
Raetia
Encyclopedia
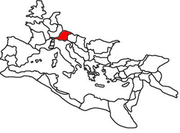
Roman province
In Ancient Rome, a province was the basic, and, until the Tetrarchy , largest territorial and administrative unit of the empire's territorial possessions outside of Italy...
of the Roman Empire
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire was the post-Republican period of the ancient Roman civilization, characterised by an autocratic form of government and large territorial holdings in Europe and around the Mediterranean....
, named after the Rhaetian (Raeti
Raeti
The Raeti was the collective "ethnic" name used by the ancient Romans to denote a number of Alpine tribes, whose language and culture may have derived, at least in part, from the Etruscans. From not later than ca...
or Rhaeti) people. It was bounded on the west by the country
Country
A country is a region legally identified as a distinct entity in political geography. A country may be an independent sovereign state or one that is occupied by another state, as a non-sovereign or formerly sovereign political division, or a geographic region associated with a previously...
of the Helvetii
Helvetii
The Helvetii were a Celtic tribe or tribal confederation occupying most of the Swiss plateau at the time of their contact with the Roman Republic in the 1st century BC...
, on the east by Noricum
Noricum
Noricum, in ancient geography, was a Celtic kingdom stretching over the area of today's Austria and a part of Slovenia. It became a province of the Roman Empire...
, on the north by Vindelicia
Vindelicia
In the pre-Roman geography of Europe, Vindelicia identifies the country inhabited by the Vindelici, a region bounded on the north by the Danube and the Hadrian's Limes Germanicus, on the east by the Oenus , on the south by Raetia and on the west by the territory of the Helvetii...
, on the west by Cisalpine Gaul
Cisalpine Gaul
Cisalpine Gaul, in Latin: Gallia Cisalpina or Citerior, also called Gallia Togata, was a Roman province until 41 BC when it was merged into Roman Italy.It bore the name Gallia, because the great body of its inhabitants, after the expulsion of the Etruscans, consisted of Gauls or Celts...
and on south by Venetia et Histria. It thus comprised the districts occupied in modern times by eastern and central Switzerland
Switzerland
Switzerland name of one of the Swiss cantons. ; ; ; or ), in its full name the Swiss Confederation , is a federal republic consisting of 26 cantons, with Bern as the seat of the federal authorities. The country is situated in Western Europe,Or Central Europe depending on the definition....
(containing the Upper Rhine
Upper Rhine
The Upper Rhine is the section of the Rhine in the Upper Rhine Plain between Basel, Switzerland and Bingen, Germany. The river is marked by Rhine-kilometers 170 to 529 ....
and Lake Constance
Lake Constance
Lake Constance is a lake on the Rhine at the northern foot of the Alps, and consists of three bodies of water: the Obersee , the Untersee , and a connecting stretch of the Rhine, called the Seerhein.The lake is situated in Germany, Switzerland and Austria near the Alps...
), southern Bavaria
Bavaria
Bavaria, formally the Free State of Bavaria is a state of Germany, located in the southeast of Germany. With an area of , it is the largest state by area, forming almost 20% of the total land area of Germany...
and the Upper Swabia
Upper Swabia
Upper Swabia is a region in Germany in the federal states of Baden-Württemberg and Bavaria. The name refers to the area between the Swabian Alb, Lake Constance and the Lech...
, Vorarlberg
Vorarlberg
Vorarlberg is the westernmost federal-state of Austria. Although it is the second smallest in terms of area and population , it borders three countries: Germany , Switzerland and Liechtenstein...
, the greater part of Tirol
Tyrol (state)
Tyrol is a state or Bundesland, located in the west of Austria. It comprises the Austrian part of the historical region of Tyrol.The state is split into two parts–called North Tyrol and East Tyrol–by a -wide strip of land where the state of Salzburg borders directly on the Italian province of...
, and part of Lombardy
Lombardy
Lombardy is one of the 20 regions of Italy. The capital is Milan. One-sixth of Italy's population lives in Lombardy and about one fifth of Italy's GDP is produced in this region, making it the most populous and richest region in the country and one of the richest in the whole of Europe...
. Later Vindelicia, today south eastern Wuerttemberg and south western Bavaria was forming part of Raetia. The northern border of Raetia during the times of Augustus and Tiberius was the River Danube. Later the northern boundary was formed by the Limes Germanicus
Limes Germanicus
The Limes Germanicus was a line of frontier fortifications that bounded the ancient Roman provinces of Germania Inferior, Germania Superior and Raetia, dividing the Roman Empire and the unsubdued Germanic tribes from the years 83 to about 260 AD...
, stretching for 166 km north of the Danube. Raetia was linked to Italy across the Alps over the Reschen Pass, by the Via Claudia Augusta
Via Claudia Augusta
The Via Claudia Augusta is an ancient Roman road, which linked the valley of the Po River with Rhaetia across the Alps. Since 2007, the Giontech Archeological Site, in Mezzocorona/Kronmetz serves as the Via Claudia Augusta International Research Center, directed by Prof...
.
History
Little is known of the origin or history of the Raetians, who appear in the records as one of the most powerful and warlike of the AlpineAlps
The Alps is one of the great mountain range systems of Europe, stretching from Austria and Slovenia in the east through Italy, Switzerland, Liechtenstein and Germany to France in the west....
tribes. Livy
Livy
Titus Livius — known as Livy in English — was a Roman historian who wrote a monumental history of Rome and the Roman people. Ab Urbe Condita Libri, "Chapters from the Foundation of the City," covering the period from the earliest legends of Rome well before the traditional foundation in 753 BC...
states distinctly that they were of Etruscan
Etruscan civilization
Etruscan civilization is the modern English name given to a civilization of ancient Italy in the area corresponding roughly to Tuscany. The ancient Romans called its creators the Tusci or Etrusci...
origin (a belief that is favored by Niebuhr
Barthold Georg Niebuhr
Barthold Georg Niebuhr was a Danish-German statesman and historian who became Germany's leading historian of Ancient Rome and a founding father of modern scholarly historiography. Classical Rome caught the admiration of German thinkers...
and Mommsen
Theodor Mommsen
Christian Matthias Theodor Mommsen was a German classical scholar, historian, jurist, journalist, politician, archaeologist, and writer generally regarded as the greatest classicist of the 19th century. His work regarding Roman history is still of fundamental importance for contemporary research...
). A tradition reported by Justin and Pliny the Elder
Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus , better known as Pliny the Elder, was a Roman author, naturalist, and natural philosopher, as well as naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and personal friend of the emperor Vespasian...
affirmed that they were a portion of that people who had settled in the plains of the Po
Po River
The Po |Ligurian]]: Bodincus or Bodencus) is a river that flows either or – considering the length of the Maira, a right bank tributary – eastward across northern Italy, from a spring seeping from a stony hillside at Pian del Re, a flat place at the head of the Val Po under the northwest face...
and were driven into the mountains by the invading Gauls
Gauls
The Gauls were a Celtic people living in Gaul, the region roughly corresponding to what is now France, Belgium, Switzerland and Northern Italy, from the Iron Age through the Roman period. They mostly spoke the Continental Celtic language called Gaulish....
, when they assumed the name of "Raetians" from an eponym
Eponym
An eponym is the name of a person or thing, whether real or fictitious, after which a particular place, tribe, era, discovery, or other item is named or thought to be named...
ous leader Raetus; a more probable derivation, however, is from Celtic rait ("mountain land"). Even if their Etruscan origin be accepted, at the time when the land became known to the Romans, Celt
Celt
The Celts were a diverse group of tribal societies in Iron Age and Roman-era Europe who spoke Celtic languages.The earliest archaeological culture commonly accepted as Celtic, or rather Proto-Celtic, was the central European Hallstatt culture , named for the rich grave finds in Hallstatt, Austria....
ic tribes were already in possession of it and had amalgamated so completely with the original inhabitants that, generally speaking, the Raetians of later times may be regarded as a Celtic people, although non-Celtic tribes (Lepontii
Lepontii
The Lepontii were an ancient people occupying portions of Rhaetia in the Alps during the time of the Roman conquest of that territory. The Lepontii have been variously described as a Celtic, Ligurian, Raetian, and Germanic tribe...
, Euganei
Euganei
The Euganei is a semi-mythical proto-Italic ethnic group that dwelt an area among Adriatic Sea and Rhaetian Alps...
) were settled among them.
The Raetians are first mentioned (but only incidentally) by Polybius
Polybius
Polybius , Greek ) was a Greek historian of the Hellenistic Period noted for his work, The Histories, which covered the period of 220–146 BC in detail. The work describes in part the rise of the Roman Republic and its gradual domination over Greece...
, and little is heard of them till after the end of the Republic
Roman Republic
The Roman Republic was the period of the ancient Roman civilization where the government operated as a republic. It began with the overthrow of the Roman monarchy, traditionally dated around 508 BC, and its replacement by a government headed by two consuls, elected annually by the citizens and...
. There is little doubt, however, that they retained their independence until their subjugation in 15 BC by Tiberius
Tiberius
Tiberius , was Roman Emperor from 14 AD to 37 AD. Tiberius was by birth a Claudian, son of Tiberius Claudius Nero and Livia Drusilla. His mother divorced Nero and married Augustus in 39 BC, making him a step-son of Octavian...
and Drusus
Nero Claudius Drusus
Nero Claudius Drusus Germanicus , born Decimus Claudius Drusus also called Drusus, Drusus I, Nero Drusus, or Drusus the Elder was a Roman politician and military commander. He was a fully patrician Claudian on his father's side but his maternal grandmother was from a plebeian family...
.
At first Raetia formed a distinct province, but towards the end of the 1st century AD Vindelicia was added to it; hence Tacitus (Germania
Germania (book)
The Germania , written by Gaius Cornelius Tacitus around 98, is an ethnographic work on the Germanic tribes outside the Roman Empire.-Contents:...
, 41) could speak of Augusta Vindelicorum (Augsburg
Augsburg
Augsburg is a city in the south-west of Bavaria, Germany. It is a university town and home of the Regierungsbezirk Schwaben and the Bezirk Schwaben. Augsburg is an urban district and home to the institutions of the Landkreis Augsburg. It is, as of 2008, the third-largest city in Bavaria with a...
) as "a colony
Colony
In politics and history, a colony is a territory under the immediate political control of a state. For colonies in antiquity, city-states would often found their own colonies. Some colonies were historically countries, while others were territories without definite statehood from their inception....
of the province of Raetia". The whole province (including Vindelicia) was at first under a military prefect
Prefect
Prefect is a magisterial title of varying definition....
, then under a procurator
Procurator (Roman)
A procurator was the title of various officials of the Roman Empire, posts mostly filled by equites . A procurator Augusti was the governor of the smaller imperial provinces...
; it had no standing army quartered in it but relied on its own native troops and militia
Militia
The term militia is commonly used today to refer to a military force composed of ordinary citizens to provide defense, emergency law enforcement, or paramilitary service, in times of emergency without being paid a regular salary or committed to a fixed term of service. It is a polyseme with...
for protection until the 2nd century AD.
During the reign of Marcus Aurelius, Raetia was governed by the commander of the Legio III Italica
Legio III Italica
Legio tertia Italica was a Roman legion levied by Marcus Aurelius around 165, for his campaign against the Marcomanni tribe. The cognomen Italica suggests that recruits were originally from Italy. The legion was still active in Raetia and other provinces in the early 5th century Legio tertia...
, which was based in Castra Regina (Regensburg
Regensburg
Regensburg is a city in Bavaria, Germany, located at the confluence of the Danube and Regen rivers, at the northernmost bend in the Danube. To the east lies the Bavarian Forest. Regensburg is the capital of the Bavarian administrative region Upper Palatinate...
) by 179 AD .
Under Diocletian
Diocletian
Diocletian |latinized]] upon his accession to Diocletian . c. 22 December 244 – 3 December 311), was a Roman Emperor from 284 to 305....
, Raetia formed part of the diocese
Diocese
A diocese is the district or see under the supervision of a bishop. It is divided into parishes.An archdiocese is more significant than a diocese. An archdiocese is presided over by an archbishop whose see may have or had importance due to size or historical significance...
of the vicarius Italiae, and was subdivided into Raetia prima, with a praeses at Curia Raetorum (Chur
Chur
Chur or Coire is the capital of the Swiss canton of Graubünden and lies in the northern part of the canton.-History:The name "chur" derives perhaps from the Celtic kora or koria, meaning "tribe", or from the Latin curia....
) and Raetia secunda, with a praeses at Augusta Vindelicorum (Augsburg), the former corresponding to the old Raetia, the latter to Vindelicia. The boundary between them is not clearly defined, but may be stated generally as a line drawn eastwards from the lacus Brigantinus (Lake Constance
Lake Constance
Lake Constance is a lake on the Rhine at the northern foot of the Alps, and consists of three bodies of water: the Obersee , the Untersee , and a connecting stretch of the Rhine, called the Seerhein.The lake is situated in Germany, Switzerland and Austria near the Alps...
) to the Oenus (River Inn).
During the last years of the Western Roman Empire
Western Roman Empire
The Western Roman Empire was the western half of the Roman Empire after its division by Diocletian in 285; the other half of the Roman Empire was the Eastern Roman Empire, commonly referred to today as the Byzantine Empire....
, the land was in a desolate condition, but its occupation by the Ostrogoths in the time of Theodoric the Great
Theodoric the Great
Theodoric the Great was king of the Ostrogoths , ruler of Italy , regent of the Visigoths , and a viceroy of the Eastern Roman Empire...
, who placed it under a dux, to some extent revived its prosperity.
Economy
The land was very mountainous, and the inhabitants, when not engaged in predatory expeditions, chiefly supported themselves by breeding cattle and cutting timber, little attention being paid to agriculture. Some of the valleys, however, were rich and fertile, and produced wine, which was considered equal to any in ItaliaItalia (Roman province)
Italia was the name of the Italian peninsula of the Roman Empire.-Under the Republic and Augustan organization:During the Republic and the first centuries of the empire, Italia was not a province, but rather the territory of the city of Rome, thus having a special status: for example, military...
. Augustus Caesar preferred Raetian wine to any other. Considerable trade in pitch
Pitch (resin)
Pitch is the name for any of a number of viscoelastic, solid polymers. Pitch can be made from petroleum products or plants. Petroleum-derived pitch is also called bitumen. Pitch produced from plants is also known as resin. Products made from plant resin are also known as rosin.Pitch was...
, honey
Honey
Honey is a sweet food made by bees using nectar from flowers. The variety produced by honey bees is the one most commonly referred to and is the type of honey collected by beekeepers and consumed by humans...
, wax
Wax
thumb|right|[[Cetyl palmitate]], a typical wax ester.Wax refers to a class of chemical compounds that are plastic near ambient temperatures. Characteristically, they melt above 45 °C to give a low viscosity liquid. Waxes are insoluble in water but soluble in organic, nonpolar solvents...
, and cheese
Cheese
Cheese is a generic term for a diverse group of milk-based food products. Cheese is produced throughout the world in wide-ranging flavors, textures, and forms....
occurred.
Human geography
The chief towns of Raetia (excluding Vindelicia) were Tridentum (TrentoTrento
Trento is an Italian city located in the Adige River valley in Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol. It is the capital of Trentino...
) and Curia (Coire or Chur
Chur
Chur or Coire is the capital of the Swiss canton of Graubünden and lies in the northern part of the canton.-History:The name "chur" derives perhaps from the Celtic kora or koria, meaning "tribe", or from the Latin curia....
). It was traversed by two great lines of Roman roads — the Via Claudia Augusta leading from Verona and Tridentum across the Reschen Pass to the Fern Pass
Fern Pass
- Geography :Fern Pass is a mountain pass in the Tyrolean Alps in Austria. It is located between the Lechtal Alps on the west and the Mieming Mountains on the east. The highest peak in Germany, the Zugspitze is only 13.5 km away to the northeast...
and thence to Augusta Vindelicorum (Augsburg
Augsburg
Augsburg is a city in the south-west of Bavaria, Germany. It is a university town and home of the Regierungsbezirk Schwaben and the Bezirk Schwaben. Augsburg is an urban district and home to the institutions of the Landkreis Augsburg. It is, as of 2008, the third-largest city in Bavaria with a...
), the other from Brigantium (Bregenz
Bregenz
-Culture:The annual summer music festival Bregenzer Festspiele is a world-famous festival which takes place on and around a stage on Lake Constance, where a different opera is performed every second year.-Sport:* A1 Bregenz HB is a handball team....
) on Lake Constance by Chur and Chiavenna to Como
Como
Como is a city and comune in Lombardy, Italy.It is the administrative capital of the Province of Como....
and Milan
Milan
Milan is the second-largest city in Italy and the capital city of the region of Lombardy and of the province of Milan. The city proper has a population of about 1.3 million, while its urban area, roughly coinciding with its administrative province and the bordering Province of Monza and Brianza ,...
.
County of Raetia (Rätien)
CharlemagneCharlemagne
Charlemagne was King of the Franks from 768 and Emperor of the Romans from 800 to his death in 814. He expanded the Frankish kingdom into an empire that incorporated much of Western and Central Europe. During his reign, he conquered Italy and was crowned by Pope Leo III on 25 December 800...
raised the district that was still governed under Frankish
Franks
The Franks were a confederation of Germanic tribes first attested in the third century AD as living north and east of the Lower Rhine River. From the third to fifth centuries some Franks raided Roman territory while other Franks joined the Roman troops in Gaul. Only the Salian Franks formed a...
rule by a praeses in the 8th century to a county of Raetia, with a reminiscence of its Roman divisions in the name Reciarum comes, "count of the Raetias", as late as 807; it was absorbed into the duchy of Swabia
Duchy of Swabia
Swabia was one of the five stem duchies of the medieval German kingdom, and its dukes were thus among the most powerful magnates of Germany.-History:...
at the beginning of the 10th century.
In the mid-8th century a surviving Lex Romana Curiensis, a "Roman Law of Chur", was an abbreviated epitome of the Breviary of Alaric
Breviary of Alaric
The Breviary of Alaric is a collection of Roman law, compiled by order of Alaric II, King of the Visigoths, with the advice of his bishops and nobles. It was promulgated on February 2, year 506, the twenty-second year of his reign...
. Under the Roman trappings of iudex provincialis or defensor civitatis, the historian of early medieval Raetia, Elizabeth Meyer-Marthaler, recognized the public officials common throughout the Frankish empire. Not much later, the power of the comes
Comes
Comes , plural comites , is the Latin word for companion, either individually or as a member of a collective known as comitatus, especially the suite of a magnate, in some cases large and/or formal enough to have a specific name, such as a cohors amicorum. The word comes derives from com- "with" +...
was invested in the bishop of Chur
Bishop of Chur
The Bishop of Chur is the Ordinary of the Roman Catholic Diocese of Chur, Grisons, Switzerland .-History:...
; this experiment was brought to an end when Hunfrid, Margrave of Istria
Hunfrid, Margrave of Istria
Hunfrid was the Margrave of Istria and, according to some sources, Duke of Friuli from 799 to circa 804, when a Duke John was ruling Istria. He was the founder of the family called the Hunfridings....
, was made count of Raetia in 807. With this as a power base, his Hunfriding heirs were able to gather enough power that Burchard II
Burchard II, Duke of Swabia
Burchard II was the Hunfriding Duke of Swabia and Count of Raetia. He was the son of Burchard I and Liutgard of Saxony....
(919-926) was able to make himself duke of Swabia, and Raetia herceforward lost its separate identity.
The Rätikon
Rätikon
The Rätikon is a mountain range of the Central Eastern Alps located at the border between Vorarlberg, Liechtenstein and Graubünden. It is the geological border between the Eastern and Western Alps and stretches from the Montafon as far as the Rhine. In the south, the Prättigau is its limit, in the...
mountain range derives its name from Raetia.
Important cities
- Alae (AalenAalenAalen is a city in the German state of Baden-Württemberg, about east of Stuttgart and north of Ulm. It is the seat of the Ostalbkreis district, and its largest city, as well as the largest city within the Ostwürttemberg region. In spatial planning, Aalen is designated a Mittelzentrum...
) - Arbor Felix (Arbon)
- Apodiacum (Epfach)
- Aquilea (Heidenheim an der Brenz)
- Augusta Vindelicorum (AugsburgAugsburgAugsburg is a city in the south-west of Bavaria, Germany. It is a university town and home of the Regierungsbezirk Schwaben and the Bezirk Schwaben. Augsburg is an urban district and home to the institutions of the Landkreis Augsburg. It is, as of 2008, the third-largest city in Bavaria with a...
) - Ausugum (Borgo ValsuganaBorgo ValsuganaBorgo Valsugana is a comune in Trentino in the northern Italian region Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol, located about 30 km east of Trento....
) - Bauzanum or Pons Drusi (Bolzano)
- Belunum (BellunoBellunoBelluno , is a town and province in the Veneto region of northern Italy. Located about 100 kilometres north of Venice, Belluno is the capital of the province of Belluno and the most important city in the Eastern Dolomiti's region. With its roughly 37,000 inhabitants, it the largest populated area...
) - Bilitio (BellinzonaBellinzonaBellinzona is the administrative capital of the canton Ticino in Switzerland. The city is famous for its three castles that have been UNESCO World Heritage Sites since 2000....
) - Brigantium (BregenzBregenz-Culture:The annual summer music festival Bregenzer Festspiele is a world-famous festival which takes place on and around a stage on Lake Constance, where a different opera is performed every second year.-Sport:* A1 Bregenz HB is a handball team....
) - Cambodunum (Kempten im AllgäuKempten im AllgäuKempten is the largest town in Allgäu, a region in the south-west of Bavaria, Germany. The population was ca 61,000 in 2006. The area was possibly settled originally by Celts, but was later overtaken by the Romans, who called the town Cambodunum...
) - Castra Batava (PassauPassauPassau is a town in Lower Bavaria, Germany. It is also known as the Dreiflüssestadt or "City of Three Rivers," because the Danube is joined at Passau by the Inn from the south and the Ilz from the north....
) - Castra Regina (RegensburgRegensburgRegensburg is a city in Bavaria, Germany, located at the confluence of the Danube and Regen rivers, at the northernmost bend in the Danube. To the east lies the Bavarian Forest. Regensburg is the capital of the Bavarian administrative region Upper Palatinate...
) - Clavenna (Chiavenna)
- Clunia (probably FeldkirchFeldkirch, Vorarlberg- Schools :* Bundesgymnasium und Bundesrealgymnasium Feldkirch * Bundeshandelsakademie und Bundeshandelsschule Feldkirch* Bundesoberstufenrealgymnasium und Bundesrealgymnasium Schillerstrasse...
or BalzersBalzersBalzers is a village and community located in southern Liechtenstein. As of the 2005 census, the community has a total population of 4,420. The main part of the village is situated along the east bank of the Rhine.- History and Culture :...
) - Curia (ChurChurChur or Coire is the capital of the Swiss canton of Graubünden and lies in the northern part of the canton.-History:The name "chur" derives perhaps from the Celtic kora or koria, meaning "tribe", or from the Latin curia....
) - Endidae (Neumarkt)
- Feltria (FeltreFeltreFeltre is a town and comune of the province of Belluno in Veneto, northern Italy. A hill town in the southern reaches of the province, it is located on the Stizzon River, about 4 km from its junction with the Piave, and 20 km southwest from Belluno...
) - Foetes (FüssenFüssenFüssen is a town in Bavaria, Germany, in the district of Ostallgäu situated from the Austrian border. It is located on the banks of the Lech river. The River Lech flows into the Forggensee...
) - Guntia (GünzburgGünzburgGünzburg is a Große Kreisstadt and capital of the district of Günzburg in Swabia, Bavaria. This district was constituted in 1972 by combining the city of Günzburg—which had not previously been assigned to a Kreis —with the district of Günzburg and the district of Krumbach.Günzburg lies...
) - Gamundia Romana (Schwäbisch GmündSchwäbisch GmündSchwäbisch Gmünd is a town in the eastern part of the German state of Baden-Württemberg. With a population of around 62,000, the town is the second largest in the Ostalbkreis and the whole region of East Württemberg after Aalen...
) - Oscela (DomodossolaDomodossolaDomodossola is a city and comune in the Province of Verbano-Cusio-Ossola, in the region of Piedmont, northern Italy...
) - Parthanum (Partenkirchen)
- Sebatum (San Lorenzo di Sebato/St. LorenzenSt. LorenzenSt. Lorenzen is a comune in South Tyrol in the Italian region Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol, located about 100 km northeast of Trento and about 50 km northeast of Bolzano...
) - Sorviodurum (StraubingStraubingStraubing is an independent city in Lower Bavaria, southern Germany. It is seat of the district of Straubing-Bogen. Annually in August the Gäubodenvolksfest, the second largest fair in Bavaria, is held....
) - Sublavio (Ponte Gardena/Waidbruck)
- Tridentum (TrentoTrentoTrento is an Italian city located in the Adige River valley in Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol. It is the capital of Trentino...
) - Veldidena (Wilten district of InnsbruckInnsbruck- Main sights :- Buildings :*Golden Roof*Kaiserliche Hofburg *Hofkirche with the cenotaph of Maximilian I, Holy Roman Emperor*Altes Landhaus...
) - Vipitenum (Vipiteno/SterzingSterzingSterzing is a comune in South Tyrol in the region of Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol, Italy. It is the main village of the southern Wipptal, and the Eisack River flows through the medieval town.-Origin:...
)
Further reading
- PC von Planta, Das alte Rätien (Berlin, 1872)
- T Mommsen in Corpus Inscriptionum Latinarum, iii. p. 706
- Joachim MarquardtJoachim MarquardtKarl Joachim Marquardt was a German historian and writer on Roman antiquities.-Biography:Marquardt was born at Danzig ....
, Römische Staatsverwaltung, 1. (2nd ed., 1881) p. 288 - Ludwig Steub, Ueber die Urbewohner Rätiens und ihren Zusammenhang mit den Etruskern (Munich, 1843)
- Julius Jung, Römer und Romanen in den Donauländern (Innsbruck, 1877)
- SmithWilliam Smith (lexicographer)Sir William Smith Kt. was a noted English lexicographer.-Early life:Born at Enfield in 1813 of Nonconformist parents, he was originally destined for a theological career, but instead was articled to a solicitor. In his spare time he taught himself classics, and when he entered University College...
's Dictionary of Greek and Roman Geography (1873) - T Mommsen, The Roman Provinces (English translation, 1886), i. pp. 16, 161, 196
- Mary B Peaks, The General Civil and Military Administration of Noricum and Raetia (Chicago, 1907).
See also
- Alpine regiments of the Roman army

