
Outline of Bulgaria
Encyclopedia
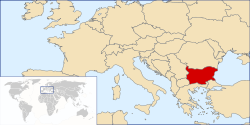
Sovereign state
A sovereign state, or simply, state, is a state with a defined territory on which it exercises internal and external sovereignty, a permanent population, a government, and the capacity to enter into relations with other sovereign states. It is also normally understood to be a state which is neither...
s in Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
. Bulgaria is located on the Balkan Peninsula in Southern Europe
Southern Europe
The term Southern Europe, at its most general definition, is used to mean "all countries in the south of Europe". However, the concept, at different times, has had different meanings, providing additional political, linguistic and cultural context to the definition in addition to the typical...
, bordering five other countries: Romania
Romania
Romania is a country located at the crossroads of Central and Southeastern Europe, on the Lower Danube, within and outside the Carpathian arch, bordering on the Black Sea...
to the north (mostly along the Danube
Danube
The Danube is a river in the Central Europe and the Europe's second longest river after the Volga. It is classified as an international waterway....
), Serbia
Serbia
Serbia , officially the Republic of Serbia , is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central and Southeast Europe, covering the southern part of the Carpathian basin and the central part of the Balkans...
and the Republic of Macedonia
Republic of Macedonia
Macedonia , officially the Republic of Macedonia , is a country located in the central Balkan peninsula in Southeast Europe. It is one of the successor states of the former Yugoslavia, from which it declared independence in 1991...
to the west, and Greece
Greece
Greece , officially the Hellenic Republic , and historically Hellas or the Republic of Greece in English, is a country in southeastern Europe....
and Turkey
Turkey
Turkey , known officially as the Republic of Turkey , is a Eurasian country located in Western Asia and in East Thrace in Southeastern Europe...
to the south. The Black Sea
Black Sea
The Black Sea is bounded by Europe, Anatolia and the Caucasus and is ultimately connected to the Atlantic Ocean via the Mediterranean and the Aegean seas and various straits. The Bosphorus strait connects it to the Sea of Marmara, and the strait of the Dardanelles connects that sea to the Aegean...
defines the extent of the country to the east.
Bulgaria comprises the classical
Ancient Rome
Ancient Rome was a thriving civilization that grew on the Italian Peninsula as early as the 8th century BC. Located along the Mediterranean Sea and centered on the city of Rome, it expanded to one of the largest empires in the ancient world....
regions of Moesia
Moesia
Moesia was an ancient region and later Roman province situated in the Balkans, along the south bank of the Danube River. It included territories of modern-day Southern Serbia , Northern Republic of Macedonia, Northern Bulgaria, Romanian Dobrudja, Southern Moldova, and Budjak .-History:In ancient...
, Thrace
Thrace
Thrace is a historical and geographic area in southeast Europe. As a geographical concept, Thrace designates a region bounded by the Balkan Mountains on the north, Rhodope Mountains and the Aegean Sea on the south, and by the Black Sea and the Sea of Marmara on the east...
, and Macedonia
Macedonia (region)
Macedonia is a geographical and historical region of the Balkan peninsula in southeastern Europe. Its boundaries have changed considerably over time, but nowadays the region is considered to include parts of five Balkan countries: Greece, the Republic of Macedonia, Bulgaria, Albania, Serbia, as...
. Old European culture in the region started to produce golden artifacts
Varna Necropolis
The Varna Necropolis is a burial site in the western industrial zone of Varna , Bulgaria, internationally considered one of the key archaeological sites in world prehistory...
by the fifth millennium BCE.
The country preserves the traditions (in ethnic name, language, and alphabet) of the First Bulgarian Empire
First Bulgarian Empire
The First Bulgarian Empire was a medieval Bulgarian state founded in the north-eastern Balkans in c. 680 by the Bulgars, uniting with seven South Slavic tribes...
(632/681 1018), which at times covered most of the Balkans and spread its alphabet, literature and culture among the Slavic
Slavic peoples
The Slavic people are an Indo-European panethnicity living in Eastern Europe, Southeast Europe, North Asia and Central Asia. The term Slavic represents a broad ethno-linguistic group of people, who speak languages belonging to the Slavic language family and share, to varying degrees, certain...
and other peoples of Eastern Europe. Centuries later, with the decline of the Second Bulgarian Empire
Second Bulgarian Empire
The Second Bulgarian Empire was a medieval Bulgarian state which existed between 1185 and 1396 . A successor of the First Bulgarian Empire, it reached the peak of its power under Kaloyan and Ivan Asen II before gradually being conquered by the Ottomans in the late 14th-early 15th century...
(1185 1396/1422), the country came under Ottoman
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman EmpireIt was usually referred to as the "Ottoman Empire", the "Turkish Empire", the "Ottoman Caliphate" or more commonly "Turkey" by its contemporaries...
rule for nearly five centuries. The Russo-Turkish War (1877-1878) re-established Bulgaria as a constitutional monarchy
Constitutional monarchy
Constitutional monarchy is a form of government in which a monarch acts as head of state within the parameters of a constitution, whether it be a written, uncodified or blended constitution...
in 1878, with the Treaty of San Stefano
Treaty of San Stefano
The Preliminary Treaty of San Stefano was a treaty between Russia and the Ottoman Empire signed at the end of the Russo-Turkish War, 1877–78...
marking the birth of the Third Bulgarian Kingdom. After World War II
World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
, Bulgaria became a communist state
Communist state
A communist state is a state with a form of government characterized by single-party rule or dominant-party rule of a communist party and a professed allegiance to a Leninist or Marxist-Leninist communist ideology as the guiding principle of the state...
and part of the Eastern Bloc
Eastern bloc
The term Eastern Bloc or Communist Bloc refers to the former communist states of Eastern and Central Europe, generally the Soviet Union and the countries of the Warsaw Pact...
. In 1990, after the Revolutions of 1989
Revolutions of 1989
The Revolutions of 1989 were the revolutions which overthrew the communist regimes in various Central and Eastern European countries.The events began in Poland in 1989, and continued in Hungary, East Germany, Bulgaria, Czechoslovakia and...
, the Communist party
Bulgarian Communist Party
The Bulgarian Communist Party was the communist and Marxist-Leninist ruling party of the People's Republic of Bulgaria from 1946 until 1990 when the country ceased to be a communist state...
gave up its monopoly on power and Bulgaria transitioned to democracy
Democracy
Democracy is generally defined as a form of government in which all adult citizens have an equal say in the decisions that affect their lives. Ideally, this includes equal participation in the proposal, development and passage of legislation into law...
and free-market capitalism.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Bulgaria:
General reference
- Pronunciation: bʌlˈɡɛəriə
- Common English country name: Bulgaria
- Official English country name: The Republic of Bulgaria
- Common endonym(s): България (Bulgariya)
- Official endonym(s): Република България (Republika Bulgariya)
- Adjectival(s): Bulgarian
- Demonym(s): Bulgarian
- EtymologyEtymologyEtymology is the study of the history of words, their origins, and how their form and meaning have changed over time.For languages with a long written history, etymologists make use of texts in these languages and texts about the languages to gather knowledge about how words were used during...
: Name of Bulgaria - International rankings of BulgariaInternational rankings of Bulgaria- Demographic rankings :- Economic rankings :- Political rankings :* 1Note: lower ranking at the FSI means more sustainable, and higher means more unstable.- Military rankings :...
- ISO country codes: BG, BGR, 100
- ISO region codes: See ISO 3166-2:BGISO 3166-2:BGISO 3166-2:BG is the entry for Bulgaria in ISO 3166-2, part of the ISO 3166 standard published by the International Organization for Standardization , which defines codes for the names of the principal subdivisions of all countries coded in ISO 3166-1.Currently for Bulgaria, ISO 3166-2 codes are...
- InternetInternetThe Internet is a global system of interconnected computer networks that use the standard Internet protocol suite to serve billions of users worldwide...
country code top-level domainCountry code top-level domainA country code top-level domain is an Internet top-level domain generally used or reserved for a country, a sovereign state, or a dependent territory....
: .bg.bgThe domain name .bg is the country code top-level domain in the Domain Name System of the Internet for Bulgaria. It is currently operated by Register.bg....
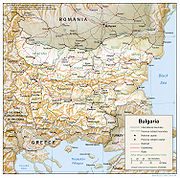
Geography of Bulgaria

- Bulgaria is: a country
- Location:
- Eastern HemisphereEastern HemisphereThe Eastern Hemisphere, also Eastern hemisphere or eastern hemisphere, is a geographical term for the half of the Earth that is east of the Prime Meridian and west of 180° longitude. It is also used to refer to Europe, Asia, Africa, and Australasia, vis-à-vis the Western Hemisphere, which includes...
- Northern HemisphereNorthern HemisphereThe Northern Hemisphere is the half of a planet that is north of its equator—the word hemisphere literally means “half sphere”. It is also that half of the celestial sphere north of the celestial equator...
- EurasiaEurasiaEurasia is a continent or supercontinent comprising the traditional continents of Europe and Asia ; covering about 52,990,000 km2 or about 10.6% of the Earth's surface located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres...
- EuropeEuropeEurope is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
- Eastern EuropeEastern EuropeEastern Europe is the eastern part of Europe. The term has widely disparate geopolitical, geographical, cultural and socioeconomic readings, which makes it highly context-dependent and even volatile, and there are "almost as many definitions of Eastern Europe as there are scholars of the region"...
- Southern EuropeSouthern EuropeThe term Southern Europe, at its most general definition, is used to mean "all countries in the south of Europe". However, the concept, at different times, has had different meanings, providing additional political, linguistic and cultural context to the definition in addition to the typical...
- BalkansBalkansThe Balkans is a geopolitical and cultural region of southeastern Europe...
(also known as "Southeastern Europe")
- Balkans
- Eastern Europe
- Europe
- Eurasia
- Time zoneTime zoneA time zone is a region on Earth that has a uniform standard time for legal, commercial, and social purposes. In order for the same clock time to always correspond to the same portion of the day as the Earth rotates , different places on the Earth need to have different clock times...
: Eastern European TimeEastern European TimeEastern European Time is one of the names of UTC+02:00 time zone, 2 hours ahead of Coordinated Universal Time. It is used in some European countries that also use Eastern European Summer Time as a summer daylight saving time.- Usage :...
(UTC+02), Eastern European Summer TimeEastern European Summer TimeEastern European Summer Time is one of the names of UTC+3 time zone, 3 hours ahead of Coordinated Universal Time. It is used as a summer daylight saving time in some European, North African, and Middle Eastern countries...
(UTC+03) - Extreme points of BulgariaExtreme points of BulgariaThe extreme points of Bulgaria include the coordinates that are further north, south, east or west than any other location in Bulgaria; and the highest and the lowest elevations in the country. Also included in this list is the southern-most Bulgaria station in Antarctica...
- High: MusalaMusalaMusala is the highest peak in Bulgaria and the entire Balkan Peninsula, standing at 2,925 m . The summit of the Rila mountain in southwestern Bulgaria, Musala is the highest peak between the Alps and the Caucasus and the highest in Eastern Europe bar the Caucasus.Between 1949–1962 the peak was...
2925 m (9,596 ft) - Low: Black SeaBlack SeaThe Black Sea is bounded by Europe, Anatolia and the Caucasus and is ultimately connected to the Atlantic Ocean via the Mediterranean and the Aegean seas and various straits. The Bosphorus strait connects it to the Sea of Marmara, and the strait of the Dardanelles connects that sea to the Aegean...
0 m
- High: Musala
- Land boundaries: 1,808 km
- Eastern Hemisphere
-
 Kingdom of Romania 608 km
Kingdom of Romania 608 km Greece 494 km
Greece 494 km Serbia 318 km
Serbia 318 km Turkey 240 km
Turkey 240 km Republic of Macedonia 148 km
Republic of Macedonia 148 km
- Coastline: 354 km
- Population of Bulgaria: 7,364,570 (2011) - 98th most populous country
- Area of Bulgaria: 110910 square kilometres (42,822.6 sq mi) - 112nd largest country
- Atlas of Bulgaria
Environment of Bulgaria

- Climate of Bulgaria
- Environmental issues in BulgariaEnvironmental issues in BulgariaEnvironmental issues in Bulgaria.Like other countries in the Soviet sphere, Bulgaria strongly emphasized heavy industry and intensive agriculture but did not mitigate the environmental consequences of such a policy...
- Ecoregions in Bulgaria
- Renewable energy in Bulgaria
- Geology of Bulgaria
- Protected areas of Bulgaria
- Biosphere reserves in Bulgaria
- National parks of Bulgaria
- Wildlife of Bulgaria
- Flora of Bulgaria
- Fauna of Bulgaria
Natural geographic features of Bulgaria
- Glaciers of Bulgaria
- Islands of Bulgaria
- Lakes of Bulgaria
- Mountains of Bulgaria
- Volcanoes in Bulgaria
- Rivers of Bulgaria
- Waterfalls of Bulgaria
- Valleys of Bulgaria
- World Heritage Sites in Bulgaria
Ecoregions of Bulgaria
- Main article: Ecoregions in Bulgaria
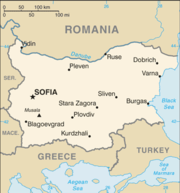
Administrative divisions of Bulgaria
- Main article: Administrative divisions of Bulgaria
- Provinces of BulgariaProvinces of BulgariaSince 1999, Bulgaria has been divided into 28 provinces which correspond approximately to the 28 districts that existed before 1987. In 1987, during the Communist regime of Todor Zhivkov, the districts were consolidated into nine larger provinces , which survived until 1999.Each province is named...
- Municipalities of BulgariaMunicipalities of BulgariaThe 28 provinces of Bulgaria are divided into 264 municipalities .-Blagoevgrad Province:# Bansko Municipality # Belitsa Municipality # Blagoevgrad Municipality...
- Municipalities of Bulgaria
Municipalities of Bulgaria
- Capital of Bulgaria: Sofia
- Cities and towns of Bulgaria
- Villages of Bulgaria
Demography of Bulgaria
- Main article: Demographics of BulgariaDemographics of BulgariaThis article is about the demographic features of the population of Bulgaria, including population density, ethnicity, education level, health of the populace, economic status, religious affiliations and other aspects of the population....
- BulgariansBulgariansThe Bulgarians are a South Slavic nation and ethnic group native to Bulgaria and neighbouring regions. Emigration has resulted in immigrant communities in a number of other countries.-History and ethnogenesis:...
- List of Bulgarians
- List of Presidents of Bulgaria
- List of Bulgarian monarchs
- List of Bulgarian actors and actresses
- List of Bulgarian writers
- List of Bulgarian composers
- List of Bulgarian musicians and singers
- List of Bulgarian architects
- List of Bulgarian footballers
- List of Bulgarians
Government and politics of Bulgaria
- Main article: Government of Bulgaria and Politics of BulgariaPolitics of BulgariaPolitics of Bulgaria take place in a framework of a parliamentary representative democratic republic, whereby the Prime minister is the head of government, and of a multi-party system. Executive power is exercised by the government. Legislative power is vested in both the government and the...
- Form of governmentForm of governmentA form of government, or form of state governance, refers to the set of political institutions by which a government of a state is organized. Synonyms include "regime type" and "system of government".-Empirical and conceptual problems:...
: parliamentary republicParliamentary republicA parliamentary republic or parliamentary constitutional republic is a type of republic which operates under a parliamentary system of government - meaning a system with no clear-cut separation of powers between the executive and legislative branches. There are a number of variations of... - Capital of Bulgaria: Sofia
- Elections in BulgariaElections in BulgariaElections in Bulgaria gives information on election and election results in Bulgaria.Bulgaria elects on national level a head of state - the president - and a legislature. The president is elected for a five year term by the people...
- (specific elections)
- Political parties in Bulgaria
- Political scandals of Bulgaria
- Taxation in Bulgaria
Executive branch of the government of Bulgaria
- Head of stateHead of StateA head of state is the individual that serves as the chief public representative of a monarchy, republic, federation, commonwealth or other kind of state. His or her role generally includes legitimizing the state and exercising the political powers, functions, and duties granted to the head of...
: President of Bulgaria, Georgi ParvanovGeorgi ParvanovGeorgi Sedefchov Parvanov is a President of Bulgaria, whose second and last mandate expires on January 22, 2012; he was elected after defeating his predecessor Petar Stoyanov in the second round of the presidential elections in November 2001 and he came into office on January 22, 2002... - Head of governmentHead of governmentHead of government is the chief officer of the executive branch of a government, often presiding over a cabinet. In a parliamentary system, the head of government is often styled prime minister, chief minister, premier, etc...
: Prime Minister of Bulgaria, Boyko BorisovBoyko BorisovBoyko Metodiev Borisov is a Bulgarian politician who has been Prime Minister of Bulgaria since July 2009. Previously he was Mayor of Sofia from 8 November 2005 until his election as Prime Minister.... - Cabinet of Bulgaria
Legislative branch of the government of Bulgaria
- National Assembly of BulgariaNational Assembly of BulgariaThe National Assembly of Bulgaria is the unicameral parliament and body of the legislative of the Republic of Bulgaria.The National Assembly of Bulgaria was established in 1879 with the Constitution of Bulgaria.-Ordinary National Assembly:...
(unicameral)
Judicial branch of the government of Bulgaria
- Supreme Court of Bulgaria
Foreign relations of Bulgaria
- Diplomatic missions in Bulgaria
- Diplomatic missions of BulgariaDiplomatic missions of BulgariaThis is a list of diplomatic missions of Bulgaria, excluding honorary consulates.-Europe:** Tirana ** Vienna ** Minsk ** Brussels ** Sarajevo ** Zagreb ** Prague...
International organization membership
The Republic of Bulgaria is a member of:- Australia GroupAustralia GroupThe Australia Group is an informal group of countries established in 1985 to help member countries to identify those of their exports which need to be controlled so as not to contribute to the spread of chemical and biological weapons .The group, initially consisting of 15 members, held its first...
- Bank for International SettlementsBank for International SettlementsThe Bank for International Settlements is an intergovernmental organization of central banks which "fosters international monetary and financial cooperation and serves as a bank for central banks." It is not accountable to any national government...
(BIS) - Black Sea Economic Cooperation Zone (BSEC)
- Central European InitiativeCentral European InitiativeThe Central European Initiative is a forum of regional cooperation in Central, Eastern and South Eastern Europe, counting 18 member states. It was formed in Budapest in 1989.-History:...
(CEI) - Council of EuropeCouncil of EuropeThe Council of Europe is an international organisation promoting co-operation between all countries of Europe in the areas of legal standards, human rights, democratic development, the rule of law and cultural co-operation...
(CE) - Euro-Atlantic Partnership CouncilEuro-Atlantic Partnership CouncilThe Euro-Atlantic Partnership Council , a NATO institution, is a multilateral forum created to improve relations between NATO and non-NATO countries in Europe and those parts of Asia on the European periphery. The member states meet to cooperate and consult on a range of political and security issues...
(EAPC) - European Bank for Reconstruction and DevelopmentEuropean Bank for Reconstruction and DevelopmentFounded in 1991, the European Bank for Reconstruction and Development uses the tools of investment to help build market economies and democracies in 30 countries from central Europe to central Asia. Its mission was to support the formerly communist countries in the process of establishing their...
(EBRD) - European Investment BankEuropean Investment BankThe European Investment Bank is the European Union's long-term lending institution established in 1958 under the Treaty of Rome. A policy-driven bank, the EIB supports the EU’s priority objectives, especially European integration and the development of economically weak regions...
(EIB) - European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN)
- European UnionEuropean UnionThe European Union is an economic and political union of 27 independent member states which are located primarily in Europe. The EU traces its origins from the European Coal and Steel Community and the European Economic Community , formed by six countries in 1958...
(EU) - Food and Agriculture OrganizationFood and Agriculture OrganizationThe Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations is a specialised agency of the United Nations that leads international efforts to defeat hunger. Serving both developed and developing countries, FAO acts as a neutral forum where all nations meet as equals to negotiate agreements and...
(FAO) - Group of 9Group of 9The Group of Nine was a group of nine European states that meet occasionally to discuss matters of mutual interest.-Members: The Group of Nine was a group of nine European states that meet occasionally to discuss matters of mutual interest.-Members: The Group of Nine was a group of nine...
(G9) - International Atomic Energy AgencyInternational Atomic Energy AgencyThe International Atomic Energy Agency is an international organization that seeks to promote the peaceful use of nuclear energy, and to inhibit its use for any military purpose, including nuclear weapons. The IAEA was established as an autonomous organization on 29 July 1957...
(IAEA) - International Bank for Reconstruction and DevelopmentInternational Bank for Reconstruction and DevelopmentThe International Bank for Reconstruction and Development is one of five institutions that compose the World Bank Group. The IBRD is an international organization whose original mission was to finance the reconstruction of nations devastated by World War II. Now, its mission has expanded to fight...
(IBRD) - International Chamber of CommerceInternational Chamber of CommerceThe International Chamber of Commerce is the largest, most representative business organization in the world. Its hundreds of thousands of member companies in over 130 countries have interests spanning every sector of private enterprise....
(ICC) - International Civil Aviation OrganizationInternational Civil Aviation OrganizationThe International Civil Aviation Organization , pronounced , , is a specialized agency of the United Nations. It codifies the principles and techniques of international air navigation and fosters the planning and development of international air transport to ensure safe and orderly growth...
(ICAO) - International Criminal CourtInternational Criminal CourtThe International Criminal Court is a permanent tribunal to prosecute individuals for genocide, crimes against humanity, war crimes, and the crime of aggression .It came into being on 1 July 2002—the date its founding treaty, the Rome Statute of the...
(ICCt) - International Criminal Police Organization (Interpol)
- International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent SocietiesInternational Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent SocietiesThe International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies is a humanitarian institution that is part of the International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement along with the ICRC and 186 distinct National Societies...
(IFRCS) - International Finance CorporationInternational Finance CorporationThe International Finance Corporation promotes sustainable private sector investment in developing countries.IFC is a member of the World Bank Group and is headquartered in Washington, D.C., United States....
(IFC) - International Labour OrganizationInternational Labour OrganizationThe International Labour Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations that deals with labour issues pertaining to international labour standards. Its headquarters are in Geneva, Switzerland. Its secretariat — the people who are employed by it throughout the world — is known as the...
(ILO) - International Maritime OrganizationInternational Maritime OrganizationThe International Maritime Organization , formerly known as the Inter-Governmental Maritime Consultative Organization , was established in Geneva in 1948, and came into force ten years later, meeting for the first time in 1959...
(IMO) - International Mobile Satellite OrganizationInternational Mobile Satellite OrganizationThe International Mobile Satellite Organization is the intergovernmental organization that oversees certain public satellite safety and security communication services provided via the Inmarsat satellites...
(IMSO) - International Monetary FundInternational Monetary FundThe International Monetary Fund is an organization of 187 countries, working to foster global monetary cooperation, secure financial stability, facilitate international trade, promote high employment and sustainable economic growth, and reduce poverty around the world...
(IMF) - International Olympic CommitteeInternational Olympic CommitteeThe International Olympic Committee is an international corporation based in Lausanne, Switzerland, created by Pierre de Coubertin on 23 June 1894 with Demetrios Vikelas as its first president...
(IOC) - International Organization for MigrationInternational Organization for MigrationThe International Organization for Migration is an intergovernmental organization. It was initially established in 1951 as the Intergovernmental Committee for European Migration to help resettle people displaced by World War II....
(IOM) - International Organization for StandardizationInternational Organization for StandardizationThe International Organization for Standardization , widely known as ISO, is an international standard-setting body composed of representatives from various national standards organizations. Founded on February 23, 1947, the organization promulgates worldwide proprietary, industrial and commercial...
(ISO) - International Red Cross and Red Crescent MovementInternational Red Cross and Red Crescent MovementThe International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement is an international humanitarian movement with approximately 97 million volunteers, members and staff worldwide which was founded to protect human life and health, to ensure respect for all human beings, and to prevent and alleviate human...
(ICRM) - International Telecommunication UnionInternational Telecommunication UnionThe International Telecommunication Union is the specialized agency of the United Nations which is responsible for information and communication technologies...
(ITU) - International Telecommunications Satellite OrganizationInternational Telecommunications Satellite OrganizationThe International Telecommunications Satellite Organization is an intergovernmental organisation charged with overseeing the public service obligations of Intelsat.-External links:*...
(ITSO)
- International Trade Union ConfederationInternational Trade Union ConfederationThe International Trade Union Confederation is the world's largest trade union federation. It was formed on November 1, 2006 out of the merger of the International Confederation of Free Trade Unions and the World Confederation of Labour...
(ITUC) - Inter-Parliamentary Union (IPU)
- Multilateral Investment Guarantee AgencyMultilateral Investment Guarantee AgencyThe Multilateral Investment Guarantee Agency is a member organization of the World Bank Group that offers political risk insurance. It was established to promote foreign direct investment into developing countries. MIGA was founded in 1988 with a capital base of $1 billion and is headquartered in...
(MIGA) - Nonaligned Movement (NAM) (guest)
- North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO)
- Nuclear Suppliers GroupNuclear Suppliers GroupNuclear Suppliers Group is a multinational body concerned with reducing nuclear proliferation by controlling the export and re-transfer of materials that may be applicable to nuclear weapon development and by improving safeguards and protection on existing materials.- History :It was founded in...
(NSG) - Organisation internationale de la Francophonie (OIF)
- Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe (OSCE)
- Organization for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons (OPCW)
- Organization of American StatesOrganization of American StatesThe Organization of American States is a regional international organization, headquartered in Washington, D.C., United States...
(OAS) (observer) - Permanent Court of ArbitrationPermanent Court of ArbitrationThe Permanent Court of Arbitration , is an international organization based in The Hague in the Netherlands.-History:The court was established in 1899 as one of the acts of the first Hague Peace Conference, which makes it the oldest institution for international dispute resolution.The creation of...
(PCA) - Southeast European Cooperative InitiativeSoutheast European Cooperative InitiativeThe Southeast European Cooperative Initiative, or the SECI, has been an initiative that, under the auspices of men like Erhard Busek and Richard Schifter, has been successful in providing stability in an unstable region and has found support in international organizations and countries...
(SECI) - United NationsUnited NationsThe United Nations is an international organization whose stated aims are facilitating cooperation in international law, international security, economic development, social progress, human rights, and achievement of world peace...
(UN) - United Nations Conference on Trade and DevelopmentUnited Nations Conference on Trade and DevelopmentThe United Nations Conference on Trade and Development was established in 1964 as a permanent intergovernmental body. It is the principal organ of the United Nations General Assembly dealing with trade, investment, and development issues....
(UNCTAD) - United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organization (UNESCO)
- United Nations Industrial Development OrganizationUnited Nations Industrial Development OrganizationThe United Nations Industrial Development Organization , French/Spanish acronym ONUDI, is a specialized agency in the United Nations system, headquartered in Vienna, Austria...
(UNIDO) - United Nations Mission in LiberiaUnited Nations Mission in LiberiaThe United Nations Mission in Liberia is a peace-keeping force established in September 2003 to monitor a ceasefire agreement in Liberia following the resignation of President Charles Taylor and the conclusion of the Second Liberian Civil War....
(UNMIL) - United Nations Mission in the Sudan (UNMIS)
- Universal Postal UnionUniversal Postal UnionThe Universal Postal Union is an international organization that coordinates postal policies among member nations, in addition to the worldwide postal system. The UPU contains four bodies consisting of the Congress, the Council of Administration , the Postal Operations Council and the...
(UPU) - Western European UnionWestern European UnionThe Western European Union was an international organisation tasked with implementing the Modified Treaty of Brussels , an amended version of the original 1948 Treaty of Brussels...
(WEU) (associate affiliate) - World Confederation of LabourWorld Confederation of LabourThe World Confederation of Labour was an international labour organization founded in 1920 and based in Europe. Totalitarian governments of the 1930s repressed the federation and imprisoned many of its leaders, limiting operations until the end of World War II...
(WCL) - World Customs OrganizationWorld Customs OrganizationThe World Customs Organization is an intergovernmental organization headquartered in Brussels, Belgium. With its worldwide membership, the WCO is recognized as the voice of the global customs community...
(WCO) - World Federation of Trade UnionsWorld Federation of Trade UnionsThe World Federation of Trade Unions was established in 1945 to replace the International Federation of Trade Unions. Its mission was to bring together trade unions across the world in a single international organization, much like the United Nations...
(WFTU) - World Health OrganizationWorld Health OrganizationThe World Health Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations that acts as a coordinating authority on international public health. Established on 7 April 1948, with headquarters in Geneva, Switzerland, the agency inherited the mandate and resources of its predecessor, the Health...
(WHO) - World Intellectual Property OrganizationWorld Intellectual Property OrganizationThe World Intellectual Property Organization is one of the 17 specialized agencies of the United Nations. WIPO was created in 1967 "to encourage creative activity, to promote the protection of intellectual property throughout the world"....
(WIPO) - World Meteorological OrganizationWorld Meteorological OrganizationThe World Meteorological Organization is an intergovernmental organization with a membership of 189 Member States and Territories. It originated from the International Meteorological Organization , which was founded in 1873...
(WMO) - World Tourism OrganizationWorld Tourism OrganizationThe World Tourism Organization , based in Madrid, Spain, is a United Nations agency dealing with questions relating to tourism. It compiles the World Tourism rankings. The World Tourism Organization is a significant global body, concerned with the collection and collation of statistical information...
(UNWTO) - World Trade OrganizationWorld Trade OrganizationThe World Trade Organization is an organization that intends to supervise and liberalize international trade. The organization officially commenced on January 1, 1995 under the Marrakech Agreement, replacing the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade , which commenced in 1948...
(WTO) - Zangger CommitteeZangger CommitteeThe Zangger Committee, also known as the Nuclear Exporters Committee, sprang from Article III.2 of the Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons which entered into force on March 5, 1970...
(ZC)
Law and order in Bulgaria
- Main article: Law of BulgariaLaw of BulgariaBulgarian law is a largely civil, as opposed to a common, law system, based on epitomes in the French and German systems. It still contains elements of Soviet legal thinking, atlhough these are now increasingly on the wane...
- Capital punishment in BulgariaCapital punishment in BulgariaCapital punishment in Bulgaria was abolished on December 12, 1998 with the last execution having been carried out by firing squad on November 4, 1989. The Parliament of Bulgaria had introduced a moratorium on July 7, 1990 and protocol number six of the European Convention on Human Rights came into...
- Constitution of BulgariaConstitution of BulgariaThe Constitution of Bulgaria is the supreme and basic law of the Republic of Bulgaria. The current constitution was adopted on 12 July 1991 by the 7th Grand National Assembly of Bulgaria, and defines the country as a unitary parliamentary republic...
- Crime in BulgariaCrime in BulgariaCrime in Bulgaria is combated by the Bulgarian police and other agencies.In 2006 the European Commission established goals for Bulgaria to improve it's fight against corruption and organised crime.- Human trafficking :...
- Human rights in BulgariaHuman rights in BulgariaAlthough Bulgaria joined the European Union in 2007, its compliance with human rights norms is far from perfect. Although the media have a record of unbiased reporting, Bulgaria’s lack of specific legislation protecting the media from state interference is a theoretical weakness. Conditions in...
- LGBT rights in Bulgaria
- Freedom of religion in BulgariaFreedom of religion in BulgariaThe constitution provides for freedom of religion, and other laws and policies contributed to the generally free practice of religion. However, the constitution designates Eastern Orthodox Christianity as the "traditional" religion, exempting it from having to register in court as required for all...
- Law enforcement in BulgariaLaw enforcement in BulgariaBulgarian law enforcement organisations are mainly subordinate to the Ministry of Interior. The National Police Service is responsible for combating general crime and supporting the operations of other law enforcement agencies, the National Investigative Service and the Central Office for Combating...
Military of Bulgaria
- Main article: Military of BulgariaMilitary of BulgariaThe Military of Bulgaria, officially the Bulgarian Army represents the Armed Forces of the Republic of Bulgaria. The Commander-in-Chief is the President of Bulgaria . The Ministry of Defence is in charge of political leadership while military command remains in the hands of the General Staff,...
- Command
- Commander-in-chiefCommander-in-ChiefA commander-in-chief is the commander of a nation's military forces or significant element of those forces. In the latter case, the force element may be defined as those forces within a particular region or those forces which are associated by function. As a practical term it refers to the military...
:- Ministry of Defence of BulgariaMinistry of Defence (Bulgaria)The Ministry of Defence of Bulgaria is the ministry charged with regulating the Military of Bulgaria.Since August 2005 , Minister of Defence was Veselin Bliznakov of the National Movement Simeon II, with Deputy Ministers Ivan Ivanov, Radoslav Bozadzhiev, Simeon Nikolov, Sonya Yankulova and Spas...
- Ministry of Defence of Bulgaria
- Commander-in-chief
- Forces
- Army of Bulgaria
- Navy of Bulgaria
- Air Force of Bulgaria
- Special forces of Bulgaria
- Military history of Bulgaria
- Military ranks of BulgariaMilitary ranks of Bulgaria-Army and Air Force ranks:-Navy ranks:-See also:*Ranks and insignia of NATO armies officers*Ranks and insignia of NATO armies enlisted- References :*...
History of Bulgaria
- Main article: History of BulgariaHistory of BulgariaThe history of Bulgaria spans from the first settlements on the lands of modern Bulgaria to its formation as a nation-state and includes the history of the Bulgarian people and their origin. The first traces of human presence on what is today Bulgaria date from 44,000 BC...
, Timeline of the history of Bulgaria, and Current events of Bulgaria
- Economic history of BulgariaEconomic history of BulgariaEconomic history of Bulgaria is the economic history of Bulgaria form the creation of the First Bulgarian Empire to now-a-days.Bulgarian economic history has six major economic periods: economy of First Bulgarian Empire and Second Bulgarian Empire , economy of Bulgarian people during Ottoman rule...
- Military history of Bulgaria
Culture of Bulgaria
- Main article: Culture of BulgariaCulture of BulgariaA number of ancient civilizations, most notably the Thracians, Ancient Greeks, Romans, Slavs, and especially Bulgars, have left their mark on the culture, history and heritage of Bulgaria. Because of this Bulgarian nation has one of the richest folk heritage in the world...
- Architecture of Bulgaria
- Cuisine of Bulgaria
- Ethnic minorities in Bulgaria
- Festivals in Bulgaria
- Humor in Bulgaria
- Languages of BulgariaLanguages of BulgariaThe official language of Bulgaria is Bulgarian. According to the 2001 census, 85.5% of the country's population speak Bulgarian natively. The most significant minority languages are Turkish, spoken by 9.6% of the population, and Romani, which is spoken by 3.1%....
- Media in Bulgaria
- National symbols of Bulgaria
- Coat of arms of BulgariaCoat of arms of BulgariaThe coat of arms of Bulgaria consists of a crowned golden lion rampant over a dark red shield; above the shield is the Bulgarian historical crown...
- Flag of BulgariaFlag of BulgariaThe flag of Bulgaria is a tricolour consisting of three equal-sized horizontal bands of white, green, and red. The flag was first adopted after the Russo-Turkish War , where Bulgaria gained independence. The national flag at times was charged with the state emblem, especially during the People's...
- National anthem of Bulgaria
- Coat of arms of Bulgaria
- People of Bulgaria
- Prostitution in Bulgaria
- Public holidays in BulgariaPublic holidays in BulgariaHolidays in Bulgaria:-Other Observances:* March 1 - Granny Martha Day * March 8 - Women's Day * Radio and Television Day on May 7...
- Records of Bulgaria
- Religion in BulgariaReligion in BulgariaBulgaria has been traditionally a Christian state since the adoption of Constantinople Christianity in 865, and therefore the dominant confession is Eastern Orthodoxy of the Bulgarian Orthodox Church...
- Buddhism in BulgariaBuddhism in BulgariaBuddhism is a small minority religion in Bulgaria, with about a thousand practitioners. The Vietnamese community in Bulgaria traditionally practices Mahayana Buddhism alongside Ancestor Worship, but the population of this community, which mostly hails from North Vietnam has declined from tens of...
- Christianity in Bulgaria
- Hinduism in BulgariaHinduism in BulgariaHinduism is a minor religion in Bulgaria.Hinduism spread to Bulgaria by ISKCON.ISKCON started spreading Krishna Consciousness to Bulgarians from 1996.-Indians in Bulgaria:...
- Islam in BulgariaIslam in BulgariaIslam is the largest minority religion in Bulgaria. According to the 2001 Census, the total number of Muslims in the country stood at 577,139, corresponding to 10 % of the population...
- Judaism in Bulgaria
- Sikhism in Bulgaria
- Buddhism in Bulgaria
- World Heritage Sites in Bulgaria
Art in Bulgaria
- Art in Bulgaria
- Cinema of BulgariaCinema of Bulgaria-Actors and actresses:*Nikolay Binev*Stoyan Bachvarov*Rusi Chanev*Georgi Cherkelov*Stefan Danailov*Itzhak Fintzi*Georgi Georgiev*Kiril Gospodinov*Stanislav Ianevski*Georgi Kaloyanchev*Velko Kanev*Apostol Karamitev*Nevena Kokanova*Todor Kolev...
- Literature of Bulgaria
- Music of BulgariaMusic of BulgariaThe music of Bulgaria refers to all forms of music associated with Bulgaria like classical, folk, popular music, etc. Bulgarian music is part of the Balkan tradition, which stretches across Southeastern Europe, and has its own distinctive sound...
- Television in Bulgaria
- Theatre in Bulgaria
Sports in Bulgaria
- Main article: Sports in Bulgaria
- Football in BulgariaFootball in BulgariaFootball is the most popular sport in Bulgaria. It was introduced in 1893–1894 by Swiss gymnastics teachers invited to the country...
- Bulgaria at the OlympicsBulgaria at the OlympicsBulgaria first participated at the Olympic Games at the inaugural 1896 Games, with a single gymnast. However, since Charles Champaud was a Swiss national living in Sofia, some sources credit his appearance to Switzerland instead....
Economy and infrastructure of Bulgaria
- Main article: Economy of BulgariaEconomy of BulgariaThe economy of Bulgaria functions on the principles of the free market, having a large private sector and a small, but strong public sector. Bulgaria is an industrialised upper-middle-income country according to the World Bank with a gross national income per capita of US$ 5,490 in 2008...
- Economic rank, by nominal GDP (2007): 73rd (seventy-third)
- Agriculture in BulgariaAgriculture in BulgariaPrior to World War II, agriculture in Bulgaria was the leading sector in the Bulgarian economy. In 1939, agriculture contributed 65 percent of NMP, and four out of every five Bulgarians were employed in agriculture. The importance and organization of Bulgarian agriculture changed drastically after...
- Banking in Bulgaria
- National Bank of Bulgaria
- Communications in BulgariaCommunications in BulgariaTelephones – main lines in use:2.3 million Telephones – mobile cellular:9.87 million Telephone system:...
- Internet in BulgariaInternet in Bulgaria-LAN:Local area network is the most common type of Internet access in Bulgaria. Over 60% of the consumers use this type of access because of the high speeds and good service. The biggest Internet service providers even offer fiber optic access, so-called fiber-to-building...
- Internet in Bulgaria
- Companies of Bulgaria
- Currency of BulgariaCurrencyIn economics, currency refers to a generally accepted medium of exchange. These are usually the coins and banknotes of a particular government, which comprise the physical aspects of a nation's money supply...
: LevBulgarian levThe lev is the currency of Bulgaria. It is divided in 100 stotinki . In archaic Bulgarian the word "lev" meant "lion".It is speculated that Bulgaria, as a member of the European Union will adopt the Euro in 2015 .- First lev, 1881–1952 :...
- ISO 4217ISO 4217ISO 4217 is a standard published by the International Standards Organization, which delineates currency designators, country codes , and references to minor units in three tables:* Table A.1 – Current currency & funds code list...
: BGNBGNBGN is a three letter acronym of:* BiGlycaN, protein* Bulgarian lev, ISO 4217 code for the currency of Bulgaria* United States Board on Geographic Names* Ben Gurion International Airport,...
- ISO 4217
- Economic history of BulgariaEconomic history of BulgariaEconomic history of Bulgaria is the economic history of Bulgaria form the creation of the First Bulgarian Empire to now-a-days.Bulgarian economic history has six major economic periods: economy of First Bulgarian Empire and Second Bulgarian Empire , economy of Bulgarian people during Ottoman rule...
- Energy in BulgariaEnergy in BulgariaEnergy in Bulgaria describes energy and electricity production, consumption and import in Bulgaria.Although Bulgaria is not very rich in natural fuels such as coal, oil and gas, it has very well developed energy sector which is of crucial importance for the Balkans and the whole South Eastern Europe...
- Energy policy of Bulgaria
- Oil industry in Bulgaria
- Health care in Bulgaria
- Mining in Bulgaria
- Bulgaria Stock Exchange
- Tourism in BulgariaTourism in BulgariaBulgaria is a country with a historical and cultural heritage, and attractive natural landscapes, one of the most visited tourist destinations in Southeast Europe. Tourism, as an industry, has been an important source of economic growth. In 2008 Bulgaria was visited by 8.9 million tourists,...
- Transport in BulgariaTransport in BulgariaTransport in Bulgaira is facilitated with road, air, rail, and water networks.- Air transport :After the second terminal of International Airport Sofia was built the total number of passengers rose and reached 3 230 696 in 2008, and in April 2011 Airport Sofia serviced 282 694 passengers, 13% more...
- Airports in Bulgaria
- Rail transport in Bulgaria
- Roads in Bulgaria
- Water supply and sanitation in Bulgaria
See also
- Index of Bulgaria-related articles
- List of Bulgaria-related topics
- List of international rankings
- Member state of the European UnionMember State of the European UnionA member state of the European Union is a state that is party to treaties of the European Union and has thereby undertaken the privileges and obligations that EU membership entails. Unlike membership of an international organisation, being an EU member state places a country under binding laws in...
- Member state of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization
- Member state of the United Nations
- Outline of Europe
- Outline of geographyOutline of geographyThe following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to geography:Geography – science that studies the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth.- Geography is :...

