
Moving Picture Experts Group
Encyclopedia
Working group
A working group is an interdisciplinary collaboration of researchers working on new research activities that would be difficult to develop under traditional funding mechanisms . The lifespan of the WG can last anywhere between a few months and several years...
of experts that was formed by ISO
International Organization for Standardization
The International Organization for Standardization , widely known as ISO, is an international standard-setting body composed of representatives from various national standards organizations. Founded on February 23, 1947, the organization promulgates worldwide proprietary, industrial and commercial...
and IEC
International Electrotechnical Commission
The International Electrotechnical Commission is a non-profit, non-governmental international standards organization that prepares and publishes International Standards for all electrical, electronic and related technologies – collectively known as "electrotechnology"...
to set standards for audio and video compression and transmission. It was established in 1988 by the initiative of Hiroshi Yasuda
Hiroshi Yasuda
Prof. Dr. of Engineering Hiroshi Yasuda is an Emeritus Professor at the University of Tokyo and works as a Consultant for Nippon Telegraph and Telephone....
(Nippon Telegraph and Telephone
Nippon Telegraph and Telephone
, commonly known as NTT, is a Japanese telecommunications company headquartered in Tokyo, Japan. Ranked the 31st in Fortune Global 500, NTT is the largest telecommunications company in Asia, and the second-largest in the world in terms of revenue....
) and Leonardo Chiariglione
Leonardo Chiariglione
Leonardo Chiariglione is an Italianengineer. He has been at the forefront of a number of initiatives that have helped shape media technology and business as we know them today, in particular he is the chairman and co-founded the Moving Picture Experts Group together with Hiroshi Yasuda.-...
, who has been from the beginning the Chairman of the group. The first MPEG meeting was in May 1988 in Ottawa, Canada. As of late 2005, MPEG has grown to include approximately 350 members per meeting from various industries, universities, and research institutions. MPEG's official designation is ISO/IEC JTC1
ISO/IEC JTC1
ISO/IEC JTC 1 is Joint Technical Committee 1 of the International Organization for Standardization and the International Electrotechnical Commission . It deals with all matters of information technology....
/SC29 WG11 - Coding of moving pictures and audio (ISO/IEC Joint Technical Committee 1, Subcommittee 29, Working Group 11).
Overview

Encoder
An encoder is a device, circuit, transducer, software program, algorithm or person that converts information from one format or code to another, for the purposes of standardization, speed, secrecy, security, or saving space by shrinking size.-Media:...
is more complex than the decoder
Decoder
A decoder is a device which does the reverse operation of an encoder, undoing the encoding so that the original information can be retrieved. The same method used to encode is usually just reversed in order to decode...
. The encoder needs to be algorithm
Algorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm is an effective method expressed as a finite list of well-defined instructions for calculating a function. Algorithms are used for calculation, data processing, and automated reasoning...
ic or adaptive whereas the decoder is 'dumb' and carries out fixed actions. This is considered advantageous in applications such as broadcasting where the number of expensive complex encoders is small but the number of simple inexpensive decoders is large. The MPEG's (ISO's) approach to standardization is novel, because it is not the encoder that is standardized, but the way a decoder interprets the bitstream
Bitstream
A bitstream or bit stream is a time series of bits.A bytestream is a series of bytes, typically of 8 bits each, and can be regarded as a special case of a bitstream....
. A decoder that can successfully interpret the bitstream is said to be compliant. The advantage of standardizing the decoder is that over time encoding algorithms can improve, yet compliant decoders continue to function with them. The MPEG standards give very little information regarding structure and operation of the encoder and implementers can supply encoders using proprietary
Proprietary software
Proprietary software is computer software licensed under exclusive legal right of the copyright holder. The licensee is given the right to use the software under certain conditions, while restricted from other uses, such as modification, further distribution, or reverse engineering.Complementary...
algorithms. This gives scope for competition between different encoder designs, which means better designs can evolve and users have greater choice, because encoders of different levels of cost and complexity can exist, yet a compliant decoder operates with all of them.
MPEG also standardizes the protocol and syntax under which it is possible to combine or multiplex
Multiplexing
The multiplexed signal is transmitted over a communication channel, which may be a physical transmission medium. The multiplexing divides the capacity of the low-level communication channel into several higher-level logical channels, one for each message signal or data stream to be transferred...
audio data with video data to produce a digital equivalent of a television program. Many such programs can be multiplexed and MPEG defines the way such multiplexes can be created and transported. The definitions include the metadata
Metadata
The term metadata is an ambiguous term which is used for two fundamentally different concepts . Although the expression "data about data" is often used, it does not apply to both in the same way. Structural metadata, the design and specification of data structures, cannot be about data, because at...
used by decoders to demultiplex correctly.
Sub Groups
ISO/IEC JTC1/SC29/WG11 - Coding of moving pictures and audio has following Sub Groups (SG):- Requirements
- Systems
- Video
- Audio
- 3D Graphics Compression
- Test
Joint Video Team
Joint Video Team (JVT) is joint project between ITU-TITU-T
The ITU Telecommunication Standardization Sector is one of the three sectors of the International Telecommunication Union ; it coordinates standards for telecommunications....
SG16/Q.6 (Study Group 16 / Question 6) - VCEG
VCEG
The Video Coding Experts Group or Visual Coding Experts Group is the informal name of Question 6 of Working Party 3 of Study Group 16 of the ITU-T. Its abbreviated title is ITU-T Q.6/SG 16...
(Video Coding Experts Group) and ISO/IEC JTC1/SC29/WG11 - MPEG for the development of new video coding recommendation and international standard. It was formed in 2001 and its main result has been H.264/MPEG-4 AVC
H.264/MPEG-4 AVC
H.264/MPEG-4 Part 10 or AVC is a standard for video compression, and is currently one of the most commonly used formats for the recording, compression, and distribution of high definition video...
(MPEG-4 Part 10).
Joint Collaborative Team on Video Coding
Joint Collaborative Team on Video Coding (JCT-VC) is a group of video coding experts from ITU-T Study Group 16 (VCEG) and ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 29/WG 11 (MPEG). It was created in 2010 to develop High Efficiency Video CodingHigh Efficiency Video Coding
High Efficiency Video Coding is a draft video compression standard, a successor to H.264/MPEG-4 AVC , currently under joint development by the ISO/IEC Moving Picture Experts Group and ITU-T Video Coding Experts Group . MPEG and VCEG have established a Joint Collaborative Team on Video Coding to...
, a new generation video coding standard that further reduces (by 50%) the data rate required for high quality video coding, as compared to the current ITU-T H.264 / ISO/IEC 14496-10 standard. JCT-VC is co-chaired by Jens-Rainer Ohm and Gary Sullivan
Gary Sullivan (engineer)
Gary J. Sullivan is an American electrical engineer who led the development of the H.264/AVC video coding standard and created the DirectX Video Acceleration API/DDI video decoding feature of the Microsoft Windows operating system platform...
.
Standards
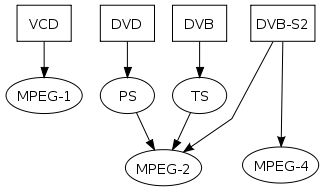
The MPEG standards consist of different Parts. Each part covers a certain aspect of the whole specification. The standards also specify Profiles and Levels. Profiles are intended to define a set of tools that are available, and Levels define the range of appropriate values for the properties associated with them. Some of the approved MPEG standards were revised by later amendments and/or new editions. MPEG has standardized the following compression formats and ancillary standards:- MPEG-1MPEG-1MPEG-1 is a standard for lossy compression of video and audio. It is designed to compress VHS-quality raw digital video and CD audio down to 1.5 Mbit/s without excessive quality loss, making video CDs, digital cable/satellite TV and digital audio broadcasting possible.Today, MPEG-1 has become...
(1993): Coding of moving pictures and associated audio for digital storage media at up to about 1.5 Mbit/s (ISO/IEC 11172). The first MPEG compression standard for audio and video. It is commonly limited to about 1.5 Mbit/s although the specification is capable of much higher bit rates. It was basically designed to allow moving pictures and sound to be encoded into the bitrateBitrateIn telecommunications and computing, bit rate is the number of bits that are conveyed or processed per unit of time....
of a Compact DiscCompact DiscThe Compact Disc is an optical disc used to store digital data. It was originally developed to store and playback sound recordings exclusively, but later expanded to encompass data storage , write-once audio and data storage , rewritable media , Video Compact Discs , Super Video Compact Discs ,...
. It is used on Video CDVideo CDBefore the advent of DVD and Blu-ray, the Video CD became the first format for distributing films on standard 120 mm optical discs. The format is a standard digital format for storing video on a Compact Disc...
, SVCD and can be used for low-quality video on DVD Video. It was used in digital satellite/cable TV services before MPEG-2 became widespread. To meet the low bit requirement, MPEG-1 downsamples the images, as well as uses picture rates of only 24–30 Hz, resulting in a moderate quality. It includes the popular MPEG-1 Audio Layer III (MP3MP3MPEG-1 or MPEG-2 Audio Layer III, more commonly referred to as MP3, is a patented digital audio encoding format using a form of lossy data compression...
) audio compression format.
- MPEG-2MPEG-2MPEG-2 is a standard for "the generic coding of moving pictures and associated audio information". It describes a combination of lossy video compression and lossy audio data compression methods which permit storage and transmission of movies using currently available storage media and transmission...
(1995): Generic coding of moving pictures and associated audio information (ISO/IEC 13818). Transport, video and audio standards for broadcast-quality television. MPEG-2 standard was considerably broader in scope and of wider appeal – supporting interlacing and high definitionHigh-definition videoHigh-definition video or HD video refers to any video system of higher resolution than standard-definition video, and most commonly involves display resolutions of 1,280×720 pixels or 1,920×1,080 pixels...
. MPEG-2 is considered important because it has been chosen as the compression scheme for over-the-air digital televisionDigital televisionDigital television is the transmission of audio and video by digital signals, in contrast to the analog signals used by analog TV...
ATSC, DVB and ISDBISDBIntegrated Services Digital Broadcasting is a Japanese standard for digital television and digital radio used by the country's radio and television stations. ISDB replaced the previously used MUSE "Hi-vision" analogue HDTV system...
, digital satellite TV services like Dish NetworkDish NetworkDish Network Corporation is the second largest pay TV provider in the United States, providing direct broadcast satellite service—including satellite television, audio programming, and interactive television services—to 14.337 million commercial and residential customers in the United States. Dish...
, digital cable televisionCable televisionCable television is a system of providing television programs to consumers via radio frequency signals transmitted to televisions through coaxial cables or digital light pulses through fixed optical fibers located on the subscriber's property, much like the over-the-air method used in traditional...
signals, SVCD and DVD Video. It is also used on Blu-ray DiscBlu-ray DiscBlu-ray Disc is an optical disc storage medium designed to supersede the DVD format. The plastic disc is 120 mm in diameter and 1.2 mm thick, the same size as DVDs and CDs. Blu-ray Discs contain 25 GB per layer, with dual layer discs being the norm for feature-length video discs...
s, but these normally use MPEG-4 Part 10 or SMPTE VC-1VC-1VC-1 is the informal name of the SMPTE 421M video codec standard, which was initially developed as a proprietary video format by Microsoft before it was released as a formal SMPTE standard video format on April 3, 2006...
for high-definition content.
- MPEG-3MPEG-3MPEG-3 is the designation for a group of audio and video coding standards agreed upon by the Moving Picture Experts Group designed to handle HDTV signals at 1080p in the range of 20 to 40 megabits per second...
: MPEG-3 dealt with standardizing scalable and multi-resolution compression and was intended for HDTV compression but was found to be redundant and was merged with MPEG-2, as a result there is no MPEG-3 standard. MPEG-3 is not to be confused with MP3MP3MPEG-1 or MPEG-2 Audio Layer III, more commonly referred to as MP3, is a patented digital audio encoding format using a form of lossy data compression...
, which is MPEG-1 Audio Layer III.
- MPEG-4MPEG-4MPEG-4 is a method of defining compression of audio and visual digital data. It was introduced in late 1998 and designated a standard for a group of audio and video coding formats and related technology agreed upon by the ISO/IEC Moving Picture Experts Group under the formal standard ISO/IEC...
(1998): Coding of audio-visual objects. (ISO/IEC 14496) MPEG-4 uses further coding tools with additional complexity to achieve higher compression factors than MPEG-2. In addition to more efficient coding of video, MPEG-4 moves closer to computer graphics applications. In more complex profiles, the MPEG-4 decoder effectively becomes a rendering processor and the compressed bitstream describes three-dimensional shapes and surface texture. MPEG-4 supports Intellectual Property Management and Protection (IPMP), which provides the facility to use proprietary technologies to manage and protect content like digital rights managementDigital rights managementDigital rights management is a class of access control technologies that are used by hardware manufacturers, publishers, copyright holders and individuals with the intent to limit the use of digital content and devices after sale. DRM is any technology that inhibits uses of digital content that...
. It also supports MPEG-J, a fully programmatic solution for creation of custom interactive multimedia applications (Java application environment with a Java API) and many other features. Several new higher-efficiency video standards (newer than MPEG-2 Video) are included, notably:- MPEG-4 Part 2MPEG-4 Part 2MPEG-4 Part 2, MPEG-4 Visual is a video compression technology developed by MPEG. It belongs to the MPEG-4 ISO/IEC standards. It is a discrete cosine transform compression standard, similar to previous standards such as MPEG-1 and MPEG-2...
(or Simple and Advanced Simple Profile) and - MPEG-4 AVCH.264/MPEG-4 AVCH.264/MPEG-4 Part 10 or AVC is a standard for video compression, and is currently one of the most commonly used formats for the recording, compression, and distribution of high definition video...
(or MPEG-4 Part 10 or H.264). MPEG-4 AVC may be used on HD DVDHD DVDHD DVD is a discontinued high-density optical disc format for storing data and high-definition video.Supported principally by Toshiba, HD DVD was envisioned to be the successor to the standard DVD format...
and Blu-ray DiscBlu-ray DiscBlu-ray Disc is an optical disc storage medium designed to supersede the DVD format. The plastic disc is 120 mm in diameter and 1.2 mm thick, the same size as DVDs and CDs. Blu-ray Discs contain 25 GB per layer, with dual layer discs being the norm for feature-length video discs...
s, along with VC-1VC-1VC-1 is the informal name of the SMPTE 421M video codec standard, which was initially developed as a proprietary video format by Microsoft before it was released as a formal SMPTE standard video format on April 3, 2006...
and MPEG-2.
- MPEG-4 Part 2
In addition, the following standards, while not sequential advances to the video encoding standard as with MPEG-1 through MPEG-4, are referred to by similar notation:
- MPEG-7MPEG-7MPEG-7 is a multimedia content description standard. It was standardized in ISO/IEC 15938 . This description will be associated with the content itself, to allow fast and efficient searching for material that is of interest to the user. MPEG-7 is formally called Multimedia Content Description...
(2002): Multimedia content description interface. (ISO/IEC 15938)
- MPEG-21MPEG-21The MPEG-21 standard, from the Moving Picture Experts Group, aims at defining an open framework for multimedia applications. MPEG-21 is ratified in the standards ISO/IEC 21000 - Multimedia framework .MPEG-21 is based on two essential concepts:...
(2001): Multimedia framework (MPEG-21). (ISO/IEC 21000) MPEG describes this standard as a multimedia frameworkMultimedia frameworkA multimedia framework is a software framework that handles media on a computer and through a network. A good multimedia framework offers an intuitive API and a modular architecture to easily add support for new audio, video and container formats and transmission protocols...
and provides for intellectual property management and protection.
Moreover, more recently than other standards above, MPEG has started following international standards; each of the standards holds multiple MPEG technologies for a way of application. (For example, MPEG-A includes a number of technologies on multimedia application format.)
- MPEG-A (2007): Multimedia application format (MPEG-A). (ISO/IEC 23000) (e.g., Purpose for multimedia application formats, MPEG music player application format, MPEG photo player application format and others)
- MPEG-B (2006): MPEG systems technologies. (ISO/IEC 23001) (e.g., Binary MPEG format for XMLBiMBiM is an international standard defining a generic binary format for encoding XML documents.The technical specifications for BiM are found in: MPEG systems technologies - Part 1: Binary MPEG format for XML It is also known as MPEG-B Part 1.- Overview :BiM addresses a broad spectrum of...
, Fragment Request Units, Bitstream Syntax Description Language (BSDL) and others)
- MPEG-C (2006): MPEG video technologies. (ISO/IEC 23002) (e.g., Accuracy requirements for implementation of integer-output 8x8 inverse discrete cosine transform and others)
- MPEG-DMPEG-DMPEG-D is a group of standards for audio coding formally known as ISO/IEC 23003 - MPEG audio technologies, published since 2007.MPEG-D consists of three parts:* MPEG-D Part 1: MPEG Surround...
(2007): MPEG audio technologies. (ISO/IEC 23003) (e.g., MPEG SurroundMPEG SurroundMPEG Surround , also known as Spatial Audio Coding is a lossy compression format for surround sound that provides a method for extending mono or stereo audio services to multi-channel audio in a backwards compatible fashion...
, SAOC-Spatial Audio Object Coding and USAC-Unified Speech and Audio CodingUnified Speech and Audio CodingUnified Speech and Audio Coding is an audio compression format and codec for both music and speech or any mix of speech and audio using very low bit rates between 12 and 64 kbit/s. It is currently under the development in MPEG and will be defined as an international standard ISO/IEC 23003-3...
)
- MPEG-E (2007): Multimedia Middleware. (ISO/IEC 23004) (a.k.a. M3W) (e.g., Architecture, Multimedia application programming interface (API), Component model and others)
- Supplemental media technologies (2008). (ISO/IEC 29116) Part 1: Media streaming application format protocols will be revised in MPEG-M Part 4 - MPEG extensible middleware (MXM) protocols.
- MPEG-V (2011): Media context and control. (ISO/IEC 23005) (a.k.a. Information exchange with Virtual Worlds) (e.g., Avatar characteristics, Sensor information, Architecture and others)
- MPEG-M (2010): MPEG eXtensible Middleware (MXM). (ISO/IEC 23006) (e.g., MXM architecture and technologies, API, MPEG extensible middleware (MXM) protocols)
- MPEG-U (2010): Rich media user interfaces. (ISO/IEC 23007) (e.g., Widgets)
| Acronym for a group of standards | Title | ISO/IEC standards | First public release date (First edition) | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MPEG-1 MPEG-1 MPEG-1 is a standard for lossy compression of video and audio. It is designed to compress VHS-quality raw digital video and CD audio down to 1.5 Mbit/s without excessive quality loss, making video CDs, digital cable/satellite TV and digital audio broadcasting possible.Today, MPEG-1 has become... |
Coding of moving pictures and associated audio for digital storage media. Commonly limited to about 1.5 Mbit/s although specification is capable of much higher bit rates | ISO/IEC 11172 | 1993 | |
| MPEG-2 MPEG-2 MPEG-2 is a standard for "the generic coding of moving pictures and associated audio information". It describes a combination of lossy video compression and lossy audio data compression methods which permit storage and transmission of movies using currently available storage media and transmission... |
Generic coding of moving pictures and associated audio information | ISO/IEC 13818 | 1995 | |
| MPEG-3 MPEG-3 MPEG-3 is the designation for a group of audio and video coding standards agreed upon by the Moving Picture Experts Group designed to handle HDTV signals at 1080p in the range of 20 to 40 megabits per second... |
abandoned, incorporated into MPEG-2 | |||
| MPEG-4 MPEG-4 MPEG-4 is a method of defining compression of audio and visual digital data. It was introduced in late 1998 and designated a standard for a group of audio and video coding formats and related technology agreed upon by the ISO/IEC Moving Picture Experts Group under the formal standard ISO/IEC... |
Coding of audio-visual objects | ISO/IEC 14496 | 1999 | |
| MPEG-7 MPEG-7 MPEG-7 is a multimedia content description standard. It was standardized in ISO/IEC 15938 . This description will be associated with the content itself, to allow fast and efficient searching for material that is of interest to the user. MPEG-7 is formally called Multimedia Content Description... |
Multimedia content description interface | ISO/IEC 15938 | 2002 | |
| MPEG-21 MPEG-21 The MPEG-21 standard, from the Moving Picture Experts Group, aims at defining an open framework for multimedia applications. MPEG-21 is ratified in the standards ISO/IEC 21000 - Multimedia framework .MPEG-21 is based on two essential concepts:... |
Multimedia framework (MPEG-21) | ISO/IEC 21000 | 2001 | |
| MPEG-A | Multimedia application format (MPEG-A) | ISO/IEC 23000 | 2007 | |
| MPEG-B | MPEG systems technologies | ISO/IEC 23001 | 2006 | |
| MPEG-C | MPEG video technologies | ISO/IEC 23002 | 2006 | |
| MPEG-D MPEG-D MPEG-D is a group of standards for audio coding formally known as ISO/IEC 23003 - MPEG audio technologies, published since 2007.MPEG-D consists of three parts:* MPEG-D Part 1: MPEG Surround... |
MPEG audio technologies | ISO/IEC 23003 | 2007 | |
| MPEG-E | Multimedia Middleware | ISO/IEC 23004 | 2007 | |
| (none) | Supplemental media technologies | ISO/IEC 29116 | 2008 | will be revised in MPEG-M Part 4 - MPEG extensible middleware (MXM) protocols |
| MPEG-V | Media context and control | ISO/IEC 23005 | 2011 | |
| MPEG-M | MPEG extensible middleware (MXM) | ISO/IEC 23006 | 2010 | |
| MPEG-U | Rich media user interfaces | ISO/IEC 23007 | 2010 | |
| MPEG-H | High-Efficiency Video Coding | (planned ISO/IEC 23008) | Under development |
Standardization process
A standard published by ISO/IEC is the last stage of a long process that starts with the proposal of new work within a committee. Here are some abbreviations used for marking a standard with its status:- PWI - Preliminary Work Item
- NP or NWIP - New Proposal / New Work Item Proposal (e.g., ISO/IEC NP 23007)
- AWI - Approved new Work Item (e.g., ISO/IEC AWI 15444-14)
- WD - Working Draft
- CD - Committee Draft (e.g., ISO/IEC CD 23000-5)
- FCD - Final Committee Draft (e.g., ISO/IEC FCD 23000-12)
- DIS - Draft International Standard
- FDIS - Final Draft International Standard
- PRF - Proof of a new International Standard
- IS - International Standard (e.g., ISO/IEC 13818-1:2007)
- CD Amd / PDAmd (PDAM) - Committee Draft Amendment / Proposed Draft Amendment (e.g., ISO/IEC 13818-1:2007/CD Amd 6)
- FPDAmd / DAM (DAmd) - Final Proposed Draft Amendment / Draft Amendment (e.g., ISO/IEC 14496-14:2003/FPDAmd 1)
- FDAM (FDAmd) - Final Draft Amendment (e.g., ISO/IEC 13818-1:2007/FDAmd 4)
- Amd - Amendment (e.g., ISO/IEC 13818-1:2007/Amd 1:2007)
Other abbreviations:
- TR - Technical Report (e.g., ISO/IEC TR 13818-5:2005)
- TS - Technical Specification
- IWA - International Workshop Agreement
- Cor - Technical Corrigendum (e.g., ISO/IEC 13818-1:2007/Cor 1:2008)
A proposal of work (New Proposal) is approved at Subcommittee and then at the Technical Committee level (SC29 and JTC1 respectively - in the case of MPEG). When the scope of new work is sufficiently clarified, MPEG usually makes open requests for proposals - known as "Call for proposals". The first document that is produced for audio and video coding standards is called a Verification Model (VM). In the case of MPEG-1 and MPEG-2 this was called Simulation and Test Model, respectively. When a sufficient confidence in the stability of the standard under development is reached, a Working Draft (WD) is produced. This is in the form of a standard but is kept internal to MPEG for revision. When a WD is sufficiently solid, becomes Committee Draft (CD) (usually at the planned time). It is then sent to National Bodies (NB) for ballot. The CD becomes Final Committee Draft (FCD) if the number of positive votes is above the quorum. After a review and comments issued by NBs, FCD is again submitted to NBs for the second ballot. If the FCD is approved, it becomes Final Draft International Standard (FDIS). ISO then holds a ballot with National Bodies, where no technical changes are allowed (yes/no ballot). If approved, the document becomes International Standard (IS).
ISO/IEC Directives allow also the so-called "Fast-track procedure". In this procedure a document is submitted directly for approval as a draft International Standard (DIS) to the ISO member bodies or as a final draft International Standard (FDIS) if the document was developed by an international standardizing body recognized by the ISO Council.
See also
- Video Coding Experts Group (VCEG)
- Joint Photographic Experts GroupJoint Photographic Experts GroupThe Joint Photographic Experts Group is the joint committee between ISO/IEC JTC1 and ITU-T that created the JPEG, JPEG 2000, and JPEG XR standards. It is one of two sub-groups of ISO/IEC Joint Technical Committee 1, Subcommittee 29, Working Group 1 - titled as Coding of still pictures...
(JPEG) - Joint Bi-level Image Experts GroupJoint Bi-level Image Experts GroupThe Joint Bi-level Image Experts Group is a group of experts nominated by national standards bodies and major companies to work to produce standards for bi-level image coding. The 'joint' refers to its status as a committee working on both ISO and ITU-T standards...
(JBIG) - Multimedia and Hypermedia information coding Expert Group (MHEG)
- Audio codecAudio codecAll codecs are devices or computer programs capable of coding or decoding a digital data stream or signal.The term audio codec has two meanings depending on the context:...
- Video codecVideo codecA video codec is a device or software that enables video compression and/or decompression for digital video. The compression usually employs lossy data compression. Historically, video was stored as an analog signal on magnetic tape...
- Video qualityVideo qualityVideo quality is a characteristic of a video passed through a video transmission/processing system, a formal or informal measure of perceived video degradation...
- Video compression
- Pro-MPEGPro-MPEGPro-MPEG – the Professional-MPEG Forum – is an association of broadcasters, program makers, equipment manufacturers, and component suppliers with interests in realizing the interoperability of professional television equipment, according to the implementation requirements of...
- MP3MP3MPEG-1 or MPEG-2 Audio Layer III, more commonly referred to as MP3, is a patented digital audio encoding format using a form of lossy data compression...
- Leonardo ChiariglioneLeonardo ChiariglioneLeonardo Chiariglione is an Italianengineer. He has been at the forefront of a number of initiatives that have helped shape media technology and business as we know them today, in particular he is the chairman and co-founded the Moving Picture Experts Group together with Hiroshi Yasuda.-...

