
Illyria
Encyclopedia
In classical antiquity
, Illyria (Ancient Greek: or ; ; see also Illyricum
) was a region in the western part of the Balkan Peninsula inhabited by the Illyrians
.
The prehistory
of Illyria and the Illyrians is known from archaeological evidence. The Romans
conquered the region in 168 BC
in the aftermath of the Illyrian Wars
. "Illyria" is thus a designation of a roughly defined region of the western Balkans as seen from a Roman perspective, just as Magna Germania is a rough geographic term not delineated by any linguistic or ethnic unity.
The term Illyris is sometimes used to define an area (now in modern Albania
) north of the Aous valley such as Illyris Graeca.
, the name of Illyria is aitiologically traced to Illyrius
, the son of Cadmus
and Harmonia
, who eventually ruled Illyria and became the eponymous ancestor of the Illyrians. A later version of the myth identifies Polyphemus
and Galatea
as parents of Celtus, Galas
and Illyrius
. The second myth could stem perhaps from the similarities to Celts and Gauls
.
in the 8th century BC. The era in which we observe other Illyrian kingdoms begins approximately at 400 BC and ends at 167 BC. The Autariatae under Pleurias
(337 BC) were considered to have been a kingdom. The Kingdom of the Ardiaei began at 230 BC and ended at 167 BC. The most notable Illyrian kingdoms and dynasties were those of Bardyllis
of the Dardani
and of Agron of the Ardiaei who created the last and best-known Illyrian kingdom. Agron ruled over the Ardiaei and had extended his rule to other tribes as well. As for the Dardanians, they always had separate domains from the rest of the Illyrians
.
The Illyrian kingdoms were composed of small areas within the region of Illyria. The exact extent of even the most prominent ones remains unknown. Only the Romans
ruled the entire region. The internal organization of the south Illyrian kingdoms points to imitation of their neighboring Greek kingdoms and influence from the Greek and Hellenistic world in the growth of their urban
centers. Polybius
gives as an image of society within an Illyrian kingdom as peasant infantry fought under aristocrats which he calls in Greek Polydynastae (Greek: Πολυδυνάστες) where each one controlled a town within the kingdom. The monarchy was established on hereditary lines and Illyrian rulers used marriages as a means of alliance with other powers. Pliny
(23–79 AD) writes that the people that formed the nucleus of the Illyrian kingdom were 'Illyrians proper' or Illyrii Proprie Dicti. They were the Taulantii
, the Pleraei, the Endirudini, Sasaei, Grabaei and the Labeatae. These later joined to form the Docleatae.
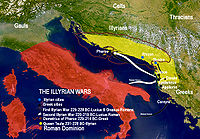 The Romans defeated Gentius, the last king of Illyria, at Scodra in 168 BC and captured him, bringing him to Rome in 165 BC. Four client-republics were set up, which were in fact ruled by Rome. Later, the region was directly governed by Rome and organized as a province
The Romans defeated Gentius, the last king of Illyria, at Scodra in 168 BC and captured him, bringing him to Rome in 165 BC. Four client-republics were set up, which were in fact ruled by Rome. Later, the region was directly governed by Rome and organized as a province
, with Scodra as its capital.
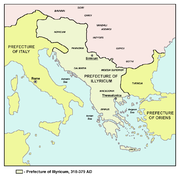 The Roman province of Illyricum replaced the formerly independent kingdom of Illyria. It stretched from the Drilon
The Roman province of Illyricum replaced the formerly independent kingdom of Illyria. It stretched from the Drilon
river in modern Albania
to Istria
(Croatia
) in the west and to the Sava river (Croatia
) in the north. Salona
(near modern Split
in Croatia) functioned as its capital.
After crushing a revolt
of Pannonians and Daesitiates, Roman administrators dissolved the province of Illyricum and divided its lands between the new provinces of Pannonia
in the north and Dalmatia
in the south.
The province of Illyricum
was divided into Dalmatia
and Pannonia
in 10 AD, but term Illyria remained in use in Late Latin
and throughout the medieval period. After the division of the Roman Empire, the bishops of Thessalonica appointed papal vicars for Illyricum. The first of these vicars is said to have been Bishop Acholius or Ascholius (died 383 or 384), the friend of St. Basil.
In the 5th century, the bishops of Illyria withdrew from communion with Rome, without attaching themselves to Constantinople, and remained for a time independent, but in 515, forty Illyrian bishops renewed their loyalty to Rome by declaring allegiance to Pope Hormisdas
.
The patriarchs of Constantinople succeeded in bringing Illyria under their jurisdiction in the 8th century.
, as Leopold I
designated as the "Illyrian nation" the Serbs on Hungarian territory.
A fictional "kingdom of Illyria" is postulated alongside historical late medieval states of the region in the Fojnica Armorial
(17th century). An extensive history of Illyria by Charles du Fresne, sieur du Cange
, was published by Joseph Keglevich
in 1746.
The name Illyria was revived by Napoleon for the "Provinces of Illyria
" that were incorporated into the French Empire
from 1809 to 1813, and the Kingdom of Illyria
was part of Austria
until 1849, after which time it was not used in the reorganised Austro-Hungarian Empire.
The land of Illyria is the setting for William Shakespeare
's Twelfth Night, Jean-Paul Sartre
's Les Mains Sales
and in Lloyd Alexander
's The Illyrian Adventure.
Classical antiquity
Classical antiquity is a broad term for a long period of cultural history centered on the Mediterranean Sea, comprising the interlocking civilizations of ancient Greece and ancient Rome, collectively known as the Greco-Roman world...
, Illyria (Ancient Greek: or ; ; see also Illyricum
Illyricum (Roman province)
The Roman province of Illyricum or Illyris Romana or Illyris Barbara or Illyria Barbara replaced most of the region of Illyria. It stretched from the Drilon river in modern north Albania to Istria in the west and to the Sava river in the north. Salona functioned as its capital...
) was a region in the western part of the Balkan Peninsula inhabited by the Illyrians
Illyrians
The Illyrians were a group of tribes who inhabited part of the western Balkans in antiquity and the south-eastern coasts of the Italian peninsula...
.
The prehistory
Prehistoric Balkans
The prehistory of Southeastern Europe , defined roughly as the territory of the wider Balkans peninsula covers the period from the Upper Paleolithic, beginning with the presence of Homo sapiens in the area some 44,000 years ago, until the...
of Illyria and the Illyrians is known from archaeological evidence. The Romans
Roman Republic
The Roman Republic was the period of the ancient Roman civilization where the government operated as a republic. It began with the overthrow of the Roman monarchy, traditionally dated around 508 BC, and its replacement by a government headed by two consuls, elected annually by the citizens and...
conquered the region in 168 BC
168 BC
Year 168 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Macedonicus and Crassus...
in the aftermath of the Illyrian Wars
Illyrian Wars
Illyrian Wars were a set of conflicts of 229 BC, 219 BC and 168 BC when Rome overran the Illyrian settlements and suppressed the piracy that had made the Adriatic unsafe for Italian commerce. There were three campaigns, the first against Teuta, the second against Demetrius of Pharos and the third...
. "Illyria" is thus a designation of a roughly defined region of the western Balkans as seen from a Roman perspective, just as Magna Germania is a rough geographic term not delineated by any linguistic or ethnic unity.
The term Illyris is sometimes used to define an area (now in modern Albania
Albania
Albania , officially known as the Republic of Albania , is a country in Southeastern Europe, in the Balkans region. It is bordered by Montenegro to the northwest, Kosovo to the northeast, the Republic of Macedonia to the east and Greece to the south and southeast. It has a coast on the Adriatic Sea...
) north of the Aous valley such as Illyris Graeca.
Mythology
In Greek mythologyGreek mythology
Greek mythology is the body of myths and legends belonging to the ancient Greeks, concerning their gods and heroes, the nature of the world, and the origins and significance of their own cult and ritual practices. They were a part of religion in ancient Greece...
, the name of Illyria is aitiologically traced to Illyrius
Illyrius
Illyrius is a name known in different stories found in ancient Greek mythology.-Cadmus and Harmonia:According to the Library and Epitome of Apollodorus, Illyrius was the youngest son of Cadmus and Harmonia who eventually ruled Illyria and became the eponymous ancestor of the whole Illyrian people...
, the son of Cadmus
Cadmus
Cadmus or Kadmos , in Greek mythology was a Phoenician prince, the son of king Agenor and queen Telephassa of Tyre and the brother of Phoenix, Cilix and Europa. He was originally sent by his royal parents to seek out and escort his sister Europa back to Tyre after she was abducted from the shores...
and Harmonia
Harmonia
-Art:* Harmonia , an outdoor sculpture by Achim Kühn in Turku, Finland-Antiquity:* Harmonia , the Greek goddess of harmony and concord* Harmonia -Art:* Harmonia (sculpture), an outdoor sculpture by Achim Kühn in Turku, Finland-Antiquity:* Harmonia (mythology), the Greek goddess of harmony and...
, who eventually ruled Illyria and became the eponymous ancestor of the Illyrians. A later version of the myth identifies Polyphemus
Polyphemus
Polyphemus is the gigantic one-eyed son of Poseidon and Thoosa in Greek mythology, one of the Cyclopes. His name means "much spoken of" or "famous". Polyphemus plays a pivotal role in Homer's Odyssey.-In Homer's Odyssey:...
and Galatea
Galatea
Galatea is an ancient Greek name meaning "she who is milk-white".Galatea or Galathea may refer to:-In mythology:* Galatea :**Galatea, a woman who prayed for her daughter to be turned into a son, Leucippus...
as parents of Celtus, Galas
Galas
In Greek mythology, the name Galas was attributed to individuals. Galas, in mythological accounts, was regarded as the eponymous founder of the Gauls.*Galas was the son of Polyphemos and Galatea and the brother of Illyrius and Keltos....
and Illyrius
Illyrius
Illyrius is a name known in different stories found in ancient Greek mythology.-Cadmus and Harmonia:According to the Library and Epitome of Apollodorus, Illyrius was the youngest son of Cadmus and Harmonia who eventually ruled Illyria and became the eponymous ancestor of the whole Illyrian people...
. The second myth could stem perhaps from the similarities to Celts and Gauls
Gauls
The Gauls were a Celtic people living in Gaul, the region roughly corresponding to what is now France, Belgium, Switzerland and Northern Italy, from the Iron Age through the Roman period. They mostly spoke the Continental Celtic language called Gaulish....
.
Kingdoms
The earliest recorded Illyrian kingdom was that of the EncheleEnchele
The Enchelei , were an Illyrian tribe, in the 8th and 7th centuries BC, living around the region of Lake Ohrid in Albania and the Republic of Macedonia. They were often at war for domination of the region with the ancient Macedonians who settled in the east...
in the 8th century BC. The era in which we observe other Illyrian kingdoms begins approximately at 400 BC and ends at 167 BC. The Autariatae under Pleurias
Pleurias
Pleurias was an Illyrian king of the Autariatae State. In 337 BC Pleurias almost succeeded in killing Philip when he was on his Balkan campaigns...
(337 BC) were considered to have been a kingdom. The Kingdom of the Ardiaei began at 230 BC and ended at 167 BC. The most notable Illyrian kingdoms and dynasties were those of Bardyllis
Bardyllis
Bardyllis was a king of the Dardanian Kingdom and probably its founder.Bardyllis created one of the most powerful Illyrian states, that of the Dardanians...
of the Dardani
Dardani
Dardania was the region of the Dardani .Located at the Thraco-Illyrian contact zone, their identification as either an Illyrian or Thracian tribe is uncertain. Their territory itself was not considered part of Illyria by Strabo. The term used for their territory was , while for other tribes had...
and of Agron of the Ardiaei who created the last and best-known Illyrian kingdom. Agron ruled over the Ardiaei and had extended his rule to other tribes as well. As for the Dardanians, they always had separate domains from the rest of the Illyrians
Illyrians
The Illyrians were a group of tribes who inhabited part of the western Balkans in antiquity and the south-eastern coasts of the Italian peninsula...
.
The Illyrian kingdoms were composed of small areas within the region of Illyria. The exact extent of even the most prominent ones remains unknown. Only the Romans
Ancient Rome
Ancient Rome was a thriving civilization that grew on the Italian Peninsula as early as the 8th century BC. Located along the Mediterranean Sea and centered on the city of Rome, it expanded to one of the largest empires in the ancient world....
ruled the entire region. The internal organization of the south Illyrian kingdoms points to imitation of their neighboring Greek kingdoms and influence from the Greek and Hellenistic world in the growth of their urban
Urban area
An urban area is characterized by higher population density and vast human features in comparison to areas surrounding it. Urban areas may be cities, towns or conurbations, but the term is not commonly extended to rural settlements such as villages and hamlets.Urban areas are created and further...
centers. Polybius
Polybius
Polybius , Greek ) was a Greek historian of the Hellenistic Period noted for his work, The Histories, which covered the period of 220–146 BC in detail. The work describes in part the rise of the Roman Republic and its gradual domination over Greece...
gives as an image of society within an Illyrian kingdom as peasant infantry fought under aristocrats which he calls in Greek Polydynastae (Greek: Πολυδυνάστες) where each one controlled a town within the kingdom. The monarchy was established on hereditary lines and Illyrian rulers used marriages as a means of alliance with other powers. Pliny
Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus , better known as Pliny the Elder, was a Roman author, naturalist, and natural philosopher, as well as naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and personal friend of the emperor Vespasian...
(23–79 AD) writes that the people that formed the nucleus of the Illyrian kingdom were 'Illyrians proper' or Illyrii Proprie Dicti. They were the Taulantii
Taulantii
Taulantii was the name of a cluster of Illyrian tribes. According to Greek mythology Taulas , one of the six sons of Illyrius, was the eponymous ancestor of the Taulanti. They lived on the Adriatic coast of Illyria , between to the vicinity of the city of Epidamnus...
, the Pleraei, the Endirudini, Sasaei, Grabaei and the Labeatae. These later joined to form the Docleatae.
Roman and Byzantine rule

Roman province
In Ancient Rome, a province was the basic, and, until the Tetrarchy , largest territorial and administrative unit of the empire's territorial possessions outside of Italy...
, with Scodra as its capital.

Drin River
The Drin is the longest river in Albania with a total length of . It has two distributaries, one going directly into the Adriatic Sea, the other one into the Bojana River .- Origin :...
river in modern Albania
Albania
Albania , officially known as the Republic of Albania , is a country in Southeastern Europe, in the Balkans region. It is bordered by Montenegro to the northwest, Kosovo to the northeast, the Republic of Macedonia to the east and Greece to the south and southeast. It has a coast on the Adriatic Sea...
to Istria
Istria
Istria , formerly Histria , is the largest peninsula in the Adriatic Sea. The peninsula is located at the head of the Adriatic between the Gulf of Trieste and the Bay of Kvarner...
(Croatia
Croatia
Croatia , officially the Republic of Croatia , is a unitary democratic parliamentary republic in Europe at the crossroads of the Mitteleuropa, the Balkans, and the Mediterranean. Its capital and largest city is Zagreb. The country is divided into 20 counties and the city of Zagreb. Croatia covers ...
) in the west and to the Sava river (Croatia
Croatia
Croatia , officially the Republic of Croatia , is a unitary democratic parliamentary republic in Europe at the crossroads of the Mitteleuropa, the Balkans, and the Mediterranean. Its capital and largest city is Zagreb. The country is divided into 20 counties and the city of Zagreb. Croatia covers ...
) in the north. Salona
Salona
Salona was an ancient Illyrian Delmati city in the first millennium BC. The Greeks had set up an emporion there. After the conquest by the Romans, Salona became the capital of the Roman province of Dalmatia...
(near modern Split
Split (city)
Split is a Mediterranean city on the eastern shores of the Adriatic Sea, centered around the ancient Roman Palace of the Emperor Diocletian and its wide port bay. With a population of 178,192 citizens, and a metropolitan area numbering up to 467,899, Split is by far the largest Dalmatian city and...
in Croatia) functioned as its capital.
After crushing a revolt
Great Illyrian revolt
The Great Illyrian Revolt, was a major conflict between an alliance of indigenous communities from Illyricum and Roman forces that lasted for four years beginning in AD 6 and ending in AD 9.-The war:...
of Pannonians and Daesitiates, Roman administrators dissolved the province of Illyricum and divided its lands between the new provinces of Pannonia
Pannonia
Pannonia was an ancient province of the Roman Empire bounded north and east by the Danube, coterminous westward with Noricum and upper Italy, and southward with Dalmatia and upper Moesia....
in the north and Dalmatia
Dalmatia (Roman province)
Dalmatia was an ancient Roman province. Its name is probably derived from the name of an Illyrian tribe called the Dalmatae which lived in the area of the eastern Adriatic coast in Classical antiquity....
in the south.
The province of Illyricum
Illyricum (Roman province)
The Roman province of Illyricum or Illyris Romana or Illyris Barbara or Illyria Barbara replaced most of the region of Illyria. It stretched from the Drilon river in modern north Albania to Istria in the west and to the Sava river in the north. Salona functioned as its capital...
was divided into Dalmatia
Dalmatia (Roman province)
Dalmatia was an ancient Roman province. Its name is probably derived from the name of an Illyrian tribe called the Dalmatae which lived in the area of the eastern Adriatic coast in Classical antiquity....
and Pannonia
Pannonia
Pannonia was an ancient province of the Roman Empire bounded north and east by the Danube, coterminous westward with Noricum and upper Italy, and southward with Dalmatia and upper Moesia....
in 10 AD, but term Illyria remained in use in Late Latin
Late Latin
Late Latin is the scholarly name for the written Latin of Late Antiquity. The English dictionary definition of Late Latin dates this period from the 3rd to the 6th centuries AD extending in Spain to the 7th. This somewhat ambiguously defined period fits between Classical Latin and Medieval Latin...
and throughout the medieval period. After the division of the Roman Empire, the bishops of Thessalonica appointed papal vicars for Illyricum. The first of these vicars is said to have been Bishop Acholius or Ascholius (died 383 or 384), the friend of St. Basil.
In the 5th century, the bishops of Illyria withdrew from communion with Rome, without attaching themselves to Constantinople, and remained for a time independent, but in 515, forty Illyrian bishops renewed their loyalty to Rome by declaring allegiance to Pope Hormisdas
Pope Hormisdas
Pope Saint Hormisdas was Pope from July 20, 514 to 523. His papacy was dominated by the Acacian schism, started in 484 by Acacius of Constantinople's efforts to placate the Monophysites...
.
The patriarchs of Constantinople succeeded in bringing Illyria under their jurisdiction in the 8th century.
Legacy
The name Illyria only disappears from the historical record after the Ottoman invasion of the Balkans in the 15th century, and re-emerges in the 17th century, acquiring a new significance in the Ottoman–Habsburg WarsOttoman-Habsburg wars
The Ottoman–Habsburg wars refers to the military conflicts between the Ottoman Empire and the Habsburg dynasties of the Austrian Empire, Habsburg Spain and in certain times, the Holy Roman Empire and the Kingdom of Hungary. The war would be dominated by land campaigns in Hungary and present day...
, as Leopold I
Leopold I
Leopold I may refer to:*Leopold I, Margrave of Austria , first Margrave of Austria*Leopold I, Duke of Austria , co-Duke of Austria and Styria with Frederick I...
designated as the "Illyrian nation" the Serbs on Hungarian territory.
A fictional "kingdom of Illyria" is postulated alongside historical late medieval states of the region in the Fojnica Armorial
Fojnica Armorial
The so-called Fojnica Armorial is an early modern roll of arms of the Balkans...
(17th century). An extensive history of Illyria by Charles du Fresne, sieur du Cange
Charles du Fresne, sieur du Cange
Charles du Fresne, sieur du Cange or Ducange was a distinguished philologist and historian of the Middle Ages and Byzantium....
, was published by Joseph Keglevich
House of Keglević
The House of Keglević is a Croatian noble family originally from Dalmatia, their members were pointed out in public life, also as soldiers...
in 1746.
The name Illyria was revived by Napoleon for the "Provinces of Illyria
Illyrian provinces
The Illyrian Provinces was an autonomous province of the Napoleonic French Empire on the north and east coasts of the Adriatic Sea between 1809 and 1816. Its capital was established at Laybach...
" that were incorporated into the French Empire
First French Empire
The First French Empire , also known as the Greater French Empire or Napoleonic Empire, was the empire of Napoleon I of France...
from 1809 to 1813, and the Kingdom of Illyria
Kingdom of Illyria
The Kingdom of Illyria was an administrative unit of the Austrian Empire from 1816 to 1849. Its administrative centre was Ljubljana and it included the western and central part of present-day Slovenia, the present Austrian state of Carinthia, as well as some territories in north-western Croatia ...
was part of Austria
Austria
Austria , officially the Republic of Austria , is a landlocked country of roughly 8.4 million people in Central Europe. It is bordered by the Czech Republic and Germany to the north, Slovakia and Hungary to the east, Slovenia and Italy to the south, and Switzerland and Liechtenstein to the...
until 1849, after which time it was not used in the reorganised Austro-Hungarian Empire.
The land of Illyria is the setting for William Shakespeare
William Shakespeare
William Shakespeare was an English poet and playwright, widely regarded as the greatest writer in the English language and the world's pre-eminent dramatist. He is often called England's national poet and the "Bard of Avon"...
's Twelfth Night, Jean-Paul Sartre
Jean-Paul Sartre
Jean-Paul Charles Aymard Sartre was a French existentialist philosopher, playwright, novelist, screenwriter, political activist, biographer, and literary critic. He was one of the leading figures in 20th century French philosophy, particularly Marxism, and was one of the key figures in literary...
's Les Mains Sales
Les Mains Sales
Dirty Hands is a play by Jean-Paul Sartre. It was first performed on 2 April 1948 at the Theatre Antoine in Paris, starring François Périer, Marie Olivier and André Luguet...
and in Lloyd Alexander
Lloyd Alexander
Lloyd Chudley Alexander was a widely influential American author of more than forty books, mostly fantasy novels for children and adolescents, as well as several adult books...
's The Illyrian Adventure.
See also
- DalmatiaDalmatiaDalmatia is a historical region on the eastern coast of the Adriatic Sea. It stretches from the island of Rab in the northwest to the Bay of Kotor in the southeast. The hinterland, the Dalmatian Zagora, ranges from fifty kilometers in width in the north to just a few kilometers in the south....
- Diocese of Illyricum
- History of the BalkansHistory of the BalkansThe Balkans is an area of southeastern Europe situated at a major crossroads between mainland Europe and the Near East. The distinct identity and fragmentation of the Balkans owes much to its common and often violent history and to its very mountainous geography.-Neolithic:Archaeologists have...
- Illyrian provincesIllyrian provincesThe Illyrian Provinces was an autonomous province of the Napoleonic French Empire on the north and east coasts of the Adriatic Sea between 1809 and 1816. Its capital was established at Laybach...
- Illyrian warfareIllyrian warfareThe history of Illyrian warfare spans from the beginning of the 2nd millennium BC up to the 1st century AD in the region of Illyria and in southern Italy where the Iapygian civilization flourished....
- Kingdom of IllyriaKingdom of IllyriaThe Kingdom of Illyria was an administrative unit of the Austrian Empire from 1816 to 1849. Its administrative centre was Ljubljana and it included the western and central part of present-day Slovenia, the present Austrian state of Carinthia, as well as some territories in north-western Croatia ...
- Praetorian prefecture of IllyricumPraetorian prefecture of IllyricumThe praetorian prefecture of Illyricum was one of four praetorian prefectures into which the Late Roman Empire was divided.The administrative centre of the prefecture was Sirmium , and, after 379, Thessalonica...
- Roman province of Illyricum

