
Labiaplasty
Encyclopedia
Plastic surgery
Plastic surgery is a medical specialty concerned with the correction or restoration of form and function. Though cosmetic or aesthetic surgery is the best-known kind of plastic surgery, most plastic surgery is not cosmetic: plastic surgery includes many types of reconstructive surgery, hand...
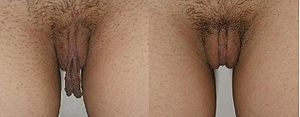
procedure for altering the labia minora
Labia minora
The labia minora , also known as the inner labia, inner lips, or nymphae, are two flaps of skin on either side of the human vaginal opening, situated between the labia majora...
and the labia majora
Labia majora
The labia majora are two prominent longitudinal cutaneous folds that extend downward and backward from the mons pubis to the perineum and form the lateral boundaries of the pudendal cleft, which contains the labia minora, interlabial sulci, clitoral hood, clitoral glans, frenulum clitoridis, the...
, the paired tissue structures bounding the vestibule of the vulva. The indications for the correction of labial hypertrophy are two-fold: (i) the correction of defect and deformity, and (ii) the cosmetic
Aesthetics
Aesthetics is a branch of philosophy dealing with the nature of beauty, art, and taste, and with the creation and appreciation of beauty. It is more scientifically defined as the study of sensory or sensori-emotional values, sometimes called judgments of sentiment and taste...
refinement of the pudendum femininum
Vulva
The vulva consists of the external genital organs of the female mammal. This article deals with the vulva of the human being, although the structures are similar for other mammals....
. Despite no formal medical definition of labia minora hypertrophy (length, width, girth), labiaplasty corrects the clinical conditions wherein a woman presents labia minora that are disproportionately greater than her labia majora; the labioplastic correction of the disproportions creates less asymmetrical labia minora that are functionally and aesthetically satisfactory to the woman. Labiaplasty corrections include clinical presentations of congenital defects and congenital abnormalities
Congenital abnormality
A congenital anomaly is a condition which is present at the time of birth which varies from the standard presentation....
, such as vaginal atresia
Vaginal atresia
Vaginal Atresia is a birth defect or congenital abnormality of the female genitourinary system that manifests itself in the absence of a vagina , or a deformed and nonfunctional vagina ....
(absent vaginal passage), Müllerian agenesis
Mullerian agenesis
Müllerian agenesis is a congenital malformation in women characterised by a failure of the müllerian ducts to develop, resulting in a missing uterus and fallopian tubes and variable malformations of the upper portion of the vagina. It is the second most common cause of primary amenorrhea after...
(malformed uterus and fallopian tubes), intersex conditions
Intersex
Intersex, in humans and other animals, is the presence of intermediate or atypical combinations of physical features that usually distinguish female from male...
(male and female sexual characteristics in a person), etc.; and the exterior cosmetic refinement of the vulvo-vaginal complex, to repair the tearing and stretching of the labia minora caused by the mechanical stresses of childbirth, accident, and age. Furthermore, in other surgical practice, within a male-to-female sexual reassignment vaginoplasty
Vaginoplasty
thumb|right|300px|Vaginoplasty: the pre-operative aspect , and the post-operative aspect of a [[Labiaplasty|labial reduction]].Vaginoplasty is a reconstructive plastic surgery procedure for correcting the defects and deformities of the vaginal canal and its mucous membrane, and of vulvo-vaginal...
operation for the creation of a neovagina, a labiaplasty procedure creates labia where once there were none.
Surgical anatomy of the vulva
The vulvo-vaginal complexThe external genitalia of a woman are collectively denoted the vulvo-vaginal complex
Vulva
The vulva consists of the external genital organs of the female mammal. This article deals with the vulva of the human being, although the structures are similar for other mammals....
, which comprises the labia majora
Labia majora
The labia majora are two prominent longitudinal cutaneous folds that extend downward and backward from the mons pubis to the perineum and form the lateral boundaries of the pudendal cleft, which contains the labia minora, interlabial sulci, clitoral hood, clitoral glans, frenulum clitoridis, the...
, the labia minora
Labia minora
The labia minora , also known as the inner labia, inner lips, or nymphae, are two flaps of skin on either side of the human vaginal opening, situated between the labia majora...
, the clitoris
Clitoris
The clitoris is a sexual organ that is present only in female mammals. In humans, the visible button-like portion is located near the anterior junction of the labia minora, above the opening of the urethra and vagina. Unlike the penis, which is homologous to the clitoris, the clitoris does not...
, the urethra
Urethra
In anatomy, the urethra is a tube that connects the urinary bladder to the genitals for the removal of fluids out of the body. In males, the urethra travels through the penis, and carries semen as well as urine...
, and the vagina
Vagina
The vagina is a fibromuscular tubular tract leading from the uterus to the exterior of the body in female placental mammals and marsupials, or to the cloaca in female birds, monotremes, and some reptiles. Female insects and other invertebrates also have a vagina, which is the terminal part of the...
. The fatty labia majora (the large outer lips) extend from the mons pubis
Mons pubis
In human anatomy or in mammals in general, the mons pubis , also known as the mons veneris or simply the mons, is the adipose tissue lying above the pubic bone of adult females, anterior to the pubic symphysis...
to the rectum
Rectum
The rectum is the final straight portion of the large intestine in some mammals, and the gut in others, terminating in the anus. The human rectum is about 12 cm long...
. The vascularized labia minora (the small inner lips) are within the labia majora; however, in some women, the minor lips are short and thin and hidden by the labia majora; and in some women, the labia minora are longer, thicker, and wider, and extend beyond the labia majora.
Composition
The labia minora consist of two (2) connective folds of flesh that contain some adipose tissue
Adipose tissue
In histology, adipose tissue or body fat or fat depot or just fat is loose connective tissue composed of adipocytes. It is technically composed of roughly only 80% fat; fat in its solitary state exists in the liver and muscles. Adipose tissue is derived from lipoblasts...
; at the front and upper portions of the pudendum femininum
Vulva
The vulva consists of the external genital organs of the female mammal. This article deals with the vulva of the human being, although the structures are similar for other mammals....
(vulva), the labia minora divide into two parts. The first part passes over the clitoris, and forms the prepuce of the clitoris (clitoral hood
Clitoral hood
In female human anatomy, the clitoral hood, , is a fold of skin that surrounds and protects the clitoral glans. It develops as part of the labia minora and is homologous with the foreskin in male genitals.-Variation:This is a protective hood of skin that covers the clitoral glans...
); the second part of the labia minora joins beneath the clitoris and forms the fourchette (labial frenulum), a transverse fold of tissue that occasionally unites the labia minora to the labia majora at their posterior extensions. The skin
Skin
-Dermis:The dermis is the layer of skin beneath the epidermis that consists of connective tissue and cushions the body from stress and strain. The dermis is tightly connected to the epidermis by a basement membrane. It also harbors many Mechanoreceptors that provide the sense of touch and heat...
and the mucosa of the labia minora are rich in sebaceous gland
Sebaceous gland
The sebaceous glands are microscopic glands in the skin that secrete an oily/waxy matter, called sebum, to lubricate and waterproof the skin and hair of mammals...
s and nerve endings
Nerve
A peripheral nerve, or simply nerve, is an enclosed, cable-like bundle of peripheral axons . A nerve provides a common pathway for the electrochemical nerve impulses that are transmitted along each of the axons. Nerves are found only in the peripheral nervous system...
, thus the labia are very sensitive to the touch. These folds of vulvo-vaginal skin have a core of connective, erectile tissue
Erectile tissue
Erectile tissue is tissue in the body that can become erect, usually by becoming engorged with blood.-Erectile tissue in the clitoris and penis:...
(analogous to the corpus spongiosum penis), and are covered by stratified, squamous epithelium
Epithelium
Epithelium is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. Epithelial tissues line the cavities and surfaces of structures throughout the body, and also form many glands. Functions of epithelial cells include secretion, selective...
— thus, the labia minora moisten and swell with extracellular fluid during sexual arousal. Furthermore, during urination
Urination
Urination, also known as micturition, voiding, peeing, weeing, pissing, and more rarely, emiction, is the ejection of urine from the urinary bladder through the urethra to the outside of the body. In healthy humans the process of urination is under voluntary control...
, the labia minora function to direct the urine stream away from the pudendum femininum.
Labial anatomic variation
The size, the shape, and the skin coloration of the labia minora
Labia minora
The labia minora , also known as the inner labia, inner lips, or nymphae, are two flaps of skin on either side of the human vaginal opening, situated between the labia majora...
vary according to the woman, thus, like most paired structures of the human body, the labia are not anatomically symmetrical — one labium minus (minor lip) usually is greater (longer, wider, thicker) than its pair — yet the asymmetry usually is not notable. Moreover, the length and the width of the labia minora determine if they protrude from, or are hidden by, the labia majora. Further increases in the sizes of the labia (majora and minora) occur when the woman is sexually aroused — in preparation for coitus — wherein the labia become engorged with blood and increase the labial diameters two-to-three times.
In the course of a woman’s life, her labia minora can become hypertrophied (over-sized) by the mechanical stresses (stretching and tearing) occurred during sexual intercourse, masturbation
Masturbation
Masturbation refers to sexual stimulation of a person's own genitals, usually to the point of orgasm. The stimulation can be performed manually, by use of objects or tools, or by some combination of these methods. Masturbation is a common form of autoeroticism...
, childbirth, lymphatic congestion (stasis), chronic dermatitis
Dermatitis
-Etymology:Dermatitis derives from Greek derma "skin" + -itis "inflammation" and genetic disorder.-Terminology:There are several different types of dermatitis. The different kinds usually have in common an allergic reaction to specific allergens. The term may describe eczema, which is also called...
, and the inflammation caused by urinary incontinence
Urinary incontinence
Urinary incontinence is any involuntary leakage of urine. It is a common and distressing problem, which may have a profound impact on quality of life. Urinary incontinence almost always results from an underlying treatable medical condition but is under-reported to medical practitioners...
. Labial hypertrophy can also be caused by the mechanical stresses inherent to the cultural practice of genital piercing
Genital piercing
Genital piercing is a form of body piercing and is considered a form of body modification. It involves piercing a part of the genitalia and subsequently inserting and keeping a foreign object in the opening until the wound heals. This forms a tunnel of skin around the foreign object, thus creating...
, the bearing of relatively heavy-weight metal ornaments attached through the perforated labium or labia, which is medically notable because bearing weight is not a usual anatomic function of the labia minora. Furthermore, over-sized labia minora can also be a genetically inherited
Heredity
Heredity is the passing of traits to offspring . This is the process by which an offspring cell or organism acquires or becomes predisposed to the characteristics of its parent cell or organism. Through heredity, variations exhibited by individuals can accumulate and cause some species to evolve...
anatomical feature of the woman’s vulva. The plastic surgery study Labiaplasty and Labia minora Reduction (2008) reported the occurrence of labia minora of like sizes (length, width, girth) in identical twin sisters treated for labial hypertrophy, which might indicate a genetic predisposition to developing over-sized labia minora.
Measures of the vulva
Because there is no formal, medical definition of labial hypertrophy (length, width, girth), nor a standardized method for grading the degree of hypertrophy present, the plastic surgeon and the woman determine the applicability of labial reduction to her case without a fixed anatomic reference. To the end of providing such a medical reference, the morphologic
Morphology (biology)
In biology, morphology is a branch of bioscience dealing with the study of the form and structure of organisms and their specific structural features....
study Female Genital Appearance: ‘Normality’ Unfolds (2005) reported the range of anatomic variations of the vulvo-vaginal complex of a 50-woman cohort (18–50 y/o, mean age 35.6 yrs.); the statistical variations of the pudendum femininum are:
| The vulvo-vaginal complex | Range of measures | Mean [Standard Deviation] |
|---|---|---|
| Clitoral Clitoris The clitoris is a sexual organ that is present only in female mammals. In humans, the visible button-like portion is located near the anterior junction of the labia minora, above the opening of the urethra and vagina. Unlike the penis, which is homologous to the clitoris, the clitoris does not... length (mm) |
5.0 – 35.0 | 19.1 [8.7] |
| Clitoral glans Clitoral glans The clitoral glans is an external portion of the clitoris.- Anatomy :It is covered by the clitoral hood, which is also external and attached to the labia minora... width (mm) |
3.0 – 10.0 | 5.5 [1.7] |
| Clitoris to urethra Urethra In anatomy, the urethra is a tube that connects the urinary bladder to the genitals for the removal of fluids out of the body. In males, the urethra travels through the penis, and carries semen as well as urine... (mm) |
16.0 – 45.0 | 28.5 [7.1] |
| Labia majora Labia majora The labia majora are two prominent longitudinal cutaneous folds that extend downward and backward from the mons pubis to the perineum and form the lateral boundaries of the pudendal cleft, which contains the labia minora, interlabial sulci, clitoral hood, clitoral glans, frenulum clitoridis, the... length (cm) |
7.0 – 12.0 | 9.3 [1.3] |
| Labia minora Labia minora The labia minora , also known as the inner labia, inner lips, or nymphae, are two flaps of skin on either side of the human vaginal opening, situated between the labia majora... length (mm) |
20 – 100 | 60.6 [17.2] |
| Labia minora width (mm) | 7.0 – 50.0 | 21.8 [9.4] |
| Perineum Perineum In human anatomy, the perineum is a region of the body including the perineal body and surrounding structures... length (mm) |
15.0 – 55.0 | 31.3 [8.5] |
| Vaginal Vagina The vagina is a fibromuscular tubular tract leading from the uterus to the exterior of the body in female placental mammals and marsupials, or to the cloaca in female birds, monotremes, and some reptiles. Female insects and other invertebrates also have a vagina, which is the terminal part of the... length (cm) |
6.5 – 12.5 | 9.6 [1.5] |
| Tanner Stage (n) | IV | 4.0 |
| Tanner Stage (n) | V | 46 |
| Color of the genital area compared to the surrounding skin (n) |
Same color | 9.0 |
| Color of the genital area compared to the surrounding skin (n) |
Darker color | 41 |
| Rugosity Rugosity Rugosity, fr, is a measure of small-scale variations or amplitude in the height of a surface,f_r = A_r/A_gwhere Ar is the real surface area and Ag is the geometric surface area.... of the labia (n) |
Smooth (unwrinkled) | 14 |
| Rugosity of the labia (n) | Moderately wrinkled | 34 |
| Rugosity of the labia (n) | Markedly wrinkled | 2.0 |
Labial hypertrophy

The causes of labial hypertrophy, the over-development of the labia minora
Labia minora
The labia minora , also known as the inner labia, inner lips, or nymphae, are two flaps of skin on either side of the human vaginal opening, situated between the labia majora...
, are etiologically
Etiology
Etiology is the study of causation, or origination. The word is derived from the Greek , aitiologia, "giving a reason for" ....
varied, and can derive from factors such as the woman having been born with over-sized labia (genetic inheritance), or having been caused by the mechanical stresses (stretching, pulling, and tearing) characteristic to coitus (sexual intercourse), masturbation
Masturbation
Masturbation refers to sexual stimulation of a person's own genitals, usually to the point of orgasm. The stimulation can be performed manually, by use of objects or tools, or by some combination of these methods. Masturbation is a common form of autoeroticism...
, childbirth, urinary incontinence
Urinary incontinence
Urinary incontinence is any involuntary leakage of urine. It is a common and distressing problem, which may have a profound impact on quality of life. Urinary incontinence almost always results from an underlying treatable medical condition but is under-reported to medical practitioners...
, lymphatic congestion
Lymphedema
Lymphedema , also known as lymphatic obstruction, is a condition of localized fluid retention and tissue swelling caused by a compromised lymphatic system....
(stasis), chronic dermatitis
Dermatitis
-Etymology:Dermatitis derives from Greek derma "skin" + -itis "inflammation" and genetic disorder.-Terminology:There are several different types of dermatitis. The different kinds usually have in common an allergic reaction to specific allergens. The term may describe eczema, which is also called...
, granulomatous disease
Granuloma
Granuloma is a medical term for a tiny collection of immune cells known as macrophages. Granulomas form when the immune system attempts to wall off substances that it perceives as foreign but is unable to eliminate. Such substances include infectious organisms such as bacteria and fungi as well as...
, myelodysplastic disease
Myelodysplastic syndrome
The myelodysplastic syndromes are a diverse collection of hematological medical conditions that involve ineffective production of the myeloid class of blood cells....
, and by the application of topical and systematic hormones.
In some women, vaginal childbirth causes the development of labial hypertrophy by means of the formation of a hematoma
Hematoma
A hematoma, or haematoma, is a localized collection of blood outside the blood vessels, usually in liquid form within the tissue. This distinguishes it from an ecchymosis, which is the spread of blood under the skin in a thin layer, commonly called a bruise...
during the parturition. Moreover, the cultural practice of genital piercing
Genital piercing
Genital piercing is a form of body piercing and is considered a form of body modification. It involves piercing a part of the genitalia and subsequently inserting and keeping a foreign object in the opening until the wound heals. This forms a tunnel of skin around the foreign object, thus creating...
can cause labial hypertrophy and asymmetry, because of the heavy weight of the metal ornaments inserted to the labium or to the labia. Furthermore, the report Labiaplasty and Labia minora Reduction (2008), indicated the occurrence of labia minora of the same size in identical-twin women treated for labial hypertrophy, which indicated a possible genetic determination
Heredity
Heredity is the passing of traits to offspring . This is the process by which an offspring cell or organism acquires or becomes predisposed to the characteristics of its parent cell or organism. Through heredity, variations exhibited by individuals can accumulate and cause some species to evolve...
of the size of the labia minora.
Clinical definition
Therapeutically, because there is no formal medical definition of labial hypertrophy, nor a standardized method for grading the degree of hypertrophy present in the labia minora of the woman (patient), the plastic surgeon gives especial consideration to the anatomic particulars of the vulvo-vaginal complex of the woman. Likewise, the surgeon must give especial consideration to the wide variance among women’s perceptions of the ideal genital body image
Body image
Body image refers to a person's perception of the aesthetics and sexual attractiveness of their own body. The phrase body image was first coined by the Austrian neurologist and psychoanalyst Paul Schilder in his masterpiece The Image and Appearance of the Human Body...
— what the woman (patient) considers and does not consider to be an aesthetically
Aesthetics
Aesthetics is a branch of philosophy dealing with the nature of beauty, art, and taste, and with the creation and appreciation of beauty. It is more scientifically defined as the study of sensory or sensori-emotional values, sometimes called judgments of sentiment and taste...
normal and proportionate vulva. (See: Body dysmorphic disorder
Body dysmorphic disorder
Body Dysmorphic Disorder is a type of mental illness, a somatoform disorder, wherein the affected person is exclusively concerned with body image, manifested as excessive concern about and preoccupation with a perceived defect of his or her physical features...
and Body image
Body image
Body image refers to a person's perception of the aesthetics and sexual attractiveness of their own body. The phrase body image was first coined by the Austrian neurologist and psychoanalyst Paul Schilder in his masterpiece The Image and Appearance of the Human Body...
)
Pathophysiology
- The dimensions of over-sized labia minora are established by:
- horizontally measuring the size of each labium minus, from the midline.
- vertically measuring the size of each labium minus the between the base and the free-edge of the labium.
- applying a 3–5 cm range of measure as “hypertrophy” of the labia minora.
- The degree of labial hypertrophy is characterized as:
- No hypertrophy — the labia minora are concealed within, or extend to, the free edge of the labia majora.
- Mild-to-moderate hypertrophy — the labia minora extend approximately 1–3 cm beyond the free edge of the labia majora.
- Severe hypertrophy — The labia minora extend an approximate distance >3.0 cm beyond the free edge of the labia majora.
Presentation
The woman seeking the surgical reduction of her over-sized labia minora often presents labial asymmetry that causes her awkward vulvo-vaginal
Vulva
The vulva consists of the external genital organs of the female mammal. This article deals with the vulva of the human being, although the structures are similar for other mammals....
hygiene (e.g. toilet-paper bits attaching to the labia); the catching of the labia in garment-zipper closures; pubic discomfort when wearing tight clothes; pubic-area pain when practicing sport (bicycling, running, et cetera); either a disrupted or a diffused urinary stream; and dyspareunia
Dyspareunia
Dyspareunia is painful sexual intercourse, due to medical or psychological causes. The symptom is reported almost exclusively by women, although the problem can also occur in men. The causes are often reversible, even when long-standing, but self-perpetuating pain is a factor after the original...
(painful sexual intercourse). In the case of labial asymmetry, wherein one labium minus is longer, wider, and thicker than the corresponding labium minus, only the over-sized lip is reduced in order to match the smaller lip. Labioplasty can be safely performed any time after sexual maturity (to a woman who is minimally 18 years of age); it can be performed either before or after pregnancy
Pregnancy
Pregnancy refers to the fertilization and development of one or more offspring, known as a fetus or embryo, in a woman's uterus. In a pregnancy, there can be multiple gestations, as in the case of twins or triplets...
, in order to minimze hormonal interference with her body’s capacity to heal a surgical wound. Yet, labiaplasty is not performed upon a woman who is menstruating
Menstruation
Menstruation is the shedding of the uterine lining . It occurs on a regular basis in sexually reproductive-age females of certain mammal species. This article focuses on human menstruation.-Overview:...
, lest she risk post-operative infection
Infection
An infection is the colonization of a host organism by parasite species. Infecting parasites seek to use the host's resources to reproduce, often resulting in disease...
of the surgical-incision site(s). Generally, the woman’s most common complaint of self perception is that, when observed in the standing position, her labia minora
Labia minora
The labia minora , also known as the inner labia, inner lips, or nymphae, are two flaps of skin on either side of the human vaginal opening, situated between the labia majora...
protrude too much beyond the labia majora
Labia majora
The labia majora are two prominent longitudinal cutaneous folds that extend downward and backward from the mons pubis to the perineum and form the lateral boundaries of the pudendal cleft, which contains the labia minora, interlabial sulci, clitoral hood, clitoral glans, frenulum clitoridis, the...
, which physical condition often leads to low self esteem, and subsequent difficulty in achieving emotional and sexual intimacy in her private life. (See: Sex appeal
Sexual attraction
Sexual attractiveness or sex appeal refers to an individual's ability to attract the sexual or erotic interest of another person, and is a factor in sexual selection or mate choice. The attraction can be to the physical or other qualities or traits of a person, or to such qualities in the context...
and Body dysmorphic disorder
Body dysmorphic disorder
Body Dysmorphic Disorder is a type of mental illness, a somatoform disorder, wherein the affected person is exclusively concerned with body image, manifested as excessive concern about and preoccupation with a perceived defect of his or her physical features...
)
The patient
IndicationsI. Over-sized labia
The woman afflicted with labial hypertrophy presents labia minora
Labia minora
The labia minora , also known as the inner labia, inner lips, or nymphae, are two flaps of skin on either side of the human vaginal opening, situated between the labia majora...
that are disproportionately over-sized in relation to the size of the labia majora
Labia majora
The labia majora are two prominent longitudinal cutaneous folds that extend downward and backward from the mons pubis to the perineum and form the lateral boundaries of the pudendal cleft, which contains the labia minora, interlabial sulci, clitoral hood, clitoral glans, frenulum clitoridis, the...
, which to her have an aesthetically displeasing appearance and cause her problematic hygiene, commonly reported as a diffused or a disrupted urinary stream; chronic irritation of the pudendal skin; painful sexual intercourse; and pubic pain when wearing tight clothes. Anatomically, like all the paired structures of the human body, it is uncommon for the labia minora to be perfectly symmetrical. Usually, the size discrepancy is slight, yet some women present one labium minus (minor lip) considerably larger (longer, wider, thicker) than its pair; some women also present redundant folding (either unilateral or bilateral webbing) between the labia majora and the labia minora that can be surgically resolved.
Therapy
- Medical — Labial hypertrophy, the over-development of the vaginal lips, is not managed medically.
- Surgical — The woman’s specific clinical indications determine the appropriate labiaplasty technique. The correction of hypertrophied labia minora can be performed upon a patient either as a discrete labiaplasty (single surgery procedure), or in conjunction with a gynecologic surgery procedure, or in conjunction with a cosmetic surgery procedure (genitoplasty).
Contraindications
- Absolute — There are no absolute contraindications to labioplastic surgery, either for altering or for reducing the labia minora or the labia majora.
- Relative — Labial reduction surgery is relatively contraindicated for the woman who has an active gynecological disease (i.e. an infectionInfectionAn infection is the colonization of a host organism by parasite species. Infecting parasites seek to use the host's resources to reproduce, often resulting in disease...
or a neoplastic malignancy); for the woman who is a tobacco smokerTobacco smokingTobacco smoking is the practice where tobacco is burned and the resulting smoke is inhaled. The practice may have begun as early as 5000–3000 BCE. Tobacco was introduced to Eurasia in the late 16th century where it followed common trade routes...
unwilling to quit (either temporarily or permanently) in order to optimize the capability of her body to heal a surgical-incision wound; and for the woman who holds unrealistic aestheticAestheticsAesthetics is a branch of philosophy dealing with the nature of beauty, art, and taste, and with the creation and appreciation of beauty. It is more scientifically defined as the study of sensory or sensori-emotional values, sometimes called judgments of sentiment and taste...
goals (ideal self-image and body imageBody imageBody image refers to a person's perception of the aesthetics and sexual attractiveness of their own body. The phrase body image was first coined by the Austrian neurologist and psychoanalyst Paul Schilder in his masterpiece The Image and Appearance of the Human Body...
), and expectations for the outcome. Such a woman (patient) should either be psychologically counselled or excluded from labioplastic surgery.
II. Sexual reassignment
In sexual reassignment surgery, in the case of the male-to-female transgender
Trans woman
A trans woman is a male-to-female transsexual or transgender person and the term trans woman is preferred by some individuals over various medical terms. Other non-medical terms include t-girl, tg-girl and ts-girl...
patient, labiaplasty usually is the second stage of a two-stage vaginoplasty
Vaginoplasty
thumb|right|300px|Vaginoplasty: the pre-operative aspect , and the post-operative aspect of a [[Labiaplasty|labial reduction]].Vaginoplasty is a reconstructive plastic surgery procedure for correcting the defects and deformities of the vaginal canal and its mucous membrane, and of vulvo-vaginal...
operation, wherein labiaplastic techniques are applied to create labia minora
Labia minora
The labia minora , also known as the inner labia, inner lips, or nymphae, are two flaps of skin on either side of the human vaginal opening, situated between the labia majora...
and a clitoral hood
Clitoris
The clitoris is a sexual organ that is present only in female mammals. In humans, the visible button-like portion is located near the anterior junction of the labia minora, above the opening of the urethra and vagina. Unlike the penis, which is homologous to the clitoris, the clitoris does not...
. In a male-to-female procedure, the labiaplasty usually is performed months after the first-stage of the vaginoplasty. As required by the (transgender) woman’s indications, after a one-stage vaginoplasty, the labiaplasty — which creates the labia majora and the labia minora — can be an elective surgery procedure for refining the aesthetics of the woman’s vulvo-vaginal complex
Vulva
The vulva consists of the external genital organs of the female mammal. This article deals with the vulva of the human being, although the structures are similar for other mammals....
. (See: Male-to-female sex reassignment surgery
Sex reassignment surgery male-to-female
Sex reassignment surgery from male to female involves reshaping the male genitals into a form with the appearance of and, as far as possible, the function of female genitalia. Prior to any surgeries, trans women usually undergo hormone replacement therapy and facial hair removal...
)
Surgical procedures

As with every paired structure of the human body, the labia minora are not perfectly symmetrical, and, although the size discrepancy usually is subtle, women often present one labium minus (minor lip) considerably greater (longer, wider, thicker) than its pair; thus, only the over-sized lip undergoes tissue resection (cutting and removal). In the woman who presents greatly over-sized labia minora, wherein one labium is considerably larger than its pair, only the over-sized lip is resected for symmetry with the smaller lip. In the case of the woman who also presents redundant folding — unilateral webbing or bilateral webbing — between the labia majora and the labia minora, said condition of excess tissues can also be resolved by means of labioplasty.
In corrective praxis, the labial reduction can be performed upon a patient under local anaesthesia, conscious sedation, or general anaesthesia
General anaesthesia
General anaesthesia is a state of unconsciousness and loss of protective reflexes resulting from the administration of one or more general anaesthetic agents...
, either as a discrete, single surgery, or in conjunction with a gynecologic surgery procedure, or with a cosmetic surgery procedure. The resection proper is facilitated with the administration of an anaesthetic solution (lidocaine + epinephrine in saline solution) that is infiltrated to the labia minora
Labia minora
The labia minora , also known as the inner labia, inner lips, or nymphae, are two flaps of skin on either side of the human vaginal opening, situated between the labia majora...
in order to achieve the tumescence (swelling) of the tissues and the constriction of the pertinent labial circulatory system, the hemostasis that limits bleeding.
Techniques for labial reduction
I. Edge resection techniqueThe original labiaplasty technique was simple resection of the excess tissues at the free edge of the labia minora. One resection-technique variation features a clamp placed across the area of labial tissue to be resected, in order to establish hemostatis (stopped blood-flow), and the surgeon resects the excess tissues, and then sutures the cut labium minus or labia minora. The technical disadvantages of the labial-edge resection technique are the loss of the natural rugosity (wrinkles) of the labia minora free edges, thus, aesthetically, it produces an unnaturally “perfect appearance” to the vulva, and also presents a greater risk of damaging the pertinent nerve endings. Moreover, there also exists the possiblity of everting (turning outwards) the inner lining of the labia, which then makes visible the normally hidden internal, pink labial tissues. The advantages of edge-resection include the precise control of all of the hyper-pigmented (darkened) irregular labial edges (which the woman reported as either functionally or aesthetically undesirable) with a linear scar that can also be used to contour the redundant tissues of the clitoral hood, when present.
II. Central wedge resection technique
Labial reduction by means of a central wedge-resection involves cutting and removing a full-thickness wedge of tissue from the thickest portion of the labium minus. Unlike the edge-resection technique, the resection pattern of the central wedge technique preserves the natural rugosity (wrinkled free-edge) of the labia minora. Yet, because it is a full-thickness resection, there exists the potential risk of damaging the pertinent labial nerves, which can result in painful neuroma
Neuroma
A neuroma is a growth or tumor of nerve tissue. Just as the Latin word for swelling is now restricted to neoplasias, the equivalent Greek suffix -oma has shared in that fate. Thus, the typical modern usage of neuroma is for nerve tumors...
s, and numbness. F. Giraldo et al. procedurally refined the central wedge resection technique with an additional 90-degree Z-plasty
Z-plasty
Z-plasty is a plastic surgery technique that is used to improve the functional and cosmetic appearance of scars. It can elongate a contracted scar or rotate the scar tension line. The middle line of the Z-shaped incision is made along the line of greatest tension or contraction, and triangular...
technique, which produces a refined surgical scar that is less tethered, and diminishes the physical tensions exerted upon the surgical-incision wound, and, therefore, reduces the likelihood of a notched (scalloped-edge) scar. The central wedge-resection technique is a demanding surgical procedure, and the difficulty can arise with judging the correct amount of labial skin to resect, which might result in either the under-correction (persistent tissue-redundancy), or the over-correction (excessive tension to the surgical wound), and an increased probability of surgical-wound separation
Wound dehiscence
Wound dehiscence is a surgical complication in which a wound breaks open along surgical suture. Risk factors are age, diabetes, obesity, poor knotting or grabbing of stitches, and trauma to the wound after surgery.-Symptoms:...
. Moreover, as appropriate, a separate incision is required to treat a prominent clitoral hood.
III. De-epithelialization technique
Labial reduction by means of the de-epithelialization of the tissues involves cutting the epithelium
Epithelium
Epithelium is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. Epithelial tissues line the cavities and surfaces of structures throughout the body, and also form many glands. Functions of epithelial cells include secretion, selective...
of a central area on the medial and lateral aspects of each labium minor (small lip), either with a scalpel or with a medical laser. This labiaplasty technique reduces the vertical excess tissue, whilst preserving the natural rugosity (corrugated free-edge) of the labia minora, and thus preserves the sensory and erectile characteristics of the labia. Yet, the technical disadvantage of de-epithelialization is that the width of the individual labium might increase if a large area of labial tissue must be de-epithelialized to achieve the labial reduction.
IV. Labiaplasty with clitoral unhooding
A labial reduction procedure occasionally includes the resection (cutting and removing) of the clitoral prepuce
Clitoris
The clitoris is a sexual organ that is present only in female mammals. In humans, the visible button-like portion is located near the anterior junction of the labia minora, above the opening of the urethra and vagina. Unlike the penis, which is homologous to the clitoris, the clitoris does not...
(clitoral hood) when the thickness of its skin interferes with the woman’s sexual response. The surgical unhooding of the clitoris involves a V–to–Y advancement of the soft tissues, which is achieved by suturing the clitoral hood to the pubic bone in the midline (to avoid the pudendal nerve
Pudendal nerve
The pudendal nerve is a sensory and somatic nerve in the pelvic region which is a large branch of the sacral plexus that innervates the external genitalia of both sexes, as well as sphincters for the bladder and the rectum...
s); thus, uncovering the clitoris further tightens the labia minora.
V. Laser labiaplasty technique
Labial reduction by means of laser-ray resection of the hypertrophied labia minora involves the de-epithelialization of the labia. The technical disadvantage of laser labiaplasty is that the removal of excess labial epidermis
Epidermis
Epidermis may refer to:* Epidermis , in plants, the outermost layer of cells covering the leaves and young parts of a plant* Epidermis , the outermost layer of the skin of a human...
risks causing the occurrence of epidermal inclusion cysts
Epidermoid cyst
An epidermoid cyst is a benign cyst usually found on the skin. The cyst develops out of ectodermal tissue. Histologically, it is made of a thin layer of squamous epithelium.-Terminology:...
.
Surgical technique
Labiaplasty by de-epithelializationLabial reduction by de-epithelialization cuts and removes the excess tissues and preserves the natural rugosity (wrinkled free-edge) of the labia minora
Labia minora
The labia minora , also known as the inner labia, inner lips, or nymphae, are two flaps of skin on either side of the human vaginal opening, situated between the labia majora...
, and so preserves the capabilities for tumescence
Corpus spongiosum
Corpus spongiosum is the mass of spongy tissue surrounding the male urethra within the penis...
and sensation
Pudendal nerve
The pudendal nerve is a sensory and somatic nerve in the pelvic region which is a large branch of the sacral plexus that innervates the external genitalia of both sexes, as well as sphincters for the bladder and the rectum...
. Yet, when the patient presents much excess labial tissue, a combination procedure of de-epithelialization and clamp-resection usually is more effective for achieving the aesthetic outcome established by the patient and her plastic surgeon. In the case of a woman with labial webbing (redundant folding) between the labia minora and the labia majora, the de-epithelialization labiaplasty includes an additional resection technique — such as the five-flap Z-plasty (“jumping man plasty”) — to establish a regular and symmetric shape for the reduced labia minora.
Pre-operative matters
- Consultation — To understand the aestheticSelf imageA person's self-image is the mental picture, generally of a kind that is quite resistant to change, that depicts not only details that are potentially available to objective investigation by others A person's self-image is the mental picture, generally of a kind that is quite resistant to change,...
goals of the patient, the plastic surgeon evaluates the labial hypertrophy that the woman presents when standing. Afterwards, in the operating room, with the patient in the lithotomy position (as if for a urinary-bladder stone-removal surgery), the surgeon then delineates the resection-pattern markings (incision plan) to each side of each labium (lip) to facilitate the de-epithelialization required for reducing its size (length and width). Afterwards an anaesthetic solution is infiltrated to the labial tissues to numb and swell them for easy resection of the excess tissues. As required by the patient’s health, the physician–surgeon might instruct the woman to take oral antibioticAntibioticAn antibacterial is a compound or substance that kills or slows down the growth of bacteria.The term is often used synonymously with the term antibiotic; today, however, with increased knowledge of the causative agents of various infectious diseases, antibiotic has come to denote a broader range of...
and anti-inflammatory medications before the operation; if not, they are intravenously administered to the patient at the start of the labiaplasty operation.
Operative technique
For the optimal exposure of the vulvo-vaginal complex
Vulva
The vulva consists of the external genital organs of the female mammal. This article deals with the vulva of the human being, although the structures are similar for other mammals....
, the patient is positioned upon the operating table in the lithotomy position. After confirming regional anaesthesia
Regional anaesthesia
Regional anaesthesia is anaesthesia affecting only a large part of the body, such as a limb or the lower half of the body. Regional anaesthetic techniques can be divided into central and peripheral techniques. The central techniques include so called neuraxial blocks...
and labial tumescence, the surgeon then cuts and removes (resects) the excess tissues of the labia minora. After the resection step, the suturing of the surgical wound is the procedural step that most influences the aesthetic outcome of the labial reduction — suturing the tissues of the labia minora with a running absorbable-suture occasionally produces a scallop-edged surgical scar-line, whereas suturing the tissues with a running buried-suture usually produces a wound closure (scar-line) of natural appearance.
Post-operative matters
- Convalescence — Post-operative pain and surgical-wound care are minimal, which conditions permit the woman to leave hospital and return home the same day she underwent the labial reduction procedure; usually, no vaginal packing is required, although she might choose to wear a sanitary pad for comfort. The physician informs the woman that the reduced labia often are very swollen during the early post-operative period, because of the edemaEdemaEdema or oedema ; both words from the Greek , oídēma "swelling"), formerly known as dropsy or hydropsy, is an abnormal accumulation of fluid beneath the skin or in one or more cavities of the body that produces swelling...
caused by the anaesthetic solution injected to swell the tissues. She also is instructed on the proper cleansing of the surgical-wound site, and the application of a topical antibiotic ointment to the reduced labia; a wound-care regimen observed 3-times daily for 2-days post-operative.
- Follow-up therapy — The woman’s initial, post-labiaplasty consultation with the plastic surgeon is recommended at 1-week post-operative. She is advised to return to the surgeon’s consultation room should she develop hematomaHematomaA hematoma, or haematoma, is a localized collection of blood outside the blood vessels, usually in liquid form within the tissue. This distinguishes it from an ecchymosis, which is the spread of blood under the skin in a thin layer, commonly called a bruise...
, an accumulation of blood outside the pertinent (venousVenous bloodVenous blood is deoxygenated blood in the circulatory system. It runs in the systemic veins from the organs to the heart. Deoxygenated blood is then pumped by the heart to lungs via the pulmonary arteries, one of the few arteries in the body that carries deoxygenated blood .Venous blood is...
and arterialArterial bloodArterial blood is the oxygenated blood in the circulatory system found in the lungs, the left chambers of the heart, and in the arteries. It is bright red in color, while venous blood is dark red in color...
) vascular system. In accordance with her wound-healing progress, the woman can resume physically un-strenuous and undemanding work at 3–4 days post-operative. Moreover, to allow the full and proper healing of the labiaplasty surgical wounds, the woman is instructed to not use tampons, to not wear tight clothes (e.g. thong underwear), and to abstain from sexual intercourse for 4-weeks post-operative.
Complications
Medical complications to a labiaplasty procedure are uncommon; yet the occasional complications — bleeding, infection
Infection
An infection is the colonization of a host organism by parasite species. Infecting parasites seek to use the host's resources to reproduce, often resulting in disease...
, labial asymmetry
Vulva
The vulva consists of the external genital organs of the female mammal. This article deals with the vulva of the human being, although the structures are similar for other mammals....
, poor wound-healing, under-correction, over-correction — do occur, and might require a revision surgery. An over-aggressive resection might damage the nerves
Nerve
A peripheral nerve, or simply nerve, is an enclosed, cable-like bundle of peripheral axons . A nerve provides a common pathway for the electrochemical nerve impulses that are transmitted along each of the axons. Nerves are found only in the peripheral nervous system...
, which condition subsequently causes painful neuromas
Neuroma
A neuroma is a growth or tumor of nerve tissue. Just as the Latin word for swelling is now restricted to neoplasias, the equivalent Greek suffix -oma has shared in that fate. Thus, the typical modern usage of neuroma is for nerve tumors...
. Furthermore, performing a flap-technique labiaplasty occasionally presents a greater risk for necrosis
Necrosis
Necrosis is the premature death of cells in living tissue. Necrosis is caused by factors external to the cell or tissue, such as infection, toxins, or trauma. This is in contrast to apoptosis, which is a naturally occurring cause of cellular death...
of the labia minora tissues.
Psychosocial criticism
PatientsTwo categories of women seek vaginoplastic surgery
Vaginoplasty
thumb|right|300px|Vaginoplasty: the pre-operative aspect , and the post-operative aspect of a [[Labiaplasty|labial reduction]].Vaginoplasty is a reconstructive plastic surgery procedure for correcting the defects and deformities of the vaginal canal and its mucous membrane, and of vulvo-vaginal...
: (i) Women physically afflicted with congenital defects, deformities, and abnormalities, such as vaginal atresia
Vaginal atresia
Vaginal Atresia is a birth defect or congenital abnormality of the female genitourinary system that manifests itself in the absence of a vagina , or a deformed and nonfunctional vagina ....
(absent vaginal passage), Müllerian agenesis
Mullerian agenesis
Müllerian agenesis is a congenital malformation in women characterised by a failure of the müllerian ducts to develop, resulting in a missing uterus and fallopian tubes and variable malformations of the upper portion of the vagina. It is the second most common cause of primary amenorrhea after...
(malformed uterus and fallopian tubes), intersex conditions
Intersex
Intersex, in humans and other animals, is the presence of intermediate or atypical combinations of physical features that usually distinguish female from male...
(male and female sexual characteristics in a person), etc.; and (ii) Women who seek genital cosmetic surgery to enhance the beauty
Beauty
Beauty is a characteristic of a person, animal, place, object, or idea that provides a perceptual experience of pleasure, meaning, or satisfaction. Beauty is studied as part of aesthetics, sociology, social psychology, and culture...
of their vulvo-vaginal complexes
Vulva
The vulva consists of the external genital organs of the female mammal. This article deals with the vulva of the human being, although the structures are similar for other mammals....
. Therefore, a woman usually seeks a labial reduction procedure to correct morphologic
Morphology (biology)
In biology, morphology is a branch of bioscience dealing with the study of the form and structure of organisms and their specific structural features....
changes caused by the mechanical stresses (stretching, pulling, tearing) of childbirth, sexual intercourse, accident, and aging. The symptoms of labial hypertrophy are vulvo-vaginal hygiene problems, chronic irritation of the pudendal skin, painful sexual intercourse (dyspareunia), and pubic pain when wearing tight clothes.
.jpg)
The psychosocial
Psychosocial
For a concept to be psychosocial means it relates to one's psychological development in, and interaction with, a social environment. The individual needs not be fully aware of this relationship with his or her environment. It was first commonly used by psychologist Erik Erikson in his stages of...
study of women who pursue beauty
Beauty
Beauty is a characteristic of a person, animal, place, object, or idea that provides a perceptual experience of pleasure, meaning, or satisfaction. Beauty is studied as part of aesthetics, sociology, social psychology, and culture...
by means of cosmetic plastic surgery, Body Dysmorphic Disorder: A Treatment Manual (2010) indicates that, in addition to labial reduction, some women pursue genital surgery to acquire a flat vulvo-vaginal complex in the style of the “prepubescent aesthetic” portrayed in pornography
Pornography
Pornography or porn is the explicit portrayal of sexual subject matter for the purposes of sexual arousal and erotic satisfaction.Pornography may use any of a variety of media, ranging from books, magazines, postcards, photos, sculpture, drawing, painting, animation, sound recording, film, video,...
and in commercial adverts
Advertising
Advertising is a form of communication used to persuade an audience to take some action with respect to products, ideas, or services. Most commonly, the desired result is to drive consumer behavior with respect to a commercial offering, although political and ideological advertising is also common...
. Nonetheless, the investigators David Veale and Fugen Neziroglu, reported that “no [psychosocial] studies have been done on the prevalence of BDD in women seeking labiaplasty. In this regard, it may be important for cosmetic gynecologists to define when the degree of protrusion, or hypertrophy, of the labia minora
Labia minora
The labia minora , also known as the inner labia, inner lips, or nymphae, are two flaps of skin on either side of the human vaginal opening, situated between the labia majora...
is no longer a minor defect (which would exclude a diagnosis of BDD
Body dysmorphic disorder
Body Dysmorphic Disorder is a type of mental illness, a somatoform disorder, wherein the affected person is exclusively concerned with body image, manifested as excessive concern about and preoccupation with a perceived defect of his or her physical features...
). One of the authors [Fugen Neziroglu] has seen several women seeking labiaplasty in recent years, because of her affiliation with gynecologists. Most of the women had either bulkiness or a slight protrusion of their labia [minora], but were not abnormal in size. Because it is not appropriate for mental health professionals
Mental health
Mental health describes either a level of cognitive or emotional well-being or an absence of a mental disorder. From perspectives of the discipline of positive psychology or holism mental health may include an individual's ability to enjoy life and procure a balance between life activities and...
to assess the size and shape of the labia of women, a [psychological] clinician must rely on a gynecologist or a family doctor
Physician
A physician is a health care provider who practices the profession of medicine, which is concerned with promoting, maintaining or restoring human health through the study, diagnosis, and treatment of disease, injury and other physical and mental impairments...
who has examined the patient.” The body dysmorphia
Body dysmorphic disorder
Body Dysmorphic Disorder is a type of mental illness, a somatoform disorder, wherein the affected person is exclusively concerned with body image, manifested as excessive concern about and preoccupation with a perceived defect of his or her physical features...
findings reported in the Veale–Neziroglu study confirm the psychosocial findings of the earlier study Female Genital Appearance: ‘Normality’ Unfolds (2005), which indicated that a woman — as a plastic surgery patient — might be motivated to seek labiaplasty (genitoplasty) because she feels that her vulva
Vulva
The vulva consists of the external genital organs of the female mammal. This article deals with the vulva of the human being, although the structures are similar for other mammals....
is not within a given “normal” aesthetic range of labial size, appearance, and color.
Patient satisfaction
The retrospective study Labiaplasty of the Labia minora: Patients’ Indications for Pursuing Surgery (2008) reported that in a 131-woman group, 32 per cent of the women underwent labial reduction to correct a functional impairment; 31 per cent to correct a functional impairment and for aesthetic reasons; and 37 per cent underwent labiaplasty solely for aesthetic correction. Concerning the technical and procedural efficacy of labiaplasty, the study Hypertrophy of Labia minora: Experience with 163 Reductions (1999) reported a 93 per cent rate of patient satisfaction with the surgical outcome of the labial reduction procedure, and concluded that labiaplasty is a technically simple surgical operation
Surgery
Surgery is an ancient medical specialty that uses operative manual and instrumental techniques on a patient to investigate and/or treat a pathological condition such as disease or injury, or to help improve bodily function or appearance.An act of performing surgery may be called a surgical...
with a high rate of patient satisfaction.
Cultural criticism
Semantic distinctionsIn Western culture
Western culture
Western culture, sometimes equated with Western civilization or European civilization, refers to cultures of European origin and is used very broadly to refer to a heritage of social norms, ethical values, traditional customs, religious beliefs, political systems, and specific artifacts and...
, the term Female Genital Cutting (FGC) denotes the cutting off of any part(s) or portion(s) of the vulva — either for religious or for cultural reasons, or both — but not the plastic surgery correction of the congenital defects and the developmental abnormalities
Congenital abnormality
A congenital anomaly is a condition which is present at the time of birth which varies from the standard presentation....
of the vulvo-vaginal complex
Vulva
The vulva consists of the external genital organs of the female mammal. This article deals with the vulva of the human being, although the structures are similar for other mammals....
, such as vaginal atresia
Vaginal atresia
Vaginal Atresia is a birth defect or congenital abnormality of the female genitourinary system that manifests itself in the absence of a vagina , or a deformed and nonfunctional vagina ....
(undeveloped vagina
Vagina
The vagina is a fibromuscular tubular tract leading from the uterus to the exterior of the body in female placental mammals and marsupials, or to the cloaca in female birds, monotremes, and some reptiles. Female insects and other invertebrates also have a vagina, which is the terminal part of the...
), Müllerian agenesis
Mullerian agenesis
Müllerian agenesis is a congenital malformation in women characterised by a failure of the müllerian ducts to develop, resulting in a missing uterus and fallopian tubes and variable malformations of the upper portion of the vagina. It is the second most common cause of primary amenorrhea after...
(absent uterus
Uterus
The uterus or womb is a major female hormone-responsive reproductive sex organ of most mammals including humans. One end, the cervix, opens into the vagina, while the other is connected to one or both fallopian tubes, depending on the species...
and fallopian tubes), and intersex
Intersex
Intersex, in humans and other animals, is the presence of intermediate or atypical combinations of physical features that usually distinguish female from male...
conditions. Yet, in social and cultural discourse, the layman opponents of such religiously- and culturally-motivated sexual mutilations inaccurately use the terms Female Genital Mutilation (FGM) and Female Circumcision (FC) as interchangeably synonymous with female genital cutting. Therefore, from the physician
Physician
A physician is a health care provider who practices the profession of medicine, which is concerned with promoting, maintaining or restoring human health through the study, diagnosis, and treatment of disease, injury and other physical and mental impairments...
’s perspective, it is important to formally observe the semantic
Semantics
Semantics is the study of meaning. It focuses on the relation between signifiers, such as words, phrases, signs and symbols, and what they stand for, their denotata....
distinction between a religious and cultural practice and the medical practice of labiaplasty, which is an elective plastic surgery operation for a woman requiring the correction of either a functional or a cosmetic problem of her vulva. The study Hypertrophy of Labia minora: Experience with 163 Reductions (1999) reported a 93 per cent rate of patient satisfaction with the labiaplasty outcomes; and the subsequent psychological improvements reported by the women included increased self-esteem
Self-esteem
Self-esteem is a term in psychology to reflect a person's overall evaluation or appraisal of his or her own worth. Self-esteem encompasses beliefs and emotions such as triumph, despair, pride and shame: some would distinguish how 'the self-concept is what we think about the self; self-esteem, the...
derived from the refined aesthetic
Aesthetics
Aesthetics is a branch of philosophy dealing with the nature of beauty, art, and taste, and with the creation and appreciation of beauty. It is more scientifically defined as the study of sensory or sensori-emotional values, sometimes called judgments of sentiment and taste...
body image
Body image
Body image refers to a person's perception of the aesthetics and sexual attractiveness of their own body. The phrase body image was first coined by the Austrian neurologist and psychoanalyst Paul Schilder in his masterpiece The Image and Appearance of the Human Body...
. The study Labiaplasty of the Labia minora: Patients’ Indications for Pursuing Surgery (2008), reported that 32 per cent of the women underwent labial reduction for the correction of a functional impairment; that 31 per cent of the women underwent the correction of functional and aesthetic impairments; and that 37 per cent of the women underwent labiaplasty solely for aesthetic corrections.
Woman as plastic surgery patient
Sociologically
Sociology
Sociology is the study of society. It is a social science—a term with which it is sometimes synonymous—which uses various methods of empirical investigation and critical analysis to develop a body of knowledge about human social activity...
, labiaplasty is a controversial subject among laymen and physicians who believe that a woman’s decision to undergo cosmetic genital surgery is psychologically induced by the commercialism
Commercialism
Commercialism, in its original meaning, is the practices, methods, aims, and spirit of commerce or business. Today, however, it primarily refers to the tendency within open-market capitalism to turn everything into objects, images, and services sold for the purpose of generating profit...
of medicalized
Medicalization
Medicalization is the process by which human conditions and problems come to be defined and treated as medical conditions and problems, and thus come under the authority of doctors and other health professionals to study, diagnose, prevent or treat...
sex appeal
Sexual attraction
Sexual attractiveness or sex appeal refers to an individual's ability to attract the sexual or erotic interest of another person, and is a factor in sexual selection or mate choice. The attraction can be to the physical or other qualities or traits of a person, or to such qualities in the context...
; that she desires a mentally unhealthy
Mental illness
A mental disorder or mental illness is a psychological or behavioral pattern generally associated with subjective distress or disability that occurs in an individual, and which is not a part of normal development or culture. Such a disorder may consist of a combination of affective, behavioural,...
sexual body image
Body image
Body image refers to a person's perception of the aesthetics and sexual attractiveness of their own body. The phrase body image was first coined by the Austrian neurologist and psychoanalyst Paul Schilder in his masterpiece The Image and Appearance of the Human Body...
derived from pornography
Pornography
Pornography or porn is the explicit portrayal of sexual subject matter for the purposes of sexual arousal and erotic satisfaction.Pornography may use any of a variety of media, ranging from books, magazines, postcards, photos, sculpture, drawing, painting, animation, sound recording, film, video,...
— hence, some opponents of cosmetic plastic surgery semantically
Semantics
Semantics is the study of meaning. It focuses on the relation between signifiers, such as words, phrases, signs and symbols, and what they stand for, their denotata....
liken labiaplasty to genital modification and mutilation
Genital modification and mutilation
The terms genital modification and genital mutilation can refer to permanent or temporary changes to human sex organs. Some forms of genital alteration are performed at the behest of an adult, with their informed consent. Others are performed on infants or children...
. Moreover, specifically regarding female genital mutilation, the World Health Organization
World Health Organization
The World Health Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations that acts as a coordinating authority on international public health. Established on 7 April 1948, with headquarters in Geneva, Switzerland, the agency inherited the mandate and resources of its predecessor, the Health...
(WHO) cited the Hippocratic Oath
Hippocratic Oath
The Hippocratic Oath is an oath historically taken by physicians and other healthcare professionals swearing to practice medicine ethically. It is widely believed to have been written by Hippocrates, often regarded as the father of western medicine, or by one of his students. The oath is written in...
to publicly declare and establish the medical and ethical obligation
Medical ethics
Medical ethics is a system of moral principles that apply values and judgments to the practice of medicine. As a scholarly discipline, medical ethics encompasses its practical application in clinical settings as well as work on its history, philosophy, theology, and sociology.-History:Historically,...
that “health professionals must never perform female genital mutilation”, and so harm a woman patient.

- In the Feminist Studies journal essay “Loose Lips Sink Ships” (2002) and in the Shameless online magazine article “Making the Cut” (2005), Prof. Simone Weil Davis said that plastic surgeons perpetuate to women the cultural concept of aesthetically ideal female genitaliaVulvaThe vulva consists of the external genital organs of the female mammal. This article deals with the vulva of the human being, although the structures are similar for other mammals....
, and that because the “labia are neither inside nor outside [the body], they are gateway tissues, and they kind of represent a [body] part that is [culturally] confusing”; and proposed that because women know only their vaginas and the pornographic pre-pubescent ideal, women readily doubt themselves as aesthetically abnormal, as being outside the ideal beauty range, which is a cultural construct.
- Moreover, in addressing the matter of FGM (labial- and clitoral-mutilation as religious and cultural practices) which is illegal in Canada and the U.S., Prof. Davis addressed the semantic dilemma that arises “when you really look carefully at the language used in some of those laws, they would also make illegal the labiaplasties that are being done by plastic surgeons in the U.S.” Nonetheless, although the official WHO resolution Eliminating Female Genital Mutilation (2008) defined FGM as “all procedures that involve partial or total removal of the external female genitalia, or other injury to the female genital organs for non-medical reasons”, the document’s “Annex 2: Note on the Classification of Female Genital Mutilation” states that: “The guiding principles for considering genital practices as female genital mutilation should be those of human rights, including the right to health, the rights of children, and the right to non-discrimination on the basis of sex. Some practices, such as genital cosmetic surgery and hymen repair, which are legally accepted in many countries, and not generally considered to constitute female genital mutilation, actually fall under the definition used here.” Therefore, the woman and her plastic surgeon resolve said semantic ambiguity in the exclusive context of the Doctor-and-Patient relationship.
- In the U.K., the medical article Requests for Cosmetic Genitoplasty: How Should Healthcare Providers Respond? (2007) indicated that “the few reports that exist on patients’ satisfaction with labial reductions are generally positive; but the assessments are short-term and lack methodologicalMethodologyMethodology is generally a guideline for solving a problem, with specificcomponents such as phases, tasks, methods, techniques and tools . It can be defined also as follows:...
rigour”; and that the increased demand for cosmetic genitoplasty (labiaplasty) was indicated by the British National Health ServiceNational Health ServiceThe National Health Service is the shared name of three of the four publicly funded healthcare systems in the United Kingdom. They provide a comprehensive range of health services, the vast majority of which are free at the point of use to residents of the United Kingdom...
(NHS) having performed double the number of genitoplasty procedures in the year 2006, than were performed in the 2001–2005 period; and that the women who elected to undergo genitoplasty did so because having a pretty pudendum feminimumVulvaThe vulva consists of the external genital organs of the female mammal. This article deals with the vulva of the human being, although the structures are similar for other mammals....
was important them. Nonetheless, the authors, the clinical psychologistClinical psychologyClinical psychology is an integration of science, theory and clinical knowledge for the purpose of understanding, preventing, and relieving psychologically-based distress or dysfunction and to promote subjective well-being and personal development...
Lih Mei Liao and the gynæcologist Sarah M. Creighton, about the women reported that “the patients consistently wanted their vulvas to be flat, with no protrusion beyond the labia majoraLabia majoraThe labia majora are two prominent longitudinal cutaneous folds that extend downward and backward from the mons pubis to the perineum and form the lateral boundaries of the pudendal cleft, which contains the labia minora, interlabial sulci, clitoral hood, clitoral glans, frenulum clitoridis, the...
. . . some women brought along images to illustrate the desired appearance, usually from advertsAdvertisingAdvertising is a form of communication used to persuade an audience to take some action with respect to products, ideas, or services. Most commonly, the desired result is to drive consumer behavior with respect to a commercial offering, although political and ideological advertising is also common...
or pornographyPornographyPornography or porn is the explicit portrayal of sexual subject matter for the purposes of sexual arousal and erotic satisfaction.Pornography may use any of a variety of media, ranging from books, magazines, postcards, photos, sculpture, drawing, painting, animation, sound recording, film, video,...
that may have been digitally altered.” The report concluded that the “designer vagina craze” originated from the commercialismCommercialismCommercialism, in its original meaning, is the practices, methods, aims, and spirit of commerce or business. Today, however, it primarily refers to the tendency within open-market capitalism to turn everything into objects, images, and services sold for the purpose of generating profit...
of sexual medicalizationMedicalizationMedicalization is the process by which human conditions and problems come to be defined and treated as medical conditions and problems, and thus come under the authority of doctors and other health professionals to study, diagnose, prevent or treat...
. Elsewhere, in OceaniaOceaniaOceania is a region centered on the islands of the tropical Pacific Ocean. Conceptions of what constitutes Oceania range from the coral atolls and volcanic islands of the South Pacific to the entire insular region between Asia and the Americas, including Australasia and the Malay Archipelago...
, The Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Obstetricians and Gynæcologists published a like concern about the commercial exploitation of psychologically insecureSelf-esteemSelf-esteem is a term in psychology to reflect a person's overall evaluation or appraisal of his or her own worth. Self-esteem encompasses beliefs and emotions such as triumph, despair, pride and shame: some would distinguish how 'the self-concept is what we think about the self; self-esteem, the...
women to undergo cosmetic genitoplasty.
- In the U.S., the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) published Committee Opinion No. 378: Vaginal “Rejuvenation” and Cosmetic Vaginal Procedures (2007), the college’s formal policy statement of opposition to the commercial misrepresentationsAdvertisingAdvertising is a form of communication used to persuade an audience to take some action with respect to products, ideas, or services. Most commonly, the desired result is to drive consumer behavior with respect to a commercial offering, although political and ideological advertising is also common...
of labiaplasty, and associated vaginoplastic procedures, as medically “accepted and routine surgical practices”. The ACOG doubted the medical safety and the therapeutic efficacy of the surgical techniques and procedures for performing labiaplasty, vaginal rejuvenationVaginoplastythumb|right|300px|Vaginoplasty: the pre-operative aspect , and the post-operative aspect of a [[Labiaplasty|labial reduction]].Vaginoplasty is a reconstructive plastic surgery procedure for correcting the defects and deformities of the vaginal canal and its mucous membrane, and of vulvo-vaginal...
, the designer vagina, revirgination, and Gräfenberg SpotG-spotThe Gräfenberg Spot, often called the G-Spot, is a bean-shaped area of the vagina. Many women report that it is an erogenous zone which, when stimulated, can lead to strong sexual arousal, powerful orgasms and female ejaculation...
amplification, and recommended that women seeking such genitoplastic surgeries must be fully informed, with the available surgical-safety statistics, of the potential health risks of surgical-wound infectionInfectionAn infection is the colonization of a host organism by parasite species. Infecting parasites seek to use the host's resources to reproduce, often resulting in disease...
, of pudendal nervePudendal nerveThe pudendal nerve is a sensory and somatic nerve in the pelvic region which is a large branch of the sacral plexus that innervates the external genitalia of both sexes, as well as sphincters for the bladder and the rectum...
damage (resulting in either an insensitive or an over-sensitive vulva), of dyspareuniaDyspareuniaDyspareunia is painful sexual intercourse, due to medical or psychological causes. The symptom is reported almost exclusively by women, although the problem can also occur in men. The causes are often reversible, even when long-standing, but self-perpetuating pain is a factor after the original...
(painful coitus), of tissue adhesions (epidermoid cystsEpidermoid cystAn epidermoid cyst is a benign cyst usually found on the skin. The cyst develops out of ectodermal tissue. Histologically, it is made of a thin layer of squamous epithelium.-Terminology:...
), and of painful scars.
- To determine whether or not women truly seek labiaplasty solely to have “more socially acceptable genitalia” the International Society for the Study of Women’s Sexual Health (ISSWSH) considered the practices of elective plastic surgery of the vulva and of FGC (female genital cutting) in the Third WorldThird WorldThe term Third World arose during the Cold War to define countries that remained non-aligned with either capitalism and NATO , or communism and the Soviet Union...
. The report, Is Elective Vulvar Plastic Surgery ever Warranted and What Screening Should be Done Preoperatively? (2007) indicated that physical variations in the external appearance of the vulvo-vaginal complex are statistically normal, but that labiaplasty — like access to all types of medical treatment — is a woman’s human rightHuman rightsHuman rights are "commonly understood as inalienable fundamental rights to which a person is inherently entitled simply because she or he is a human being." Human rights are thus conceived as universal and egalitarian . These rights may exist as natural rights or as legal rights, in both national...
. Nonetheless, the ISSWSH report concluded that vaginoplasticVaginoplastythumb|right|300px|Vaginoplasty: the pre-operative aspect , and the post-operative aspect of a [[Labiaplasty|labial reduction]].Vaginoplasty is a reconstructive plastic surgery procedure for correcting the defects and deformities of the vaginal canal and its mucous membrane, and of vulvo-vaginal...
surgery might be medically warranted only after the woman undergoes a pre-operative psychological screening, and only if the woman afterwards remains so decided — yet also recommended that the vaginal surgery can be performed if the surgeon deems it medically necessary for her health.
- In the U.S., the feminist organization The New View Campaign formally opposed labiaplasty (genitoplasty) as part of the medicalizationMedicalizationMedicalization is the process by which human conditions and problems come to be defined and treated as medical conditions and problems, and thus come under the authority of doctors and other health professionals to study, diagnose, prevent or treat...
of female sexuality, which the organization said is a great public mental healthMental healthMental health describes either a level of cognitive or emotional well-being or an absence of a mental disorder. From perspectives of the discipline of positive psychology or holism mental health may include an individual's ability to enjoy life and procure a balance between life activities and...
problem of contemporary American society. The specific opposition was to the existence and operation of legally un-regulated cosmetic surgery clinics that function as business enterprises trading upon the medicalized sexualitySociology of health and illnessThe Sociology of Health and Illness examines the interaction between society and health. The objective of this topic is to see how social life has an impact on morbidity and mortality rate, and vice versa...
of women, by appealing to their low self esteem and poor body imageBody imageBody image refers to a person's perception of the aesthetics and sexual attractiveness of their own body. The phrase body image was first coined by the Austrian neurologist and psychoanalyst Paul Schilder in his masterpiece The Image and Appearance of the Human Body...
, thereby creating new health risks, and social norms about what prettinessBeautyBeauty is a characteristic of a person, animal, place, object, or idea that provides a perceptual experience of pleasure, meaning, or satisfaction. Beauty is studied as part of aesthetics, sociology, social psychology, and culture...
is and what prettiness is not. To the end of making socially legitimateLegitimationLegitimation or legitimization is the act of providing legitimacy. Legitimation in the social sciences refers to the process whereby an act, process, or ideology becomes legitimate by its attachment to norms and values within in given society...
the natural morphologicMorphology (biology)In biology, morphology is a branch of bioscience dealing with the study of the form and structure of organisms and their specific structural features....
diversity of the bodies of women, The New View Campaign proposed that countering sexual and bodily self-hatred among American women requires changing the U.S. societal norms defining what beautyBeautyBeauty is a characteristic of a person, animal, place, object, or idea that provides a perceptual experience of pleasure, meaning, or satisfaction. Beauty is studied as part of aesthetics, sociology, social psychology, and culture...
is and what beauty is not, and by re-defining what social and personal behaviors constitute mental healthMental illnessA mental disorder or mental illness is a psychological or behavioral pattern generally associated with subjective distress or disability that occurs in an individual, and which is not a part of normal development or culture. Such a disorder may consist of a combination of affective, behavioural,...
.
See also
- Anal bleachingAnal bleachingAnal bleaching is the process of lightening the color of the skin around the anus. It is done for cosmetic purposes, to make the anus more uniform with the surrounding area....
- Clitoral hood reductionClitoral hood reductionthumb|right|350px|Clitoral hood reduction: the pre-operative aspects of clitoral prepuce and labia minora hypertrophy , and the post-operative aspects of the reduced prepuce and labia minora...
- Elongated labiaElongated labiaElongated labia is an possibly genetic feature of certain Khoisan groups, whose female members develop relatively elongated labia minora, hanging up to four inches outside their vulva when they are standing in an upright position...
- Labia stretchingLabia stretchingLabia stretching is the act of elongating the labia minora through manual manipulation or physical equipment .It is a familial cultural practice in Rwanda, common in Sub-Saharan Africa, and a body modification practice elsewhere...
- VaginoplastyVaginoplastythumb|right|300px|Vaginoplasty: the pre-operative aspect , and the post-operative aspect of a [[Labiaplasty|labial reduction]].Vaginoplasty is a reconstructive plastic surgery procedure for correcting the defects and deformities of the vaginal canal and its mucous membrane, and of vulvo-vaginal...
Further reading
- Boston Women’s Health Book Collective. "Our Bodies, Ourselves", Simon and Schuster, 2005.
- Revill Jo. "The new nose job: designer vaginas", The Observer 17 August 2003.
- Rogers Lisa. "The quest for the perfect vagina", The Guardian 15 August 2008.
- Rogers Lisa. "The Perfect Vagina", Channel 4 documentary, 17 August 2008, accessed 18 September 2011.

