
Mef2
Encyclopedia
Molecular biology
Molecular biology is the branch of biology that deals with the molecular basis of biological activity. This field overlaps with other areas of biology and chemistry, particularly genetics and biochemistry...
, myocyte enhancer factor-2 (Mef2) protein
Protein
Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form, facilitating a biological function. A polypeptide is a single linear polymer chain of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of...
s are a family of transcription factor
Transcription factor
In molecular biology and genetics, a transcription factor is a protein that binds to specific DNA sequences, thereby controlling the flow of genetic information from DNA to mRNA...
s which through control of gene expression
Gene expression
Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product. These products are often proteins, but in non-protein coding genes such as ribosomal RNA , transfer RNA or small nuclear RNA genes, the product is a functional RNA...
are important regulators of cellular differentiation
Cellular differentiation
In developmental biology, cellular differentiation is the process by which a less specialized cell becomes a more specialized cell type. Differentiation occurs numerous times during the development of a multicellular organism as the organism changes from a simple zygote to a complex system of...
and consequently play a critical role in embryonic development
Developmental biology
Developmental biology is the study of the process by which organisms grow and develop. Modern developmental biology studies the genetic control of cell growth, differentiation and "morphogenesis", which is the process that gives rise to tissues, organs and anatomy.- Related fields of study...
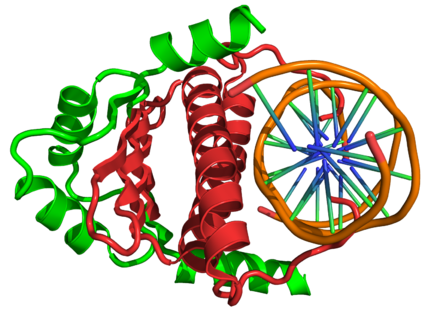
. In adult organisms, Mef2 proteins mediate the stress response in some tissues. Mef2 proteins contain both MADS-box
MADS-box
The MADS box is a conserved sequence motif found in genes which comprise the MADS-box gene family. The MADS box encodes the DNA-binding MADS domain. The MADS domain binds to DNA sequences of high similarity to the motif CC[A/T]6GG termed the CArG-box. MADS-domain proteins are generally...
and Mef2 DNA-binding domain
DNA-binding domain
A DNA-binding domain is an independently folded protein domain that contains at least one motif that recognizes double- or single-stranded DNA. A DBD can recognize a specific DNA sequence or have a general affinity to DNA...
s.
Discovery
Mef2 was originally identified as a transcription factor complex through promoter analysis of the muscle creatine kinaseCreatine kinase
Creatine kinase , also known as creatine phosphokinase or phospho-creatine kinase , is an enzyme expressed by various tissues and cell types. CK catalyses the conversion of creatine and consumes adenosine triphosphate to create phosphocreatine and adenosine diphosphate...
(mck) gene
Gene
A gene is a molecular unit of heredity of a living organism. It is a name given to some stretches of DNA and RNA that code for a type of protein or for an RNA chain that has a function in the organism. Living beings depend on genes, as they specify all proteins and functional RNA chains...
to identify nuclear factors interacting with the mck enhancer
Enhancer (genetics)
In genetics, an enhancer is a short region of DNA that can be bound with proteins to enhance transcription levels of genes in a gene cluster...
region during muscle differentiation.
Species distribution
The Mef2 gene is widely expressed in all branches of eukaryoteEukaryote
A eukaryote is an organism whose cells contain complex structures enclosed within membranes. Eukaryotes may more formally be referred to as the taxon Eukarya or Eukaryota. The defining membrane-bound structure that sets eukaryotic cells apart from prokaryotic cells is the nucleus, or nuclear...
s from yeast
Yeast
Yeasts are eukaryotic micro-organisms classified in the kingdom Fungi, with 1,500 species currently described estimated to be only 1% of all fungal species. Most reproduce asexually by mitosis, and many do so by an asymmetric division process called budding...
to humans. While drosophila has a single Mef2 gene, vertebrate
Vertebrate
Vertebrates are animals that are members of the subphylum Vertebrata . Vertebrates are the largest group of chordates, with currently about 58,000 species described. Vertebrates include the jawless fishes, bony fishes, sharks and rays, amphibians, reptiles, mammals, and birds...
s have four versions of the Mef2 gene (human versions are denoted as MEF2A
Myocyte-specific enhancer factor 2A
Myocyte-specific enhancer factor 2A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MEF2A gene. MEF2A is a transcription factor in the Mef2 family. In humans it is located on chromosome 15q26...
, MEF2B
MEF2B
MADS box transcription enhancer factor 2, polypeptide B , also known as MEF2B, is a human gene.-Further reading:...
, MEF2C
MEF2C
Myocyte-specific enhancer factor 2C also known as MADS box transcription enhancer factor 2, polypeptide C is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MEF2C gene. MEF2C is a transcription factor in the Mef2 family.-Genomics:...
, and MEF2D
MEF2D
Myocyte-specific enhancer factor 2D is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MEF2D gene.-Interactions:MEF2D has been shown to interact with YWHAQ, MAPK7, EP300, Sp1 transcription factor, Myocyte-specific enhancer factor 2A, NFATC2 and CABIN1....
), all expressed
Gene expression
Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product. These products are often proteins, but in non-protein coding genes such as ribosomal RNA , transfer RNA or small nuclear RNA genes, the product is a functional RNA...
in distinct but overlapping patterns during embryogenesis through adulthood.
Sequence and structure
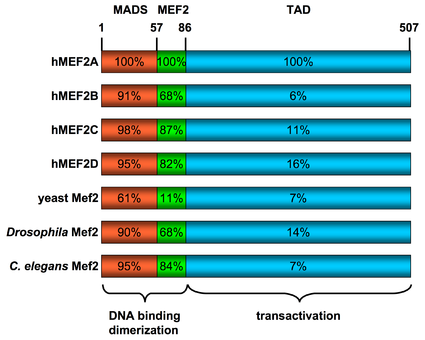
All of the mammalian Mef2 genes share approximately 50% overall amino acid identity and about 95% similarity throughout the highly conserved N-terminal MADS-box and Mef2 domains, however their sequences diverge in their C-terminal transactivation domain (see figure to the right).The MADS-box serves as the minimal DNA-binding domain, however an adjacent 29-amino acid extension called the Mef2 domain is required for high affinity DNA-binding and dimerization. Through an interaction with the MADS-box, Mef2 transcription factors have the ability to homo- and heterodimerize, and a classic nuclear localization sequence (NLS
NLS
-Computing:* NLS or oN-Line System, a pioneering computer system by Douglas Engelbart* National Language Support or Native Language Support, in software-Organisations:* National Language Services, South Africa...
) in the C-terminus of Mef2A, -C, and – D ensures nuclear localization of the protein. Interestingly, D-Mef2 and human MEF2B lack this conserved NLS but are still found in the nucleus.
Development
In drosophila, Mef2 regulates muscle development. Vertebrate skeletal muscle differentiation in conjunction with bHLHBasic-helix-loop-helix
A basic helix-loop-helix is a protein structural motif that characterizes a family of transcription factors.- Structure :The motif is characterized by two α-helices connected by a loop. In general, transcription factors including this domain are dimeric, each with one helix containing basic amino...
transcription factors is also regulated by Mef2.
Loss of Mef2c in neural crest
Neural crest
Neural crest cells are a transient, multipotent, migratory cell population unique to vertebrates that gives rise to a diverse cell lineage including melanocytes, craniofacial cartilage and bone, smooth muscle, peripheral and enteric neurons and glia....
cells results in results in craniofacial
Craniofacial
Craniofacial may be used to describe certain congenital malformations, injuries, surgeons who subspecialize in this area, multi-disciplinary medical-surgical teams that treat and do research on disorders affecting this region, and organizations with interest in...
defects in the developing embryo and neonatal death caused by blocking of the upper airway passages. Mef2c upregulates the expression of the homeodomain transcription factors DLX5
DLX5
Homeobox protein DLX-5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DLX5 gene.- Function :This gene encodes a member of a homeobox transcription factor gene family similar to the Drosophila distal-less gene. The encoded protein may play a role in bone development and fracture healing...
and DLX6
DLX6
Homeobox protein DLX-6 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DLX6 gene.-Further reading:...
, two transcription factors that are necessary for craniofacial development.
Stress response
In adult tissues, Mef2 proteins regulate the stress-response during cardiac hypertrophyVentricular hypertrophy
Ventricular hypertrophy is the enlargement of ventricles in the heart. Although left ventricular hypertrophy is more common, enlargement can also occur in the right ventricle, or both ventricles.- Physiology :...
and tissue remodeling in cardiac and skeletal muscle.

