Outline of Barbados
Encyclopedia
Barbados
Barbados is an island country in the Lesser Antilles. It is in length and as much as in width, amounting to . It is situated in the western area of the North Atlantic and 100 kilometres east of the Windward Islands and the Caribbean Sea; therein, it is about east of the islands of Saint...
(old Portuguese
Portuguese language
Portuguese is a Romance language that arose in the medieval Kingdom of Galicia, nowadays Galicia and Northern Portugal. The southern part of the Kingdom of Galicia became independent as the County of Portugal in 1095...
for bearded-ones) is a sovereign island nation
Island nation
An island country is a state whose primary territory consists of one or more islands or parts of islands. As of 2011, 47 of the 193 UN member states are island countries.-Politics:...
located east of the Caribbean Sea
Caribbean Sea
The Caribbean Sea is a sea of the Atlantic Ocean located in the tropics of the Western hemisphere. It is bounded by Mexico and Central America to the west and southwest, to the north by the Greater Antilles, and to the east by the Lesser Antilles....
in the western Atlantic Ocean
Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's oceanic divisions. With a total area of about , it covers approximately 20% of the Earth's surface and about 26% of its water surface area...
. At roughly 13° North of the equator
Equator
An equator is the intersection of a sphere's surface with the plane perpendicular to the sphere's axis of rotation and containing the sphere's center of mass....
and 59° West of the prime meridian
Prime Meridian
The Prime Meridian is the meridian at which the longitude is defined to be 0°.The Prime Meridian and its opposite the 180th meridian , which the International Date Line generally follows, form a great circle that divides the Earth into the Eastern and Western Hemispheres.An international...
, the country lies in the southern Caribbean
Southern Caribbean
The Southern Caribbean is a group of islands that neighbor mainland South America in the West Indies. St. Lucia lies to the north of the region, Barbados in the east, Trinidad & Tobago at its southern most point, and Aruba at the most westerly section....
region, where it is considered a part of the Lesser Antilles
Lesser Antilles
The Lesser Antilles are a long, partly volcanic island arc in the Western Hemisphere. Most of its islands form the eastern boundary of the Caribbean Sea with the Atlantic Ocean, with the remainder located in the southern Caribbean just north of South America...
. Its closest island neighbours are Saint Vincent & the Grenadines and Saint Lucia
Saint Lucia
Saint Lucia is an island country in the eastern Caribbean Sea on the boundary with the Atlantic Ocean. Part of the Lesser Antilles, it is located north/northeast of the island of Saint Vincent, northwest of Barbados and south of Martinique. It covers a land area of 620 km2 and has an...
to the west. To the south lies Trinidad and Tobago
Trinidad and Tobago
Trinidad and Tobago officially the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago is an archipelagic state in the southern Caribbean, lying just off the coast of northeastern Venezuela and south of Grenada in the Lesser Antilles...
—with which Barbados now shares a fixed official maritime boundary
Maritime boundary
Maritime boundary is a conceptual means of division of the water surface of the planet into maritime areas that are defined through surrounding physical geography or by human geography. As such it usually includes areas of exclusive national rights over the mineral and biological resources,...
—and also the South American mainland. Barbados's total land area is about 430 square kilometres (166 sq mi), and is primarily low-lying, with some higher regions in the country's interior. The highest point in Barbados is Mount Hillaby
Mount Hillaby
The peak of Mount Hillaby is the highest point on the Eastern Caribbean island nation of Barbados. The peak is located in the parish of Saint Andrew. It immediately overlooks the area known as the Scotland District to the north and east which comprises geologically old sediments prone to...
in the parish of Saint Andrew. The geological composition of Barbados is thought to be of non-volcanic origin and is predominantly composed of limestone
Limestone
Limestone is a sedimentary rock composed largely of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of calcium carbonate . Many limestones are composed from skeletal fragments of marine organisms such as coral or foraminifera....
-coral
Coral
Corals are marine animals in class Anthozoa of phylum Cnidaria typically living in compact colonies of many identical individual "polyps". The group includes the important reef builders that inhabit tropical oceans and secrete calcium carbonate to form a hard skeleton.A coral "head" is a colony of...
formed by subduction of the South American plate colliding with the Caribbean plate. The island's climate is tropical, with constant trade wind
Trade wind
The trade winds are the prevailing pattern of easterly surface winds found in the tropics, within the lower portion of the Earth's atmosphere, in the lower section of the troposphere near the Earth's equator...
s off the Atlantic Ocean serving to keep temperatures mild. Some less developed areas of the country contain tropical woodland and mangroves. Other parts of the interior which contribute to the agriculture industry are dotted with large sugarcane
Sugarcane
Sugarcane refers to any of six to 37 species of tall perennial grasses of the genus Saccharum . Native to the warm temperate to tropical regions of South Asia, they have stout, jointed, fibrous stalks that are rich in sugar, and measure two to six metres tall...
estates and wide, gently sloping pastures, with panoramic views down to the coast.
Barbados's human development index
Human Development Index
The Human Development Index is a composite statistic used to rank countries by level of "human development" and separate "very high human development", "high human development", "medium human development", and "low human development" countries...
ranking is consistently among the top 50 in the world. For example, in 2006, it was ranked 31st in the world, and third in the Americas, behind Canada
Canada
Canada is a North American country consisting of ten provinces and three territories. Located in the northern part of the continent, it extends from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west, and northward into the Arctic Ocean...
and the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and introduction to Barbados:
General reference
- Pronunciation:
- Barbadian English: bɑrˈbeɪdoʊz
- British English: bɑrˈbeɪdɒs
- American English: bɑrˈbeɪdoʊz
- PronunciationInternational Phonetic AlphabetThe International Phonetic Alphabet "The acronym 'IPA' strictly refers [...] to the 'International Phonetic Association'. But it is now such a common practice to use the acronym also to refer to the alphabet itself that resistance seems pedantic...
: - Common English country name: BarbadosBarbadosBarbados is an island country in the Lesser Antilles. It is in length and as much as in width, amounting to . It is situated in the western area of the North Atlantic and 100 kilometres east of the Windward Islands and the Caribbean Sea; therein, it is about east of the islands of Saint...
- Official English country name: BarbadosBarbadosBarbados is an island country in the Lesser Antilles. It is in length and as much as in width, amounting to . It is situated in the western area of the North Atlantic and 100 kilometres east of the Windward Islands and the Caribbean Sea; therein, it is about east of the islands of Saint...
- Common endonym(s):
- Official endonym(s):
- Adjectival(s): Barbadian
- Demonym(s):
- EtymologyEtymologyEtymology is the study of the history of words, their origins, and how their form and meaning have changed over time.For languages with a long written history, etymologists make use of texts in these languages and texts about the languages to gather knowledge about how words were used during...
: Name of Barbados - International rankings of BarbadosInternational rankings of BarbadosThe following are international rankings of Barbados.-Economic:* The Wall Street Journal and the Heritage Foundation: Index of Economic Freedom 2006, ranked out of 157 countries**2005 ranked 32nd of 155 countries...
- International Telecommunications Union callsign prefix: 8P
- ISO country codes: BB, BRB, 052
- ISO region codes: See ISO 3166-2:BBISO 3166-2:BBISO 3166-2:BB is the entry for Barbados in ISO 3166-2, part of the ISO 3166 standard published by the International Organization for Standardization , which defines codes for the names of the principal subdivisions of all countries coded in ISO 3166-1.Currently for Barbados, ISO 3166-2 codes are...
- InternetInternetThe Internet is a global system of interconnected computer networks that use the standard Internet protocol suite to serve billions of users worldwide...
country code top-level domainCountry code top-level domainA country code top-level domain is an Internet top-level domain generally used or reserved for a country, a sovereign state, or a dependent territory....
: .bb.bb.bb is the Internet country code top-level domain for Barbados. The .bb top-level domain has been maintained by several administrators since its creation. The first of which was the University of Puerto Rico. In 1996 the Government of Barbados sought the relegation of .bb to the incumbent local...
Geography of Barbados
- Barbados is...
- an islandIslandAn island or isle is any piece of sub-continental land that is surrounded by water. Very small islands such as emergent land features on atolls can be called islets, cays or keys. An island in a river or lake may be called an eyot , or holm...
- a countryCountryA country is a region legally identified as a distinct entity in political geography. A country may be an independent sovereign state or one that is occupied by another state, as a non-sovereign or formerly sovereign political division, or a geographic region associated with a previously...
- an island country
- a nation state
- a Commonwealth RealmCommonwealth RealmA Commonwealth realm is a sovereign state within the Commonwealth of Nations that has Elizabeth II as its monarch and head of state. The sixteen current realms have a combined land area of 18.8 million km² , and a population of 134 million, of which all, except about two million, live in the six...
- an island
- Location:
- Northern HemisphereNorthern HemisphereThe Northern Hemisphere is the half of a planet that is north of its equator—the word hemisphere literally means “half sphere”. It is also that half of the celestial sphere north of the celestial equator...
and Western HemisphereWestern HemisphereThe Western Hemisphere or western hemisphere is mainly used as a geographical term for the half of the Earth that lies west of the Prime Meridian and east of the Antimeridian , the other half being called the Eastern Hemisphere.In this sense, the western hemisphere consists of the western portions... - North AmericaNorth AmericaNorth America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas...
(just north of South AmericaSouth AmericaSouth America is a continent situated in the Western Hemisphere, mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere. The continent is also considered a subcontinent of the Americas. It is bordered on the west by the Pacific Ocean and on the north and east...
, off the coast of VenezuelaVenezuelaVenezuela , officially called the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela , is a tropical country on the northern coast of South America. It borders Colombia to the west, Guyana to the east, and Brazil to the south...
) - Atlantic OceanAtlantic OceanThe Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's oceanic divisions. With a total area of about , it covers approximately 20% of the Earth's surface and about 26% of its water surface area...
- North Atlantic
- West Indies
- Southern CaribbeanSouthern CaribbeanThe Southern Caribbean is a group of islands that neighbor mainland South America in the West Indies. St. Lucia lies to the north of the region, Barbados in the east, Trinidad & Tobago at its southern most point, and Aruba at the most westerly section....
- AntillesAntillesThe Antilles islands form the greater part of the West Indies in the Caribbean Sea. The Antilles are divided into two major groups: the "Greater Antilles" to the north and west, including the larger islands of Cuba, Jamaica, Hispaniola , and Puerto Rico; and the smaller "Lesser Antilles" on the...
- Lesser AntillesLesser AntillesThe Lesser Antilles are a long, partly volcanic island arc in the Western Hemisphere. Most of its islands form the eastern boundary of the Caribbean Sea with the Atlantic Ocean, with the remainder located in the southern Caribbean just north of South America...
- Lesser Antilles
- Southern Caribbean
- West Indies
- North Atlantic
- Northern Hemisphere
-
- Time zoneTime zoneA time zone is a region on Earth that has a uniform standard time for legal, commercial, and social purposes. In order for the same clock time to always correspond to the same portion of the day as the Earth rotates , different places on the Earth need to have different clock times...
: Eastern Caribbean Time (UTC-04) - Extreme points of Barbados
- Northernmost Point – North Point, Saint Lucy (N 13.334851, W -59.614742)
- Southernmost Point – South Point, Christ Church (N 13.045294, W -59.526722)
- Easternmost Point – Kitridge Point, Saint Philip (N 13.149207, W -59.420292)
- Westernmost Point – Harrisons, Saint Lucy, Saint Lucy (N 13.305756, W -59.651022)
- High: Mount HillabyMount HillabyThe peak of Mount Hillaby is the highest point on the Eastern Caribbean island nation of Barbados. The peak is located in the parish of Saint Andrew. It immediately overlooks the area known as the Scotland District to the north and east which comprises geologically old sediments prone to...
336 m (1,102 ft) - Low: North Atlantic Ocean 0 m
- Land boundaries: none
- Coastline: 97 km
- Time zone
- Population of Barbados: 279,000(2006) - 175th most populous country
- Area of Barbados: 431 square kilometres (166.4 sq mi) - 199th largest country
- Atlas of Barbados
Environment of Barbados

- Climate of Barbados
- Environmental issues in Barbados
- Ecoregions in Barbados
- Renewable energy in Barbados
- Geology of Barbados
- Protected areas of Barbados
- Biosphere reserves in Barbados
- National parks of Barbados
- Wildlife of Barbados
- Flora of Barbados
- Fauna of BarbadosFauna of BarbadosThe Fauna of Barbados is less diverse than that of other Caribbean islands. The island's fauna has been greatly affected by anthropogenic activities; these range from habitat destruction to the introduction of non-native species...
Natural geographic features of Barbados
- Beaches in Barbados
- Islands of Barbados
- Lakes of Barbados
- Mountains of Barbados
- Volcanoes in Barbados
- Rivers of Barbados
- Waterfalls of Barbados
- Valleys of Barbados
- World Heritage Sites in Barbados: None
Ecoregions of Barbados
- Main article: Ecoregions in Barbados
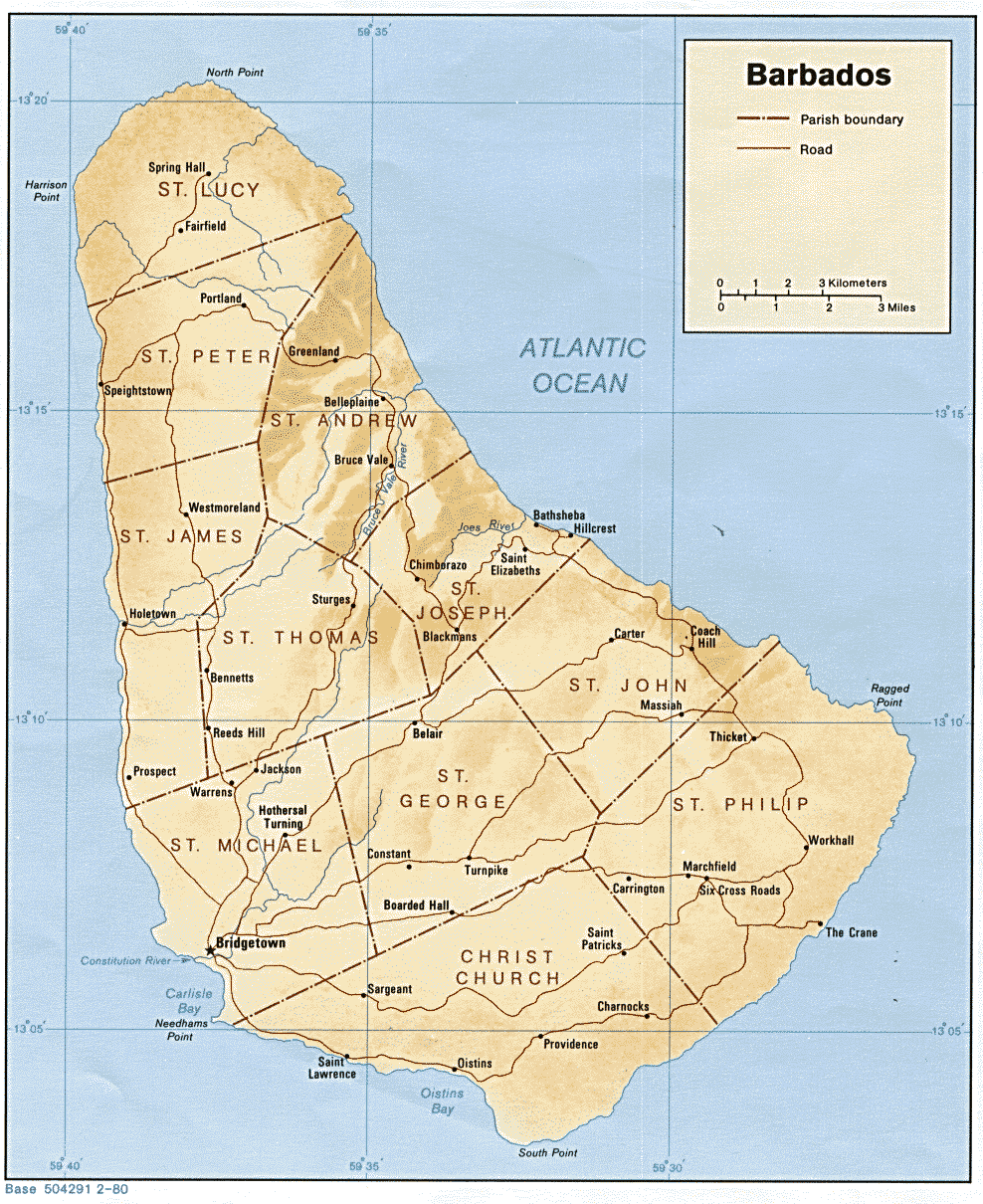
Administrative divisions of Barbados
- Main article: Administrative divisions of Barbados
- Parishes of BarbadosParishes of BarbadosThe country of Barbados is currently subdivided into sub-regions known as parishes. According to the Act of the Barbados Parliament they are officially styled as the "Parish of as opposed to the U.S. styled naming convention with the name "Parish" coming after the name...
Parishes of Barbados
- Christ Church
- Saint Andrew
- Saint George
- Saint James
- Saint John
- Saint Joseph
- Saint Lucy
- Saint Michael
- Saint Peter
- Saint Philip
- Saint Thomas
Government and politics of Barbados
- Main article: Government of BarbadosGovernment of BarbadosGovernment of Barbados consists of: The Monarch, HM Queen Elizabeth II ; The Prime Minister, The Hon. Freundel Stuart, and his Cabinet; as legislature, divided into two chambers , and an independent judiciary...
and Politics of BarbadosPolitics of BarbadosThe politics of Barbados function within a framework of constitutional monarchy and a parliamentary government with strong democratic traditions; constitutional safeguards for nationals of Barbados include: freedom of speech, press, worship, movement, and association.Executive power is vested in...
- Form of governmentForm of governmentA form of government, or form of state governance, refers to the set of political institutions by which a government of a state is organized. Synonyms include "regime type" and "system of government".-Empirical and conceptual problems:...
: constitutional monarchyConstitutional monarchyConstitutional monarchy is a form of government in which a monarch acts as head of state within the parameters of a constitution, whether it be a written, uncodified or blended constitution...
and a parliamentary governmentParliament of BarbadosThe Parliament of Barbados is the national legislature of Barbados. It is accorded legislative supremacy by Chapter V of the Constitution of Barbados. The Parliament is bicameral in composition and is formally made up of: HM Queen Elizabeth II, Queen of Barbados The Parliament of Barbados is the...
with strong democraticDemocracyDemocracy is generally defined as a form of government in which all adult citizens have an equal say in the decisions that affect their lives. Ideally, this includes equal participation in the proposal, development and passage of legislation into law...
traditions - Capital of Barbados: Bridgetown
- Elections in BarbadosElections in BarbadosElections in Barbados is the process of conducting general elections and formulating election results in Barbados. An election is a process in which a vote is held to democratically elect national candidates to an office. In the case of Barbados, it is the mechanism by which the electors choose...
- (specific elections)
- Political parties in Barbados
- Political scandals of Barbados
- Taxation in Barbados
Executive branch of the government of Barbados
- Head of stateHead of StateA head of state is the individual that serves as the chief public representative of a monarchy, republic, federation, commonwealth or other kind of state. His or her role generally includes legitimizing the state and exercising the political powers, functions, and duties granted to the head of...
: Queen of Barbados, Elizabeth II- Her Majesty's representative: Governor-General of Barbados, Clifford HusbandsClifford HusbandsSir Clifford Straughn Husbands, GCMG, KA, QC was the Governor-General of Barbados. He held this office from 1996, when he was appointed after the death of Dame Nita Barrow, until he retired on 31 October 2011.-External links:*...
- Her Majesty's representative: Governor-General of Barbados, Clifford Husbands
- Head of governmentHead of governmentHead of government is the chief officer of the executive branch of a government, often presiding over a cabinet. In a parliamentary system, the head of government is often styled prime minister, chief minister, premier, etc...
: Prime Minister of BarbadosPrime Minister of BarbadosThe Prime Minister of Barbados is a very influential position as head of government of Barbados. According to Barbados Constitution, the Prime Minister must always be a member of Parliament, and is appointed by the Governor-General who is responsible for conducting parliamentary elections, and for...
, David ThompsonDavid Thompson (Barbadian politician)David John Howard Thompson, QC, MP was the sixth Prime Minister of Barbados from January 2008 until his death from pancreatic cancer on 23 October 2010.... - Cabinet of BarbadosCabinet of BarbadosThe Cabinet of Barbados is the executive committee that looks after the management of the country. It is chaired by Prime Minister Freundel Stuart and is composed of 18 Ministers....
Legislative branch of the government of Barbados
- Parliament of BarbadosParliament of BarbadosThe Parliament of Barbados is the national legislature of Barbados. It is accorded legislative supremacy by Chapter V of the Constitution of Barbados. The Parliament is bicameral in composition and is formally made up of: HM Queen Elizabeth II, Queen of Barbados The Parliament of Barbados is the...
(bicameral)- Upper houseUpper houseAn upper house, often called a senate, is one of two chambers of a bicameral legislature, the other chamber being the lower house; a legislature composed of only one house is described as unicameral.- Possible specific characteristics :...
: Senate of BarbadosSenate of BarbadosThe Senate is the name given to the Upper House of the bicameral legislature the Parliament of Barbados. The Senate is accorded legitimacy by Chapter V of the Constitution of Barbados. It is the smaller of both chambers and also includes HM Queen Elizabeth II, Queen of Barbados... - Lower houseLower houseA lower house is one of two chambers of a bicameral legislature, the other chamber being the upper house.Despite its official position "below" the upper house, in many legislatures worldwide the lower house has come to wield more power...
: Barbados House of AssemblyBarbados House of AssemblyThe House of Assembly is the lower house of the bicameral Parliament of Barbados. It has 30 Members of Parliament , MPs are directly elected in single member constituencies using the simple-majority system for a term of five years....
- Upper house
Judicial branch of the government of Barbados
- Caribbean Court of JusticeCaribbean Court of JusticeThe Caribbean Court of Justice is the judicial institution of the Caribbean Community . Established in 2001, it is based in Port of Spain, Trinidad and Tobago....
- Supreme Court of BarbadosSupreme Court of BarbadosThe Supreme Court of Judicature of Barbados is the highest judicial body in the country of Barbados. It is made up of the High Court and the Court of Appeals....
- Magistrate Courts of Barbados
- Supreme Court of Barbados
Foreign relations of Barbados
- Diplomatic missions in Barbados
- Diplomatic missions of BarbadosDiplomatic missions of BarbadosThis is a list of diplomatic missions of Barbados, excluding honorary consulates. The Caribbean island of Barbados has a modest diplomatic presence. Barbados has thirteen missions and consulates located abroad, with many of these missions accredited to other countries...
International organization membership
Barbados is a member of:- African, Caribbean, and Pacific Group of States (ACP)
- Agency for the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons in Latin America and the Caribbean (OPANAL)
- Caribbean Community and Common Market (Caricom)
- Caribbean Development BankCaribbean Development BankThe Caribbean Development Bank is a financial institution which assists Caribbean nations in financing social and economic programs in its member countries...
(CDB) - Commonwealth of NationsCommonwealth of NationsThe Commonwealth of Nations, normally referred to as the Commonwealth and formerly known as the British Commonwealth, is an intergovernmental organisation of fifty-four independent member states...
- Food and Agriculture OrganizationFood and Agriculture OrganizationThe Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations is a specialised agency of the United Nations that leads international efforts to defeat hunger. Serving both developed and developing countries, FAO acts as a neutral forum where all nations meet as equals to negotiate agreements and...
(FAO) - Group of 77Group of 77The Group of 77 at the United Nations is a loose coalition of developing nations, designed to promote its members' collective economic interests and create an enhanced joint negotiating capacity in the United Nations. There were 77 founding members of the organization, but the organization has...
(G77) - Inter-American Development BankInter-American Development BankThe Inter-American Development Bank is the largest source of development financing for Latin America and the Caribbean...
(IADB) - International Bank for Reconstruction and DevelopmentInternational Bank for Reconstruction and DevelopmentThe International Bank for Reconstruction and Development is one of five institutions that compose the World Bank Group. The IBRD is an international organization whose original mission was to finance the reconstruction of nations devastated by World War II. Now, its mission has expanded to fight...
(IBRD) - International Civil Aviation OrganizationInternational Civil Aviation OrganizationThe International Civil Aviation Organization , pronounced , , is a specialized agency of the United Nations. It codifies the principles and techniques of international air navigation and fosters the planning and development of international air transport to ensure safe and orderly growth...
(ICAO) - International Criminal CourtInternational Criminal CourtThe International Criminal Court is a permanent tribunal to prosecute individuals for genocide, crimes against humanity, war crimes, and the crime of aggression .It came into being on 1 July 2002—the date its founding treaty, the Rome Statute of the...
(ICCt) - International Criminal Police Organization (Interpol)
- International Development AssociationInternational Development AssociationThe International Development Association , is the part of the World Bank that helps the world’s poorest countries. It complements the World Bank's other lending arm — the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development — which serves middle-income countries with capital investment and...
(IDA) - International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent SocietiesInternational Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent SocietiesThe International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies is a humanitarian institution that is part of the International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement along with the ICRC and 186 distinct National Societies...
(IFRCS) - International Finance CorporationInternational Finance CorporationThe International Finance Corporation promotes sustainable private sector investment in developing countries.IFC is a member of the World Bank Group and is headquartered in Washington, D.C., United States....
(IFC) - International Fund for Agricultural DevelopmentInternational Fund for Agricultural DevelopmentThe International Fund for Agricultural Development , a specialized agency of the United Nations, was established as an international financial institution in 1977 as one of the major outcomes of the 1974 World Food Conference. IFAD is dedicated to eradicating rural poverty in developing countries...
(IFAD) - International Labour OrganizationInternational Labour OrganizationThe International Labour Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations that deals with labour issues pertaining to international labour standards. Its headquarters are in Geneva, Switzerland. Its secretariat — the people who are employed by it throughout the world — is known as the...
(ILO) - International Maritime OrganizationInternational Maritime OrganizationThe International Maritime Organization , formerly known as the Inter-Governmental Maritime Consultative Organization , was established in Geneva in 1948, and came into force ten years later, meeting for the first time in 1959...
(IMO) - International Monetary FundInternational Monetary FundThe International Monetary Fund is an organization of 187 countries, working to foster global monetary cooperation, secure financial stability, facilitate international trade, promote high employment and sustainable economic growth, and reduce poverty around the world...
(IMF) - International Olympic CommitteeInternational Olympic CommitteeThe International Olympic Committee is an international corporation based in Lausanne, Switzerland, created by Pierre de Coubertin on 23 June 1894 with Demetrios Vikelas as its first president...
(IOC) - International Organization for StandardizationInternational Organization for StandardizationThe International Organization for Standardization , widely known as ISO, is an international standard-setting body composed of representatives from various national standards organizations. Founded on February 23, 1947, the organization promulgates worldwide proprietary, industrial and commercial...
(ISO)
- International Red Cross and Red Crescent MovementInternational Red Cross and Red Crescent MovementThe International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement is an international humanitarian movement with approximately 97 million volunteers, members and staff worldwide which was founded to protect human life and health, to ensure respect for all human beings, and to prevent and alleviate human...
(ICRM) - International Telecommunication UnionInternational Telecommunication UnionThe International Telecommunication Union is the specialized agency of the United Nations which is responsible for information and communication technologies...
(ITU) - International Telecommunications Satellite OrganizationInternational Telecommunications Satellite OrganizationThe International Telecommunications Satellite Organization is an intergovernmental organisation charged with overseeing the public service obligations of Intelsat.-External links:*...
(ITSO) - International Trade Union ConfederationInternational Trade Union ConfederationThe International Trade Union Confederation is the world's largest trade union federation. It was formed on November 1, 2006 out of the merger of the International Confederation of Free Trade Unions and the World Confederation of Labour...
(ITUC) - Latin American Economic SystemLatin American Economic SystemThe Latin American and the Caribbean Economic System, officially known as Sistema Económico Latinoamericano y del Caribe , is an organization founded in 1975 to promote economic cooperation and social development between Latin American and the Caribbean countries...
(LAES) - Multilateral Investment Guarantee AgencyMultilateral Investment Guarantee AgencyThe Multilateral Investment Guarantee Agency is a member organization of the World Bank Group that offers political risk insurance. It was established to promote foreign direct investment into developing countries. MIGA was founded in 1988 with a capital base of $1 billion and is headquartered in...
(MIGA) - Nonaligned Movement (NAM)
- Organization for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons (OPCW)
- Organization of American StatesOrganization of American StatesThe Organization of American States is a regional international organization, headquartered in Washington, D.C., United States...
(OAS) - United NationsUnited NationsThe United Nations is an international organization whose stated aims are facilitating cooperation in international law, international security, economic development, social progress, human rights, and achievement of world peace...
(UN) - United Nations Conference on Trade and DevelopmentUnited Nations Conference on Trade and DevelopmentThe United Nations Conference on Trade and Development was established in 1964 as a permanent intergovernmental body. It is the principal organ of the United Nations General Assembly dealing with trade, investment, and development issues....
(UNCTAD) - United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organization (UNESCO)
- United Nations Industrial Development OrganizationUnited Nations Industrial Development OrganizationThe United Nations Industrial Development Organization , French/Spanish acronym ONUDI, is a specialized agency in the United Nations system, headquartered in Vienna, Austria...
(UNIDO) - Universal Postal UnionUniversal Postal UnionThe Universal Postal Union is an international organization that coordinates postal policies among member nations, in addition to the worldwide postal system. The UPU contains four bodies consisting of the Congress, the Council of Administration , the Postal Operations Council and the...
(UPU) - World Customs OrganizationWorld Customs OrganizationThe World Customs Organization is an intergovernmental organization headquartered in Brussels, Belgium. With its worldwide membership, the WCO is recognized as the voice of the global customs community...
(WCO) - World Federation of Trade UnionsWorld Federation of Trade UnionsThe World Federation of Trade Unions was established in 1945 to replace the International Federation of Trade Unions. Its mission was to bring together trade unions across the world in a single international organization, much like the United Nations...
(WFTU) - World Health OrganizationWorld Health OrganizationThe World Health Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations that acts as a coordinating authority on international public health. Established on 7 April 1948, with headquarters in Geneva, Switzerland, the agency inherited the mandate and resources of its predecessor, the Health...
(WHO) - World Intellectual Property OrganizationWorld Intellectual Property OrganizationThe World Intellectual Property Organization is one of the 17 specialized agencies of the United Nations. WIPO was created in 1967 "to encourage creative activity, to promote the protection of intellectual property throughout the world"....
(WIPO) - World Meteorological OrganizationWorld Meteorological OrganizationThe World Meteorological Organization is an intergovernmental organization with a membership of 189 Member States and Territories. It originated from the International Meteorological Organization , which was founded in 1873...
(WMO) - World Trade OrganizationWorld Trade OrganizationThe World Trade Organization is an organization that intends to supervise and liberalize international trade. The organization officially commenced on January 1, 1995 under the Marrakech Agreement, replacing the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade , which commenced in 1948...
(WTO)
Law and order in Barbados
- Main article: Law of Barbados
- Capital punishment in Barbados
- Constitution of BarbadosConstitution of BarbadosThe Constitution of Barbados is the supreme law under which Barbados is governed. The Constitution provides a legal establishment of the structure and various roles of administration of the Sovereign , the Vice-Royal , the Government of Barbados, as well as legal rights and responsibilities of the...
- Crime in Barbados
- Human rights in Barbados
- LGBT rights in BarbadosLGBT rights in BarbadosLesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender persons in Barbados face legal risks not experienced by non-LGBT citizens. Homosexual acts are illegal in Barbados, with a life sentence; but the law is rarely enforced. The law is currently in effect, but under review. Recent polls conducted by Caribbean...
- Freedom of religion in Barbados
- LGBT rights in Barbados
- Law enforcement in Barbados
Military of Barbados
- Main article: Military of BarbadosMilitary of Barbados-History:Throughout the colonial history of Barbados, Britain routinely stationed large segments of its West India regimental troops on the island of Barbados. The troops acted principally as a force to secure the island against any invasion by other European powers as well as to help protect...
- Command
- Commander-in-chiefCommander-in-ChiefA commander-in-chief is the commander of a nation's military forces or significant element of those forces. In the latter case, the force element may be defined as those forces within a particular region or those forces which are associated by function. As a practical term it refers to the military...
- Ministry of Defence of Barbados
- Commander-in-chief
- Forces
- Army of Barbados
- Navy of Barbados
- Air Force of Barbados
- Special forces of Barbados
- Military history of Barbados
- Military ranks of Barbados
- Project HARPProject HARPProject HARP, short for High Altitude Research Project, was a joint project of the United States Department of Defense and Canada's Department of National Defence created with the goal of studying ballistics of re-entry vehicles at low cost; whereas most such projects used expensive rockets, HARP...
History of Barbados
- Main article: History of BarbadosHistory of BarbadosBarbados was inhabited by Arawaks and Caribs at the time of European colonization in the 16th century.The island was a British colony from 1625 until 1966....
, Timeline of the history of Barbados, and Current events of Barbados
- Economic history of Barbados
- Military history of Barbados
Culture of Barbados
- Main article: Culture of BarbadosCulture of BarbadosThe culture of Barbados is a blend of West African and British cultures present in Barbados. The Bajan, or Barbadian dialect is an iconic part of the culture. But English is still the official language, reflecting centuries of British rule....
- Architecture of Barbados
- Cuisine of Barbados
- Ethnic minorities in Barbados
- Festivals in Barbados
- Humor in Barbados
- Languages of Barbados
- Media in Barbados
- National symbols of Barbados
- Coat of arms of BarbadosCoat of arms of BarbadosThe coat of arms of Barbados was adopted upon independence in 1966 by decree of Queen Elizabeth. Like other former British possessions in the Caribbean, the coat of arms has a helmet with a national symbol on top, and a shield beneath that is supported by two animals.The national symbol found on...
- Flag of BarbadosFlag of BarbadosThe national flag of Barbados was officially adopted on 30 November 1966, the island's first Independence Day. It consists of a triband of two bands of ultramarine separated by a golden middle band. A black trident-head is centred within the golden band...
- National anthem of BarbadosNational Anthem of BarbadosIn Plenty and In Time of Need is the national anthem of the country of Barbados. It was written by Irving Burgie and was composed by C. Van Roland Edwards . As one part of the West Indies Federation Barbados' anthem was supposed to be Forged from the Love of Liberty, however the current anthem was...
- Coat of arms of Barbados
- People of Barbados
- Prostitution in Barbados
- Public holidays in BarbadosPublic holidays in BarbadosHolidays in the country of Barbados29 novbarbados day-External links:* public holidays during 2009....
- Records of Barbados
- Religion in BarbadosReligion in BarbadosAccording to the 2000 official census, more than 95 percent of the population of Barbados is considered Christian, although persons may not be active in any particular denomination. The Anglican Church constitutes the largest religious group, with 70,000 members; an estimated 67 percent are active...
- Buddhism in Barbados
- Christianity in Barbados
- Hinduism in Barbados
- Islam in BarbadosIslam in BarbadosStatistics for Islam in Barbados estimate a Muslim population of over 4000, most of whom are immigrants or descendants of immigrants from the Indian state of Gujarat...
- Judaism in Barbados
- Sikhism in Barbados
- World Heritage Sites in Barbados: None
Art in Barbados
- Art in Barbados
- Cinema of Barbados
- Literature of Barbados
- Music of BarbadosMusic of BarbadosThe music of Barbados includes distinctive national styles of folk and popular music, including elements of Western classical and religious music...
- Television in Barbados
- Theatre in Barbados
Sports in Barbados
- Main article: Sports in Barbados
- Football in BarbadosFootball in BarbadosFootball is one of the most popular sports in Barbados. While it lags behind cricket in participation and spectatorship, interest in football has been growing in recent years.-The Barbados Football Association:...
- BarbadosBarbadosBarbados is an island country in the Lesser Antilles. It is in length and as much as in width, amounting to . It is situated in the western area of the North Atlantic and 100 kilometres east of the Windward Islands and the Caribbean Sea; therein, it is about east of the islands of Saint...
Economy and infrastructure of Barbados
- Main article: Economy of BarbadosEconomy of BarbadosSince achieving independence in 1966, the island nation of Barbados has transformed itself from a low-income economy dependent upon sugar production, into an upper-middle-income economy based on tourism and the offshore sector. Barbados went into a deep recession in the 1990s after 3 years of...
- Economic rank, by nominal GDP (2007): 144th (one hundred and forty fourth)
- Agriculture in Barbados
- Banking in Barbados
- Central Bank of BarbadosCentral Bank of BarbadosThe Central Bank of Barbados is the national monetary authority responsible for providing advice to government of Barbados on banking and other financial and monetary matters. The Central Bank of Barbados, was established by Act of parliament on 2 May 1972...
- Communications in BarbadosCommunications in BarbadosCommunications in Barbados refers to the telephony, internet, postal, radio, and television systems of Barbados. Barbados has long been an informational and communications centre in the Caribbean region. Electricity coverage throughout Barbados is good and reliable. Usage is high and provided by...
- Internet in Barbados
- Companies of Barbados
- Currency of BarbadosCurrencyIn economics, currency refers to a generally accepted medium of exchange. These are usually the coins and banknotes of a particular government, which comprise the physical aspects of a nation's money supply...
: Dollar- ISO 4217ISO 4217ISO 4217 is a standard published by the International Standards Organization, which delineates currency designators, country codes , and references to minor units in three tables:* Table A.1 – Current currency & funds code list...
: BBD
- ISO 4217
- Economic history of Barbados
- Energy in Barbados
- Energy policy of Barbados
- Oil industry in Barbados
- Mining in Barbados
- Tourism in Barbados
- Transport in BarbadosTransport in BarbadosBarbados has of public paved roads; some historic, mostly unpaved railroad trail; two active marine ports , and one airport, the Sir Grantley Adams International Airport, located in Christ Church....
- Barbados Stock ExchangeBarbados Stock ExchangeThe Barbados Stock Exchange or BSE is Barbados' main stock exchange. Its headquarters are in the capital-city Bridgetown.The Barbados Stock Exchange is among the four major regional Caribbean stock exchanges. The other three being the exchanges of Jamaica, the Eastern Caribbean, and Trinidad and...
Infrastructure of Barbados
- Health care in Barbados
- Transportation in Barbados
- Airports in Barbados
- Port of BridgetownPort of BridgetownThe Port of Bridgetown , is a seaport in Bridgetown on the southwest coast of Barbados...
- Rail transport in Barbados
- Roads in Barbados
- Water supply and sanitation in Barbados
See also
- Commonwealth realmCommonwealth RealmA Commonwealth realm is a sovereign state within the Commonwealth of Nations that has Elizabeth II as its monarch and head of state. The sixteen current realms have a combined land area of 18.8 million km² , and a population of 134 million, of which all, except about two million, live in the six...
- Index of Barbados-related articles
- List of Barbados-related topics
- List of international rankings
- Member state of the Commonwealth of Nations
- Member state of the United Nations
- Monarchy of BarbadosMonarchy of BarbadosThe monarchy of Barbados is a constitutional system of government in which a hereditary monarch is the sovereign and head of state of Barbados, forming the core of the country's Westminster style parliamentary democracy...
- Outline of geographyOutline of geographyThe following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to geography:Geography – science that studies the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth.- Geography is :...
- Outline of North America
- Outline of the Caribbean
External links
- Barbados Government - official website
- Barbados Cricket Association
- Barbados Investment and Development Corporation
- Barbados Museum & Historical Society
- Barbados Statistical Service (BSS)
- Barbados Tourism Authority - The Ministry of Tourism
- Central Bank of Barbados website
- Parliament of Barbados official website
- Parliament of Barbados - Some facts about Barbados

