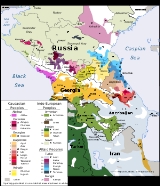
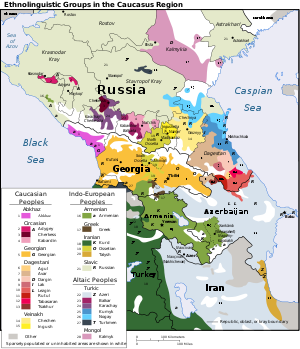
Languages of the Caucasus
Encyclopedia
Caucasus
The Caucasus, also Caucas or Caucasia , is a geopolitical region at the border of Europe and Asia, and situated between the Black and the Caspian sea...
Mountains, which lie between the Black Sea
Black Sea
The Black Sea is bounded by Europe, Anatolia and the Caucasus and is ultimately connected to the Atlantic Ocean via the Mediterranean and the Aegean seas and various straits. The Bosphorus strait connects it to the Sea of Marmara, and the strait of the Dardanelles connects that sea to the Aegean...
and the Caspian Sea
Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the largest enclosed body of water on Earth by area, variously classed as the world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. The sea has a surface area of and a volume of...
.
Linguistic comparison allows these languages to be classified into several language families, with little or no discernible affinity to each other.
Families indigenous to the Caucasus
Three of these families have no current members outside the Caucasus, and are considered indigenous to the area. The term Caucasian languages is generally restricted to these families, which are spoken by about 11.2 million people.- Kartvelian language family with a total of about 5.2 million speakers. Includes GeorgianGeorgian languageGeorgian is the native language of the Georgians and the official language of Georgia, a country in the Caucasus.Georgian is the primary language of about 4 million people in Georgia itself, and of another 500,000 abroad...
, the official language of GeorgiaGeorgia (country)Georgia is a sovereign state in the Caucasus region of Eurasia. Located at the crossroads of Western Asia and Eastern Europe, it is bounded to the west by the Black Sea, to the north by Russia, to the southwest by Turkey, to the south by Armenia, and to the southeast by Azerbaijan. The capital of...
, with four million speakers, Mingrelian, Laz languageLaz languageThe Laz language is a South Caucasian language spoken by the Laz people on the Southeast shore of the Black Sea...
and Svan languageSvan languageThe Svan language is a Kartvelian language spoken in the Western Georgian region of Svaneti primarily by the Georgians of Svan origin...
.
- Northwest CaucasianNorthwest Caucasian languagesThe Northwest Caucasian languages, also called Abkhazo-Adyghean, or sometimes Pontic as opposed to Caspian for the Northeast Caucasian languages, are a group of languages spoken in the Caucasus region, chiefly in Russia , the disputed territory of Abkhazia, and Turkey, with smaller communities...
, also called the Abkhaz–Adyghe, Circassian, or Pontic family, with a total of about 2.5 million speakers. Includes the Kabardian languageKabardian languageThe Kabardian language, also known as East Circassian , is a Northwest Caucasian language, closely related to the Adyghe language. It is spoken mainly in the Russian republics of Kabardino-Balkaria and Karachay-Cherkessia and in Turkey and the Middle East...
, with one million speakers.
- Northeast CaucasianNortheast Caucasian languagesThe Northeast Caucasian languages constitute a language family spoken in the Russian republics of Dagestan, Chechnya, Ingushetia, northern Azerbaijan, and in northeastern Georgia, as well as in diaspora populations in Russia, Turkey, and the Middle East...
, also called the Dagestanian, Nakho-Dagestanian, or Caspian family, with a total of about 3.5 million speakers. Includes the Chechen languageChechen languageThe Chechen language is spoken by more than 1.5 million people, mostly in Chechnya and by Chechen people elsewhere. It is a member of the Northeast Caucasian languages.-Classification:...
with 1.5 million speakers, the Avar languageAvar languageThe modern Avar language belongs to the Avar–Andic group of the Northeast Caucasian language family....
with 1 million speakers, the Ingush languageIngush languageIngush is a language spoken by about 413,000 people , known as the Ingush, across a region covering Ingushetia, Chechnya, Kazakhstan and Russia. In Ingush, the language is called ГІалгІай Ğalğaj .-Classification:...
with 500,000 speakers, the Lezgian language and others.
It is commonly believed that all Caucasian languages have a large number of consonant
Consonant
In articulatory phonetics, a consonant is a speech sound that is articulated with complete or partial closure of the vocal tract. Examples are , pronounced with the lips; , pronounced with the front of the tongue; , pronounced with the back of the tongue; , pronounced in the throat; and ,...
s. While this is certainly true for most members of the Northwest and Northeast Caucasian families (inventories range up to the 80–84 consonants of Ubykh
Ubykh language
Ubykh or Ubyx is an extinct language of the Northwestern Caucasian group, spoken by the Ubykh people...
), the consonant inventories of the South Caucasian languages are not nearly as extensive, ranging from 28 (Georgian) to 30 (Laz
Laz language
The Laz language is a South Caucasian language spoken by the Laz people on the Southeast shore of the Black Sea...
) – comparable to languages like Arabic
Arabic phonology
While many languages have numerous dialects that differ in pronunciation, the Arabic language is more properly described as a continuum of varieties. This article deals primarily with Modern Standard Arabic, which is the standard variety shared by educated speakers throughout Arabic-speaking regions...
(28 consonants), Western European languages (20–21), and Russian
Russian phonology
This article discusses the phonological system of standard Russian based on the Moscow dialect . For discussion of other dialects, see Russian dialects...
(35–37 consonants).
The autochthonous languages of the Caucasus share some areal features, such as the presence of ejective consonant
Ejective consonant
In phonetics, ejective consonants are voiceless consonants that are pronounced with simultaneous closure of the glottis. In the phonology of a particular language, ejectives may contrast with aspirated or tenuis consonants...
s and a highly agglutinative structure, and, with the sole exception of Mingrelian, all of them exhibit a greater or lesser degree of ergativity. Many of these features are shared with other languages that have been in the Caucasus for a long time, such as Ossetian.
External relations
Since the birth of comparative linguistics in the 19th century, the riddle of the apparently isolated Caucasian language families has attracted the attention of many scholars, who have endeavored to relate them to each other or to languages outside the Caucasus region. The most promising proposals are connections between the Northwest and Northeast Caucasian families and each other or with languages formerly spoken in AnatoliaAnatolia
Anatolia is a geographic and historical term denoting the westernmost protrusion of Asia, comprising the majority of the Republic of Turkey...
and northern Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a toponym for the area of the Tigris–Euphrates river system, largely corresponding to modern-day Iraq, northeastern Syria, southeastern Turkey and southwestern Iran.Widely considered to be the cradle of civilization, Bronze Age Mesopotamia included Sumer and the...
.
North Caucasian languages
Linguists such as Sergei StarostinSergei Starostin
Dr. Sergei Anatolyevich Starostin was a Russian historical linguist and scholar, best known for his work with hypothetical proto-languages, including his work on the reconstruction of the Proto-Borean language, the controversial theory of Altaic languages and the formulation of the Dené–Caucasian...
see the Northwest (Abkhaz–Adyghe) and Northeast (Nahk-Dagestanian) families as related and propose uniting them in a single North Caucasian family, sometimes called Caucasic or simply Caucasian. This theory excludes the South Caucasian languages, thereby proposing two indigenous language families. While these two families share many similarities, their morphological structure, with many morpheme
Morpheme
In linguistics, a morpheme is the smallest semantically meaningful unit in a language. The field of study dedicated to morphemes is called morphology. A morpheme is not identical to a word, and the principal difference between the two is that a morpheme may or may not stand alone, whereas a word,...
s consisting of a single consonant, make comparison between them unusually difficult, and it has not been possible to establish a genetic relationship with any certainty.
Ibero-Caucasian languages
There are no known affinities between the South Caucasian and North Caucasian families. Nevertheless, some scholars have proposed the single name Ibero-Caucasian for all the Caucasian language families, North and South, in an attempt to unify the Caucasian languages under one family.Hattic
Some linguists have claimed affinities between the Northwest Caucasian (Circassian) family and the extinct Hattic languageHattic language
Hattic was a language spoken by the Hattians in Asia Minor between the 3rd and the 2nd millennia BC. Scholars call this language 'Hattic' to distinguish it from the Hittite language--the Indo-European language of the Hittite Empire....
of central Anatolia. See the article on Northwest Caucasian languages
Northwest Caucasian languages
The Northwest Caucasian languages, also called Abkhazo-Adyghean, or sometimes Pontic as opposed to Caspian for the Northeast Caucasian languages, are a group of languages spoken in the Caucasus region, chiefly in Russia , the disputed territory of Abkhazia, and Turkey, with smaller communities...
for details.
Alarodian
Alarodian is a proposed connection between Northeast Caucasian and the extinct Hurro-Urartian languagesHurro-Urartian languages
The Hurro-Urartian languages are an extinct language family of the Ancient Near East, comprising only two known languages: Hurrian and Urartian, both of which were spoken in the Taurus mountains area.-Classification:...
of Anatolia
Anatolia
Anatolia is a geographic and historical term denoting the westernmost protrusion of Asia, comprising the majority of the Republic of Turkey...
.
Dené–Caucasian macrofamily
Linguists such as Sergei StarostinSergei Starostin
Dr. Sergei Anatolyevich Starostin was a Russian historical linguist and scholar, best known for his work with hypothetical proto-languages, including his work on the reconstruction of the Proto-Borean language, the controversial theory of Altaic languages and the formulation of the Dené–Caucasian...
have proposed a Dené–Caucasian macrofamily
Macrofamily
In historical linguistics, a macro-family, also called a superfamily or phylum, is defined as a proposed genetic relationship grouping together language families in a larger scale clasification.However, Campbell regards this term as superfluous, preferring language family for those clasifications...
, which includes the North Caucasian languages together with Basque
Basque language
Basque is the ancestral language of the Basque people, who inhabit the Basque Country, a region spanning an area in northeastern Spain and southwestern France. It is spoken by 25.7% of Basques in all territories...
, Burushaski
Burushaski language
The Burushaski or Burushko language , is a language isolate . It is spoken by some 87,000 Burusho people in the Hunza, Nagar, Yasin, and Ishkoman valleys, and some parts of the Gilgit valley, in Gilgit–Baltistan in Pakistan and by about 300 Burusho people in Srinagar in Jammu and Kashmir, India...
, Na-Dené
Na-Dené languages
Na-Dene is a Native American language family which includes at least the Athabaskan languages, Eyak, and Tlingit languages. An inclusion of Haida is controversial....
, Sino-Tibetan
Sino-Tibetan languages
The Sino-Tibetan languages are a language family comprising, at least, the Chinese and the Tibeto-Burman languages, including some 250 languages of East Asia, Southeast Asia and parts of South Asia. They are second only to the Indo-European languages in terms of the number of native speakers...
, and Yeniseian
Yeniseian languages
The Yeniseian language family is spoken in central Siberia.-Family division:0. Proto-Yeniseian...
. This proposal is rejected by most linguists.
Families with wider distribution
Other languages historically and currently spoken in the Caucasus area can be placed into families with a much wider geographical distribution.Indo-European
The predominant Indo-EuropeanIndo-European languages
The Indo-European languages are a family of several hundred related languages and dialects, including most major current languages of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and South Asia and also historically predominant in Anatolia...
language in the Caucasus is Armenian
Armenian language
The Armenian language is an Indo-European language spoken by the Armenian people. It is the official language of the Republic of Armenia as well as in the region of Nagorno-Karabakh. The language is also widely spoken by Armenian communities in the Armenian diaspora...
, spoken by the Armenians
Armenians
Armenian people or Armenians are a nation and ethnic group native to the Armenian Highland.The largest concentration is in Armenia having a nearly-homogeneous population with 97.9% or 3,145,354 being ethnic Armenian....
(circa 4 million speakers). The Ossetians, speaking the Ossetic language
Ossetic language
Ossetian , also sometimes called Ossete, is an East Iranian language spoken in Ossetia, a region on the slopes of the Caucasus Mountains....
, form another group of around 700,000 speakers. Other Indo-European languages spoken in the Caucasus include Pontic Greek, Persian
Persian language
Persian is an Iranian language within the Indo-Iranian branch of the Indo-European languages. It is primarily spoken in Iran, Afghanistan, Tajikistan and countries which historically came under Persian influence...
, Kurdish
Kurdish language
Kurdish is a dialect continuum spoken by the Kurds in western Asia. It is part of the Iranian branch of the Indo-Iranian group of Indo-European languages....
, Talysh
Talysh language
The Talyshi language is a Northwestern Iranian language spoken in the northern regions of the Iranian provinces of Gilan and Ardabil and the southern regions of the Republic of Azerbaijan. Historically, the language and its people can be traced through the middle Iranian period back to the ancient...
, Judeo-Tat, Bukhori and of the Slavic languages
Slavic languages
The Slavic languages , a group of closely related languages of the Slavic peoples and a subgroup of Indo-European languages, have speakers in most of Eastern Europe, in much of the Balkans, in parts of Central Europe, and in the northern part of Asia.-Branches:Scholars traditionally divide Slavic...
, Russian
Russian language
Russian is a Slavic language used primarily in Russia, Belarus, Uzbekistan, Kazakhstan, Tajikistan and Kyrgyzstan. It is an unofficial but widely spoken language in Ukraine, Moldova, Latvia, Turkmenistan and Estonia and, to a lesser extent, the other countries that were once constituent republics...
and Ukrainian
Ukrainian language
Ukrainian is a language of the East Slavic subgroup of the Slavic languages. It is the official state language of Ukraine. Written Ukrainian uses a variant of the Cyrillic alphabet....
, whose speakers number over a third of the total population of the Caucasus.
Altaic
Several Turkic languagesTurkic languages
The Turkic languages constitute a language family of at least thirty five languages, spoken by Turkic peoples across a vast area from Eastern Europe and the Mediterranean to Siberia and Western China, and are considered to be part of the proposed Altaic language family.Turkic languages are spoken...
are spoken in the Caucasus. Of these, Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani language
Azerbaijani or Azeri or Torki is a language belonging to the Turkic language family, spoken in southwestern Asia by the Azerbaijani people, primarily in Azerbaijan and northwestern Iran...
is predominant, with around 9 million speakers in Azerbaijan. Other Turkic languages spoken include Balkar, Karachay, Kumyk
Kumyk language
Kumyk is a Turkic language, spoken by about 365,000 speakers in the Dagestan republic of Russian Federation....
, Nogai
Nogai language
Nogai , is a Turkic language spoken in southwestern Russia. Three distinct dialects are recognized: Qara-Nogay , spoken in Dagestan; Nogai Proper, in Stavropol; and Aqnogay , by the Kuban River, its tributaries in Karachay-Cherkessia, and in the Mineralnye Vody District...
.
Kalmyk
Kalmyk language
The Kalmyk language , or Russian Oirat, is the native speech of the Kalmyk people of the Republic of Kalmykia, a federal subject of the Russian Federation. In Russia, it is the normative form of the Oirat language , which belongs to the Mongolic language family...
, spoken by the Oirat
Oirat language
Oirat belongs to the group of Mongolic languages. Scholars differ as to whether Oirat is a distinct language or a major dialect of the Mongolian language...
descendant Kalmyks in the region is a Mongolic language.
Semitic
The only Semitic language spoken in the Caucasus is Assyrian Neo-AramaicAssyrian Neo-Aramaic
Assyrian Neo-Aramaic is a Neo-Aramaic dialect, spoken by an estimated 220,000 people , formerly in the area between Lake Urmia, north-western Iran, and Siirt, south-eastern Turkey, but now more widely throughout the...
, spoken by around 30,000 speakers, largely living in cities, who fled to Russia from Turkey as the aftermath of Assyrian Genocide
Assyrian genocide
The Assyrian Genocide refers to the mass slaughter of the Assyrian/Chaldean/Syriac population of the Ottoman Empire during the 1890s, the First World War, and the period of 1922-1925...
at the close of the First World War.
External links
- Caucasian Languages (North and South) Academic Mailing List, run by the Ravenscraig Press
- Map of the Languages of the Caucasus
- TITUS: Caucasian languages map by Jost Gippert& projects Armazi& Ecling
- CIA ethnolinguistic map
- Linguistic families map by Matthew Dryer
- Caucausian Dictionary
- Caucausian section of the Red Book of the Peoples of the Russian Empire
- The Iberian-Caucasian Connection in a Typological Perspective – An in-depth linguistic study of Basque, Georgian, and other ergative languages, concluding that the similarities are not strong enough to prove a genetic link.
- The A. Chikobava Institute of Linguistics, Georgian Academy of Sciences
- Atlas of the Caucasian Languages with very detailed Language Guide (by Yuri B. Koryakov)
- The Graphic Model and the Maps of the Urheimat of the North Caucasian and Abkhaz–Adyghean Languages
- Comparative Notes on Hurro-Urartian, Northern Caucasian and Indo-European by V. V. Ivanov

