Mughal era
Encyclopedia
The Mughal era is a historic period of the Mughal Empire
in South Asia (mainly Northern India, North Eastern Pakistan and Bangladesh). It ran from the early 15th century to a point in the early 18th century when the Mughal Emperors' power had dwindled. It ended in several generations of conflicts between rival warlords.
The imperial family directly descended from two of the worlds greatest conquerors: Genghis Khan
, founder of the largest contiguous empire in the history of the world; and the Amir, Taimurlong or Tamerlane the Great
. The direct ancestors of the Mughal emperors, at one point or another, directly ruled all areas from Eastern Europe
to the Sea of Japan
, and from the Middle East
to Russian Plains
. They also ruled some of the most powerful states of the medieval world such as Turkey
, Persia, India
and China
. Their ancestors were further also credited with stabilizing the social, cultural and economic aspects of life
between, Europe
and Asia
and opening the extensive trade route known as the Silk Road
that connected various parts of the continent. Due to descent from Genghis Khan, the family was called Mughal, or mogul, persianized version of the former's clan name Mongol.The English word 'mogul
' (e.g. media mogul, business mogul) was coined by this dynasty, meaning influential or powerful, or a tycoon. From their descent from Tamerlane, also called the Amir, the family used the title of Mirza
, shortened Amirzade, literally meaning 'born of the Amir'. The burial places of the Emperors illustrate their expanding empire, as the first Emperor Babur
, born in Uzbekistan
is buried in Afghanistan
, his sons and grandsons, namely Akbar the Great
and Jahangir
in India
and Pakistan
respectively and later descendants, Shah Jahan
and Aurangzeb
in Hindustan
. The last Emperor, Bahadur Shah Zafar is buried in Burma.
They were also a prominent influence of literature in urdu
, hindi
and bengali
. They have been continuously portrayed in many films, the most famous of which, multi-million dollar Mughal-e-Azam
about Emperor Jahangir
's love story; considered an Indian classic and epic film
and also the Bollywood film Jodhaa Akbar about Emperor Akbar's (Emperor Jahangir's father) love story. Emperor Jahangir's son was the Prince Khurram
who later went on to become Emperor Shah Jahan
and built one of the seven wonders of the world
, the famous Taj Mahal
to memorialize his love for his wife.
 The Mughal Empire lasted for more than three centuries. The Mughal Empire was one of the largest centralized states in pre-modern history and was the precursor to the British Indian Empire
The Mughal Empire lasted for more than three centuries. The Mughal Empire was one of the largest centralized states in pre-modern history and was the precursor to the British Indian Empire
.
The titles of the first of the six Mughal Emperors receive varying degrees of prominence in present-day Pakistan and India. Some favour Babur
the pioneer and others his great-grandson, Shah Jahan
(r. 1628-58), builder of the Taj Mahal
and other magnificent buildings. The other two prominent rulers were Akbar (r. 1556-1605) and Aurangzeb
(r. 1658-1707). Both rulers expanded the empire greatly and were able administrators. However, Akbar was known for his religious tolerance and administrative genius, whereas Aurangzeb was a just ruler but a proselytizer of orthodox Islam across the heterodox Indian landscape.
was the first Mughal emperor. He was born on 14 Feb 1483 in present day Uzbekistan
, the eldest son of Amir Umar Shaykh Mirza, the son of Abū Saʿīd Mirza
(and grandson of [Miran Shah], who was himself son of Timur
) and his wife Qutlugh Nigar Khanum
, daughter of Younus Khan, the ruler of Moghulistan
(and great-great grandson of Tughlugh Timur
, the son of Esen Buqa II
, who was the great-great-great grandson of Chaghatai Khan, the second born son of Genghis Khan
). Babur was known for his love of beauty in addition to his military ability. Babur concentrated on gaining control of northwestern India.He was invited to India by Daulat Khan Lodi and Rana Sanga
who wanted to end the Lodi dynasty. He defeated Ibrahim Lodi in 1526 at the First battle of Panipat
, a town north of Delhi
. In 1527 he defeated Rana Sanga, rajput rulers and allies at khanua. Babur then turned to the tasks of persuading his Central Asian followers to stay on in India and of overcoming other contenders for power, mainly the Rajput
s and the Afghans. He succeeded in both tasks but died shortly thereafter on 25 December 1530 in Agra
. He was later buried in Kabul
.
Babur kept the record of his life in Chagatay Turkish, the spoken language of the Timurids and the whole Turco-Mongol world at the time. Baburnama is one of the longest examples of sustained narrative prose in Chagatay Turkish. Akbar's regent, Bairam Khan
, a Turcoman of eastern Anatolian and Azerbaijani origin whose father and grandfather had joined Babur's service. Bayram Khan wrote poetry in Chaghatay and Persian. His son, Abdul-Rahim Khankhanan, was fluent in Chaghatay, Hindi, and Persian and composed in all three languages. Using Babur's own text he translated the Baburnama into Persian. The Chaghatay original was last seen in the imperial library sometime between 1628 and 1638 during Jahangir
's reign.
took the reins of the empire after his father succumbed to disease at the young age of forty-seven.
In 1539, Humayun and Sher Khan met in battle in Chausa, between Varanasi and Patna. Humayun barely escaped with his own life and in the next year, in 1540, his army of 40,000 lost to the Afghan army of 15,000 of Sher Khan. A popular Pashtun Afghan General "Khulas Khan Marwat" was leading Sher Shah Suri's Army. This was the first Military Adventure of Khulas Khan Marwat and he became soon, a nightmare for Mughals.
Sher Khan's Army under the command of Khulas Khan Marwat had now become the monarch in Delhi under the name Sher Shah Suri
and ruled from 1540 to 1545. Sher Shah Suri consolidated his kingdom from Punjab to Bengal (the first to enter Bengal after Ala-ud-din Khilji, more than two centuries earlier). He was credited with having organized and administered the government and military in such a way that future Mughal kings used it as their own models. He also added to the fort in Delhi (supposed site of Indraprastha), first started by Humayun, and now called the Purana Qila (Old Fort). The Masjid Qila-i-Kuhna inside the fort is a masterpiece of the period, though only parts of it have survived.
The charred remains of Sher Shah were taken to a tomb
at Sasaram
(in present day Bihar
), midway between Varanasi and Gaya. Although rarely visited, the future great Mughal builders like Akbar, Jahangir and Shah Jahan emulated the architecture of this tomb. The massive palace like mausoleum is three stories and fifty meters high., Sher Shah’s son Islam Shah held on to power until 1553 and following his death the Sur dynasty lost most of its clout due to strife and famine.
Humayun was a keen astronomer.In fact he died due to a fall from the rooftop of Sher Shah’s Delhi palace in 1554. Thus Humayun ruled in India barely for ten years and died at the age of forty-eight, leaving behind Akbar then only thirteen-year-old as his heir. As a tribute to his father, Akbar later built the Humayun’s tomb
in Delhi (completed in 1571), from red sandstone, that would become the precursor of future Mughal architecture. Akbar’s mother and Humayun’s wife Hamida Banu Begum
personally supervised the building of the tomb.
whose rule was interrupted by the Afghan Sur Dynasty
, which rebelled against him. It was only just before his death that Humayun was able to regain the empire and leave it to his son. In restoring and expanding Mughal rule, Akbar based his authority on the ability and loyalty of his followers, irrespective of their religion. In 1564 the jizya
tax on non-Muslims was abolished, and bans on temple building and Hindu pilgrimages were lifted.
Akbar's methods of administration reinforced his power against two possible sources of challenge—the Afghan-Turkish aristocracy and the traditional interpreters of Islamic law, the ulama
. He created a ranked imperial service based on ability rather than birth, whose members were obliged to serve wherever required. They were remunerated with cash rather than land and were kept away from their inherited estates, thus centralizing the imperial power base and assuring its supremacy. The military and political functions of the imperial service were separate from those of revenue collection, which was supervised by the imperial treasury. This system of administration, known as the mansabdari, was based on loyal service and cash payments and was the backbone of the Mughal Empire; its effectiveness depended on personal loyalty to the emperor and his ability and willingness to choose, remunerate, and supervise.
Akbar declared himself the final arbiter in all disputes of law derived from the Qur'an
and the sharia. He backed his religious authority primarily with his authority in the state. In 1580 he also initiated a syncretic court religion called the Din-i-Ilahi
(Divine Faith). In theory, the new faith was compatible with any other, provided that the devotee was loyal to the emperor. In practice, however, its ritual and content profoundly offended orthodox Muslims. The ulema
found their influence undermined.
Several well known heritage sites were built during the reign of Akbar. The fort city of Fatehpur Sikri
was used as the political capital of the Empire from 1571 to 1578. The numerous palaces and the grand entrances
with intricate art work have been recognized as a world heritage site
by UNESCO. Akbar also began construction of his own tomb
at Sikandra
near Agra
in 1600 CE.
showed signs of restlessness at the end of a long reign by his father Akbar. During the absence of his father from Agra he pronounced himself as the king and turned rebellious. Akbar was able to wrestle the throne back.
Salim did not have to worry about his sibling’s aspirations to the throne. His two brothers, Murad and Daniyal, had both died early from alcoholism.
Jahangir began his era as a Mughal emperor after the death of Akbar in the year 1605. He considered his third son Prince Khurram (future Shah Jahan-born 1592 of Hindu Rajput princess Manmati), his favourite. Rana of Mewar and Prince Khurram had a standoff that resulted in a treaty acceptable to both parties. Khurram was kept busy with several campaigns in Bengal and Kashmir. Jahangir claimed the victories of Khurram – Shah Jahan as his own.
He also had unlimited sources of revenue largely due to a systematic organization of the administration by his father, Akbar. The Mughal Empire reached its pinnacle during Jahangir and Shah Jahan’s rule. Jahangir built his famous gardens in Kashmir though the daily administration was delegated to close aides. One such person was Jahangir’s wife, Nur Jahan, whom he married in 1611. She was the thirty-year-old widow of one of his Afghan nobles. Her father, Persian born Itimad-ud-Daula became a minister and closest advisor to the emperor. Very able Nur Jahan along with her father and brother Asaf Khan, who was a successful general, ran the kingdom.
Jahangir had kept a diary are used as his memoirs. Though not a soldier, Jahangir was an ardent patron of Mughal art and an avid builder. He completed Akbar’s five-tiered tomb
in Sikandra. The emperor kept busy building in Lahore, Allahabad and Agra. While the de facto emperor, Nur Jahan was attending to administrative details, Jahangir found solace in loitering in his gardens and appreciating art and nature.
The darkest incident of his rule perhaps was the disposition of a peaceful leader of newly formed religion called Sikhism
. Akbar had watched the blossoming of the new religion founded by Guru Nanak, with fascination. Jahangir, in a controversy with its leader, was responsible for the death of Sikh Guru Arjan (who was placed on a hot iron until he died, unwilling to convert to Islam) and this would have lasting consequences for future Mughal emperors. The peaceful religion of Sikhism would turn militant later when Jahangir’s grandson Aurangzeb murdered the ninth Sikh Guru Tegh Bahadur. Jahangir, died in 1627 from alcohol abuse and Prince Khurram (Shah Jahan)’s reign as the emperor began.
, ascended to the throne after a tumultuous succession battle. With the wealth created by Akbar, the Mughal kingdom was probably the richest in the world. Prince Khurram gave himself the title of Shah Jahan, the ‘King of the World’ and this was the name that was immortalized by history. With his imagination and aspiration, Shah Jahan gained a reputation as an aesthete par excellence. He built the black marble pavilion at the Shalimar Gardens in Srinagar and a white marble palace in Ajmer. He also built a tomb for his father, Jahangir in Lahore and built a massive city Shahajanabad in Delhi but his imagination surpassed all Mughal glory in his most famous building the Taj Mahal
. It was in Shahajanabad that his daughter Jahanara built the marketplace called Chandni Chowk
.
His beloved wife Arjuman Banu (daughter of Asaf Khan and niece of Nur Jahan) died while delivering their fourteenth child in the year 1631. The distraught emperor started building a memorial for her the following year. The Taj Mahal
, named for Arjuman Banu, who was called Mumtaz Mahal, became one of the Seven Wonders of the World.
The great Jama Masjid
built by him was the largest in India at the time. He renamed Delhi after himself as Shahjahanabad. The Red Fort made of red sandstone built during his reign near Jama Masjid around the same time came to be regarded as the seat of power of India itself. The Prime Minister of India addresses the nation from the ramparts of this fort on Independence day even to this age.Shah Jahan also built or renovated forts in Delhi and in Agra. White marble chambers that served as living quarters and other halls for public audiences are examples of classic Mughal architecture. Here in Agra fort, Shah Jahan would spend eight of his last years as a prisoner of his son, Aurangzeb shuffling between the hallways of the palace, squinting at the distant silhouette of his famous Taj Mahal on the banks of River Jamuna..
Sultanates which had been reduced to vassalage by Shah Jahan
were formally annexed). Although he was an outstanding general and a rigorous administrator, Mughal fiscal and military standards declined as security and luxury increased. Land rather than cash became the usual means of remunerating high-ranking officials, and divisive tendencies in his large empire further undermined central authority.
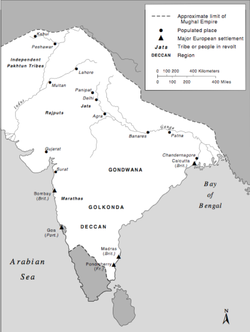
In 1679, Aurangzeb reimposed the jizyah tax on Non-Muslims. This action by the emperor, incited rebellion among Hindus and others in many parts of the empire notably the Jats
, Sikhs, and Rajputs forces in the north and Maratha
forces in the Deccan. The emperor managed to crush the rebellions in the north. Aurangzeb was compelled to move his headquarters to Aurangabad in the Deccan to mount a costly campaign against Maratha guerrilla fighters led by Shivaji and his successors, which lasted twenty-six years until he died in 1707 at the age of seventy nine.
In the century and a half that followed, effective control by Aurangzeb's successors weakened. The mansabdari system gave way to the zamindari system, in which high-ranking officials took on the appearance of aristocracy who were hereditary land barons with powers of collecting rents. As Delhi's control waned, other contenders for power emerged and clashed, thus preparing the way for the eventual British takeover.
Aurangzeb, as is his father before him, is remembered as a builder-emperor. The Badshahi Masjid (Imperial Mosque) in Lahore was constructed in 1673 on his orders. It was not only the largest mosque ever built by a Mughal emperor but was at that point the largest mosque in the world. He also constructed the Alamgiri Gate
of the Lahore Fort
, which is today a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Moti Masjid inside Delhi's Red Fort was also finalized by him.
or Shah Alam I.
After the death of Bahadur Shah I
, a civil war broke out. Jahandar Shah
,a son of Bahadur Shah I
, emerged victorious in it with the support of Zulfiqar Khan who was the most powerful noble of the time. In Deccan Saiyid Husain Ali Khan colluded with the Marathas and attacked Delhi and using trickery and intrigue seized Farrukhsiyar in the Red Fort. The emperor was blinded and caged and later poisoned as well as stabbed to death. However, prior to his death, Farrukhsiyar
had the dubious distinction of aiding the British to have a firm foothold in India, by signing the much-coveted farman an imperial directive that would seal the future of British takeover of India.
Marathas were now constantly attacking Delhi. Of more consequence and humiliation was the plunder of Delhi by Nadir Shah. A Timur descendent, Nadir Shah usurped the throne in Persia and seized Kandahar
and Kabul
. He marched through Panjab and was invited by Muhammad Shah
as a guest to Delhi (only because he had neither the will nor the resources to fight him). Within forty-eight hours, using a lame excuse, Nadir Shah ordered a general massacre of Delhi citizens and looted every bit of wealth they could extort out of the royalty as well as Delhi’s citizenry. Nadir Shah remained in Delhi for forty eight days and departed with millions worth of gold, jewelry and coins. Even the emperor’s bejeweled peacock throne made during Shah Jahan's reign was packed on elephants and carried away to Persia. Another prize, the Koh-I-nur diamond (Humayun’s diamond) now passed into Persian hands. Later an Afghani, Ahmad Shah Abdali started his incursions into Delhi
just for the purpose of looting the capital. In a series of attacks starting in 1748 until 1761, Abdali would not only pillage and loot Delhi, he also cleaned out Mathura, Kashmir
and cities in Panjab. From the east the British defeated the Nawab of Bengal
and occupied the state of Bengal.
The raids by Nadir Shah and repeated incursions of Abdali resulted in quick disposal of the next two emperors Ahmad Shah and Alamgir II
until in 1759 Shah Alam II
ascended the throne. His reign would last several decades. However, he would preside over more loss of territory to the British. When the Nawab of Bengal lost to Robert Clive, Shah Alam II was forced to recognize Clive as a diwan (chancellor) and Bengal slipped to the British hands permanently.
In 1806 Shah Alam’s son Akbar Shah II
acceded to the much diminished empire of the Mughals and ruled until 1837.He gave the title "raja" to Ram mohan roy. His son Bahadur Shah Zafar
would be the last emperor of Mughals before the British deposed him in 1858 and the Mughal dynasty would officially come to an end. During the Indian Rebellion of 1857
, Bahadur Shah II was forced to take the side of the mutineers though he had no power to affect the outcome of the events. The mutineers had outwitted his British sponsors and now the emperor neither had the troops nor the competence. He had no choice but to join the winning side. However, the success of the mutineers was soon reversed and the octogenarian (he was eighty-two years old) was relieved of his empire and deposed in 1858. The emperor was then exiled to Rangoon in Burma where he died in obscurity in 1862.
. Besides their wives, they also had a number of concubines in their harem
, who produced children. This makes it difficult to identify all the offspring of each emperor. The principal offspring of each emperor are provided in the chart below.
captured Goa, which became the seat of their activity. Under Admiral Afonso de Albuquerque
, Portugal successfully challenged Arab power in the Indian Ocean and dominated the sea routes for a century. Jesuits came to convert, to converse, and to record observations of India. The Protestant countries of the Netherlands
and England
, upset by the Portuguese monopoly, formed private trading companies at the turn of the 17th century to challenge the Portuguese.
Mughal officials permitted the new carriers of India's considerable export trade to establish trading posts (factories) in India. The Dutch East India Company
concentrated mainly on the spice trade from present-day Indonesia. Britain's East India Company carried on trade with India. The French East India Company also set up factories.
 During the wars of the 18th century, the factories served not only as collection and transshipment points for trade but also increasingly as fortified centres of refuge for both foreigners and Indians. British factories gradually began to apply British law to disputes arising within their jurisdiction. The posts also began to grow in area and population. Armed company servants were effective protectors of trade. As rival contenders for power called for armed assistance and as individual European adventurers found permanent homes in India, British and French companies found themselves more and more involved in local politics in the south and in Bengal
During the wars of the 18th century, the factories served not only as collection and transshipment points for trade but also increasingly as fortified centres of refuge for both foreigners and Indians. British factories gradually began to apply British law to disputes arising within their jurisdiction. The posts also began to grow in area and population. Armed company servants were effective protectors of trade. As rival contenders for power called for armed assistance and as individual European adventurers found permanent homes in India, British and French companies found themselves more and more involved in local politics in the south and in Bengal
. Plots and counterplots climaxed when British East India Company
forces, led by Robert Clive, defeated the forces of Nawab through treachery, Siraj-ud-Dawlah at Plassey
(Pilasi) in Bengal in 1757.
Shivaji Bhonsle
(1630–80)
Shivaji was a fighter regarded as the "father of the Maratha nation," who took advantage of this conflict and carved out his own principality near Pune
, which later became the Maratha capital. Adopting guerrilla tactics, he waylaid caravans in order to sustain and expand his army, which soon had money, arms, and horses. Shivaji led a series of successful assaults in the 1660s against Mughal strongholds, including the major port of Surat
. Shivaji's battle cries were swaraj (translated variously as freedom, self-rule, independence), swadharma (religious freedom), and goraksha (cow protection). Aurangzeb relentlessly pursued Shivaji's successors between 1681 and 1705 but eventually retreated to the north as his treasury became depleted and as thousands of lives had been lost either on the battlefield or to natural calamities. In 1717 a Mughal emissary signed a treaty with the Marathas confirming their claims to rule in the Deccan in return for acknowledge the fictional Mughal suzerainty and remission of annual taxes.
The Marathas, despite their military prowess and leadership, were not equipped to administer the state or to undertake socioeconomic reform. Pursuing a policy characterized by plunder and indiscriminate raids, they antagonized the peasants. They were primarily suited for stirring the Maharashtrian regional pride rather than for attracting loyalty to an all-India confederacy. They were left virtually alone and without supplies before the invading Afghan forces, headed by Ahmad Shah Abdali (later called Ahmad Shah Durrani), who routed them on the at the Third Battle of Panipat|Panipat in 1761. The shock of defeat hastened the break-up of their loosely knit confederacy into five independent states and extinguished the hope of Maratha dominance in India.
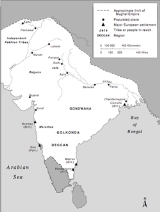
, Kandesh, Gujarat and Malwa resumed after the death of Aurangzeb, and loosened Mughal control in the Deccan. In 1724 Asaf Jah, the Mughal Nizam ul Mulk, or viceroy, of the Deccan, defeated several contenders for control of the Mughal southern provinces, and established himself of ruler of an independent state
with its capital at Hyderabad. He and his successors ruled as hereditary Nizam
s, and their state, known as Hyderabad
after the capital, outlasted the Mughal empire, persisting until it was incorporated into newly-independent India in 1948. Nizam-ul-Mulk Asaf Jahi was a strong ruler and established an orderly system of administration. He also attempted to reform the revenue system. The dynasty founded by him came to be known as the Asaf Jahi dynasty and lasted until the accession of Hyderabad to Independent India
from Delhi and helped the founding of Sikh overlordship in the northwest. Rooted in the bhakti movements that developed in the 2nd century BC. but swept across North India during the 15th and 16th centuries, the teachings of the Sikh gurus appealed to the hard-working peasants. Facing extended persecution from the Mughals, the Sikhs, under Guru Gobind Singh formed the Khalsa (Army of Pure). The khalsa rose up against the economic and political repressions in Punjab toward the end of Aurangzeb's rule. Guerrilla fighters took advantage of the political instability created by the Persian and Afghan onslaught against Delhi, enriching themselves and expanding territorial control. By the 1770s, Sikh hegemony extended from the Indus in the west to the Yamuna in the east, from Multan
in the south to Jammu
in the north. Jassa Singh Ahluwahlia entered Delhi with a large Sikh army in 1776, established hegemony, but then decided unilaterally to return to Punjab.
The Sikhs, however, were a loose and disunited conglomerate of twelve kin-groups. Ultimately, Ranjit Singh was able to unite these groups by force, and start Sikh rule that would extend from Afghanistan to the River Sutlej, and from Kashmir and Ladakh to the borders of Sindh. Ranjit Singh employed French and British officers and introduced strict military discipline into his army. It is said that his guns were cast with the utmost of excellence and quality, in that they were superior to any that the British had at the time. Further fired by the prayers of the Sikh Dharma, the Sikhs became a potent power in North-west India, plugging the Khyber pass from which numerous invasions had been launched into India, including by Alexander the Great, Chengiz Khan the Mongol nomad, Nader Shah the Persian king, and Mahmud Ghazni and Ahmad Shah Abdali the Afghans.
Ranjit Singh wrested Kashmir from Afghan rule after the Afghans backtracked on fulfilling their part of the promise for the conquest of Kashmir for which Ranjit Singh committed troops from the outside in the form of assistance, for which he was to be paid a certain sum from the Kashmir treasury. But, the ruler of Afghan instructed his brother, Dost Muhamed, the new Governor of Kashmir, to withhold payment to Ranjit Singh. At that insult, Ranjit Singh quietly withdrew his troops, and ambushed near Khyber pass the whole Afghan army returning from Kashmir. Only six people managed to escape that ambush—the ruler of Afghanistan, his brother, and four others—who ran from battle, leaving their army to be slaughtered by the Sikhs.
 The quest for wealth and power brought European
The quest for wealth and power brought European
s to Indian shores in 1498 when Vasco da Gama
, the Portuguese
voyager, arrived in Calicut
(modern Kozhikode
, Kerala
) on the west coast. In their search for spices and Christian
converts, the Portuguese challenged Arab
supremacy in the Indian Ocean
, and, with their galleon
s fitted with powerful cannon
s, set up a network of strategic trading posts along the Arabian Sea
and the Persian Gulf
. In 1510 the Portuguese took over the enclave of Goa
, which became the center of their commercial
and political power in India and which they controlled for nearly four and a half centuries.
(the East India Company
, founded in 1600) and in the Netherlands
(Verenigde Oost-Indische Compagnie
-- the United East India Company, founded in 1602), whose primary aim was to capture the spice
trade
by breaking the Portuguese monopoly
in Asia
. Although the Dutch, with a large supply of capital and support from their government, preempted and ultimately excluded the British from the heartland of spices in the East Indies
(modern-day Indonesia
), both companies managed to establish trading "factories" (actually warehouses) along the Indian coast. The Dutch, for example, used various ports on the Coromandel Coast
in South India
, especially Pulicat
(about twenty kilometers north of Madras), as major sources for slaves for their plantations in the East Indies and for cotton
cloth as early as 1609. (The English, however, established their first factory at what today is known as Madras only in 1639.) Indian rulers enthusiastically accommodated the newcomers in hopes of pitting them against the Portuguese. In 1619 Jahangir
granted them permission to trade in his territories at Surat (in Gujarat) on the west coast and Hughli (in West Bengal
) in the east. These and other locations on the peninsula became centers of international
trade
in spices, cotton
, sugar
, raw silk
, saltpeter
, calico, and indigo
.
and Persia
n, the unifying official language under the Mughals. In many ways, the English agents of that period lived like Indians, intermarried willingly, and a large number of them never returned to their home country. The knowledge of India thus acquired and the mutual ties forged with Indian trading groups gave the English a competitive edge over other Europeans. The French commercial interest—Compagnie des Indes Orientales (East India Company
, founded in 1664)--came late, but the French also established themselves in India, emulating the precedents set by their competitors as they founded their enclave at Pondicherry (Puduchcheri) on the Coromandel Coast.
In 1717 the Mughal emperor, Farrukhsiyar
(r. 1713-19), gave the British—who by then had already established themselves in the south and the west—a grant of thirty-eight villages near Calcutta, acknowledging their importance to the continuity of international trade in the Bengal economy. As did the Dutch and the French, the British brought silver
bullion and copper
to pay for transactions, helping the smooth functioning of the Mughal revenue system and increasing the benefits to local artisans and traders
.
The fortified warehouses of the British brought extraterritorial status, which enabled them to administer their own civil and criminal laws and offered numerous employment opportunities as well as asylum to foreigners and Indians. The British factories successfully competed with their rivals as their size and population grew. The original clusters of fishing villages (Madras and Calcutta) or series of islands (Bombay) became headquarters of the British administrative zones, or presidencies as they generally came to be known. The factories and their immediate environs, known as the White-town, represented the actual and symbolic preeminence of the British—in terms of their political power—as well as their cultural values and social practices; meanwhile, their Indian collaborators lived in the Black-town, separated from the factories by several kilometres.
The British company employed sepoys--European-trained and European-led Indian soldiers—to protect its trade, but local rulers sought their services to settle scores in regional power struggles. South India
witnessed the first open confrontation between the British and the French, whose forces were led by Robert Clive and François Dupleix, respectively. Both companies desired to place their own candidate as the nawab, or ruler, of Arcot, the area around Madras. At the end of a protracted struggle between 1744 and 1763, when the Peace of Paris was signed, the British gained an upper hand over the French and installed their man in power, supporting him further with arms and lending large sums as well. The French and the British also backed different factions in the succession struggle for Mughal viceroyalty in Bengal, but Clive intervened successfully and defeated Nawab Siraj-ud-daula in the Battle of Plassey (Palashi, about 150 kilometres north of Calcutta) in 1757. Clive found help from a combination of vested interests that opposed the existing nawab: disgruntled soldiers, landholders, and influential merchants whose commercial profits were closely linked to British fortunes.
Later, Clive defeated the Mughal forces at Buxar
(Baksar, west of Patna in Bihar) in 1765, and the Mughal emperor (Shah Alam
, r. 1759-1806) conferred on the company administrative rights over Bengal
, Bihar
, and Orissa
, a region of roughly 25 million people with an annual revenue of 40 million rupees (for current value of the rupee). The imperial grant virtually established the company as a sovereign power, and Clive became the first British governor of Bengal.
Besides the presence of the Portuguese, Dutch, British, and French, there were two lesser but noteworthy colonial groups. Danish entrepreneurs established themselves at several ports on the Malabar coast
and the Coromandel coast notably Tranquebar
, in the vicinity of Calcutta, and inland at Patna between 1695 and 1740. Austrian enterprises were set up in the 1720s on the vicinity of Surat in modern-day southeastern Gujarat. As with the other non-British enterprises, the Danish and Austrian enclaves were taken over by the British between 1765 and 1815.
Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire , or Mogul Empire in traditional English usage, was an imperial power from the Indian Subcontinent. The Mughal emperors were descendants of the Timurids...
in South Asia (mainly Northern India, North Eastern Pakistan and Bangladesh). It ran from the early 15th century to a point in the early 18th century when the Mughal Emperors' power had dwindled. It ended in several generations of conflicts between rival warlords.
The imperial family directly descended from two of the worlds greatest conquerors: Genghis Khan
Genghis Khan
Genghis Khan , born Temujin and occasionally known by his temple name Taizu , was the founder and Great Khan of the Mongol Empire, which became the largest contiguous empire in history after his death....
, founder of the largest contiguous empire in the history of the world; and the Amir, Taimurlong or Tamerlane the Great
Timur
Timur , historically known as Tamerlane in English , was a 14th-century conqueror of West, South and Central Asia, and the founder of the Timurid dynasty in Central Asia, and great-great-grandfather of Babur, the founder of the Mughal Dynasty, which survived as the Mughal Empire in India until...
. The direct ancestors of the Mughal emperors, at one point or another, directly ruled all areas from Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is the eastern part of Europe. The term has widely disparate geopolitical, geographical, cultural and socioeconomic readings, which makes it highly context-dependent and even volatile, and there are "almost as many definitions of Eastern Europe as there are scholars of the region"...
to the Sea of Japan
Sea of Japan
The Sea of Japan is a marginal sea of the western Pacific Ocean, between the Asian mainland, the Japanese archipelago and Sakhalin. It is bordered by Japan, North Korea, Russia and South Korea. Like the Mediterranean Sea, it has almost no tides due to its nearly complete enclosure from the Pacific...
, and from the Middle East
Middle East
The Middle East is a region that encompasses Western Asia and Northern Africa. It is often used as a synonym for Near East, in opposition to Far East...
to Russian Plains
Siberia
Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th...
. They also ruled some of the most powerful states of the medieval world such as Turkey
Turkey
Turkey , known officially as the Republic of Turkey , is a Eurasian country located in Western Asia and in East Thrace in Southeastern Europe...
, Persia, India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
and China
China
Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture...
. Their ancestors were further also credited with stabilizing the social, cultural and economic aspects of life
Pax Mongolica
The Pax Mongolica is a Latin phrase meaning "Mongol Peace" coined by Western scholars to describe the stabilizing effects of the conquests of the Mongol Empire on the social, cultural, and economic life of the inhabitants of the vast Eurasian territory that the Mongols conquered in the 13th and...
between, Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
and Asia
Asia
Asia is the world's largest and most populous continent, located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres. It covers 8.7% of the Earth's total surface area and with approximately 3.879 billion people, it hosts 60% of the world's current human population...
and opening the extensive trade route known as the Silk Road
Silk Road
The Silk Road or Silk Route refers to a historical network of interlinking trade routes across the Afro-Eurasian landmass that connected East, South, and Western Asia with the Mediterranean and European world, as well as parts of North and East Africa...
that connected various parts of the continent. Due to descent from Genghis Khan, the family was called Mughal, or mogul, persianized version of the former's clan name Mongol.The English word 'mogul
Business magnate
A business magnate, sometimes referred to as a capitalist, czar, mogul, tycoon, baron, oligarch, or industrialist, is an informal term used to refer to an entrepreneur who has reached prominence and derived a notable amount of wealth from a particular industry .-Etymology:The word magnate itself...
' (e.g. media mogul, business mogul) was coined by this dynasty, meaning influential or powerful, or a tycoon. From their descent from Tamerlane, also called the Amir, the family used the title of Mirza
Mirza
Mirza , is of Persian origin, denoting the rank of a high nobleman or Prince. It is usually translated into English as a royal or imperial Prince of the Blood...
, shortened Amirzade, literally meaning 'born of the Amir'. The burial places of the Emperors illustrate their expanding empire, as the first Emperor Babur
Babur
Babur was a Muslim conqueror from Central Asia who, following a series of setbacks, finally succeeded in laying the basis for the Mughal dynasty of South Asia. He was a direct descendant of Timur through his father, and a descendant also of Genghis Khan through his mother...
, born in Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan , officially the Republic of Uzbekistan is a doubly landlocked country in Central Asia and one of the six independent Turkic states. It shares borders with Kazakhstan to the west and to the north, Kyrgyzstan and Tajikistan to the east, and Afghanistan and Turkmenistan to the south....
is buried in Afghanistan
Afghanistan
Afghanistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located in the centre of Asia, forming South Asia, Central Asia and the Middle East. With a population of about 29 million, it has an area of , making it the 42nd most populous and 41st largest nation in the world...
, his sons and grandsons, namely Akbar the Great
Akbar the Great
Akbar , also known as Shahanshah Akbar-e-Azam or Akbar the Great , was the third Mughal Emperor. He was of Timurid descent; the son of Emperor Humayun, and the grandson of the Mughal Emperor Zaheeruddin Muhammad Babur, the ruler who founded the Mughal dynasty in India...
and Jahangir
Jahangir
Jahangir was the ruler of the Mughal Empire from 1605 until his death. The name Jahangir is from Persian جهانگیر,meaning "Conqueror of the World"...
in India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
and Pakistan
Pakistan
Pakistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan is a sovereign state in South Asia. It has a coastline along the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Oman in the south and is bordered by Afghanistan and Iran in the west, India in the east and China in the far northeast. In the north, Tajikistan...
respectively and later descendants, Shah Jahan
Shah Jahan
Shah Jahan Shah Jahan (also spelled Shah Jehan, Shahjehan, , Persian: شاه جهان) (January 5, 1592 – January 22, 1666) Shah Jahan (also spelled Shah Jehan, Shahjehan, , Persian: شاه جهان) (January 5, 1592 – January 22, 1666) (Full title: His Imperial Majesty Al-Sultan al-'Azam wal Khaqan...
and Aurangzeb
Aurangzeb
Abul Muzaffar Muhy-ud-Din Muhammad Aurangzeb Alamgir , more commonly known as Aurangzeb or by his chosen imperial title Alamgir , was the sixth Mughal Emperor of India, whose reign lasted from 1658 until his death in 1707.Badshah Aurangzeb, having ruled most of the Indian subcontinent for nearly...
in Hindustan
Hindustan
Hindustan or Indostan, literal translation "Land of River Sindhu ", is one of the popular names of South Asia. It can also mean "the land of the Hindus"...
. The last Emperor, Bahadur Shah Zafar is buried in Burma.
They were also a prominent influence of literature in urdu
Urdu
Urdu is a register of the Hindustani language that is identified with Muslims in South Asia. It belongs to the Indo-European family. Urdu is the national language and lingua franca of Pakistan. It is also widely spoken in some regions of India, where it is one of the 22 scheduled languages and an...
, hindi
Hindi
Standard Hindi, or more precisely Modern Standard Hindi, also known as Manak Hindi , High Hindi, Nagari Hindi, and Literary Hindi, is a standardized and sanskritized register of the Hindustani language derived from the Khariboli dialect of Delhi...
and bengali
Bengali language
Bengali or Bangla is an eastern Indo-Aryan language. It is native to the region of eastern South Asia known as Bengal, which comprises present day Bangladesh, the Indian state of West Bengal, and parts of the Indian states of Tripura and Assam. It is written with the Bengali script...
. They have been continuously portrayed in many films, the most famous of which, multi-million dollar Mughal-e-Azam
Mughal-e-Azam
Mughal-E-Azam is a 1960 Indian historical epic film produced under the banner of Sterling Investment Corporation Pvt Ltd, and directed by K. Asif. With its unmatched production, K. Asif's magnum opus took nine years and $3 million to complete this movie. This was when a typical Bollywood film...
about Emperor Jahangir
Jahangir
Jahangir was the ruler of the Mughal Empire from 1605 until his death. The name Jahangir is from Persian جهانگیر,meaning "Conqueror of the World"...
's love story; considered an Indian classic and epic film
Epic film
An epic is a genre of film that emphasizes human drama on a grand scale. Epics are more ambitious in scope than other film genres, and their ambitious nature helps to differentiate them from similar genres such as the period piece or adventure film...
and also the Bollywood film Jodhaa Akbar about Emperor Akbar's (Emperor Jahangir's father) love story. Emperor Jahangir's son was the Prince Khurram
Shah Jahan
Shah Jahan Shah Jahan (also spelled Shah Jehan, Shahjehan, , Persian: شاه جهان) (January 5, 1592 – January 22, 1666) Shah Jahan (also spelled Shah Jehan, Shahjehan, , Persian: شاه جهان) (January 5, 1592 – January 22, 1666) (Full title: His Imperial Majesty Al-Sultan al-'Azam wal Khaqan...
who later went on to become Emperor Shah Jahan
Shah Jahan
Shah Jahan Shah Jahan (also spelled Shah Jehan, Shahjehan, , Persian: شاه جهان) (January 5, 1592 – January 22, 1666) Shah Jahan (also spelled Shah Jehan, Shahjehan, , Persian: شاه جهان) (January 5, 1592 – January 22, 1666) (Full title: His Imperial Majesty Al-Sultan al-'Azam wal Khaqan...
and built one of the seven wonders of the world
Wonders of the World
Various lists of the Wonders of the World have been compiled from antiquity to the present day, to catalogue the world's most spectacular natural wonders and manmade structures....
, the famous Taj Mahal
Taj Mahal
The Taj Mahal is a white Marble mausoleum located in Agra, India. It was built by Mughal emperor Shah Jahan in memory of his third wife, Mumtaz Mahal...
to memorialize his love for his wife.

Mughal Empire

British Empire
The British Empire comprised the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom. It originated with the overseas colonies and trading posts established by England in the late 16th and early 17th centuries. At its height, it was the...
.
The titles of the first of the six Mughal Emperors receive varying degrees of prominence in present-day Pakistan and India. Some favour Babur
Babur
Babur was a Muslim conqueror from Central Asia who, following a series of setbacks, finally succeeded in laying the basis for the Mughal dynasty of South Asia. He was a direct descendant of Timur through his father, and a descendant also of Genghis Khan through his mother...
the pioneer and others his great-grandson, Shah Jahan
Shah Jahan
Shah Jahan Shah Jahan (also spelled Shah Jehan, Shahjehan, , Persian: شاه جهان) (January 5, 1592 – January 22, 1666) Shah Jahan (also spelled Shah Jehan, Shahjehan, , Persian: شاه جهان) (January 5, 1592 – January 22, 1666) (Full title: His Imperial Majesty Al-Sultan al-'Azam wal Khaqan...
(r. 1628-58), builder of the Taj Mahal
Taj Mahal
The Taj Mahal is a white Marble mausoleum located in Agra, India. It was built by Mughal emperor Shah Jahan in memory of his third wife, Mumtaz Mahal...
and other magnificent buildings. The other two prominent rulers were Akbar (r. 1556-1605) and Aurangzeb
Aurangzeb
Abul Muzaffar Muhy-ud-Din Muhammad Aurangzeb Alamgir , more commonly known as Aurangzeb or by his chosen imperial title Alamgir , was the sixth Mughal Emperor of India, whose reign lasted from 1658 until his death in 1707.Badshah Aurangzeb, having ruled most of the Indian subcontinent for nearly...
(r. 1658-1707). Both rulers expanded the empire greatly and were able administrators. However, Akbar was known for his religious tolerance and administrative genius, whereas Aurangzeb was a just ruler but a proselytizer of orthodox Islam across the heterodox Indian landscape.
Babur
Zahir ud-Din Muhammad BaburBabur
Babur was a Muslim conqueror from Central Asia who, following a series of setbacks, finally succeeded in laying the basis for the Mughal dynasty of South Asia. He was a direct descendant of Timur through his father, and a descendant also of Genghis Khan through his mother...
was the first Mughal emperor. He was born on 14 Feb 1483 in present day Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan , officially the Republic of Uzbekistan is a doubly landlocked country in Central Asia and one of the six independent Turkic states. It shares borders with Kazakhstan to the west and to the north, Kyrgyzstan and Tajikistan to the east, and Afghanistan and Turkmenistan to the south....
, the eldest son of Amir Umar Shaykh Mirza, the son of Abū Saʿīd Mirza
Abu Sa'id (Timurid dynasty)
Abū Saʿīd b. Muḥammad b. Mīrānshāh b. Timūr , was a Timurid Empire ruler in what is today parts of Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, Iran and Afghanistan and member of the Timurid dynasty....
(and grandson of [Miran Shah], who was himself son of Timur
Timur
Timur , historically known as Tamerlane in English , was a 14th-century conqueror of West, South and Central Asia, and the founder of the Timurid dynasty in Central Asia, and great-great-grandfather of Babur, the founder of the Mughal Dynasty, which survived as the Mughal Empire in India until...
) and his wife Qutlugh Nigar Khanum
Qutlugh Nigar Khanum
Qutlugh Nigar Khanum was a Turkman noble and a descendant of Genghis Khan. She was the mother of Babur, founder of the Mughal empire of India. She is believed to have been born a princess in the Ak Koyunlu dynasty....
, daughter of Younus Khan, the ruler of Moghulistan
Moghulistan
Moghulistan or Mughalistan is a historical geographic unit in Central Asia that included parts of modern-day Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, and the Chinese Autonomous Region of Xinjiang...
(and great-great grandson of Tughlugh Timur
Tughlugh Timur
Tughlugh Timur was the Khan of Moghulistan from c. 1347 and Khan of the whole Chagatai Khanate from c. 1360 until his death. He is believed to be the son of Esen Buqa...
, the son of Esen Buqa II
Esen Buqa II
Esen Buqa II was Khan of Moghulistan from 1429 until his death. He was the younger son of Uwais Khan.When Uwais Khan was killed in 1428 the Moghuls were thrown into a state of confusion. Some of them supported Esen Buqa, while others supported his older brother, Yunus Khan...
, who was the great-great-great grandson of Chaghatai Khan, the second born son of Genghis Khan
Genghis Khan
Genghis Khan , born Temujin and occasionally known by his temple name Taizu , was the founder and Great Khan of the Mongol Empire, which became the largest contiguous empire in history after his death....
). Babur was known for his love of beauty in addition to his military ability. Babur concentrated on gaining control of northwestern India.He was invited to India by Daulat Khan Lodi and Rana Sanga
Rana Sanga
-Historical Fact:Maharana Sangram Singh was the ruler of Mewar state, a region lying within the present-day Indian state of Rajasthan, a desert region, between 1509 and 1527. He was a scion of the Sisodia clan of Suryavanshi Rajputs...
who wanted to end the Lodi dynasty. He defeated Ibrahim Lodi in 1526 at the First battle of Panipat
First battle of Panipat
The first battle of Panipat took place in Northern India, and marked the beginning of the Mughal Empire. This was one of the earliest battles involving gunpowder firearms and field artillery.-Details:...
, a town north of Delhi
Delhi
Delhi , officially National Capital Territory of Delhi , is the largest metropolis by area and the second-largest by population in India, next to Mumbai. It is the eighth largest metropolis in the world by population with 16,753,265 inhabitants in the Territory at the 2011 Census...
. In 1527 he defeated Rana Sanga, rajput rulers and allies at khanua. Babur then turned to the tasks of persuading his Central Asian followers to stay on in India and of overcoming other contenders for power, mainly the Rajput
Rajput
A Rajput is a member of one of the patrilineal clans of western, central, northern India and in some parts of Pakistan. Rajputs are descendants of one of the major ruling warrior classes in the Indian subcontinent, particularly North India...
s and the Afghans. He succeeded in both tasks but died shortly thereafter on 25 December 1530 in Agra
Agra
Agra a.k.a. Akbarabad is a city on the banks of the river Yamuna in the northern state of Uttar Pradesh, India, west of state capital, Lucknow and south from national capital New Delhi. With a population of 1,686,976 , it is one of the most populous cities in Uttar Pradesh and the 19th most...
. He was later buried in Kabul
Kabul
Kabul , spelt Caubul in some classic literatures, is the capital and largest city of Afghanistan. It is also the capital of the Kabul Province, located in the eastern section of Afghanistan...
.
Babur kept the record of his life in Chagatay Turkish, the spoken language of the Timurids and the whole Turco-Mongol world at the time. Baburnama is one of the longest examples of sustained narrative prose in Chagatay Turkish. Akbar's regent, Bairam Khan
Bairam Khan
Bairam Khan also Bayram Khan was a important military commander, general of the Mughal army, a powerful statesman and regent at the court of the Mughal emperors Humayun and Akbar.-Background:...
, a Turcoman of eastern Anatolian and Azerbaijani origin whose father and grandfather had joined Babur's service. Bayram Khan wrote poetry in Chaghatay and Persian. His son, Abdul-Rahim Khankhanan, was fluent in Chaghatay, Hindi, and Persian and composed in all three languages. Using Babur's own text he translated the Baburnama into Persian. The Chaghatay original was last seen in the imperial library sometime between 1628 and 1638 during Jahangir
Jahangir
Jahangir was the ruler of the Mughal Empire from 1605 until his death. The name Jahangir is from Persian جهانگیر,meaning "Conqueror of the World"...
's reign.
Humayun
Babur’s favorite son HumayunHumayun
Nasir ud-din Muhammad Humayun was the second Mughal Emperor who ruled present day Afghanistan, Pakistan, and parts of northern India from 1530–1540 and again from 1555–1556. Like his father, Babur, he lost his kingdom early, but with Persian aid, he eventually regained an even larger one...
took the reins of the empire after his father succumbed to disease at the young age of forty-seven.
In 1539, Humayun and Sher Khan met in battle in Chausa, between Varanasi and Patna. Humayun barely escaped with his own life and in the next year, in 1540, his army of 40,000 lost to the Afghan army of 15,000 of Sher Khan. A popular Pashtun Afghan General "Khulas Khan Marwat" was leading Sher Shah Suri's Army. This was the first Military Adventure of Khulas Khan Marwat and he became soon, a nightmare for Mughals.
Sher Khan's Army under the command of Khulas Khan Marwat had now become the monarch in Delhi under the name Sher Shah Suri
Sher Shah Suri
Sher Shah Suri , birth name Farid Khan, also known as Sher Khan , was the founder of the short-lived Sur Empire in northern India, with its capital at Delhi, before its demise in the hands of the resurgent Mughal Empire...
and ruled from 1540 to 1545. Sher Shah Suri consolidated his kingdom from Punjab to Bengal (the first to enter Bengal after Ala-ud-din Khilji, more than two centuries earlier). He was credited with having organized and administered the government and military in such a way that future Mughal kings used it as their own models. He also added to the fort in Delhi (supposed site of Indraprastha), first started by Humayun, and now called the Purana Qila (Old Fort). The Masjid Qila-i-Kuhna inside the fort is a masterpiece of the period, though only parts of it have survived.
The charred remains of Sher Shah were taken to a tomb
Sher Shah Suri Tomb
The tomb of Sher Shah Suri is in the Sasaram town of Bihar state, India. The tomb was built in memory of Emperor Sher Shah Suri, a Pathan from Bihar who defeated the Mughal Empire and founded the Suri Empire in northern India. He died in an accidental gunpowder explosion in the fort of Kalinjar on...
at Sasaram
Sasaram
Sasaram , sometimes also spelled as Sahasram, is the administrative headquarters of the Rohtas district in the Indian state of Bihar.It is one of the oldest cities in India, and is famous for production of stone chips and for the local quarrying industry...
(in present day Bihar
Bihar
Bihar is a state in eastern India. It is the 12th largest state in terms of geographical size at and 3rd largest by population. Almost 58% of Biharis are below the age of 25, which is the highest proportion in India....
), midway between Varanasi and Gaya. Although rarely visited, the future great Mughal builders like Akbar, Jahangir and Shah Jahan emulated the architecture of this tomb. The massive palace like mausoleum is three stories and fifty meters high., Sher Shah’s son Islam Shah held on to power until 1553 and following his death the Sur dynasty lost most of its clout due to strife and famine.
Humayun was a keen astronomer.In fact he died due to a fall from the rooftop of Sher Shah’s Delhi palace in 1554. Thus Humayun ruled in India barely for ten years and died at the age of forty-eight, leaving behind Akbar then only thirteen-year-old as his heir. As a tribute to his father, Akbar later built the Humayun’s tomb
Humayun's Tomb
Humayun's tomb is the tomb of the Mughal Emperor Humayun. The tomb was commissioned by Humayun's wife Hamida Banu Begum in 1562 AD, and designed by Mirak Mirza Ghiyath, a Persian architect...
in Delhi (completed in 1571), from red sandstone, that would become the precursor of future Mughal architecture. Akbar’s mother and Humayun’s wife Hamida Banu Begum
Hamida Banu Begum
Hamida Banu Begam, Maryam Makani was a wife of the second Mughal Emperor, Humayun, and the mother of Mughal Emperor , Akbar...
personally supervised the building of the tomb.
Akbar
Akbar succeeded his father, HumayunHumayun
Nasir ud-din Muhammad Humayun was the second Mughal Emperor who ruled present day Afghanistan, Pakistan, and parts of northern India from 1530–1540 and again from 1555–1556. Like his father, Babur, he lost his kingdom early, but with Persian aid, he eventually regained an even larger one...
whose rule was interrupted by the Afghan Sur Dynasty
Sur Dynasty
The Suri Empire was established by a Muslim dynasty of Afghan origin who ruled a vast territory in the Indian subcontinent between 1540 to 1557, with Delhi serving as its capital...
, which rebelled against him. It was only just before his death that Humayun was able to regain the empire and leave it to his son. In restoring and expanding Mughal rule, Akbar based his authority on the ability and loyalty of his followers, irrespective of their religion. In 1564 the jizya
Jizya
Under Islamic law, jizya or jizyah is a per capita tax levied on a section of an Islamic state's non-Muslim citizens, who meet certain criteria...
tax on non-Muslims was abolished, and bans on temple building and Hindu pilgrimages were lifted.
Akbar's methods of administration reinforced his power against two possible sources of challenge—the Afghan-Turkish aristocracy and the traditional interpreters of Islamic law, the ulama
Ulema
Ulama , also spelt ulema, refers to the educated class of Muslim legal scholars engaged in the several fields of Islamic studies. They are best known as the arbiters of shari‘a law...
. He created a ranked imperial service based on ability rather than birth, whose members were obliged to serve wherever required. They were remunerated with cash rather than land and were kept away from their inherited estates, thus centralizing the imperial power base and assuring its supremacy. The military and political functions of the imperial service were separate from those of revenue collection, which was supervised by the imperial treasury. This system of administration, known as the mansabdari, was based on loyal service and cash payments and was the backbone of the Mughal Empire; its effectiveness depended on personal loyalty to the emperor and his ability and willingness to choose, remunerate, and supervise.
Akbar declared himself the final arbiter in all disputes of law derived from the Qur'an
Qur'an
The Quran , also transliterated Qur'an, Koran, Alcoran, Qur’ān, Coran, Kuran, and al-Qur’ān, is the central religious text of Islam, which Muslims consider the verbatim word of God . It is regarded widely as the finest piece of literature in the Arabic language...
and the sharia. He backed his religious authority primarily with his authority in the state. In 1580 he also initiated a syncretic court religion called the Din-i-Ilahi
Din-i-Ilahi
The Dīn-i Ilāhī was a syncretic religious doctrine propounded by the Mughal emperor Jalālu d-Dīn Muḥammad Akbar , who ruled the Indian subcontinent from 1556 to 1605, intending to merge the best elements of the religions of his empire, and thereby reconcile the differences that divided his subjects...
(Divine Faith). In theory, the new faith was compatible with any other, provided that the devotee was loyal to the emperor. In practice, however, its ritual and content profoundly offended orthodox Muslims. The ulema
Ulema
Ulama , also spelt ulema, refers to the educated class of Muslim legal scholars engaged in the several fields of Islamic studies. They are best known as the arbiters of shari‘a law...
found their influence undermined.
Several well known heritage sites were built during the reign of Akbar. The fort city of Fatehpur Sikri
Fatehpur Sikri
Fatehpur Sikri is a city and a municipal board in Agra district in the state of Uttar Pradesh, India. Built near the much older Sikri, the historical city of Fatehabad, as it was first named, was constructed by Mughal emperor Akbar beginning in 1570...
was used as the political capital of the Empire from 1571 to 1578. The numerous palaces and the grand entrances
Buland Darwaza
Buland Darwaza , meaning 'high' or 'great' gate in Persian, is the largest of gateways in the world. It is located in Fatehpur Sikri which is located 43 km away from Agra, India. It is also known as the "Gate of Magnificence".Buland Darwaza or the loft gateway was built by the great Mughal...
with intricate art work have been recognized as a world heritage site
World Heritage Site
A UNESCO World Heritage Site is a place that is listed by the UNESCO as of special cultural or physical significance...
by UNESCO. Akbar also began construction of his own tomb
Tomb of Akbar the Great
The Tomb of Akbar the Great is an important Mughal architectural masterpiece, built 1605-1613, set in 48 Ha of grounds in Sikandra, a suburb of Agra, Uttar Pradesh, India.-History:...
at Sikandra
Sikandra
Sikandra is a town and a nagar panchayat in Kanpur Dehat district in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh.Sikandra is also spelled as Sikandara....
near Agra
Agra
Agra a.k.a. Akbarabad is a city on the banks of the river Yamuna in the northern state of Uttar Pradesh, India, west of state capital, Lucknow and south from national capital New Delhi. With a population of 1,686,976 , it is one of the most populous cities in Uttar Pradesh and the 19th most...
in 1600 CE.
Jahangir
Prince Salim (b. 1569 son of Hindu Rajput princess from Amber), who would later be known as Emperor JahangirJahangir
Jahangir was the ruler of the Mughal Empire from 1605 until his death. The name Jahangir is from Persian جهانگیر,meaning "Conqueror of the World"...
showed signs of restlessness at the end of a long reign by his father Akbar. During the absence of his father from Agra he pronounced himself as the king and turned rebellious. Akbar was able to wrestle the throne back.
Salim did not have to worry about his sibling’s aspirations to the throne. His two brothers, Murad and Daniyal, had both died early from alcoholism.
Jahangir began his era as a Mughal emperor after the death of Akbar in the year 1605. He considered his third son Prince Khurram (future Shah Jahan-born 1592 of Hindu Rajput princess Manmati), his favourite. Rana of Mewar and Prince Khurram had a standoff that resulted in a treaty acceptable to both parties. Khurram was kept busy with several campaigns in Bengal and Kashmir. Jahangir claimed the victories of Khurram – Shah Jahan as his own.
He also had unlimited sources of revenue largely due to a systematic organization of the administration by his father, Akbar. The Mughal Empire reached its pinnacle during Jahangir and Shah Jahan’s rule. Jahangir built his famous gardens in Kashmir though the daily administration was delegated to close aides. One such person was Jahangir’s wife, Nur Jahan, whom he married in 1611. She was the thirty-year-old widow of one of his Afghan nobles. Her father, Persian born Itimad-ud-Daula became a minister and closest advisor to the emperor. Very able Nur Jahan along with her father and brother Asaf Khan, who was a successful general, ran the kingdom.
Jahangir had kept a diary are used as his memoirs. Though not a soldier, Jahangir was an ardent patron of Mughal art and an avid builder. He completed Akbar’s five-tiered tomb
Tomb of Akbar the Great
The Tomb of Akbar the Great is an important Mughal architectural masterpiece, built 1605-1613, set in 48 Ha of grounds in Sikandra, a suburb of Agra, Uttar Pradesh, India.-History:...
in Sikandra. The emperor kept busy building in Lahore, Allahabad and Agra. While the de facto emperor, Nur Jahan was attending to administrative details, Jahangir found solace in loitering in his gardens and appreciating art and nature.
The darkest incident of his rule perhaps was the disposition of a peaceful leader of newly formed religion called Sikhism
Sikhism
Sikhism is a monotheistic religion founded during the 15th century in the Punjab region, by Guru Nanak Dev and continued to progress with ten successive Sikh Gurus . It is the fifth-largest organized religion in the world and one of the fastest-growing...
. Akbar had watched the blossoming of the new religion founded by Guru Nanak, with fascination. Jahangir, in a controversy with its leader, was responsible for the death of Sikh Guru Arjan (who was placed on a hot iron until he died, unwilling to convert to Islam) and this would have lasting consequences for future Mughal emperors. The peaceful religion of Sikhism would turn militant later when Jahangir’s grandson Aurangzeb murdered the ninth Sikh Guru Tegh Bahadur. Jahangir, died in 1627 from alcohol abuse and Prince Khurram (Shah Jahan)’s reign as the emperor began.
Shah Jahan
Prince Khurram, who would later be known as Emperor Shah JahanShah Jahan
Shah Jahan Shah Jahan (also spelled Shah Jehan, Shahjehan, , Persian: شاه جهان) (January 5, 1592 – January 22, 1666) Shah Jahan (also spelled Shah Jehan, Shahjehan, , Persian: شاه جهان) (January 5, 1592 – January 22, 1666) (Full title: His Imperial Majesty Al-Sultan al-'Azam wal Khaqan...
, ascended to the throne after a tumultuous succession battle. With the wealth created by Akbar, the Mughal kingdom was probably the richest in the world. Prince Khurram gave himself the title of Shah Jahan, the ‘King of the World’ and this was the name that was immortalized by history. With his imagination and aspiration, Shah Jahan gained a reputation as an aesthete par excellence. He built the black marble pavilion at the Shalimar Gardens in Srinagar and a white marble palace in Ajmer. He also built a tomb for his father, Jahangir in Lahore and built a massive city Shahajanabad in Delhi but his imagination surpassed all Mughal glory in his most famous building the Taj Mahal
Taj Mahal
The Taj Mahal is a white Marble mausoleum located in Agra, India. It was built by Mughal emperor Shah Jahan in memory of his third wife, Mumtaz Mahal...
. It was in Shahajanabad that his daughter Jahanara built the marketplace called Chandni Chowk
Chandni Chowk
Chandni Chowk , originally meaning moonlit square or market, is one of the oldest and busiest markets in Old Delhi, now in central north Delhi, India...
.
His beloved wife Arjuman Banu (daughter of Asaf Khan and niece of Nur Jahan) died while delivering their fourteenth child in the year 1631. The distraught emperor started building a memorial for her the following year. The Taj Mahal
Taj Mahal
The Taj Mahal is a white Marble mausoleum located in Agra, India. It was built by Mughal emperor Shah Jahan in memory of his third wife, Mumtaz Mahal...
, named for Arjuman Banu, who was called Mumtaz Mahal, became one of the Seven Wonders of the World.
The great Jama Masjid
Jama Masjid, Delhi
The Masjid-i Jahān-Numā , commonly known as the Jama Masjid of Delhi, is the principal mosque of Old Delhi in India. Commissioned by the Mughal Emperor Shah Jahan, builder of the Taj Mahal,in the year 1644 CE and completed in the year 1658 AD, it is the largest and best-known mosque in India...
built by him was the largest in India at the time. He renamed Delhi after himself as Shahjahanabad. The Red Fort made of red sandstone built during his reign near Jama Masjid around the same time came to be regarded as the seat of power of India itself. The Prime Minister of India addresses the nation from the ramparts of this fort on Independence day even to this age.Shah Jahan also built or renovated forts in Delhi and in Agra. White marble chambers that served as living quarters and other halls for public audiences are examples of classic Mughal architecture. Here in Agra fort, Shah Jahan would spend eight of his last years as a prisoner of his son, Aurangzeb shuffling between the hallways of the palace, squinting at the distant silhouette of his famous Taj Mahal on the banks of River Jamuna..
Aurangzeb
Aurangzeb, who was given the title "Alamgir" or "world-seizer," by his father, was known for aggressively expanding the empire's frontiers and for his acceptance of orthodox Sunni Islam. During his reign, the Mughal empire reached its greatest extent (the Bijapur and GolcondaGolconda
Golconda may be:Places:* Golkonda, ruined city and fortress in India* Golconda, Illinois, town in the United States* Golconda, Nevada, former town in the United StatesOther:* Golconda...
Sultanates which had been reduced to vassalage by Shah Jahan
Shah Jahan
Shah Jahan Shah Jahan (also spelled Shah Jehan, Shahjehan, , Persian: شاه جهان) (January 5, 1592 – January 22, 1666) Shah Jahan (also spelled Shah Jehan, Shahjehan, , Persian: شاه جهان) (January 5, 1592 – January 22, 1666) (Full title: His Imperial Majesty Al-Sultan al-'Azam wal Khaqan...
were formally annexed). Although he was an outstanding general and a rigorous administrator, Mughal fiscal and military standards declined as security and luxury increased. Land rather than cash became the usual means of remunerating high-ranking officials, and divisive tendencies in his large empire further undermined central authority.
In 1679, Aurangzeb reimposed the jizyah tax on Non-Muslims. This action by the emperor, incited rebellion among Hindus and others in many parts of the empire notably the Jats
Jat people
The Jat people are a community of traditionally non-elite tillers and herders in Northern India and Pakistan. Originally pastoralists in the lower Indus river-valley of Sindh, Jats migrated north into the Punjab region in late medieval times, and subsequently into the Delhi Territory,...
, Sikhs, and Rajputs forces in the north and Maratha
Maratha
The Maratha are an Indian caste, predominantly in the state of Maharashtra. The term Marāthā has three related usages: within the Marathi speaking region it describes the dominant Maratha caste; outside Maharashtra it can refer to the entire regional population of Marathi-speaking people;...
forces in the Deccan. The emperor managed to crush the rebellions in the north. Aurangzeb was compelled to move his headquarters to Aurangabad in the Deccan to mount a costly campaign against Maratha guerrilla fighters led by Shivaji and his successors, which lasted twenty-six years until he died in 1707 at the age of seventy nine.
In the century and a half that followed, effective control by Aurangzeb's successors weakened. The mansabdari system gave way to the zamindari system, in which high-ranking officials took on the appearance of aristocracy who were hereditary land barons with powers of collecting rents. As Delhi's control waned, other contenders for power emerged and clashed, thus preparing the way for the eventual British takeover.
Aurangzeb, as is his father before him, is remembered as a builder-emperor. The Badshahi Masjid (Imperial Mosque) in Lahore was constructed in 1673 on his orders. It was not only the largest mosque ever built by a Mughal emperor but was at that point the largest mosque in the world. He also constructed the Alamgiri Gate
Alamgiri Gate
The Alamgiri Gate , built in 1673 A.D., is the main entrance to the Lahore Fort in present day Lahore, Pakistan. It was constructed to face west towards the Badshahi Mosque in the days of the Mughal Emperor Aurangzeb...
of the Lahore Fort
Lahore Fort
The Lahore Fort, locally referred to as Shahi Qila is citadel of the city of Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan. It is located in the northwestern corner of the Walled City of Lahore...
, which is today a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Moti Masjid inside Delhi's Red Fort was also finalized by him.
Later Mughals
When Aurangzeb died close to the age of eighty, there were seventeen legitimate claimants to the throne that included not only his sons but also his grandsons and great grandsons. After the death of the emperor two brothers fought near Agra in the same battle site that Aurangzeb had fought his brother Dara Shikoh. Prince Muazzam prevailed and killed his brother Prince Azam Shah and assumed the title Bahadur Shah IBahadur Shah I
Bahadur Shah was a Mughal Emperor, who ruled India from 1707 to 1712. His original name was Qutb ud-Din Muhammad Mu'azzam later titled as Shah Alam by his father. He took the throne name Bahadur Shah in 1707. His name Bahādur means "brave" & "hero" in Turko-Mongol languages...
or Shah Alam I.
After the death of Bahadur Shah I
Bahadur Shah I
Bahadur Shah was a Mughal Emperor, who ruled India from 1707 to 1712. His original name was Qutb ud-Din Muhammad Mu'azzam later titled as Shah Alam by his father. He took the throne name Bahadur Shah in 1707. His name Bahādur means "brave" & "hero" in Turko-Mongol languages...
, a civil war broke out. Jahandar Shah
Jahandar Shah
Jahandar Shah was a Mughal Emperor who ruled India for a brief period in 1712-1713. His title was Shahanshah-i-Ghazi Abu'l Fath Muiz-ud-Din Muhammad Jahandar Shah Sahib-i-Quran Padshah-i-Jahan .-Early life:...
,a son of Bahadur Shah I
Bahadur Shah I
Bahadur Shah was a Mughal Emperor, who ruled India from 1707 to 1712. His original name was Qutb ud-Din Muhammad Mu'azzam later titled as Shah Alam by his father. He took the throne name Bahadur Shah in 1707. His name Bahādur means "brave" & "hero" in Turko-Mongol languages...
, emerged victorious in it with the support of Zulfiqar Khan who was the most powerful noble of the time. In Deccan Saiyid Husain Ali Khan colluded with the Marathas and attacked Delhi and using trickery and intrigue seized Farrukhsiyar in the Red Fort. The emperor was blinded and caged and later poisoned as well as stabbed to death. However, prior to his death, Farrukhsiyar
Farrukhsiyar
Abu'l Muzaffar Muin ud-din Muhammad Shah Farrukh-siyar Alim Akbar Sani Wala Shan Padshah-i-bahr-u-bar [Shahid-i-Mazlum] was the Mughal emperor between 1713 and 1719. Noted as a handsome but weak ruler, easily swayed by his advisers, Farukhsiyar lacked the ability and character to rule independently...
had the dubious distinction of aiding the British to have a firm foothold in India, by signing the much-coveted farman an imperial directive that would seal the future of British takeover of India.
Marathas were now constantly attacking Delhi. Of more consequence and humiliation was the plunder of Delhi by Nadir Shah. A Timur descendent, Nadir Shah usurped the throne in Persia and seized Kandahar
Kandahar
Kandahar is the second largest city in Afghanistan, with a population of about 512,200 as of 2011. It is the capital of Kandahar Province, located in the south of the country at about 1,005 m above sea level...
and Kabul
Kabul
Kabul , spelt Caubul in some classic literatures, is the capital and largest city of Afghanistan. It is also the capital of the Kabul Province, located in the eastern section of Afghanistan...
. He marched through Panjab and was invited by Muhammad Shah
Muhammad Shah
Muhammad Shah also known as Roshan Akhtar, was a Mughal emperor of India between 1719 and 1748. He was son of Khujista Akhtar Jahan Shah, the fourth son of Bahadur Shah I. Ascending the throne at 17 with the help of the Sayyid Brothers, he later got rid of them with the help of Nizam-ul-Mulk Chin...
as a guest to Delhi (only because he had neither the will nor the resources to fight him). Within forty-eight hours, using a lame excuse, Nadir Shah ordered a general massacre of Delhi citizens and looted every bit of wealth they could extort out of the royalty as well as Delhi’s citizenry. Nadir Shah remained in Delhi for forty eight days and departed with millions worth of gold, jewelry and coins. Even the emperor’s bejeweled peacock throne made during Shah Jahan's reign was packed on elephants and carried away to Persia. Another prize, the Koh-I-nur diamond (Humayun’s diamond) now passed into Persian hands. Later an Afghani, Ahmad Shah Abdali started his incursions into Delhi
Delhi
Delhi , officially National Capital Territory of Delhi , is the largest metropolis by area and the second-largest by population in India, next to Mumbai. It is the eighth largest metropolis in the world by population with 16,753,265 inhabitants in the Territory at the 2011 Census...
just for the purpose of looting the capital. In a series of attacks starting in 1748 until 1761, Abdali would not only pillage and loot Delhi, he also cleaned out Mathura, Kashmir
Kashmir
Kashmir is the northwestern region of the Indian subcontinent. Until the mid-19th century, the term Kashmir geographically denoted only the valley between the Great Himalayas and the Pir Panjal mountain range...
and cities in Panjab. From the east the British defeated the Nawab of Bengal
Bengal
Bengal is a historical and geographical region in the northeast region of the Indian Subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal. Today, it is mainly divided between the sovereign land of People's Republic of Bangladesh and the Indian state of West Bengal, although some regions of the previous...
and occupied the state of Bengal.
The raids by Nadir Shah and repeated incursions of Abdali resulted in quick disposal of the next two emperors Ahmad Shah and Alamgir II
Alamgir II
Aziz-ud-din Alamgir II was the Mughal Emperor of India from 3 June 1754 to 29 November 1759. He was the son of Jahandar Shah....
until in 1759 Shah Alam II
Shah Alam II
Shah Alam II , also known as Ali Gauhar, was a Mughal emperor of India. A son of Alamgir II, he was exiled to Allahabad in December 1759 by Ghazi-ud-Din, who appointed Shah Jahan III as the emperor. Later, he was nominated as the emperor by Ahmad Shah.Shah Alam II was considered the only and...
ascended the throne. His reign would last several decades. However, he would preside over more loss of territory to the British. When the Nawab of Bengal lost to Robert Clive, Shah Alam II was forced to recognize Clive as a diwan (chancellor) and Bengal slipped to the British hands permanently.
In 1806 Shah Alam’s son Akbar Shah II
Akbar Shah II
Akbar Shah II , also known as Mirza Akbar, was the second-to-last of the Mughal emperors of India. He held the title from 1806 to 1837. He was the second son of Shah Alam II and the father of Bahadur Shah Zafar II....
acceded to the much diminished empire of the Mughals and ruled until 1837.He gave the title "raja" to Ram mohan roy. His son Bahadur Shah Zafar
Bahadur Shah II
His Royal Highness Abu Zafar Sirajuddin Muhammad Bahadur Shah Zafar , also known as Bahadur Shah or Bahadur Shah II was the last of the Mughal emperors in India, as well as the last ruler of the Timurid Dynasty.He was the son of Akbar Shah II and Lalbai, who was a Hindu Rajput...
would be the last emperor of Mughals before the British deposed him in 1858 and the Mughal dynasty would officially come to an end. During the Indian Rebellion of 1857
Indian Rebellion of 1857
The Indian Rebellion of 1857 began as a mutiny of sepoys of the British East India Company's army on 10 May 1857, in the town of Meerut, and soon escalated into other mutinies and civilian rebellions largely in the upper Gangetic plain and central India, with the major hostilities confined to...
, Bahadur Shah II was forced to take the side of the mutineers though he had no power to affect the outcome of the events. The mutineers had outwitted his British sponsors and now the emperor neither had the troops nor the competence. He had no choice but to join the winning side. However, the success of the mutineers was soon reversed and the octogenarian (he was eighty-two years old) was relieved of his empire and deposed in 1858. The emperor was then exiled to Rangoon in Burma where he died in obscurity in 1862.
The Mughals
| Portrait | Titular Name | Personal Name | Birth | Reign | Death |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
Bābur |
Zahir-ud-din Muhammad Babur Babur was a Muslim conqueror from Central Asia who, following a series of setbacks, finally succeeded in laying the basis for the Mughal dynasty of South Asia. He was a direct descendant of Timur through his father, and a descendant also of Genghis Khan through his mother... |
February 23 [O.S. February 14] 1483 | 30 April 1526 – 26 December 1530 | January 5 [O.S. December 26, 1530] 1531 (age 47) |
| Humayun |
Nasir-ud-din Muhammad Humayun Humayun Nasir ud-din Muhammad Humayun was the second Mughal Emperor who ruled present day Afghanistan, Pakistan, and parts of northern India from 1530–1540 and again from 1555–1556. Like his father, Babur, he lost his kingdom early, but with Persian aid, he eventually regained an even larger one... |
17 March 1508 | 26 December 1530 – 17 May 1540 | 27 January 1556 (age 47) | |
 |
Sher Shah Suri |
Farid Khan Sher Shah Suri Sher Shah Suri , birth name Farid Khan, also known as Sher Khan , was the founder of the short-lived Sur Empire in northern India, with its capital at Delhi, before its demise in the hands of the resurgent Mughal Empire... |
1486 | 1540–1545 | May 22, 1545 |
| Islam Shah Suri |
Jalal Khan Islam Shah Suri Islam Shah Suri was the second ruler of the Sur dynasty which ruled part of India in the mid-16th century. His original name was Jalal Khan and he was the second son of Sher Shah Suri. On his father's death, an emergency meeting of nobles chose him to be successor instead of his elder brother Adil... |
? | 1545 – 1554 | 22 November 1554 | |
| Humayun |
Nasir-ud-din Muhammad Humayun Humayun Nasir ud-din Muhammad Humayun was the second Mughal Emperor who ruled present day Afghanistan, Pakistan, and parts of northern India from 1530–1540 and again from 1555–1556. Like his father, Babur, he lost his kingdom early, but with Persian aid, he eventually regained an even larger one... |
17 March 1508 | 22 February 1555 – 27 January 1556 ) | 27 January 1556 (age 47) | |
| Akbar-e-Azam |
Jalal-ud-din Muhammad Akbar |
14 October 1542 | 27 January 1556 - 25 October 1605 | 27 October 1605 (aged 63) | |
| Jahangir |
Nur-ud-din Muhammad Salim Jahangir Jahangir was the ruler of the Mughal Empire from 1605 until his death. The name Jahangir is from Persian جهانگیر,meaning "Conqueror of the World"... |
20 September 1569 | 15 October 1605 - 8 November 1627 | 8 November 1627 (aged 58) | |
 |
Shah-Jahan-e-Azam |
Shahab-ud-din Muhammad Khurram Shah Jahan Shah Jahan Shah Jahan (also spelled Shah Jehan, Shahjehan, , Persian: شاه جهان) (January 5, 1592 – January 22, 1666) Shah Jahan (also spelled Shah Jehan, Shahjehan, , Persian: شاه جهان) (January 5, 1592 – January 22, 1666) (Full title: His Imperial Majesty Al-Sultan al-'Azam wal Khaqan... |
5 January 1592 | 8 November 1627 - 2 August 1658 | 22 January 1666 (aged 74) |
| Alamgir |
Muhy-ud-din Muhammad Aurangzeb Aurangzeb Abul Muzaffar Muhy-ud-Din Muhammad Aurangzeb Alamgir , more commonly known as Aurangzeb or by his chosen imperial title Alamgir , was the sixth Mughal Emperor of India, whose reign lasted from 1658 until his death in 1707.Badshah Aurangzeb, having ruled most of the Indian subcontinent for nearly... |
4 November 1618 | 31 July 1658 – 3 March 1707 | 3 March 1707 (aged 88) | |
- Silver Rows signify the brief interregnum during which the Suri Dynasty ruled Northern India.
The Later Mughals
| Emperor | Birth | Reign Period | Death | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bahadur Shah Bahadur Shah I Bahadur Shah was a Mughal Emperor, who ruled India from 1707 to 1712. His original name was Qutb ud-Din Muhammad Mu'azzam later titled as Shah Alam by his father. He took the throne name Bahadur Shah in 1707. His name Bahādur means "brave" & "hero" in Turko-Mongol languages... |
1643 | 1707–1712 | Feb 1712 | |
| Jahandar Shah Jahandar Shah Jahandar Shah was a Mughal Emperor who ruled India for a brief period in 1712-1713. His title was Shahanshah-i-Ghazi Abu'l Fath Muiz-ud-Din Muhammad Jahandar Shah Sahib-i-Quran Padshah-i-Jahan .-Early life:... |
1664 | 1712–1713 | Feb 1713 | He was highly influenced by his Grand Vizier Grand Vizier Grand Vizier, in Turkish Vezir-i Azam or Sadr-ı Azam , deriving from the Arabic word vizier , was the greatest minister of the Sultan, with absolute power of attorney and, in principle, dismissable only by the Sultan himself... Zulfikar Khan. |
| Furrukhsiyar | 1683 | 1713–1719 | 1719 | In 1717 he granted a firman to the English East India Company granting them duty free trading rights for Bengal Bengal Bengal is a historical and geographical region in the northeast region of the Indian Subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal. Today, it is mainly divided between the sovereign land of People's Republic of Bangladesh and the Indian state of West Bengal, although some regions of the previous... and confirmed their position in India. |
| Rafi Ul-Darjat Rafi Ul-Darjat Rafi-ul Darjat , the youngest son of Rafi-us-Shan and the nephew of Azim ush Shan, was the 11th Mughal Emperor. He succeeded Furrukhsiyar on 28 February 1719, being proclaimed Badshah by the Syed Brothers.... |
Unknown | 1719 | 1719 | |
| Rafi Ud-Daulat Rafi Ud-Daulat Rafi- ud- Daulah also known as Shah Jahan II was Mughal emperor for a brief period in 1719. He succeeded his short-lived brother Rafi Ul-Darjat in that year, being proclaimed Badshah by the Syed Brothers. Despite this, he was never allowed to venture out of the Red Fort... a.k.a Shah Jahan II |
Unknown | 1719 | 1719 | |
| Nikusiyar Nikusiyar Neku Siyar, or Nikusiyar Mohammed, was a claimaint to the throne of India. He had been in prison from 1681 to 1719 and initiated a war to seize the throne in 1719. He was son of rebel Muhammad Akbar, son of Aurangzeb and was brought up in a harem in Agra... |
Unknown | 1719 | 1743 | |
| Muhammad Ibrahim | Unknown | 1720 | 1744 | |
| Muhammad Shah Muhammad Shah Muhammad Shah also known as Roshan Akhtar, was a Mughal emperor of India between 1719 and 1748. He was son of Khujista Akhtar Jahan Shah, the fourth son of Bahadur Shah I. Ascending the throne at 17 with the help of the Sayyid Brothers, he later got rid of them with the help of Nizam-ul-Mulk Chin... |
1702 | 1719–1720, 1720–1748 | 1748 | Got rid of the Syed Brothers. Fought a long war with the Maratha Empire Maratha Empire The Maratha Empire or the Maratha Confederacy was an Indian imperial power that existed from 1674 to 1818. At its peak, the empire covered much of South Asia, encompassing a territory of over 2.8 million km².... , losing Deccan and Malwa in the process. Suffered the invasion of Nadir-Shah of Persia in 1739. He was the last Mughal Emperor to preside effective control over the empire. |
| Ahmad Shah Bahadur Ahmad Shah Bahadur Ahmad Shah Bahadur was born to Mughal Emperor Muhammad Shah. He succeeded his father to the throne as the 15th Mughal Emperor in 1748 at the age of 22. His mother was Udhambai, . When Ahmed Shah came to power the rule of the Mughal Empire was collapsing... |
1725 | 1748–54 | 1754 | Mughal forces massacred by the Maratha Maratha The Maratha are an Indian caste, predominantly in the state of Maharashtra. The term Marāthā has three related usages: within the Marathi speaking region it describes the dominant Maratha caste; outside Maharashtra it can refer to the entire regional population of Marathi-speaking people;... during the Battle of Sikandarabad Battle of Sikandarabad The Battle of Sikandarabad was fought during May, 1754; between the Mughal Emperor Ahmad Shah Bahadur and his ruthless rebellious Turani, Mir Bakshi Ghazi ud-Din supported by the Maratha leader Malhar Rao Holkar... ; |
| Alamgir II Alamgir II Aziz-ud-din Alamgir II was the Mughal Emperor of India from 3 June 1754 to 29 November 1759. He was the son of Jahandar Shah.... |
1699 | 1754–1759 | 1759 | |
| Shah Jahan III Shah Jahan III Shah Jahan III also known as Muhi-ul-millat was Mughal Emperor briefly. He was the son of Muhi-us-sunnat, the eldest son of Muhammad Kam Baksh who was the youngest son of Aurangzeb... |
Unknown | In 1759 | 1770s | consolidation of the Nizam of Bengal, Bihar, and Orissa, during the Battle of Buxar Battle of Buxar The Battle of Buxar was fought on 22 October 1764 between the forces under the command of the British East India Company, and the combined armies of Mir Qasim, the Nawab of Bengal; Shuja-ud-Daula Nawab of Awadh; and Shah Alam II, the Mughal Emperor... . Hyder Ali Hyder Ali Hyder Ali was the de facto ruler of the Kingdom of Mysore in southern India. Born Hyder Naik, he distinguished himself militarily, eventually drawing the attention of Mysore's rulers... becomes Nawab Nawab A Nawab or Nawaab is an honorific title given to Muslim rulers of princely states in South Asia. It is the Muslim equivalent of the term "maharaja" that was granted to Hindu rulers.... of Mysore in 1761; |
| Shah Alam II Shah Alam II Shah Alam II , also known as Ali Gauhar, was a Mughal emperor of India. A son of Alamgir II, he was exiled to Allahabad in December 1759 by Ghazi-ud-Din, who appointed Shah Jahan III as the emperor. Later, he was nominated as the emperor by Ahmad Shah.Shah Alam II was considered the only and... |
1728 | 1759–1806 | 1806 | Ahmed-Shah-Abdali in 1761 defeated the Maratha Maratha The Maratha are an Indian caste, predominantly in the state of Maharashtra. The term Marāthā has three related usages: within the Marathi speaking region it describes the dominant Maratha caste; outside Maharashtra it can refer to the entire regional population of Marathi-speaking people;... s during the Third Battle of Panipat Third battle of Panipat The Third Battle of Panipat took place on 14 January 1761, at Panipat , about 60 miles north of Delhi between a northern expeditionary force of the Maratha Confederacy and a coalition of the King of Afghanistan, Ahmad Shah Abdali with 2 Indian Muslim allies—the Rohilla Afghans of the Doab, and the... ; The fall of Tipu Sultan Tipu Sultan Tipu Sultan , also known as the Tiger of Mysore, was the de facto ruler of the Kingdom of Mysore. He was the son of Hyder Ali, at that time an officer in the Mysorean army, and his second wife, Fatima or Fakhr-un-Nissa... of Mysore in 1799; |
| Akbar Shah II Akbar Shah II Akbar Shah II , also known as Mirza Akbar, was the second-to-last of the Mughal emperors of India. He held the title from 1806 to 1837. He was the second son of Shah Alam II and the father of Bahadur Shah Zafar II.... |
1760 | 1806–1837 | 1837 | Titular figurehead under British protection |
| Bahadur Shah Zafar Bahadur Shah II His Royal Highness Abu Zafar Sirajuddin Muhammad Bahadur Shah Zafar , also known as Bahadur Shah or Bahadur Shah II was the last of the Mughal emperors in India, as well as the last ruler of the Timurid Dynasty.He was the son of Akbar Shah II and Lalbai, who was a Hindu Rajput... |
1775 | 1837–1857 | 1862 | The last Mughal emperor was deposed by the British and exiled to Burma Myanmar Burma , officially the Republic of the Union of Myanmar , is a country in Southeast Asia. Burma is bordered by China on the northeast, Laos on the east, Thailand on the southeast, Bangladesh on the west, India on the northwest, the Bay of Bengal to the southwest, and the Andaman Sea on the south.... following the Indian Rebellion of 1857 Indian Rebellion of 1857 The Indian Rebellion of 1857 began as a mutiny of sepoys of the British East India Company's army on 10 May 1857, in the town of Meerut, and soon escalated into other mutinies and civilian rebellions largely in the upper Gangetic plain and central India, with the major hostilities confined to... . |
Mughal family
The Mughal Emperors practiced polygamyPolygamy
Polygamy is a marriage which includes more than two partners...
. Besides their wives, they also had a number of concubines in their harem
Harem
Harem refers to the sphere of women in what is usually a polygynous household and their enclosed quarters which are forbidden to men...
, who produced children. This makes it difficult to identify all the offspring of each emperor. The principal offspring of each emperor are provided in the chart below.
Arrival of the Europeans
Vasco da Gama led the first documented European expedition to India, sailing into Calicut on the southwest coast in 1498. In 1510 the PortuguesePortugal
Portugal , officially the Portuguese Republic is a country situated in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula. Portugal is the westernmost country of Europe, and is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the West and South and by Spain to the North and East. The Atlantic archipelagos of the...
captured Goa, which became the seat of their activity. Under Admiral Afonso de Albuquerque
Afonso de Albuquerque
Afonso de Albuquerque[p][n] was a Portuguese fidalgo, or nobleman, an admiral whose military and administrative activities as second governor of Portuguese India conquered and established the Portuguese colonial empire in the Indian Ocean...
, Portugal successfully challenged Arab power in the Indian Ocean and dominated the sea routes for a century. Jesuits came to convert, to converse, and to record observations of India. The Protestant countries of the Netherlands
Netherlands
The Netherlands is a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, located mainly in North-West Europe and with several islands in the Caribbean. Mainland Netherlands borders the North Sea to the north and west, Belgium to the south, and Germany to the east, and shares maritime borders...
and England
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Scotland to the north and Wales to the west; the Irish Sea is to the north west, the Celtic Sea to the south west, with the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south separating it from continental...
, upset by the Portuguese monopoly, formed private trading companies at the turn of the 17th century to challenge the Portuguese.
Mughal officials permitted the new carriers of India's considerable export trade to establish trading posts (factories) in India. The Dutch East India Company
Dutch East India Company
The Dutch East India Company was a chartered company established in 1602, when the States-General of the Netherlands granted it a 21-year monopoly to carry out colonial activities in Asia...
concentrated mainly on the spice trade from present-day Indonesia. Britain's East India Company carried on trade with India. The French East India Company also set up factories.

Bengal
Bengal is a historical and geographical region in the northeast region of the Indian Subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal. Today, it is mainly divided between the sovereign land of People's Republic of Bangladesh and the Indian state of West Bengal, although some regions of the previous...
. Plots and counterplots climaxed when British East India Company
British East India Company
The East India Company was an early English joint-stock company that was formed initially for pursuing trade with the East Indies, but that ended up trading mainly with the Indian subcontinent and China...
forces, led by Robert Clive, defeated the forces of Nawab through treachery, Siraj-ud-Dawlah at Plassey
Battle of Plassey
The Battle of Plassey , 23 June 1757, was a decisive British East India Company victory over the Nawab of Bengal and his French allies, establishing Company rule in South Asia which expanded over much of the Indies for the next hundred years...
(Pilasi) in Bengal in 1757.
Marathas
Maratha chieftains were originally in the service of Bijapur sultans in the western Deccan, which was under siege by the Mughals.Shivaji Bhonsle
Bhonsle
The Bhonsle were a prominent clan within the Maratha clan system who served as rulers of several states in India.The most prominent member of the clan was Shivaji, the founder of the Maratha empire...
(1630–80)
Shivaji was a fighter regarded as the "father of the Maratha nation," who took advantage of this conflict and carved out his own principality near Pune
Pune
Pune , is the eighth largest metropolis in India, the second largest in the state of Maharashtra after Mumbai, and the largest city in the Western Ghats. Once the centre of power of the Maratha Empire, it is situated 560 metres above sea level on the Deccan plateau at the confluence of the Mula ...
, which later became the Maratha capital. Adopting guerrilla tactics, he waylaid caravans in order to sustain and expand his army, which soon had money, arms, and horses. Shivaji led a series of successful assaults in the 1660s against Mughal strongholds, including the major port of Surat
Surat
Surat , also known as Suryapur, is the commercial capital city of the Indian state of Gujarat. Surat is India's Eighth most populous city and Ninth-most populous urban agglomeration. It is also administrative capital of Surat district and one of the fastest growing cities in India. The city proper...
. Shivaji's battle cries were swaraj (translated variously as freedom, self-rule, independence), swadharma (religious freedom), and goraksha (cow protection). Aurangzeb relentlessly pursued Shivaji's successors between 1681 and 1705 but eventually retreated to the north as his treasury became depleted and as thousands of lives had been lost either on the battlefield or to natural calamities. In 1717 a Mughal emissary signed a treaty with the Marathas confirming their claims to rule in the Deccan in return for acknowledge the fictional Mughal suzerainty and remission of annual taxes.
The Marathas, despite their military prowess and leadership, were not equipped to administer the state or to undertake socioeconomic reform. Pursuing a policy characterized by plunder and indiscriminate raids, they antagonized the peasants. They were primarily suited for stirring the Maharashtrian regional pride rather than for attracting loyalty to an all-India confederacy. They were left virtually alone and without supplies before the invading Afghan forces, headed by Ahmad Shah Abdali (later called Ahmad Shah Durrani), who routed them on the at the Third Battle of Panipat|Panipat in 1761. The shock of defeat hastened the break-up of their loosely knit confederacy into five independent states and extinguished the hope of Maratha dominance in India.
Nizams of Hyderabad
Maratha raids into BerarBerar Subah
-Origin of name:According to the Ain-i-Akbari, the original name of Berar was Waradatat .-History:Before the Mughal occupation, Berar was part of the Nizam Shahi sultanate of Ahmadnagar. It was ceded to the emperor Akbar by Chand Bibi in 1596, unable to stand against the imperial forces led by...
, Kandesh, Gujarat and Malwa resumed after the death of Aurangzeb, and loosened Mughal control in the Deccan. In 1724 Asaf Jah, the Mughal Nizam ul Mulk, or viceroy, of the Deccan, defeated several contenders for control of the Mughal southern provinces, and established himself of ruler of an independent state
Hyderabad State
-After Indian independence :When India gained independence in 1947 and Pakistan came into existence in 1947, the British left the local rulers of the princely states the choice of whether to join one of the new dominions or to remain independent...
with its capital at Hyderabad. He and his successors ruled as hereditary Nizam
Nizam
Nizam-ul-Mulk of Hyderabad popularly known as Nizams of Hyderabad was a former monarchy of the Hyderabad State, now in the states of Andhra Pradesh , Karnataka , and Maharashtra in India...
s, and their state, known as Hyderabad
Hyderabad State
-After Indian independence :When India gained independence in 1947 and Pakistan came into existence in 1947, the British left the local rulers of the princely states the choice of whether to join one of the new dominions or to remain independent...
after the capital, outlasted the Mughal empire, persisting until it was incorporated into newly-independent India in 1948. Nizam-ul-Mulk Asaf Jahi was a strong ruler and established an orderly system of administration. He also attempted to reform the revenue system. The dynasty founded by him came to be known as the Asaf Jahi dynasty and lasted until the accession of Hyderabad to Independent India
Sikhs
The Afghan defeat of the Maratha armies accelerated the breakaway of PunjabPunjab region
The Punjab , also spelled Panjab |water]]s"), is a geographical region straddling the border between Pakistan and India which includes Punjab province in Pakistan and the states of the Punjab, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Chandigarh and some northern parts of the National Capital Territory of Delhi...
from Delhi and helped the founding of Sikh overlordship in the northwest. Rooted in the bhakti movements that developed in the 2nd century BC. but swept across North India during the 15th and 16th centuries, the teachings of the Sikh gurus appealed to the hard-working peasants. Facing extended persecution from the Mughals, the Sikhs, under Guru Gobind Singh formed the Khalsa (Army of Pure). The khalsa rose up against the economic and political repressions in Punjab toward the end of Aurangzeb's rule. Guerrilla fighters took advantage of the political instability created by the Persian and Afghan onslaught against Delhi, enriching themselves and expanding territorial control. By the 1770s, Sikh hegemony extended from the Indus in the west to the Yamuna in the east, from Multan
Multan
Multan , is a city in the Punjab Province of Pakistan and capital of Multan District. It is located in the southern part of the province on the east bank of the Chenab River, more or less in the geographic centre of the country and about from Islamabad, from Lahore and from Karachi...
in the south to Jammu
Jammu
Jammu , also known as Duggar, is one of the three administrative divisions within Jammu and Kashmir, the northernmost state in India.Jammu city is the largest city in Jammu and the winter capital of Jammu and Kashmir...
in the north. Jassa Singh Ahluwahlia entered Delhi with a large Sikh army in 1776, established hegemony, but then decided unilaterally to return to Punjab.
The Sikhs, however, were a loose and disunited conglomerate of twelve kin-groups. Ultimately, Ranjit Singh was able to unite these groups by force, and start Sikh rule that would extend from Afghanistan to the River Sutlej, and from Kashmir and Ladakh to the borders of Sindh. Ranjit Singh employed French and British officers and introduced strict military discipline into his army. It is said that his guns were cast with the utmost of excellence and quality, in that they were superior to any that the British had at the time. Further fired by the prayers of the Sikh Dharma, the Sikhs became a potent power in North-west India, plugging the Khyber pass from which numerous invasions had been launched into India, including by Alexander the Great, Chengiz Khan the Mongol nomad, Nader Shah the Persian king, and Mahmud Ghazni and Ahmad Shah Abdali the Afghans.
Ranjit Singh wrested Kashmir from Afghan rule after the Afghans backtracked on fulfilling their part of the promise for the conquest of Kashmir for which Ranjit Singh committed troops from the outside in the form of assistance, for which he was to be paid a certain sum from the Kashmir treasury. But, the ruler of Afghan instructed his brother, Dost Muhamed, the new Governor of Kashmir, to withhold payment to Ranjit Singh. At that insult, Ranjit Singh quietly withdrew his troops, and ambushed near Khyber pass the whole Afghan army returning from Kashmir. Only six people managed to escape that ambush—the ruler of Afghanistan, his brother, and four others—who ran from battle, leaving their army to be slaughtered by the Sikhs.
Establishment of the Europeans

European ethnic groups
The ethnic groups in Europe are the various ethnic groups that reside in the nations of Europe. European ethnology is the field of anthropology focusing on Europe....
s to Indian shores in 1498 when Vasco da Gama
Vasco da Gama
Vasco da Gama, 1st Count of Vidigueira was a Portuguese explorer, one of the most successful in the Age of Discovery and the commander of the first ships to sail directly from Europe to India...
, the Portuguese
Portugal
Portugal , officially the Portuguese Republic is a country situated in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula. Portugal is the westernmost country of Europe, and is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the West and South and by Spain to the North and East. The Atlantic archipelagos of the...
voyager, arrived in Calicut
History of Kozhikode
Kozhikode , also known as Calicut, is a city in the southern Indian state of Kerala. It is the third largest city in Kerala and the headquarters of Kozhikode district....
(modern Kozhikode
Kozhikode
Kozhikode During Classical antiquity and the Middle Ages, Kozhikkode was dubbed the "City of Spices" for its role as the major trading point of eastern spices. Kozhikode was once the capital of an independent kingdom of the same name and later of the erstwhile Malabar District...
, Kerala
Kerala
or Keralam is an Indian state located on the Malabar coast of south-west India. It was created on 1 November 1956 by the States Reorganisation Act by combining various Malayalam speaking regions....
) on the west coast. In their search for spices and Christian
Christian
A Christian is a person who adheres to Christianity, an Abrahamic, monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth as recorded in the Canonical gospels and the letters of the New Testament...
converts, the Portuguese challenged Arab
Arab
Arab people, also known as Arabs , are a panethnicity primarily living in the Arab world, which is located in Western Asia and North Africa. They are identified as such on one or more of genealogical, linguistic, or cultural grounds, with tribal affiliations, and intra-tribal relationships playing...
supremacy in the Indian Ocean
Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third largest of the world's oceanic divisions, covering approximately 20% of the water on the Earth's surface. It is bounded on the north by the Indian Subcontinent and Arabian Peninsula ; on the west by eastern Africa; on the east by Indochina, the Sunda Islands, and...
, and, with their galleon
Galleon
A galleon was a large, multi-decked sailing ship used primarily by European states from the 16th to 18th centuries. Whether used for war or commerce, they were generally armed with the demi-culverin type of cannon.-Etymology:...
s fitted with powerful cannon
Cannon
A cannon is any piece of artillery that uses gunpowder or other usually explosive-based propellents to launch a projectile. Cannon vary in caliber, range, mobility, rate of fire, angle of fire, and firepower; different forms of cannon combine and balance these attributes in varying degrees,...
s, set up a network of strategic trading posts along the Arabian Sea
Arabian Sea
The Arabian Sea is a region of the Indian Ocean bounded on the east by India, on the north by Pakistan and Iran, on the west by the Arabian Peninsula, on the south, approximately, by a line between Cape Guardafui in northeastern Somalia and Kanyakumari in India...
and the Persian Gulf
Persian Gulf
The Persian Gulf, in Southwest Asia, is an extension of the Indian Ocean located between Iran and the Arabian Peninsula.The Persian Gulf was the focus of the 1980–1988 Iran-Iraq War, in which each side attacked the other's oil tankers...
. In 1510 the Portuguese took over the enclave of Goa
Goa
Goa , a former Portuguese colony, is India's smallest state by area and the fourth smallest by population. Located in South West India in the region known as the Konkan, it is bounded by the state of Maharashtra to the north, and by Karnataka to the east and south, while the Arabian Sea forms its...
, which became the center of their commercial
Commerce
While business refers to the value-creating activities of an organization for profit, commerce means the whole system of an economy that constitutes an environment for business. The system includes legal, economic, political, social, cultural, and technological systems that are in operation in any...
and political power in India and which they controlled for nearly four and a half centuries.
Economic competition
Economic competition among the European nations led to the founding of commercial companies in EnglandEngland
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Scotland to the north and Wales to the west; the Irish Sea is to the north west, the Celtic Sea to the south west, with the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south separating it from continental...
(the East India Company
British East India Company
The East India Company was an early English joint-stock company that was formed initially for pursuing trade with the East Indies, but that ended up trading mainly with the Indian subcontinent and China...
, founded in 1600) and in the Netherlands
Netherlands
The Netherlands is a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, located mainly in North-West Europe and with several islands in the Caribbean. Mainland Netherlands borders the North Sea to the north and west, Belgium to the south, and Germany to the east, and shares maritime borders...
(Verenigde Oost-Indische Compagnie
Dutch East India Company
The Dutch East India Company was a chartered company established in 1602, when the States-General of the Netherlands granted it a 21-year monopoly to carry out colonial activities in Asia...
-- the United East India Company, founded in 1602), whose primary aim was to capture the spice
Spice
A spice is a dried seed, fruit, root, bark, or vegetative substance used in nutritionally insignificant quantities as a food additive for flavor, color, or as a preservative that kills harmful bacteria or prevents their growth. It may be used to flavour a dish or to hide other flavours...
trade
Trade
Trade is the transfer of ownership of goods and services from one person or entity to another. Trade is sometimes loosely called commerce or financial transaction or barter. A network that allows trade is called a market. The original form of trade was barter, the direct exchange of goods and...
by breaking the Portuguese monopoly
Monopoly
A monopoly exists when a specific person or enterprise is the only supplier of a particular commodity...
in Asia
Asia
Asia is the world's largest and most populous continent, located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres. It covers 8.7% of the Earth's total surface area and with approximately 3.879 billion people, it hosts 60% of the world's current human population...
. Although the Dutch, with a large supply of capital and support from their government, preempted and ultimately excluded the British from the heartland of spices in the East Indies
East Indies
East Indies is a term used by Europeans from the 16th century onwards to identify what is now known as Indian subcontinent or South Asia, Southeastern Asia, and the islands of Oceania, including the Malay Archipelago and the Philippines...
(modern-day Indonesia
Indonesia
Indonesia , officially the Republic of Indonesia , is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania. Indonesia is an archipelago comprising approximately 13,000 islands. It has 33 provinces with over 238 million people, and is the world's fourth most populous country. Indonesia is a republic, with an...
), both companies managed to establish trading "factories" (actually warehouses) along the Indian coast. The Dutch, for example, used various ports on the Coromandel Coast
Coromandel Coast
The Coromandel Coast is the name given to the southeastern coast of the Indian Subcontinent between Cape Comorin and False Divi Point...
in South India
South India
South India is the area encompassing India's states of Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala and Tamil Nadu as well as the union territories of Lakshadweep and Pondicherry, occupying 19.31% of India's area...
, especially Pulicat
Pulicat
Pulicat is a historic seashore town in Thiruvallur District, of Tamil Nadu state, South India. It is about 60 km north of Chennai and 3 km from Elavur, on the barrier island of Sriharikota, which separates Pulicat Lake from the Bay of Bengal. Pulicat lake is a shallow salt water lagoon...
(about twenty kilometers north of Madras), as major sources for slaves for their plantations in the East Indies and for cotton
Cotton
Cotton is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective capsule, around the seeds of cotton plants of the genus Gossypium. The fiber is almost pure cellulose. The botanical purpose of cotton fiber is to aid in seed dispersal....
cloth as early as 1609. (The English, however, established their first factory at what today is known as Madras only in 1639.) Indian rulers enthusiastically accommodated the newcomers in hopes of pitting them against the Portuguese. In 1619 Jahangir
Jahangir
Jahangir was the ruler of the Mughal Empire from 1605 until his death. The name Jahangir is from Persian جهانگیر,meaning "Conqueror of the World"...
granted them permission to trade in his territories at Surat (in Gujarat) on the west coast and Hughli (in West Bengal
West Bengal
West Bengal is a state in the eastern region of India and is the nation's fourth-most populous. It is also the seventh-most populous sub-national entity in the world, with over 91 million inhabitants. A major agricultural producer, West Bengal is the sixth-largest contributor to India's GDP...
) in the east. These and other locations on the peninsula became centers of international
International
----International mostly means something that involves more than one country. The term international as a word means involvement of, interaction between or encompassing more than one nation, or generally beyond national boundaries...
trade
Trade
Trade is the transfer of ownership of goods and services from one person or entity to another. Trade is sometimes loosely called commerce or financial transaction or barter. A network that allows trade is called a market. The original form of trade was barter, the direct exchange of goods and...
in spices, cotton
Cotton
Cotton is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective capsule, around the seeds of cotton plants of the genus Gossypium. The fiber is almost pure cellulose. The botanical purpose of cotton fiber is to aid in seed dispersal....
, sugar
Sugar
Sugar is a class of edible crystalline carbohydrates, mainly sucrose, lactose, and fructose, characterized by a sweet flavor.Sucrose in its refined form primarily comes from sugar cane and sugar beet...
, raw silk
Silk
Silk is a natural protein fiber, some forms of which can be woven into textiles. The best-known type of silk is obtained from the cocoons of the larvae of the mulberry silkworm Bombyx mori reared in captivity...
, saltpeter
Potassium nitrate
Potassium nitrate is a chemical compound with the formula KNO3. It is an ionic salt of potassium ions K+ and nitrate ions NO3−.It occurs as a mineral niter and is a natural solid source of nitrogen. Its common names include saltpetre , from medieval Latin sal petræ: "stone salt" or possibly "Salt...
, calico, and indigo
Indigo
Indigo is a color named after the purple dye derived from the plant Indigofera tinctoria and related species. The color is placed on the electromagnetic spectrum between about 420 and 450 nm in wavelength, placing it between blue and violet...
.
British influence
English company agents became familiar with Indian customs and languages, including UrduUrdu
Urdu is a register of the Hindustani language that is identified with Muslims in South Asia. It belongs to the Indo-European family. Urdu is the national language and lingua franca of Pakistan. It is also widely spoken in some regions of India, where it is one of the 22 scheduled languages and an...
and Persia
Persian language
Persian is an Iranian language within the Indo-Iranian branch of the Indo-European languages. It is primarily spoken in Iran, Afghanistan, Tajikistan and countries which historically came under Persian influence...
n, the unifying official language under the Mughals. In many ways, the English agents of that period lived like Indians, intermarried willingly, and a large number of them never returned to their home country. The knowledge of India thus acquired and the mutual ties forged with Indian trading groups gave the English a competitive edge over other Europeans. The French commercial interest—Compagnie des Indes Orientales (East India Company
French East India Company
The French East India Company was a commercial enterprise, founded in 1664 to compete with the British and Dutch East India companies in colonial India....
, founded in 1664)--came late, but the French also established themselves in India, emulating the precedents set by their competitors as they founded their enclave at Pondicherry (Puduchcheri) on the Coromandel Coast.
In 1717 the Mughal emperor, Farrukhsiyar
Farrukhsiyar
Abu'l Muzaffar Muin ud-din Muhammad Shah Farrukh-siyar Alim Akbar Sani Wala Shan Padshah-i-bahr-u-bar [Shahid-i-Mazlum] was the Mughal emperor between 1713 and 1719. Noted as a handsome but weak ruler, easily swayed by his advisers, Farukhsiyar lacked the ability and character to rule independently...
(r. 1713-19), gave the British—who by then had already established themselves in the south and the west—a grant of thirty-eight villages near Calcutta, acknowledging their importance to the continuity of international trade in the Bengal economy. As did the Dutch and the French, the British brought silver
Silver
Silver is a metallic chemical element with the chemical symbol Ag and atomic number 47. A soft, white, lustrous transition metal, it has the highest electrical conductivity of any element and the highest thermal conductivity of any metal...
bullion and copper
Copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu and atomic number 29. It is a ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. Pure copper is soft and malleable; an exposed surface has a reddish-orange tarnish...
to pay for transactions, helping the smooth functioning of the Mughal revenue system and increasing the benefits to local artisans and traders
Merchant
A merchant is a businessperson who trades in commodities that were produced by others, in order to earn a profit.Merchants can be one of two types:# A wholesale merchant operates in the chain between producer and retail merchant...
.
The fortified warehouses of the British brought extraterritorial status, which enabled them to administer their own civil and criminal laws and offered numerous employment opportunities as well as asylum to foreigners and Indians. The British factories successfully competed with their rivals as their size and population grew. The original clusters of fishing villages (Madras and Calcutta) or series of islands (Bombay) became headquarters of the British administrative zones, or presidencies as they generally came to be known. The factories and their immediate environs, known as the White-town, represented the actual and symbolic preeminence of the British—in terms of their political power—as well as their cultural values and social practices; meanwhile, their Indian collaborators lived in the Black-town, separated from the factories by several kilometres.
The British company employed sepoys--European-trained and European-led Indian soldiers—to protect its trade, but local rulers sought their services to settle scores in regional power struggles. South India
South India
South India is the area encompassing India's states of Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala and Tamil Nadu as well as the union territories of Lakshadweep and Pondicherry, occupying 19.31% of India's area...
witnessed the first open confrontation between the British and the French, whose forces were led by Robert Clive and François Dupleix, respectively. Both companies desired to place their own candidate as the nawab, or ruler, of Arcot, the area around Madras. At the end of a protracted struggle between 1744 and 1763, when the Peace of Paris was signed, the British gained an upper hand over the French and installed their man in power, supporting him further with arms and lending large sums as well. The French and the British also backed different factions in the succession struggle for Mughal viceroyalty in Bengal, but Clive intervened successfully and defeated Nawab Siraj-ud-daula in the Battle of Plassey (Palashi, about 150 kilometres north of Calcutta) in 1757. Clive found help from a combination of vested interests that opposed the existing nawab: disgruntled soldiers, landholders, and influential merchants whose commercial profits were closely linked to British fortunes.
Later, Clive defeated the Mughal forces at Buxar
Buxar
Buxar district is one of the thirty-eight districts of Bihar state, India. The district headquarters are located at Buxar.-Mythology:This place was also known as "Siddhashram", "Vedgarbhapuri", "Karush", "Tapovan", "Chaitrath", "VyaghraSar", "Buxar" in ancient history. The History of Buxar dates...
(Baksar, west of Patna in Bihar) in 1765, and the Mughal emperor (Shah Alam
Shah Alam
Shah Alam is the state capital of Selangor, Malaysia situated within the Petaling District and a small portion of the neighboring Klang District. It is located about west of the country's capital, Kuala Lumpur. Shah Alam replaced Kuala Lumpur as the capital city of the state of Selangor in 1978...
, r. 1759-1806) conferred on the company administrative rights over Bengal
Bengal
Bengal is a historical and geographical region in the northeast region of the Indian Subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal. Today, it is mainly divided between the sovereign land of People's Republic of Bangladesh and the Indian state of West Bengal, although some regions of the previous...
, Bihar
Bihar
Bihar is a state in eastern India. It is the 12th largest state in terms of geographical size at and 3rd largest by population. Almost 58% of Biharis are below the age of 25, which is the highest proportion in India....
, and Orissa
Orissa
Orissa , officially Odisha since Nov 2011, is a state of India, located on the east coast of India, by the Bay of Bengal. It is the modern name of the ancient nation of Kalinga, which was invaded by the Maurya Emperor Ashoka in 261 BC. The modern state of Orissa was established on 1 April...
, a region of roughly 25 million people with an annual revenue of 40 million rupees (for current value of the rupee). The imperial grant virtually established the company as a sovereign power, and Clive became the first British governor of Bengal.
Besides the presence of the Portuguese, Dutch, British, and French, there were two lesser but noteworthy colonial groups. Danish entrepreneurs established themselves at several ports on the Malabar coast
Malabar Coast
The Malabar Coast is a long and narrow coastline on the south-western shore line of the mainland Indian subcontinent. Geographically, it comprises the wettest regions of southern India, as the Western Ghats intercept the moisture-laden monsoon rains, especially on their westward-facing mountain...
and the Coromandel coast notably Tranquebar
Tranquebar
Tharangambadi is a panchayat town in Nagapattinam district in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu, 15 km north of Karaikal, near the mouth of a distributary of the Kaveri River. Its name means "place of the singing waves"...
, in the vicinity of Calcutta, and inland at Patna between 1695 and 1740. Austrian enterprises were set up in the 1720s on the vicinity of Surat in modern-day southeastern Gujarat. As with the other non-British enterprises, the Danish and Austrian enclaves were taken over by the British between 1765 and 1815.
Further reading
- Elliot and Dowson: The History of India as told by its own HistoriansThe History of India as told by its own HistoriansThe History of India, as Told by Its Own Historians. The Muhammadan Period is a book with eight volumes written by H. M. Elliot and edited by John Dowson. The book was published in 1867-1877 in London. It is a well-known and reputed reference work for the history of medieval India. Despite being...
, New Delhi reprint, 1990. - Elliot, Sir H. M., Edited by Dowson, John. The History of India, as Told by Its Own Historians. The Muhammadan Period; published by London Trubner Company 1867–1877. (Online Copy: The History of India, as Told by Its Own Historians. The Muhammadan Period; by Sir H. M. Elliot; Edited by John Dowson; London Trubner Company 1867–1877 - This online Copy has been posted by: The Packard Humanities Institute; Persian Texts in Translation; Also find other historical books: Author List and Title List)
- Majumdar, R. C. (ed.), The History and Culture of the Indian People, Volume VI, The Delhi Sultanate, Bombay, 1960; Volume VII, The Mughal Empire, Bombay, 1973.
External links
- Aurangzeb, as he was according to Mughal Records
- The Great Mughals Timurids-Mongolian dynasty of Turkish origin
- British India
- British Education in India

