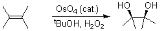
Milas hydroxylation
Encyclopedia
The Milas hydroxylation is an organic reaction
converting an alkene
to a vicinal
diol
, and was developed by N. A. Milas in the 1930s. The cis-diol is formed by reaction of alkenes with hydrogen peroxide
and either ultraviolet light or a catalytic osmium
, vanadium
, or chromium
oxide.
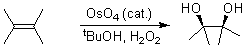
The reaction has been superseded in synthetic chemistry by the Upjohn dihydroxylation
and later by the Sharpless asymmetric dihydroxylation
.
Organic reaction
Organic reactions are chemical reactions involving organic compounds. The basic organic chemistry reaction types are addition reactions, elimination reactions, substitution reactions, pericyclic reactions, rearrangement reactions, photochemical reactions and redox reactions. In organic synthesis,...
converting an alkene
Alkene
In organic chemistry, an alkene, olefin, or olefine is an unsaturated chemical compound containing at least one carbon-to-carbon double bond...
to a vicinal
Vicinal (chemistry)
In chemistry vicinal stands for any two functional groups bonded to two adjacent carbon atoms. For example the molecule 2,3-dibromobutane carries two vicinal bromine atoms and 1,3-dibromobutane does not....
diol
Diol
A diol or glycol is a chemical compound containing two hydroxyl groups A geminal diol has two hydroxyl groups bonded to the same atom...
, and was developed by N. A. Milas in the 1930s. The cis-diol is formed by reaction of alkenes with hydrogen peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide is the simplest peroxide and an oxidizer. Hydrogen peroxide is a clear liquid, slightly more viscous than water. In dilute solution, it appears colorless. With its oxidizing properties, hydrogen peroxide is often used as a bleach or cleaning agent...
and either ultraviolet light or a catalytic osmium
Osmium
Osmium is a chemical element with the symbol Os and atomic number 76. Osmium is a hard, brittle, blue-gray or blue-blacktransition metal in the platinum family, and is the densest natural element. Osmium is twice as dense as lead. The density of osmium is , slightly greater than that of iridium,...
, vanadium
Vanadium
Vanadium is a chemical element with the symbol V and atomic number 23. It is a hard, silvery gray, ductile and malleable transition metal. The formation of an oxide layer stabilizes the metal against oxidation. The element is found only in chemically combined form in nature...
, or chromium
Chromium
Chromium is a chemical element which has the symbol Cr and atomic number 24. It is the first element in Group 6. It is a steely-gray, lustrous, hard metal that takes a high polish and has a high melting point. It is also odorless, tasteless, and malleable...
oxide.
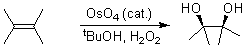
The reaction has been superseded in synthetic chemistry by the Upjohn dihydroxylation
Upjohn dihydroxylation
Upjohn dihydroxylation is an organic reaction converting an alkene to a cis vicinal diol, and was developed by V. VanRheenen, R. C. Kelly and D. Y. Cha of the Upjohn Company, USA in 1976...
and later by the Sharpless asymmetric dihydroxylation
Sharpless asymmetric dihydroxylation
Sharpless asymmetric dihydroxylation is the chemical reaction of an alkene with osmium tetroxide in the presence of a chiral quinine ligand to form a vicinal diol....
.

