
Illyrian provinces
Encyclopedia
The Illyrian Provinces was an autonomous province of the Napoleonic French Empire
on the north and east coasts of the Adriatic Sea
between 1809 and 1816. Its capital was established at Laybach (modern-day Ljubljana in Slovenia
). The name "Illyrian" was used to refer to ancient Illyrians
who once lived in the area and constitutes a classicist relabeling of the Dalmatian coast, which was known as Illyria in antiquity.
- in March of 1797- led by General Bonaparte
caused huge civil disturbances. The Slovene
territories were mostly occupied by the troops under the command of General Bernadotte
who tried to calm the worried and scared population by issuing special public notices which were published also in the Slovene language. During the withdrawal of the French army
the commanding general Bonaparte
and his escort made a stop in Ljubljana
on April 28, 1797. In the blitzkrieg war of 1805-1806 the French troops once again occupied parts of the Slovene territory. Supply of the French troops and steep war dues were a huge burden for the population of the occupied territories. The foundation of the provincial brigades in June 1808 and extensive preparations for the new war did not stop Napoleon's army which completely defeated the Austria
n troops at the battle of Wagram
on July 6, 1809.
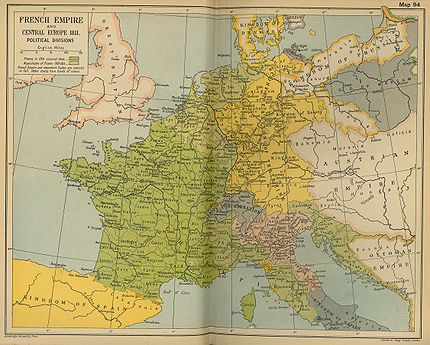
The Illyrian Provinces were created by the Treaty of Schönbrunn
in 1809 when the Austrian Empire
ceded the territories of western or Upper Carinthia
with Lienz
in the East Tyrol
, Carniola
, southwest of the river Sava, Gorizia and Gradisca
, and Trieste
to the French Empire
after the Austrian defeat at the Battle of Wagram
. These territories lying north and east of the Adriatic Sea
were amalgamated with Dalmatia into the Illyrian Provinces, technically part of France, the capital of which was established at "Laybach", i.e.Ljubljana
in modern Slovenia
. The territory of the Republic of Ragusa
, which was annexed to the Napoleonic Kingdom of Italy in 1808, was also integrated into the Illyrian Provinces.
The French administration, headed by a Governor-General, introduced civil law
(Code civil) across the provinces. August de Marmont was the first to be appointed as the Governor-General of the provinces on 8 October 1809, and held his post until January 1811. On 9 April the same year, Henri-Gratien Bertrand was appointed, who held this post until February 1812, when, on 21 February, he was succeeded by Jean-Andoche Junot
. The last Governor-General was Joseph Fouché
, who was appointed in July 1813 and held his post for only one month.
The British Navy imposed a blockade of the Adriatic Sea, effective since the Treaty of Tilsit (July 1807), which brought merchant shipping to a standstill, a measure most seriously affecting the economy of the Dalmatian port cities. An attempt by joint French and Italian forces to seize the British-held Dalmatian island of Vis
failed on 22 October 1810.
In August 1813, Austria declared war on France. Austrian troops led by General Franz Tomassich invaded the Illyrian Provinces. Croat troops enrolled in the French army switched sides. Zara (now called Zadar
) surrendered to Austrian forces after a 34-day siege on 6 December 1813. At Dubrovnik an insurrection expelled the French and a provisional Ragusan administration was established, hoping for the restoration of the Republic. It was occupied by Austrian troops on 20 September 1813. The Cattaro area (now called Bay of Kotor
) and its environs were occupied in 1813 by Montenegrin
forces, which held it until 1814, when the appearance of an Austrian force caused the Prince of Montenegro to turn over the territory to Austrian administration on 11 June. The British withdrew from the occupied Dalmatian islands in July 1815, following the Battle of Waterloo
.
(capital Lienz
), Istria
(Trieste), Carniola
(Ljubljana), Civil Croatia
(Karlovac
), Military Croatia (Senj
), Dalmatia
(Zara
), and the Ragusa
and Cattaro
province (Dubrovnik
).
In 1811 the Illyrian provinces saw an administrative reorganization. The seat of the Governor General was Ljubljana
; the country was initially divided in 4 intendancies (Ljubljana, Karlovac, Trieste, Zara) and 10 sub-intendancies. Later that year, the number of intendancies was extended to eight, with Villach, Gorizia
, Fiume
and Ragusa
being elevated to intendancy rank.
Two Chambers of Commerce
were established, at Trieste and at Ragusa. The ecclesiastical administration was reorganized in accordance with the new political borders; two archdioceses were established with seats at Ljubljana and Zara, with suffragan dioceses at Gorizia, Capodistria, Šibenik
, Spalato
and Ragusa (1811).
regulation which had forbidden Jews to settle within Carniola.
Among the main changes the French empire brought were the overhaul of administration, the changing of the schooling system – creating universities and making Slovene a learning language – and the usage of the Napoleonic code (the French Code Civil) and the Penal Code.
 Although the French did not entirely abolish the feudal system, their rule familiarized in more detail the inhabitants of the Illyrian Provinces with the achievements of the French revolution
Although the French did not entirely abolish the feudal system, their rule familiarized in more detail the inhabitants of the Illyrian Provinces with the achievements of the French revolution
and with contemporary bourgeois society. They introduced equality before the law, compulsory military service and a uniform tax system, and also abolished certain tax privileges, introduced modern administration, separated powers between the state and the church (the introduction of the civil wedding, keeping civil registration of births etc.), and nationalized the judiciary. The occupants made all the citizens theoretically equal under the law for the first time.
The French also founded a university ("École central") in 1810 (which was disbanded in 1813, when Austria regained control, but whose Basic Decree of 4 July 1810, which ordered the reorganization of the former Austrian lycees in Ljubljana and Zara into ecoles centrales, is now considered the charter of the University of Ljubljana). They established the first botanic garden at the city’s edge, redesigned the streets and made vaccination of children obligatory. At Karlovac, the headquarters of the Croatian military, a special French-language military school was established in 1811.
The linguist Jernej Kopitar
and the poet Valentin Vodnik
succeeded in instructing the authorities at that time that the language of the inhabitants living in the present-day Slovenian part of the Illyrian Provinces was actually the Slovene language.
Although at the time of the Illyrian Provinces the educational reform did not come to life to its fullest ability, it was nevertheless of considerable social significance. The plan for reorganisation of the school system provided for education in elementary and secondary schools in the provincial Slovene language in Slovenian areas. There were 25 gymnasia
in the Illyrian provinces.
Proclamations were published in the provinces' official journal, , simultaneously in French, Italian, German and Slovene; this elevation of a Slavic language to an official language had a great impact on the development of the modern Slovene language. Between 1811 and 1813, the French author Charles Nodier
worked in Ljubljana as the editor of the journal.
The “French gift” of letting the Slovene language be used at school was one of the most important reforms and it won the sympathy of members of the so-called Slovene National Awakening Movement. The Marmont's school reform introduced, in the fall of 1810, a uniform four-year primary school and an extended network of lower and upper gymnasiums and crafts schools. Valentin Vodnik
, author of the poem "Illyria Arise", wrote numerous school books for primary schools and lower gymnasiums; since textbooks (and teachers) were scarce, these books made the realization of the idea of Slovene language as a teaching language possible.
It could also be established today that the short period of the Illyrian Provinces was the beginning of a period of an enhanced awareness of the principles of liberty, equality and fraternity.
confirmed Austria in the possession of the former Illyrian Provinces. In 1816 they were reconstituted without Dalmatia and Croatia, yet now with all of Carinthia, as a Kingdom of Illyria
, which was formally abolished only in 1849, even though the civil administration of the Croatian districts had already been placed under Hungarian administration in 1822.
The memory of the French and of the Emperor Napoleon is embedded in Slovene traditions, in their folk art and folk songs. The presence of the French on Slovene territories reflects also in the surnames and house names of French origin, in frescoes, bee hive paintings and other paintings depicting French soldiers as well as in rich immovable cultural heritage (roads, bridges, fountains).
In 1929, a great national ceremony was held in Ljubljana
during which a monument was erected to Napoleon and Illyria in the French Revolution Square.
First French Empire
The First French Empire , also known as the Greater French Empire or Napoleonic Empire, was the empire of Napoleon I of France...
on the north and east coasts of the Adriatic Sea
Adriatic Sea
The Adriatic Sea is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkan peninsula, and the system of the Apennine Mountains from that of the Dinaric Alps and adjacent ranges...
between 1809 and 1816. Its capital was established at Laybach (modern-day Ljubljana in Slovenia
Slovenia
Slovenia , officially the Republic of Slovenia , is a country in Central and Southeastern Europe touching the Alps and bordering the Mediterranean. Slovenia borders Italy to the west, Croatia to the south and east, Hungary to the northeast, and Austria to the north, and also has a small portion of...
). The name "Illyrian" was used to refer to ancient Illyrians
Illyrians
The Illyrians were a group of tribes who inhabited part of the western Balkans in antiquity and the south-eastern coasts of the Italian peninsula...
who once lived in the area and constitutes a classicist relabeling of the Dalmatian coast, which was known as Illyria in antiquity.
History
The first occupation by the French armyFrench Army
The French Army, officially the Armée de Terre , is the land-based and largest component of the French Armed Forces.As of 2010, the army employs 123,100 regulars, 18,350 part-time reservists and 7,700 Legionnaires. All soldiers are professionals, following the suspension of conscription, voted in...
- in March of 1797- led by General Bonaparte
Bonaparte
The House of Bonaparte is an imperial and royal European dynasty founded by Napoleon I of France in 1804, a French military leader who rose to notability out of the French Revolution and transformed the French Republic into the First French Empire within five years of his coup d'état...
caused huge civil disturbances. The Slovene
Slovenia
Slovenia , officially the Republic of Slovenia , is a country in Central and Southeastern Europe touching the Alps and bordering the Mediterranean. Slovenia borders Italy to the west, Croatia to the south and east, Hungary to the northeast, and Austria to the north, and also has a small portion of...
territories were mostly occupied by the troops under the command of General Bernadotte
Bernadotte
The House of Bernadotte, the current royal house of Sweden, has reigned since 1818. Between 1818 and 1905, it was also the royal house of the Norway...
who tried to calm the worried and scared population by issuing special public notices which were published also in the Slovene language. During the withdrawal of the French army
French Army
The French Army, officially the Armée de Terre , is the land-based and largest component of the French Armed Forces.As of 2010, the army employs 123,100 regulars, 18,350 part-time reservists and 7,700 Legionnaires. All soldiers are professionals, following the suspension of conscription, voted in...
the commanding general Bonaparte
Bonaparte
The House of Bonaparte is an imperial and royal European dynasty founded by Napoleon I of France in 1804, a French military leader who rose to notability out of the French Revolution and transformed the French Republic into the First French Empire within five years of his coup d'état...
and his escort made a stop in Ljubljana
Ljubljana
Ljubljana is the capital of Slovenia and its largest city. It is the centre of the City Municipality of Ljubljana. It is located in the centre of the country in the Ljubljana Basin, and is a mid-sized city of some 270,000 inhabitants...
on April 28, 1797. In the blitzkrieg war of 1805-1806 the French troops once again occupied parts of the Slovene territory. Supply of the French troops and steep war dues were a huge burden for the population of the occupied territories. The foundation of the provincial brigades in June 1808 and extensive preparations for the new war did not stop Napoleon's army which completely defeated the Austria
Austria
Austria , officially the Republic of Austria , is a landlocked country of roughly 8.4 million people in Central Europe. It is bordered by the Czech Republic and Germany to the north, Slovakia and Hungary to the east, Slovenia and Italy to the south, and Switzerland and Liechtenstein to the...
n troops at the battle of Wagram
Battle of Wagram
The Battle of Wagram was the decisive military engagement of the War of the Fifth Coalition. It took place on the Marchfeld plain, on the north bank of the Danube. An important site of the battle was the village of Deutsch-Wagram, 10 kilometres northeast of Vienna, which would give its name to the...
on July 6, 1809.
The Illyrian Provinces were created by the Treaty of Schönbrunn
Treaty of Schönbrunn
The Treaty of Schönbrunn , sometimes known as the Treaty of Vienna, was signed between France and Austria at the Schönbrunn Palace of Vienna on 14 October 1809. This treaty ended the Fifth Coalition during the Napoleonic Wars...
in 1809 when the Austrian Empire
Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire was a modern era successor empire, which was centered on what is today's Austria and which officially lasted from 1804 to 1867. It was followed by the Empire of Austria-Hungary, whose proclamation was a diplomatic move that elevated Hungary's status within the Austrian Empire...
ceded the territories of western or Upper Carinthia
Duchy of Carinthia
The Duchy of Carinthia was a duchy located in southern Austria and parts of northern Slovenia. It was separated from the Duchy of Bavaria in 976, then the first newly created Imperial State beside the original German stem duchies....
with Lienz
Lienz
Lienz is a medieval town in the Austrian state of Tyrol. It is the administrative centre of the Lienz district, which covers all of East Tyrol. The municipality also includes the cadastral subdivision of Patriasdorf.-Geography:...
in the East Tyrol
East Tyrol
East Tyrol, or East Tirol , is an exclave of the Austrian state of Tyrol, sharing no border with the main North Tyrol part of the state. It corresponds with the administrative district of Lienz....
, Carniola
Carniola
Carniola was a historical region that comprised parts of what is now Slovenia. As part of Austria-Hungary, the region was a crown land officially known as the Duchy of Carniola until 1918. In 1849, the region was subdivided into Upper Carniola, Lower Carniola, and Inner Carniola...
, southwest of the river Sava, Gorizia and Gradisca
Gorizia and Gradisca
The County of Gorizia and Gradisca was a Habsburg county in Central Europe, in what is now a multilingual border area of Italy and Slovenia. It was named for its two major urban centers, Gorizia and Gradisca d'Isonzo.-Province of the Habsburg Empire:...
, and Trieste
Trieste
Trieste is a city and seaport in northeastern Italy. It is situated towards the end of a narrow strip of land lying between the Adriatic Sea and Italy's border with Slovenia, which lies almost immediately south and east of the city...
to the French Empire
First French Empire
The First French Empire , also known as the Greater French Empire or Napoleonic Empire, was the empire of Napoleon I of France...
after the Austrian defeat at the Battle of Wagram
Battle of Wagram
The Battle of Wagram was the decisive military engagement of the War of the Fifth Coalition. It took place on the Marchfeld plain, on the north bank of the Danube. An important site of the battle was the village of Deutsch-Wagram, 10 kilometres northeast of Vienna, which would give its name to the...
. These territories lying north and east of the Adriatic Sea
Adriatic Sea
The Adriatic Sea is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkan peninsula, and the system of the Apennine Mountains from that of the Dinaric Alps and adjacent ranges...
were amalgamated with Dalmatia into the Illyrian Provinces, technically part of France, the capital of which was established at "Laybach", i.e.Ljubljana
Ljubljana
Ljubljana is the capital of Slovenia and its largest city. It is the centre of the City Municipality of Ljubljana. It is located in the centre of the country in the Ljubljana Basin, and is a mid-sized city of some 270,000 inhabitants...
in modern Slovenia
Slovenia
Slovenia , officially the Republic of Slovenia , is a country in Central and Southeastern Europe touching the Alps and bordering the Mediterranean. Slovenia borders Italy to the west, Croatia to the south and east, Hungary to the northeast, and Austria to the north, and also has a small portion of...
. The territory of the Republic of Ragusa
Republic of Ragusa
The Republic of Ragusa or Republic of Dubrovnik was a maritime republic centered on the city of Dubrovnik in Dalmatia , that existed from 1358 to 1808...
, which was annexed to the Napoleonic Kingdom of Italy in 1808, was also integrated into the Illyrian Provinces.
The French administration, headed by a Governor-General, introduced civil law
Civil law (legal system)
Civil law is a legal system inspired by Roman law and whose primary feature is that laws are codified into collections, as compared to common law systems that gives great precedential weight to common law on the principle that it is unfair to treat similar facts differently on different...
(Code civil) across the provinces. August de Marmont was the first to be appointed as the Governor-General of the provinces on 8 October 1809, and held his post until January 1811. On 9 April the same year, Henri-Gratien Bertrand was appointed, who held this post until February 1812, when, on 21 February, he was succeeded by Jean-Andoche Junot
Jean-Andoche Junot
Jean-Andoche Junot, 1st Duke of Abrantès was a French general during the Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars.-Early life:...
. The last Governor-General was Joseph Fouché
Joseph Fouché
Joseph Fouché, 1st Duc d'Otrante was a French statesman and Minister of Police under Napoleon Bonaparte. In English texts his title is often translated as Duke of Otranto.-Youth:Fouché was born in Le Pellerin, a small village near Nantes...
, who was appointed in July 1813 and held his post for only one month.
The British Navy imposed a blockade of the Adriatic Sea, effective since the Treaty of Tilsit (July 1807), which brought merchant shipping to a standstill, a measure most seriously affecting the economy of the Dalmatian port cities. An attempt by joint French and Italian forces to seize the British-held Dalmatian island of Vis
Vis (island)
Vis is the most outerly lying larger Croatian island in the Adriatic Sea, and is part of the Central Dalmatian group of islands, with an area of 90.26 km² and a population of 3,617 . Of all the inhabited Croatian islands, it is the farthest from the coast...
failed on 22 October 1810.
In August 1813, Austria declared war on France. Austrian troops led by General Franz Tomassich invaded the Illyrian Provinces. Croat troops enrolled in the French army switched sides. Zara (now called Zadar
Zadar
Zadar is a city in Croatia on the Adriatic Sea. It is the centre of Zadar county and the wider northern Dalmatian region. Population of the city is 75,082 citizens...
) surrendered to Austrian forces after a 34-day siege on 6 December 1813. At Dubrovnik an insurrection expelled the French and a provisional Ragusan administration was established, hoping for the restoration of the Republic. It was occupied by Austrian troops on 20 September 1813. The Cattaro area (now called Bay of Kotor
Bay of Kotor
The Bay of Kotor in south-western Montenegro is a winding bay on the Adriatic Sea. The bay, sometimes called Europe's southernmost fjord, is in fact a submerged river canyon of the disintegrated Bokelj River which used to run from the high mountain plateaus of Mount Orjen...
) and its environs were occupied in 1813 by Montenegrin
Principality of Montenegro
The Principality of Montenegro was a former realm in Southeastern Europe. It existed from 13 March 1852 to 28 August 1910. It was then proclaimed a kingdom by Knjaz Nikola, who then became king....
forces, which held it until 1814, when the appearance of an Austrian force caused the Prince of Montenegro to turn over the territory to Austrian administration on 11 June. The British withdrew from the occupied Dalmatian islands in July 1815, following the Battle of Waterloo
Battle of Waterloo
The Battle of Waterloo was fought on Sunday 18 June 1815 near Waterloo in present-day Belgium, then part of the United Kingdom of the Netherlands...
.
Administrative divisions
The area initially consisted of seven provinces: Upper CarinthiaDuchy of Carinthia
The Duchy of Carinthia was a duchy located in southern Austria and parts of northern Slovenia. It was separated from the Duchy of Bavaria in 976, then the first newly created Imperial State beside the original German stem duchies....
(capital Lienz
Lienz
Lienz is a medieval town in the Austrian state of Tyrol. It is the administrative centre of the Lienz district, which covers all of East Tyrol. The municipality also includes the cadastral subdivision of Patriasdorf.-Geography:...
), Istria
Istria
Istria , formerly Histria , is the largest peninsula in the Adriatic Sea. The peninsula is located at the head of the Adriatic between the Gulf of Trieste and the Bay of Kvarner...
(Trieste), Carniola
Carniola
Carniola was a historical region that comprised parts of what is now Slovenia. As part of Austria-Hungary, the region was a crown land officially known as the Duchy of Carniola until 1918. In 1849, the region was subdivided into Upper Carniola, Lower Carniola, and Inner Carniola...
(Ljubljana), Civil Croatia
Croatia
Croatia , officially the Republic of Croatia , is a unitary democratic parliamentary republic in Europe at the crossroads of the Mitteleuropa, the Balkans, and the Mediterranean. Its capital and largest city is Zagreb. The country is divided into 20 counties and the city of Zagreb. Croatia covers ...
(Karlovac
Karlovac
Karlovac is a city and municipality in central Croatia. The city proper has a population of 49,082, while the municipality has a population of 59,395 inhabitants .Karlovac is the administrative centre of Karlovac County...
), Military Croatia (Senj
Senj
Senj , German Zengg, Hungarian Zeng and Italian Segna) is the oldest town on the upper Adriatic, and it was founded in the time before the Romans some 3000 years ago on the hill Kuk. It was the center of the Illyrian tribe Iapydes. The current settlement is situated at the foot of the slopes Mala...
), Dalmatia
Dalmatia
Dalmatia is a historical region on the eastern coast of the Adriatic Sea. It stretches from the island of Rab in the northwest to the Bay of Kotor in the southeast. The hinterland, the Dalmatian Zagora, ranges from fifty kilometers in width in the north to just a few kilometers in the south....
(Zara
Zadar
Zadar is a city in Croatia on the Adriatic Sea. It is the centre of Zadar county and the wider northern Dalmatian region. Population of the city is 75,082 citizens...
), and the Ragusa
Dubrovnik
Dubrovnik is a Croatian city on the Adriatic Sea coast, positioned at the terminal end of the Isthmus of Dubrovnik. It is one of the most prominent tourist destinations on the Adriatic, a seaport and the centre of Dubrovnik-Neretva county. Its total population is 42,641...
and Cattaro
Kotor
Kotor is a coastal city in Montenegro. It is located in a secluded part of the Gulf of Kotor. The city has a population of 13,510 and is the administrative center of the municipality....
province (Dubrovnik
Dubrovnik
Dubrovnik is a Croatian city on the Adriatic Sea coast, positioned at the terminal end of the Isthmus of Dubrovnik. It is one of the most prominent tourist destinations on the Adriatic, a seaport and the centre of Dubrovnik-Neretva county. Its total population is 42,641...
).
In 1811 the Illyrian provinces saw an administrative reorganization. The seat of the Governor General was Ljubljana
Ljubljana
Ljubljana is the capital of Slovenia and its largest city. It is the centre of the City Municipality of Ljubljana. It is located in the centre of the country in the Ljubljana Basin, and is a mid-sized city of some 270,000 inhabitants...
; the country was initially divided in 4 intendancies (Ljubljana, Karlovac, Trieste, Zara) and 10 sub-intendancies. Later that year, the number of intendancies was extended to eight, with Villach, Gorizia
Gorizia
Gorizia is a town and comune in northeastern Italy, in the autonomous region of Friuli Venezia Giulia. It is located at the foot of the Julian Alps, bordering Slovenia. It is the capital of the Province of Gorizia, and it is a local center of tourism, industry, and commerce. Since 1947, a twin...
, Fiume
Rijeka
Rijeka is the principal seaport and the third largest city in Croatia . It is located on Kvarner Bay, an inlet of the Adriatic Sea and has a population of 128,735 inhabitants...
and Ragusa
Dubrovnik
Dubrovnik is a Croatian city on the Adriatic Sea coast, positioned at the terminal end of the Isthmus of Dubrovnik. It is one of the most prominent tourist destinations on the Adriatic, a seaport and the centre of Dubrovnik-Neretva county. Its total population is 42,641...
being elevated to intendancy rank.
Two Chambers of Commerce
Chamber of commerce
A chamber of commerce is a form of business network, e.g., a local organization of businesses whose goal is to further the interests of businesses. Business owners in towns and cities form these local societies to advocate on behalf of the business community...
were established, at Trieste and at Ragusa. The ecclesiastical administration was reorganized in accordance with the new political borders; two archdioceses were established with seats at Ljubljana and Zara, with suffragan dioceses at Gorizia, Capodistria, Šibenik
Šibenik
Šibenik is a historic town in Croatia, with population of 51,553 . It is located in central Dalmatia where the river Krka flows into the Adriatic Sea...
, Spalato
Split (city)
Split is a Mediterranean city on the eastern shores of the Adriatic Sea, centered around the ancient Roman Palace of the Emperor Diocletian and its wide port bay. With a population of 178,192 citizens, and a metropolitan area numbering up to 467,899, Split is by far the largest Dalmatian city and...
and Ragusa (1811).
Population
The population (1811) was given at 460,116 for the intendancy of Ljubljana, 381,000 for the intendancy of Karlovac, 357,857 for the intendancy of Trieste and 305,285 for the intendancy of Zara, in total 1,504,258 for all of Illyria. A French decree emancipated the Jews; in effect the decree abolished a HabsburgHabsburg
The House of Habsburg , also found as Hapsburg, and also known as House of Austria is one of the most important royal houses of Europe and is best known for being an origin of all of the formally elected Holy Roman Emperors between 1438 and 1740, as well as rulers of the Austrian Empire and...
regulation which had forbidden Jews to settle within Carniola.
Social and political arrangements
Despite the fact that not all French laws applied to the territory of the Illyrian Provinces, Illyrian offices were accountable to ministries in Paris and to the Higher Court of Paris. Inhabitants of the Illyrian Provinces had Illyrian nationality. Initially the official languages were French, Italian and German, but in 1811 Slovenian was added for the first time in History.Among the main changes the French empire brought were the overhaul of administration, the changing of the schooling system – creating universities and making Slovene a learning language – and the usage of the Napoleonic code (the French Code Civil) and the Penal Code.

French Revolution
The French Revolution , sometimes distinguished as the 'Great French Revolution' , was a period of radical social and political upheaval in France and Europe. The absolute monarchy that had ruled France for centuries collapsed in three years...
and with contemporary bourgeois society. They introduced equality before the law, compulsory military service and a uniform tax system, and also abolished certain tax privileges, introduced modern administration, separated powers between the state and the church (the introduction of the civil wedding, keeping civil registration of births etc.), and nationalized the judiciary. The occupants made all the citizens theoretically equal under the law for the first time.
The French also founded a university ("École central") in 1810 (which was disbanded in 1813, when Austria regained control, but whose Basic Decree of 4 July 1810, which ordered the reorganization of the former Austrian lycees in Ljubljana and Zara into ecoles centrales, is now considered the charter of the University of Ljubljana). They established the first botanic garden at the city’s edge, redesigned the streets and made vaccination of children obligatory. At Karlovac, the headquarters of the Croatian military, a special French-language military school was established in 1811.
The linguist Jernej Kopitar
Jernej Kopitar
Jernej Bartol Kopitar was a Slovene linguist and philologist working in Vienna. He also worked as the Imperial censor for Slovene literature in Vienna...
and the poet Valentin Vodnik
Valentin Vodnik
Valentin Vodnik was a Slovene priest, journalist and poet from the late Enlightenment period.-Life and work:He was born in Šiška, now a suburb of Ljubljana, then part of the Habsburg Monarchy...
succeeded in instructing the authorities at that time that the language of the inhabitants living in the present-day Slovenian part of the Illyrian Provinces was actually the Slovene language.
Although at the time of the Illyrian Provinces the educational reform did not come to life to its fullest ability, it was nevertheless of considerable social significance. The plan for reorganisation of the school system provided for education in elementary and secondary schools in the provincial Slovene language in Slovenian areas. There were 25 gymnasia
Gymnasium (school)
A gymnasium is a type of school providing secondary education in some parts of Europe, comparable to English grammar schools or sixth form colleges and U.S. college preparatory high schools. The word γυμνάσιον was used in Ancient Greece, meaning a locality for both physical and intellectual...
in the Illyrian provinces.
Proclamations were published in the provinces' official journal, , simultaneously in French, Italian, German and Slovene; this elevation of a Slavic language to an official language had a great impact on the development of the modern Slovene language. Between 1811 and 1813, the French author Charles Nodier
Charles Nodier
Jean Charles Emmanuel Nodier , was a French author who introduced a younger generation of Romanticists to the conte fantastique, gothic literature, vampire tales, and the importance of dreams as part of literary creation, and whose career as a librarian is often underestimated by literary...
worked in Ljubljana as the editor of the journal.
The “French gift” of letting the Slovene language be used at school was one of the most important reforms and it won the sympathy of members of the so-called Slovene National Awakening Movement. The Marmont's school reform introduced, in the fall of 1810, a uniform four-year primary school and an extended network of lower and upper gymnasiums and crafts schools. Valentin Vodnik
Valentin Vodnik
Valentin Vodnik was a Slovene priest, journalist and poet from the late Enlightenment period.-Life and work:He was born in Šiška, now a suburb of Ljubljana, then part of the Habsburg Monarchy...
, author of the poem "Illyria Arise", wrote numerous school books for primary schools and lower gymnasiums; since textbooks (and teachers) were scarce, these books made the realization of the idea of Slovene language as a teaching language possible.
Significance
Although French rule in the Illyrian Provinces was short-lived and did not enjoy the same level of popularity among people, it significantly contributed to greater national self-confidence and awareness of freedoms, especially in the Slovene lands. The opinion of Napoleon's rule and the Illyrian Provinces changed significantly at the end of the 19th century and the beginning of the 20th century, when liberal Slovene intellectuals began to praise the French for liberation from Austrian rule.It could also be established today that the short period of the Illyrian Provinces was the beginning of a period of an enhanced awareness of the principles of liberty, equality and fraternity.
Legacy
The Congress of ViennaCongress of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna was a conference of ambassadors of European states chaired by Klemens Wenzel von Metternich, and held in Vienna from September, 1814 to June, 1815. The objective of the Congress was to settle the many issues arising from the French Revolutionary Wars, the Napoleonic Wars,...
confirmed Austria in the possession of the former Illyrian Provinces. In 1816 they were reconstituted without Dalmatia and Croatia, yet now with all of Carinthia, as a Kingdom of Illyria
Kingdom of Illyria
The Kingdom of Illyria was an administrative unit of the Austrian Empire from 1816 to 1849. Its administrative centre was Ljubljana and it included the western and central part of present-day Slovenia, the present Austrian state of Carinthia, as well as some territories in north-western Croatia ...
, which was formally abolished only in 1849, even though the civil administration of the Croatian districts had already been placed under Hungarian administration in 1822.
The memory of the French and of the Emperor Napoleon is embedded in Slovene traditions, in their folk art and folk songs. The presence of the French on Slovene territories reflects also in the surnames and house names of French origin, in frescoes, bee hive paintings and other paintings depicting French soldiers as well as in rich immovable cultural heritage (roads, bridges, fountains).
In 1929, a great national ceremony was held in Ljubljana
Ljubljana
Ljubljana is the capital of Slovenia and its largest city. It is the centre of the City Municipality of Ljubljana. It is located in the centre of the country in the Ljubljana Basin, and is a mid-sized city of some 270,000 inhabitants...
during which a monument was erected to Napoleon and Illyria in the French Revolution Square.
List of Governors-General
- Auguste de Marmont (8 October 1809 - January 1811)
- Henri Gatien Bertrand (9 April 1811 - 21 February 1812)
- Jean-Andoche JunotJean-Andoche JunotJean-Andoche Junot, 1st Duke of Abrantès was a French general during the Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars.-Early life:...
(21 February 1812 - July 1813) - Joseph FouchéJoseph FouchéJoseph Fouché, 1st Duc d'Otrante was a French statesman and Minister of Police under Napoleon Bonaparte. In English texts his title is often translated as Duke of Otranto.-Youth:Fouché was born in Le Pellerin, a small village near Nantes...
(July 1813 - August 1813)
See also
- Septinsular RepublicSeptinsular RepublicThe Septinsular Republic was an island republic that existed from 1800 to 1807 under nominal Ottoman sovereignty in the Ionian Islands. It was the first time Greeks had been granted even limited self-government since the fall of the last remnants of the Byzantine Empire to the Ottomans in the...
- List of French possessions and colonies
- Napoleonic Kingdom of Italy

