
Parvocellular part
Encyclopedia
Parvocellular cells, also called P-cells, are neuron
s located within the parvocellular layers of the lateral geniculate nucleus
(LGN) of the thalamus
. "Parvus" means "small" in Latin
, and the name "parvocellular" refers to the small size of the cell compared to the larger magnocellular cells. Phylogenetically, parvocellular neurons are more modern than magnocellular ones.
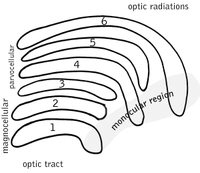 The parvocellular neurons of the visual system
The parvocellular neurons of the visual system
receive their input from midget cell
s, a type of retinal ganglion cell, whose axons are exiting the optic tract
. These synapse
s occur in one of the four dorsal parvocellular layers of the lateral geniculate nucleus. The information from each eye is kept separate at this point, and continues to be segrated until processing in the visual cortex
. The electrically-encoded visual information leaves the parvocellular cells via relay cells
in the optic radiation
s, traveling to the primary visual cortex layer 4C-β. The parvocellular neurons are sensitive to color, and are more capable of discriminating fine details than their magnocellular counterparts. Parvocellular cells have greater spatial resolution, but lower temporal resolution, than the magnocellular cells.
Neuron
A neuron is an electrically excitable cell that processes and transmits information by electrical and chemical signaling. Chemical signaling occurs via synapses, specialized connections with other cells. Neurons connect to each other to form networks. Neurons are the core components of the nervous...
s located within the parvocellular layers of the lateral geniculate nucleus
Lateral geniculate nucleus
The lateral geniculate nucleus is the primary relay center for visual information received from the retina of the eye. The LGN is found inside the thalamus of the brain....
(LGN) of the thalamus
Thalamus
The thalamus is a midline paired symmetrical structure within the brains of vertebrates, including humans. It is situated between the cerebral cortex and midbrain, both in terms of location and neurological connections...
. "Parvus" means "small" in Latin
Latin
Latin is an Italic language originally spoken in Latium and Ancient Rome. It, along with most European languages, is a descendant of the ancient Proto-Indo-European language. Although it is considered a dead language, a number of scholars and members of the Christian clergy speak it fluently, and...
, and the name "parvocellular" refers to the small size of the cell compared to the larger magnocellular cells. Phylogenetically, parvocellular neurons are more modern than magnocellular ones.
Input to cells

Visual system
The visual system is the part of the central nervous system which enables organisms to process visual detail, as well as enabling several non-image forming photoresponse functions. It interprets information from visible light to build a representation of the surrounding world...
receive their input from midget cell
Midget cell
A midget cell is one type of retinal ganglion cell. Midget cells originate in the ganglion cell layer of the retina, and project to the parvocellular layers of the lateral geniculate nucleus . The axons of midget cells travel through the optic nerve and optic tract, ultimately synapsing with...
s, a type of retinal ganglion cell, whose axons are exiting the optic tract
Optic tract
The optic tract is a part of the visual system in the brain.It is a continuation of the optic nerve and runs from the optic chiasm to the lateral geniculate nucleus....
. These synapse
Synapse
In the nervous system, a synapse is a structure that permits a neuron to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another cell...
s occur in one of the four dorsal parvocellular layers of the lateral geniculate nucleus. The information from each eye is kept separate at this point, and continues to be segrated until processing in the visual cortex
Visual cortex
The visual cortex of the brain is the part of the cerebral cortex responsible for processing visual information. It is located in the occipital lobe, in the back of the brain....
. The electrically-encoded visual information leaves the parvocellular cells via relay cells
Interneuron
An interneuron is a multipolar neuron which connects afferent neurons and efferent neurons in neural pathways...
in the optic radiation
Optic radiation
The optic radiation is a collection of axons from relay neurons in the lateral geniculate nucleus of the thalamus carrying visual information to the visual cortex along the calcarine fissure.There is one such tract on each side of the brain.-Parts:A distinctive...
s, traveling to the primary visual cortex layer 4C-β. The parvocellular neurons are sensitive to color, and are more capable of discriminating fine details than their magnocellular counterparts. Parvocellular cells have greater spatial resolution, but lower temporal resolution, than the magnocellular cells.
External links
- NIF Search - Parvocellular Cell via the Neuroscience Information FrameworkNeuroscience Information FrameworkThe Neuroscience Information Framework is a repository of global neuroscience web resources, including experimental, clinical, and translational neuroscience databases, knowledge bases, atlases, and genetic/genomic resources.-Description:...

