858. The western part remained unorganized until its incorporation into the Dakota Territory
Dakota Territory
The Territory of Dakota was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from March 2, 1861, until November 2, 1889, when the final extent of the reduced territory was split and admitted to the Union as the states of North and South Dakota.The Dakota Territory consisted of...
on March 2, 1861.
Civil War era and Dakota War of 1862
Although Minnesota was a new state when the American Civil WarAmerican Civil War
The American Civil War was a civil war fought in the United States of America. In response to the election of Abraham Lincoln as President of the United States, 11 southern slave states declared their secession from the United States and formed the Confederate States of America ; the other 25...
started, it was the first to contribute troops to the Union
Union (American Civil War)
During the American Civil War, the Union was a name used to refer to the federal government of the United States, which was supported by the twenty free states and five border slave states. It was opposed by 11 southern slave states that had declared a secession to join together to form the...
effort, with about 22,000 Minnesotans serving. Alexander Ramsey
Alexander Ramsey
Alexander Ramsey was an American politician. He was born near Harrisburg, Pennsylvania.Alexander Ramsey was elected from Pennsylvania as a Whig to the U.S. House of Representatives and served in the 28th and 29th congresses from March 4, 1843 to March 4, 1847...
(R)
Republican Party (United States)
The Republican Party is one of the two major contemporary political parties in the United States, along with the Democratic Party. Founded by anti-slavery expansion activists in 1854, it is often called the GOP . The party's platform generally reflects American conservatism in the U.S...
, the second governor of Minnesota, was in Washington on April 13, 1861, when the war broke out. He sent a telegram back to Saint Paul urging his lieutenant governor, Ignatius L. Donnelly (R), to call out volunteers. The 1st Minnesota Volunteer Infantry
1st Minnesota Volunteer Infantry
The 1st Regiment, Minnesota Volunteer Infantry was a volunteer infantry regiment that served in the Union Army during the American Civil War. It was noted in particular for its gallant service and heavy casualties at the Battle of Gettysburg....
was particularly important to the Battle of Gettysburg
Battle of Gettysburg
The Battle of Gettysburg , was fought July 1–3, 1863, in and around the town of Gettysburg, Pennsylvania. The battle with the largest number of casualties in the American Civil War, it is often described as the war's turning point. Union Maj. Gen. George Gordon Meade's Army of the Potomac...
.

Dakota War of 1862
The Dakota War of 1862, also known as the Sioux Uprising, was an armed conflict between the United States and several bands of the eastern Sioux. It began on August 17, 1862, along the Minnesota River in southwest Minnesota...
broke out. The Dakota had signed the Treaty of Traverse des Sioux
Treaty of Traverse des Sioux
The Treaty of Traverse des Sioux was a treaty signed on July 23, 1851, between the United States government and Sioux Indian bands in Minnesota Territory by which the Sioux ceded territory. The treaty was instigated by Alexander Ramsey, the first governor of Minnesota Territory, and Luke Lea,...
and Treaty of Mendota
Treaty of Mendota
The Treaty of Mendota was signed in Mendota, Minnesota on August 5, 1851 between the United States federal government and the Sioux tribes of Minnesota ....
in 1851 because they were concerned that without money from the United States government, they would starve, due to the loss of habitat of huntable game. They were initially given a strip of land of ten miles (16 km) north and south of the Minnesota River
Minnesota River
The Minnesota River is a tributary of the Mississippi River, approximately 332 miles long, in the U.S. state of Minnesota. It drains a watershed of nearly , in Minnesota and about in South Dakota and Iowa....
, but they were later forced to sell the northern half of the land. In 1862, crop failures left the Dakota with food shortages, and government money was delayed. After four young Dakota men, searching for food, shot a family of white settlers near Acton, the Dakota leadership decided to continue the attacks in an effort to drive out the settlers. Over a period of several days, Dakota attacks at the Lower Sioux Agency, New Ulm
New Ulm, Minnesota
New Ulm is a city in Brown County, Minnesota, United States. The population was 13,522 at the 2010 census. It is the county seat of Brown County....
and Hutchinson
Hutchinson, Minnesota
According to the 2000 United States Census , there were 13,080 people, 5,333 households, and 3,418 families residing in the city. The population density was 1,763.6 people per square mile . There were 5,667 housing units at an average density of 764.1 per square mile...
, as well as in the surrounding farmlands, resulted in the deaths of at least 300 to 400 white settlers and government employees, causing panic in the settlements and provoking counterattacks by state militia and federal forces which spread throughout the Minnesota River Valley
Minnesota River
The Minnesota River is a tributary of the Mississippi River, approximately 332 miles long, in the U.S. state of Minnesota. It drains a watershed of nearly , in Minnesota and about in South Dakota and Iowa....
and as far away as the Red River Valley
Red River Valley
The Red River Valley is a region in central North America that is drained by the Red River of the North. It is significant in the geography of North Dakota, Minnesota, and Manitoba for its relatively fertile lands and the population centers of Fargo, Moorhead, Grand Forks, and Winnipeg...
. The ensuing battles at Fort Ridgely
Battle of Fort Ridgely
Fort Ridgely was built in 1851 in the territory of southern Minnesota. It wasn't much of a fort, but it was the only military post between the Sioux Reservations and the settlers. On August 18, 1862, the Lower Sioux Agency in Renville County, Minnesota, was attacked by Indians...
, Birch Coulee
Battle of Birch Coulee
The Battle of Birch Coulee occurred September 2, 1862 during the Dakota War of 1862. After the Battle of Fort Ridgely and the Battle of New Ulm, Colonel Henry Hastings Sibley was planning to punish the Sioux and to obtain the release of the settlers they were holding captive...
, Fort Abercrombie
Fort Abercrombie
Fort Abercrombie, in North Dakota, was an American fort established by authority of an act of Congress, March 3, 1857. The act allocated twenty-five square miles of land on the Red River in Dakota Territory to be used for a military outpost, but the exact location was left to the discretion of...
, and Wood Lake
Battle of Wood Lake
The Battle of Wood Lake was a battle in the Dakota War of 1862 in September. By that time in the Dakota War of 1862, the Sioux offensive had slowed considerably, and the Minnesota forces were beginning to implement a plan formulated by Governor Alexander Ramsey...
punctuated a six-week war, which ended with the trial of 425 Native Americans for their participation in the war. Of this number, 303 men were convicted and sentenced to death.
Episcopal Bishop Henry Benjamin Whipple
Henry Benjamin Whipple
Henry Benjamin Whipple was the first Episcopal bishop of Minnesota, a humanitarian and an advocate for Native Americans.-Summary of his life:...
pled to President Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln was the 16th President of the United States, serving from March 1861 until his assassination in April 1865. He successfully led his country through a great constitutional, military and moral crisis – the American Civil War – preserving the Union, while ending slavery, and...
for clemency, and the death sentences of all but 39 men were reduced to prison terms. On December 26, 1862, 38 men were hanged in the largest mass execution in the United States. Many of the remaining Dakota Native Americans, including non-combatants, were confined in a prison camp at Pike Island
Pike Island
Pike Island is an island at the confluence of the Mississippi and Minnesota Rivers in the southwestern part of St. Paul in the Twin Cities metropolitan area of Minnesota. It is a portion of the 100,000 acres of land purchased from the Mdewakanton Sioux Indians by Zebulon Pike in September 1805,...
over the winter of 1862–1863, where more than 300 died of disease. Survivors were later exiled to the Crow Creek Reservation
Crow Creek Reservation
The Crow Creek Indian Reservation is located in parts of Buffalo, Hughes, and Hyde counties on the east bank of the Missouri River in central South Dakota in the United States. It has a land area of 421.658 sq mi and a 2000 census population of 2,225 persons...
, then later to a reservation near Niobrara, Nebraska
Niobrara, Nebraska
Niobrara is a village in Knox County, Nebraska, United States. The population was 370 at the 2010 census.-Geography:Niobrara is located at ....
. A small number of Dakota Native Americans managed to return to Minnesota in the 1880s and establish communities near Granite Falls
Granite Falls, Minnesota
As of the census of 2000, there were 3,070 people, 1,344 households, and 806 families residing in the city. The population density was 890.5 people per square mile . There were 1,472 housing units at an average density of 427.0 per square mile...
, Morton
Morton, Minnesota
Morton is a city in Renville County, Minnesota, United States. The population was 411 at the 2010 census.-Geography:According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of , of which, of it is land and of it is water.U.S...
, Prior Lake
Prior Lake, Minnesota
In 2007, there are an estimated 19,319 residents. The population density was 1,207 people per square mile . There were 5,791 housing units at an average density of 428.9 per square mile . The racial makeup of the city was 94.5% White, 0.8% African American, 2.1% Native American, 0.9% Asian, 0.3%...
, and Red Wing
Red Wing, Minnesota
Red Wing is a city in Goodhue County, Minnesota, United States, on the Mississippi River. The population was 16,459 at the 2010 census. It is the county seat of Goodhue County....
.
Farming and railroad development
After the Civil War, Minnesota became an attractive region for European immigration and settlement as farmland. Minnesota's population in 1870 was 439,000; this number tripled during the two subsequent decades. The Homestead ActHomestead Act
A homestead act is one of three United States federal laws that gave an applicant freehold title to an area called a "homestead" – typically 160 acres of undeveloped federal land west of the Mississippi River....
in 1862 facilitated land claims by settlers, who regarded the land as being cheap and fertile. The railroad industry, led by the Northern Pacific Railway
Northern Pacific Railway
The Northern Pacific Railway was a railway that operated in the west along the Canadian border of the United States. Construction began in 1870 and the main line opened all the way from the Great Lakes to the Pacific when former president Ulysses S. Grant drove in the final "golden spike" in...
and Saint Paul and Pacific Railroad
Saint Paul and Pacific Railroad
The Saint Paul and Pacific Railroad was a shortline railroad in the state of Minnesota in the United States which existed from 1857 to 1879. Founded as the Minnesota and Pacific Railroad, it was the state's first active railroad. It went bankrupt, and the state changed its name to the Saint Paul...
, advertised the many opportunities in the state and worked to get immigrants to settle in Minnesota. James J. Hill
James J. Hill
James Jerome Hill , was a Canadian-American railroad executive. He was the chief executive officer of a family of lines headed by the Great Northern Railway, which served a substantial area of the Upper Midwest, the northern Great Plains, and Pacific Northwest...
, in particular, was instrumental in reorganizing the Saint Paul and Pacific Railroad and extending lines from the Minneapolis-Saint Paul area into the Red River
Red River of the North
The Red River is a North American river. Originating at the confluence of the Bois de Sioux and Otter Tail rivers in the United States, it flows northward through the Red River Valley and forms the border between the U.S. states of Minnesota and North Dakota before continuing into Manitoba, Canada...
Valley and to Winnipeg
Winnipeg
Winnipeg is the capital and largest city of Manitoba, Canada, and is the primary municipality of the Winnipeg Capital Region, with more than half of Manitoba's population. It is located near the longitudinal centre of North America, at the confluence of the Red and Assiniboine Rivers .The name...
. Hill was also responsible for building a new passenger depot in Minneapolis, served by the landmark Stone Arch Bridge which was completed in 1883. During the 1880s, Hill continued building tracks through North Dakota and Montana. In 1890, the railroad, now known as the Great Northern Railway, started building tracks through the mountains west to Seattle. Other railroads, such as the Lake Superior and Mississippi Railroad
Lake Superior and Mississippi Railroad
The Lake Superior and Mississippi Railroad is the name for two different railroads in Minnesota.-Historic railroad:The Lake Superior and Mississippi Railroad was the first rail link between the Twin Cities and Duluth and came into existence in 1863 when financier Jay Cooke selected Duluth as the...
and the Milwaukee Road, also played an important role in the early days of Minnesota's statehood. Later railways, such as the Soo Line
Soo Line Railroad
The Soo Line Railroad is the primary United States railroad subsidiary of the Canadian Pacific Railway , controlled through the Soo Line Corporation, and one of seven U.S. Class I railroads. Although it is named for the Minneapolis, St. Paul and Sault Ste...
and Minneapolis and St. Louis Railway
Minneapolis and St. Louis Railway
The Minneapolis and St. Louis Railway was an American Class I railroad that built and operated lines radiating south and west from Minneapolis, Minnesota which existed for 90 years from 1870 to 1960....
facilitated the sale of Minneapolis flour and other products, although they were not as involved in attracting settlers.

Oliver Hudson Kelley
Oliver Hudson Kelley is considered the "Father" of the Order of Patrons of Husbandry.-Biography:In Boston, he moved to the Minnesota frontier in 1849, where he became a farmer...
played an important role in farming as one of the founders of the National Grange, along with several other clerks in the United States Department of Agriculture
United States Department of Agriculture
The United States Department of Agriculture is the United States federal executive department responsible for developing and executing U.S. federal government policy on farming, agriculture, and food...
. The movement grew out of his interest in cooperative farm associations following the end of the Civil War, and he established local Grange chapters in Elk River
Elk River, Minnesota
As of the census of 2000, there were 16,447 people, 5,664 households, and 4,400 families residing in the city. Recent estimates show the population at 21,329 as of 2005. The population density was 385.5 people per square mile . There were 5,782 housing units at an average density of 135.5 per...
and Saint Paul. The organization worked to provide education on new farming methods, as well as to influence government and public opinion on matters important to farmers. One of these areas of concern was the freight rates charged by the railroads and by the grain elevators. Since there was little or no competition between railroads serving Minnesota farm communities, railroads could charge as much as the traffic would bear. By 1871, the situation was so heated that both the Republican and Democratic candidates in state elections promised to regulate railroad rates. The state established an office of railroad commissioner and imposed maximum charges for shipping. Populist
Populism
Populism can be defined as an ideology, political philosophy, or type of discourse. Generally, a common theme compares "the people" against "the elite", and urges social and political system changes. It can also be defined as a rhetorical style employed by members of various political or social...
Ignatius L. Donnelly also served the Grange as an organizer.
Saint Anthony Falls
Saint Anthony Falls
Saint Anthony Falls, or the Falls of Saint Anthony, located northeast of downtown Minneapolis, Minnesota, was the only natural major waterfall on the Upper Mississippi River. The natural falls was replaced by a concrete overflow spillway after it partially collapsed in 1869...
, the only waterfall of its height on the Mississippi, played an important part in the development of Minneapolis. The power of the waterfall first fueled sawmills, but later it was tapped to serve flour mills. In 1870, only a small number of flour mills were in the Minneapolis area, but by 1900 Minnesota mills were grinding 14.1% of the nation's grain. Advances in transportation, milling technology, and water power combined to give Minneapolis a dominance in the milling industry. Spring wheat could be sown in the spring and harvested in late summer, but it posed special problems for milling. To get around these problems, Minneapolis millers made use of new technology. They invented the middlings purifier
Middlings purifier
A middlings purifier is a device used in the production of flour to remove the husks from the kernels of wheat.It was developed in Minnesota by Edmund LaCroix, a French inventor hired by Cadwallader C...
, a device that used jets of air to remove the husks from the flour early in the milling process. They also started using roller mills, as opposed to grindstones. A series of rollers gradually broke down the kernels and integrated the gluten
Gluten
Gluten is a protein composite found in foods processed from wheat and related grain species, including barley and rye...
with the starch
Starch
Starch or amylum is a carbohydrate consisting of a large number of glucose units joined together by glycosidic bonds. This polysaccharide is produced by all green plants as an energy store...
. These improvements led to the production of "patent" flour, which commanded almost double the price of "bakers" or "clear" flour, which it replaced. Pillsbury and the Washburn-Crosby Company (a forerunner of General Mills
General Mills
General Mills, Inc. is an American Fortune 500 corporation, primarily concerned with food products, which is headquartered in Golden Valley, Minnesota, a suburb of Minneapolis. The company markets many well-known brands, such as Betty Crocker, Yoplait, Colombo, Totinos, Jeno's, Pillsbury, Green...
) became the leaders in the Minneapolis milling industry. This leadership in milling later declined as milling was no longer dependent on water power, but the dominance of the mills contributed greatly to the economy of Minneapolis and Minnesota, attracting people and money to the region.
Industrial development

Hydroelectricity
Hydroelectricity is the term referring to electricity generated by hydropower; the production of electrical power through the use of the gravitational force of falling or flowing water. It is the most widely used form of renewable energy...
power plant was built at Saint Anthony Falls, marking one of the first developments of hydroelectric power in the United States. Iron mining began in northern Minnesota with the opening of the Soudan Mine in 1884. The Vermilion Range
Vermilion Range (Minnesota)
The Vermilion Range exists between Tower and Ely, Minnesota, and contains significant deposits of iron ore. The Vermilion, along with the Mesabi and Cuyuna Ranges, constitute the Iron Ranges of northern Minnesota which were deposited in the Animikie Group...
was surveyed and mapped by a party financed by Charlemagne Tower
Charlemagne Tower
Charlemagne Tower, was an American lawyer, soldier, and businessman.-Early life and start of law career:Charlemagne Tower was born on April 18, 1809 in Paris, Oneida County, New York, the eldest of the eight children of Reuben Tower, a New York State Legislator, and Deborah Taylor Pierce...
. Another mining town, Ely
Ely, Minnesota
As of the census of 2000, there were 3,724 people, 1,912 households, and 916 families residing in the city. The population density was 1,369.5 people per square mile . There were 1,912 housing units at an average density of 703.2 per square mile...
began with the foundation of the Chandler Mine in 1888. Soon after, the Mesabi Range
Mesabi Range
The Mesabi Iron Range is a vast deposit of iron ore and the largest of four major iron ranges in the region collectively known as the Iron Range of Minnesota. Discovered in 1866, it is the chief deposit of iron ore in the United States. The deposit is located in northeast Minnesota, largely in...
was established when ore was found just under the surface of the ground in Mountain Iron
Mountain Iron, Minnesota
As of the census of 2000, there were 2,999 people, 1,326 households, and 847 families residing in the city. The population density was 60.7 people per square mile . There were 1,409 housing units at an average density of 28.5 per square mile...
. The Mesabi Range ultimately had much more ore than the Vermilion Range, and it was easy to extract because the ore was closer to the surface. As a result, open-pit mines
Open-pit mining
Open-pit mining or opencast mining refers to a method of extracting rock or minerals from the earth by their removal from an open pit or borrow....
became well-established on the Mesabi Range, with 111 mines operating by 1904. To ship the iron ore to refineries, railroads such as the Duluth, Missabe and Iron Range Railway
Duluth, Missabe and Iron Range Railway
The Duluth, Missabe and Iron Range Railway is a railroad operating in northern Minnesota and Wisconsin that hauls iron ore and later taconite to the Great Lakes ports of Duluth and Two Harbors, Minnesota...
were built from the iron ranges to Two Harbors
Two Harbors, Minnesota
As of the census of 2000, there were 3,613 people, 1,636 households, and 953 families residing in the city. The population density was 1,120.7 people per square mile . There were 1,631 housing units at an average density of 505.9 per square mile...
and Duluth on Lake Superior. Large ore docks were used at these cities to load the iron ore onto ships for transport east on the Great Lakes
Great Lakes
The Great Lakes are a collection of freshwater lakes located in northeastern North America, on the Canada – United States border. Consisting of Lakes Superior, Michigan, Huron, Erie, and Ontario, they form the largest group of freshwater lakes on Earth by total surface, coming in second by volume...
. The mining industry helped to propel Duluth from a small town to a large, thriving city. In 1904, iron was discovered in the Cuyuna Range
Cuyuna Range
The Cuyuna Range is an iron range to the southwest of the Mesabi Range, largely within Crow Wing County, Minnesota. It lies along a line between Brainerd and Aitkin, although those communities are not mining towns....
in Crow Wing County
Crow Wing County, Minnesota
Crow Wing County is a county located in the U.S. state of Minnesota. As of 2010, the population was 62,500. Its county seat is Brainerd.-Geography:...
. Between 1904 and 1984, when mining ceased, more than 106 million tons of ore were mined. Iron from the Cuyuna Range also contained significant proportions of manganese
Manganese
Manganese is a chemical element, designated by the symbol Mn. It has the atomic number 25. It is found as a free element in nature , and in many minerals...
, increasing its value.
Mayo Clinic

William Worrall Mayo
William Worrall Mayo was a British medical doctor and chemist, best known for establishing the private medical practice that later evolved into the Mayo Clinic. He was a descendant of a famous English chemist, John Mayow. His sons, William James Mayo and Charles Horace Mayo, joined the private...
, the founder of the Mayo Clinic
Mayo Clinic
Mayo Clinic is a not-for-profit medical practice and medical research group specializing in treating difficult patients . Patients are referred to Mayo Clinic from across the U.S. and the world, and it is known for innovative and effective treatments. Mayo Clinic is known for being at the top of...
, emigrated from Salford, United Kingdom to the United States in 1846 and became a medical doctor in 1850. In 1864, Mayo and his two sons, William James Mayo
William James Mayo
William James Mayo, M.D. was a physician in the United States and one of the seven founders of the Mayo Clinic. He and his brother, Charles Horace Mayo, both joined their father's private medical practice in Rochester, Minnesota, USA, after graduating from medical school in the 1880s...
(1861–1939) and Charles Horace Mayo
Charles Horace Mayo
-External links:*...
(1865–1939) moved to Rochester
Rochester, Minnesota
Rochester is a city in the U.S. state of Minnesota and is the county seat of Olmsted County. Located on both banks of the Zumbro River, The city has a population of 106,769 according to the 2010 United States Census, making it Minnesota's third-largest city and the largest outside of the...
. In the summer of 1883, an F5
Fujita scale
The Fujita scale , or Fujita-Pearson scale, is a scale for rating tornado intensity, based primarily on the damage tornadoes inflict on human-built structures and vegetation...
tornado struck, dubbed the 1883 Rochester tornado
1883 Rochester Tornado
The 1883 Rochester tornado was an F5 tornado that hit Rochester, Minnesota on August 21, 1883. It was one in a series of tornadoes that hit Southeast Minnesota that day, causing at least 37 deaths and over 200 injuries, and was the impetus for the creation of the Mayo Clinic. On July 21, two...
, causing a substantial number of deaths and injuries. Dr. W. W. Mayo worked with nuns from the Sisters of St. Francis
Sisters of Saint Francis of Rochester, Minnesota
The Sisters of Saint Francis of Rochester, Minnesota is a Roman Catholic religious congregation for women. The congregation was founded in 1877 by Mother Mary Alfred Moes in the Roman Catholic Diocese of Winona...
to treat the survivors. After the disaster, Mother Alfred Moes
Alfred Moes
Mother Mary Alfred Moes, O.S.F., was instrumental in establishing first, the Sisters of St. Francis of Mary Immaculate in Joliet, Illinois, as well as the Sisters of Saint Francis of Rochester, Minnesota. She was also the founder of St...
and the Drs. Mayo recognized the need for a hospital and joined together to build the 27-bed Saint Marys Hospital
Saint Marys Hospital (Rochester)
Saint Marys Hospital is one of two hospitals in Rochester, Minnesota operated by the Mayo Clinic, the other being Rochester Methodist Hospital. St Marys has a 61-bed emergency department but no obstetrics department, while Rochester Methodist lacks an emergency department but contains an obstetrics...
which opened in 1889; today, the hospital has 1,157 beds. Dr. Henry Stanley Plummer
Henry Stanley Plummer
Henry Stanley Plummer, M.D. was a prominent internist and endocrinologist who, along with Drs. William Mayo, Charles Mayo, Stinchfield, E. Starr Judd, Christopher Graham, and Donald Balfour founded Mayo Clinic. Dr...
joined the Mayo Brothers' practice in 1901. Plummer developed many of the systems of group practice which are universal around the world today in medicine and other fields, such as a single medical record
Medical record
The terms medical record, health record, and medical chart are used somewhat interchangeably to describe the systematic documentation of a single patient's medical history and care across time within one particular health care provider's jurisdiction....
and an interconnecting telephone system.
Urbanization and government
As a result of industrialization, the population became more concentrated into urban areas. By 1900, the Twin Cities were becoming a center of commerce, led by the Minneapolis Grain ExchangeMinneapolis Grain Exchange
The Minneapolis Grain Exchange was formed in 1881 as a regional cash marketplace to promote fair trade and to prevent trade abuses in wheat, oats and corn....
and the foundation of the Federal Reserve Bank
Federal Reserve Bank
The twelve Federal Reserve Banks form a major part of the Federal Reserve System, the central banking system of the United States. The twelve federal reserve banks together divide the nation into twelve Federal Reserve Districts, the twelve banking districts created by the Federal Reserve Act of...
with its ninth district in Minneapolis. Many of the businessmen who had made money in the railroad, flour milling, and logging industries lived in the Twin Cities and personified the gilded age
Gilded Age
In United States history, the Gilded Age refers to the era of rapid economic and population growth in the United States during the post–Civil War and post-Reconstruction eras of the late 19th century. The term "Gilded Age" was coined by Mark Twain and Charles Dudley Warner in their book The Gilded...
. They started to donate money for cultural institutions such as the Minneapolis Symphony Orchestra (now the Minnesota Orchestra
Minnesota Orchestra
The Minnesota Orchestra is an American orchestra based in Minneapolis, Minnesota.Emil Oberhoffer founded the orchestra as the Minneapolis Symphony Orchestra in 1903, and it gave its first performance on November 5 of that year. In 1968 the orchestra changed to its name to the Minnesota Orchestra...
). The parks of Minneapolis, under the direction of Theodore Wirth
Theodore Wirth
Theodore Wirth was instrumental in designing the Minneapolis system of parks. Swiss-born, he was widely regarded as the dean of the local parks movement in America. The various titles he was given included administrator of parks, horticulturalist, and park planner. Before emigrating to America...
became famous, and the new Minnesota State Capitol
Minnesota State Capitol
The Minnesota State Capitol is located in Minnesota's capital city, Saint Paul, and houses the Minnesota Senate, Minnesota House of Representatives, the Office of the Attorney General and the Office of the Governor...
building and the Cathedral of Saint Paul
Cathedral of Saint Paul (Minnesota)
The Cathedral of Saint Paul is a Roman Catholic cathedral in the city of St. Paul, Minnesota. It is the Co-Cathedral of the Archdiocese of Saint Paul and Minneapolis, along with the Basilica of St. Mary in Minneapolis. One of the most distinctive cathedrals in the United States, it sits on...
attracted attention to Saint Paul.
The role of government also grew during the early 20th century. In the rural areas, most people obtained food and manufactured goods from neighbors and other people they knew personally. As industry and commerce grew, goods such as food, materials, and medicines were no longer made by neighbors, but by large companies. In response, citizens called on their government for consumer protection, inspection of goods, and regulation of public utilities. The growth of the automobile spurred calls to develop roads and to enforce traffic laws. The state officially started its trunk highway system in 1920, with the passage of the Babcock Amendment that established 70 Constitutional Route
Constitutional route
In the U.S. state of Minnesota, a legislative route is a highway number defined by the Minnesota State Legislature. The routes from 1 to 70 are constitutional routes, defined as part of the Babcock Amendment to the Minnesota State Constitution, passed November 2, 1920. All of them were listed in...
s around the state. New regulation was necessary for banking and insurance. The safety of industrial workers and miners became an increasing concern, and brought about the workers' compensation
Workers' compensation
Workers' compensation is a form of insurance providing wage replacement and medical benefits to employees injured in the course of employment in exchange for mandatory relinquishment of the employee's right to sue his or her employer for the tort of negligence...
system. Since government was getting more complex, citizens demanded more of a role in their government, and became more politically active.
Great Depression
Wilbur FoshayWilbur Foshay
Wilbur B. Foshay was an American businessman, who built a fortune buying utilities throughout the Midwest in the early 20th century. Foshay built the Foshay Tower in Minneapolis, Minnesota, which opened in August 1929. In 1932 he was convicted of conducting a "pyramid scheme" with shares of his...
, an owner of several utility companies, built the Foshay Tower
Foshay Tower
The Foshay Tower, now the W Minneapolis – The Foshay hotel, is a skyscraper in Minneapolis, Minnesota. Modeled after the Washington Monument, the building was completed in 1929, months before the stock market crash in October of that year. It has 32 floors and stands high, plus an antenna mast...
in 1929, just before the Wall Street Crash of 1929
Wall Street Crash of 1929
The Wall Street Crash of 1929 , also known as the Great Crash, and the Stock Market Crash of 1929, was the most devastating stock market crash in the history of the United States, taking into consideration the full extent and duration of its fallout...
. The building was the tallest building in Minnesota at the time. It remained the tallest building in Minneapolis until 1973, when the IDS Tower surpassed it. The tower was a symbol of the wealth of the times, but when the stock market crashed, Foshay lost his fortune in the crash.
The Great Depression
Great Depression
The Great Depression was a severe worldwide economic depression in the decade preceding World War II. The timing of the Great Depression varied across nations, but in most countries it started in about 1929 and lasted until the late 1930s or early 1940s...
had several effects on Minnesota, with layoffs on the Iron Range
Iron Range
The Iron Range is a region that makes up the northeastern section of Minnesota in the United States. "The Range", as it is known by locals, is a region with multiple distinct bands of iron ore...
and a drought in the Great Plains
Great Plains
The Great Plains are a broad expanse of flat land, much of it covered in prairie, steppe and grassland, which lies west of the Mississippi River and east of the Rocky Mountains in the United States and Canada. This area covers parts of the U.S...
from 1931 through 1936. While the Depression had several causes, one most relevant to Minnesota was that United States businesses in the 1920s had improved their efficiency through standardizing production methods and eliminating waste. Business owners were reaping the benefits of this increase in productivity, but they were not sharing it with their employees because of the weakness of organized labor, nor were they sharing it with the public in the form of lowered prices. Instead, the windfall went to stockholders. The eventual result was that consumers could no longer afford the goods that factories were producing.
Floyd B. Olson
Floyd B. Olson
Floyd Bjørnstjerne Olson was an American politician. He served as the 22nd Governor of Minnesota from January 6, 1931 to August 22, 1936. He died in office from stomach cancer. He was a member of the Minnesota Farmer-Labor Party, and was the first member of the Farmer-Labor Party to win the...
of the Minnesota Farmer-Labor Party
Minnesota Farmer-Labor Party
The Minnesota Farmer–Labor Party was a political party in the United States state of Minnesota, the most successful and longest-lasting of the constituent elements of the national Farmer–Labor Party movement, which had a presence in other states...
was elected as the governor in the 1930 election. In his first term, he signed a bonding bill that authorized $15 million ($ as of ) for highway construction, in an effort to provide work for the unemployed. He also signed an executive order that provided for a minimum wage of 45 cents per hour for up to 48 hours weekly. This effort predated the Fair Labor Standards Act
Fair Labor Standards Act
The Fair Labor Standards Act of 1938 is a federal statute of the United States. The FLSA established a national minimum wage, guaranteed 'time-and-a-half' for overtime in certain jobs, and prohibited most employment of minors in "oppressive child labor," a term that is defined in the statute...
of 1938 that established a nationwide minimum wage. By 1932, with the Depression worsening, the Farmer-Labor Party platform was proposing a state income tax, a graduated tax on nationwide chain stores (such as J.C. Penney
J.C. Penney
J. C. Penney Company, Inc. is a chain of American mid-range department stores based in Plano, Texas, a suburb north of Dallas. The company operates 1,107 department stores in all 50 U.S. states and Puerto Rico. JCPenney also operates catalog sales merchant offices nationwide in many...
and Sears, Roebuck and Company
Sears, Roebuck and Company
Sears, officially named Sears, Roebuck and Co., is an American chain of department stores which was founded by Richard Warren Sears and Alvah Curtis Roebuck in the late 19th century...
), low-interest farm loans, and a state unemployment insurance program. The progressive
Progressivism
Progressivism is an umbrella term for a political ideology advocating or favoring social, political, and economic reform or changes. Progressivism is often viewed by some conservatives, constitutionalists, and libertarians to be in opposition to conservative or reactionary ideologies.The...
1933 legislative session saw a comprehensive response to the depression including a moratorium on mortgage foreclosure
Foreclosure
Foreclosure is the legal process by which a mortgage lender , or other lien holder, obtains a termination of a mortgage borrower 's equitable right of redemption, either by court order or by operation of law...
s, a reduction in property taxes for farmers and homeowners, the state income tax, and chain store taxes, tavern reform, ratification of a child labor
Child labor
Child labour refers to the employment of children at regular and sustained labour. This practice is considered exploitative by many international organizations and is illegal in many countries...
amendment, a state old-age pension system, and steps toward preserving the area that later became the Boundary Waters Canoe Area Wilderness
Boundary Waters Canoe Area Wilderness
The Boundary Waters Canoe Area Wilderness , is a wilderness area within the Superior National Forest in northeastern Minnesota under the administration of the U.S. Forest Service...
.
Meanwhile, formerly quiet labor unions began asserting themselves rather forcefully. The Minneapolis Teamsters Strike of 1934
Minneapolis Teamsters Strike of 1934
The Minneapolis General Strike of 1934 grew out of a strike by Teamsters against most of the trucking companies operating in Minneapolis, a major distribution center for the Upper Midwest. The strike began on May 16, 1934 in the Market District and ensuing violence lasted periodically throughout...
turned ugly, with the union demanding the right to speak for all trucking employees. As a result of this strike and many others across the nation, Congress passed the National Labor Relations Act
National Labor Relations Act
The National Labor Relations Act or Wagner Act , is a 1935 United States federal law that limits the means with which employers may react to workers in the private sector who create labor unions , engage in collective bargaining, and take part in strikes and other forms of concerted activity in...
in 1935. Government programs such as the Civilian Conservation Corps
Civilian Conservation Corps
The Civilian Conservation Corps was a public work relief program that operated from 1933 to 1942 in the United States for unemployed, unmarried men from relief families, ages 18–25. A part of the New Deal of President Franklin D...
and Works Progress Administration
Works Progress Administration
The Works Progress Administration was the largest and most ambitious New Deal agency, employing millions of unskilled workers to carry out public works projects, including the construction of public buildings and roads, and operated large arts, drama, media, and literacy projects...
brought much-needed work projects to the state. Congress passed the Indian Reorganization Act
Indian Reorganization Act
The Indian Reorganization Act of June 18, 1934 the Indian New Deal, was U.S. federal legislation that secured certain rights to Native Americans, including Alaska Natives...
in 1934, giving Minnesota's Ojibwa and Dakota tribes more autonomy over their own affairs.
Arts and culture
The Minneapolis Institute of ArtsMinneapolis Institute of Arts
The Minneapolis Institute of Arts is a fine art museum located in the Whittier neighborhood of Minneapolis, Minnesota, on a campus that covers nearly 8 acres , formerly Morrison Park...
was established in 1883. The present building, a neoclassical
Neoclassical architecture
Neoclassical architecture was an architectural style produced by the neoclassical movement that began in the mid-18th century, manifested both in its details as a reaction against the Rococo style of naturalistic ornament, and in its architectural formulas as an outgrowth of some classicizing...
structure, was opened in 1915, with additions in 1974 by Kenzo Tange
Kenzo Tange
was a Japanese architect, and winner of the 1987 Pritzker Prize for architecture. He was one of the most significant architects of the 20th century, combining traditional Japanese styles with modernism, and designed major buildings on five continents. Tange was also an influential protagonist of...
and in 2006 by Michael Graves
Michael Graves
Michael Graves is an American architect. Identified as one of The New York Five, Graves has become a household name with his designs for domestic products sold at Target stores in the United States....
.
The Minnesota Orchestra
Minnesota Orchestra
The Minnesota Orchestra is an American orchestra based in Minneapolis, Minnesota.Emil Oberhoffer founded the orchestra as the Minneapolis Symphony Orchestra in 1903, and it gave its first performance on November 5 of that year. In 1968 the orchestra changed to its name to the Minnesota Orchestra...
dates back to 1903 when it was founded as the Minneapolis Symphony Orchestra. It was renamed the Minnesota Orchestra in 1968 and moved into its own building, Orchestra Hall
Orchestra Hall (Minneapolis)
Orchestra Hall, located at Nicollet Mall and 12th Street in Minneapolis, Minnesota, United States, is home to the Minnesota Orchestra. The Hall was built in 1974 and opened for the 1974 concert season...
, in downtown Minneapolis in 1974. The building has a modern look with a brick, glass, and steel exterior, in contrast to the old-world look of traditional concert halls. The interior of the building features more than 100 large cubes that deflect sound and provide excellent acoustics. Later the Saint Paul Chamber Orchestra
Saint Paul Chamber Orchestra
The Saint Paul Chamber Orchestra , based in Saint Paul, Minnesota, is the United States' only full-time professional chamber orchestra...
became the second full-time professional orchestral ensemble in the cities.
The Walker Art Center
Walker Art Center
The Walker Art Center is a contemporary art center in Minneapolis, Minnesota, United States. The Walker is considered one of the nation's "big five" museums for modern art along with the Museum of Modern Art, the San Francisco Museum of Modern Art, the Guggenheim Museum and the Hirshhorn...
was established in 1927 as the first public art gallery in the Upper Midwest. In the 1940s, the museum shifted its focus toward modern art, after a gift from Mrs. Gilbert Walker made it possible to acquire works by Pablo Picasso
Pablo Picasso
Pablo Diego José Francisco de Paula Juan Nepomuceno María de los Remedios Cipriano de la Santísima Trinidad Ruiz y Picasso known as Pablo Ruiz Picasso was a Spanish expatriate painter, sculptor, printmaker, ceramicist, and stage designer, one of the greatest and most influential artists of the...
, Henry Moore
Henry Moore
Henry Spencer Moore OM CH FBA was an English sculptor and artist. He was best known for his semi-abstract monumental bronze sculptures which are located around the world as public works of art....
, Alberto Giacometti
Alberto Giacometti
Alberto Giacometti was a Swiss sculptor, painter, draughtsman, and printmaker.Alberto Giacometti was born in the canton Graubünden's southerly alpine valley Val Bregaglia and came from an artistic background; his father, Giovanni, was a well-known post-Impressionist painter...
, and others. The museum continued its focus on modern art with traveling shows in the 1960s.
The Guthrie Theater
Guthrie Theater
The Guthrie Theater is a center for theater performance, production, education, and professional training in Minneapolis, Minnesota. It is the result of the desire of Sir Tyrone Guthrie, Oliver Rea, and Peter Zeisler to create a resident acting company that would produce and perform the classics in...
, opened in 1963, was the brainchild of Sir Tyrone Guthrie, who wanted to found a regional theater without the commercial constraints of Broadway
Broadway theatre
Broadway theatre, commonly called simply Broadway, refers to theatrical performances presented in one of the 40 professional theatres with 500 or more seats located in the Theatre District centered along Broadway, and in Lincoln Center, in Manhattan in New York City...
. The high cost of staging Broadway productions meant that shows had to be immediately successful and return a high amount of revenue. This discouraged innovation and experimentation, and made it difficult to stage important works of literature. These ideas were first disseminated in a 1959 article in the drama section of the New York Times, and citizens in the Minneapolis-Saint Paul area were eager to support the idea. The theater served as a prototype for other resident non-profit theaters.
Minnesota in World War II

United States Navy
The United States Navy is the naval warfare service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the seven uniformed services of the United States. The U.S. Navy is the largest in the world; its battle fleet tonnage is greater than that of the next 13 largest navies combined. The U.S...
contracted with Cargill
Cargill
Cargill, Incorporated is a privately held, multinational corporation based in Minnetonka, Minnesota. Founded in 1865, it is now the largest privately held corporation in the United States in terms of revenue. If it were a public company, it would rank, as of 2011, number 13 on the Fortune 500,...
to build ships after seeing their success in building ships and barges used to haul grain. Cargill built facilities in Savage, Minnesota
Savage, Minnesota
Savage is a suburban city south-southwest of downtown Minneapolis in Scott County in the U.S. state of Minnesota. The city is situated on the south bank of the Minnesota River in a region commonly referred to as South of the River, comprising the southern portion of Minneapolis-St. Paul, the...
on the south bank of the Minnesota River and turned out 18 refueling ships and four towboats in four years. After the war, the Cargill facilities became a major grain shipping terminal. Honeywell
Honeywell
Honeywell International, Inc. is a major conglomerate company that produces a variety of consumer products, engineering services, and aerospace systems for a wide variety of customers, from private consumers to major corporations and governments....
built airplane control systems and periscope sights for submarines, and also developed a proximity fuse for anti-aircraft
Anti-aircraft warfare
NATO defines air defence as "all measures designed to nullify or reduce the effectiveness of hostile air action." They include ground and air based weapon systems, associated sensor systems, command and control arrangements and passive measures. It may be to protect naval, ground and air forces...
shells. The United States government built the Twin Cities Ordnance Plant to produce munitions. The plant employed 8,500 workers in 1941, and since there was a shortage of male workers during the war, more than half of the workers at the munitions plant were women. The plant also employed nearly 1000 African American workers, as President Roosevelt had issued an executive order forbidding racial discrimination in defense industries. Native American workers also found opportunities due to workforce shortages in wartime.
During the wartime years, Savage was also the home of Camp Savage
Camp Savage
Camp Savage is the former site of a Military Intelligence Service language school operating during World War II. The school itself was established in San Francisco, but was moved in 1942 to Savage, Minnesota in the interest of national security. The purpose of the school was to teach the Japanese...
, a school designed to improve the foreign language skills of Japanese-American soldiers and to train them in military intelligence gathering. The school was originally established in San Francisco, but moved to Minnesota after the bombing of Pearl Harbor
Pearl Harbor
Pearl Harbor, known to Hawaiians as Puuloa, is a lagoon harbor on the island of Oahu, Hawaii, west of Honolulu. Much of the harbor and surrounding lands is a United States Navy deep-water naval base. It is also the headquarters of the U.S. Pacific Fleet...
. Eventually, the school outgrew its facilities in Savage and was moved to Fort Snelling. Fort Snelling itself served a major role as a reception center for newly drafted recruits after the Selective Service Act
Selective Training and Service Act of 1940
The Selective Training and Service Act of 1940, also known as the Burke-Wadsworth Act, was passed by the Congress of the United States on September 17, 1940, becoming the first peacetime conscription in United States history when President Franklin D. Roosevelt signed it into law two days later...
was passed in 1940. New recruits were given a physical exam and the Army General Qualification Test to determine their fitness for service in a particular branch. The most intelligent recruits, about 37% of Minnesotans going through Fort Snelling, were assigned to the Army Air Corps
United States Army Air Corps
The United States Army Air Corps was a forerunner of the United States Air Force. Renamed from the Air Service on 2 July 1926, it was part of the United States Army and the predecessor of the United States Army Air Forces , established in 1941...
. Recruits were also issued uniforms and sent from the fort to other training centers. Over 300,000 recruits were processed through Fort Snelling during the World War II years.
Modern economy
Feedlot
A feedlot or feedyard is a type of animal feeding operation which is used in factory farming for finishing livestock, notably beef cattle, but also swine, horses, sheep, turkeys, chickens or ducks, prior to slaughter. Large beef feedlots are called Concentrated Animal Feeding Operations . They...
s for hogs and cattle, machine milking at dairy farms, and raising chickens in large buildings. Planting also became more specialized with hybridization of corn and wheat, fertilization, and mechanical equipment such as tractors and combines
Combine harvester
The combine harvester, or simply combine, is a machine that harvests grain crops. The name derives from the fact that it combines three separate operations, reaping, threshing, and winnowing, into a single process. Among the crops harvested with a combine are wheat, oats, rye, barley, corn ,...
became the norm. University of Minnesota professor Norman Borlaug
Norman Borlaug
Norman Ernest Borlaug was an American agronomist, humanitarian, and Nobel laureate who has been called "the father of the Green Revolution". Borlaug was one of only six people to have won the Nobel Peace Prize, the Presidential Medal of Freedom and the Congressional Gold Medal...
contributed to this knowledge as part of the Green Revolution
Green Revolution
Green Revolution refers to a series of research, development, and technology transfer initiatives, occurring between the 1940s and the late 1970s, that increased agriculture production around the world, beginning most markedly in the late 1960s....
. Large canneries such as the Minnesota Valley Canning Company
Green Giant
Green Giant and Le Sueur are brands of frozen and canned vegetables owned by General Mills. The mascot of Green Giant is the Jolly Green Giant....
fed the country from Minnesota's productive farmland.
The Minnesota Mining and Manufacturing Company
3M
3M Company , formerly known as the Minnesota Mining and Manufacturing Company, is an American multinational conglomerate corporation based in Maplewood, Minnesota, United States....
(3M) was founded in 1902 in Two Harbors, Minnesota
Two Harbors, Minnesota
As of the census of 2000, there were 3,613 people, 1,636 households, and 953 families residing in the city. The population density was 1,120.7 people per square mile . There were 1,631 housing units at an average density of 505.9 per square mile...
, and was later moved to Duluth, Saint Paul, and then Maplewood
Maplewood, Minnesota
As of the census of 2000, there were 34,947 people, 13,758 households, and 9,190 families residing in the city. The population density was 2,017.5 people per square mile . There were 14,004 housing units at an average density of 808.5 per square mile...
. The founders of 3M got their start by manufacturing sandpaper. Under the leadership of William L. McKnight
William L. McKnight
William L. McKnight was an American businessman and philanthropist who served his entire career in the 3M corporation, rising to chairman of the board from 1949 to 1966. He founded The McKnight Foundation in 1953....
, the company established product lines such as abrasives for wet sanding, masking tape
Masking tape
Masking tape is a type of pressure sensitive tape made of a thin and easy-to-tear paper, and an easily released pressure sensitive adhesive. It is available in a variety of widths. It is used mainly in painting, to mask off areas that should not be painted...
and other adhesive
Adhesive
An adhesive, or glue, is a mixture in a liquid or semi-liquid state that adheres or bonds items together. Adhesives may come from either natural or synthetic sources. The types of materials that can be bonded are vast but they are especially useful for bonding thin materials...
s, roofing granules, resin
Resin
Resin in the most specific use of the term is a hydrocarbon secretion of many plants, particularly coniferous trees. Resins are valued for their chemical properties and associated uses, such as the production of varnishes, adhesives, and food glazing agents; as an important source of raw materials...
s, and films.
Suburb
Suburb
The word suburb mostly refers to a residential area, either existing as part of a city or as a separate residential community within commuting distance of a city . Some suburbs have a degree of administrative autonomy, and most have lower population density than inner city neighborhoods...
an development intensified after the war, fueled by the demand for new housing. In 1957, the Legislature created a planning commission for the Twin Cities metropolitan area. This became the Metropolitan Council
Metropolitan Council
The Metropolitan Council or Met Council is the regional governmental agency and metropolitan planning organization in Minnesota serving the Twin Cities seven-county metropolitan area. The Met Council is granted regional authority powers in state statutes by the Minnesota Legislature. These powers...
in 1967. Minnesota also became a center of technology after the war. Engineering Research Associates
Engineering Research Associates
Engineering Research Associates, commonly known as ERA, was a pioneering computer firm from the 1950s. They became famous for their numerical computers, but as the market expanded they became better known for their drum memory systems. They were eventually purchased by Remington Rand and merged...
was formed in 1946 to develop computers for the United States Navy
United States Navy
The United States Navy is the naval warfare service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the seven uniformed services of the United States. The U.S. Navy is the largest in the world; its battle fleet tonnage is greater than that of the next 13 largest navies combined. The U.S...
. It later merged with Remington Rand
Remington Rand
Remington Rand was an early American business machines manufacturer, best known originally as a typewriter manufacturer and in a later incarnation as the manufacturer of the UNIVAC line of mainframe computers but with antecedents in Remington Arms in the early nineteenth century. For a time, the...
, and later became Sperry Rand. William Norris
William Norris
William Charles Norris was the pioneering CEO of Control Data Corporation, at one time one of the most powerful and respected computer companies in the world...
left Sperry in 1957 to form Control Data Corporation
Control Data Corporation
Control Data Corporation was a supercomputer firm. For most of the 1960s, it built the fastest computers in the world by far, only losing that crown in the 1970s after Seymour Cray left the company to found Cray Research, Inc....
(CDC). Cray Research
Cray
Cray Inc. is an American supercomputer manufacturer based in Seattle, Washington. The company's predecessor, Cray Research, Inc. , was founded in 1972 by computer designer Seymour Cray. Seymour Cray went on to form the spin-off Cray Computer Corporation , in 1989, which went bankrupt in 1995,...
was formed when Seymour Cray
Seymour Cray
Seymour Roger Cray was an American electrical engineer and supercomputer architect who designed a series of computers that were the fastest in the world for decades, and founded Cray Research which would build many of these machines. Called "the father of supercomputing," Cray has been credited...
left CDC to form his own company. Medical device maker Medtronic
Medtronic
Medtronic, Inc. , based in suburban Minneapolis, Minnesota, is the world's largest medical technology company and is a Fortune 500 company.- History :...
also was founded in the Twin Cities in 1949.
Northwest Airlines
Northwest Airlines
Northwest Airlines, Inc. was a major United States airline founded in 1926 and absorbed into Delta Air Lines by a merger approved on October 29, 2008, making Delta the largest airline in the world...
, the dominant airline at Minneapolis-Saint Paul International Airport
Minneapolis-Saint Paul International Airport
Minneapolis-Saint Paul International Airport is the largest and busiest airport in the five-state upper Midwest region of Minnesota, Iowa, South Dakota, North Dakota, and Wisconsin.-Overview:...
, was founded in 1926 carrying mail from the Twin Cities to Chicago. The airline, long headquartered in Eagan
Eagan, Minnesota
Eagan is a city south of Saint Paul in Dakota County in the U.S. state of Minnesota. The city lies on the south bank of the Minnesota River, upstream from the confluence with the Mississippi River. Eagan and nearby suburbs form the southern portion of Minneapolis-St. Paul, the fifteenth largest...
, merged with Delta Air Lines
Delta Air Lines
Delta Air Lines, Inc. is a major airline based in the United States and headquartered in Atlanta, Georgia. The airline operates an extensive domestic and international network serving all continents except Antarctica. Delta and its subsidiaries operate over 4,000 flights every day...
in October 2008. The company will keep the Delta name and will be headquartered in Atlanta.
Postwar politics

Hubert Humphrey
Hubert Horatio Humphrey, Jr. , served under President Lyndon B. Johnson as the 38th Vice President of the United States. Humphrey twice served as a United States Senator from Minnesota, and served as Democratic Majority Whip. He was a founder of the Minnesota Democratic-Farmer-Labor Party and...
was a Minnesotan who became a nationally prominent politician. He first ran for mayor of Minneapolis in 1943, but lost the election to the Republican candidate by just a few thousand votes. As a Democrat, Humphrey recognized that his best chance for political success was to obtain the support of the Minnesota Farmer-Labor Party
Minnesota Farmer-Labor Party
The Minnesota Farmer–Labor Party was a political party in the United States state of Minnesota, the most successful and longest-lasting of the constituent elements of the national Farmer–Labor Party movement, which had a presence in other states...
. Other members of the Farmer-Labor Party had been considering the idea, as encouraged by Franklin D. Roosevelt
Franklin D. Roosevelt
Franklin Delano Roosevelt , also known by his initials, FDR, was the 32nd President of the United States and a central figure in world events during the mid-20th century, leading the United States during a time of worldwide economic crisis and world war...
, but the merger only became reality after Humphrey traveled to Washington, D.C. to discuss the issue. Rather than simply absorbing the Farmer-Labor party, with its constituency of 200,000 voters, Humphrey suggested calling the party the Minnesota Democratic-Farmer-Labor Party
Minnesota Democratic-Farmer-Labor Party
The Minnesota Democratic–Farmer–Labor Party is a major political party in the state of Minnesota and the state affiliate of the Democratic Party. It was created on April 15, 1944, with the merger of the Minnesota Democratic Party and the Farmer–Labor Party...
. He was elected mayor of Minneapolis in 1945, and one of his first actions was to propose an ordinance making racial discrimination by employers subject to a fine. This ordinance was adopted in 1947, and although few fines were issued, the city's banks and department stores realized that public relations would improve by hiring blacks in increasing numbers. Humphrey delivered an impassioned speech at the 1948 Democratic National Convention
1948 Democratic National Convention
The 1948 Democratic National Convention was held at Convention Hall in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, from July 12 to July 14, and resulted in the nominations of incumbent Harry S Truman for President and U.S. Senator Alben W...
encouraging the party to adopt a civil rights plank in their platform. He was elected to the United States Senate
United States Senate
The United States Senate is the upper house of the bicameral legislature of the United States, and together with the United States House of Representatives comprises the United States Congress. The composition and powers of the Senate are established in Article One of the U.S. Constitution. Each...
in 1948 and was re-elected in 1954 and 1960.
In the early 1960s, the topic of civil rights was coming to national prominence with sit-ins and marches organized by Martin Luther King Jr. and other black leaders. In 1963, President John F. Kennedy
John F. Kennedy
John Fitzgerald "Jack" Kennedy , often referred to by his initials JFK, was the 35th President of the United States, serving from 1961 until his assassination in 1963....
sent a comprehensive civil rights bill to Congress, based largely on the ideas that Humphrey had been placing before the Senate for the previous fifteen years. The bill passed the House in early 1964, but passage through the Senate was more difficult, due to southern
Southern United States
The Southern United States—commonly referred to as the American South, Dixie, or simply the South—constitutes a large distinctive area in the southeastern and south-central United States...
segregationists who filibuster
Filibuster
A filibuster is a type of parliamentary procedure. Specifically, it is the right of an individual to extend debate, allowing a lone member to delay or entirely prevent a vote on a given proposal...
ed for 75 days. Finally, in June 1964, the Civil Rights Act of 1964
Civil Rights Act of 1964
The Civil Rights Act of 1964 was a landmark piece of legislation in the United States that outlawed major forms of discrimination against African Americans and women, including racial segregation...
became law. Humphrey called this his greatest achievement. Lyndon B. Johnson
Lyndon B. Johnson
Lyndon Baines Johnson , often referred to as LBJ, was the 36th President of the United States after his service as the 37th Vice President of the United States...
recruited Humphrey for his running mate in the 1964 presidential election
United States presidential election, 1964
The United States presidential election of 1964 was held on November 3, 1964. Incumbent President Lyndon B. Johnson had come to office less than a year earlier following the assassination of his predecessor, John F. Kennedy. Johnson, who had successfully associated himself with Kennedy's...
, and Humphrey became Vice President of the United States
Vice President of the United States
The Vice President of the United States is the holder of a public office created by the United States Constitution. The Vice President, together with the President of the United States, is indirectly elected by the people, through the Electoral College, to a four-year term...
. Governor Karl Rolvaag
Karl Rolvaag
Karl Fritjof Rolvaag was a U.S. politician and the son of Norwegian-American author and professor Ole E. Rølvaag...
(DFL)
Minnesota Democratic-Farmer-Labor Party
The Minnesota Democratic–Farmer–Labor Party is a major political party in the state of Minnesota and the state affiliate of the Democratic Party. It was created on April 15, 1944, with the merger of the Minnesota Democratic Party and the Farmer–Labor Party...
appointed Walter Mondale
Walter Mondale
Walter Frederick "Fritz" Mondale is an American Democratic Party politician, who served as the 42nd Vice President of the United States , under President Jimmy Carter, and as a United States Senator for Minnesota...
to fill Humphrey's Senate seat. Humphrey voiced doubts about the 1965 bombings of North Vietnam
North Vietnam
The Democratic Republic of Vietnam , was a communist state that ruled the northern half of Vietnam from 1954 until 1976 following the Geneva Conference and laid claim to all of Vietnam from 1945 to 1954 during the First Indochina War, during which they controlled pockets of territory throughout...
, which alienated him from Johnson. He later defended Johnson's conduct of the Vietnam War
Vietnam War
The Vietnam War was a Cold War-era military conflict that occurred in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia from 1 November 1955 to the fall of Saigon on 30 April 1975. This war followed the First Indochina War and was fought between North Vietnam, supported by its communist allies, and the government of...
, alienating himself from liberals
Liberalism in the United States
Liberalism in the United States is a broad political philosophy centered on the unalienable rights of the individual. The fundamental liberal ideals of freedom of speech, freedom of the press, freedom of religion for all belief systems, and the separation of church and state, right to due process...
, who were beginning to oppose the war around 1967. In the 1968 presidential election
United States presidential election, 1968
The United States presidential election of 1968 was the 46th quadrennial United States presidential election. Coming four years after Democrat Lyndon B. Johnson won in a historic landslide, it saw Johnson forced out of the race and Republican Richard Nixon elected...
, Humphrey ran against Richard Nixon
Richard Nixon
Richard Milhous Nixon was the 37th President of the United States, serving from 1969 to 1974. The only president to resign the office, Nixon had previously served as a US representative and senator from California and as the 36th Vice President of the United States from 1953 to 1961 under...
and Independent
American Independent Party
The American Independent Party is a right-wing political party of the United States that was established in 1967 by Bill and Eileen Shearer. In 1968, the American Independent Party nominated George C. Wallace as its presidential candidate and retired Air Force General Curtis E. LeMay as the vice...
candidate George Wallace
George Wallace
George Corley Wallace, Jr. was the 45th Governor of Alabama, serving four terms: 1963–1967, 1971–1979 and 1983–1987. "The most influential loser" in 20th-century U.S. politics, according to biographers Dan T. Carter and Stephan Lesher, he ran for U.S...
and lost the popular vote by only 0.7%. Humphrey later returned to the Senate in 1971 after Eugene McCarthy left office.
Eugene McCarthy
Eugene McCarthy
Eugene Joseph "Gene" McCarthy was an American politician, poet, and a long-time member of the United States Congress from Minnesota. He served in the U.S. House of Representatives from 1949 to 1959 and the U.S. Senate from 1959 to 1971.In the 1968 presidential election, McCarthy was the first...
(DFL)
Minnesota Democratic-Farmer-Labor Party
The Minnesota Democratic–Farmer–Labor Party is a major political party in the state of Minnesota and the state affiliate of the Democratic Party. It was created on April 15, 1944, with the merger of the Minnesota Democratic Party and the Farmer–Labor Party...
served in the United States House of Representatives
United States House of Representatives
The United States House of Representatives is one of the two Houses of the United States Congress, the bicameral legislature which also includes the Senate.The composition and powers of the House are established in Article One of the Constitution...
from 1949 through 1959 and in the United States Senate from 1959 through 1971. He gained a reputation as an intellectual with strong convictions and integrity. In 1967, he challenged Lyndon B. Johnson for the presidential nomination, running on an anti-war platform in contrast to Johnson's policies. His strong support in the New Hampshire primary convinced Johnson to leave the race.
Democrat Walter Mondale
Walter Mondale
Walter Frederick "Fritz" Mondale is an American Democratic Party politician, who served as the 42nd Vice President of the United States , under President Jimmy Carter, and as a United States Senator for Minnesota...
also achieved national prominence as Vice President under Jimmy Carter
Jimmy Carter
James Earl "Jimmy" Carter, Jr. is an American politician who served as the 39th President of the United States and was the recipient of the 2002 Nobel Peace Prize, the only U.S. President to have received the Prize after leaving office...
. He served in the Senate from his appointment in 1964 until becoming Vice President in 1977. In 1984, he ran for President of the United States, choosing Geraldine Ferraro
Geraldine Ferraro
Geraldine Anne Ferraro was an American attorney, a Democratic Party politician, and a member of the United States House of Representatives. She was the first female Vice Presidential candidate representing a major American political party....
as his running mate. The election
United States presidential election, 1984
The United States presidential election of 1984 was a contest between the incumbent President Ronald Reagan, the Republican candidate, and former Vice President Walter Mondale, the Democratic candidate. Reagan was helped by a strong economic recovery from the deep recession of 1981–1982...
proved to be a landslide victory for popular incumbent Ronald Reagan
Ronald Reagan
Ronald Wilson Reagan was the 40th President of the United States , the 33rd Governor of California and, prior to that, a radio, film and television actor....
. In 2002, just 11 days before election day, when incumbent Senator Paul Wellstone
Paul Wellstone
Paul David Wellstone was a two-term U.S. Senator from the state of Minnesota and member of the Democratic-Farmer-Labor Party, which is affiliated with the national Democratic Party. Before being elected to the Senate in 1990, he was a professor of political science at Carleton College...
was killed in a plane crash, Mondale stepped into the race as the Democratic candidate for the U.S. Senate. He lost the bid by two percentage points to the Republican, Norm Coleman
Norm Coleman
Norman Bertram Coleman, Jr. is an American attorney and politician. He was a United States senator from Minnesota from 2003 to 2009. Coleman was elected in 2002 and served in the 108th, 109th, and 110th Congresses. Before becoming a senator, he was mayor of Saint Paul, Minnesota, from 1994 to 2002...
.
In 1970, Wendell Anderson
Wendell Anderson
Wendell Richard "Wendy" Anderson is an American politician and was the 33rd Governor of Minnesota from January 4, 1971 to December 29, 1976. In late 1976, he resigned the governor's office in order to be named U.S. Senator to replace Walter Mondale, who had been elected Vice President of the...
(DFL)
Minnesota Democratic-Farmer-Labor Party
The Minnesota Democratic–Farmer–Labor Party is a major political party in the state of Minnesota and the state affiliate of the Democratic Party. It was created on April 15, 1944, with the merger of the Minnesota Democratic Party and the Farmer–Labor Party...
was elected as governor of Minnesota. He spent two years working with a split Minnesota Legislature
Minnesota Legislature
The Minnesota Legislature is the legislative branch of government in the U.S. state of Minnesota. It is a bicameral legislature located at the Minnesota Capitol in Saint Paul and it consists of two houses: the lower Minnesota House of Representatives and the Minnesota Senate...
to enact a tax and school finance reform package that shifted the source of public education funding from local property taxes to state sales taxes, as well as adding excise
Excise
Excise tax in the United States is a indirect tax on listed items. Excise taxes can be and are made by federal, state and local governments and are far from uniform throughout the United States...
taxes to liquor and cigarettes. This achievement, dubbed the "Minnesota Miracle", was immensely popular. In the next few years, the Legislature enacted other facets of their "new liberalism", including ratification of the Equal Rights Amendment
Equal Rights Amendment
The Equal Rights Amendment was a proposed amendment to the United States Constitution. The ERA was originally written by Alice Paul and, in 1923, it was introduced in the Congress for the first time...
, strong environmental laws, increases in workers' compensation and unemployment benefits, and elimination of income taxes for the working poor. Time Magazine featured Wendell Anderson and the state in an article entitled, "Minnesota: A State That Works". In 1976 when Mondale resigned his Senate seat to become Jimmy Carter's running mate, Anderson resigned the governor's seat and turned it over to Lieutenant Governor Rudy Perpich
Rudy Perpich
Rudolph George "Rudy" Perpich, Sr. was an American politician and the longest-serving governor of Minnesota. A member of the Democratic-Farmer-Labor Party, he served as the 34th and 36th Governor of Minnesota from December 29, 1976 to January 4, 1979, and from January 3, 1983, to January 7, 1991...
(DFL), who promptly appointed Anderson to fill Mondale's vacant Senate seat. Voters turned Perpich and Anderson out of office in 1978, in an election dubbed the "Minnesota Massacre". Perpich was again elected as governor in 1983 and served until 1991.
Paul Wellstone
Paul Wellstone
Paul David Wellstone was a two-term U.S. Senator from the state of Minnesota and member of the Democratic-Farmer-Labor Party, which is affiliated with the national Democratic Party. Before being elected to the Senate in 1990, he was a professor of political science at Carleton College...
(DFL) was elected to the United States Senate in 1990, defeating incumbent Rudy Boschwitz
Rudy Boschwitz
Rudolph Ely "Rudy" Boschwitz is a former Independent-Republican United States Senator from Minnesota. He served in the Senate from December 1978 to January 1991, in the 96th, 97th, 98th, 99th, 100th, and 101st congresses. He was then defeated by Paul Wellstone.-Life and career:Boschwitz was born...
(R) in one of the biggest election upsets of the decade. In 1996, he defeated Boschwitz again in a rematch of the 1990 election. Wellstone was known for being a liberal activist, as evidenced by his books How the Rural Poor Got Power: Narrative of a Grassroots Organizer, describing his work with the group Organization for a Better Rice County, and The Conscience of a Liberal: Reclaiming the Compassionate Agenda. He explored a possible presidential bid in 1998, telling people he represented the "Democratic wing of the Democratic Party". On October 25, 2002, he was killed in a plane crash near Eveleth, Minnesota
Eveleth, Minnesota
As of the census of 2000, there were 3,865 people, 1,717 households, and 971 families residing in the city. The population density was 611.0 people per square mile . There were 1,965 housing units at an average density of 310.6 per square mile...
, along with his wife, his daughter, three campaign staffers, and the two pilots.
Jesse Ventura
Jesse Ventura
James George Janos , better known as Jesse Ventura, is an American politician, the 38th Governor of Minnesota from 1999 to 2003, Navy UDT veteran, former SEAL reservist, actor, and former radio and television talk show host...
, elected governor in 1998, had a colorful past as a Navy SEAL, a professional wrestler, an actor, mayor of Brooklyn Park
Brooklyn Park, Minnesota
According to the 2010 census, there were 75,781 people residing in the city. The racial makeup of the city was 52% White, 24% African American, 1% Native American, 15% Asian, 42 residents identifying themselves as Pacific Islander, 4% from other races, and 4% from two or more races...
, and a radio and TV broadcaster. He left office after one term. His election brought international attention to the Independence Party
Independence Party of Minnesota
The Independence Party of Minnesota , formerly the Reform Party of Minnesota, is the third largest political party in Minnesota, behind the Democratic-Farmer-Labor Party and Republican Party . It is the political party of former Minnesota Governor Jesse Ventura , and endorsed former U.S...
.
See also
- Demographics of MinnesotaDemographics of MinnesotaThe U.S. Census Bureau counted Minnesota's population at 5,303,925 in the 2010 Census.-Population:From fewer than 6,100 people in 1850, Minnesota's population grew to over 1.75 million by 1900. Each of the next six decades saw a 15.0% rise in population, reaching 3.41 million in 1960...
- Geology of Minnesota
- Glacial history of MinnesotaGlacial history of MinnesotaThe glacial history of Minnesota is most defined since the onset of the last glacial period, which ended some 10,000 years ago. Within the last million years, most of the Midwestern United States and much of Canada were covered at one time or another with an ice sheet. This continental glacier had...
- Music of MinnesotaMusic of MinnesotaThe music of Minnesota began with the native rhythms and songs of native Americans, the first inhabitants of the lands which later became the U.S. state of Minnesota. Their relatives, the half-breed Métis fur-trading voyageurs, introduced the chansons of their French ancestors in the late...
- National Register of Historic Places listings in Hennepin County, Minnesota
- National Register of Historic Places listings in Ramsey County, Minnesota
- National Register of Historic Places listings in Dakota County, Minnesota

