
Outline of Luxembourg
Encyclopedia
Western Europe
Western Europe is a loose term for the collection of countries in the western most region of the European continents, though this definition is context-dependent and carries cultural and political connotations. One definition describes Western Europe as a geographic entity—the region lying in the...
, bordered by Belgium
Belgium
Belgium , officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a federal state in Western Europe. It is a founding member of the European Union and hosts the EU's headquarters, and those of several other major international organisations such as NATO.Belgium is also a member of, or affiliated to, many...
, France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
, and Germany
Germany
Germany , officially the Federal Republic of Germany , is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km2 and has a largely temperate seasonal climate...
. Luxembourg has a population of half a million people in an area of approximately 2,586 square kilometres (999 sq mi).
Luxembourg is a parliamentary representative democracy
Representative democracy
Representative democracy is a form of government founded on the principle of elected individuals representing the people, as opposed to autocracy and direct democracy...
with a constitutional monarchy
Constitutional monarchy
Constitutional monarchy is a form of government in which a monarch acts as head of state within the parameters of a constitution, whether it be a written, uncodified or blended constitution...
, ruled by a Grand Duke
Grand Duke
The title grand duke is used in Western Europe and particularly in Germanic countries for provincial sovereigns. Grand duke is of a protocolary rank below a king but higher than a sovereign duke. Grand duke is also the usual and established translation of grand prince in languages which do not...
. It is the world's only remaining sovereign Grand Duchy
Grand duchy
A grand duchy, sometimes referred to as a grand dukedom, is a territory whose head of state is a monarch, either a grand duke or grand duchess.Today Luxembourg is the only remaining grand duchy...
. The country has a highly developed economy, with the highest Gross Domestic Product per capita in the world (U.S. Central Intelligence Agency 2007). Its historic and strategic importance dates back to its founding as a Roman era
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire was the post-Republican period of the ancient Roman civilization, characterised by an autocratic form of government and large territorial holdings in Europe and around the Mediterranean....
fortress
Fortification
Fortifications are military constructions and buildings designed for defence in warfare and military bases. Humans have constructed defensive works for many thousands of years, in a variety of increasingly complex designs...
site and Frankish count's
County
A county is a jurisdiction of local government in certain modern nations. Historically in mainland Europe, the original French term, comté, and its equivalents in other languages denoted a jurisdiction under the sovereignty of a count A county is a jurisdiction of local government in certain...
castle
Castle
A castle is a type of fortified structure built in Europe and the Middle East during the Middle Ages by European nobility. Scholars debate the scope of the word castle, but usually consider it to be the private fortified residence of a lord or noble...
site in the Early Middle Ages
Early Middle Ages
The Early Middle Ages was the period of European history lasting from the 5th century to approximately 1000. The Early Middle Ages followed the decline of the Western Roman Empire and preceded the High Middle Ages...
. It was an important bastion along the Spanish road
Spanish Road
The "Spanish Road" was a military supply/trade route used from 1567–1620, which stretched from Northern Italy to the Low Countries. It crossed through relatively neutral territory, and was therefore Europe's most preferred military route...
when Spain was the principal European power
International Power
International Power PLC is an international electricity generator formed in 2000 by the demerger of National Power. It is headquartered at Senator House, 85 Queen Victoria Street in the City of London...
influencing the whole western hemisphere and beyond in the 14th–17th centuries.
Luxembourg is a founding member of the European Union
European Union
The European Union is an economic and political union of 27 independent member states which are located primarily in Europe. The EU traces its origins from the European Coal and Steel Community and the European Economic Community , formed by six countries in 1958...
, NATO, the United Nations
United Nations
The United Nations is an international organization whose stated aims are facilitating cooperation in international law, international security, economic development, social progress, human rights, and achievement of world peace...
, Benelux
Benelux
The Benelux is an economic union in Western Europe comprising three neighbouring countries, Belgium, the Netherlands, and Luxembourg. These countries are located in northwestern Europe between France and Germany...
, and the Western European Union
Western European Union
The Western European Union was an international organisation tasked with implementing the Modified Treaty of Brussels , an amended version of the original 1948 Treaty of Brussels...
, reflecting the political consensus in favour of economic
Economic integration
Economic integration refers to trade unification between different states by the partial or full abolishing of customs tariffs on trade taking place within the borders of each state...
, political, and military integration. The city of Luxembourg
Luxembourg (city)
The city of Luxembourg , also known as Luxembourg City , is a commune with city status, and the capital of the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg. It is located at the confluence of the Alzette and Pétrusse Rivers in southern Luxembourg...
, the capital and largest city, is the seat of several institutions and agencies of the European Union.
Luxembourg lies on the cultural divide between Romance Europe and Germanic
Germanic languages
The Germanic languages constitute a sub-branch of the Indo-European language family. The common ancestor of all of the languages in this branch is called Proto-Germanic , which was spoken in approximately the mid-1st millennium BC in Iron Age northern Europe...
Europe, borrowing customs from each of the distinct traditions. Luxembourg is a trilingual country; French
French language
French is a Romance language spoken as a first language in France, the Romandy region in Switzerland, Wallonia and Brussels in Belgium, Monaco, the regions of Quebec and Acadia in Canada, and by various communities elsewhere. Second-language speakers of French are distributed throughout many parts...
, German
German language
German is a West Germanic language, related to and classified alongside English and Dutch. With an estimated 90 – 98 million native speakers, German is one of the world's major languages and is the most widely-spoken first language in the European Union....
, and Luxembourgish
Luxembourgish language
Luxembourgish is a High German language spoken mainly in Luxembourg. About 320,000 people worldwide speak Luxembourgish.-Language family:...
are official languages. Although a secular state
Secular state
A secular state is a concept of secularism, whereby a state or country purports to be officially neutral in matters of religion, supporting neither religion nor irreligion. A secular state also claims to treat all its citizens equally regardless of religion, and claims to avoid preferential...
, Luxembourg is predominantly Roman Catholic.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Luxembourg:
General reference
- PronunciationInternational Phonetic AlphabetThe International Phonetic Alphabet "The acronym 'IPA' strictly refers [...] to the 'International Phonetic Association'. But it is now such a common practice to use the acronym also to refer to the alphabet itself that resistance seems pedantic...
: - Common English country name: LuxembourgLuxembourgLuxembourg , officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg , is a landlocked country in western Europe, bordered by Belgium, France, and Germany. It has two principal regions: the Oesling in the North as part of the Ardennes massif, and the Gutland in the south...
- Official English country name: The Grand Duchy of Luxembourg
- Common endonym(s):
- Official endonym(s):
- Adjectival(s): LuxembourgLuxembourgLuxembourg , officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg , is a landlocked country in western Europe, bordered by Belgium, France, and Germany. It has two principal regions: the Oesling in the North as part of the Ardennes massif, and the Gutland in the south...
- Demonym(s): Luxembourger
- EtymologyEtymologyEtymology is the study of the history of words, their origins, and how their form and meaning have changed over time.For languages with a long written history, etymologists make use of texts in these languages and texts about the languages to gather knowledge about how words were used during...
: Lucilinburhuc, little castle - International rankings of LuxembourgInternational rankings of Luxembourg-Economy:* International Monetary Fund: Income per capita in purchasing power parity ranked 1 out of 182 *United Nations Development Programme: Human Development Index ranked 24 out of 169 * ranked 28 out of 155...
- ISO country codes: LU, LUX, 442
- ISO region codes: See ISO 3166-2:LUISO 3166-2:LUISO 3166-2:LU is the entry for Luxembourg in ISO 3166-2, part of the ISO 3166 standard published by the International Organization for Standardization , which defines codes for the names of the principal subdivisions of all countries coded in ISO 3166-1.Currently for Luxembourg, ISO 3166-2 codes...
- InternetInternetThe Internet is a global system of interconnected computer networks that use the standard Internet protocol suite to serve billions of users worldwide...
country code top-level domainCountry code top-level domainA country code top-level domain is an Internet top-level domain generally used or reserved for a country, a sovereign state, or a dependent territory....
: .lu.lu.lu is the Internet country code top-level domain for Luxembourg. .lu domains are administered by Restena. Since February 1, 2010, the administrative contact no longer needs to be based in Luxembourg....
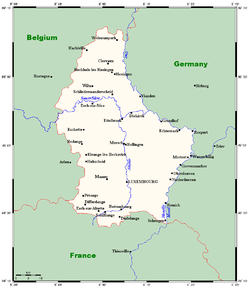
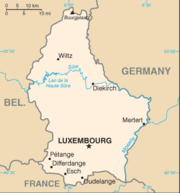
Geography of Luxembourg

- Luxembourg is: a landlocked country
- Location:
- Northern HemisphereNorthern HemisphereThe Northern Hemisphere is the half of a planet that is north of its equator—the word hemisphere literally means “half sphere”. It is also that half of the celestial sphere north of the celestial equator...
and Eastern HemisphereEastern HemisphereThe Eastern Hemisphere, also Eastern hemisphere or eastern hemisphere, is a geographical term for the half of the Earth that is east of the Prime Meridian and west of 180° longitude. It is also used to refer to Europe, Asia, Africa, and Australasia, vis-à-vis the Western Hemisphere, which includes... - EurasiaEurasiaEurasia is a continent or supercontinent comprising the traditional continents of Europe and Asia ; covering about 52,990,000 km2 or about 10.6% of the Earth's surface located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres...
- EuropeEuropeEurope is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
- Western EuropeWestern EuropeWestern Europe is a loose term for the collection of countries in the western most region of the European continents, though this definition is context-dependent and carries cultural and political connotations. One definition describes Western Europe as a geographic entity—the region lying in the...
- Western Europe
- Europe
- Time zoneTime zoneA time zone is a region on Earth that has a uniform standard time for legal, commercial, and social purposes. In order for the same clock time to always correspond to the same portion of the day as the Earth rotates , different places on the Earth need to have different clock times...
: Central European TimeCentral European TimeCentral European Time , used in most parts of the European Union, is a standard time that is 1 hour ahead of Coordinated Universal Time . The time offset from UTC can be written as +01:00...
(UTC+01), Central European Summer TimeCentral European Summer TimeCentral European Summer Time is one of the names of the Daylight saving time offset using the UTC offset of UTC+02:00, 2 hours ahead of Coordinated Universal Time. It is used as a summer daylight saving time in most European countries. During the winter, Central European Time is used...
(UTC+02) - Extreme points of Luxembourg
- High: KneiffKneiffKneiff is a hill in the commune of Troisvierges, in northern Luxembourg, near the tripoint shared with Belgium and Germany. At 560 metres, it is the highest point in the country; it is 1 m taller than Buurgplaatz, which is often erroneously considered Luxembourg's highest point. It lies close to...
560 m (1,837 ft) - Low: Moselle RiverMoselle RiverThe Moselle is a river flowing through France, Luxembourg, and Germany. It is a left tributary of the Rhine, joining the Rhine at Koblenz. A small part of Belgium is also drained by the Mosel through the Our....
133 m (436 ft)
- High: Kneiff
- Land boundaries: 359 km
- Northern Hemisphere
-
 Belgium 148 km
Belgium 148 km Germany 138 km
Germany 138 km Early Modern France 73 km
Early Modern France 73 km
- Coastline: none
- Population of LuxembourgLuxembourgLuxembourg , officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg , is a landlocked country in western Europe, bordered by Belgium, France, and Germany. It has two principal regions: the Oesling in the North as part of the Ardennes massif, and the Gutland in the south...
: 502,202 (2010 estimate) - 169th most populous country - Area of LuxembourgLuxembourgLuxembourg , officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg , is a landlocked country in western Europe, bordered by Belgium, France, and Germany. It has two principal regions: the Oesling in the North as part of the Ardennes massif, and the Gutland in the south...
: 2,586 km2 - Atlas of Luxembourg
Environment of Luxembourg

- Climate of Luxembourg
- Environmental issues in Luxembourg
- Ecoregions in Luxembourg
- Renewable energy in LuxembourgRenewable energy in the European UnionThe countries of the European Union are currently the number two global leaders in the development and application of renewable energy. Promoting the use of renewable energy sources is important both to the reduction of the EU's dependence on foreign energy imports, and in meeting targets to combat...
- Geology of Luxembourg
- Protected areas of Luxembourg
- Biosphere reserves in Luxembourg
- National parks of Luxembourg
- Wildlife of Luxembourg
- Flora of Luxembourg
- Fauna of Luxembourg
- Birds of Luxembourg
- Mammals of Luxembourg
Natural geographic features of Luxembourg
- Rivers of Luxembourg
- World Heritage Sites in Luxembourg
Ecoregions of Luxembourg
Administrative divisions of Luxembourg
- Districts of LuxembourgDistricts of LuxembourgThe three districts of Luxembourg are the top-level administrative divisions of the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg. The districts are further subdivided into cantons:#Diekirch District#*Diekirch#*Clervaux#*Redange#*Vianden#*Wiltz#Grevenmacher District...
- Cantons of LuxembourgCantons of Luxembourg||The districts of Luxembourg are divided into 12 cantons. These cantons are subdivided into 116 communes. The cantons, listed by district, include:Diekirch District*Clervaux *Diekirch *Redange *Vianden *Wiltz Grevenmacher District...
- Communes of LuxembourgCommunes of LuxembourgThe communes of Luxembourg are the lowest nation-wide administrative division in Luxembourg. They conform to LAU level 2.Within the hierarchy of administrative subdivisions, communes come directly below cantons, which are directly below districts. Communes are often re-arranged, being merged or...
- Communes of Luxembourg
- Cantons of Luxembourg
Municipalities of Luxembourg
- Capital of Luxembourg: Luxembourg City
- Cities of Luxembourg
Government and politics of Luxembourg
- Main article: Government of Luxembourg and Politics of LuxembourgPolitics of LuxembourgPolitics of Luxembourg takes place in a framework of a parliamentary representative democratic monarchy, whereby the Prime Minister of Luxembourg is the head of government, and of a multi-party system...
- Form of governmentForm of governmentA form of government, or form of state governance, refers to the set of political institutions by which a government of a state is organized. Synonyms include "regime type" and "system of government".-Empirical and conceptual problems:...
: - Capital of Luxembourg: Luxembourg City
- Elections in LuxembourgElections in LuxembourgElections in Luxembourg are held to determine the political composition of the representative institutions of Grand Duchy of Luxembourg. Luxembourg is a liberal representative democracy, with universal suffrage guaranteed under the constitution...
- (specific elections)
- Political parties in Luxembourg
- Political scandals of Luxembourg
- Taxation in Luxembourg
Executive branch of the government of Luxembourg
- Head of stateHead of StateA head of state is the individual that serves as the chief public representative of a monarchy, republic, federation, commonwealth or other kind of state. His or her role generally includes legitimizing the state and exercising the political powers, functions, and duties granted to the head of...
: Grand Duke of LuxembourgGrand Duke of LuxembourgThe Grand Duke of Luxembourg is the sovereign monarch and head of state of Luxembourg. Luxembourg has been a grand duchy since 15 March 1815, when it was elevated from a duchy when placed in personal union with the United Kingdom of the Netherlands...
, - Head of governmentHead of governmentHead of government is the chief officer of the executive branch of a government, often presiding over a cabinet. In a parliamentary system, the head of government is often styled prime minister, chief minister, premier, etc...
: Prime Minister of Luxembourg, - Cabinet of Luxembourg
Legislative branch of the government of Luxembourg
- Chamber of Deputies (Parliament) of Luxembourg (unicameral)
Judicial branch of the government of Luxembourg
- Supreme Court of Luxembourg
Foreign relations of Luxembourg
- Diplomatic missions in Luxembourg
- Diplomatic missions of LuxembourgDiplomatic missions of LuxembourgThis is a list of diplomatic missions of Luxembourg, excluding honorary consulates. It is represented by Belgium in countries that do not host a Luxembourgish diplomatic mission.-Europe:** Vienna ** Brussels ** Prague...
International organization membership
The Grand Duchy of Luxembourg is a member of:- Asian Development BankAsian Development BankThe Asian Development Bank is a regional development bank established on 22 August 1966 to facilitate economic development of countries in Asia...
(ADB) (nonregional member) - Australia GroupAustralia GroupThe Australia Group is an informal group of countries established in 1985 to help member countries to identify those of their exports which need to be controlled so as not to contribute to the spread of chemical and biological weapons .The group, initially consisting of 15 members, held its first...
- Benelux Economic Union (Benelux)
- Council of EuropeCouncil of EuropeThe Council of Europe is an international organisation promoting co-operation between all countries of Europe in the areas of legal standards, human rights, democratic development, the rule of law and cultural co-operation...
(CE) - Economic and Monetary UnionEconomic and monetary unionAn economic and monetary union is a type of trade bloc which is composed of an economic union with a monetary union. It is to be distinguished from a mere monetary union , which does not involve a common market. This is the fifth stage of economic integration...
(EMU) - Euro-Atlantic Partnership CouncilEuro-Atlantic Partnership CouncilThe Euro-Atlantic Partnership Council , a NATO institution, is a multilateral forum created to improve relations between NATO and non-NATO countries in Europe and those parts of Asia on the European periphery. The member states meet to cooperate and consult on a range of political and security issues...
(EAPC) - European Bank for Reconstruction and DevelopmentEuropean Bank for Reconstruction and DevelopmentFounded in 1991, the European Bank for Reconstruction and Development uses the tools of investment to help build market economies and democracies in 30 countries from central Europe to central Asia. Its mission was to support the formerly communist countries in the process of establishing their...
(EBRD) - European Investment BankEuropean Investment BankThe European Investment Bank is the European Union's long-term lending institution established in 1958 under the Treaty of Rome. A policy-driven bank, the EIB supports the EU’s priority objectives, especially European integration and the development of economically weak regions...
(EIB) - European Space AgencyEuropean Space AgencyThe European Space Agency , established in 1975, is an intergovernmental organisation dedicated to the exploration of space, currently with 18 member states...
(ESA) - European UnionEuropean UnionThe European Union is an economic and political union of 27 independent member states which are located primarily in Europe. The EU traces its origins from the European Coal and Steel Community and the European Economic Community , formed by six countries in 1958...
(EU) - Food and Agriculture OrganizationFood and Agriculture OrganizationThe Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations is a specialised agency of the United Nations that leads international efforts to defeat hunger. Serving both developed and developing countries, FAO acts as a neutral forum where all nations meet as equals to negotiate agreements and...
(FAO) - International Atomic Energy AgencyInternational Atomic Energy AgencyThe International Atomic Energy Agency is an international organization that seeks to promote the peaceful use of nuclear energy, and to inhibit its use for any military purpose, including nuclear weapons. The IAEA was established as an autonomous organization on 29 July 1957...
(IAEA) - International Bank for Reconstruction and DevelopmentInternational Bank for Reconstruction and DevelopmentThe International Bank for Reconstruction and Development is one of five institutions that compose the World Bank Group. The IBRD is an international organization whose original mission was to finance the reconstruction of nations devastated by World War II. Now, its mission has expanded to fight...
(IBRD) - International Chamber of CommerceInternational Chamber of CommerceThe International Chamber of Commerce is the largest, most representative business organization in the world. Its hundreds of thousands of member companies in over 130 countries have interests spanning every sector of private enterprise....
(ICC) - International Civil Aviation OrganizationInternational Civil Aviation OrganizationThe International Civil Aviation Organization , pronounced , , is a specialized agency of the United Nations. It codifies the principles and techniques of international air navigation and fosters the planning and development of international air transport to ensure safe and orderly growth...
(ICAO) - International Criminal CourtInternational Criminal CourtThe International Criminal Court is a permanent tribunal to prosecute individuals for genocide, crimes against humanity, war crimes, and the crime of aggression .It came into being on 1 July 2002—the date its founding treaty, the Rome Statute of the...
(ICCt) - International Criminal Police Organization (Interpol)
- International Development AssociationInternational Development AssociationThe International Development Association , is the part of the World Bank that helps the world’s poorest countries. It complements the World Bank's other lending arm — the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development — which serves middle-income countries with capital investment and...
(IDA) - International Energy AgencyInternational Energy AgencyThe International Energy Agency is a Paris-based autonomous intergovernmental organization established in the framework of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development in 1974 in the wake of the 1973 oil crisis...
(IEA) - International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent SocietiesInternational Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent SocietiesThe International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies is a humanitarian institution that is part of the International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement along with the ICRC and 186 distinct National Societies...
(IFRCS) - International Finance CorporationInternational Finance CorporationThe International Finance Corporation promotes sustainable private sector investment in developing countries.IFC is a member of the World Bank Group and is headquartered in Washington, D.C., United States....
(IFC) - International Fund for Agricultural DevelopmentInternational Fund for Agricultural DevelopmentThe International Fund for Agricultural Development , a specialized agency of the United Nations, was established as an international financial institution in 1977 as one of the major outcomes of the 1974 World Food Conference. IFAD is dedicated to eradicating rural poverty in developing countries...
(IFAD) - International Labour OrganizationInternational Labour OrganizationThe International Labour Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations that deals with labour issues pertaining to international labour standards. Its headquarters are in Geneva, Switzerland. Its secretariat — the people who are employed by it throughout the world — is known as the...
(ILO) - International Maritime OrganizationInternational Maritime OrganizationThe International Maritime Organization , formerly known as the Inter-Governmental Maritime Consultative Organization , was established in Geneva in 1948, and came into force ten years later, meeting for the first time in 1959...
(IMO) - International Monetary FundInternational Monetary FundThe International Monetary Fund is an organization of 187 countries, working to foster global monetary cooperation, secure financial stability, facilitate international trade, promote high employment and sustainable economic growth, and reduce poverty around the world...
(IMF) - International Olympic CommitteeInternational Olympic CommitteeThe International Olympic Committee is an international corporation based in Lausanne, Switzerland, created by Pierre de Coubertin on 23 June 1894 with Demetrios Vikelas as its first president...
(IOC) - International Organization for MigrationInternational Organization for MigrationThe International Organization for Migration is an intergovernmental organization. It was initially established in 1951 as the Intergovernmental Committee for European Migration to help resettle people displaced by World War II....
(IOM) - International Organization for StandardizationInternational Organization for StandardizationThe International Organization for Standardization , widely known as ISO, is an international standard-setting body composed of representatives from various national standards organizations. Founded on February 23, 1947, the organization promulgates worldwide proprietary, industrial and commercial...
(ISO) - International Red Cross and Red Crescent MovementInternational Red Cross and Red Crescent MovementThe International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement is an international humanitarian movement with approximately 97 million volunteers, members and staff worldwide which was founded to protect human life and health, to ensure respect for all human beings, and to prevent and alleviate human...
(ICRM) - International Telecommunication UnionInternational Telecommunication UnionThe International Telecommunication Union is the specialized agency of the United Nations which is responsible for information and communication technologies...
(ITU) - International Telecommunications Satellite OrganizationInternational Telecommunications Satellite OrganizationThe International Telecommunications Satellite Organization is an intergovernmental organisation charged with overseeing the public service obligations of Intelsat.-External links:*...
(ITSO)
- International Trade Union ConfederationInternational Trade Union ConfederationThe International Trade Union Confederation is the world's largest trade union federation. It was formed on November 1, 2006 out of the merger of the International Confederation of Free Trade Unions and the World Confederation of Labour...
(ITUC) - Inter-Parliamentary Union (IPU)
- Multilateral Investment Guarantee AgencyMultilateral Investment Guarantee AgencyThe Multilateral Investment Guarantee Agency is a member organization of the World Bank Group that offers political risk insurance. It was established to promote foreign direct investment into developing countries. MIGA was founded in 1988 with a capital base of $1 billion and is headquartered in...
(MIGA) - North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO)
- Nuclear Energy AgencyNuclear Energy AgencyThe Nuclear Energy Agency is an intergovernmental multinational agency that is organized under the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development...
(NEA) - Nuclear Suppliers GroupNuclear Suppliers GroupNuclear Suppliers Group is a multinational body concerned with reducing nuclear proliferation by controlling the export and re-transfer of materials that may be applicable to nuclear weapon development and by improving safeguards and protection on existing materials.- History :It was founded in...
(NSG) - Organisation internationale de la Francophonie (OIF)
- Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD)
- Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe (OSCE)
- Organization for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons (OPCW)
- Organization of American StatesOrganization of American StatesThe Organization of American States is a regional international organization, headquartered in Washington, D.C., United States...
(OAS) (observer) - Permanent Court of ArbitrationPermanent Court of ArbitrationThe Permanent Court of Arbitration , is an international organization based in The Hague in the Netherlands.-History:The court was established in 1899 as one of the acts of the first Hague Peace Conference, which makes it the oldest institution for international dispute resolution.The creation of...
(PCA) - Schengen Convention
- United NationsUnited NationsThe United Nations is an international organization whose stated aims are facilitating cooperation in international law, international security, economic development, social progress, human rights, and achievement of world peace...
(UN) - United Nations Conference on Trade and DevelopmentUnited Nations Conference on Trade and DevelopmentThe United Nations Conference on Trade and Development was established in 1964 as a permanent intergovernmental body. It is the principal organ of the United Nations General Assembly dealing with trade, investment, and development issues....
(UNCTAD) - United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organization (UNESCO)
- United Nations High Commissioner for RefugeesUnited Nations High Commissioner for RefugeesThe Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees , also known as The UN Refugee Agency is a United Nations agency mandated to protect and support refugees at the request of a government or the UN itself and assists in their voluntary repatriation, local integration or resettlement to...
(UNHCR) - United Nations Industrial Development OrganizationUnited Nations Industrial Development OrganizationThe United Nations Industrial Development Organization , French/Spanish acronym ONUDI, is a specialized agency in the United Nations system, headquartered in Vienna, Austria...
(UNIDO) - United Nations Interim Force in LebanonUnited Nations Interim Force in LebanonThe United Nations Interim Force in Lebanon, or UNIFIL, was created by the United Nations, with the adoption of Security Council Resolution 425 and 426 on 19 March 1978, to confirm Israeli withdrawal from Lebanon which Israel had invaded five days prior, restore international peace and security,...
(UNIFIL) - United Nations Relief and Works Agency for Palestine Refugees in the Near EastUnited Nations Relief and Works Agency for Palestine Refugees in the Near EastUnited Nations Relief and Works Agency for Palestine Refugees in the Near East is a relief and human development agency, providing education, health care, social services and emergency aid to 5 million Palestine refugees living in Jordan, Lebanon and Syria, as well as in the West Bank and the Gaza...
(UNRWA) - Universal Postal UnionUniversal Postal UnionThe Universal Postal Union is an international organization that coordinates postal policies among member nations, in addition to the worldwide postal system. The UPU contains four bodies consisting of the Congress, the Council of Administration , the Postal Operations Council and the...
(UPU) - Western European UnionWestern European UnionThe Western European Union was an international organisation tasked with implementing the Modified Treaty of Brussels , an amended version of the original 1948 Treaty of Brussels...
(WEU) - World Confederation of LabourWorld Confederation of LabourThe World Confederation of Labour was an international labour organization founded in 1920 and based in Europe. Totalitarian governments of the 1930s repressed the federation and imprisoned many of its leaders, limiting operations until the end of World War II...
(WCL) - World Customs OrganizationWorld Customs OrganizationThe World Customs Organization is an intergovernmental organization headquartered in Brussels, Belgium. With its worldwide membership, the WCO is recognized as the voice of the global customs community...
(WCO) - World Federation of Trade UnionsWorld Federation of Trade UnionsThe World Federation of Trade Unions was established in 1945 to replace the International Federation of Trade Unions. Its mission was to bring together trade unions across the world in a single international organization, much like the United Nations...
(WFTU) - World Health OrganizationWorld Health OrganizationThe World Health Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations that acts as a coordinating authority on international public health. Established on 7 April 1948, with headquarters in Geneva, Switzerland, the agency inherited the mandate and resources of its predecessor, the Health...
(WHO) - World Intellectual Property OrganizationWorld Intellectual Property OrganizationThe World Intellectual Property Organization is one of the 17 specialized agencies of the United Nations. WIPO was created in 1967 "to encourage creative activity, to promote the protection of intellectual property throughout the world"....
(WIPO) - World Meteorological OrganizationWorld Meteorological OrganizationThe World Meteorological Organization is an intergovernmental organization with a membership of 189 Member States and Territories. It originated from the International Meteorological Organization , which was founded in 1873...
(WMO) - World Trade OrganizationWorld Trade OrganizationThe World Trade Organization is an organization that intends to supervise and liberalize international trade. The organization officially commenced on January 1, 1995 under the Marrakech Agreement, replacing the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade , which commenced in 1948...
(WTO) - Zangger CommitteeZangger CommitteeThe Zangger Committee, also known as the Nuclear Exporters Committee, sprang from Article III.2 of the Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons which entered into force on March 5, 1970...
(ZC)
Law and order in Luxembourg
- Capital punishment in Luxembourg
- Constitution of LuxembourgConstitution of LuxembourgThe Constitution of Luxembourg is the supreme law of the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg. The modern constitution was adopted on 17 October 1868.Whilst the constitution of 1868 marked a radical change in Luxembourg's constitutional settlement, it was technically an amendment of the original constitution...
- Crime in Luxembourg
- Human rights in Luxembourg
- LGBT rights in Luxembourg
- Freedom of religion in Luxembourg
- Law enforcement in Luxembourg
Military of Luxembourg
- Command
- Commander-in-chiefCommander-in-ChiefA commander-in-chief is the commander of a nation's military forces or significant element of those forces. In the latter case, the force element may be defined as those forces within a particular region or those forces which are associated by function. As a practical term it refers to the military...
:- Ministry of Defence of Luxembourg
- Commander-in-chief
- Forces
- Army of Luxembourg
- NavyNavyA navy is the branch of a nation's armed forces principally designated for naval and amphibious warfare; namely, lake- or ocean-borne combat operations and related functions...
of Luxembourg: None - Air Force of Luxembourg
- Special forces of Luxembourg
- Military history of LuxembourgMilitary history of LuxembourgThe military history of Luxembourg is central to the formation of Luxembourg as a nation from its formation around Luxembourg Castle in 693. A place of strategic military significance, Luxembourg had been a fortified since the 10th century by over of walls and towers...
- Military ranks of Luxembourg
History of Luxembourg
- Main article: History of LuxembourgHistory of LuxembourgThe history of Luxembourg is inherently entwined with the histories of surrounding countries, peoples, and ruling dynasties. Over time, the territory of Luxembourg has been eroded, whilst its ownership has changed repeatedly, and its political independence has grown gradually.'Although recorded...
, Timeline of the history of Luxembourg, and Current events of Luxembourg
- Economic history of Luxembourg
- Military history of LuxembourgMilitary history of LuxembourgThe military history of Luxembourg is central to the formation of Luxembourg as a nation from its formation around Luxembourg Castle in 693. A place of strategic military significance, Luxembourg had been a fortified since the 10th century by over of walls and towers...
Culture of Luxembourg
- Architecture of LuxembourgArchitecture of LuxembourgThe architecture of Luxembourg probably extends back to the Treveri, a Celtic tribe who prospered in the 1st century BC. A few ruins remain from the Roman occupation but the most significant contributions over the centuries have been the country's castles and churches...
- Cuisine of Luxembourg
- Ethnic minorities in Luxembourg
- Festivals in Luxembourg
- Humor in Luxembourg
- Languages of LuxembourgLanguages of LuxembourgThe linguistic situation in Luxembourg is characterised by the practice and the recognition of three official languages: French and German and the national language Luxembourgish established in law in 1984...
- Luxembourg American Cultural Society
- Media in Luxembourg
- National symbols of LuxembourgNational symbols of LuxembourgThere are a number of national symbols of Luxembourg, representing Luxembourg or its people in either official or unofficial capacities.Note that, under Luxembourgian law, the term 'national emblem' is a strictly-defined term that refers to only four of Luxembourg's official symbols of the state:...
- Coat of arms of LuxembourgCoat of arms of LuxembourgThe coat of arms of Luxembourg has its origins in the Middle Ages, and was derived from that of the Duchy of Limburg, in modern day Belgium and the Netherlands...
- Flag of LuxembourgFlag of LuxembourgThe flag of Luxembourg consists of three horizontal stripes, red, white and blue, and can be in 1:2 or 3:5 ratio. It was first used between 1845 and 1848 and officially adopted on June 23, 1972....
- National anthem of Luxembourg
- Coat of arms of Luxembourg
- People of Luxembourg
- Prostitution in Luxembourg
- Public holidays in Luxembourg
- Records of Luxembourg
- Religion in LuxembourgReligion in LuxembourgThere are many active religions in Luxembourg. The most important, in terms of size of congregation and historical importance, is Roman Catholicism, but the state does not support, or discriminate against, any one single religion.-Demographics:...
- Buddhism in Luxembourg
- Christianity in Luxembourg
- Hinduism in Luxembourg
- Islam in LuxembourgIslam in LuxembourgMuslims in Luxembourg are a super-minority together with: Protestants, Orthodox Christians, and Jews. Since 2008, Islam is legally recognized in the country....
- Judaism in Luxembourg
- Sikhism in Luxembourg
- World Heritage Sites in Luxembourg
Art in Luxembourg
- Architecture of LuxembourgArchitecture of LuxembourgThe architecture of Luxembourg probably extends back to the Treveri, a Celtic tribe who prospered in the 1st century BC. A few ruins remain from the Roman occupation but the most significant contributions over the centuries have been the country's castles and churches...
- Photography in LuxembourgPhotography in LuxembourgPhotography in Luxembourg is often associated with two figures who were born in Luxembourg but left when very young: Edward Steichen was an American who made outstanding contributions to fashion and military photography during the first half of the 20th century; while Gabriel Lippmann , a...
- Cinema of LuxembourgCinema of LuxembourgThe Luxembourg film industry is quite small, but this is unsurprising given that the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg has a population of only about 400,000 people...
- Literature of Luxembourg
- Music of LuxembourgMusic of LuxembourgThe Music of Luxembourg is an important component of the country's cultural life. The prestigious new Philharmonie concert hall provides an excellent venue for orchestral concerts while opera is frequently presented in the theatres. Rock, pop and jazz are also popular with a number of successful...
- Television in Luxembourg
- Theatre in Luxembourg
Sports in Luxembourg
- Football in LuxembourgFootball in LuxembourgFootball is the most popular sport in Luxembourg. Football in Luxembourg is governed by the Luxembourg Football Federation , which is a member of FIFA and UEFA. The FLF organises the men's, women's and futsal national teams. In additional to the main domestic competitions: the National Division...
- Luxembourg at the Olympics
Economy and infrastructure of Luxembourg
- Economic rank, by nominal GDP (2007): 65th (sixty-fifth)
- Agriculture in Luxembourg
- Banking in Luxembourg
- National Bank of Luxembourg
- Communications in LuxembourgCommunications in LuxembourgTelephones - main lines in use:314,700 Telephones - mobile cellular:215,741 Telephone system:highly developed, completely automated and efficient system, mainly buried cablesdomestic:...
- Internet in Luxembourg
- Companies of Luxembourg
- Currency of LuxembourgCurrencyIn economics, currency refers to a generally accepted medium of exchange. These are usually the coins and banknotes of a particular government, which comprise the physical aspects of a nation's money supply...
: EuroEuroThe euro is the official currency of the eurozone: 17 of the 27 member states of the European Union. It is also the currency used by the Institutions of the European Union. The eurozone consists of Austria, Belgium, Cyprus, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Ireland, Italy, Luxembourg,...
(see also: Euro topics)- ISO 4217ISO 4217ISO 4217 is a standard published by the International Standards Organization, which delineates currency designators, country codes , and references to minor units in three tables:* Table A.1 – Current currency & funds code list...
: EUREuroThe euro is the official currency of the eurozone: 17 of the 27 member states of the European Union. It is also the currency used by the Institutions of the European Union. The eurozone consists of Austria, Belgium, Cyprus, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Ireland, Italy, Luxembourg,...
- ISO 4217
- Economic history of Luxembourg
- Energy in LuxembourgEnergy in LuxembourgEnergy in Luxembourg describes energy and electricity production, consumption and import in Luxembourg. Energy policy of Luxembourg will describe the politics of Luxembourg related to energy more in detail. Electricity sector in Luxembourg is the main article of electricity in Luxembourg.Luxembourg...
- Energy policy of Luxembourg
- Oil industry in Luxembourg
- Mining in Luxembourg
- Tourism in LuxembourgTourism in LuxembourgTourism in Luxembourg is an important component of the national economy, representing about 8.3% of GDP in 2009 and employing some 25,000 people or 11.7% of the working population. Despite the current crisis, the Grand Duchy still welcomes over 900,000 visitors a year who spend an average of 2.5...
- Transport in LuxembourgTransport in LuxembourgTransport in Luxembourg is ensured principally by road, rail and air. There are also services along the River Moselle which forms the border with Germany. The road network has been significantly modernised in recent years with motorways to adjacent countries...
- Luxembourg Stock ExchangeLuxembourg Stock ExchangeThe Luxembourg Stock Exchange is a stock exchange based in Luxembourg City, in southern Luxembourg.The Exchange is located on avenue de la Porte-Neuve,...
Infrastructure of Luxembourg
- Health care in Luxembourg
- Transportation in Luxembourg
- Airports in Luxembourg
- Rail transport in Luxembourg
- Roads in Luxembourg
- Water supply and sanitation in Luxembourg
See also
- Index of Luxembourg-related articles
- List of international rankings
- List of Luxembourg-related topics
- Member state of the European UnionMember State of the European UnionA member state of the European Union is a state that is party to treaties of the European Union and has thereby undertaken the privileges and obligations that EU membership entails. Unlike membership of an international organisation, being an EU member state places a country under binding laws in...
- Member state of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization
- Member state of the United Nations
- Outline of Europe
- Outline of geographyOutline of geographyThe following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to geography:Geography – science that studies the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth.- Geography is :...
- Ranked list of Luxembourg cantonsRanked list of Luxembourg cantonsThese are ranked lists of the cantons of Luxembourg. Population figures are from 2005 estimates.-By population:-By area:-By density:...
External links
- Governments on the WWW: Luxembourg
- History of Luxembourg: Primary Documents
- Official Governmental Site
- Official Website for Luxembourg
- Luxembourg National Tourist Office
- Luxembourg Tourist Office - London
- Luxembourg City Tourist Guide
- Luxembourg Geography
- Luxembourg European Capital of Culture 2007
- World Factbook: Information on Luxembourg
- Over 200 images of important sights in Luxembourg
- Chabad Lubavitch of Luxembourg
- Worldwide Governance Indicators for Luxembourg, 1996-2006
- Luxembourg Earth science portal

