
Zadar
Encyclopedia
Zadar is a city in Croatia
on the Adriatic Sea
. It is the centre of Zadar county
and the wider northern Dalmatia
n region. Population of the city is 75,082 citizens (2011). Zadar is a historical center of Dalmatia as well as the seat of the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Zadar
.
, Iadera and Iader, the much older roots of the settlement's names were hidden, the names being most probably related to a hydrographical term. It was coined by an ancient Mediterranean people and their Pre-Indo-European language. They transmitted it to later settlers, the Liburnians
. The name of the Liburnian settlement was first mentioned by a Greek
inscription from Pharos (Stari grad
) on the island of Hvar
in 384 BC, where the citizens of Zadar were noted as (Iadasinoi). According to the Greek source Periplus of Pseudo-Scylax
the city was (Idassa), probably a vulgar Greek form of the original Liburnian name.
During Antiquity
the name was often recorded in sources in Latin in two forms: Iader in the inscriptions and in the writings of classic writers, Iadera predominantly among the late Antiquity writers, while usual ethnonyms were Iadestines and Iadertines. The accent was on the first syllable in both Iader and Iadera forms, which influenced the early-Medieval Dalmatian language
forms Jadra, Jadera and Jadertina, where the accent kept its original place.
In the Dalmatian language, Jadra (Jadera) was pronounced Zadra (Zadera), due to the phonetic transformation of Ja- to Za-. That early change was also reflected in the Croatian
name Zadar (recorded as Zader in the 12th century ), developed from Zadъrъ by vocalizations of the semi-vowel and a shift to male gender. An ethnonym graphic Jaderani from the legend of St. Krševan in 9th century, was identical to the initial old-Slavic
form Zadъrane, or Renaissance
Croatian Zadrani.
The Dalmatian names Jadra, Jadera were transferred to other languages; in Venetian language
Jatara (hyper urbanism in 9th century) and Zara, Tuscan
Giara, Latin Diadora (Constantine VII
in DAI
, 10th century), Old French
Jadres (Geoffroy de Villehardouinin in the chronicles of the Fourth Crusade
in 1202), Arabic
Jādhara (جاذَرة) & Jādara (جادَرة) (Al-Idrisi, 12th century), Iadora (Guido, 12th century), Spanish
Jazara, Jara, Sarra (14th century) and the others.
Jadera became Zara when it fell under the authority of the Republic of Venice
in the 15th century.
Zara was later used by the Austrian Empire
in the 19th century, but it was provisionally changed to Zadar/Zara from 1910 to 1920; from 1920 to 1947 the city became part of Italy
as Zara, and finally was named Zadar later on.
and Pašman
, from which it is separated by the narrow Zadar Strait. The promontory on which the old city stands used to be separated from the mainland by a deep moat which has since become landfilled. The harbor, to the north-east of the town, is safe and spacious.
, with very mild, humid winters and very warm, dry summers.
Average annual rainfall is in excess of 917 mm (36.1 in). July and August are the hottest months, with an average high temperature around 28 °C (82 °F). Sometimes in July and August temperatures reach over 35 °C (95 °F) and can consistently reach over 30 °C (86 °F) during the summer months. Temperatures below 0 °C (32 °F) are rare, and are not maintained for more than a few days. January is the coldest month, with an average temperature around 6.7 °C (44 °F) and a record low of -9.1 °C. October, November and December are the wettest months, with a total precipitation of about 100 mm (3.94 in). July is the driest month, with a total precipitation of around 35 mm (1.38 in). Winter is the wettest season, however it can rain in Zadar at any time of the year. Snow is exceedingly rare, but it may fall in December, January, February and much more rarely in March. Also the sea temperature is from 10 °C (50 °F) in February to 24 °C (75 °F) in August, but is possible to swim from May until October.
, while numerous settlements have been dated as early as the Neolithic
. Before the Illyrians
, the area was inhabited by an ancient Mediterranean people of a pre-Indo-European culture. They assimilated with the Indo-Europeans
who settled between the 4th and 2nd millennium BC into a new ethnical unity, that of the Liburnians
. Zadar was a Liburnian settlement, laid out in the 9th century BC, built on a small stone islet and embankments where the old city stands and tied to the mainland by the overflown narrow isthmus, which created a natural port in its northern strait.
ns, Etruscans
, Ancient Greeks
and other Mediterranean peoples. Its population at that time is estimated at 2,000. From 9th to 6th century there was certain koine - cultural unity in the Adriatic Sea, with the general Liburninan seal, whose naval supremacy meant both political and economical authority through several centuries. Due to its geographical position, Zadar developed into a main seat of the Liburnian thalassocracy and took a leading role in the Liburnian tetradekapolis, an organization of 14 communes.
The people of Zadar, the Iadasinoi, were first mentioned in 384 BC as the allies of the natives of Hvar
and the leaders of an eastern Adriatic coast coalition in the fight against the Greek colonizers. An expedition of 10,000 men in 300 ships sailed out from Zadar and laid siege to the Greek colony Pharos
in the island of Hvar, but the Syracusan fleet of Dionysus was alerted and attacked the siege fleet. The naval victory went to the Greeks which allowed them relatively safer further colonization in the southern Adriatic
.
The archaeological remains have shown that the main centres of Liburnian territorial units or municipalities were already urbanized in the last centuries BC; before the Roman conquest, Zadar held a territory of more than 600 km2 in the 2nd century BC.
In the middle of the 2nd century BC, the Romans
began to gradually invade the region. Although being first Roman enemies in the Adriatic Sea, the Liburnians, mostly stood aside in more than 230 years of Roman wars with the Illyrians, to protect their naval and trade connections in the sea. In 59 BC Illyricum was assigned as a provincia (zone of responsibility) to Julius Caesar
and Liburnian Iadera became a Roman municipium
.
The Liburnian naval force was dragged into the Roman civil war between Julius Caesar
and Pompey
in 49 BC, partially by force, partially because of the local interests of the participants, the Liburnian cities. Caesar was supported by the urban Liburnian centres, like Iader (Zadar), Aenona (Nin
) and Curicum (Krk
), while the city of Issa (Vis
) and the rest of the Liburnians gave their support to Pompey. In 49 BC near the island of Krk, the "Navy of Zadar", equipped by the fleets of a few Liburnian cities and supported by some Roman ships, lost an important naval battle against Pompey supporting the "Liburnian navy". The civil war was prolonged until the end of 48 BC, when Caesar rewarded his supporters in Liburnian Iader and Dalmatian
Salona
, by giving the status of the Roman colonies
to their communities. Thus the city was granted the title colonia Iulia Iader, after its founder, and in the next period some of the Roman colonists (mostly legionary
veterans) settled there.
The real establishment of the Roman province of Illyricum occurred not earlier than 33 BC and Octavian
’s military campaign in Illyria and Liburnia, when the Liburnians finally lost their naval independence and their galleys and sailors were incorporated into the Roman naval fleets.
 From the early days of Roman rule, Zadar gained its Roman urban character and developed into one of the most flourishing centres on the eastern Adriatic coast, a state of affairs which lasted for several hundred years. The town was organised according to the typical Roman street system with a rectangular street plan, a forum, thermae, a sewage and water supply system that came from lake Vrana, by way of a 40 km long aqueduct. It did not play a significant role in the Roman administration of Dalmatia, although the archaeological finds tell us about a significant growth of economy and culture.
From the early days of Roman rule, Zadar gained its Roman urban character and developed into one of the most flourishing centres on the eastern Adriatic coast, a state of affairs which lasted for several hundred years. The town was organised according to the typical Roman street system with a rectangular street plan, a forum, thermae, a sewage and water supply system that came from lake Vrana, by way of a 40 km long aqueduct. It did not play a significant role in the Roman administration of Dalmatia, although the archaeological finds tell us about a significant growth of economy and culture.
The new religion Christianity
did not bypass the Roman province of Dalmatia
. Already by the end of the 3rd century Zadar had its own bishop and founding of the Zadar Christian community took place; a new religious centre was built north of the forum together with a basilica and a baptistery, as well as other ecclesiastical buildings. According to some estimates, in the 4th century it had probably around ten thousand citizens, including the population from its Ager
, the nearby islands and hinterland, an admixture of the indigenous Liburnians and Roman colonists.
and the Barbarian invasions, Zadar underwent a stagnation. In 441 and 447 Dalmatia was ravaged by the Huns
, after the fall of the Western Roman Empire, in 481 Dalmatia became part of the Ostrogothic kingdom
, which, besides Italy, already included the more northerly parts of Illyricum
, i.e. Pannonia
and Noricum
.
In the 5th century, under the rule of the Ostrogothic Kingdom
, Zadar became poor with many civic buildings turning into ruins due to its advanced age. About the same time (6th century) it was hit by an earthquake, which destroyed entire complexes of monumental Roman architecture, whose parts would later serve as material for building houses. This caused a loss of population and created demographic changes in the city, then gradually repopulated by the inhabitants from its hinterland. However, during six decades of Gothic rule, the Goths saved those old Roman Municipal institutions that were still in function, while religious life in Dalmatia even intensified in the last years, so that there was a need for the foundation of additional bishoprics.
In 536 the Byzantine emperor Justinian the Great started a military campaign to reconquer the territories of the former Western Empire (see Gothic War
); and in 553 Zadar passed to the Byzantine Empire
. In 568 Dalmatia was devastated by an Avar
invasion; although further waves of attacks by Avar and Slav tribes kept up the pressure, it was the only city which survived due to its protective belt of inland plains. The Dalmatian capital Salona
was captured and destroyed in the 40s of the 7th century, so Zadar became the new seat of the Byzantine archonty of Dalmatia
, territorially reduced to a few coastal cities with their agers and municipal lands at the coast and the islands nearby. The prior of Zadar had jurisdiction over all Byzantine Dalmatia, so Zadar enjoyed metropolitan status at the eastern Adriatic coast. At this time rebuilding began to take place in the city.
 At the beginning of the 9th century the Zadar bishop Donatus and the city duke Paul mediated in the dispute between the Holy Roman empire
At the beginning of the 9th century the Zadar bishop Donatus and the city duke Paul mediated in the dispute between the Holy Roman empire
under Pepin and the Byzantine Empire. The Franks
held Zadar for a short time, but the city was returned to Byzantium by a decision of the 812 Treaty of Aachen.
Zadar's economy revolved around sea, fishing and sea trade in the first centuries of the Middle Ages. Thanks to saved Antique ager, adjusted municipal structure and a new strategic position, it became the most important city between the Kvarner islands and Kaštela
Bay. Byzantine Dalmatia wasn't territorially unified, but an alliance of city municipalities headed by Zadar, and the large degree of city autonomy allowed the development of Dalmatian cities as free communes. Forced to turn their attention seawards, the inhabitants of Zadar focused on shipping, and the city became a naval power to rival Venice
. The citizens were Dalmatian language
speakers, but from the 7th century Croatian language
started to spread in a region, becoming predominant in the inland and the islands to the end of the 9th century.
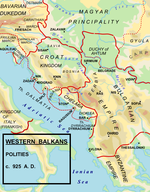 The Mediterranean and Adriatic cities developed significantly during a period of peace from the last decades of the 9th to the middle of the 10th century. Especially favourable conditions for navigation in the Adriatic Sea occurred since the Saracen
The Mediterranean and Adriatic cities developed significantly during a period of peace from the last decades of the 9th to the middle of the 10th century. Especially favourable conditions for navigation in the Adriatic Sea occurred since the Saracen
raids had finished. Also the adjustment of relations with the Croats
enabled Zadar merchants to trade with its rich agriculture hinterland where the Kingdom of Croatia
had formed, and trade and political links with Zadar began to develop. Croatian settlers began to arrive, becoming commonplace by the 10th century, occupying all city classes, as well as important posts, like those of prior, judge, priest and others. In 925, Tomislav, the Duke of Croatian Dalmatia, united Croatian Dalmatia
and Pannonia establishing the Croatian Kingdom
. He was also granted the position of protector of Dalmatia (the cities) by the Byzantine Emperor. He thus politically united the Dalmatian cities with their hinterland.
At the time of the Zadar medieval development, the city became a threat to Venice's ambitions, because of its strategic position at the centre of the eastern Adriatic coast.
In 998 Zadar sought Venetian protection against the Neretvian pirates. The Venetians were quick to fully exploit this opportunity: in 998 a fleet commanded by Doge
Pietro Orseolo II, after having defeated pirates, landed in Korčula
and Lastovo
. Dalmatia was taken by surprise and offered little serious resistance. Trogir
was the exception and was subjected to Venetian rule only after a bloody struggle, whereas the Republic of Dubrovnik was forced to pay tribute. Tribute previously paid by Zadar to Croatian kings, was redirected to Venice, a state of affairs which lasted for several years.
 Zadar citizens started to work for the full independence of Zadar and from the 30's of the 11th century the city was just formally a vassal of the Byzantine Empire. The head of this movement was the mightiest Zadar patrician family - the Madi. After negotiations with Byzantium, Zadar was attached to the Croatian state led by king Petar Krešimir IV
Zadar citizens started to work for the full independence of Zadar and from the 30's of the 11th century the city was just formally a vassal of the Byzantine Empire. The head of this movement was the mightiest Zadar patrician family - the Madi. After negotiations with Byzantium, Zadar was attached to the Croatian state led by king Petar Krešimir IV
in 1069. Later, after the death of king Dmitar Zvonimir
in 1089 and ensuing dynastic run-ins, in 1105 Zadar accepted the rule of the first Croato-Hungarian king Coloman.
In the meantime Venice developed into a true trading force in the Adriatic and started attacks on
Zadar. The city was repeatedly invaded by Venice between 1111 and 1154 and then once more between 1160 and 1183, when it finally rebelled, appealing to the Pope and to the Croato-Hungarian throne for protection.
Zadar was especially devastated in 1202 after the Venetian Doge Enrico Dandolo
used the Crusaders, on their Fourth Crusade
to Palestine
, to lay siege to the city. The crusaders
were obliged to pay Venice for sea transport to Egypt
. As they were not able to produce enough money, the Venetians used them to initiate the Siege of Zadar, when the city was ransacked, demolished and robbed. The king of Croatia and Hungary, Emeric of Hungary
, condemned the crusade, because of an argument about the possible heresy committed by God's army in attacking a Christian city. Nonetheless, Zadar was devastated and captured, with the population escaped into the surrounding countryside. Pope Innocent III
excommunicated the Venetians and crusaders involved in the siege.
Two years later (1204), under the leadership of the Croatian nobleman Domald from Šibenik
, most of the refugees returned and liberated the city from what remained of the crusader force. In 1204 Domald was comes (duke) of Zadar, but the following year (1205) Venetian authority was re-established and a peace agreement signed with hard conditions for the citizens. The only profit which the Communal Council of Zadar derived from this was one third of the city's harbour taxes, probably insufficient even for the most indispensable communal needs.
.jpg) This did not break the spirit of the city, however. Its commerce was suffering due to a lack of autonomy under Venice, while it enjoyed considerable autonomy under the much more feudal Croatian-Hungarian Kingdom. A number of insurrections followed (1242–1243, 1320s, 1345–1346) which finally resulted in Zadar coming back under the crown of the Croatian-Hungarian king Louis I under the Treaty of Zadar
This did not break the spirit of the city, however. Its commerce was suffering due to a lack of autonomy under Venice, while it enjoyed considerable autonomy under the much more feudal Croatian-Hungarian Kingdom. A number of insurrections followed (1242–1243, 1320s, 1345–1346) which finally resulted in Zadar coming back under the crown of the Croatian-Hungarian king Louis I under the Treaty of Zadar
, in 1358. After the War of Chioggia
between Genoa and Venice, Chioggia
concluded on 14 March 1381 an alliance with Zadar and Trogir
against Venice, and finally Chioggia became better protected by Venice in 1412, because Šibenik
became in 1412 the seat of the main customs
office and the seat of the salt consumers office with a monopoly
on the salt trade in Chioggia and on the whole Adriatic Sea
. After the death of Louis, Zadar recognized the rule of king Sigismund
, and after him, that of Ladislaus of Naples. During his reign Croatia-Hungary was enveloped in a bloody civil war. In 1409, Venice, seeing that Ladislaus was about to be defeated, and eager to exploit the situation despite its relative military weakness, offered to buy his "rights" on Dalmatia for a mere 100,000 ducats. Knowing he had lost the region in any case, Ladislaus accepted. Zadar was, thus sold back to the Venetians for a paltry sum.
The population of Zadar during the Medieval period was predominantly Croatian, according to numerous archival documents, and the Croatian language was used in liturgy, as shown by the writings of cardinal Boson, who followed Pope Alexander III
en route to Venice in 1177. When the papal ships took shelter in the harbour of Zadar, the inhabitants greeted the Pope by singing lauds and canticles in Croatian.
Even though interspersed by sieges and destruction, the time between 11th and 14th century was the golden age of Zadar. Thanks to its political and trading achievements, and also to its skilled seamen, Zadar played an important role among the cities on the east coast of the Adriatic. This affected its appearance and culture: many churches, rich monasteries and palaces for powerful families were built, together with the Chest of Saint Simeon
. One of the best examples of the culture and prosperity of Zadar at that time was the founding of the University of Zadar
, built in 1396 by the Dominican Order
(the oldest university in present day Croatia).
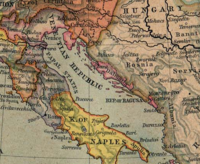 After the death of Louis I, Zadar came under the rule of Sigmund of Luxembourg and later Ladislaus of Naples, who, witnessing his loss of influence in Dalmatia, sold Zadar and his dynasty's rights to Dalmatia to Venice for 100,000 ducats on July 31, 1409. Venice therefore obtained control over Zadar without a fight, but was confronted by the resistance and tensions of important Zadar families. These attempts were met with persecution and confiscation. Zadar remained the administrative seat of Dalmatia, but this time under the rule of Venice, which expanded over the whole Dalmatia, barring the Republic of Dubrovnik. The Venetians restrained the political and economical autonomy of Zadar, which, regardless, remained a prosperous city. During that time Juraj Dalmatinac, one of the best known renaissance men, famous for his work on the Cathedral of Šibenik, was born in Zadar. Other important people followed, such as the Lucijan and Franjo Vranjanin, best known in Italy
After the death of Louis I, Zadar came under the rule of Sigmund of Luxembourg and later Ladislaus of Naples, who, witnessing his loss of influence in Dalmatia, sold Zadar and his dynasty's rights to Dalmatia to Venice for 100,000 ducats on July 31, 1409. Venice therefore obtained control over Zadar without a fight, but was confronted by the resistance and tensions of important Zadar families. These attempts were met with persecution and confiscation. Zadar remained the administrative seat of Dalmatia, but this time under the rule of Venice, which expanded over the whole Dalmatia, barring the Republic of Dubrovnik. The Venetians restrained the political and economical autonomy of Zadar, which, regardless, remained a prosperous city. During that time Juraj Dalmatinac, one of the best known renaissance men, famous for his work on the Cathedral of Šibenik, was born in Zadar. Other important people followed, such as the Lucijan and Franjo Vranjanin, best known in Italy
for their sculptures and buildings.
 The 16th and 17th centuries were noted in Zadar for Ottoman attacks. Ottomans captured the continental part of Zadar at the beginning of the 16th century and the city itself was all the time in the range of Turkish artillery. Due to that threat, the construction of a new system of castles and walls began. These defense systems changed the way the city looked. To make place for the pentagon castles many houses and churches were taken down, along with an entire suburb: Varoš of St. Martin. After the 40-year-long construction Zadar became the biggest fortified city in Dalmatia, empowered by a system of castles, bastions and canals filled with seawater. The city was supplied by the water from public city cisterns. During the complete makeover of Zadar, many new civic buildings were built, such as the City Lodge and City Guard on the Gospodski Square, several army barracks, but also some large new palaces.
The 16th and 17th centuries were noted in Zadar for Ottoman attacks. Ottomans captured the continental part of Zadar at the beginning of the 16th century and the city itself was all the time in the range of Turkish artillery. Due to that threat, the construction of a new system of castles and walls began. These defense systems changed the way the city looked. To make place for the pentagon castles many houses and churches were taken down, along with an entire suburb: Varoš of St. Martin. After the 40-year-long construction Zadar became the biggest fortified city in Dalmatia, empowered by a system of castles, bastions and canals filled with seawater. The city was supplied by the water from public city cisterns. During the complete makeover of Zadar, many new civic buildings were built, such as the City Lodge and City Guard on the Gospodski Square, several army barracks, but also some large new palaces.
In contrast to the insecurity and Ottoman sieges and destruction, an important culture evolved midst the city walls. During the 16th and the 17th century the activity of the Croatian writers and poets became prolific (Jerolim Vidolić, Petar Zoranić
, Brne Karnarutić
, Juraj Baraković
, Šime Budinić). Also noteworthy is the painter Andrija Medulić (c. 1510/1515–1563), who, when in Venice, signed his name as "Andrea Schiavone."
During the continuous Ottoman danger the population stagnated by a significant degree along with the economy. During the 16th and 17th century several large-scale epidemics of bubonic plague erupted in the city. After more than 150 years of Turkish threat Zadar was not only scarce in population, but also in material wealth. Venice sent new colonists and, under the firm hand of archbishop Vicko Zmajević, the Arbanasi (Catholic Albanian refugees) settled in the city, forming a new suburb. Despite the shortage of money, the Teatro Nobile (Theater for Nobility) was built in 1783. It functioned for over 100 years.
, Zadar come under the Austria
n crown and once again became united with the rest of Croatia. In 1806 it was briefly given to the Napoleonic Kingdom of Italy
, until in 1809 it was added to the French Illyrian Provinces
. In 1813, all of Dalmatia was reconquered and brought back under the control of the Austrian Empire. During this time, it maintained its position as the capital of Dalmatia.
During the Napoleonic era, the first Dalmatian newspaper, Kraglski Dalmatin - Il Regio Dalmata ("The Royal Dalmatian"), was printed in the city.
After 1815 Dalmatia (including Dubrovnik) came under the Austrian
crown. After 1848, Italian and Slavic nationalism became accentuated and the city became divided between the Croats and the Italians, both of whom founded their respective political parties. There are conflicting sources for both sides claiming to have formed the majority in this period; in general the era saw Slavs grow more than Italians throughout Dalmatia, fostering a distinct national spirit.
(12 November 1920) gave Zadar with other local territory to Italy. The Zadar enclave, a total of 104 km², included the city of Zadar, the municipalities of Bokanjac, Arbanasi, Crno, part of Diklo (a total of 51 km2. of territory and 17,065 inhabitants) and the islands of Lastovo
and Palagruža
(53 km², 1,710 inhabitants). The territory was organized into an Italian province.
, with limited Italian assistance, invaded the Kingdom of Yugoslavia
on April 6, 1941. Zadar held a force of 9,000 that after limited fighting reached Šibenik and Split on April 15, a mere 2 days before surrender, with civilians having previously been evacuated to Ancona
and Pula
. Occupying Mostar
and Dubrovnik, on April 17 they met invading troops that had started out from Italian-occupied Albania
. On April 17 the Yugoslav government surrendered, faced with the Wehrmacht
's overwhelming superiority.
Within a few weeks, Benito Mussolini
required the newly formed Nazi puppet-state, the so-called Independent State of Croatia
(NDH) to hand over almost all of Dalmatia (including Split) to fascist Italy under the Treaty of Rome.
The city became the centre of a new Italian territorial entity, called Governorship of Dalmatia
, including the provinces of Zadar, Split and Kotor.
Under fascist reign the Slavic population was subjected to a policy of forced assimilation. This created immense resentment among the Yugoslav people and the Yugoslav Partisan movement
(which was already successfully spreading in the rest of Yugoslavia) did not take root here since more than 70% of population of Zara was Italian.
After Mussolini was removed from power on 25 July 1943 and arrested, the government of Pietro Badoglio
signed an armistice
with the Allies
on 3 September 1943, which was made public only on 8 September 1943, and the Italian army collapsed. However, just four days later on 12 September 1943, "Il Duce
", was rescued by a German military raid from his secret prison on the Gran Sasso mountain, and formed the Nazi-puppet Italian Social Republic
in the north of the Country. The NDH proclaimed the Treaty of Rome to be void and occupied Dalmatia with German support. The Germans entered Zadar first, and on September 10 the German 114th Jäger Division took over. This avoided a temporary liberation by Partisans, as was the case in Split and Šibenik where several Italian fascist government officials were killed by an angry crowd.
The city was prevented from joining the NDH on the grounds that Zadar itself was not subject to the conditions of the Treaty of Rome. Despite this, the NDH's leader Ante Pavelić
designated Zadar as the capital of the Sidraga-Ravni Kotari County, although its administrator was prevented from entering the city. Zadar remained under the local administration of the Italian Social Republic. Zadar was bombed by the Allies, with serious civilian casualties. Many died in the carpet bombings, and many landmarks and centuries old works of art were destroyed. A significant number of civilians fled the city.
In late October, 1944 the German army and a significant amount of the civilian population abandoned the city. On October 31, 1944, the Partisans seized the city, until then a part of Mussolini's Italian Social Republic
. At the start of World War II
, Zadar had a population of 24,000 which was mostly Italian and by the end of 1944 this had decreased to 6,000. Formally, the city remained under Italian sovereignty until February 10, 1947 (Paris Peace Treaties
).
The Italian exodus from the city continued and in a few years was almost total. The last stroke to the Italian presence was made by the local administration in October 1953, wwhen the last Italian schools were closed and the students forced to move, from a day to the other, into Croatioan schools. Today the Italian community counts only a few hundreds people.
During this period Zadar underwent intensive reconstruction and revitalisation, followed by a large increase in both population and economic power. The Federal government sponsored numerous public works to this end, including the Adriatic Highway (Jadranska magistrala) which provided a modern road connection to the rest of the country. Besides the local infrastructure, the SFRY government initiated the industrialization of the city and nearly all its factories were either built or significantly revitalized and modernized in this period. In the 1970s Zadar particularly enjoyed a high standard of living as international tourism
came to Dalmatia.
However, during this period the city lost its status as the capital of the region, with Split
overwhelmingly surpassing Zadar in population numbers, which, though increasing throughout the 20th century, boomed in the new, post-WWII, Yugoslavia.
All in all, by the 1990s the city had not only been rebuilt after the Second World War, but had emerged as a modern and completely industrialized regional centre, with as yet unsurpassed tourist numbers, GDP and employment rates, which were, surprisingly, significantly higher than the present day's. After the death of Tito
, Yugoslavia rapidly began to destabilize.
began to devastate the country. Zadar became a part of the new Republic of Croatia. Its economy suffered greatly at this time not only because of the war but also due to the shadowy and controversial privatization process, which caused most of its prosperous companies to go under.
In 1990, Serbian separatists from the Krajina
region of Croatia just inland from Dalmatia
sealed roads and effectively blocked Dalmatia from the rest of Croatia. A number of non-Serbs were expelled from the area and several Croatian policemen were killed resulting in the Dalmatian anti-Serb riots of May 1991. Serbs at that time accounted for about 15% of the population.
During the Croatian War of Independence
, Krajina rebels
and the Yugoslav People's Army
(JNA) (at the time under Slobodan Milošević
's control) converged on the city and subjected it to artillery bombardment during Operation Coast-91 in which they tried to take control of northern Dalmatia.
Along with other Croatian towns in the area, Zadar was shelled sporadically for several years, resulting in damage to buildings and homes as well as UNESCO
protected sites. A number of nearby towns and villages were also attacked, the most brutal being the Škabrnja massacre
in which 86 people were killed.
Connections with Zagreb
were severed for over a year. The only link between the north and south of the country was via the island of Pag
. The siege
of the city lasted from 1991 until January 1993 when Zadar and the surrounding area came under the control of Croatian forces and the bridge link with the rest of Croatia was reestablished in Operation Maslenica
. Attacks on the city continued until the end of the war
in 1995.
Some of the countryside along the No. 8 highway running north east is still sectioned off due to land mine
s.
structure in Roman times; during the time of Julius Caesar
and Emperor Augustus
, the town was fortified and the city walls with towers and gates were built. On the western side of the town were the forum
, the basilica
and the temple
, while outside the town were the amphitheatre
and cemeteries
. The aqueduct
which supplied the town with water is partially preserved. Inside the ancient town, a medieval town had developed with a series of churches and monasteries
being built.
During the Middle Ages
, Zadar fully gained its urban aspect, which has been maintained until today. In the first half of the 16th century Venice fortified the town with a new system of defensive walls on the side facing land. In the course of the century architectural building in the Renaissance
style was continued and defensive trenches (Foša) were also built. They were completely buried during the Italian occupation until that in 1873, under Austria
n rule, the ramparts of Zadar were converted from fortifications into elevated promenades commanding extensive seaward and landward views, thus being the wall lines preserved; of its four old gates one, the Porta Marina, incorporates the relics of a Roman arch, and another, the Porta di Terraferma, was designed in the 16th century by the Veronese artist Michele Sanmicheli. In the bombardments during the Second World War entire blocks were destroyed, but some structures survived.
 Most important landmarks:
Most important landmarks:
The chief interest of Zadar lies in its churches.
Other architectural landmarks:
monastery. It closed in 1807.
Zadar was, along with Split
and Dubrovnik
, one of the centres of the development of Croatian literature
.
The 15th and 16th centuries were marked by important activities of Croatians writing in the national language: Jerolim Vidolić, Petar Zoranić
(who wrote the first Croatian novel, Planine
), Brne Karnarutić
, Juraj Baraković
, Šime Budinić.
Under French rule (1806–1810), the first Dalmatian newspaper Kraglski Dalmatin - Il Regio Dalmata was published in Zadar. It was printed in Italian and Croatian; this last used for the first time in a newspaper.
In the second half of the 19th century, Zadar was a centre of the movement for the cultural and national revivals in Dalmatia (Italian and Croatian).
Today Zadar's cultural institutions include:
and Petrčane, as well as the islands of Ist
, Iž
, Molat, Olib
, Premuda
, Rava
and Silba
. The total city area, including the islands, covers 194 km2.
Zadar is divided into 21 local districts: Arbanasi, Bili Brig, Bokanjac, Brodarica, Crvene Kuće, Diklo, Dračevac, Gaženica, Jazine I, Jazine II, Maslina, Novi Bokanjac, Poluotok, Ploča, Puntamika, Ričina, Smiljevac, Stanovi, Vidikovac, Višnjik, Voštarnica.
The farmland just northeast of Zadar, Ravni Kotari, is a well known source of marasca cherries
. Distilleries in Zadar have produced Maraschino
since the 16th century.
, finished up to Split in 2005. Zadrans can access to the highway by two interchanges: Zadar 1 exit in the north and Zadar 2 highway hub near Zemunik in the south. The southern interchange is connected to Zadar port of Gaženica
by the D424 expressway. Since 1966, a railway has linked Zadar with Knin
, where it joins the main railway from Zagreb to Split. It has an international sea line to Ancona in Italy. There is a plan for an "Adriatic Railway" line linking Zadar with Gospić
and Split. Zadar International Airport is located in Zemunik, around 14 km to the east of Zadar and accessible via the expressway. The airport is experiencing year on year an average of 30% increase in passenger traffic mainly due to arrivals of lowcost carriers (Ryanair
, Germanwings
, Intersky
, Danubewings
, JobAir) connecting Zadar from the end of March through October with over 20 cities throughout Europe. Currently, the arrivals and departures terminal building is expanding to accommodate the increasing number of passengers, with completion scheduled for March 2011. The extension of the runway for an additional 500m from the current 2500m is scheduled for late 2011.
 The local basketball club is KK Zadar
The local basketball club is KK Zadar
, and the football club NK Zadar
. The bowling club Kuglački klub Zadar is also very successful. Zadar is also the hometown of Croatian football player Luka Modrić
.
Krešimir Ćosić Hall is new multi-use indoor arena, built and completed in May 2008 with a capacity for 9,200 people, named after Krešimir Ćosić
, "a legend" of Zadar basketball game. Until then KK Zadar is played in Jazine Basketball Hall
.
, or maintains cultural, economic and educational ties with: Dundee
, United Kingdom
Reggio Emilia
, Italy
Romans-sur-Isère
, France
Fürstenfeldbruck
, Germany
Székesfehérvár
, Hungary
Padua
, Italy
Iquique
, Chile
Banská Bystrica
, Slovakia
, since 1995
Croatia
Croatia , officially the Republic of Croatia , is a unitary democratic parliamentary republic in Europe at the crossroads of the Mitteleuropa, the Balkans, and the Mediterranean. Its capital and largest city is Zagreb. The country is divided into 20 counties and the city of Zagreb. Croatia covers ...
on the Adriatic Sea
Adriatic Sea
The Adriatic Sea is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkan peninsula, and the system of the Apennine Mountains from that of the Dinaric Alps and adjacent ranges...
. It is the centre of Zadar county
Zadar County
Zadar County is a county in Croatia, it encompasses northern Dalmatia and southeastern Lika. Its center is the city of Zadar.- Population :According to the 2001 census, Zadar County has population of 162,045...
and the wider northern Dalmatia
Dalmatia
Dalmatia is a historical region on the eastern coast of the Adriatic Sea. It stretches from the island of Rab in the northwest to the Bay of Kotor in the southeast. The hinterland, the Dalmatian Zagora, ranges from fifty kilometers in width in the north to just a few kilometers in the south....
n region. Population of the city is 75,082 citizens (2011). Zadar is a historical center of Dalmatia as well as the seat of the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Zadar
Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Zadar
The Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Zadar takes its name from its episcopal see, the city of Zadar, in Croatia.-History:Zadar has been a Roman Catholic diocese in Dalmatia since AD 381 and, since 1146, an archdiocese. Its succession of bishops numbers over eighty without noteworthy interruption....
.
Name
In antiquityAncient history
Ancient history is the study of the written past from the beginning of recorded human history to the Early Middle Ages. The span of recorded history is roughly 5,000 years, with Cuneiform script, the oldest discovered form of coherent writing, from the protoliterate period around the 30th century BC...
, Iadera and Iader, the much older roots of the settlement's names were hidden, the names being most probably related to a hydrographical term. It was coined by an ancient Mediterranean people and their Pre-Indo-European language. They transmitted it to later settlers, the Liburnians
Liburnians
The Liburnians were an ancient Illyrian tribe inhabiting the district called Liburnia, a coastal region of the northeastern Adriatic between the rivers Arsia and Titius in what is now Croatia....
. The name of the Liburnian settlement was first mentioned by a Greek
Greek language
Greek is an independent branch of the Indo-European family of languages. Native to the southern Balkans, it has the longest documented history of any Indo-European language, spanning 34 centuries of written records. Its writing system has been the Greek alphabet for the majority of its history;...
inscription from Pharos (Stari grad
Stari Grad, Croatia
Stari Grad is a town on the northern side of the island of Hvar in Dalmatia, Croatia. One of the oldest towns in Europe, its position at the end of a long, protected bay and next to prime agricultural land, has long made it attractive for human settlement...
) on the island of Hvar
Hvar
- Climate :The climate of Hvar is characterized by mild winters and warm summers. The yearly average air temperature is , 686 mm of precipitation fall on the town of Hvar on average every year and the town has a total of 2800 sunshine hours per year. For comparison Hvar has an average of 7.7...
in 384 BC, where the citizens of Zadar were noted as (Iadasinoi). According to the Greek source Periplus of Pseudo-Scylax
Periplus of Pseudo-Scylax
The Periplus of Pseudo-Scylax is an ancient Greek periplus that ranks among the minor Greek geographers, dating from 4th or 3rd century BC. The name of Scylax applied to the text is thought to be a pseudepigraphical appeal to authority: Herodotus mentions a Scylax of Caryanda, a Greek navigator...
the city was (Idassa), probably a vulgar Greek form of the original Liburnian name.
During Antiquity
Classical antiquity
Classical antiquity is a broad term for a long period of cultural history centered on the Mediterranean Sea, comprising the interlocking civilizations of ancient Greece and ancient Rome, collectively known as the Greco-Roman world...
the name was often recorded in sources in Latin in two forms: Iader in the inscriptions and in the writings of classic writers, Iadera predominantly among the late Antiquity writers, while usual ethnonyms were Iadestines and Iadertines. The accent was on the first syllable in both Iader and Iadera forms, which influenced the early-Medieval Dalmatian language
Dalmatian language
Dalmatian was a Romance language spoken in the Dalmatia region of Croatia, and as far south as Kotor in Montenegro. The name refers to a pre-Roman tribe of the Illyrian linguistic group, Dalmatae...
forms Jadra, Jadera and Jadertina, where the accent kept its original place.
In the Dalmatian language, Jadra (Jadera) was pronounced Zadra (Zadera), due to the phonetic transformation of Ja- to Za-. That early change was also reflected in the Croatian
Croatian language
Croatian is the collective name for the standard language and dialects spoken by Croats, principally in Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, the Serbian province of Vojvodina and other neighbouring countries...
name Zadar (recorded as Zader in the 12th century ), developed from Zadъrъ by vocalizations of the semi-vowel and a shift to male gender. An ethnonym graphic Jaderani from the legend of St. Krševan in 9th century, was identical to the initial old-Slavic
Old Church Slavonic
Old Church Slavonic or Old Church Slavic was the first literary Slavic language, first developed by the 9th century Byzantine Greek missionaries Saints Cyril and Methodius who were credited with standardizing the language and using it for translating the Bible and other Ancient Greek...
form Zadъrane, or Renaissance
Renaissance
The Renaissance was a cultural movement that spanned roughly the 14th to the 17th century, beginning in Italy in the Late Middle Ages and later spreading to the rest of Europe. The term is also used more loosely to refer to the historical era, but since the changes of the Renaissance were not...
Croatian Zadrani.
The Dalmatian names Jadra, Jadera were transferred to other languages; in Venetian language
Venetian language
Venetian or Venetan is a Romance language spoken as a native language by over two million people, mostly in the Veneto region of Italy, where of five million inhabitants almost all can understand it. It is sometimes spoken and often well understood outside Veneto, in Trentino, Friuli, Venezia...
Jatara (hyper urbanism in 9th century) and Zara, Tuscan
Tuscan dialect
The Tuscan language , or the Tuscan dialect is an Italo-Dalmatian language spoken in Tuscany, Italy.Standard Italian is based on Tuscan, specifically on its Florentine variety...
Giara, Latin Diadora (Constantine VII
Constantine VII
Constantine VII Porphyrogennetos or Porphyrogenitus, "the Purple-born" was the fourth Emperor of the Macedonian dynasty of the Byzantine Empire, reigning from 913 to 959...
in DAI
De Administrando Imperio
De Administrando Imperio is the Latin title of a Greek work written by the 10th-century Eastern Roman Emperor Constantine VII. The Greek title of the work is...
, 10th century), Old French
Old French
Old French was the Romance dialect continuum spoken in territories that span roughly the northern half of modern France and parts of modern Belgium and Switzerland from the 9th century to the 14th century...
Jadres (Geoffroy de Villehardouinin in the chronicles of the Fourth Crusade
Fourth Crusade
The Fourth Crusade was originally intended to conquer Muslim-controlled Jerusalem by means of an invasion through Egypt. Instead, in April 1204, the Crusaders of Western Europe invaded and conquered the Christian city of Constantinople, capital of the Eastern Roman Empire...
in 1202), Arabic
Arabic language
Arabic is a name applied to the descendants of the Classical Arabic language of the 6th century AD, used most prominently in the Quran, the Islamic Holy Book...
Jādhara (جاذَرة) & Jādara (جادَرة) (Al-Idrisi, 12th century), Iadora (Guido, 12th century), Spanish
Spanish language
Spanish , also known as Castilian , is a Romance language in the Ibero-Romance group that evolved from several languages and dialects in central-northern Iberia around the 9th century and gradually spread with the expansion of the Kingdom of Castile into central and southern Iberia during the...
Jazara, Jara, Sarra (14th century) and the others.
Jadera became Zara when it fell under the authority of the Republic of Venice
Republic of Venice
The Republic of Venice or Venetian Republic was a state originating from the city of Venice in Northeastern Italy. It existed for over a millennium, from the late 7th century until 1797. It was formally known as the Most Serene Republic of Venice and is often referred to as La Serenissima, in...
in the 15th century.
Zara was later used by the Austrian Empire
Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire was a modern era successor empire, which was centered on what is today's Austria and which officially lasted from 1804 to 1867. It was followed by the Empire of Austria-Hungary, whose proclamation was a diplomatic move that elevated Hungary's status within the Austrian Empire...
in the 19th century, but it was provisionally changed to Zadar/Zara from 1910 to 1920; from 1920 to 1947 the city became part of Italy
Italy
Italy , officially the Italian Republic languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Italy's official name is as follows:;;;;;;;;), is a unitary parliamentary republic in South-Central Europe. To the north it borders France, Switzerland, Austria and...
as Zara, and finally was named Zadar later on.
Geography
Zadar faces the islands of UgljanUgljan
Ugljan is a Croatian island and the first in the Zadar Archipelago. It is located northwest of the island of Pašman and southeast of the islands of Rivanj and Sestrunj. Separated from the mainland by the Zadar Channel, it is connected with the island of Pašman by a bridge spanning over the Ždrelac...
and Pašman
Pašman
Pašman is an island off the coast of the Adriatic Sea in Croatia, located to the south of Zadar, surrounded by the islands Ugljan, Iž, Dugi otok and Kornati...
, from which it is separated by the narrow Zadar Strait. The promontory on which the old city stands used to be separated from the mainland by a deep moat which has since become landfilled. The harbor, to the north-east of the town, is safe and spacious.
Climate
Zadar has a Mediterranean climateMediterranean climate
A Mediterranean climate is the climate typical of most of the lands in the Mediterranean Basin, and is a particular variety of subtropical climate...
, with very mild, humid winters and very warm, dry summers.
Average annual rainfall is in excess of 917 mm (36.1 in). July and August are the hottest months, with an average high temperature around 28 °C (82 °F). Sometimes in July and August temperatures reach over 35 °C (95 °F) and can consistently reach over 30 °C (86 °F) during the summer months. Temperatures below 0 °C (32 °F) are rare, and are not maintained for more than a few days. January is the coldest month, with an average temperature around 6.7 °C (44 °F) and a record low of -9.1 °C. October, November and December are the wettest months, with a total precipitation of about 100 mm (3.94 in). July is the driest month, with a total precipitation of around 35 mm (1.38 in). Winter is the wettest season, however it can rain in Zadar at any time of the year. Snow is exceedingly rare, but it may fall in December, January, February and much more rarely in March. Also the sea temperature is from 10 °C (50 °F) in February to 24 °C (75 °F) in August, but is possible to swim from May until October.
Prehistory
The district of present day Zadar has been populated since prehistoric times. The earliest evidence of human life comes from the Late Stone AgeStone Age
The Stone Age is a broad prehistoric period, lasting about 2.5 million years , during which humans and their predecessor species in the genus Homo, as well as the earlier partly contemporary genera Australopithecus and Paranthropus, widely used exclusively stone as their hard material in the...
, while numerous settlements have been dated as early as the Neolithic
Neolithic
The Neolithic Age, Era, or Period, or New Stone Age, was a period in the development of human technology, beginning about 9500 BC in some parts of the Middle East, and later in other parts of the world. It is traditionally considered as the last part of the Stone Age...
. Before the Illyrians
Illyrians
The Illyrians were a group of tribes who inhabited part of the western Balkans in antiquity and the south-eastern coasts of the Italian peninsula...
, the area was inhabited by an ancient Mediterranean people of a pre-Indo-European culture. They assimilated with the Indo-Europeans
Proto-Indo-Europeans
The Proto-Indo-Europeans were the speakers of the Proto-Indo-European language , a reconstructed prehistoric language of Eurasia.Knowledge of them comes chiefly from the linguistic reconstruction, along with material evidence from archaeology and archaeogenetics...
who settled between the 4th and 2nd millennium BC into a new ethnical unity, that of the Liburnians
Liburnians
The Liburnians were an ancient Illyrian tribe inhabiting the district called Liburnia, a coastal region of the northeastern Adriatic between the rivers Arsia and Titius in what is now Croatia....
. Zadar was a Liburnian settlement, laid out in the 9th century BC, built on a small stone islet and embankments where the old city stands and tied to the mainland by the overflown narrow isthmus, which created a natural port in its northern strait.
Antiquity
The Liburnians were known as great sailors and merchants, but also had a reputation for piracy in the later years. By the 7th century BC, Zadar had become an important centre for their trading activities with the PhoeniciaPhoenicia
Phoenicia , was an ancient civilization in Canaan which covered most of the western, coastal part of the Fertile Crescent. Several major Phoenician cities were built on the coastline of the Mediterranean. It was an enterprising maritime trading culture that spread across the Mediterranean from 1550...
ns, Etruscans
Etruscan civilization
Etruscan civilization is the modern English name given to a civilization of ancient Italy in the area corresponding roughly to Tuscany. The ancient Romans called its creators the Tusci or Etrusci...
, Ancient Greeks
Ancient Greece
Ancient Greece is a civilization belonging to a period of Greek history that lasted from the Archaic period of the 8th to 6th centuries BC to the end of antiquity. Immediately following this period was the beginning of the Early Middle Ages and the Byzantine era. Included in Ancient Greece is the...
and other Mediterranean peoples. Its population at that time is estimated at 2,000. From 9th to 6th century there was certain koine - cultural unity in the Adriatic Sea, with the general Liburninan seal, whose naval supremacy meant both political and economical authority through several centuries. Due to its geographical position, Zadar developed into a main seat of the Liburnian thalassocracy and took a leading role in the Liburnian tetradekapolis, an organization of 14 communes.
The people of Zadar, the Iadasinoi, were first mentioned in 384 BC as the allies of the natives of Hvar
Hvar
- Climate :The climate of Hvar is characterized by mild winters and warm summers. The yearly average air temperature is , 686 mm of precipitation fall on the town of Hvar on average every year and the town has a total of 2800 sunshine hours per year. For comparison Hvar has an average of 7.7...
and the leaders of an eastern Adriatic coast coalition in the fight against the Greek colonizers. An expedition of 10,000 men in 300 ships sailed out from Zadar and laid siege to the Greek colony Pharos
Stari Grad, Croatia
Stari Grad is a town on the northern side of the island of Hvar in Dalmatia, Croatia. One of the oldest towns in Europe, its position at the end of a long, protected bay and next to prime agricultural land, has long made it attractive for human settlement...
in the island of Hvar, but the Syracusan fleet of Dionysus was alerted and attacked the siege fleet. The naval victory went to the Greeks which allowed them relatively safer further colonization in the southern Adriatic
Adriatic Sea
The Adriatic Sea is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkan peninsula, and the system of the Apennine Mountains from that of the Dinaric Alps and adjacent ranges...
.
The archaeological remains have shown that the main centres of Liburnian territorial units or municipalities were already urbanized in the last centuries BC; before the Roman conquest, Zadar held a territory of more than 600 km2 in the 2nd century BC.
In the middle of the 2nd century BC, the Romans
Ancient Rome
Ancient Rome was a thriving civilization that grew on the Italian Peninsula as early as the 8th century BC. Located along the Mediterranean Sea and centered on the city of Rome, it expanded to one of the largest empires in the ancient world....
began to gradually invade the region. Although being first Roman enemies in the Adriatic Sea, the Liburnians, mostly stood aside in more than 230 years of Roman wars with the Illyrians, to protect their naval and trade connections in the sea. In 59 BC Illyricum was assigned as a provincia (zone of responsibility) to Julius Caesar
Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar was a Roman general and statesman and a distinguished writer of Latin prose. He played a critical role in the gradual transformation of the Roman Republic into the Roman Empire....
and Liburnian Iadera became a Roman municipium
Municipium
Municipium , the prototype of English municipality, was the Latin term for a town or city. Etymologically the municipium was a social contract between municipes, the "duty holders," or citizens of the town. The duties, or munera, were a communal obligation assumed by the municipes in exchange for...
.
The Liburnian naval force was dragged into the Roman civil war between Julius Caesar
Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar was a Roman general and statesman and a distinguished writer of Latin prose. He played a critical role in the gradual transformation of the Roman Republic into the Roman Empire....
and Pompey
Pompey
Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus, also known as Pompey or Pompey the Great , was a military and political leader of the late Roman Republic...
in 49 BC, partially by force, partially because of the local interests of the participants, the Liburnian cities. Caesar was supported by the urban Liburnian centres, like Iader (Zadar), Aenona (Nin
Nin, Croatia
Nin is a town in the Zadar county of Croatia, population 1,256 , total municipality population 4,603 .Nin was historically important as a centre of a Christian Bishopric in the Middle Ages. Up to the abolition and Latinization imposed by King Tomislav in the first half of the 10th century, Nin was...
) and Curicum (Krk
Krk
Krk is a Croatian island in the northern Adriatic Sea, located near Rijeka in the Bay of Kvarner and part of the Primorje-Gorski Kotar county....
), while the city of Issa (Vis
Vis (town)
Vis is a town on the Vis island of the same name in Croatia. It has a population of 1960 residents . It is the center of the Vis municipality and part of Split-Dalmatia County.-History:...
) and the rest of the Liburnians gave their support to Pompey. In 49 BC near the island of Krk, the "Navy of Zadar", equipped by the fleets of a few Liburnian cities and supported by some Roman ships, lost an important naval battle against Pompey supporting the "Liburnian navy". The civil war was prolonged until the end of 48 BC, when Caesar rewarded his supporters in Liburnian Iader and Dalmatian
Dalmatae
The Dalmatae or Delmatae were an ancient people who inhabited the core of what would then become known as Dalmatia after the Roman conquest - now the eastern Adriatic coast in Croatia, between the rivers Krka and Neretva...
Salona
Salona
Salona was an ancient Illyrian Delmati city in the first millennium BC. The Greeks had set up an emporion there. After the conquest by the Romans, Salona became the capital of the Roman province of Dalmatia...
, by giving the status of the Roman colonies
Colonia (Roman)
A Roman colonia was originally a Roman outpost established in conquered territory to secure it. Eventually, however, the term came to denote the highest status of Roman city.-History:...
to their communities. Thus the city was granted the title colonia Iulia Iader, after its founder, and in the next period some of the Roman colonists (mostly legionary
Legionary
The Roman legionary was a professional soldier of the Roman army after the Marian reforms of 107 BC. Legionaries had to be Roman citizens under the age of 45. They enlisted in a legion for twenty-five years of service, a change from the early practice of enlisting only for a campaign...
veterans) settled there.
The real establishment of the Roman province of Illyricum occurred not earlier than 33 BC and Octavian
Augustus
Augustus ;23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14) is considered the first emperor of the Roman Empire, which he ruled alone from 27 BC until his death in 14 AD.The dates of his rule are contemporary dates; Augustus lived under two calendars, the Roman Republican until 45 BC, and the Julian...
’s military campaign in Illyria and Liburnia, when the Liburnians finally lost their naval independence and their galleys and sailors were incorporated into the Roman naval fleets.

The new religion Christianity
Christianity
Christianity is a monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus as presented in canonical gospels and other New Testament writings...
did not bypass the Roman province of Dalmatia
Dalmatia (Roman province)
Dalmatia was an ancient Roman province. Its name is probably derived from the name of an Illyrian tribe called the Dalmatae which lived in the area of the eastern Adriatic coast in Classical antiquity....
. Already by the end of the 3rd century Zadar had its own bishop and founding of the Zadar Christian community took place; a new religious centre was built north of the forum together with a basilica and a baptistery, as well as other ecclesiastical buildings. According to some estimates, in the 4th century it had probably around ten thousand citizens, including the population from its Ager
Ager
Ager can refer to:People:*Cecilia Ager , American film critic*Maurice Ager , American basketball player*Milton Ager , American pianist and composer*Nikolaus Ager , French botanist born in Alsace...
, the nearby islands and hinterland, an admixture of the indigenous Liburnians and Roman colonists.
Early Middle Ages
During the Migration PeriodMigration Period
The Migration Period, also called the Barbarian Invasions , was a period of intensified human migration in Europe that occurred from c. 400 to 800 CE. This period marked the transition from Late Antiquity to the Early Middle Ages...
and the Barbarian invasions, Zadar underwent a stagnation. In 441 and 447 Dalmatia was ravaged by the Huns
Huns
The Huns were a group of nomadic people who, appearing from east of the Volga River, migrated into Europe c. AD 370 and established the vast Hunnic Empire there. Since de Guignes linked them with the Xiongnu, who had been northern neighbours of China 300 years prior to the emergence of the Huns,...
, after the fall of the Western Roman Empire, in 481 Dalmatia became part of the Ostrogothic kingdom
Ostrogothic Kingdom
The Kingdom established by the Ostrogoths in Italy and neighbouring areas lasted from 493 to 553. In Italy the Ostrogoths replaced Odoacer, the de facto ruler of Italy who had deposed the last emperor of the Western Roman Empire in 476. The Gothic kingdom reached its zenith under the rule of its...
, which, besides Italy, already included the more northerly parts of Illyricum
Praetorian prefecture of Illyricum
The praetorian prefecture of Illyricum was one of four praetorian prefectures into which the Late Roman Empire was divided.The administrative centre of the prefecture was Sirmium , and, after 379, Thessalonica...
, i.e. Pannonia
Pannonia
Pannonia was an ancient province of the Roman Empire bounded north and east by the Danube, coterminous westward with Noricum and upper Italy, and southward with Dalmatia and upper Moesia....
and Noricum
Noricum
Noricum, in ancient geography, was a Celtic kingdom stretching over the area of today's Austria and a part of Slovenia. It became a province of the Roman Empire...
.
In the 5th century, under the rule of the Ostrogothic Kingdom
Ostrogothic Kingdom
The Kingdom established by the Ostrogoths in Italy and neighbouring areas lasted from 493 to 553. In Italy the Ostrogoths replaced Odoacer, the de facto ruler of Italy who had deposed the last emperor of the Western Roman Empire in 476. The Gothic kingdom reached its zenith under the rule of its...
, Zadar became poor with many civic buildings turning into ruins due to its advanced age. About the same time (6th century) it was hit by an earthquake, which destroyed entire complexes of monumental Roman architecture, whose parts would later serve as material for building houses. This caused a loss of population and created demographic changes in the city, then gradually repopulated by the inhabitants from its hinterland. However, during six decades of Gothic rule, the Goths saved those old Roman Municipal institutions that were still in function, while religious life in Dalmatia even intensified in the last years, so that there was a need for the foundation of additional bishoprics.
In 536 the Byzantine emperor Justinian the Great started a military campaign to reconquer the territories of the former Western Empire (see Gothic War
Gothic War (535–552)
The Gothic War between the Eastern Roman Empire and the Ostrogothic Kingdom of Italy was fought from 535 until 554 in Italy, Dalmatia, Sardinia, Sicily and Corsica. It is commonly divided into two phases. The first phase lasted from 535 to 540 and ended with the fall of Ravenna and the apparent...
); and in 553 Zadar passed to the Byzantine Empire
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire was the Eastern Roman Empire during the periods of Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, centred on the capital of Constantinople. Known simply as the Roman Empire or Romania to its inhabitants and neighbours, the Empire was the direct continuation of the Ancient Roman State...
. In 568 Dalmatia was devastated by an Avar
Eurasian Avars
The Eurasian Avars or Ancient Avars were a highly organized nomadic confederacy of mixed origins. They were ruled by a khagan, who was surrounded by a tight-knit entourage of nomad warriors, an organization characteristic of Turko-Mongol groups...
invasion; although further waves of attacks by Avar and Slav tribes kept up the pressure, it was the only city which survived due to its protective belt of inland plains. The Dalmatian capital Salona
Salona
Salona was an ancient Illyrian Delmati city in the first millennium BC. The Greeks had set up an emporion there. After the conquest by the Romans, Salona became the capital of the Roman province of Dalmatia...
was captured and destroyed in the 40s of the 7th century, so Zadar became the new seat of the Byzantine archonty of Dalmatia
Dalmatia (theme)
The Theme of Dalmatia was a Byzantine theme on the eastern coast of the Adriatic Sea in Southeastern Europe, headquartered at Zadar.- History :...
, territorially reduced to a few coastal cities with their agers and municipal lands at the coast and the islands nearby. The prior of Zadar had jurisdiction over all Byzantine Dalmatia, so Zadar enjoyed metropolitan status at the eastern Adriatic coast. At this time rebuilding began to take place in the city.

Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a realm that existed from 962 to 1806 in Central Europe.It was ruled by the Holy Roman Emperor. Its character changed during the Middle Ages and the Early Modern period, when the power of the emperor gradually weakened in favour of the princes...
under Pepin and the Byzantine Empire. The Franks
Franks
The Franks were a confederation of Germanic tribes first attested in the third century AD as living north and east of the Lower Rhine River. From the third to fifth centuries some Franks raided Roman territory while other Franks joined the Roman troops in Gaul. Only the Salian Franks formed a...
held Zadar for a short time, but the city was returned to Byzantium by a decision of the 812 Treaty of Aachen.
Zadar's economy revolved around sea, fishing and sea trade in the first centuries of the Middle Ages. Thanks to saved Antique ager, adjusted municipal structure and a new strategic position, it became the most important city between the Kvarner islands and Kaštela
Kaštela
Kaštela is a series of seven towns in central Dalmatia, located northwest of Split, west of Solin and east of Trogir, in Croatia. They are part of the Split-Dalmatia county and are treated as a single city with a population of 38,474 , although they are individually between 3,000 and 7,000...
Bay. Byzantine Dalmatia wasn't territorially unified, but an alliance of city municipalities headed by Zadar, and the large degree of city autonomy allowed the development of Dalmatian cities as free communes. Forced to turn their attention seawards, the inhabitants of Zadar focused on shipping, and the city became a naval power to rival Venice
Venice
Venice is a city in northern Italy which is renowned for the beauty of its setting, its architecture and its artworks. It is the capital of the Veneto region...
. The citizens were Dalmatian language
Dalmatian language
Dalmatian was a Romance language spoken in the Dalmatia region of Croatia, and as far south as Kotor in Montenegro. The name refers to a pre-Roman tribe of the Illyrian linguistic group, Dalmatae...
speakers, but from the 7th century Croatian language
Croatian language
Croatian is the collective name for the standard language and dialects spoken by Croats, principally in Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, the Serbian province of Vojvodina and other neighbouring countries...
started to spread in a region, becoming predominant in the inland and the islands to the end of the 9th century.
Middle Ages

Saracen
Saracen was a term used by the ancient Romans to refer to a people who lived in desert areas in and around the Roman province of Arabia, and who were distinguished from Arabs. In Europe during the Middle Ages the term was expanded to include Arabs, and then all who professed the religion of Islam...
raids had finished. Also the adjustment of relations with the Croats
Croats
Croats are a South Slavic ethnic group mostly living in Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina and nearby countries. There are around 4 million Croats living inside Croatia and up to 4.5 million throughout the rest of the world. Responding to political, social and economic pressure, many Croats have...
enabled Zadar merchants to trade with its rich agriculture hinterland where the Kingdom of Croatia
Kingdom of Croatia (medieval)
The Kingdom of Croatia , also known as the Kingdom of the Croats , was a medieval kingdom covering most of what is today Croatia and Bosnia and Herzegovina in the Balkans.Established in 925, it ruled as a sovereign state for almost two centuries...
had formed, and trade and political links with Zadar began to develop. Croatian settlers began to arrive, becoming commonplace by the 10th century, occupying all city classes, as well as important posts, like those of prior, judge, priest and others. In 925, Tomislav, the Duke of Croatian Dalmatia, united Croatian Dalmatia
Dalmatia
Dalmatia is a historical region on the eastern coast of the Adriatic Sea. It stretches from the island of Rab in the northwest to the Bay of Kotor in the southeast. The hinterland, the Dalmatian Zagora, ranges from fifty kilometers in width in the north to just a few kilometers in the south....
and Pannonia establishing the Croatian Kingdom
Kingdom of Croatia (Medieval)
The Kingdom of Croatia , also known as the Kingdom of the Croats , was a medieval kingdom covering most of what is today Croatia and Bosnia and Herzegovina in the Balkans.Established in 925, it ruled as a sovereign state for almost two centuries...
. He was also granted the position of protector of Dalmatia (the cities) by the Byzantine Emperor. He thus politically united the Dalmatian cities with their hinterland.
At the time of the Zadar medieval development, the city became a threat to Venice's ambitions, because of its strategic position at the centre of the eastern Adriatic coast.
In 998 Zadar sought Venetian protection against the Neretvian pirates. The Venetians were quick to fully exploit this opportunity: in 998 a fleet commanded by Doge
Doge of Venice
The Doge of Venice , often mistranslated Duke was the chief magistrate and leader of the Most Serene Republic of Venice for over a thousand years. Doges of Venice were elected for life by the city-state's aristocracy. Commonly the person selected as Doge was the shrewdest elder in the city...
Pietro Orseolo II, after having defeated pirates, landed in Korčula
Korcula
Korčula is an island in the Adriatic Sea, in the Dubrovnik-Neretva County of Croatia. The island has an area of ; long and on average wide — and lies just off the Dalmatian coast. Its 16,182 inhabitants make it the second most populous Adriatic island after Krk...
and Lastovo
Lastovo
Lastovo is an island municipality in the Dubrovnik-Neretva County in Croatia. The municipality consists of 46 islands with a total population of 792 people, of which 93% are ethnic Croats, and a land area of approximately . The biggest island in the municipality is also named Lastovo, as is the...
. Dalmatia was taken by surprise and offered little serious resistance. Trogir
Trogir
Trogir is a historic town and harbour on the Adriatic coast in Split-Dalmatia County, Croatia, with a population of 12,995 and a total municipality population of 13,322 . The historic city of Trogir is situated on a small island between the Croatian mainland and the island of Čiovo...
was the exception and was subjected to Venetian rule only after a bloody struggle, whereas the Republic of Dubrovnik was forced to pay tribute. Tribute previously paid by Zadar to Croatian kings, was redirected to Venice, a state of affairs which lasted for several years.

Petar Krešimir IV of Croatia
Peter Krešimir IV, called the Great , was a notably energetic King of Croatia from 1059 to his death in 1074/1075. He was the last great ruler of the Krešimirović branch of the House of Trpimirović....
in 1069. Later, after the death of king Dmitar Zvonimir
Dmitar Zvonimir
Demetrius Zvonimir was King of Croatia from 8 October 1076 until his death. He also ruled as Ban of Slavonia , and was named Duke of Croatia in around 1075. His native name was Zvonimir, while the name Demetrius was adopted at his coronation.He began as a Ban of Slavonia in the service of King...
in 1089 and ensuing dynastic run-ins, in 1105 Zadar accepted the rule of the first Croato-Hungarian king Coloman.
In the meantime Venice developed into a true trading force in the Adriatic and started attacks on
Zadar. The city was repeatedly invaded by Venice between 1111 and 1154 and then once more between 1160 and 1183, when it finally rebelled, appealing to the Pope and to the Croato-Hungarian throne for protection.
Zadar was especially devastated in 1202 after the Venetian Doge Enrico Dandolo
Enrico Dandolo
Enrico Dandolo — anglicised as Henry Dandolo and Latinized as Henricus Dandulus — was the 41st Doge of Venice from 1195 until his death...
used the Crusaders, on their Fourth Crusade
Fourth Crusade
The Fourth Crusade was originally intended to conquer Muslim-controlled Jerusalem by means of an invasion through Egypt. Instead, in April 1204, the Crusaders of Western Europe invaded and conquered the Christian city of Constantinople, capital of the Eastern Roman Empire...
to Palestine
Palestine
Palestine is a conventional name, among others, used to describe the geographic region between the Mediterranean Sea and the Jordan River, and various adjoining lands....
, to lay siege to the city. The crusaders
Crusaders
The Crusaders are a New Zealand professional rugby union team based in Christchurch that competes in the Super Rugby competition. They are the most successful team in Super Rugby history with seven titles...
were obliged to pay Venice for sea transport to Egypt
Egypt
Egypt , officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, Arabic: , is a country mainly in North Africa, with the Sinai Peninsula forming a land bridge in Southwest Asia. Egypt is thus a transcontinental country, and a major power in Africa, the Mediterranean Basin, the Middle East and the Muslim world...
. As they were not able to produce enough money, the Venetians used them to initiate the Siege of Zadar, when the city was ransacked, demolished and robbed. The king of Croatia and Hungary, Emeric of Hungary
Emeric of Hungary
Emeric I , , King of Hungary and Croatia . He was crowned during his father's lifetime, but after his father's death he had to fight against his brother, Andrew, who forced Emeric to assign the government of Croatia and Dalmatia to him...
, condemned the crusade, because of an argument about the possible heresy committed by God's army in attacking a Christian city. Nonetheless, Zadar was devastated and captured, with the population escaped into the surrounding countryside. Pope Innocent III
Pope Innocent III
Pope Innocent III was Pope from 8 January 1198 until his death. His birth name was Lotario dei Conti di Segni, sometimes anglicised to Lothar of Segni....
excommunicated the Venetians and crusaders involved in the siege.
Two years later (1204), under the leadership of the Croatian nobleman Domald from Šibenik
Šibenik
Šibenik is a historic town in Croatia, with population of 51,553 . It is located in central Dalmatia where the river Krka flows into the Adriatic Sea...
, most of the refugees returned and liberated the city from what remained of the crusader force. In 1204 Domald was comes (duke) of Zadar, but the following year (1205) Venetian authority was re-established and a peace agreement signed with hard conditions for the citizens. The only profit which the Communal Council of Zadar derived from this was one third of the city's harbour taxes, probably insufficient even for the most indispensable communal needs.
.jpg)
Treaty of Zara
The Treaty of Zadar, also known as the Treaty of Zara, was a peace treaty signed in Zadar, Dalmatia on February 18, 1358 by which the Venetian Republic lost influence over its Dalmatian holdings...
, in 1358. After the War of Chioggia
War of Chioggia
The War of Chioggia was a conflict between Genoa and Venice which lasted from 1378 to 1381, from which Venice emerged triumphant. It was a part of the larger Venetian-Genoese War which began in 1350.-Background:...
between Genoa and Venice, Chioggia
Chioggia
Chioggia is a coastal town and comune of the province of Venice in the Veneto region of northern Italy.-Geography:...
concluded on 14 March 1381 an alliance with Zadar and Trogir
Trogir
Trogir is a historic town and harbour on the Adriatic coast in Split-Dalmatia County, Croatia, with a population of 12,995 and a total municipality population of 13,322 . The historic city of Trogir is situated on a small island between the Croatian mainland and the island of Čiovo...
against Venice, and finally Chioggia became better protected by Venice in 1412, because Šibenik
Šibenik
Šibenik is a historic town in Croatia, with population of 51,553 . It is located in central Dalmatia where the river Krka flows into the Adriatic Sea...
became in 1412 the seat of the main customs
Customs
Customs is an authority or agency in a country responsible for collecting and safeguarding customs duties and for controlling the flow of goods including animals, transports, personal effects and hazardous items in and out of a country...
office and the seat of the salt consumers office with a monopoly
Monopoly
A monopoly exists when a specific person or enterprise is the only supplier of a particular commodity...
on the salt trade in Chioggia and on the whole Adriatic Sea
Adriatic Sea
The Adriatic Sea is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkan peninsula, and the system of the Apennine Mountains from that of the Dinaric Alps and adjacent ranges...
. After the death of Louis, Zadar recognized the rule of king Sigismund
Sigismund, Holy Roman Emperor
Sigismund of Luxemburg KG was King of Hungary, of Croatia from 1387 to 1437, of Bohemia from 1419, and Holy Roman Emperor for four years from 1433 until 1437, the last Emperor of the House of Luxemburg. He was also King of Italy from 1431, and of Germany from 1411...
, and after him, that of Ladislaus of Naples. During his reign Croatia-Hungary was enveloped in a bloody civil war. In 1409, Venice, seeing that Ladislaus was about to be defeated, and eager to exploit the situation despite its relative military weakness, offered to buy his "rights" on Dalmatia for a mere 100,000 ducats. Knowing he had lost the region in any case, Ladislaus accepted. Zadar was, thus sold back to the Venetians for a paltry sum.
The population of Zadar during the Medieval period was predominantly Croatian, according to numerous archival documents, and the Croatian language was used in liturgy, as shown by the writings of cardinal Boson, who followed Pope Alexander III
Pope Alexander III
Pope Alexander III , born Rolando of Siena, was Pope from 1159 to 1181. He is noted in history for laying the foundation stone for the Notre Dame de Paris.-Church career:...
en route to Venice in 1177. When the papal ships took shelter in the harbour of Zadar, the inhabitants greeted the Pope by singing lauds and canticles in Croatian.
Even though interspersed by sieges and destruction, the time between 11th and 14th century was the golden age of Zadar. Thanks to its political and trading achievements, and also to its skilled seamen, Zadar played an important role among the cities on the east coast of the Adriatic. This affected its appearance and culture: many churches, rich monasteries and palaces for powerful families were built, together with the Chest of Saint Simeon
Chest of Saint Simeon
The Chest of Saint Simeon or Saint Simeon's Casket is a rectangular silvery wooden sarcophagus located over the main altar in the Church of Saint Simeon in Zadar, Croatia...
. One of the best examples of the culture and prosperity of Zadar at that time was the founding of the University of Zadar
University of Zadar
The University of Zadar is a university located in Zadar, Croatia. It was founded in 2002.- University Departments :The University of Zadar is entirely integrated university, consisting at present of over 20 departments:...
, built in 1396 by the Dominican Order
Dominican Order
The Order of Preachers , after the 15th century more commonly known as the Dominican Order or Dominicans, is a Catholic religious order founded by Saint Dominic and approved by Pope Honorius III on 22 December 1216 in France...
(the oldest university in present day Croatia).
From 15th to 18th century

Italy
Italy , officially the Italian Republic languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Italy's official name is as follows:;;;;;;;;), is a unitary parliamentary republic in South-Central Europe. To the north it borders France, Switzerland, Austria and...
for their sculptures and buildings.

In contrast to the insecurity and Ottoman sieges and destruction, an important culture evolved midst the city walls. During the 16th and the 17th century the activity of the Croatian writers and poets became prolific (Jerolim Vidolić, Petar Zoranić
Petar Zoranic
Petar Zoranić was a Croatian Renaissance writer from Zadar.He is most important as the author of Planine, the first Croatian novel. Pastoral in nature, the novel shows influence of Virgil, Ovid, Dante Alighieri, Francesco Petrarca and Giovanni Boccaccio. The novel was written in 1538 and published...
, Brne Karnarutić
Brne Karnarutic
Brne Karnarutić was Croatian Renaissance poet and writer.He was born in Zadar probably in 1515 as a descent of old noble family. After schooling in Zadar he studied law, probably in Padua...
, Juraj Baraković
Juraj Barakovic
Juraj Baraković is a Croatian Renaissance poet from Zadar.He wrote several distinguished pieces , but one work excels in his literary opus: complicated and the most explicitly manneristic epic in 13 books "Vila slovinka"...
, Šime Budinić). Also noteworthy is the painter Andrija Medulić (c. 1510/1515–1563), who, when in Venice, signed his name as "Andrea Schiavone."
During the continuous Ottoman danger the population stagnated by a significant degree along with the economy. During the 16th and 17th century several large-scale epidemics of bubonic plague erupted in the city. After more than 150 years of Turkish threat Zadar was not only scarce in population, but also in material wealth. Venice sent new colonists and, under the firm hand of archbishop Vicko Zmajević, the Arbanasi (Catholic Albanian refugees) settled in the city, forming a new suburb. Despite the shortage of money, the Teatro Nobile (Theater for Nobility) was built in 1783. It functioned for over 100 years.
19th and 20th century
After the fall of Venice (1797) with the Treaty of Campo FormioTreaty of Campo Formio
The Treaty of Campo Formio was signed on 18 October 1797 by Napoleon Bonaparte and Count Philipp von Cobenzl as representatives of revolutionary France and the Austrian monarchy...
, Zadar come under the Austria
Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire was a modern era successor empire, which was centered on what is today's Austria and which officially lasted from 1804 to 1867. It was followed by the Empire of Austria-Hungary, whose proclamation was a diplomatic move that elevated Hungary's status within the Austrian Empire...
n crown and once again became united with the rest of Croatia. In 1806 it was briefly given to the Napoleonic Kingdom of Italy
Kingdom of Italy (Napoleonic)
The Kingdom of Italy was a state founded in Northern Italy by Napoleon, fully influenced by revolutionary France, that ended with his defeat and fall.-Constitutional statutes:...
, until in 1809 it was added to the French Illyrian Provinces
Illyrian provinces
The Illyrian Provinces was an autonomous province of the Napoleonic French Empire on the north and east coasts of the Adriatic Sea between 1809 and 1816. Its capital was established at Laybach...
. In 1813, all of Dalmatia was reconquered and brought back under the control of the Austrian Empire. During this time, it maintained its position as the capital of Dalmatia.
During the Napoleonic era, the first Dalmatian newspaper, Kraglski Dalmatin - Il Regio Dalmata ("The Royal Dalmatian"), was printed in the city.
After 1815 Dalmatia (including Dubrovnik) came under the Austrian
Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire was a modern era successor empire, which was centered on what is today's Austria and which officially lasted from 1804 to 1867. It was followed by the Empire of Austria-Hungary, whose proclamation was a diplomatic move that elevated Hungary's status within the Austrian Empire...
crown. After 1848, Italian and Slavic nationalism became accentuated and the city became divided between the Croats and the Italians, both of whom founded their respective political parties. There are conflicting sources for both sides claiming to have formed the majority in this period; in general the era saw Slavs grow more than Italians throughout Dalmatia, fostering a distinct national spirit.
Italy (1920-1947)
During 1918, political life in Zadar intensified. The development of the Declaration movement was underway. The collapse of the Austro-Hungarian Monarchy led to the renewal of national conflicts in the city. With the arrival of an Italian army of occupation in the city on 4 November 1918, the Italian faction gradually assumed control, a process which was completed on 5 December when it took over the governorship. The Treaty of RapalloTreaty of Rapallo, 1920
The Treaty of Rapallo was a treaty between the Kingdom of Italy and the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes , signed to solve the dispute over some territories in the upper Adriatic, in Dalmatia and in the region which became known as the Julian March.The treaty was signed on 12 November 1920 in...
(12 November 1920) gave Zadar with other local territory to Italy. The Zadar enclave, a total of 104 km², included the city of Zadar, the municipalities of Bokanjac, Arbanasi, Crno, part of Diklo (a total of 51 km2. of territory and 17,065 inhabitants) and the islands of Lastovo
Lastovo
Lastovo is an island municipality in the Dubrovnik-Neretva County in Croatia. The municipality consists of 46 islands with a total population of 792 people, of which 93% are ethnic Croats, and a land area of approximately . The biggest island in the municipality is also named Lastovo, as is the...
and Palagruža
Palagruža
Palagruža is a small, remote archipelago of dolomite in the middle of the Adriatic Sea in Croatia. It consists of one main island, called Vela or Velika Palagruža, and one smaller one, Mala Palagruža, and there are twenty or so other closely associated rocks or reefs...
(53 km², 1,710 inhabitants). The territory was organized into an Italian province.
World War II
GermanyNazi Germany
Nazi Germany , also known as the Third Reich , but officially called German Reich from 1933 to 1943 and Greater German Reich from 26 June 1943 onward, is the name commonly used to refer to the state of Germany from 1933 to 1945, when it was a totalitarian dictatorship ruled by...
, with limited Italian assistance, invaded the Kingdom of Yugoslavia
Invasion of Yugoslavia
The Invasion of Yugoslavia , also known as the April War , was the Axis Powers' attack on the Kingdom of Yugoslavia which began on 6 April 1941 during World War II...
on April 6, 1941. Zadar held a force of 9,000 that after limited fighting reached Šibenik and Split on April 15, a mere 2 days before surrender, with civilians having previously been evacuated to Ancona
Ancona
Ancona is a city and a seaport in the Marche region, in central Italy, with a population of 101,909 . Ancona is the capital of the province of Ancona and of the region....
and Pula
Pula
Pula is the largest city in Istria County, Croatia, situated at the southern tip of the Istria peninsula, with a population of 62,080 .Like the rest of the region, it is known for its mild climate, smooth sea, and unspoiled nature. The city has a long tradition of winemaking, fishing,...
. Occupying Mostar
Mostar
Mostar is a city and municipality in Bosnia and Herzegovina, the largest and one of the most important cities in the Herzegovina region and the center of the Herzegovina-Neretva Canton of the Federation. Mostar is situated on the Neretva river and is the fifth-largest city in the country...
and Dubrovnik, on April 17 they met invading troops that had started out from Italian-occupied Albania
Albania
Albania , officially known as the Republic of Albania , is a country in Southeastern Europe, in the Balkans region. It is bordered by Montenegro to the northwest, Kosovo to the northeast, the Republic of Macedonia to the east and Greece to the south and southeast. It has a coast on the Adriatic Sea...
. On April 17 the Yugoslav government surrendered, faced with the Wehrmacht
Wehrmacht
The Wehrmacht – from , to defend and , the might/power) were the unified armed forces of Nazi Germany from 1935 to 1945. It consisted of the Heer , the Kriegsmarine and the Luftwaffe .-Origin and use of the term:...
's overwhelming superiority.
Within a few weeks, Benito Mussolini
Benito Mussolini
Benito Amilcare Andrea Mussolini was an Italian politician who led the National Fascist Party and is credited with being one of the key figures in the creation of Fascism....
required the newly formed Nazi puppet-state, the so-called Independent State of Croatia
Independent State of Croatia
The Independent State of Croatia was a World War II puppet state of Nazi Germany, established on a part of Axis-occupied Yugoslavia. The NDH was founded on 10 April 1941, after the invasion of Yugoslavia by the Axis powers. All of Bosnia and Herzegovina was annexed to NDH, together with some parts...
(NDH) to hand over almost all of Dalmatia (including Split) to fascist Italy under the Treaty of Rome.
The city became the centre of a new Italian territorial entity, called Governorship of Dalmatia
Governorship of Dalmatia
The Governorate of Dalmatia was a province of Italy, created in April 1941 from occupied Yugoslav territory annexed after the German blitzkrieg Invasion of Yugoslavia.-Characteristics:...
, including the provinces of Zadar, Split and Kotor.
Under fascist reign the Slavic population was subjected to a policy of forced assimilation. This created immense resentment among the Yugoslav people and the Yugoslav Partisan movement
Partisans (Yugoslavia)
The Yugoslav Partisans, or simply the Partisans were a Communist-led World War II anti-fascist resistance movement in Yugoslavia...
(which was already successfully spreading in the rest of Yugoslavia) did not take root here since more than 70% of population of Zara was Italian.
After Mussolini was removed from power on 25 July 1943 and arrested, the government of Pietro Badoglio
Pietro Badoglio
Pietro Badoglio, 1st Duke of Addis Abeba, 1st Marquess of Sabotino was an Italian soldier and politician...
signed an armistice
Armistice with Italy
The Armistice with Italy was an armistice signed on September 3 and publicly declared on September 8, 1943, during World War II, between Italy and the Allied armed forces, who were then occupying the southern end of the country, entailing the capitulation of Italy...
with the Allies
Allies of World War II
The Allies of World War II were the countries that opposed the Axis powers during the Second World War . Former Axis states contributing to the Allied victory are not considered Allied states...
on 3 September 1943, which was made public only on 8 September 1943, and the Italian army collapsed. However, just four days later on 12 September 1943, "Il Duce
Duce
Duce is an Italian title, derived from the Latin word dux, and cognate with duke. National Fascist Party leader Benito Mussolini was identified by Fascists as Il Duce of the movement and became a reference to the dictator position of Head of Government and Duce of Fascism of Italy was established...
", was rescued by a German military raid from his secret prison on the Gran Sasso mountain, and formed the Nazi-puppet Italian Social Republic
Italian Social Republic
The Italian Social Republic was a puppet state of Nazi Germany led by the "Duce of the Nation" and "Minister of Foreign Affairs" Benito Mussolini and his Republican Fascist Party. The RSI exercised nominal sovereignty in northern Italy but was largely dependent on the Wehrmacht to maintain control...
in the north of the Country. The NDH proclaimed the Treaty of Rome to be void and occupied Dalmatia with German support. The Germans entered Zadar first, and on September 10 the German 114th Jäger Division took over. This avoided a temporary liberation by Partisans, as was the case in Split and Šibenik where several Italian fascist government officials were killed by an angry crowd.
The city was prevented from joining the NDH on the grounds that Zadar itself was not subject to the conditions of the Treaty of Rome. Despite this, the NDH's leader Ante Pavelić
Ante Pavelic
Ante Pavelić was a Croatian fascist leader, revolutionary, and politician. He ruled as Poglavnik or head, of the Independent State of Croatia , a World War II puppet state of Nazi Germany in Axis-occupied Yugoslavia...
designated Zadar as the capital of the Sidraga-Ravni Kotari County, although its administrator was prevented from entering the city. Zadar remained under the local administration of the Italian Social Republic. Zadar was bombed by the Allies, with serious civilian casualties. Many died in the carpet bombings, and many landmarks and centuries old works of art were destroyed. A significant number of civilians fled the city.
In late October, 1944 the German army and a significant amount of the civilian population abandoned the city. On October 31, 1944, the Partisans seized the city, until then a part of Mussolini's Italian Social Republic
Italian Social Republic
The Italian Social Republic was a puppet state of Nazi Germany led by the "Duce of the Nation" and "Minister of Foreign Affairs" Benito Mussolini and his Republican Fascist Party. The RSI exercised nominal sovereignty in northern Italy but was largely dependent on the Wehrmacht to maintain control...
. At the start of World War II
World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
, Zadar had a population of 24,000 which was mostly Italian and by the end of 1944 this had decreased to 6,000. Formally, the city remained under Italian sovereignty until February 10, 1947 (Paris Peace Treaties
Paris Peace Treaties, 1947
The Paris Peace Conference resulted in the Paris Peace Treaties signed on February 10, 1947. The victorious wartime Allied powers negotiated the details of treaties with Italy, Romania, Hungary, Bulgaria, and Finland .The...
).
The Italian exodus from the city continued and in a few years was almost total. The last stroke to the Italian presence was made by the local administration in October 1953, wwhen the last Italian schools were closed and the students forced to move, from a day to the other, into Croatioan schools. Today the Italian community counts only a few hundreds people.
SFR Yugoslavia (1947-1991)
After the bombing, the city progressively recovered and became once more an important regional city in the newly established Democratic Federal Yugoslavia.During this period Zadar underwent intensive reconstruction and revitalisation, followed by a large increase in both population and economic power. The Federal government sponsored numerous public works to this end, including the Adriatic Highway (Jadranska magistrala) which provided a modern road connection to the rest of the country. Besides the local infrastructure, the SFRY government initiated the industrialization of the city and nearly all its factories were either built or significantly revitalized and modernized in this period. In the 1970s Zadar particularly enjoyed a high standard of living as international tourism
Tourism in Croatia
Tourism in Croatia is a well-developed industry. Many tourists visit to experience the country's extensive coastline and well-preserved coastal Renaissance towns...
came to Dalmatia.
However, during this period the city lost its status as the capital of the region, with Split
Split (city)
Split is a Mediterranean city on the eastern shores of the Adriatic Sea, centered around the ancient Roman Palace of the Emperor Diocletian and its wide port bay. With a population of 178,192 citizens, and a metropolitan area numbering up to 467,899, Split is by far the largest Dalmatian city and...
overwhelmingly surpassing Zadar in population numbers, which, though increasing throughout the 20th century, boomed in the new, post-WWII, Yugoslavia.
All in all, by the 1990s the city had not only been rebuilt after the Second World War, but had emerged as a modern and completely industrialized regional centre, with as yet unsurpassed tourist numbers, GDP and employment rates, which were, surprisingly, significantly higher than the present day's. After the death of Tito
Josip Broz Tito
Marshal Josip Broz Tito – 4 May 1980) was a Yugoslav revolutionary and statesman. While his presidency has been criticized as authoritarian, Tito was a popular public figure both in Yugoslavia and abroad, viewed as a unifying symbol for the nations of the Yugoslav federation...
, Yugoslavia rapidly began to destabilize.
Croatian War of Independence (1991 - 1995)
In the early 1990s the tragic Yugoslav warsYugoslav wars
The Yugoslav Wars were a series of wars, fought throughout the former Yugoslavia between 1991 and 1995. The wars were complex: characterized by bitter ethnic conflicts among the peoples of the former Yugoslavia, mostly between Serbs on the one side and Croats and Bosniaks on the other; but also...
began to devastate the country. Zadar became a part of the new Republic of Croatia. Its economy suffered greatly at this time not only because of the war but also due to the shadowy and controversial privatization process, which caused most of its prosperous companies to go under.
In 1990, Serbian separatists from the Krajina
Krajina
-Etymology:In old-Croatian, this earliest geographical term appeared at least from 10th century within the Glagolitic inscriptions in Chakavian dialect, e.g. in Baška tablet about 1105, and also in some subsequent Glagolitic texts as krayna in the original medieval meaning of inlands or mainlands...
region of Croatia just inland from Dalmatia
Dalmatia
Dalmatia is a historical region on the eastern coast of the Adriatic Sea. It stretches from the island of Rab in the northwest to the Bay of Kotor in the southeast. The hinterland, the Dalmatian Zagora, ranges from fifty kilometers in width in the north to just a few kilometers in the south....
sealed roads and effectively blocked Dalmatia from the rest of Croatia. A number of non-Serbs were expelled from the area and several Croatian policemen were killed resulting in the Dalmatian anti-Serb riots of May 1991. Serbs at that time accounted for about 15% of the population.
During the Croatian War of Independence
Croatian War of Independence
The Croatian War of Independence was fought from 1991 to 1995 between forces loyal to the government of Croatia—which had declared independence from the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia —and the Serb-controlled Yugoslav People's Army and local Serb forces, with the JNA ending its combat...
, Krajina rebels
Republic of Serbian Krajina
The Republic of Serbian Krajina was a self-proclaimed Serb entity within Croatia. Established in 1991, it was not recognized internationally. It formally existed from 1991 to 1995, having been initiated a year earlier via smaller separatist regions. The name Krajina means "frontier"...
and the Yugoslav People's Army
Yugoslav People's Army
The Yugoslav People's Army , also referred to as the Yugoslav National Army , was the military of the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia.-Origins:The origins of the JNA can...
(JNA) (at the time under Slobodan Milošević
Slobodan Milošević
Slobodan Milošević was President of Serbia and Yugoslavia. He served as the President of Socialist Republic of Serbia and Republic of Serbia from 1989 until 1997 in three terms and as President of the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia from 1997 to 2000...
's control) converged on the city and subjected it to artillery bombardment during Operation Coast-91 in which they tried to take control of northern Dalmatia.
Along with other Croatian towns in the area, Zadar was shelled sporadically for several years, resulting in damage to buildings and homes as well as UNESCO
UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations...
protected sites. A number of nearby towns and villages were also attacked, the most brutal being the Škabrnja massacre
Škabrnja massacre
Škabrnja massacre was a war crime committed by Serb Army forces during the Croatian War of Independence. On November 18, 1991, Serb paramilitaries, supported by the JNA, captured the village of Škabrnja and killed 25 Prisoners of war and 61 civilians over the next several days.-Before the...
in which 86 people were killed.
Connections with Zagreb
Zagreb
Zagreb is the capital and the largest city of the Republic of Croatia. It is in the northwest of the country, along the Sava river, at the southern slopes of the Medvednica mountain. Zagreb lies at an elevation of approximately above sea level. According to the last official census, Zagreb's city...
were severed for over a year. The only link between the north and south of the country was via the island of Pag
Pag (island)
Pag is a Croatian island in the northern Adriatic Sea. It is the fifth-largest island of the Croatian coast, and the one with the longest coastline....
. The siege
Siege
A siege is a military blockade of a city or fortress with the intent of conquering by attrition or assault. The term derives from sedere, Latin for "to sit". Generally speaking, siege warfare is a form of constant, low intensity conflict characterized by one party holding a strong, static...
of the city lasted from 1991 until January 1993 when Zadar and the surrounding area came under the control of Croatian forces and the bridge link with the rest of Croatia was reestablished in Operation Maslenica
Operation Maslenica
In early September, 1991, during the opening stages of the Croatian War of Independence, Serb-dominated units of the Knin Corps of the Yugoslav People's Army , under the command of Colonel Ratko Mladić and supported by the ethnic Serb Krajina militia, conducted offensive operations against areas...
. Attacks on the city continued until the end of the war
Operation Storm
Operation Storm is the code name given to a large-scale military operation carried out by Croatian Armed Forces, in conjunction with the Army of the Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina, to gain back control of parts of Croatia which had been claimed by separatist ethnic Serbs, since early...
in 1995.
Some of the countryside along the No. 8 highway running north east is still sectioned off due to land mine
Land mine
A land mine is usually a weight-triggered explosive device which is intended to damage a target—either human or inanimate—by means of a blast and/or fragment impact....
s.
Architecture
Zadar gained its urbanUrbanization
Urbanization, urbanisation or urban drift is the physical growth of urban areas as a result of global change. The United Nations projected that half of the world's population would live in urban areas at the end of 2008....
structure in Roman times; during the time of Julius Caesar
Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar was a Roman general and statesman and a distinguished writer of Latin prose. He played a critical role in the gradual transformation of the Roman Republic into the Roman Empire....
and Emperor Augustus
Augustus
Augustus ;23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14) is considered the first emperor of the Roman Empire, which he ruled alone from 27 BC until his death in 14 AD.The dates of his rule are contemporary dates; Augustus lived under two calendars, the Roman Republican until 45 BC, and the Julian...
, the town was fortified and the city walls with towers and gates were built. On the western side of the town were the forum
Forum (Roman)
A forum was a public square in a Roman municipium, or any civitas, reserved primarily for the vending of goods; i.e., a marketplace, along with the buildings used for shops and the stoas used for open stalls...
, the basilica
Basilica
The Latin word basilica , was originally used to describe a Roman public building, usually located in the forum of a Roman town. Public basilicas began to appear in Hellenistic cities in the 2nd century BC.The term was also applied to buildings used for religious purposes...
and the temple
Temple
A temple is a structure reserved for religious or spiritual activities, such as prayer and sacrifice, or analogous rites. A templum constituted a sacred precinct as defined by a priest, or augur. It has the same root as the word "template," a plan in preparation of the building that was marked out...
, while outside the town were the amphitheatre
Amphitheatre
An amphitheatre is an open-air venue used for entertainment and performances.There are two similar, but distinct, types of structure for which the word "amphitheatre" is used: Ancient Roman amphitheatres were large central performance spaces surrounded by ascending seating, and were commonly used...
and cemeteries
Cemetery
A cemetery is a place in which dead bodies and cremated remains are buried. The term "cemetery" implies that the land is specifically designated as a burying ground. Cemeteries in the Western world are where the final ceremonies of death are observed...
. The aqueduct
Aqueduct
An aqueduct is a water supply or navigable channel constructed to convey water. In modern engineering, the term is used for any system of pipes, ditches, canals, tunnels, and other structures used for this purpose....
which supplied the town with water is partially preserved. Inside the ancient town, a medieval town had developed with a series of churches and monasteries
Monastery
Monastery denotes the building, or complex of buildings, that houses a room reserved for prayer as well as the domestic quarters and workplace of monastics, whether monks or nuns, and whether living in community or alone .Monasteries may vary greatly in size – a small dwelling accommodating only...
being built.
During the Middle Ages
Middle Ages
The Middle Ages is a periodization of European history from the 5th century to the 15th century. The Middle Ages follows the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476 and precedes the Early Modern Era. It is the middle period of a three-period division of Western history: Classic, Medieval and Modern...
, Zadar fully gained its urban aspect, which has been maintained until today. In the first half of the 16th century Venice fortified the town with a new system of defensive walls on the side facing land. In the course of the century architectural building in the Renaissance
Renaissance
The Renaissance was a cultural movement that spanned roughly the 14th to the 17th century, beginning in Italy in the Late Middle Ages and later spreading to the rest of Europe. The term is also used more loosely to refer to the historical era, but since the changes of the Renaissance were not...
style was continued and defensive trenches (Foša) were also built. They were completely buried during the Italian occupation until that in 1873, under Austria
Austria
Austria , officially the Republic of Austria , is a landlocked country of roughly 8.4 million people in Central Europe. It is bordered by the Czech Republic and Germany to the north, Slovakia and Hungary to the east, Slovenia and Italy to the south, and Switzerland and Liechtenstein to the...
n rule, the ramparts of Zadar were converted from fortifications into elevated promenades commanding extensive seaward and landward views, thus being the wall lines preserved; of its four old gates one, the Porta Marina, incorporates the relics of a Roman arch, and another, the Porta di Terraferma, was designed in the 16th century by the Veronese artist Michele Sanmicheli. In the bombardments during the Second World War entire blocks were destroyed, but some structures survived.

- Roman ForumForum (Roman)A forum was a public square in a Roman municipium, or any civitas, reserved primarily for the vending of goods; i.e., a marketplace, along with the buildings used for shops and the stoas used for open stalls...
- the largest on the eastern side of the Adriatic, founded by the first Roman Emperor AugustusAugustusAugustus ;23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14) is considered the first emperor of the Roman Empire, which he ruled alone from 27 BC until his death in 14 AD.The dates of his rule are contemporary dates; Augustus lived under two calendars, the Roman Republican until 45 BC, and the Julian...
, as shown by two stone inscriptions about its completion dating from the 3rd century. - Most Roman remains were used in the construction of the fortifications, but two squares are embellished with lofty marble columns; a Roman tower stands on the eastern side of the town; and some remains of a Roman aqueductRoman aqueductThe Romans constructed numerous aqueducts to serve any large city in their empire, as well as many small towns and industrial sites. The city of Rome had the largest concentration of aqueducts, with water being supplied by eleven aqueducts constructed over a period of about 500 years...
may be seen outside the ramparts.
The chief interest of Zadar lies in its churches.
- St Donatus'Saint Donatus of ZadarSaint Donatus was an Irishman who became a Dalmatian bishop and a diplomat of the city of Zadar....
Church - a monumental round building from the 9th century in pre-Romanesque style, traditionally but erroneously said to have been erected on the site of a temple of Juno. It is the most important preserved structure of its period in Dalmatia; the massive dome of the rotundaRotunda (architecture)A rotunda is any building with a circular ground plan, sometimes covered by a dome. It can also refer to a round room within a building . The Pantheon in Rome is a famous rotunda. A Band Rotunda is a circular bandstand, usually with a dome...
is surrounded by a vaulted gallery in two stories which also extends around the three apses to the east. The church treasury contains some of the finest Dalmatian metalwork; notably the pastoral staff of Bishop Valaresso (1460). - St. Anastasia's CathedralCathedral of St. Anastasia, ZadarThe Cathedral of St. Anastasia is a Roman Catholic cathedral in Zadar, Croatia. It is the seat of the Archdiocese of Zadar.Today's cathedral was built in the Romanesque style. It is the largest church in all of Dalmatia...
(Croatian: Sv. Stošija), basilica in RomanesqueRomanesque architectureRomanesque architecture is an architectural style of Medieval Europe characterised by semi-circular arches. There is no consensus for the beginning date of the Romanesque architecture, with proposals ranging from the 6th to the 10th century. It developed in the 12th century into the Gothic style,...
style built in the 12th to 13th century (high Romanesque style), the largest cathedral in Dalmatia. - The churches of St. ChrysogonusSaint ChrysogonusSaint Chrysogonus is a saint and martyr of ancient Rome venerated by the Roman Catholic Church and the Orthodox Church.-Life:Chrysogonus was martyred at Aquileia, probably during the Persecution of Diocletian, was buried there, and publicly venerated by the faithful of that region. He is the...
and St. Simeon, where the silver ark or reliquary of St. Simeon (1380) is located, are also fine architectural examples in the Romanesque style. - St. Krševan's Church - monumental Romanesque church of very fine proportions and refined Romanesque ornaments.
- St. Elijah's Church (Croatian: Sv. Ilija)
- St. Francis' Church, gothic styled church, site of the signing of the Zadar Peace Treaty 1358
- Five Wells Square
- St. Mary's Church, which retains a fine Romanesque campanileCampanileCampanile is an Italian word meaning "bell tower" . The term applies to bell towers which are either part of a larger building or free-standing, although in American English, the latter meaning has become prevalent.The most famous campanile is probably the Leaning Tower of Pisa...
from 1105, belongs to a Benedictine Convent founded in 1066 by a noblewoman of Zadar by the name of Cika with The Permanent Ecclesiastical Art Exhibition "The Gold and Silver of Zadar"
Other architectural landmarks:
- Citadel - built in 1409, southwest of the Land gate, it has remained the same to this day.
- The Land Gate - built to a design by the Venetian architect Michele Sanmicheli in 1543
- The unique sea organSea organThe Sea organ is an architectural object located in Zadar, Croatia and an experimental musical instrument which plays music by way of sea waves and tubes located underneath a set of large marble steps. The waves create somewhat random but harmonic sounds...
- The Great Arsenal http://www.arsenalzadar.com
- Among the other chief buildings are the Loggia del Comune, rebuilt in 1565, and containing a public library; the old palace of the priors, now the governor's residence; and the episcopal palaces.
Culture
The first university of Zadar was mentioned in writing as early as in 1396 and it was a part of a DominicanDominican Order
The Order of Preachers , after the 15th century more commonly known as the Dominican Order or Dominicans, is a Catholic religious order founded by Saint Dominic and approved by Pope Honorius III on 22 December 1216 in France...
monastery. It closed in 1807.
Zadar was, along with Split
Split (city)
Split is a Mediterranean city on the eastern shores of the Adriatic Sea, centered around the ancient Roman Palace of the Emperor Diocletian and its wide port bay. With a population of 178,192 citizens, and a metropolitan area numbering up to 467,899, Split is by far the largest Dalmatian city and...
and Dubrovnik
Dubrovnik
Dubrovnik is a Croatian city on the Adriatic Sea coast, positioned at the terminal end of the Isthmus of Dubrovnik. It is one of the most prominent tourist destinations on the Adriatic, a seaport and the centre of Dubrovnik-Neretva county. Its total population is 42,641...
, one of the centres of the development of Croatian literature
Croatian literature
Croatian literature is a definition given to the compilation of novels, dramas, short stories, poems and other various work of written kind entirely attributed to the medieval and modern culture of the Croats and the Croatian language....
.
The 15th and 16th centuries were marked by important activities of Croatians writing in the national language: Jerolim Vidolić, Petar Zoranić
Petar Zoranic
Petar Zoranić was a Croatian Renaissance writer from Zadar.He is most important as the author of Planine, the first Croatian novel. Pastoral in nature, the novel shows influence of Virgil, Ovid, Dante Alighieri, Francesco Petrarca and Giovanni Boccaccio. The novel was written in 1538 and published...
(who wrote the first Croatian novel, Planine
Planine
Planine is the title of the first Croatian novel, written by Petar Zoranić in 1536 and published posthumously in Venice in 1569....
), Brne Karnarutić
Brne Karnarutic
Brne Karnarutić was Croatian Renaissance poet and writer.He was born in Zadar probably in 1515 as a descent of old noble family. After schooling in Zadar he studied law, probably in Padua...
, Juraj Baraković
Juraj Barakovic
Juraj Baraković is a Croatian Renaissance poet from Zadar.He wrote several distinguished pieces , but one work excels in his literary opus: complicated and the most explicitly manneristic epic in 13 books "Vila slovinka"...
, Šime Budinić.
Under French rule (1806–1810), the first Dalmatian newspaper Kraglski Dalmatin - Il Regio Dalmata was published in Zadar. It was printed in Italian and Croatian; this last used for the first time in a newspaper.
In the second half of the 19th century, Zadar was a centre of the movement for the cultural and national revivals in Dalmatia (Italian and Croatian).
Today Zadar's cultural institutions include:
- The Croatian Theatre House
- The National Museum
- The Archaeological Museum (established in 1830)
- The University of ZadarUniversity of ZadarThe University of Zadar is a university located in Zadar, Croatia. It was founded in 2002.- University Departments :The University of Zadar is entirely integrated university, consisting at present of over 20 departments:...
(founded in 1396, active until 1807 and refounded in 2002) - The Maritime Museum
- Permanent Exhibition of Sacral Art
- Croatian Singing Musical Society Zoranić (established 1885)
- Musical Evenings in St. DonatusMusical Evenings in St. DonatusMusical evenings in St. Donatus in Zadar, Croatia is an international music festival, it has been held since 1960 at St. Donatus Church and at other historical locations of the city of Zadar. Performing are renowned musicians from Croatia and abroad....
http://www.donat-festival.com (established 1961) - International Choirs Competition (established 1997)
- Arsenal Zadar http://www.arsenalzadar.com
Government
The administrative area of the City of Zadar includes the nearby villages of Babindub, Crno, KožinoKožino
Kožino is a small village located 9 km northwest of Zadar, in northern Dalmatia, Croatia.The parish church of St. Michael the Archangel was built in 1522....
and Petrčane, as well as the islands of Ist
Ist (island)
Ist is a small island off the Dalmatian coast of Croatia. The closest city to Ist is Zadar. The island has an area of 9.65 km2. Ist is located between the islands of Škarda and Molat....
, Iž
Iž
Iž is an island in the Zadar Archipelago in the Croatian part of Adriatic Sea. It is situated between Ugljan on the north-east and Dugi otok on the south-west and is about an hour's ferry ride from Zadar. It has an area of 17.59 km² and a population of 557. It's mineralogy is composed of...
, Molat, Olib
Olib
Olib is an island in northern Dalmatia, located northwest of Zadar, southwest of Pag, southeast of Lošinj and just east of Silba. The population is 147.-History:...
, Premuda
Premuda
Premuda is a little island in Croatia, off the northern Adriatic coast. It belongs to the north Dalmatian islands which are situated north-west from the county center Zadar. Premuda is approximately 10 km long, up to 1 km wide, and has an area of 9.2 square kilometers...
, Rava
Rava (island)
Rava is an island in the Croatian part of the Adriatic Sea. It is situated in the Zadar archipelago, between Iž and Dugi Otok, from Zadar. Its area is 3.6 km2, and it has a population of 98 . The only settlements on the island are Vela Rava and Mala Rava. The coast of the island is very indented...
and Silba
Silba
Silba is an island in Croatia, northern Dalmatia, south-east of Lošinj, between the islands of Premuda and Olib. It has a Mediterranean climate with 2570 hours a year of sunshine...
. The total city area, including the islands, covers 194 km2.
Zadar is divided into 21 local districts: Arbanasi, Bili Brig, Bokanjac, Brodarica, Crvene Kuće, Diklo, Dračevac, Gaženica, Jazine I, Jazine II, Maslina, Novi Bokanjac, Poluotok, Ploča, Puntamika, Ričina, Smiljevac, Stanovi, Vidikovac, Višnjik, Voštarnica.
Population
Zadar is the fifth largest city in Croatia and the second largest in Dalmatia, with a population of 75,082 according to the 2011 census. According to the 2001 census, 93% of its citizens are ethnic Croats.Economy
Major industries include tourism, traffic, seaborne trade, agriculture, fishing and fish farming activities, metal manufacturing and mechanical engineering industry, chemicals and non-metal industry and banking. The headquarters of the following companies are located in Zadar:- Maraska (food industry)
- Adria, Mardešić (fish production)
- Tankerska plovidba Zadar (shipping company)
- SAS (machine tools)
- Aluflexpack
- Arsenal Holdings http://www.arsenalholdings.com (Tourism)
The farmland just northeast of Zadar, Ravni Kotari, is a well known source of marasca cherries
Cherry
The cherry is the fruit of many plants of the genus Prunus, and is a fleshy stone fruit. The cherry fruits of commerce are usually obtained from a limited number of species, including especially cultivars of the wild cherry, Prunus avium....
. Distilleries in Zadar have produced Maraschino
Maraschino
Maraschino .The liqueur's distinctive flavor comes from the Marasca cherries, and the crushed cherry pits lend an almond-like flavor to Maraschino...
since the 16th century.
Transportation
In the 20th century, roads became more important than sea routes, but Zadar remained an important traffic point. The main road along the Adriatic passes through the city. In the immediate vicinity, there is the Zagreb-Dubrovnik highwayA1 (Croatia)
The A1 motorway is the longest motorway in Croatia spanning . As it connects Zagreb, the nation's capital, to Split, the second largest city in the country and the largest city in Dalmatia, the motorway represents a major north–south transportation corridor in Croatia and a significant part of the...
, finished up to Split in 2005. Zadrans can access to the highway by two interchanges: Zadar 1 exit in the north and Zadar 2 highway hub near Zemunik in the south. The southern interchange is connected to Zadar port of Gaženica
Gaženica
Gaženica is a suburb of Zadar, Croatia, located about 3 miles southeast from the city center, by the Adriatic Sea. It is connected by the D424 highway.-Luka Gaženica:Gaženica is location of the commercial port of the city of Zadar—Port of Gaženica...
by the D424 expressway. Since 1966, a railway has linked Zadar with Knin
Knin
Knin is a historical town in the Šibenik-Knin county of Croatia, located near the source of the river Krka at , in the Dalmatian hinterland, on the railroad Zagreb–Split. Knin rose to prominence twice in history, as a one-time capital of both the Kingdom of Croatia and briefly of the...
, where it joins the main railway from Zagreb to Split. It has an international sea line to Ancona in Italy. There is a plan for an "Adriatic Railway" line linking Zadar with Gospić
Gospic
Gospić is a town in the mountainous and sparsely populated region of Lika, Croatia. It is the administrative centre of Lika-Senj county. Gospić is located near the Lika River in the middle of a karst field....
and Split. Zadar International Airport is located in Zemunik, around 14 km to the east of Zadar and accessible via the expressway. The airport is experiencing year on year an average of 30% increase in passenger traffic mainly due to arrivals of lowcost carriers (Ryanair
Ryanair
Ryanair is an Irish low-cost airline. Its head office is at Dublin Airport and its primary operational bases at Dublin Airport and London Stansted Airport....
, Germanwings
Germanwings
Germanwings GmbH is a low-cost airline based in Cologne, Germany, and is wholly owned by Lufthansa. Cologne Bonn Airport, Stuttgart Airport and Berlin-Schönefeld Airport are the important hubs in the airline's network of approximately 70 destinations...
, Intersky
InterSky
Intersky Luftfahrt GmbH is an airline headquartered in Bregenz, Austria, operating scheduled services from its base at Friedrichshafen Airport, Germany, to major cities in Germany, Austria and Switzerland, as well as seasonal holiday flights to the Mediterranean.- History :Intersky was established...
, Danubewings
DanubeWings
Danube Wings is brand name for passenger air transport services operated by Vip Wings, a.s. It is the flag carrier and major airline of Slovakia. Its main hub is M. R. Štefánik Airport. The brand belongs to VIP WINGS which is the AOC holder and holder of the licences. VIP WINGS was created from VIP...
, JobAir) connecting Zadar from the end of March through October with over 20 cities throughout Europe. Currently, the arrivals and departures terminal building is expanding to accommodate the increasing number of passengers, with completion scheduled for March 2011. The extension of the runway for an additional 500m from the current 2500m is scheduled for late 2011.
Sports

KK Zadar
KK Zadar is a Croatian professional basketball team from the city of Zadar playing in the A-1 Liga.Zadar is the place where Croatian basketball was born in 1930. Zadar's reputation has been of a basketball hotbed with a team that can capture trophies at any given moment...
, and the football club NK Zadar
NK Zadar
NK Zadar is a Croatian football club based in Zadar, a city on the Adriatic coast. The club was founded in 1945.Josip Skoblar, Đovani Roso, Dado Pršo and Luka Modrić, are among their most notable former players....
. The bowling club Kuglački klub Zadar is also very successful. Zadar is also the hometown of Croatian football player Luka Modrić
Luka Modric
Luka Modrić is a Croatian footballer who plays for Tottenham Hotspur and for the Croatia national football team.Modrić's childhood coincided with the Croatian War of Independence. After showing promise in hometown club Zadar's youth team, he was signed by Dinamo Zagreb as a teenager in 2002. His...
.
Krešimir Ćosić Hall is new multi-use indoor arena, built and completed in May 2008 with a capacity for 9,200 people, named after Krešimir Ćosić
Krešimir Cosic
Krešimir Ćosić was a Croatian professional basketball player who represented Yugoslavia internationally, a member of FIBA Hall of Fame and Basketball Hall of Fame...
, "a legend" of Zadar basketball game. Until then KK Zadar is played in Jazine Basketball Hall
Jazine Basketball Hall
Jazine Basketball Hall is an indoor sporting arena located in Zadar, Croatia. The capacity of the arena is 3,000 people and opened in 1968 after a construction period of 70 days. It was home to the KK Zadar basketball team up until 2008.-External links:*...
.
Twin towns — Sister cities
Zadar is twinnedTown twinning
Twin towns and sister cities are two of many terms used to describe the cooperative agreements between towns, cities, and even counties in geographically and politically distinct areas to promote cultural and commercial ties.- Terminology :...
, or maintains cultural, economic and educational ties with: Dundee
Dundee
Dundee is the fourth-largest city in Scotland and the 39th most populous settlement in the United Kingdom. It lies within the eastern central Lowlands on the north bank of the Firth of Tay, which feeds into the North Sea...
, United Kingdom
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
Reggio Emilia
Reggio Emilia
Reggio Emilia is an affluent city in northern Italy, in the Emilia-Romagna region. It has about 170,000 inhabitants and is the main comune of the Province of Reggio Emilia....
, Italy
Italy
Italy , officially the Italian Republic languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Italy's official name is as follows:;;;;;;;;), is a unitary parliamentary republic in South-Central Europe. To the north it borders France, Switzerland, Austria and...
Romans-sur-Isère
Romans-sur-Isère
Romans-sur-Isère or Romans is a commune in the Drôme department in southeastern France.-Geography:...
, France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
Fürstenfeldbruck
Fürstenfeldbruck
Fürstenfeldbruck is a town in Bavaria, Germany. It is the capital of the district of Fürstenfeldbruck. it has a population of 35,494. Since the 1930s, Fürstenfeldbruck has had an air force base....
, Germany
Germany
Germany , officially the Federal Republic of Germany , is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km2 and has a largely temperate seasonal climate...
Székesfehérvár
Székesfehérvár
Székesfehérvár is a city in central Hungary and is the 9th largest in the country. Located around southwest of Budapest. It is inhabited by 101,973 people , with 136,995 in the Székesfehérvár Subregion. The city is the centre of Fejér county and the regional centre of Central Transdanubia...
, Hungary
Hungary
Hungary , officially the Republic of Hungary , is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is situated in the Carpathian Basin and is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine and Romania to the east, Serbia and Croatia to the south, Slovenia to the southwest and Austria to the west. The...
Padua
Padua
Padua is a city and comune in the Veneto, northern Italy. It is the capital of the province of Padua and the economic and communications hub of the area. Padua's population is 212,500 . The city is sometimes included, with Venice and Treviso, in the Padua-Treviso-Venice Metropolitan Area, having...
, Italy
Italy
Italy , officially the Italian Republic languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Italy's official name is as follows:;;;;;;;;), is a unitary parliamentary republic in South-Central Europe. To the north it borders France, Switzerland, Austria and...
Iquique
Iquique
Iquique is a port city and commune in northern Chile, capital of both the Iquique Province and Tarapacá Region. It lies on the Pacific coast, west of the Atacama Desert and the Pampa del Tamarugal. It had a population of 216,419 as of the 2002 census...
, Chile
Chile
Chile ,officially the Republic of Chile , is a country in South America occupying a long, narrow coastal strip between the Andes mountains to the east and the Pacific Ocean to the west. It borders Peru to the north, Bolivia to the northeast, Argentina to the east, and the Drake Passage in the far...
Banská Bystrica
Banská Bystrica
Banská Bystrica is a key city in central Slovakia located on the Hron River in a long and wide valley encircled by the mountain chains of the Low Tatras, the Veľká Fatra, and the Kremnica Mountains. With 81,281 inhabitants, Banská Bystrica is the sixth most populous municipality in Slovakia...
, Slovakia
Slovakia
The Slovak Republic is a landlocked state in Central Europe. It has a population of over five million and an area of about . Slovakia is bordered by the Czech Republic and Austria to the west, Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east and Hungary to the south...
, since 1995
See also
- Archdiocese of Zadar
- Bombing of Zadar in World War II
- History of CroatiaHistory of CroatiaCroatia first appeared as a duchy in the 7th century and then as a kingdom in the 10th century. From the 12th century it remained a distinct state with its ruler and parliament, but it obeyed the kings and emperors of various neighboring powers, primarily Hungary and Austria. The period from the...
- History of DalmatiaHistory of DalmatiaThe History of Dalmatia concerns the history of the eastern coast of the Adriatic Sea and its inland regions, stretching from the 2nd century BC up to the present....
- Krešimir Ćosić Hall
- LiburniaLiburniaLiburnia in ancient geography was the land of the Liburnians, a region along the northeastern Adriatic coast in Europe, in modern Croatia, whose borders shifted according to the extent of Liburnian dominance at a given time between 11th and 1st century BC...
- Ottavio Missoni

