
MOS Technology SID
Encyclopedia

MOS Technology
MOS Technology, Inc., also known as CSG , was a semiconductor design and fabrication company based in Norristown, Pennsylvania, in the United States. It is most famous for its 6502 microprocessor, and various designs for Commodore International's range of home computers.-History:MOS Technology, Inc...
6581/8580 SID (Sound Interface Device) is the built-in Programmable Sound Generator
Programmable sound generator
A Programmable Sound Generator is a sound chip that generates sound waves by synthesizing multiple basic waveforms, and often some kind of noise generator, and combining and mixing these waveforms into a complex waveform, then shaping the amplitude of the resulting waveform using...
chip of Commodore
Commodore International
Commodore is the commonly used name for Commodore Business Machines , the U.S.-based home computer manufacturer and electronics manufacturer headquartered in West Chester, Pennsylvania, which also housed Commodore's corporate parent company, Commodore International Limited...
's CBM-II
Commodore CBM-II
The Commodore CBM-II series was a short-lived range of 8-bit personal computers from Commodore Business Machines , intended as a follow-on to the Commodore PET series, released in 1982.-Technical description:...
, Commodore 64
Commodore 64
The Commodore 64 is an 8-bit home computer introduced by Commodore International in January 1982.Volume production started in the spring of 1982, with machines being released on to the market in August at a price of US$595...
, Commodore 128
Commodore 128
The Commodore 128 home/personal computer was the last 8-bit machine commercially released by Commodore Business Machines...
and Commodore MAX Machine
Commodore MAX Machine
The Commodore MAX Machine, also known as Ultimax in the United States and VC-10 in Germany, was a home computer designed and sold by Commodore International in Japan, beginning in early 1982, a predecessor to the popular Commodore 64...
home computer
Home computer
Home computers were a class of microcomputers entering the market in 1977, and becoming increasingly common during the 1980s. They were marketed to consumers as affordable and accessible computers that, for the first time, were intended for the use of a single nontechnical user...
s. It was one of the first sound chips of its kind to be included in a home computer
Home computer
Home computers were a class of microcomputers entering the market in 1977, and becoming increasingly common during the 1980s. They were marketed to consumers as affordable and accessible computers that, for the first time, were intended for the use of a single nontechnical user...
prior to the digital sound revolution
Digital sound revolution
The digital sound revolution refers to the widespread adoption of digital audio technology in the computer industry beginning in the 1980s.- Software-based pulse-width modulation :...
.
Together with the VIC-II
MOS Technology VIC-II
The VIC-II , specifically known as the MOS Technology 6567/8562/8564 , 6569/8565/8566 , is the microchip tasked with generating Y/C/composite video graphics and DRAM refresh signals in the Commodore 64 and C128 home computers.Succeeding MOS's original VIC , the VIC-II was one of the two chips...
graphics chip, the SID was instrumental in making the C64 the best selling computer in history, and is partly credited for initiating the demoscene
Demoscene
The demoscene is a computer art subculture that specializes in producing demos, which are non-interactive audio-visual presentations that run in real-time on a computer...
.
The SID has , which was filed on February 27, 1983, and issued on July 7, 1987. The patent expired on July 7, 2004.
Design process
The SID was devised by engineerEngineer
An engineer is a professional practitioner of engineering, concerned with applying scientific knowledge, mathematics and ingenuity to develop solutions for technical problems. Engineers design materials, structures, machines and systems while considering the limitations imposed by practicality,...
Robert "Bob" Yannes, who later co-founded the Ensoniq
Ensoniq
Ensoniq Corp. was an American electronics manufacturer, best known throughout the mid 1980s and 1990s for its musical instruments, principally samplers and synthesizers.- Company history :...
digital synthesizer
Synthesizer
A synthesizer is an electronic instrument capable of producing sounds by generating electrical signals of different frequencies. These electrical signals are played through a loudspeaker or set of headphones...
company. Yannes headed a team that included himself, two technicians and a CAD
Electronic design automation
Electronic design automation is a category of software tools for designing electronic systems such as printed circuit boards and integrated circuits...
operator, who designed and completed the chip in five months, in the latter half of 1981. Yannes was inspired by previous work in the synthesizer industry and was not impressed by the current state of computer sound chips. Instead, he wanted a high-quality instrument chip, which is the reason why the SID has features like the envelope generator, previously not found in home computer sound chips.
Emphasis during chip design was on high-precision frequency control, and the SID was originally designed to have 32 independent voices, sharing a common oscillator. However these features could not be finished in time, so instead the mask work for a certain working oscillator was simply replicated three times across the chip surface, creating three voices with a unique oscillator for each voice. Another feature that was not incorporated in the final design was a frequency look-up table for the most common musical notes, a feature that was dropped because of space limitations. The support for an audio input pin was a feature Yannes added without asking, even though this had no practical use in a computer, although it enabled the chip to be used as a simple effect processor
Effects unit
Effects units are electronic devices that alter how a musical instrument or other audio source sounds. Some effects subtly "color" a sound, while others transform it dramatically. Effects are used during live performances or in the studio, typically with electric guitar, keyboard and bass...
. The masks were produced in 7-micrometer technology in order to gain a high yield: the current state-of-the-art at the time was 6-micrometer technologies.
The chip, like the first product using it (the Commodore 64
Commodore 64
The Commodore 64 is an 8-bit home computer introduced by Commodore International in January 1982.Volume production started in the spring of 1982, with machines being released on to the market in August at a price of US$595...
), was finished in time for the Consumer Electronics Show
Consumer Electronics Show
The International Consumer Electronics Show is a major technology-related trade show held each January in the Las Vegas Convention Center, Las Vegas, Nevada, United States. Not open to the public, the Consumer Electronics Association-sponsored show typically hosts previews of products and new...
in the first weekend of January 1982. Even though Yannes was partly displeased with the result, his colleague Charles Winterble said: "This thing is already 10 times better than anything out there and 20 times better than it needs to be."
The specifications for the chip were not used as a blueprint. Rather, they were written as the development work progressed, and not all planned features made it into the final product. Yannes claims he had a feature-list of which three quarters made it into the final design. This is the reason why some of the specifications for the first version (6581) were accidentally incorrect. The later revision (8580) was revised to match the specification. For example, the 8580 expanded on the ability to perform a logical AND between two waveforms, something that the 6581 could only do in a somewhat limited and unintuitive manner. Another feature that differs between the two revisions is the filter: the 6581 version is far away from the specification.
Manufacturing, Remarking, and Forgery
Since 6581 and 8580 SID ICs are no longer produced, they have become highly sought after. In late 2007, various defective remarked SIDs started appearing on eBay as supposedly "new" chips. All of these remarked SIDs have a defective filter, but some also have defective channels/noise generators, and some are completely dead. The remarked chips are assumed to either be factory rejects from back when the chip was still produced, or possibly 'reject culls' from one of the chip pulling operations which were used to supply the chips used in the Elektron SIDStation and the HardSID cards.Fake SID chips have also been supplied to unwitting buyers from unscrupulous manufacturers in China; the supplied chips are laser-etched with completely bogus markings, and the chip inside the package is not a SID at all.
Features
- three separately programmable independent audio oscillatorsElectronic oscillatorAn electronic oscillator is an electronic circuit that produces a repetitive electronic signal, often a sine wave or a square wave. They are widely used in innumerable electronic devices...
(8 octaveOctaveIn music, an octave is the interval between one musical pitch and another with half or double its frequency. The octave relationship is a natural phenomenon that has been referred to as the "basic miracle of music", the use of which is "common in most musical systems"...
range, approximately 16 - 4000 HzHertzThe hertz is the SI unit of frequency defined as the number of cycles per second of a periodic phenomenon. One of its most common uses is the description of the sine wave, particularly those used in radio and audio applications....
) - four different waveformWaveformWaveform means the shape and form of a signal such as a wave moving in a physical medium or an abstract representation.In many cases the medium in which the wave is being propagated does not permit a direct visual image of the form. In these cases, the term 'waveform' refers to the shape of a graph...
s per audio oscillator (sawtoothSawtooth waveThe sawtooth wave is a kind of non-sinusoidal waveform. It is named a sawtooth based on its resemblance to the teeth on the blade of a saw....
, triangleTriangle waveA triangle wave is a non-sinusoidal waveform named for its triangular shape.Like a square wave, the triangle wave contains only odd harmonics...
, pulseSquare waveA square wave is a kind of non-sinusoidal waveform, most typically encountered in electronics and signal processing. An ideal square wave alternates regularly and instantaneously between two levels...
, noiseWhite noiseWhite noise is a random signal with a flat power spectral density. In other words, the signal contains equal power within a fixed bandwidth at any center frequency...
) - one multi mode filterElectronic filterElectronic filters are electronic circuits which perform signal processing functions, specifically to remove unwanted frequency components from the signal, to enhance wanted ones, or both...
featuring low-passLow-pass filterA low-pass filter is an electronic filter that passes low-frequency signals but attenuates signals with frequencies higher than the cutoff frequency. The actual amount of attenuation for each frequency varies from filter to filter. It is sometimes called a high-cut filter, or treble cut filter...
, high-passHigh-pass filterA high-pass filter is a device that passes high frequencies and attenuates frequencies lower than its cutoff frequency. A high-pass filter is usually modeled as a linear time-invariant system...
and band-passBand-pass filterA band-pass filter is a device that passes frequencies within a certain range and rejects frequencies outside that range.Optical band-pass filters are of common usage....
outputs with 6 dB/oct (bandpass) or 12 dBDecibelThe decibel is a logarithmic unit that indicates the ratio of a physical quantity relative to a specified or implied reference level. A ratio in decibels is ten times the logarithm to base 10 of the ratio of two power quantities...
/octaveOctaveIn music, an octave is the interval between one musical pitch and another with half or double its frequency. The octave relationship is a natural phenomenon that has been referred to as the "basic miracle of music", the use of which is "common in most musical systems"...
(lowpass/highpass) rolloff. The different filter-modes are sometimes combined to produce additional timbres, for instance a notch-reject filter. - three attack/decay/sustain/release (ADSR) volume controls, one for each audio oscillator.
- three ring modulatorsRing modulationRing modulation is a signal-processing effect in electronics, an implementation of amplitude modulation or frequency mixing, performed by multiplying two signals, where one is typically a sine-wave or another simple waveform. It is referred to as "ring" modulation because the analog circuit of...
. - oscillator syncOscillator syncOscillator sync is a feature in some synthesizers with two or more VCOs . One oscillator will restart the period of another oscillator, so that they will have the same base frequency...
for each audio oscillator. - two 8-bit8-bitThe first widely adopted 8-bit microprocessor was the Intel 8080, being used in many hobbyist computers of the late 1970s and early 1980s, often running the CP/M operating system. The Zilog Z80 and the Motorola 6800 were also used in similar computers...
A/D converters (typically used for game control paddlesPaddle (game controller)A paddle is a game controller with a round wheel and one or more fire buttons, where the wheel is typically used to control movement of the player object along one axis of the video screen...
, but later also used for a mouse) - external audio input (for sound mixing with external signal sources)
- random numberStatistical randomnessA numeric sequence is said to be statistically random when it contains no recognizable patterns or regularities; sequences such as the results of an ideal dice roll, or the digits of π exhibit statistical randomness....
/modulation generator
Technical details
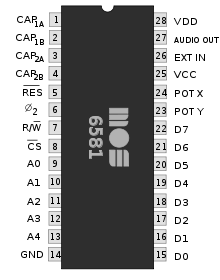
Mixed-signal integrated circuit
A mixed-signal integrated circuit is any integrated circuit that has both analog circuits and digital circuits on a single semiconductor die.- Examples :...
, featuring both digital and analog circuitry. All control ports are digital, while the output ports are analog. The SID features three-voice synthesis, where each voice may use one of at least five different waveforms: square wave
Square wave
A square wave is a kind of non-sinusoidal waveform, most typically encountered in electronics and signal processing. An ideal square wave alternates regularly and instantaneously between two levels...
(with variable duty cycle), triangle wave
Triangle wave
A triangle wave is a non-sinusoidal waveform named for its triangular shape.Like a square wave, the triangle wave contains only odd harmonics...
, sawtooth wave
Sawtooth wave
The sawtooth wave is a kind of non-sinusoidal waveform. It is named a sawtooth based on its resemblance to the teeth on the blade of a saw....
, pseudo-random (but not white
White noise
White noise is a random signal with a flat power spectral density. In other words, the signal contains equal power within a fixed bandwidth at any center frequency...
) noise, and certain complex/combined waveforms when multiple waveforms are selected simultaneously. A voice playing Triangle waveform may be ring-modulated
Ring modulation
Ring modulation is a signal-processing effect in electronics, an implementation of amplitude modulation or frequency mixing, performed by multiplying two signals, where one is typically a sine-wave or another simple waveform. It is referred to as "ring" modulation because the analog circuit of...
with one of the other voices, where the triangle waveform's bits are inverted when the modulating voice's msb is set, producing a discontinuity and change of direction with the Triangle's ramp. Oscillators may also be hard-synced to each other, where the synced oscillator is reset whenever the syncing oscillator's msb raises.
Each voice may be routed into a common, digitally controlled analog multistate filter, which is constructed with aid of external capacitors to the chip. The filter has lowpass, bandpass and highpass outputs, which can be individually selected for final output amplification via master volume register. Using a combined state of lowpass and highpass results in a notch (or inverted bandpass) output.
The programmer may vary the filter's cut-off frequency and resonance. An external audio-in port enables external audio to be passed through the filter.
The ring modulation, filter, and programming techniques such as arpeggio (rapid cycling between 2 or more frequencies to make chord-like sounds) together produce the characteristic feel of SID music.
Due to imperfect manufacturing technologies of the time and poor separation between the analog and digital parts of the chip, the 6581's output (before the amplifier stage) was always slightly biased from the zero level. By adjusting the amplifier's gain through the main 4-bit volume register, this bias could be modulated as PCM, resulting in a "virtual" fourth channel allowing 4-bit digital sample playback. The glitch was known and used from an early point on, first by Electronic Speech Systems
Electronic Speech Systems
ESS Technology Incorporated ) is a listed manufacturer of computer multimedia products based in Fremont, California. It was founded by Fred Chan and Forrest Mozer in 1984. The firm employs more than 500 people worldwide. Robert L. Blair is the CEO and President of the company.Historically, ESS...
to produce sampled speech in games such as Impossible Mission
Impossible Mission
Impossible Mission is a platform computer game for several home computers. The original version for the Commodore 64 was programmed by Dennis Caswell and published by Epyx in 1984.-Description:...
(1983, Epyx) and Ghostbusters (1984, Activision). The first instance of samples being used in actual musical compositions was by Martin Galway
Martin Galway
Martin Galway is one of the best known composers of music for the Commodore 64 sound chip, the SID soundchip, and for the Sinclair ZX Spectrum...
in Arkanoid
Arkanoid
is an arcade game developed by Taito in 1986. It is based upon Atari's Breakout games of the 1970s. The title refers to a doomed "mothership" from which the player's ship, the Vaus, escapes.-Overview:...
(1987, Imagine), although he had copied the idea from an earlier drum synthesizer package called Digidrums. The length of sampled sound playback was limited first by memory and later technique. Kung Fu Fighting (1986), a popular early sample, has a playback length measured in seconds. c64mp3 (2010) and Cubase64 (2010) demonstrate playback lengths measured in minutes. Also, it was hugely CPU intensive - one had to output the samples very fast (in comparison to the speed of the 6510
MOS Technology 6510
thumb|300px|Image of the internals of a [[Commodore 64]] showing the 6510 CPU . The chip on the right is the [[MOS Technology SID|6581 SID]]...
CPU).
The better manufacturing technology in the 8580 used in the later revisions of Commodore 64
Commodore 64
The Commodore 64 is an 8-bit home computer introduced by Commodore International in January 1982.Volume production started in the spring of 1982, with machines being released on to the market in August at a price of US$595...
C and the Commodore 128
Commodore 128
The Commodore 128 home/personal computer was the last 8-bit machine commercially released by Commodore Business Machines...
DCR caused the bias to almost entirely disappear, causing the digitized sound samples to become very quiet. Fortunately, the volume level could be mostly restored with either a hardware modification (biasing the audio-in pin), or more commonly a software trick involving using the Pulse waveform to intentionally recreate the required bias. The software trick generally renders one voice temporarily unusable, although clever musical compositions can make this problem less noticeable.
At the X'2008 demo party, a completely new method of playing digitized samples was unveiled. The method allows for an unprecedented four (software-mixed) channels of 8-bit samples with optional filtering on top of all samples, as well as two ordinary SID sound channels. The method works by resetting the oscillator using the waveform generator test bit, quickly ramping up the new waveform with the Triangle waveform selected, and then disabling all waveforms, resulting in the DAC continuing to output the last value---which is the desired sample. This continues for as long as two scanlines, which is ample time for glitch-free, arbitrary sample output. It is however more CPU-intensive than the 4-bit volume register DAC trick described above. Because the filtering in a SID chip is applied after the waveform generators, samples produced this way can be filtered normally.
The original manual for the SID mentions that if several waveforms are enabled at the same time, the result will be a binary AND between them. What happens in reality is that the input to the waveform DAC pins receive several waveforms at once. For instance, the Triangle waveform is made with a separate XOR circuit and a shift-to-left circuit. The top bit drives whether the XOR circuit inverts the accumulator value seen by the DAC. Thus, enabling triangle and sawtooth simultaneously causes adjacent accumulator bits in the DAC input to mix together. (The XOR circuit does not come to play because it is always disabled whenever the sawtooth waveform is selected.) The pulse waveform is built by joining all the DAC bits together via a long strip of polysilicon, connected to the pulse control logic that digitally compares current accumulator value to the pulse width value. Thus, selecting the pulse waveform together with any other waveform causes every bit on the DAC to partially mix together, and the loudness of the waveform is affected by the state of the pulse.
The noise generator is implemented as a 23-bit-length Fibonacci LFSR (Feedback polynomial: x^22+x^17+1). When using noise waveform simultaneously with any other waveform, the pull-down via waveform selector tends to quickly reduce the XOR shift register to 0 for all bits that are connected to the output DAC. As the zeroes shift in the register when the noise is clocked, and no 1-bits are produced to replace them, a situation can arise where the XOR shift register becomes fully zeroed. Luckily, the situation can be remedied by using the waveform control test bit, which in that condition injects one 1-bit into the XOR shift register. Some musicians are also known to use noise's combined waveforms and test bit to construct unusual sounds.
The 6581 and 8580 differ from each other in several ways. The original 6581 was manufactured using the older NMOS
NMOS logic
N-type metal-oxide-semiconductor logic uses n-type metal-oxide-semiconductor field effect transistors to implement logic gates and other digital circuits...
process, which used 12V DC
Direct current
Direct current is the unidirectional flow of electric charge. Direct current is produced by such sources as batteries, thermocouples, solar cells, and commutator-type electric machines of the dynamo type. Direct current may flow in a conductor such as a wire, but can also flow through...
to operate. The 8580 was made using the HMOS-II process, which required less power (9V DC
Direct current
Direct current is the unidirectional flow of electric charge. Direct current is produced by such sources as batteries, thermocouples, solar cells, and commutator-type electric machines of the dynamo type. Direct current may flow in a conductor such as a wire, but can also flow through...
), and therefore made the IC
Integrated circuit
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit is an electronic circuit manufactured by the patterned diffusion of trace elements into the surface of a thin substrate of semiconductor material...
run cooler. The 8580 was thus far more durable than the 6581. Also, due to stabler waveform generators, the bit-mixing effects are less noticeable and thus the combined waveforms come close to matching the original SID specification (which stated that they will be combined as a binary AND). The filter is also very different between the two models, with the 6581 cutoff range being a relatively straight line on a log scale, while the cutoff range on the 8580 is a straight line on a linear scale, and is close to the designers' actual specifications. Additionally, a better separation between the analog and the digital circuits made the 8580's output less noisy and distorted. The noise in 6xxx-series systems can be reduced by disconnecting the audio-in pin.
The consumer version of the 8580 was rebadged the 6582, even though the die on the chip is identical to a stock 8580 chip, including the '8580R5' mark. Creative Micro Designs
Creative Micro Designs
Creative Micro Designs is a computer technologies company which today sells PCs and related equipment, but which started out in 1987 selling self-designed firmware updates and hardware for the Commodore 64 and C128 8-bit home/personal computers....
used it in their SID Symphony expansion cartridge, and it was used in a few other places as well, including one PC sound-card.
Despite its documented shortcomings, many SID musicians prefer the flawed 6581 chip over the corrected 8580 chip. The main reason for this is that the filter produces strong distortion that is sometimes used to produce simulation of instruments such as a distorted electric guitar. Also, the highpass component of the filter was mixed in 3 dB attenuated compared to the other outputs, making the sound more bassy. In addition to nonlinearities in filter, the D/A circuitry used in the waveform generators produces yet more additional distortion that made its sound richer in character.
Revisions
No instances reading "6581 R1" ever reached the market. In fact, Yannes has stated that "[the] SID chip came out pretty well the first time, it made sound. Everything we needed for the show was working after the second pass." High-resolution photos of Charles Winterble's prototype C64 show the markings "MOS 6581 2082", the last number being a date code indicating that his prototype SID chip was produced during the 20th week of 1982, which would be within 6 days of May 14, 1982.These are the known revisions of the various SID chips: (datecodes are in WWYY w=week y=year format)
- 6581 R1 - Prototype, only appeared on the CES machines, has a datecode of 4981 to 0482 or so. Has the full 12 bit filter cutoff range. An unknown number were produced, probably between 50 and 100 chips. All are ceramic packages.
- 6581 R2 - Will say "6581" only on the package. Filter cutoff range was reduced to 11 bits and the MSB bit disconnected/forced permanently on, but is still on the die. Made from 1182 until at least 5182. First 10 weeks or so of chips have ceramic packages (these usually appear on engineering prototypes but a few are on sold machines), the rest have plastic packages.
- 6581 R3 - Will say "6581" only, "6581 R3" or "6581 CBM" on the package. Had a minor change to the protection/buffering of the input pins. Made from before 2083 until 0786 or so.
- 6581 R4 - Will say "6581 R4" on the package. Silicon grade changed to HMOS-II "HC-30" grade, though the manufacturing process for the chip remained NMOS. Produced from 4985 until at least 2590.
- 6581 R4 AR - Will say "6581 R4 AR" on the package. Minor adjustment to the silicon grade, no die change from R4. Produced from around 1986 (week 22) until at least the year 1992.
- 6582 - Will say "6582" on the package. Typically produced around the year 1986 in Hong Kong.
- 6582 A - Will say "6582A" (or "6582 A") on the package. Typically produced around the years 1989, 1990 and 1992 in the Philippines.
- 8580 R5 - Will say "8580R5" on the package. Produced from the years 1986 to 1993 in the Philippines, Hong Kong and in the US.
Some of these chips are marked "CSG" ("Commodore Semiconductor Group") and the Commodore Logo, while others are marked with "MOS". This includes chips produced during the same week (and thus, receiving the same date code), indicating that at least two different factory lines were in operation during that week. The markings of chips varied by factory and even by line within a factory throughout most of the manufacturing run of the chip.
Game audio
The majority of games produced for the Commodore 64 made use of the SID chip, with sounds ranging from simply clicks and beeps to complex musical extravaganzas or even entire digital audio tracks.Well known composers of game music for this chip are Martin Galway
Martin Galway
Martin Galway is one of the best known composers of music for the Commodore 64 sound chip, the SID soundchip, and for the Sinclair ZX Spectrum...
, known for many titles, including Wizball
Wizball
Wizball is a computer game written by Jon Hare and Chris Yates and released in 1987 for the Commodore 64, ZX Spectrum and Amstrad CPC. Versions for the Amiga, Atari ST and PC were also released...
, and Rob Hubbard
Rob Hubbard
Rob Hubbard is a music composer best known for his composition of computer game theme music, especially for microcomputers of the 1980s such as the Commodore 64...
, known for titles such as ACE 2, Delta, International Karate
International Karate
International Karate is a karate fighting game created and published by System 3 for various home computers. Of these versions the 1986 releases for Commodore 64 and Atari 8-bit computers, created by Archer MacLean with music by Rob Hubbard, stand out for their good playability and overall high...
, IK+, and Monty on the Run
Monty on the Run
Monty on the Run is a computer game created by the software house Gremlin Graphics and released in 1985 for the C64, Spectrum, Amstrad CPC and Commodore Plus/4, written by Peter Harrap for the Spectrum with music by Rob Hubbard....
. Other noteworthies include Jeroen Tel
Jeroen Tel
Jeroen Godfried Tel is a Dutch composer. Best known for numerous computer game tunes he wrote in the 1980s and early 1990s for the Commodore 64, Tel is a founding member of the computer music group Maniacs of Noise....
(Cybernoid and Myth), David Dunn (Finders Keepers and Flight Path 737) and Chris Hülsbeck
Chris Hülsbeck
Chris Hülsbeck is a video game music composer from Germany.He has written soundtracks for more than 70 titles, the latest being Star Wars: Rebel Strike for Nintendo GameCube. Many of his scores for the Commodore 64 are regarded as classics among enthusiasts today, most notably The Great Giana...
, whose composition career started with the SID but has spanned nearly every kind of computer music and other synthesizers since.
Emulation
The fact that many enthusiasts prefer the real chip sound over software emulators have led to several recording projects aiming to preserve the authentic sound of the SID chip for modern hardware.The sid.oth4 project has over 380 songs of high quality mp3 available recorded on hardsid hardware and the SOASC= project have the entire high voltage sid collection release 49 (over 35,000 songs) recorded in from real Commodore 64's in high quality mp3. Both projects emphasize the importance of preserving the authentic sound of the SID chip.
Software emulation
- In 1989 on the Amiga computer, the demo "The 100 Most Remembered C64 Tunes" and later the PlaySID application was released, developed by Per Håkan SundellPer Håkan SundellPer Håkan Sundell is a programmer and computer scientist with roots in the scene and early computer enthusiasts of the eighties, when he was known as PHS of CCS .- Biography :Håkan currently holds a Ph.D...
and Ron Birk. This was one of the first attempts to emulate the SID in software only, and also introduced the file format for representing songs made on the C64 using the SID chip. This later spawned the creation of similar applications for other platforms as well as the creation of a community of people fascinated by SID music, resulting in The High Voltage SID CollectionThe High Voltage SID CollectionThe High Voltage SID Collection is both the name of a project to build a collection of music created on the MOS Technology 6581/8580 SID sound chip in Commodore CBM-II, Commodore 64 and Commodore 128 home computers and the collection itself...
which contains over 30,000 SID tunes.
A SID file contains the 6510
MOS Technology 6510
thumb|300px|Image of the internals of a [[Commodore 64]] showing the 6510 CPU . The chip on the right is the [[MOS Technology SID|6581 SID]]...
program code and associated data needed to replay the music on the SID. The SID files have the MIME
MIME
Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions is an Internet standard that extends the format of email to support:* Text in character sets other than ASCII* Non-text attachments* Message bodies with multiple parts...
media type
audio/prs.sid.The actual file format of a SID file has had several versions. The older standard is PSID (current version V2 NG). The newer standard, RSID, is intended for music that requires a more complete emulation of the Commodore 64 hardware.
The SID file format is not a native format used on the Commodore 64 or 128, but a format specifically created for emulator-assisted music players such as PlaySID , Sidplay and JSidplay2. However, there are loaders like RealSIDPlay and converters such as PSID64 that make it possible to play a substantial portion of SID files on original Commodore computers.
- In June 1998, a cycle-based SID emulator engine called reSIDReSIDreSID is a reverse engineered software emulation of the MOS6581 SID . This chip was used in the Commodore 64 computer. reSID is free software, published under the GNU General Public License....
became available. The all-software emulator, available with C++C++C++ is a statically typed, free-form, multi-paradigm, compiled, general-purpose programming language. It is regarded as an intermediate-level language, as it comprises a combination of both high-level and low-level language features. It was developed by Bjarne Stroustrup starting in 1979 at Bell...
source codeSource codeIn computer science, source code is text written using the format and syntax of the programming language that it is being written in. Such a language is specially designed to facilitate the work of computer programmers, who specify the actions to be performed by a computer mostly by writing source...
, is licensed under the GPLGNU General Public LicenseThe GNU General Public License is the most widely used free software license, originally written by Richard Stallman for the GNU Project....
by the author, Dag Lem. In 2008, Antti Lankila significantly improved the filter and distortion simulation in reSID. The improvements were included in VICEVICEThe software program VICE, standing for VersatIle Commodore Emulator, is an emulator for Commodore's 8-bit computers, running on Amiga, Unix, MS-DOS, Win32, Mac OS X, OS/2, Acorn RISC OS, and BeOS host machines...
version 2.1 as well.
- In 2007 the JSidplay2 project was released, a pure Java based SID player developed by Ken Händel.
Hardware reimplementations
- In 2008 the HyperSID project is released. HyperSID is a VSTi which acts like a MIDI controller for HyperSID hardware unit (synthesizer based on SID chip) and developed by HyperSynth company.
Hardware Implementations using the SID chip
- In 1997, an electronic musical instrumentElectronic musical instrumentAn electronic musical instrument is a musical instrument that produces its sounds using electronics. Such an instrument sounds by outputting an electrical audio signal that ultimately drives a loudspeaker....
utilizing the SID chip as its synthesis engine was released. It is called the SidStation, built around the 6581 model SID chip (as opposed to the newer 8580), and it's produced by SwedishSwedenSweden , officially the Kingdom of Sweden , is a Nordic country on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. Sweden borders with Norway and Finland and is connected to Denmark by a bridge-tunnel across the Öresund....
company ElektronElektron (company)Elektron is an electronic musical instrument company, based in Gothenburg, Sweden, founded in 1998.Its products include the SID-based SidStation, the Machinedrum percussion synthesizer, the Monomachine synthesizer, and the Octatrack performance sampler....
. As the SID chip had been discontinued for years, Elektron allegedly bought up almost all of the remaining stock. In 2004, Elektron released the Monomachine pattern-based sequencerMusic sequencerThe music sequencer is a device or computer software to record, edit, play back the music, by handling note and performance information in several forms, typically :...
with optional keyboard. The Monomachine contains several synthesis engines, including an emulated 6581 oscillator using a DSPDigital signal processorA digital signal processor is a specialized microprocessor with an architecture optimized for the fast operational needs of digital signal processing.-Typical characteristics:...
.
- In 1999, a sound cardSound cardA sound card is an internal computer expansion card that facilitates the input and output of audio signals to and from a computer under control of computer programs. The term sound card is also applied to external audio interfaces that use software to generate sound, as opposed to using hardware...
for IBM PC compatibleIBM PC compatibleIBM PC compatible computers are those generally similar to the original IBM PC, XT, and AT. Such computers used to be referred to as PC clones, or IBM clones since they almost exactly duplicated all the significant features of the PC architecture, facilitated by various manufacturers' ability to...
s called HardSIDHardSIDThe HardSID is a family of sound cards, produced by a Hungarian company Hard Software and originally conceived by Teli Sándor.The HardSID cards are based on the MOS Technology SID chip which was popularised and immortalized by the Commodore 64 home computer...
was released. The card uses from one to four SID chips and allows a PC to utilize the sound capabilities of the chip directly, instead of by emulation via generic sound cards (e.g. SoundBlaster).
- The CatWeaselCatWeaselThe Catweasel is a family of enhanced floppy disk controllers from German company Individual Computers. These controllers are designed to allow more recent computers, such as PCs, to access a wide variety of older disk formats using standard floppy drives....
from GermanGermanyGermany , officially the Federal Republic of Germany , is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km2 and has a largely temperate seasonal climate...
company Individual ComputersIndividual ComputersIndividual Computers is a German computer hardware company specializing in retrocomputing accessories for the Commodore 64, Amiga, and PC platforms. Individual Computers produced the C-One reconfigurable computer in 2003...
, a PCIPeripheral Component InterconnectConventional PCI is a computer bus for attaching hardware devices in a computer...
+ Zorro multiformat floppy diskFloppy diskA floppy disk is a disk storage medium composed of a disk of thin and flexible magnetic storage medium, sealed in a rectangular plastic carrier lined with fabric that removes dust particles...
controller and digital joystick adapter for PCsIBM PC compatibleIBM PC compatible computers are those generally similar to the original IBM PC, XT, and AT. Such computers used to be referred to as PC clones, or IBM clones since they almost exactly duplicated all the significant features of the PC architecture, facilitated by various manufacturers' ability to...
, Macs, and AmigaAmigaThe Amiga is a family of personal computers that was sold by Commodore in the 1980s and 1990s. The first model was launched in 1985 as a high-end home computer and became popular for its graphical, audio and multi-tasking abilities...
s, includes a hardware SID option, i.e. an option to insert a real SID chip in a socket for use when playing.MUSfiles.
- The MIDIbox SID is a MIDI-controlled synthesizer which can contain up to eight SID chips. It is a free open sourceOpen sourceThe term open source describes practices in production and development that promote access to the end product's source materials. Some consider open source a philosophy, others consider it a pragmatic methodology...
project using a PIC microcontrollerPIC microcontrollerPIC is a family of Harvard architecture microcontrollers made by Microchip Technology, derived from the PIC1650 originally developed by General Instrument's Microelectronics Division...
. Control of the synthesizer is realized with software or via a control panel with knobs, LEDsLight-emitting diodeA light-emitting diode is a semiconductor light source. LEDs are used as indicator lamps in many devices and are increasingly used for other lighting...
, LCDLiquid crystal displayA liquid crystal display is a flat panel display, electronic visual display, or video display that uses the light modulating properties of liquid crystals . LCs do not emit light directly....
, etc., which may optionally be mounted on a keyboardless Commodore 64 body.
- The Prophet64 is a cartridge for the Commodore 64. It features four separate music applications, mimicking everything from modern sequencers to the Roland 303/909 series. With an optional User Port peripheral, the Prophet64 may synchronized to other equipment using DIN SyncDIN SyncThe SYNC standard, often called "DIN sync" or "sync24" , defines an interface for electronic music instruments. It was introduced in the 1980s by Roland Corporation for synchronization of music sequencers, drum machines, arpeggiators and similar devices. The SYNC standard uses the signals clock ...
standard (SYNC 24). The website now states "Prophet64 has been replaced with the MSSIAH."
- The MSSIAH is a cartridge for the Commodore 64 that replaces the Prophet64.
- Artist/Hacker Paul Slocum developed the Cynthcart cartridge that enables you to turn your C64 into an analogue synthesizer. The Cynthcart is available through atariage.com.
- The Parallel Port SID Interface allows those with very slim budgets to connect the SID chip to a PC.
- In May 2009 the SID chip was interfaced to the BBC Micro and BBC Master range of computers via the 1MHz bus allowing music written for the SID chip on the Commodore 64 to be ported and played on the BBC Micro.
- In October 2009 thrashbarg's project interfaced an SID chip to an ATmega8 to play MIDI files on a MOS 6581 SID.
- In March 2010 STG published the SIDBlaster/USB - an open source, open hardware implementation of the SID that connects to (and is powered by) a USB port, using an FTDI chip for the USB interface and a PIC to interface the SID.
- In August 2010 SuperSoniqs published the Playsoniq, a cartridge for MSX computers, with (in addition to other features) a real SID on it, ready to use on any MSX machine.
SID hardware clones
- The SwinSID is hardware emulation of SID on the Atmel AVR processor and real SID player using Atmel AVR processor.
- The V-SID 1.0 project (code name SID 6581D, 'D' for digital) from David Amoros was born in 2005. This project is a hardware emulation of the SID chip from the Bob Yannes's interview, datasheets. The V-SID 1.0 engine had been implemented in a FPGA EP1C12 Cyclone from ALTERA, on an ALTIUM development board, and emulates all the characteristics of the original SID, except the filter which is a digital version (IIR filter controlled by a CPU).
- The PhoenixSID 65X81 project (2006) aimed to faithfully create the SID sound using modern hardware. The workings of a SID chip were recreated on an FPGA, based on interviews with the SID's creator, original datasheets, and comparisons with real SID chips. It was distinguished from similar attempts by its use of real analog circuitry instead of emulation for the legendary SID filter. However, the project was discontinued, because George Pantazopoulos, who was the head of this project, died on April 23, 2007, at the age of 29.
- The C64 Direct-to-TVC64 Direct-to-TVThe C64 Direct-to-TV, called C64DTV for short, is a single-chip implementation of the Commodore 64 computer, contained in a joystick with 30 built-in games. The design is similar to the Atari Classics 10-in-1 TV Game...
emulates large portions the SID hardware, minus certain features. It reduces the entire C64 to a small circuit that fits into a joystick.
Conventional music
SID sounds and snippets of SID music has been introduced into mainstream music at several occasions:- In the spring of 1999 Zombie NationZombie Nation (band)Zombie Nation is a German techno and electro project of the Munich based DJ and producer Florian Senfter.-History:The first Zombie Nation five track EP was released in the spring of 1999 on DJ Hell's label, International DeeJay Gigolo Records...
released a remix of game musician David Whittaker's Lazy JonesLazy JonesLazy Jones is a computer game for the Commodore 64, ZX Spectrum, MSX and Tatung Einstein. It was written by David Whittaker and released by Terminal Software in 1984. The Spectrum version was ported by Simon Cobb....
(originally written for the SID in 1984) under the title Kernkraft 400Kernkraft 400"Kernkraft 400" is a song performed by German techno and electro artist Zombie Nation and the first single from their album Leichenschmaus. The first Zombie Nation record contained the song "Kernkraft 400", German for "Nuclear Energy 400", which is a remix of a tune from the 1984 Commodore 64 game...
. They used an Elektron SidStation for the sound. - In RollergirlRollergirlNicole Safft , professionally known as Rollergirl, is a German singer with a number of successful tracks such as "Dear Jessie" and "Luv U More," the latter being a cover of a song by Sunscreem.The love for rollerskates developed early when working at a rollerskating rink...
's 2000 hit Superstar a SID arpeggio can be clearly heard in the background, probably originating in a SidStationElektron SidStationThe Elektron SidStation is a musical synthesizer sound module, built around the MOS Technology SID mixed-mode synthesizer chip originally used in the Commodore 64 home computer. It was produced by the Swedish synthesizer company Elektron, and was introduced in 1999...
. - In 2001 Bas BronBas BronBas Bron is a musical artist and a producer of mostly electronic music from Amsterdam, The Netherlands.-Bastian:Bas Bron is perhaps most famous in the Netherlands under the moniker Bastian...
sampled the drums from Jeroen TelJeroen TelJeroen Godfried Tel is a Dutch composer. Best known for numerous computer game tunes he wrote in the 1980s and early 1990s for the Commodore 64, Tel is a founding member of the computer music group Maniacs of Noise....
's and Reyn Ouwehand's song made for the Rubicon game in the song You've got my love. - In 2002 Instant Remedy released a C64Commodore 64The Commodore 64 is an 8-bit home computer introduced by Commodore International in January 1982.Volume production started in the spring of 1982, with machines being released on to the market in August at a price of US$595...
remix album named Instant Remedy. - In 2004, Diplo extensively sampled the lead theme from Jonathan Dunn's SID music for the game Platoon and used as a backdrop for his song "Diplo Rhythm".
- In the same year, house producer Abe Duque used a classic SID arpeggio sound in the track Champagne Days, Cocaine Nights.
- In 2007 TimbalandTimbalandTimothy Zachery Mosley , better known by his stage name Timbaland, is an American record producer, songwriter and rapper....
's extensive use of the SidStation led to the 2007 Timbaland plagiarism controversy2007 Timbaland plagiarism controversyTimbaland's plagiarism controversy occurred in January 2007, when several news sources reported that Timbaland was alleged to have plagiarized several elements in the song "Do It" on the 2006 album Loose by Nelly Furtado without giving credit or compensation...
around his tracks Block Party and Do ItDo It"Do It" is a popsong by Canadian recording artist Nelly Furtado for her third album, Loose . It was produced by Timbaland and Nate "Danja" Hills...
(written for Nelly FurtadoNelly FurtadoNelly Kim Furtado is a Canadian singer-songwriter, record producer and actress. Furtado grew up in Victoria, British Columbia, Canada.Furtado first gained fame with her debut album, Whoa, Nelly!, and its single "I'm Like a Bird", which won a 2001 Juno Award for Single of the Year and a 2002 Grammy...
). - SidStation is essential to the sound of Swedish band Machinae SupremacyMachinae SupremacyMachinae Supremacy is a Swedish band that combines modern heavy metal and alternative rock with chiptunes. Self-defined as "SID metal", many of their songs use a SidStation that features the SID chip of the Commodore 64...
. The band defines itself as SID metal. - The Swedish acid ambient artist Carbon Based LifeformsCarbon Based LifeformsCarbon Based Lifeforms is a psychedelic ambient music group made up of Johannes Hedberg and Daniel Segerstad , in Gothenburg, Sweden...
features a song called MOS 6581 on their 2003 album Hydroponic Garden. - In 2010, UK based Techno producer 'Luke's Anger' released an album named 'Live Wrong And Prosper', featuring a huge C64 on the 2x vinyl cover. Tracks like 'Worried Sid' show extreme use of MOS6581 technology.
See also
- MOS Technology VICMOS Technology VICThe VIC , specifically known as the MOS Technology 6560 / 6561 , is the integrated circuit chip responsible for generating video graphics and sound in the Commodore VIC-20 home computer...
- the combined graphics and sound chip of the VIC-20 - Atari POKEYAtari POKEYThe Pot Keyboard Integrated Circuit is a digital I/O chip found in the Atari 8-bit family of home computers and many arcade games in the 1980s. It was commonly used to sample potentiometers and scan matrices of switches...
- MOS Technology 8364 "Paula"
- ChiptuneChiptuneA chiptune, also known as chip music, is synthesized electronic music often produced with the sound chips of vintage computers and video game consoles, as well as with other methods such as emulation. In the early 1980s, personal computers became cheaper and more accessible than they had previously...
- Sound chipSound chipA sound chip is an integrated circuit designed to produce sound . It might be doing this through digital, analog or mixed-mode electronics...
- The High Voltage SID CollectionThe High Voltage SID CollectionThe High Voltage SID Collection is both the name of a project to build a collection of music created on the MOS Technology 6581/8580 SID sound chip in Commodore CBM-II, Commodore 64 and Commodore 128 home computers and the collection itself...
- Press Play on Tape, a C64 revival band
- Machinae SupremacyMachinae SupremacyMachinae Supremacy is a Swedish band that combines modern heavy metal and alternative rock with chiptunes. Self-defined as "SID metal", many of their songs use a SidStation that features the SID chip of the Commodore 64...
Further reading
- Karen Collins, "Loops and bloops". Music of the Commodore 64 games, soundscapes, volume 8, Feb 2006
External links
SID information- SID in-depth information page
- The c64org portal
- Tim Boscke's SID decapsulation pictures
- The 6581 SID Datasheet
- SID programming info
- MOS 8580 SID die shots
Hardware
- SIDblaster/USB - HardSID compatible DIY SID-dongle
- Prophet 64 "The future of SID music"
- Home of MIDIbox SID
- Elektron Sidstation
- Elektron Monomachine
- HardSIDHardSIDThe HardSID is a family of sound cards, produced by a Hungarian company Hard Software and originally conceived by Teli Sándor.The HardSID cards are based on the MOS Technology SID chip which was popularised and immortalized by the Commodore 64 home computer...
- HyperSID
- thrashbarg's MOS-ATmega8 project
- Example of interfacing a SID with an Atmel ATmega168
Software / emulators
- ReSIDReSIDreSID is a reverse engineered software emulation of the MOS6581 SID . This chip was used in the Commodore 64 computer. reSID is free software, published under the GNU General Public License....
- Dag Lem's ReSID SID emulator - ReSID filter distortion simulation - Antti Lankila's patch to ReSID to vastly improve the analog filtering emulation, among other things.
- SidTool - Multi SID emulator frontend for Windows
- PlaySID - SID emulator for Amiga
- JAM - JAM multiformat player with SID plugin for Atari TOSAtari TOSTOS is the operating system of the Atari ST range of computers. This range includes the 520 and 1040ST, their STF/M/FM and STE variants and the Mega ST/STE. Later, 32-bit machines were developed using a new version of TOS, called MultiTOS, which allowed multitasking...
compatible machines - PlaySID - SID emulator for Atari ST/E/TT/Falcon
- FlaySID - SID emulator for Atari Falcon
- PSID64 — Converts SID files to executables for playing SID music on a real C64
- SIDplay2 - SID emulator for Windows and Linux
- Java SIDplay2 - SID emulator for Java platforms
- SIDPLAY - SID emulator for Mac OS X
- JSIDplay Java based SID player (with HVSC on-line)
- ACID64 PlayerACID64 PlayerACID64 Player is a music player application by the High Voltage SID Collection team-member Wilfred Bos, that plays Commodore 64 music files through an MOS Technology SID sound interface device chip, using an instruction cycle-based emulation of the C64's core processors to achieve true fidelity.The...
- Commodore 64 Music Player for Windows - unknown64 - a VSTi Commodore64/SID Chip emulator
- SE64 - Commodore64/SID Chip inspired VSTi
- quadraSID - a commercial VST-SID Chip emulator
- Chipamp - Winamp plug-in bundle compiled by OverClocked ReMixOverClocked ReMixOverClocked ReMix, also known as OC ReMix and OCR, is a non-profit organization dedicated to preserving and paying tribute to video game music through arranging and re-interpreting the songs with new technology and software, as well as by various traditional means...
allowing playback of over 40 chiptune and tracker formats - foo_sid - SID file plugin for foobar2000Foobar2000foobar2000 is a freeware audio player for Windows developed by Peter Pawlowski, a former freelance contractor for Nullsoft. It is known for its highly modular design and extensive SDK which allows third-party developers to do such things as completely replace the interface...
- RockboxRockboxRockbox is a replacement for the standard firmware in various forms of digital audio players . It offers an alternative to the player's operating system, in many cases without removing the original firmware, which provides a plug-in architecture for adding various enhancements and functions...
plays SID files - SIDplay2/w - SID Player for Windows (Win32 GUI front-end for SIDplay2)
- The Audacious Media PlayerAudacious Media PlayerAudacious is a free software audio player with a focus on low resource usage, high audio quality, and support for a wide range of audio formats. It is designed primarily for use on POSIX-compatible systems such as Linux, with limited support for Microsoft Windows...
also plays SID files - SIDPlayer - SID player for BeOS and Linux
- Sid Player Sid Player for iPhone 2G, 3G / iPod Touch 1. & 2.Gen
- Sid Player Pro a special Sid Player of Sid Player with more features
- http://www.plogue.com/ Chipsounds - VST/AU/RTAS - Emulations of 2A03, AY-3-8910, DMG-CPU, P8244, POKEY, SID, SN76489, TIA, UVI and the VIC-I.
- SIDizer - Advanced emulation of SID chip (commercial VST/Standalone)
Music
- The High Voltage SID Collection – The SID music preservation project
- 6581-8580 Project (SOASC) - The entire HVSCThe High Voltage SID CollectionThe High Voltage SID Collection is both the name of a project to build a collection of music created on the MOS Technology 6581/8580 SID sound chip in Commodore CBM-II, Commodore 64 and Commodore 128 home computers and the collection itself...
#49 recorded on three types of SID chips with real Commodore 64Commodore 64The Commodore 64 is an 8-bit home computer introduced by Commodore International in January 1982.Volume production started in the spring of 1982, with machines being released on to the market in August at a price of US$595...
computers Also included are all the .sid files from HVSC. - Paulie's Ocean SID Page - Site discussing Ocean's SID player, the Ocean Loading Music and source code for Ocean's SID player.
- Compute's Gazette SID Collection
- remix.kwed.org – a collection of over 2100 C64 SID remixes (as of May 1, 2008)
- Remix64.com – Community for C64 SID and Amiga music remixes
- C64 Music – Commodore 64 music in the real world and other SID related stories blog
- SLAY Radio – Radio station that features remixed Commodore 64 music and live shows
- 8Bit Mayhem C64 Scene Music Podcast, Obvious, not so obvious, forgotten and classic Commodore 64 scene music.
- Machinae Supremacy The Origin Of SID Metal
- Mini Melodies SID meets female
- PRESS PLAY ON TAPE The C64 revival band, PRESS PLAY ON TAPE
- STA$D400 Little music project partly using multiple SID chips
- Vibrants The SID music composed by Vibrants
- nata's SID music Songs, Sources, Pictures..

