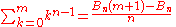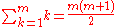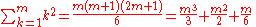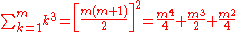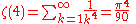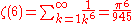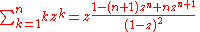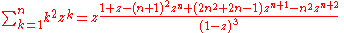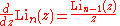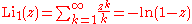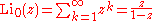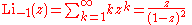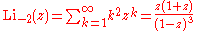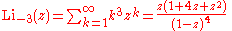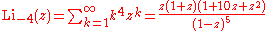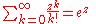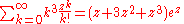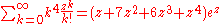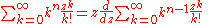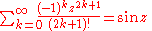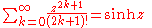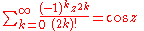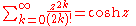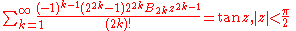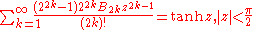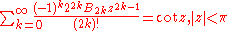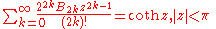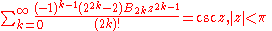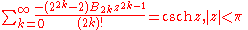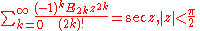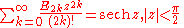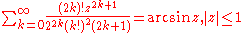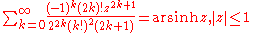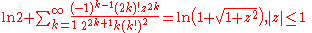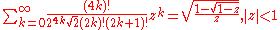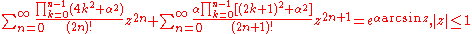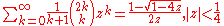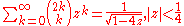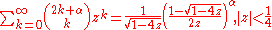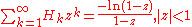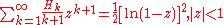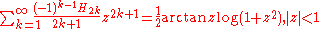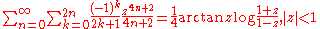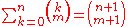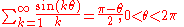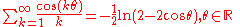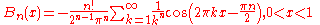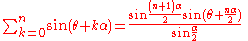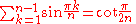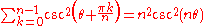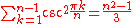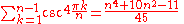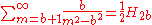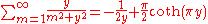List of mathematical series
Encyclopedia
This list of mathematical series contains formulae for finite and infinite sums. It can be used in conjunction with other tools for evaluating sums
.
The first few values are:
See zeta constants.
The first few values are:
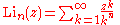
Infinite sums, valid for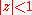 (see polylogarithm):
(see polylogarithm):
The following is a useful property to calculate low-integer-order polylogarithms recursively in closed form
:
s and cosines arise in Fourier series
.
Evaluating sums
In mathematics, a series is the sum of the elements of a sequence. This article mentions a few common series and how to compute their values...
.
- Here,
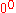 is taken to have the value 1.
is taken to have the value 1. 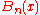 is a Bernoulli polynomial.
is a Bernoulli polynomial.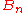 is a Bernoulli numberBernoulli numberIn mathematics, the Bernoulli numbers Bn are a sequence of rational numbers with deep connections to number theory. They are closely related to the values of the Riemann zeta function at negative integers....
is a Bernoulli numberBernoulli numberIn mathematics, the Bernoulli numbers Bn are a sequence of rational numbers with deep connections to number theory. They are closely related to the values of the Riemann zeta function at negative integers....
, and here,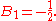
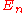 is an Euler number.
is an Euler number.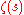 is the Riemann zeta function.
is the Riemann zeta function.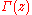 is the Gamma functionGamma functionIn mathematics, the gamma function is an extension of the factorial function, with its argument shifted down by 1, to real and complex numbers...
is the Gamma functionGamma functionIn mathematics, the gamma function is an extension of the factorial function, with its argument shifted down by 1, to real and complex numbers...
.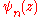 is a polygamma function.
is a polygamma function.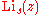 is a polylogarithm.
is a polylogarithm.
Sums of powers
See Faulhaber's formula.The first few values are:
See zeta constants.
The first few values are:
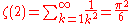 (the Basel problemBasel problemThe Basel problem is a famous problem in mathematical analysis with relevance to number theory, first posed by Pietro Mengoli in 1644 and solved by Leonhard Euler in 1735. Since the problem had withstood the attacks of the leading mathematicians of the day, Euler's solution brought him immediate...
(the Basel problemBasel problemThe Basel problem is a famous problem in mathematical analysis with relevance to number theory, first posed by Pietro Mengoli in 1644 and solved by Leonhard Euler in 1735. Since the problem had withstood the attacks of the leading mathematicians of the day, Euler's solution brought him immediate...
)
Low-order polylogarithms
Finite sums: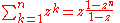 , (geometric series)
, (geometric series)
Infinite sums, valid for
 (see polylogarithm):
(see polylogarithm):
The following is a useful property to calculate low-integer-order polylogarithms recursively in closed form
Closed-form expression
In mathematics, an expression is said to be a closed-form expression if it can be expressed analytically in terms of a bounded number of certain "well-known" functions...
:
Exponential function
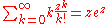 (c.f. mean of Poisson distributionPoisson distributionIn probability theory and statistics, the Poisson distribution is a discrete probability distribution that expresses the probability of a given number of events occurring in a fixed interval of time and/or space if these events occur with a known average rate and independently of the time since...
(c.f. mean of Poisson distributionPoisson distributionIn probability theory and statistics, the Poisson distribution is a discrete probability distribution that expresses the probability of a given number of events occurring in a fixed interval of time and/or space if these events occur with a known average rate and independently of the time since...
)
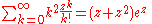 (c.f. second moment of Poisson distribution)
(c.f. second moment of Poisson distribution)
Trigonometric, inverse trigonometric, hyperbolic, and inverse hyperbolic functions
Modified-factorial denominators
Binomial coefficients
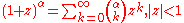 (see Binomial theoremBinomial theoremIn elementary algebra, the binomial theorem describes the algebraic expansion of powers of a binomial. According to the theorem, it is possible to expand the power n into a sum involving terms of the form axbyc, where the exponents b and c are nonnegative integers with , and the coefficient a of...
(see Binomial theoremBinomial theoremIn elementary algebra, the binomial theorem describes the algebraic expansion of powers of a binomial. According to the theorem, it is possible to expand the power n into a sum involving terms of the form axbyc, where the exponents b and c are nonnegative integers with , and the coefficient a of...
)-
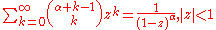
Harmonic Numbers
Binomial coefficients
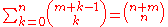 (see Multiset)
(see Multiset)
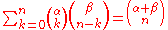 (see Vandermonde identity)
(see Vandermonde identity)
Trigonometric functions
Sums of sineSine
In mathematics, the sine function is a function of an angle. In a right triangle, sine gives the ratio of the length of the side opposite to an angle to the length of the hypotenuse.Sine is usually listed first amongst the trigonometric functions....
s and cosines arise in Fourier series
Fourier series
In mathematics, a Fourier series decomposes periodic functions or periodic signals into the sum of a set of simple oscillating functions, namely sines and cosines...
.
Unclassified
See also
- Series (mathematics)Series (mathematics)A series is the sum of the terms of a sequence. Finite sequences and series have defined first and last terms, whereas infinite sequences and series continue indefinitely....
- List of integrals
- Summation
- Taylor seriesTaylor seriesIn mathematics, a Taylor series is a representation of a function as an infinite sum of terms that are calculated from the values of the function's derivatives at a single point....
- Binomial theoremBinomial theoremIn elementary algebra, the binomial theorem describes the algebraic expansion of powers of a binomial. According to the theorem, it is possible to expand the power n into a sum involving terms of the form axbyc, where the exponents b and c are nonnegative integers with , and the coefficient a of...
- Gregory's seriesGregory's seriesGregory's series, also known as the Madhava-Gregory series or Leibniz's series, is a mathematical series that was discovered by the Indian mathematician Madhava of Sangamagrama...