
Multivariate mutual information
Encyclopedia
In information theory
there have been various attempts over the years to extend the definition of mutual information
to more than two random variable
s. These attempts have met with a great deal of confusion and a realization that interactions among many random variables are poorly understood.
can be used to inductively define a multivariate mutual information (MMI) in a set- or measure-theoretic sense
in the context of information diagram
s. In this sense we define the multivariate mutual information as follows:
where
This definition is identical to that of interaction information
except for a change in sign in the case of an odd number of random variables.
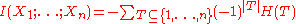
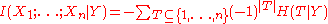
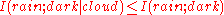 . The result is positive MMI
. The result is positive MMI 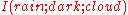 .
.
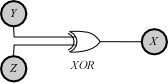 The case of negative MMI is infamously non-intuitive. A prototypical example of negative
The case of negative MMI is infamously non-intuitive. A prototypical example of negative  has
has  as the output of an XOR gate to which
as the output of an XOR gate to which  and
and  are the independent random inputs. In this case
are the independent random inputs. In this case 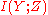 will be zero, but
will be zero, but  will be positive (1 bit
will be positive (1 bit
) since once output is known, the value on input
is known, the value on input  completely determines the value on input
completely determines the value on input  . Since
. Since 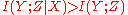 , the result is negative MMI
, the result is negative MMI 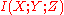 . It may seem that this example relies on a peculiar ordering of
. It may seem that this example relies on a peculiar ordering of 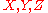 to obtain the positive interaction, but the symmetry of the definition for
to obtain the positive interaction, but the symmetry of the definition for  indicates that the same positive interaction information results regardless of which variable we consider as the interloper or conditioning variable. For example, input
indicates that the same positive interaction information results regardless of which variable we consider as the interloper or conditioning variable. For example, input  and output
and output  are also independent until input
are also independent until input  is fixed, at which time they are totally dependent.
is fixed, at which time they are totally dependent.
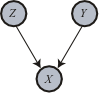 This situation is an instance where fixing the common effect
This situation is an instance where fixing the common effect  of causes
of causes  and
and  induces a dependency among the causes that did not formerly exist. This behavior is colloquially referred to as explaining away and is thoroughly discussed in the Bayesian Network
induces a dependency among the causes that did not formerly exist. This behavior is colloquially referred to as explaining away and is thoroughly discussed in the Bayesian Network
literature (e.g., Pearl 1988}. Pearl's example is auto diagnostics: A car's engine can fail to start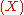 due either to a dead battery
due either to a dead battery 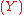 or due to a blocked fuel pump
or due to a blocked fuel pump 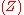 . Ordinarily, we assume that battery death and fuel pump blockage are independent events, because of the essential modularity of such automotive systems. Thus, in the absence of other information, knowing whether or not the battery is dead gives us no information about whether or not the fuel pump is blocked. However, if we happen to know that the car fails to start (i.e., we fix common effect
. Ordinarily, we assume that battery death and fuel pump blockage are independent events, because of the essential modularity of such automotive systems. Thus, in the absence of other information, knowing whether or not the battery is dead gives us no information about whether or not the fuel pump is blocked. However, if we happen to know that the car fails to start (i.e., we fix common effect  ), this information induces a dependency between the two causes battery death and fuel blockage. Thus, knowing that the car fails to start, if an inspection shows the battery to be in good health, we conclude the fuel pump is blocked.
), this information induces a dependency between the two causes battery death and fuel blockage. Thus, knowing that the car fails to start, if an inspection shows the battery to be in good health, we conclude the fuel pump is blocked.
Battery death and fuel blockage are thus dependent, conditional on their common effect car starting. The obvious directionality in the common-effect graph belies a deep informational symmetry: If conditioning on a common effect
increases the dependency between its two parent causes, then conditioning on one of the causes must create the same increase in dependency between the second cause and the common effect. In Pearl's automotive example, if conditioning on car starts induces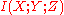 bits of dependency between the two causes battery dead and fuel blocked, then conditioning on
bits of dependency between the two causes battery dead and fuel blocked, then conditioning on
fuel blocked must induce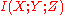 bits of dependency between battery dead and car starts. This may seem odd because battery dead and car starts are governed by the implication battery dead
bits of dependency between battery dead and car starts. This may seem odd because battery dead and car starts are governed by the implication battery dead 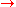 car doesn't start. However, these variables are still not totally correlated because the converse is not true. Conditioning on fuel blocked removes the major alternate cause of failure to start, and strengthens the converse relation and therefore the association between battery dead and car starts.
car doesn't start. However, these variables are still not totally correlated because the converse is not true. Conditioning on fuel blocked removes the major alternate cause of failure to start, and strengthens the converse relation and therefore the association between battery dead and car starts.
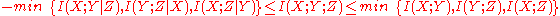
) can be positive, negative, or zero, which makes this quantity difficult to interpret intuitively. In fact, for n random variables, there are degrees of freedom for how they might be correlated in an information-theoretic sense, corresponding to each non-empty subset of these variables. These degrees of freedom are bounded by the various inequalities in information theory
degrees of freedom for how they might be correlated in an information-theoretic sense, corresponding to each non-empty subset of these variables. These degrees of freedom are bounded by the various inequalities in information theory
.
Information theory
Information theory is a branch of applied mathematics and electrical engineering involving the quantification of information. Information theory was developed by Claude E. Shannon to find fundamental limits on signal processing operations such as compressing data and on reliably storing and...
there have been various attempts over the years to extend the definition of mutual information
Mutual information
In probability theory and information theory, the mutual information of two random variables is a quantity that measures the mutual dependence of the two random variables...
to more than two random variable
Random variable
In probability and statistics, a random variable or stochastic variable is, roughly speaking, a variable whose value results from a measurement on some type of random process. Formally, it is a function from a probability space, typically to the real numbers, which is measurable functionmeasurable...
s. These attempts have met with a great deal of confusion and a realization that interactions among many random variables are poorly understood.
Definition
The conditional mutual informationConditional mutual information
In probability theory, and in particular, information theory, the conditional mutual information is, in its most basic form, the expected value of the mutual information of two random variables given the value of a third.-Definition:...
can be used to inductively define a multivariate mutual information (MMI) in a set- or measure-theoretic sense
Information theory and measure theory
- Measures in information theory :Many of the formulas in information theory have separate versions for continuous and discrete cases, i.e. integrals for the continuous case and sums for the discrete case. These versions can often be generalized using measure theory...
in the context of information diagram
Information diagram
An information diagram is a type of Venn diagram used in information theory to illustrate relationships among Shannon's basic measures of information: entropy, joint entropy, conditional entropy and mutual information...
s. In this sense we define the multivariate mutual information as follows:

where

This definition is identical to that of interaction information
Interaction information
The interaction information or co-information is one of several generalizations of the mutual information, and expresses the amount information bound up in a set of variables, beyond that which is present in any subset of those variables...
except for a change in sign in the case of an odd number of random variables.
Properties
Multi-variate information and conditional multi-variate information can be decomposed into a sum of entropies.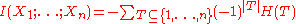
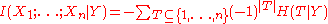
Example of Positive Multivariate mutual information
Positive MMI is typical of common-cause structures. For example, clouds cause rain and also block the sun; therefore, the correlation between rain and darkness is partly accounted for by the presence of clouds,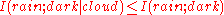 . The result is positive MMI
. The result is positive MMI 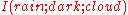 .
.Example of Negative Multivariate mutual information
 The case of negative MMI is infamously non-intuitive. A prototypical example of negative
The case of negative MMI is infamously non-intuitive. A prototypical example of negative  has
has  as the output of an XOR gate to which
as the output of an XOR gate to which  and
and  are the independent random inputs. In this case
are the independent random inputs. In this case 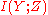 will be zero, but
will be zero, but  will be positive (1 bit
will be positive (1 bitBit
A bit is the basic unit of information in computing and telecommunications; it is the amount of information stored by a digital device or other physical system that exists in one of two possible distinct states...
) since once output
 is known, the value on input
is known, the value on input  completely determines the value on input
completely determines the value on input  . Since
. Since 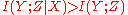 , the result is negative MMI
, the result is negative MMI 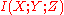 . It may seem that this example relies on a peculiar ordering of
. It may seem that this example relies on a peculiar ordering of 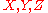 to obtain the positive interaction, but the symmetry of the definition for
to obtain the positive interaction, but the symmetry of the definition for  indicates that the same positive interaction information results regardless of which variable we consider as the interloper or conditioning variable. For example, input
indicates that the same positive interaction information results regardless of which variable we consider as the interloper or conditioning variable. For example, input  and output
and output  are also independent until input
are also independent until input  is fixed, at which time they are totally dependent.
is fixed, at which time they are totally dependent. This situation is an instance where fixing the common effect
This situation is an instance where fixing the common effect  of causes
of causes  and
and  induces a dependency among the causes that did not formerly exist. This behavior is colloquially referred to as explaining away and is thoroughly discussed in the Bayesian Network
induces a dependency among the causes that did not formerly exist. This behavior is colloquially referred to as explaining away and is thoroughly discussed in the Bayesian NetworkBayesian network
A Bayesian network, Bayes network, belief network or directed acyclic graphical model is a probabilistic graphical model that represents a set of random variables and their conditional dependencies via a directed acyclic graph . For example, a Bayesian network could represent the probabilistic...
literature (e.g., Pearl 1988}. Pearl's example is auto diagnostics: A car's engine can fail to start
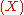 due either to a dead battery
due either to a dead battery 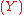 or due to a blocked fuel pump
or due to a blocked fuel pump 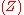 . Ordinarily, we assume that battery death and fuel pump blockage are independent events, because of the essential modularity of such automotive systems. Thus, in the absence of other information, knowing whether or not the battery is dead gives us no information about whether or not the fuel pump is blocked. However, if we happen to know that the car fails to start (i.e., we fix common effect
. Ordinarily, we assume that battery death and fuel pump blockage are independent events, because of the essential modularity of such automotive systems. Thus, in the absence of other information, knowing whether or not the battery is dead gives us no information about whether or not the fuel pump is blocked. However, if we happen to know that the car fails to start (i.e., we fix common effect  ), this information induces a dependency between the two causes battery death and fuel blockage. Thus, knowing that the car fails to start, if an inspection shows the battery to be in good health, we conclude the fuel pump is blocked.
), this information induces a dependency between the two causes battery death and fuel blockage. Thus, knowing that the car fails to start, if an inspection shows the battery to be in good health, we conclude the fuel pump is blocked.Battery death and fuel blockage are thus dependent, conditional on their common effect car starting. The obvious directionality in the common-effect graph belies a deep informational symmetry: If conditioning on a common effect
increases the dependency between its two parent causes, then conditioning on one of the causes must create the same increase in dependency between the second cause and the common effect. In Pearl's automotive example, if conditioning on car starts induces
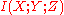 bits of dependency between the two causes battery dead and fuel blocked, then conditioning on
bits of dependency between the two causes battery dead and fuel blocked, then conditioning onfuel blocked must induce
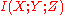 bits of dependency between battery dead and car starts. This may seem odd because battery dead and car starts are governed by the implication battery dead
bits of dependency between battery dead and car starts. This may seem odd because battery dead and car starts are governed by the implication battery dead  car doesn't start. However, these variables are still not totally correlated because the converse is not true. Conditioning on fuel blocked removes the major alternate cause of failure to start, and strengthens the converse relation and therefore the association between battery dead and car starts.
car doesn't start. However, these variables are still not totally correlated because the converse is not true. Conditioning on fuel blocked removes the major alternate cause of failure to start, and strengthens the converse relation and therefore the association between battery dead and car starts.Bounds
The bounds for the 3-variable case are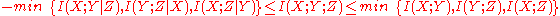
Difficulties
A complication is that this multivariate mutual information (as well as the interaction informationInteraction information
The interaction information or co-information is one of several generalizations of the mutual information, and expresses the amount information bound up in a set of variables, beyond that which is present in any subset of those variables...
) can be positive, negative, or zero, which makes this quantity difficult to interpret intuitively. In fact, for n random variables, there are
 degrees of freedom for how they might be correlated in an information-theoretic sense, corresponding to each non-empty subset of these variables. These degrees of freedom are bounded by the various inequalities in information theory
degrees of freedom for how they might be correlated in an information-theoretic sense, corresponding to each non-empty subset of these variables. These degrees of freedom are bounded by the various inequalities in information theoryInequalities in information theory
Inequalities are very important in the study of information theory. There are a number of different contexts in which these inequalities appear.-Shannon-type inequalities:...
.
See also
- Mutual informationMutual informationIn probability theory and information theory, the mutual information of two random variables is a quantity that measures the mutual dependence of the two random variables...
- Conditional mutual informationConditional mutual informationIn probability theory, and in particular, information theory, the conditional mutual information is, in its most basic form, the expected value of the mutual information of two random variables given the value of a third.-Definition:...
- Interaction informationInteraction informationThe interaction information or co-information is one of several generalizations of the mutual information, and expresses the amount information bound up in a set of variables, beyond that which is present in any subset of those variables...
- Information theory and measure theoryInformation theory and measure theory- Measures in information theory :Many of the formulas in information theory have separate versions for continuous and discrete cases, i.e. integrals for the continuous case and sums for the discrete case. These versions can often be generalized using measure theory...
- Inequalities in information theoryInequalities in information theoryInequalities are very important in the study of information theory. There are a number of different contexts in which these inequalities appear.-Shannon-type inequalities:...

