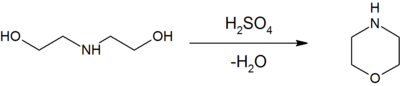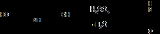
Morpholine
Encyclopedia
Morpholine is an organic
chemical compound
having the chemical formula
O
(C
H
2CH2)2N
H. This heterocycle, pictured at right, features both amine
and ether
functional group
s. Because of the amine, morpholine is a base
; its conjugate acid
is called morpholinium. For example, neutralizing morpholine with hydrochloric acid
makes the salt
morpholinium chloride.
:
s, for pH
adjustment in both fossil fuel
and nuclear power plant
steam
systems. Morpholine is used because its volatility
is about the same as water, so once it is added to the water, its concentration becomes distributed rather evenly in both the water and steam phases
. Its pH adjusting qualities then become distributed throughout the steam plant to provide corrosion
protection. Morpholine is often used in conjunction with low concentrations of hydrazine
or ammonia
to provide a comprehensive all-volatile treatment chemistry for corrosion protection for the steam systems of such plants. Morpholine decomposes reasonably slowly in the absence of oxygen
at the high temperature
s and pressure
s in these steam systems.
s typical for other secondary amine
s, though the presence of the ether oxygen withdraws electron density from the nitrogen, rendering it less nucleophilic (and less basic) than structurally similar secondary amines such as piperidine
. For this reason, it forms a stable chloramine (CAS#23328-69-0).
It is commonly used to generate enamine
s.
Morpholine is widely used in organic synthesis
. For example, it is a building block in the preparation of the antibiotic linezolid
and the anticancer agent gefitinib
(Iressa).
In research and in industry, the low cost and polarity of morpholine lead to its common use as a solvent for chemical reactions.
Organic compound
An organic compound is any member of a large class of gaseous, liquid, or solid chemical compounds whose molecules contain carbon. For historical reasons discussed below, a few types of carbon-containing compounds such as carbides, carbonates, simple oxides of carbon, and cyanides, as well as the...
chemical compound
Chemical compound
A chemical compound is a pure chemical substance consisting of two or more different chemical elements that can be separated into simpler substances by chemical reactions. Chemical compounds have a unique and defined chemical structure; they consist of a fixed ratio of atoms that are held together...
having the chemical formula
Chemical formula
A chemical formula or molecular formula is a way of expressing information about the atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound....
O
Oxygen
Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
(C
Carbon
Carbon is the chemical element with symbol C and atomic number 6. As a member of group 14 on the periodic table, it is nonmetallic and tetravalent—making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds...
H
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
2CH2)2N
Nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element that has the symbol N, atomic number of 7 and atomic mass 14.00674 u. Elemental nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, and mostly inert diatomic gas at standard conditions, constituting 78.08% by volume of Earth's atmosphere...
H. This heterocycle, pictured at right, features both amine
Amine
Amines are organic compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are derivatives of ammonia, wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent such as an alkyl or aryl group. Important amines include amino acids, biogenic amines,...
and ether
Ether
Ethers are a class of organic compounds that contain an ether group — an oxygen atom connected to two alkyl or aryl groups — of general formula R–O–R'. A typical example is the solvent and anesthetic diethyl ether, commonly referred to simply as "ether"...
functional group
Functional group
In organic chemistry, functional groups are specific groups of atoms within molecules that are responsible for the characteristic chemical reactions of those molecules. The same functional group will undergo the same or similar chemical reaction regardless of the size of the molecule it is a part of...
s. Because of the amine, morpholine is a base
Base (chemistry)
For the term in genetics, see base A base in chemistry is a substance that can accept hydrogen ions or more generally, donate electron pairs. A soluble base is referred to as an alkali if it contains and releases hydroxide ions quantitatively...
; its conjugate acid
Conjugate acid
Within the Brønsted–Lowry acid-base theory , a conjugate acid is the acid member, HX, of a pair of two compounds that transform into each other by gain or loss of a proton. A conjugate acid can also be seen as the chemical substance that releases, or donates, a proton in the forward chemical...
is called morpholinium. For example, neutralizing morpholine with hydrochloric acid
Hydrochloric acid
Hydrochloric acid is a solution of hydrogen chloride in water, that is a highly corrosive, strong mineral acid with many industrial uses. It is found naturally in gastric acid....
makes the salt
Salt
In chemistry, salts are ionic compounds that result from the neutralization reaction of an acid and a base. They are composed of cations and anions so that the product is electrically neutral...
morpholinium chloride.
Production
Morpholine may be produced by the dehydration of diethanolamine with sulfuric acidSulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid is a strong mineral acid with the molecular formula . Its historical name is oil of vitriol. Pure sulfuric acid is a highly corrosive, colorless, viscous liquid. The salts of sulfuric acid are called sulfates...
:
Industrial applications
Morpholine is a common additive, in parts per million concentrationConcentration
In chemistry, concentration is defined as the abundance of a constituent divided by the total volume of a mixture. Four types can be distinguished: mass concentration, molar concentration, number concentration, and volume concentration...
s, for pH
PH
In chemistry, pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity of an aqueous solution. Pure water is said to be neutral, with a pH close to 7.0 at . Solutions with a pH less than 7 are said to be acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are basic or alkaline...
adjustment in both fossil fuel
Fossil fuel power plant
A fossil-fuel power station is a power station that burns fossil fuels such as coal, natural gas or petroleum to produce electricity. Central station fossil-fuel power plants are designed on a large scale for continuous operation...
and nuclear power plant
Nuclear power plant
A nuclear power plant is a thermal power station in which the heat source is one or more nuclear reactors. As in a conventional thermal power station the heat is used to generate steam which drives a steam turbine connected to a generator which produces electricity.Nuclear power plants are usually...
steam
Steam
Steam is the technical term for water vapor, the gaseous phase of water, which is formed when water boils. In common language it is often used to refer to the visible mist of water droplets formed as this water vapor condenses in the presence of cooler air...
systems. Morpholine is used because its volatility
Volatility (chemistry)
In chemistry and physics, volatility is the tendency of a substance to vaporize. Volatility is directly related to a substance's vapor pressure. At a given temperature, a substance with higher vapor pressure vaporizes more readily than a substance with a lower vapor pressure.The term is primarily...
is about the same as water, so once it is added to the water, its concentration becomes distributed rather evenly in both the water and steam phases
Phase (matter)
In the physical sciences, a phase is a region of space , throughout which all physical properties of a material are essentially uniform. Examples of physical properties include density, index of refraction, and chemical composition...
. Its pH adjusting qualities then become distributed throughout the steam plant to provide corrosion
Corrosion
Corrosion is the disintegration of an engineered material into its constituent atoms due to chemical reactions with its surroundings. In the most common use of the word, this means electrochemical oxidation of metals in reaction with an oxidant such as oxygen...
protection. Morpholine is often used in conjunction with low concentrations of hydrazine
Hydrazine
Hydrazine is an inorganic compound with the formula N2H4. It is a colourless flammable liquid with an ammonia-like odor. Hydrazine is highly toxic and dangerously unstable unless handled in solution. Approximately 260,000 tons are manufactured annually...
or ammonia
Ammonia
Ammonia is a compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . It is a colourless gas with a characteristic pungent odour. Ammonia contributes significantly to the nutritional needs of terrestrial organisms by serving as a precursor to food and fertilizers. Ammonia, either directly or...
to provide a comprehensive all-volatile treatment chemistry for corrosion protection for the steam systems of such plants. Morpholine decomposes reasonably slowly in the absence of oxygen
Oxygen
Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
at the high temperature
Temperature
Temperature is a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notions of hot and cold. Objects of low temperature are cold, while various degrees of higher temperatures are referred to as warm or hot...
s and pressure
Pressure
Pressure is the force per unit area applied in a direction perpendicular to the surface of an object. Gauge pressure is the pressure relative to the local atmospheric or ambient pressure.- Definition :...
s in these steam systems.
Organic synthesis
Morpholine undergoes most chemical reactionChemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Chemical reactions can be either spontaneous, requiring no input of energy, or non-spontaneous, typically following the input of some type of energy, such as heat, light or electricity...
s typical for other secondary amine
Amine
Amines are organic compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are derivatives of ammonia, wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent such as an alkyl or aryl group. Important amines include amino acids, biogenic amines,...
s, though the presence of the ether oxygen withdraws electron density from the nitrogen, rendering it less nucleophilic (and less basic) than structurally similar secondary amines such as piperidine
Piperidine
Piperidine is an organic compound with the molecular formula 5NH. This heterocyclic amine consists of a six-membered ring containing five methylene units and one nitrogen atom...
. For this reason, it forms a stable chloramine (CAS#23328-69-0).
It is commonly used to generate enamine
Enamine
An enamine is an unsaturated compound derived by the reaction of an aldehyde or ketone with a secondary amine followed by loss of H2O.The word "enamine" is derived from the affix en-, used as the suffix of alkene, and the root amine. This can be compared with enol, which is a functional group...
s.
Morpholine is widely used in organic synthesis
Organic synthesis
Organic synthesis is a special branch of chemical synthesis and is concerned with the construction of organic compounds via organic reactions. Organic molecules can often contain a higher level of complexity compared to purely inorganic compounds, so the synthesis of organic compounds has...
. For example, it is a building block in the preparation of the antibiotic linezolid
Linezolid
Linezolid is a synthetic antibiotic used for the treatment of serious infections caused by Gram-positive bacteria that are resistant to several other antibiotics...
and the anticancer agent gefitinib
Gefitinib
Gefitinib INN , trade name Iressa, is a drug used in the treatment of certain types of cancer, particularly those with mutated and overactive EGFR. Gefitinib is an EGFR inhibitor, like erlotinib, which interrupts signaling through the epidermal growth factor receptor in target cells...
(Iressa).
In research and in industry, the low cost and polarity of morpholine lead to its common use as a solvent for chemical reactions.
Producers
Most (as above) is widespread in Europe and the USA; accordingly, producers in Europe and the USA are able to cover the domestic and export markets.As a fruit coating
Morpholine is used as a chemical emulsifier in the process of waxing fruit. Naturally, fruits make waxes to protect against insects and fungal contamination, but this can be lost as the fruit is cleaned. A small amount of new wax is applied to replace it. Morpholine is used as an emulsifier and solubility aid for shellac, which is used as a wax for fruit coating.As a component in fungicides
Morpholine derivatives used as agricultural fungicides in cereals are known as ergosterol biosynthesis inhibitors.- AmorolfineAmorolfineAmorolfine , is a morpholine antifungal drug that inhibits D14 reductase and D7-D8 isomerase, which depletes ergosterol and causes ignosterol to accumulate in the fungal cytoplasmic cell membranes....
- Fenpropimorph
- Tridemorph