
Long-term effects of alcohol
Encyclopedia
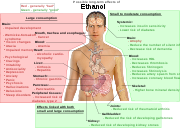
Alcohol abuse
Alcohol abuse, as described in the DSM-IV, is a psychiatric diagnosis describing the recurring use of alcoholic beverages despite negative consequences. Alcohol abuse eventually progresses to alcoholism, a condition in which an individual becomes dependent on alcoholic beverages in order to avoid...
. There is a strong correlation between 'high levels' [ See mayo Clinic for details] of alcohol consumption and an increased risk of developing alcoholism
Alcoholism
Alcoholism is a broad term for problems with alcohol, and is generally used to mean compulsive and uncontrolled consumption of alcoholic beverages, usually to the detriment of the drinker's health, personal relationships, and social standing...
, cardiovascular disease
Cardiovascular disease
Heart disease or cardiovascular disease are the class of diseases that involve the heart or blood vessels . While the term technically refers to any disease that affects the cardiovascular system , it is usually used to refer to those related to atherosclerosis...
, malabsorption
Malabsorption
Malabsorption is a state arising from abnormality in absorption of food nutrients across the gastrointestinal tract.Impairment can be of single or multiple nutrients depending on the abnormality...
, chronic pancreatitis
Chronic pancreatitis
Chronic pancreatitis is a long-standing inflammation of the pancreas that alters its normal structure and functions. It can present as episodes of acute inflammation in a previously injured pancreas, or as chronic damage with persistent pain or malabsorption....
, alcoholic liver disease
Alcoholic liver disease
Alcoholic liver disease is a term that encompasses the hepatic manifestations of alcohol overconsumption, including fatty liver, alcoholic hepatitis, and chronic hepatitis with hepatic fibrosis or cirrhosis. It is the major cause of liver disease in Western countries...
, and cancer
Cancer
Cancer , known medically as a malignant neoplasm, is a large group of different diseases, all involving unregulated cell growth. In cancer, cells divide and grow uncontrollably, forming malignant tumors, and invade nearby parts of the body. The cancer may also spread to more distant parts of the...
. Damage to the central nervous system
Central nervous system
The central nervous system is the part of the nervous system that integrates the information that it receives from, and coordinates the activity of, all parts of the bodies of bilaterian animals—that is, all multicellular animals except sponges and radially symmetric animals such as jellyfish...
and peripheral nervous system
Peripheral nervous system
The peripheral nervous system consists of the nerves and ganglia outside of the brain and spinal cord. The main function of the PNS is to connect the central nervous system to the limbs and organs. Unlike the CNS, the PNS is not protected by the bone of spine and skull, or by the blood–brain...
can occur from chronic alcohol abuse. Long-term use of alcohol in excessive quantities is capable of damaging nearly every organ and system in the body. The developing adolescent brain is particularly vulnerable to the toxic effects of alcohol.
Historically doctors have promoted alcohol for its perceived health benefits and most recently for protection against coronary heart disease
Coronary heart disease
Coronary artery disease is the end result of the accumulation of atheromatous plaques within the walls of the coronary arteries that supply the myocardium with oxygen and nutrients. It is sometimes also called coronary heart disease...
. There is evidence of cardiovascular benefits from drinking 1 - 2 drinks per day; however, the health benefits from moderate intake of alcohol are controversial. Alcohol should be regarded as a recreational drug with potentially serious adverse effects on health and it is not recommended for cardio-protection in the place of safer and proven traditional methods such as exercise, a balanced diet, and pharmacotherapy.
Some experts argue that the benefits of moderate alcohol consumption may be outweighed by other increased risks, including those of injuries, violence
Violence
Violence is the use of physical force to apply a state to others contrary to their wishes. violence, while often a stand-alone issue, is often the culmination of other kinds of conflict, e.g...
, fetal damage, certain forms of cancer
Cancer
Cancer , known medically as a malignant neoplasm, is a large group of different diseases, all involving unregulated cell growth. In cancer, cells divide and grow uncontrollably, forming malignant tumors, and invade nearby parts of the body. The cancer may also spread to more distant parts of the...
, liver disease
Liver disease
Liver disease is a broad term describing any single number of diseases affecting the liver.-Diseases:* Hepatitis, inflammation of the liver, caused mainly by various viruses but also by some poisons , autoimmunity or hereditary conditions...
and hypertension
Hypertension
Hypertension or high blood pressure is a cardiac chronic medical condition in which the systemic arterial blood pressure is elevated. What that means is that the heart is having to work harder than it should to pump the blood around the body. Blood pressure involves two measurements, systolic and...
. As the apparent health benefits of moderate alcohol consumption are limited for populations at low risk of heart disease, other experts urge caution because of the possibility that recommending moderate alcohol consumption may lead to an increased risk of alcohol abuse.
Background
The adverse effects of long-term excessive use of alcohol are close to those seen with other sedative-hypnotics (apart from organ toxicity which is much more problematic with alcohol). WithdrawalWithdrawal
Withdrawal can refer to any sort of separation, but is most commonly used to describe the group of symptoms that occurs upon the abrupt discontinuation/separation or a decrease in dosage of the intake of medications, recreational drugs, and alcohol...
effects and dependence are also almost identical. Alcohol at moderate levels has some positive and negative effects on health. The negative effects include increased risk of liver diseases, oropharyngeal cancer
Cancer
Cancer , known medically as a malignant neoplasm, is a large group of different diseases, all involving unregulated cell growth. In cancer, cells divide and grow uncontrollably, forming malignant tumors, and invade nearby parts of the body. The cancer may also spread to more distant parts of the...
, esophageal cancer
Esophageal cancer
Esophageal cancer is malignancy of the esophagus. There are various subtypes, primarily squamous cell cancer and adenocarcinoma . Squamous cell cancer arises from the cells that line the upper part of the esophagus...
and pancreatitis
Pancreatitis
Pancreatitis is inflammation of the pancreas. It occurs when pancreatic enzymes that digest food are activated in the pancreas instead of the small intestine. It may be acute – beginning suddenly and lasting a few days, or chronic – occurring over many years...
. Conversely moderate intake of alcohol may have some beneficial effects on gastritis
Gastritis
Gastritis is an inflammation of the lining of the stomach, and has many possible causes. The main acute causes are excessive alcohol consumption or prolonged use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as aspirin or ibuprofen. Sometimes gastritis develops after major surgery, traumatic...
and cholelithiasis. Chronic alcohol misuse and abuse has serious effects on physical and mental health. Chronic excess alcohol intake, or alcohol dependence, can lead to a wide range of neuropsychiatric or neurological impairment, cardiovascular disease, liver disease
Liver disease
Liver disease is a broad term describing any single number of diseases affecting the liver.-Diseases:* Hepatitis, inflammation of the liver, caused mainly by various viruses but also by some poisons , autoimmunity or hereditary conditions...
, and malignant neoplasms. The psychiatric disorders which are associated with alcoholism include major depression, dysthymia, mania
Mania
Mania, the presence of which is a criterion for certain psychiatric diagnoses, is a state of abnormally elevated or irritable mood, arousal, and/ or energy levels. In a sense, it is the opposite of depression...
, hypomania
Hypomania
Hypomania is a mood state characterized by persistent and pervasive elevated or irritable mood, as well as thoughts and behaviors that are consistent with such a mood state...
, panic disorder
Panic disorder
Panic disorder is an anxiety disorder characterized by recurring severe panic attacks. It may also include significant behavioral change lasting at least a month and of ongoing worry about the implications or concern about having other attacks. The latter are called anticipatory attacks...
, phobias, generalized anxiety disorder, personality disorders, schizophrenia
Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a mental disorder characterized by a disintegration of thought processes and of emotional responsiveness. It most commonly manifests itself as auditory hallucinations, paranoid or bizarre delusions, or disorganized speech and thinking, and it is accompanied by significant social...
, suicide
Suicide
Suicide is the act of intentionally causing one's own death. Suicide is often committed out of despair or attributed to some underlying mental disorder, such as depression, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, alcoholism, or drug abuse...
, neurologic deficits (e.g. impairments of working memory
Working memory
Working memory has been defined as the system which actively holds information in the mind to do verbal and nonverbal tasks such as reasoning and comprehension, and to make it available for further information processing...
, emotions, executive functions
Executive functions
The executive system is a theorized cognitive system in psychology that controls and manages other cognitive processes. It is responsible for processes that are sometimes referred to as the executive function, executive functions, supervisory attentional system, or cognitive control...
, visuospatial abilities and gait
Gait
Gait is the pattern of movement of the limbs of animals, including humans, during locomotion over a solid substrate. Most animals use a variety of gaits, selecting gait based on speed, terrain, the need to maneuver, and energetic efficiency...
and balance
Balance (ability)
In biomechanics, balance is an ability to maintain the center of gravity of a body within the base of support with minimal postural sway. When exercising the ability to balance, one is said to be balancing....
) and brain damage
Brain damage
"Brain damage" or "brain injury" is the destruction or degeneration of brain cells. Brain injuries occur due to a wide range of internal and external factors...
. Alcohol dependence is associated with hypertension
Hypertension
Hypertension or high blood pressure is a cardiac chronic medical condition in which the systemic arterial blood pressure is elevated. What that means is that the heart is having to work harder than it should to pump the blood around the body. Blood pressure involves two measurements, systolic and...
, coronary heart disease
Coronary heart disease
Coronary artery disease is the end result of the accumulation of atheromatous plaques within the walls of the coronary arteries that supply the myocardium with oxygen and nutrients. It is sometimes also called coronary heart disease...
, and ischemic stroke, cancer
Cancer
Cancer , known medically as a malignant neoplasm, is a large group of different diseases, all involving unregulated cell growth. In cancer, cells divide and grow uncontrollably, forming malignant tumors, and invade nearby parts of the body. The cancer may also spread to more distant parts of the...
of the respiratory system
Respiratory system
The respiratory system is the anatomical system of an organism that introduces respiratory gases to the interior and performs gas exchange. In humans and other mammals, the anatomical features of the respiratory system include airways, lungs, and the respiratory muscles...
, and also cancers of the digestive system, liver
Liver
The liver is a vital organ present in vertebrates and some other animals. It has a wide range of functions, including detoxification, protein synthesis, and production of biochemicals necessary for digestion...
, breast
Breast
The breast is the upper ventral region of the torso of a primate, in left and right sides, which in a female contains the mammary gland that secretes milk used to feed infants.Both men and women develop breasts from the same embryological tissues...
and ovaries. Heavy drinking is associated with liver disease
Liver disease
Liver disease is a broad term describing any single number of diseases affecting the liver.-Diseases:* Hepatitis, inflammation of the liver, caused mainly by various viruses but also by some poisons , autoimmunity or hereditary conditions...
, such as cirrhosis
Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis is a consequence of chronic liver disease characterized by replacement of liver tissue by fibrosis, scar tissue and regenerative nodules , leading to loss of liver function...
. Studies have focused on both men and women, various age groups, and people of many ethnic groups. Published papers now total in the many hundreds, with studies having shown correlation between moderate alcohol use and health that may instead have been due to the beneficial effects of socialization that is often accompanied by alcohol consumption. Some of the specific ways alcohol affects cardiovascular health have been studied. The impact of alcohol on aging
Impact of alcohol on aging
The impact of alcohol on aging is multifaceted. Evidence shows that alcoholism or chronic alcohol consumption can cause both accelerated aging – in which symptoms of aging appear earlier than normal – and exaggerated aging, in which the symptoms appear at the appropriate time but in a...
is negative when excessive amounts of alcohol are consumed.
Maximum quantity recommended
Different countries recommend different maximum quantities. For most countries, the maximum quantity for men is 140 g–210 g per week. For women, the range is 84 g–140 g per week. Most countries recommend total abstinence whilst pregnant or breastfeeding.Alcohol-related deaths
Over-consumption of alcohol is one of the leading preventable causes of death worldwide. One study links alcohol to 1 in every 25 deaths worldwide and that 5% of years lived with disability are attributable to alcohol consumption.Countries collect statistics on alcohol-related deaths. While some categories relate to short-term effects, such as accidents, many relate to long-term effects of alcohol.
Russia
One study claims that "excessive alcohol consumption in Russia, particularly by men, has in recent years caused more than half of all the deaths at ages 15-54 years." However, there are some difficulties with this study. For instance the same study also found a protective effect of heavy drinking on breast cancer mortality. This contradicts the well established scientific view that alcohol increases breast cancer risk. On this account in further correspondence it was advised that "careful interpretation of mortality statistics in relation to alcohol use is needed, taking into account other relevant risk factors, incidence, and survival."The authors replied that "whether or not the apparent shortfall in breast cancer mortality among heavy drinkers is real, it accounts for only about 0·1% of adult deaths in Russia. Careful interpretation of it is therefore of little relevance to the findings for alcohol and overall mortality".
United Kingdom
Alcohol-related deaths in the United Kingdom are coded using the Tenth Revision of the International Classification of DiseasesICD
The International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems is a medical classification that provides codes to classify diseases and a wide variety of signs, symptoms, abnormal findings, complaints, social circumstances, and external causes of injury or disease...
(ICD-10).
ICD-10
ICD-10
The International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems, 10th Revision is a medical classification list for the coding of diseases, signs and symptoms, abnormal findings, complaints, social circumstances, and external causes of injury or diseases, as maintained by the...
comprises:
- Mental and behavioural disorders due to use of alcohol – ICD-10 F10
- Degeneration of nervous system due to alcohol – ICD-10 G31.2
- Alcoholic polyneuropathy – ICD-10 G62.1
- Alcoholic cardiomyopathy – ICD-10 I42.6
- Alcoholic gastritis – ICD-10 K29.2
- Alcoholic liver disease – ICD-10 K70
- Chronic hepatitis, not elsewhere classified – ICD-10 K73
- Fibrosis and cirrhosis of liver – ICD-10 K74 (Excluding K74.3-K74.5 – Biliary cirrhosis)
- Alcohol induced chronic pancreatitis – ICD-10 K86.0
- Accidental poisoning by and exposure to alcohol – ICD-10 X45
- Intentional self-poisoning by and exposure to alcohol – ICD-10 X65
- Poisoning by and exposure to alcohol, undetermined intent – ICD-10 Y15
UK statistical bodies report that "There were 8,724 alcohol-related deaths in 2007, lower than 2006, but more than double the 4,144 recorded in 1991. The alcohol-related death rate was 13.3 per 100,000 population in 2007, compared with 6.9 per 100,000 population in 1991."
In Scotland, the NHS estimate that in 2003 one in every 20 deaths could be attributed to alcohol.
A 2009 study found that 9,000 people are dying from alcohol-related diseases every year, three times the number 25 years previously.
United States
The Centers for Disease Control and PreventionCenters for Disease Control and Prevention
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention are a United States federal agency under the Department of Health and Human Services headquartered in Druid Hills, unincorporated DeKalb County, Georgia, in Greater Atlanta...
report, "From 2001–2005, there were approximately 79,000 deaths annually attributable to excessive alcohol use. In fact, excessive alcohol use is the 3rd leading lifestyle-related cause of death for people in the United States each year." A 1993 study estimated US deaths through alcohol at 100,000.
Overall mortality
A 23-year prospective study of 12,000 male BritishUnited Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
physician
Physician
A physician is a health care provider who practices the profession of medicine, which is concerned with promoting, maintaining or restoring human health through the study, diagnosis, and treatment of disease, injury and other physical and mental impairments...
s aged 48–78, found that overall mortality was significantly lower in the group consuming less than 2 "units" (British unit = 8 g) per day than in the non-alcohol-drinking group. Greater than 2 units per day was associated with an increased risk of mortality.
This is consistent with other research that found a J-curve dependency between alcohol consumption and total mortality among middle aged and older men. While the mortality rates of ex-drinkers and those drinking beyond moderation are significantly elevated, the all-cause mortality rates may be 15-18% lower among moderate drinkers (1–2 drinks per day) than among abstainers - a meta-analysis found. This claim was challenged by another study that found that in certain low quality studies occasional drinkers or ex-drinkers where included as abstainers, resulting in the increased mortality in that group. However, the J-curve for total and CHD mortality was reconfirmed by studies that took the mentioned confounders into account
The observed decrease in mortality of light-to-moderate drinkers comparing to abstainers can be partially explained by superior health and social status of the drinking group, however the protective effect of alcohol in light to moderate drinkers remains significant even after adjusting for these confounders. Additionally, confounders such as underreporting of alcohol intake might lead to the underestimation of how much mortality is reduced in light-to-moderate drinkers.
Heavy drinking leads to increased mortality. For example a US study found that men who consumed 5 or more drinks on drinking days had a 30% higher mortality rate than those consuming only 1 drink. According to another study, drinkers with heavy drinking occasions (six or more drinks at a time) have a 57% higher all-cause mortality than drinkers without heavy drinking occasions.
Cardiovascular system
A meta-analysis of 34 studies found a reduced risk of mortality from coronary heart disease in men who drank 2 - 4 drinks per day and women who drank 1 - 2 drinks per day. A meta-analysis of randomized trials found that alcohol consumption in moderation decreases serum levels of fibrinogen, a protein that promotes clot formation and increases levels of tissue type plasminogen activator, an enzyme that helps dissolve clots. The serum levels of C-reactive protein (CRP), a marker of inflammation and predictor of CHD (coronary heart disease) risk, are lower in people who drink moderately than those who abstain from alcohol suggesting that alcohol consumption in moderation might have anti-inflammatory effects. In addition to its psychotropic properties, alcohol has anticoagulation properties similar to warfarinWarfarin
Warfarin is an anticoagulant. It is most likely to be the drug popularly referred to as a "blood thinner," yet this is a misnomer, since it does not affect the thickness or viscosity of blood...
. Additionally, thrombosis
Thrombosis
Thrombosis is the formation of a blood clot inside a blood vessel, obstructing the flow of blood through the circulatory system. When a blood vessel is injured, the body uses platelets and fibrin to form a blood clot to prevent blood loss...
is lower among moderate drinkers than teetotalers.
Despite epidemiological evidence, some criticize the idea of recommending alcohol for health benefits. A doctor at the World Health Organisation stated that recommending moderate alcohol consumption for health benefits is "ridiculous and dangerous". There have been no randomised controlled trials to demonstrate the cardio benefits of alcohol. Due to the risks of abuse, dependence, adverse effects, alcohol should never be recommended for cardio benefits as a substitute to well-proven measures, such as a good diet, exercise or pharmaceutical drugs. It has been argued that the health benefits from alcohol are at best debatable and may have been exaggerated by the alcohol industry
Alcohol industry
The alcohol industry is a term used to describe the commercial industry which is involved in the manufacturer, distribution and sale of alcohol. The industry has been criticised in the 1990s for deflecting attention away from the problems associated with alcohol use. The alcohol industry has also...
. Alcohol should be regarded as a recreational drug with potentially serious adverse effects on health and should not be promoted for cardio-protection.
Peripheral arterial disease
"Moderate alcohol consumption appears to decrease the risk of PAD in apparently healthy men." "In this large population-based study, moderate alcohol consumption was inversely associated with peripheral arterial disease in women but not in men. Residual confounding by smoking may have influenced the results. Among nonsmokers an inverse association was found between alcohol consumption and peripheral arterial disease in both men and women."Intermittent claudication (IC)
A study found that moderate consumption of alcohol had a protective effect against intermittent claudicationIntermittent claudication
Intermittent claudication is a clinical diagnosis given for muscle pain , classically in the calf muscle, which occurs during exercise, such as walking, and is relieved by a short period of rest.Claudication derives from the Latin verb claudicare, "to limp".-Signs:One of the hallmarks of arterial...
. The lowest risk was seen in men who drank 1 to 2 drinks per day and in women who drank half to 1 drink per day.
Heart attack and stroke
Drinking in moderation has been found to help those who have suffered a heart attack survive it. However, excessive alcohol consumption leads to an increased risk of heart failure. A review of the literature found that half a drink of alcohol offered the best level of protection. However, they noted that at present there have been no randomised trials to confirm the evidence which suggests a protective role of low doses of alcohol against heart attacks. However, moderate alcohol consumption is associated with hypertension. There is an increased risk of hypertriglyceridemiaHypertriglyceridemia
In medicine, hypertriglyceridemia denotes high blood levels of triglycerides, the most abundant fatty molecule in most organisms. It has been associated with atherosclerosis, even in the absence of hypercholesterolemia . It can also lead to pancreatitis in excessive concentrations In medicine,...
, cardiomyopathy
Cardiomyopathy
Cardiomyopathy, which literally means "heart muscle disease," is the deterioration of the function of the myocardium for any reason. People with cardiomyopathy are often at risk of arrhythmia or sudden cardiac death or both. Cardiomyopathy can often go undetected, making it especially dangerous to...
, hypertension
Hypertension
Hypertension or high blood pressure is a cardiac chronic medical condition in which the systemic arterial blood pressure is elevated. What that means is that the heart is having to work harder than it should to pump the blood around the body. Blood pressure involves two measurements, systolic and...
, and stroke
Stroke
A stroke, previously known medically as a cerebrovascular accident , is the rapidly developing loss of brain function due to disturbance in the blood supply to the brain. This can be due to ischemia caused by blockage , or a hemorrhage...
if 3 or more standard drinks of alcohol are taken per day.
Cardiomyopathy
Large amount of alcohol over the long term can lead to alcoholic cardiomyopathyCardiomyopathy
Cardiomyopathy, which literally means "heart muscle disease," is the deterioration of the function of the myocardium for any reason. People with cardiomyopathy are often at risk of arrhythmia or sudden cardiac death or both. Cardiomyopathy can often go undetected, making it especially dangerous to...
. Alcoholic cardiomyopathy presents in a manner clinically identical to idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy
Dilated cardiomyopathy
Dilated cardiomyopathy or DCM is a condition in which the heart becomes weakened and enlarged and cannot pump blood efficiently. The decreased heart function can affect the lungs, liver, and other body systems....
, involving hypertrophy of the musculature of the heart that can lead to congestive heart failure.
Hematologic diseases
Alcoholics may have anemiaAnemia
Anemia is a decrease in number of red blood cells or less than the normal quantity of hemoglobin in the blood. However, it can include decreased oxygen-binding ability of each hemoglobin molecule due to deformity or lack in numerical development as in some other types of hemoglobin...
from several causes; they may also develop thrombocytopenia
Thrombocytopenia
Thrombocytopenia is a relative decrease of platelets in blood.A normal human platelet count ranges from 150,000 to 450,000 platelets per microliter of blood. These limits are determined by the 2.5th lower and upper percentile, so values outside this range do not necessarily indicate disease...
from direct toxic effect on megakaryocytes, or from hypersplenism.
Nervous system
Chronic heavy alcohol consumption impairs brain development, causes brain shrinkage, dementiaDementia
Dementia is a serious loss of cognitive ability in a previously unimpaired person, beyond what might be expected from normal aging...
, physical dependence
Physical dependence
Physical dependence refers to a state resulting from chronic use of a drug that has produced tolerance and where negative physical symptoms of withdrawal result from abrupt discontinuation or dosage reduction...
, increases neuropsychiatric and cognitive disorders and causes distortion of the brain chemistry. Some studies however have shown that moderate alcohol consumption may decrease risk of dementia, including Alzheimer disease, although there are studies which find the opposite. At present, due to poor study design, and methodology the literature is inconclusive on whether moderate alcohol consumptions increases the risk of dementia or decreases it. Evidence for a protective effect of low to moderate alcohol consumption on age related cognitive decline and dementia has been suggested by some research, however, other research has not found a protective effect of low to moderate alcohol consumption. Some evidence suggests that low to moderate alcohol consumption may speed up brain volume loss. Chronic consumption of alcohol may result in increased plasma levels of the toxic amino acid homocysteine
Homocysteine
Homocysteine is a non-protein amino acid with the formula HSCH2CH2CHCO2H. It is a homologue of the amino acid cysteine, differing by an additional methylene group. It is biosynthesized from methionine by the removal of its terminal Cε methyl group...
; which may explain alcohol withdrawal seizures, alcohol-induced brain atrophy and alcohol-related cognitive disturbances.
Strokes
Epidemiological studies of middle-aged populations generally find the relationship between alcohol intake and the risk of stroke to be either U- or J-shaped."The consistency in the vascular benefit associated with moderate drinking (compared with non-drinking) observed across different studies, together with the existence of credible biological pathways, strongly suggests that at least some of this benefit is real. However, because of biases introduced by: choice of reference categories; reverse causality bias; variations in alcohol intake over time; and confounding, some of it is likely to be an artefact."
Drinking lots of alcohol has been negatively linked to stroke. According to the National Stroke Association, more than 2 drinks per day (one drink is ~5 ounces of wine) may increase stroke risk by 50% and lead to other medical problems. Because of this and other known harmful effects of heavy drinking, care should be taken when considering safe amounts of alcohol intake.
Brain
Alcohol abuse is associated with wide spread and significant brain lesions. Alcohol related brain damage is due not only to the direct toxic effects of alcohol; alcohol withdrawal, nutritional deficiency, electrolyte disturbances, and liver damage are also believed to contribute to alcohol related brain damage.Brain development
Consuming large amounts of alcohol over a period of time can impair normal brain development in humans. Deficits in retrieval of verbal and nonverbal information and in visuospatial functioning were evident in youths with histories of heavy drinking during early and middle adolescence.During adolescence critical stages of neurodevelopment occur. Binge drinking, which is common among adolescents, interferes with this important stage of development. Heavy alcohol consumption inhibits new brain cell development.
Nearly half of chronic alcoholics may have myopathy
Myopathy
In medicine, a myopathy is a muscular disease in which the muscle fibers do not function for any one of many reasons, resulting in muscular weakness. "Myopathy" simply means muscle disease...
. Proximal muscle groups are especially affected. Twenty-five percent of alcoholics may have peripheral neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy is the term for damage to nerves of the peripheral nervous system, which may be caused either by diseases of or trauma to the nerve or the side-effects of systemic illness....
, including autonomic.
Cognition and dementia
Excessive alcohol intake is associated with impaired prospective memoryProspective memory
Prospective memory is a form of memory that involves remembering to perform a planned action or intention at the appropriate time. Prospective memory tasks are highly prevalent in daily life and range from relatively simple tasks to extreme life-or-death situations...
. This impaired cognitive ability leads to increased failure to carry out an intended task at a later date, for example, forgetting to lock the door or to post a letter on time. The higher the volume of alcohol consumed and the longer consumed, the more severe the impairments. One of the organs most sensitive to the toxic effects of chronic alcohol consumption is the brain. In France approximately 20% of admissions to mental health facilities are related to alcohol related cognitive impairment, most notably alcohol related dementia. Chronic excessive alcohol intake is also associated with serious cognitive decline and a range of neuropsychiatric complications. The elderly are the most sensitive to the toxic effects of alcohol on the brain. There is some inconclusive evidence that small amounts of alcohol taken in earlier adult life is protective in later life against cognitive decline and dementia. However, a study concluded, "Our findings suggest that, despite previous suggestions, moderate alcohol consumption does not protect older people from cognitive decline."
Acetaldehyde
Acetaldehyde
Acetaldehyde is an organic chemical compound with the formula CH3CHO or MeCHO. It is one of the most important aldehydes, occurring widely in nature and being produced on a large scale industrially. Acetaldehyde occurs naturally in coffee, bread, and ripe fruit, and is produced by plants as part...
is produced by the liver during breakdown of ethanol. People who have a genetic deficiency for the subsequent conversion of acetaldehyde into acetic acid
Acetic acid
Acetic acid is an organic compound with the chemical formula CH3CO2H . It is a colourless liquid that when undiluted is also called glacial acetic acid. Acetic acid is the main component of vinegar , and has a distinctive sour taste and pungent smell...
(a trait more prevalent in those of East Asian descent) may have a greater risk of Alzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's disease also known in medical literature as Alzheimer disease is the most common form of dementia. There is no cure for the disease, which worsens as it progresses, and eventually leads to death...
. "These results indicate that the ALDH2
ALDH2
Aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 family , also known as ALDH2, is a human gene found on chromosome 12.-Function:The enzyme encoded by this gene belongs to the aldehyde dehydrogenase family of enzymes that catalyze the chemical transformation from acetaldehyde to acetic acid...
deficiency is a risk factor for LOAD [late-onset Alzheimer's disease] …"
Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome
Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome
Wernicke–Korsakoff syndrome is a manifestation of thiamine deficiency, or beriberi. This is usually secondary to alcohol abuse...
is a manifestation of thiamine
Thiamine
Thiamine or thiamin or vitamin B1 , named as the "thio-vitamine" is a water-soluble vitamin of the B complex. First named aneurin for the detrimental neurological effects if not present in the diet, it was eventually assigned the generic descriptor name vitamin B1. Its phosphate derivatives are...
deficiency, usually as a secondary effect of alcohol abuse. The syndrome is a combined manifestation of two eponymous disorders, Korsakoff's Psychosis
Korsakoff's syndrome
Korsakoff's syndrome is a neurological disorder caused by the lack of thiamine in the brain. Its onset is linked to chronic alcohol abuse and/or severe malnutrition...
and Wernicke's encephalopathy
Wernicke's encephalopathy
Wernicke encephalopathy is a syndrome characterised by ataxia, ophthalmoplegia, confusion, and impairment of short-term memory.It is caused by lesions in the medial thalamic nuclei, mammillary bodies, periaqueductal and periventricular brainstem nuclei, and superior cerebellar vermis, often...
, named after Drs. Sergei Korsakoff
Sergei Korsakoff
Sergei Sergeievich Korsakoff was a Russian neuropsychiatrist.Sergei Korsakoff was the first of great Russian neuropsychiatrists. He studied medicine at the University of Moscow, graduated in 1875 and subsequently became physician to "Preobrazhenski" mental hospital. From 1876 to 1879 he gained...
and Carl Wernicke. Wernicke's encephalopathy is the acute presentation of the syndrome and is characterised by a confusion
ConFusion
ConFusion is an annual science fiction convention organized by the Stilyagi Air Corps and its parent organization, the Ann Arbor Science Fiction Association. Commonly, it is held the third weekend of January. It is the oldest science fiction convention in Michigan, a regional, general SF con...
al state while Korsakoff's psychosis main symptoms are amnesia
Amnesia
Amnesia is a condition in which one's memory is lost. The causes of amnesia have traditionally been divided into categories. Memory appears to be stored in several parts of the limbic system of the brain, and any condition that interferes with the function of this system can cause amnesia...
and executive dysfunction
Executive functions
The executive system is a theorized cognitive system in psychology that controls and manages other cognitive processes. It is responsible for processes that are sometimes referred to as the executive function, executive functions, supervisory attentional system, or cognitive control...
.
Essential tremor
Essential tremorEssential tremor
Essential tremor is a slowly progressive neurological disorder whose most recognizable feature is a tremor of the arms that is apparent during voluntary movements such as eating and writing...
s can be temporarily relieved in up to two-thirds of patients by drinking small amounts of alcohol.
Sleep
Chronic use of alcohol used to induce sleep can lead to insomniaInsomnia
Insomnia is most often defined by an individual's report of sleeping difficulties. While the term is sometimes used in sleep literature to describe a disorder demonstrated by polysomnographic evidence of disturbed sleep, insomnia is often defined as a positive response to either of two questions:...
. Frequent moving between sleep stages occurs, with awakenings due to headaches and diaphoresis
Diaphoresis
Diaphoresis is excessive sweating commonly associated with shock and other medical emergency conditions.Diaphoretic is the state of perspiring profusely, or something that has the power to cause increased perspiration....
. Stopping chronic alcohol abuse can also lead to profound disturbances of sleep with vivid dreams. Chronic alcohol abuse is associated with NREM
NREM
Non-rapid eye movement, or NREM is, collectively, sleep stages 1 – 3, previously known as stages 1 – 4. Rapid eye movement sleep is not included. There are distinct electroencephalographic and other characteristics seen in each stage. Unlike REM sleep, there is usually little or no eye movement...
stage 3 and 4 sleep as well as suppression of REM sleep and REM sleep fragmentation. During withdrawal REM sleep is typically exaggerated as part of a rebound effect
Rebound effect
The rebound effect, or rebound phenomenon, is the tendency of some medications, when discontinued suddenly, to cause a return of the symptoms it relieved, and that, to a degree stronger than they were before treatment first began...
.
Mental health effects
High rates of major depressive disorder occur in heavy drinkers and those who abuse alcohol. Whether it is more true that major depressive disorder causes self-medicating alcohol abuse, or the increased incidence of the disorder in alcohol abusers is caused by the drinking, is not known though some evidence suggests drinking causes the disorder. Alcohol misuse is associated with a number of mental health disorders and alcoholics have a very high suicideSuicide
Suicide is the act of intentionally causing one's own death. Suicide is often committed out of despair or attributed to some underlying mental disorder, such as depression, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, alcoholism, or drug abuse...
rate. A study of people hospitalised for suicide attempts found that those who were alcoholics were 75 times more likely to go on to successfully commit suicide than non-alcoholic suicide attempters. In the general alcoholic population the increased risk of suicide compared to the general public is 5 - 20 times greater. About 15 percent of alcoholics commit suicide. Abuse of other drugs is also associated with an increased risk of suicide. About 33 percent of suicides in the under 35s are due to alcohol or other substance misuse.
Studies have shown that alcohol dependence relates directly to cravings and irritability
Irritability
Irritability is an excessive response to stimuli. The term is used for both the physiological reaction to stimuli and for the pathological, abnormal or excessive sensitivity to stimuli; It is usually used to refer to anger or frustration....
. Another study has shown that alcohol use is a significant predisposing factor towards antisocial behavior in children. Depression, anxiety and panic disorder are disorders commonly reported by alcohol dependent people. Alcoholism is associated with dampened activation in brain networks responsible for emotional processing (e.g. the amygdala
Amygdala
The ' are almond-shaped groups of nuclei located deep within the medial temporal lobes of the brain in complex vertebrates, including humans. Shown in research to perform a primary role in the processing and memory of emotional reactions, the amygdalae are considered part of the limbic system.-...
and hippocampus
Hippocampus
The hippocampus is a major component of the brains of humans and other vertebrates. It belongs to the limbic system and plays important roles in the consolidation of information from short-term memory to long-term memory and spatial navigation. Humans and other mammals have two hippocampi, one in...
). Evidence that the mental health disorders are often induced by alcohol misuse via distortion of brain neurochemistry is indicated by the improvement or disappearance of symptoms that occurs after prolonged abstinence, although problems may worsen in early withdrawal and recovery periods. Psychosis is secondary to several alcohol-related conditions including acute intoxication and withdrawal after significant exposure. Chronic alcohol misuse can cause psychotic type symptoms to develop, more so than with other drugs of abuse. Alcohol abuse has been shown to cause an 800% increased risk of psychotic disorders in men and a 300% increased risk of psychotic disorders in women which are not related to pre-existing psychiatric disorders. This is significantly higher than the increased risk of psychotic disorders seen from cannabis use making alcohol abuse a very significant cause of psychotic disorders. Prominent hallucination
Hallucination
A hallucination, in the broadest sense of the word, is a perception in the absence of a stimulus. In a stricter sense, hallucinations are defined as perceptions in a conscious and awake state in the absence of external stimuli which have qualities of real perception, in that they are vivid,...
s and/or delusion
Delusion
A delusion is a false belief held with absolute conviction despite superior evidence. Unlike hallucinations, delusions are always pathological...
s are usually present when a patient is intoxicated or recently withdrawn from alcohol.
Whilst alcohol
Ethanol
Ethanol, also called ethyl alcohol, pure alcohol, grain alcohol, or drinking alcohol, is a volatile, flammable, colorless liquid. It is a psychoactive drug and one of the oldest recreational drugs. Best known as the type of alcohol found in alcoholic beverages, it is also used in thermometers, as a...
initially helps social phobia or panic symptoms, with longer term alcohol misuse can often worsen social phobia symptoms and can cause panic disorder to develop or worsen, during alcohol intoxication and especially during the alcohol withdrawal syndrome
Alcohol withdrawal syndrome
-Protracted withdrawal:A protracted alcohol withdrawal syndrome occurs in many alcoholics where withdrawal symptoms continue beyond the acute withdrawal stage but usually at a subacute level of intensity and gradually decreasing with severity over time. This syndrome is also sometimes referred to...
. This effect is not unique to alcohol but can also occur with long term use of drugs which have a similar mechanism of action to alcohol such as the benzodiazepines which are sometimes prescribed as tranquillisers to people with alcohol problems. Approximately half of patients attending mental health services for conditions including anxiety disorders such as panic disorder
Panic disorder
Panic disorder is an anxiety disorder characterized by recurring severe panic attacks. It may also include significant behavioral change lasting at least a month and of ongoing worry about the implications or concern about having other attacks. The latter are called anticipatory attacks...
or social phobia
Social anxiety disorder
Social anxiety disorder , also known as social phobia, is an anxiety disorder characterized by intense fear in social situations causing considerable distress and impaired ability to function in at least some parts of daily life...
are the result of alcohol or benzodiazepine dependence
Benzodiazepine dependence
Benzodiazepine dependence or benzodiazepine addiction is a condition during which a person is dependent on benzodiazepine drugs. Dependence can be either a psychological dependence, physical dependence, or a combination of the two...
. It was noted that every individual has an individual sensitivity level to alcohol or sedative hypnotic drugs and what one person can tolerate without ill health another will suffer very ill health and that even moderate drinking can cause rebound anxiety syndromes and sleep disorders. A person who is suffering the toxic effects of alcohol will not benefit from other therapies or medications as they do not address the root cause of the symptoms.
Digestive system and weight gain
The impact of alcohol on weight-gain is contentious: some studies find no effect, others find decreased or increased effect on weight gain.Alcohol use increases the risk of chronic gastritis
Gastritis
Gastritis is an inflammation of the lining of the stomach, and has many possible causes. The main acute causes are excessive alcohol consumption or prolonged use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as aspirin or ibuprofen. Sometimes gastritis develops after major surgery, traumatic...
(stomach inflammation); it is one cause of cirrhosis
Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis is a consequence of chronic liver disease characterized by replacement of liver tissue by fibrosis, scar tissue and regenerative nodules , leading to loss of liver function...
, hepatitis
Hepatitis
Hepatitis is a medical condition defined by the inflammation of the liver and characterized by the presence of inflammatory cells in the tissue of the organ. The name is from the Greek hepar , the root being hepat- , meaning liver, and suffix -itis, meaning "inflammation"...
, and pancreatitis
Pancreatitis
Pancreatitis is inflammation of the pancreas. It occurs when pancreatic enzymes that digest food are activated in the pancreas instead of the small intestine. It may be acute – beginning suddenly and lasting a few days, or chronic – occurring over many years...
in both its chronic
Chronic pancreatitis
Chronic pancreatitis is a long-standing inflammation of the pancreas that alters its normal structure and functions. It can present as episodes of acute inflammation in a previously injured pancreas, or as chronic damage with persistent pain or malabsorption....
and acute
Acute pancreatitis
Acute pancreatitis or acute pancreatic necrosis is a sudden inflammation of the pancreas. It can have severe complications and high mortality despite treatment...
forms.
Metabolic syndrome
A study concluded, "Mild to moderate alcohol consumption is associated with a lower prevalence of the metabolic syndromeMetabolic syndrome
Metabolic syndrome is a combination of medical disorders that, when occurring together, increase the risk of developing cardiovascular disease and diabetes. It affects one in five people in the United States and prevalence increases with age...
, with a favorable influence on lipids, waist circumference, and fasting insulin. This association was strongest among whites and among beer and wine drinkers." This is also true for Asians. A J-curve association between alcohol intake and metabolic syndrome was found: "The results of the present study suggest that the metabolic syndrome is negatively associated with light alcohol consumption (1–15 g alcohol/d) in Korean adults". However, "odds ratios for the metabolic syndrome and its components tended to increase with increasing alcohol consumption."
Gallbladder effects
Research has found that drinking reduces the risk of developing gallstones. Compared with alcohol abstainers, the relative risk of gallstone disease, controlling for age, sex, education, smoking, and body mass index, is 0.83 for occasional and regular moderate drinkers (< 25 ml of ethanol per day), 0.67 for intermediate drinkers (25-50 ml per day), and 0.58 for heavy drinkers. This inverse association was consistent across strata of age, sex, and body mass index." Frequency of drinking also appears to be a factor. "An increase in frequency of alcohol consumption also was related to decreased risk. Combining the reports of quantity and frequency of alcohol intake, a consumption pattern that reflected frequent intake (5-7 days/week) of any given amount of alcohol was associated with a decreased risk, as compared with nondrinkers. In contrast, infrequent alcohol intake (1-2 days/week) showed no significant association with risk.”Consumption of alcohol is unrelated to gallbladder disease. However one study suggested that drinkers who take vitamin C
Vitamin C
Vitamin C or L-ascorbic acid or L-ascorbate is an essential nutrient for humans and certain other animal species. In living organisms ascorbate acts as an antioxidant by protecting the body against oxidative stress...
(ascorbic acid
Ascorbic acid
Ascorbic acid is a naturally occurring organic compound with antioxidant properties. It is a white solid, but impure samples can appear yellowish. It dissolves well in water to give mildly acidic solutions. Ascorbic acid is one form of vitamin C. The name is derived from a- and scorbutus , the...
) might reduce their risk of gallbladder disease.
Liver disease
Alcoholic liver diseaseAlcoholic liver disease
Alcoholic liver disease is a term that encompasses the hepatic manifestations of alcohol overconsumption, including fatty liver, alcoholic hepatitis, and chronic hepatitis with hepatic fibrosis or cirrhosis. It is the major cause of liver disease in Western countries...
is a major public health problem. For example in the United States up to two million people have alcohol related liver disorders. Chronic alcohol abuse can cause fatty liver
Fatty liver
Fatty liver, also known as fatty liver disease , is a reversible condition where large vacuoles of triglyceride fat accumulate in liver cells via the process of steatosis...
, cirrhosis
Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis is a consequence of chronic liver disease characterized by replacement of liver tissue by fibrosis, scar tissue and regenerative nodules , leading to loss of liver function...
and alcoholic hepatitis
Alcoholic hepatitis
Alcoholic hepatitis is hepatitis due to excessive intake of alcohol. While distinct from cirrhosis, it is regarded as the earliest stage of alcoholic liver disease. Symptoms are jaundice, ascites , fatigue and hepatic encephalopathy...
. Treatment options are limited and consist of most importantly discontinuing alcohol consumption. In cases of severe liver disease, the only treatment option may be a liver transplant in alcohol abstinent patients. Research is being conducted into the effectiveness of anti-TNFs. Certain complimentary medications, e.g., milk thistle
Milk thistle
The milk thistle is a thistle of the genus Silybum Adans., a flowering plant of the daisy family . They are native to the Mediterranean regions of Europe, North Africa and the Middle East...
and silymarin, appear to offer some benefit. Alcohol is a leading cause of liver cancer
Liver cancer
Liver tumors or hepatic tumors are tumors or growths on or in the liver . Several distinct types of tumors can develop in the liver because the liver is made up of various cell types. These growths can be benign or malignant...
in the Western world, accounting for 32-45% of hepatic cancers. Up to half a million people in the United States develop alcohol related liver cancer
Liver cancer
Liver tumors or hepatic tumors are tumors or growths on or in the liver . Several distinct types of tumors can develop in the liver because the liver is made up of various cell types. These growths can be benign or malignant...
. Moderate alcohol consumption also increases the risk of liver disease.
Pancreatitis
Alcohol misuse is a leading cause of both acute pancreatitisAcute pancreatitis
Acute pancreatitis or acute pancreatic necrosis is a sudden inflammation of the pancreas. It can have severe complications and high mortality despite treatment...
and chronic pancreatitis
Chronic pancreatitis
Chronic pancreatitis is a long-standing inflammation of the pancreas that alters its normal structure and functions. It can present as episodes of acute inflammation in a previously injured pancreas, or as chronic damage with persistent pain or malabsorption....
. Chronic excessive intake of alcohol can cause destruction of the pancreas resulting in severe chronic pain, which may progress to pancreatic cancer
Pancreatic cancer
Pancreatic cancer refers to a malignant neoplasm of the pancreas. The most common type of pancreatic cancer, accounting for 95% of these tumors is adenocarcinoma, which arises within the exocrine component of the pancreas. A minority arises from the islet cells and is classified as a...
. Chronic pancreatitis often results in malabsorption
Malabsorption
Malabsorption is a state arising from abnormality in absorption of food nutrients across the gastrointestinal tract.Impairment can be of single or multiple nutrients depending on the abnormality...
problems and diabetes.
Alcoholic Lung disease
Chronic alcohol ingestion impairs multiple critical cellular functions in the lung. These cellular impairments lead to increased susceptibility to serious complications from lung disease. Recent research cites alcoholic lung diseaseAlcoholic lung disease
Alcoholic lung disease is disease of the lungs caused by excessive alcohol consumption. Chronic alcohol ingestion impairs multiple critical cellular functions in the lung. These cellular impairments lead to increased susceptibility to serious complications from lung disease. Recent research...
as comparable to liver disease in alcohol related mortality. Alcoholics have a higher risk of developing acute respiratory distress syndrome
Acute respiratory distress syndrome
Acute respiratory distress syndrome , also known as respiratory distress syndrome or adult respiratory distress syndrome is a serious reaction to various forms of injuries to the lung....
(ARDS) and experience higher rates of mortality from ARDS when compared to non-alcoholics.
Kidney stones
Research indicates that drinking alcohol is associated with a lower risk of developing kidney stones. One study concludes, "Since beer seemed to be protective against kidney stones, the physiologic effects of other substances besides ethanol, especially those of hops, should also be examined." "...consumption of coffee, alcohol, and vitamin C supplements were negatively associated with stones." "After mutually adjusting for the intake of other beverages, the risk of stone formation decreased by the following amount for each 240-ml (8-oz) serving consumed daily: caffeinated coffee, 10%; decaffeinated coffee, 10%; tea, 14%; beer, 21%; and wine, 39%." "...stone formation decreased by the following amount for each 240-mL (8-oz) serving consumed daily: 10% for caffeinated coffee, 9% for decaffeinated coffee, 8% for tea, and 59% for wine." (CIConfidence interval
In statistics, a confidence interval is a particular kind of interval estimate of a population parameter and is used to indicate the reliability of an estimate. It is an observed interval , in principle different from sample to sample, that frequently includes the parameter of interest, if the...
data excised from last two quotes.).
Sexual dysfunction
Long term excessive intake of alcohol can lead to damage to the central nervous systemCentral nervous system
The central nervous system is the part of the nervous system that integrates the information that it receives from, and coordinates the activity of, all parts of the bodies of bilaterian animals—that is, all multicellular animals except sponges and radially symmetric animals such as jellyfish...
and the peripheral nervous system
Peripheral nervous system
The peripheral nervous system consists of the nerves and ganglia outside of the brain and spinal cord. The main function of the PNS is to connect the central nervous system to the limbs and organs. Unlike the CNS, the PNS is not protected by the bone of spine and skull, or by the blood–brain...
resulting in loss of sexual desire and impotence in men. This can result due to a reduction of testosterone from ethanol-induced testicular atrophy
Testicular atrophy
Testicular atrophy is a medical condition in which the male reproductive organs diminish in size and may be accompanied by loss of function. This does not refer to temporary changes, such as those brought on by cold.Some medications can cause testicular atrophy...
, resulting in increased feminisation of males and is a clinical feature of alcohol abusing males who have cirrhosis
Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis is a consequence of chronic liver disease characterized by replacement of liver tissue by fibrosis, scar tissue and regenerative nodules , leading to loss of liver function...
of the liver.
Hormonal Imbalance
Excessive alcohol intake can result in hyperoestrogenisation. It has been speculated that alcohol beverages may contain estrogenEstrogen
Estrogens , oestrogens , or œstrogens, are a group of compounds named for their importance in the estrous cycle of humans and other animals. They are the primary female sex hormones. Natural estrogens are steroid hormones, while some synthetic ones are non-steroidal...
like compounds. In men, high levels of estrogen can lead to testicular failure and the development of feminine traits including development of male breasts, called gynecomastia
Gynecomastia
Gynecomastia or Gynaecomastia, , is the abnormal development of large mammary glands in males resulting in breast enlargement. The term comes from the Greek γυνή gyné meaning "woman" and μαστός mastós meaning "breast"...
. In women, increased levels of estrogen due to excessive alcohol intake have been related to an increased risk of breast cancer
Breast cancer
Breast cancer is cancer originating from breast tissue, most commonly from the inner lining of milk ducts or the lobules that supply the ducts with milk. Cancers originating from ducts are known as ductal carcinomas; those originating from lobules are known as lobular carcinomas...
.
Diabetes mellitus
Moderate drinkers may have a lower risk of diabetes than non-drinkers. On the other hand, binge drinking and high alcohol consumption may increase the risk of type 2 diabetes in women." Alcohol consumption promotes insulin sensitivity.Rheumatoid arthritis
Regular consumption of alcohol is associated with an increased risk of gouty arthritis and a decreased risk of rheumatoid arthritisRheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic, systemic inflammatory disorder that may affect many tissues and organs, but principally attacks synovial joints. The process produces an inflammatory response of the synovium secondary to hyperplasia of synovial cells, excess synovial fluid, and the development...
. Two recent studies report that the more alcohol consumed, the lower the risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis. Among those who drank regularly, the one-quarter who drank the most were up to 50% less likely to develop the disease compared to the half who drank the least.
The researchers noted that moderate alcohol consumption also reduces the risk of other inflammatory processes such as cardiovascualar disease. Some of the biological mechanisms by which ethanol reduces the risk of destructive arthritis and prevents the loss of bone mineral density (BMD), which is part of the disease process.
A study concluded, "Alcohol either protects from RA or, subjects with RA curtail their drinking after the manifestation of RA". Another study found, "Postmenopausal women who averaged more than 14 alcoholic drinks per week had a reduced risk of rheumatoid arthritis..."
Osteoporosis
Moderate alcohol consumption is associated with higher bone mineral density in postmenopausal women. "...Alcohol consumption significantly decreased the likelihood [of osteoporosisOsteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a disease of bones that leads to an increased risk of fracture. In osteoporosis the bone mineral density is reduced, bone microarchitecture is deteriorating, and the amount and variety of proteins in bone is altered...
]." "Moderate alcohol intake was associated with higher BMD in postmenopausal elderly women." "Social drinking is associated with higher bone mineral density in men and women [over 45]." However, alcohol abuse is associated with bone loss.
Skin
Chronic excessive alcohol abuse is associated with a wide range of skin disorders including urticariaUrticaria
Urticaria is a kind of skin rash notable for pale red, raised, itchy bumps. Hives is frequently caused by allergic reactions; however, there are many non-allergic causes...
, porphyria cutanea tarda
Porphyria cutanea tarda
Porphyria cutanea tarda is the most common subtype of porphyria. The disorder results from low levels of the enzyme responsible for the fifth step in heme production. Heme is a vital molecule for all of the body's organs...
, flushing
Flushing (physiology)
For a person to flush is to become markedly red in the face and often other areas of the skin, from various physiological conditions. Flushing is generally distinguished, despite a close physiological relation between them, from blushing, which is milder, generally restricted to the face, cheeks or...
, cutaneous stigmata of cirrhosis
Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis is a consequence of chronic liver disease characterized by replacement of liver tissue by fibrosis, scar tissue and regenerative nodules , leading to loss of liver function...
, psoriasis
Psoriasis
Psoriasis is an autoimmune disease that appears on the skin. It occurs when the immune system mistakes the skin cells as a pathogen, and sends out faulty signals that speed up the growth cycle of skin cells. Psoriasis is not contagious. However, psoriasis has been linked to an increased risk of...
, pruritus, seborrheic dermatitis and rosacea
Rosacea
Rosacea is a chronic condition characterized by facial erythema . Pimples are sometimes included as part of the definition. Unless it affects the eyes, it is typically a harmless cosmetic condition...
.
A 2010 study concluded, "Nonlight beer intake is associated with an increased risk of developing psoriasis among women. Other alcoholic beverages did not increase the risk of psoriasis in this study."
Bacterial infection
There is a protective effect of alcohol consumption against active infection with H. pylori In contrast, alcohol intake (comparing those who drink > 30g of alcohol per day to non-drinkers) is not associated with higher risk of duodenal ulcer. Excessive alcohol consumption seen in alcoholics is a known risk factor for pneumonia.Common cold
A study on the common cold found that "Greater numbers of alcoholic drinks (up to three or four per day) were associated with decreased risk for developing colds because drinking was associated with decreased illness following infection. However, the benefits of drinking occurred only among nonsmokers. [...] Although alcohol consumption did not influence risk of clinical illness for smokers, moderate alcohol consumption was associated with decreased risk for nonsmokers."Another study concluded, "Findings suggest that wine intake, especially red wine, may have a protective effect against common cold. Beer, spirits, and total alcohol intakes do not seem to affect the incidence of common cold."
Cancer
The International Agency for Research on CancerInternational Agency for Research on Cancer
The International Agency for Research on Cancer is an intergovernmental agency forming part of the World Health Organisation of the United Nations....
(Centre International de Recherche sur le Cancer) of the World Health Organization
World Health Organization
The World Health Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations that acts as a coordinating authority on international public health. Established on 7 April 1948, with headquarters in Geneva, Switzerland, the agency inherited the mandate and resources of its predecessor, the Health...
has classified alcohol as a Group 1 carcinogen. Its evaluation states, "There is sufficient evidence for the carcinogenicity of alcoholic beverages in humans.... Alcoholic beverages are carcinogenic to humans (Group 1)."
The U.S. Department of Health & Human Services’
United States Department of Health and Human Services
The United States Department of Health and Human Services is a Cabinet department of the United States government with the goal of protecting the health of all Americans and providing essential human services. Its motto is "Improving the health, safety, and well-being of America"...
National Toxicology
Toxicology
Toxicology is a branch of biology, chemistry, and medicine concerned with the study of the adverse effects of chemicals on living organisms...
Program listed alcohol as a known carcinogen
Carcinogen
A carcinogen is any substance, radionuclide, or radiation that is an agent directly involved in causing cancer. This may be due to the ability to damage the genome or to the disruption of cellular metabolic processes...
in 2000.
One study determined that "3.6% of all cancer cases worldwide are related to alcohol drinking, resulting in 3.5% of all cancer deaths." A 2011 study found that one in 10 of all cancers in men and one in 33 in women were caused by past or current alcohol intake.
The World Cancer Research Fund
World Cancer Research Fund
World Cancer Research Fund International is a not-for-profit association, established by royal decree in Belgium, with headquarters in London, UK...
panel report Food, Nutrition, Physical Activity and the Prevention of Cancer: a Global Perspective finds the evidence "convincing" that alcoholic drinks increase the risk of the following cancers: mouth, pharynx and larynx, oesophagus, colorectum (men), breast (pre- and postmenopause).
High concentrations of acetaldehyde
Acetaldehyde
Acetaldehyde is an organic chemical compound with the formula CH3CHO or MeCHO. It is one of the most important aldehydes, occurring widely in nature and being produced on a large scale industrially. Acetaldehyde occurs naturally in coffee, bread, and ripe fruit, and is produced by plants as part...
, which is produced as the body breaks down ethanol, may damage DNA in healthy cells. The National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism
National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism
The National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism , as part of the U.S. National Institutes of Health, supports and conducts biomedical and behavioral research on the causes, consequences, treatment, and prevention of alcoholism and alcohol-related problems...
have shown that acetaldehyde reacts with polyamines which are naturally occurring compounds essential for cell growth—to create a particularly dangerous type of mutagenic DNA base called a Cr-Pdg adduct. Even moderate levels of alcohol consumption are associated with an increased risk of certain forms of cancer.
Alcohol's effect on the fetus
Fetal alcohol syndromeFetal alcohol syndrome
Fetal alcohol syndrome is a pattern of mental and physical defects that can develop in a fetus in association with high levels of alcohol consumption during pregnancy. Current research also implicates other lifestyle choices made by the prospective mother...
or FAS is a disorder of permanent birth defects that occurs in the offspring of women who drink alcohol
Alcohol
In chemistry, an alcohol is an organic compound in which the hydroxy functional group is bound to a carbon atom. In particular, this carbon center should be saturated, having single bonds to three other atoms....
during pregnancy. Drinking heavily or during the early stages of prenatal development has been conclusively linked to FAS; moderate consumption is associated with fetal damage. Alcohol crosses the placental barrier and can stunt fetal growth or weight, create distinctive facial stigmata, damaged neurons and brain structures, and cause other physical, mental, or behavioural problems. Fetal alcohol exposure is the leading known cause of mental retardation
Mental retardation
Mental retardation is a generalized disorder appearing before adulthood, characterized by significantly impaired cognitive functioning and deficits in two or more adaptive behaviors...
in the Western world. Alcohol consumption during pregnancy is associated with brain insulin
Insulin
Insulin is a hormone central to regulating carbohydrate and fat metabolism in the body. Insulin causes cells in the liver, muscle, and fat tissue to take up glucose from the blood, storing it as glycogen in the liver and muscle....
and insulin-like growth factor resistance.
See also
- Self-medication on CNS depressants (alcohol)
- Self-medicated effectiveness on alcohol
- Alcohol and suicide

