
Russian car number plates
Encyclopedia



Russia
Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
(Russian
Russian language
Russian is a Slavic language used primarily in Russia, Belarus, Uzbekistan, Kazakhstan, Tajikistan and Kyrgyzstan. It is an unofficial but widely spoken language in Ukraine, Moldova, Latvia, Turkmenistan and Estonia and, to a lesser extent, the other countries that were once constituent republics...
(singular): автомобильный номер) has changed since the collapse of the Soviet Union
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991....
. Soviet plates prior to 1982 were white-on-black. They had combination of four digits, grouped by two and three Cyrillic letters in smaller type. Rear plate was square with letters located below the numbers. From those letters, first two indicated the region. For example, the combination 75-63 КЛЖ referred to a car from the Kaliningrad Region. After 1982 a new black-on-white format for newly registered cars was adopted. The 1982 format differentiated privately owned from government owned cars and trucks (virtually all vehicles used for business, as all businesses belonged to the government). The government owned vehicles retained the NNNN LLL scheme (the digits were no longer grouped by two and all characters were the same size) and the rear plate was square on trucks and buses/coaches but oblong on passenger cars, while private vehicles used L NNNN LL (with a smaller-sized first letter - for example, c 5969 ME on a van fom the Moscow Region) and invariably oblong format. The last two letters indicated regions or large cities. Largest cities usually had several two-letter codes to account for a larger number of cars. For example, the city of Kiev used КИ and ХТ codes while the Kiev Oblast' region (excluding the city itself) used КХ. The use of Cyrillic characters meant that in some cases replacement plates with characters looking like Latin characters had to be temporarily issued to vehicles going abroad.
The current format uses a letter followed by 3 digits and two more letters. To improve legibility of the numbers for Russian cars abroad, only a small subset of Cyrillic characters that look like Latin characters are used (12 letters: А, В, Е, К, М, Н, О, Р, С, Т, У, Х). Finally, the region number (77, 97, 99, 177, 197, and 199 for Moscow
Moscow
Moscow is the capital, the most populous city, and the most populous federal subject of Russia. The city is a major political, economic, cultural, scientific, religious, financial, educational, and transportation centre of Russia and the continent...
, 78, 98, and 178 for Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg is a city and a federal subject of Russia located on the Neva River at the head of the Gulf of Finland on the Baltic Sea...
, etc.) and letters "RUS" are included, as well as the national flag (the flag was not used on some of the earliest plates of this format). There is a different format for trailers (2 letters and 4 digits).
The standard size for the license plate is 520 mm by 110 mm.
Some vehicles, like trolleybus
Trolleybus
A trolleybus is an electric bus that draws its electricity from overhead wires using spring-loaded trolley poles. Two wires and poles are required to complete the electrical circuit...
es, are not required to have license plates, because they can not leave the network they operate on and can be identified by number that is painted and is given by local public transport authority. Trucks and buses generally have their licence numbers repeated in large letters on the rear of the vehicle for easier identification (a practice continued from Soviet days), although they also bear licence plates. Some autonomous regions are not required to have the flag on the licence plates.
Vehicles used by certain organisations or categories of persons carry special plates:
- Police forces have special numbers on blue colored plates and the format is one letter and four digits. The letter signifies the branch of the police force, and its meaning may change from city to city; for example, in Moscow, A ####|99 rus stands for traffic police, У ####|99 rus for patrol cars, O ####|99 rus for police guard service etc.
- Diplomatic cars have white characters on a red background. The first three digits on the plate are a code identifying the embassy to which they belong, assigned in order based on the date at which that country established diplomatic relations with Russia or the Soviet Union. For example, the United KingdomUnited KingdomThe United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
is 001, the United StatesUnited StatesThe United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
is 004, and ParaguayParaguayParaguay , officially the Republic of Paraguay , is a landlocked country in South America. It is bordered by Argentina to the south and southwest, Brazil to the east and northeast, and Bolivia to the northwest. Paraguay lies on both banks of the Paraguay River, which runs through the center of the...
is 157. On cars assigned to rank-and-file diplomats this code is followed by D and three digits (for example, 004 D 108|77 rus), while ambassadors' cars have a slightly different license plate format (004 CD 1|77 rus). - The Armed Forces have white characters on a black background and the format is NNNN LL for vehicles and LL NNNN for trailers. In this case the two digits on the right are not a regional code but a code for the Armed forces branch or service and go with a certain letter combination. For example, #### CA|14 rus is a vehicle belonging to the Railroad Troops; #### BC|27 rus denotes the Air Defence Force, #### TO|18 rus denotes the Ministry of Emergency Situations etc.
- Public transport vehicles (such as buses, licensed taxis and licensed share taxisMarshrutkaMarshrutka , from marshrutnoye taksi is a share taxi in the CIS countries, the Baltic states, and Bulgaria. Marshrutnoye taksi literally means routed taxicab...
) have black characters on a yellow background and the format is LL NNN. Since such vehicles are relatively few, the region code does not change often; in Moscow, for example, yellow "public transport" plates are still issued with the code 77 in December 2009. (Note: This type is not to be confused with similar-looking yellow license plates having the format LL NNN L, which were issued to cars registered to foreign companies operating in Russia; the latter type has now been withdrawn.)
Special plates in the above four categories never carry the Russian flag.
There are special series (usually numbers starting with A) reserved for government officials (for example, A 001 AA usually belongs to the governor
Governor
A governor is a governing official, usually the executive of a non-sovereign level of government, ranking under the head of state...
of the region). The license plates for federal government officials originally had a larger flag instead of the regional code but this type has now been withdrawn as well.
Rich businessmen, prominent politicians and crime lords often use para-legally acquired special licence plates (government or police) to get preferential treatment from the transport police and as a status symbol. Often this is used in conjunction with a flashing siren, the Society of blue buckets
Society of blue buckets
The Society of Blue Buckets is a free protest movement that has recently emerged in Russia as a response to arbitrary, self-serving use of emergency rotating blue flashers by public servants...
is a leading opposition movement to this trend.
Runout problem
As per GOSTGOST
GOST refers to a set of technical standards maintained by the Euro-Asian Council for Standardization, Metrology and Certification , a regional standards organization operating under the auspices of the Commonwealth of Independent States .All sorts of regulated standards are included, with examples...
provision, only 1,726,272 combinations may be issued within one administration unit. In certain regions, the amount of vehicles exceeds that number, and the combination may not be reused after a vehicle was taken off the registration. All this creates an issue of running out of numbers.
A short-term solution was introducing more codes for those regions. Thus, some regions have 2 codes issued to them, Perm Krai
Perm Krai
Perm Krai is a federal subject of Russia that came into existence on December 1, 2005 as a result of the 2004 referendum on the merger of Perm Oblast and Komi-Permyak Autonomous Okrug. The city of Perm became the administrative center of the new federal subject...
and city of St. Petersburg have 3, Krasnoyarsk Krai
Krasnoyarsk Krai
Krasnoyarsk Krai is a federal subject of Russia . It is the second largest federal subject after the Sakha Republic, and Russia's largest krai, occupying an area of , which is 13% of the country's total territory. The administrative center of the krai is the city of Krasnoyarsk...
and Moscow Oblast
Moscow Oblast
Moscow Oblast , or Podmoskovye , is a federal subject of Russia . Its area, at , is relatively small compared to other federal subjects, but it is one of the most densely populated regions in the country and, with the 2010 population of 7,092,941, is the second most populous federal subject...
both have 4, and the city of Moscow
Moscow
Moscow is the capital, the most populous city, and the most populous federal subject of Russia. The city is a major political, economic, cultural, scientific, religious, financial, educational, and transportation centre of Russia and the continent...
has 6 codes. But this does not fully solve the problem, as the authorities may eventually run out of regional codes because any code containing three-numeral code with any first numeral except for 1 will not fit without changing the standardized layout of the plate.
Introduction of new style license plate is being considered as a future solution.
Regional codes
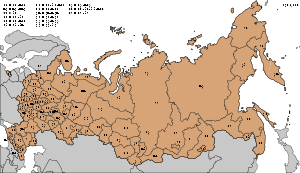
| Code | The region of Russian Federation |
|---|---|
| 01 | Republic of Adygea |
| 02, 102 | Republic of Bashkortostan Bashkortostan The Republic of Bashkortostan , also known as Bashkiria is a federal subject of Russia . It is located between the Volga River and the Ural Mountains. Its capital is the city of Ufa... |
| 03 | Buryat Republic |
| 04 | Altai Republic Altai Republic Altai Republic is a federal subject of Russia . Its capital is the town of Gorno-Altaysk. The area of the republic is . Population: -Geography:... |
| 05 | Republic of Dagestan |
| 06 | Republic of Ingushetia Ingushetia The Republic of Ingushetia is a federal subject of Russia , located in the North Caucasus region with its capital at Magas. In terms of area, the republic is the smallest of Russia's federal subjects except for the two federal cities, Moscow and Saint Petersburg... |
| 07 | Kabardino-Balkar Republic Kabardino-Balkaria The Kabardino-Balkar Republic , or Kabardino-Balkaria , is a federal subject of Russia located in the North Caucasus. Population: -Geography:The republic is situated in the North Caucasus mountains, with plains in the northern part.... |
| 08 | Republic of Kalmykia Kalmykia The Republic of Kalmykia is a federal subject of Russia . Population: It is the only Buddhist region in Europe. It has also become well-known as an international chess mecca because its former President, Kirsan Ilyumzhinov, is the head of the International Chess Federation .-Geography:*Area:... |
| 09 | Karachay-Cherkess Republic Karachay-Cherkessia The Karachay-Cherkess Republic , or Karachay-Cherkessia is a federal subject of Russia . Population: -Geography:*Area: *Borders:**internal: Krasnodar Krai , Kabardino-Balkar Republic , Stavropol Krai .... |
| 10 | Republic of Karelia Republic of Karelia The Republic of Karelia is a federal subject of Russia .-Geography:The republic is located in the northwestern part of Russia, taking intervening position between the basins of White and Baltic seas... |
| 11 | Komi Republic Komi Republic The Komi Republic is a federal subject of Russia .-Geography:The republic is situated to the west of the Ural mountains, in the north-east of the East European Plain... |
| 12 | Mari El Republic Mari El The Mari El Republic is a federal subject of Russia . Its capital is the city of Yoshkar-Ola. Population: -Geography:The republic is located in the eastern part of the East European Plain of Russia, along the Volga River. The swampy Mari Depression is located in the west of the republic... |
| 13, 113 | Republic of Mordovia Mordovia The Republic of Mordovia , also known as Mordvinia, is a federal subject of Russia . Its capital is the city of Saransk. Population: -Geography:The republic is located in the eastern part of the East European Plain of Russia... |
| 14 | Sakha Republic |
| 15 | Republic of North Ossetia-Alania North Ossetia-Alania The Republic of North Ossetia–Alania is a federal subject of Russia . Its population according to the 2010 Census was 712,877.-Name:... |
| 16, 116 | Republic of Tatarstan Tatarstan The Republic of Tatarstan is a federal subject of Russia located in the Volga Federal District. Its capital is the city of Kazan, which is one of Russia's largest and most prosperous cities. The republic borders with Kirov, Ulyanovsk, Samara, and Orenburg Oblasts, and with the Mari El, Udmurt,... |
| 17 | Tuva Republic Tuva The Tyva Republic , or Tuva , is a federal subject of Russia . It lies in the geographical center of Asia, in southern Siberia. The republic borders with the Altai Republic, the Republic of Khakassia, Krasnoyarsk Krai, Irkutsk Oblast, and the Republic of Buryatia in Russia and with Mongolia to the... |
| 18 | Udmurt Republic Udmurtia The Udmurt Republic , or Udmurtia is a federal subject of Russia . Its capital is the city of Izhevsk. Population: -History:... |
| 19 | Republic of Khakassia Khakassia The Republic of Khakassia or Khakasiya is a federal subject of Russia located in south-central Siberia. Its capital city is Abakan, which is also the largest city in the republic... |
| 21, 121 | Chuvash Republic |
| 22 | Altai Krai Altai Krai Altai Krai is a federal subject of Russia . It borders with, clockwise from the south, Kazakhstan, Novosibirsk and Kemerovo Oblasts, and the Altai Republic. The krai's administrative center is the city of Barnaul... |
| 23, 93, 123 | Krasnodar Krai Krasnodar Krai -External links:* **... |
| 24, 84, 88, 124 | Krasnoyarsk Krai Krasnoyarsk Krai Krasnoyarsk Krai is a federal subject of Russia . It is the second largest federal subject after the Sakha Republic, and Russia's largest krai, occupying an area of , which is 13% of the country's total territory. The administrative center of the krai is the city of Krasnoyarsk... |
| 25, 125 | Primorsky Krai Primorsky Krai Primorsky Krai , informally known as Primorye , is a federal subject of Russia . Primorsky means "maritime" in Russian, hence the region is sometimes referred to as Maritime Province or Maritime Territory. Its administrative center is in the city of Vladivostok... |
| 26 | Stavropol Krai Stavropol Krai Stavropol Krai is a federal subject of Russia . Its administrative center is the city of Stavropol. Population: -Geography:Stavropol Krai encompasses the central part of the Fore-Caucasus and most of the northern slopes of Caucasus Major... |
| 27 | Khabarovsk Krai Khabarovsk Krai Khabarovsk Krai is a federal subject of Russia , located in the Russian Far East. It lies mostly in the basin of the lower Amur River, but also occupies a vast mountainous area along the coastline of the Sea of Okhotsk, an arm of the Pacific Ocean. The administrative center of the krai is the... |
| 28 | Amur Oblast Amur Oblast Amur Oblast is a federal subject of Russia , situated about east of Moscow on the banks of the Amur and Zeya Rivers. It shares its border with the Sakha Republic in the north, Khabarovsk Krai and the Jewish Autonomous Oblast in the east, People's Republic of China in the south, and Zabaykalsky... |
| 29 | Arkhangelsk Oblast Arkhangelsk Oblast Arkhangelsk Oblast is a federal subject of Russia . It includes the Arctic archipelagos of Franz Josef Land and Novaya Zemlya, as well as the Solovetsky Islands in the White Sea.... |
| 30 | Astrakhan Oblast Astrakhan Oblast Astrakhan Oblast is a federal subject of Russia . Its administrative center is the city of Astrakhan.-Demographics:Population: Ethnic groups... |
| 31 | Belgorod Oblast Belgorod Oblast Belgorod Oblast is a federal subjects of Russia . Its administrative center is the city of Belgorod. Population: 1,532,670 .-History:... |
| 32 | Bryansk Oblast Bryansk Oblast Bryansk Oblast is a federal subject of Russia . Its administrative center is the city of Bryansk. Population: 1,278,087 .-History:... |
| 33 | Vladimir Oblast Vladimir Oblast Vladimir Oblast is a federal subject of Russia . Its administrative center is the city of Vladimir, which is located east of Moscow... |
| 34 | Volgograd Oblast Volgograd Oblast Volgograd Oblast is a federal subject of Russia . Its administrative center is the city of Volgograd. Population: -Geography:*Area: 113,900 km²;*Borders length: 2221,9 km².... |
| 35 | Vologda Oblast Vologda Oblast Vologda Oblast is a federal subject of Russia . Its administrative center is Vologda. The largest city is Cherepovets.Vologda Oblast is rich in historic monuments, such as the magnificent Kirillo-Belozersky Monastery, Ferapontov Convent , medieval towns of Velikiy Ustyug and Belozersk, baroque... |
| 36, 136 | Voronezh Oblast Voronezh Oblast Voronezh Oblast is a federal subject of Russia . It was established on June 13, 1934.-Main rivers:*Don*Voronezh*Bityug*Khopyor-Economy:... |
| 37 | Ivanovo Oblast Ivanovo Oblast Ivanovo Oblast is a federal subject of Russia .Its three largest cities are Ivanovo , Kineshma, and Shuya.The principal center of tourism is Plyos. The Volga River flows through the northern part of the oblast.... |
| 38, 85 | Irkutsk Oblast Irkutsk Oblast Irkutsk Oblast is a federal subject of Russia , located in southeastern Siberia in the basins of Angara River, Lena, and Nizhnyaya Tunguska Rivers. The administrative center is the city of Irkutsk. Population: -History:... |
| 39, 91 | Kaliningrad Oblast Kaliningrad Oblast Kaliningrad Oblast is a federal subject of Russia situated on the Baltic coast. It has a population of The oblast forms the westernmost part of the Russian Federation, but it has no land connection to the rest of Russia. Since its creation it has been an exclave of the Russian SFSR and then the... |
| 40 | Kaluga Oblast Kaluga Oblast Kaluga Oblast is a federal subject of Russia . Its administrative center is the city of Kaluga.-Geography:Kaluga Oblast is located in the central part of the East European Plain. The Smolensk Highland lays in the western and north-western part of the oblast, while the Central Russian Highland -... |
| 41, 82 | Kamchatka Krai |
| 42, 142 | Kemerovo Oblast Kemerovo Oblast Kemerovo Oblast , also known as Kuzbass after the Kuznetsk Basin, is a federal subject of Russia , located in southwestern Siberia, where the West Siberian Plain meets the South Siberian mountains... |
| 43 | Kirov Oblast Kirov Oblast Kirov Oblast is a federal subject of Russia . Its administrative center is the city of Kirov. Population: -History:In the late 19th and early 20th centuries, Vyatka remained a place of exile for opponents of the tsarist regime, including many prominent revolutionary figures.In 1920, a number of... |
| 44 | Kostroma Oblast Kostroma Oblast Kostroma Oblast is a federal subject of Russia . Its administrative center is the city of Kostroma.Major historic towns include Kostroma, Sharya, Nerekhta, Galich, Soligalich, and Makaryev. Textile industries have been developed there since the early 18th century... |
| 45 | Kurgan Oblast Kurgan Oblast Kurgan Oblast is a federal subject of Russia . Its administrative center is the city of Kurgan. Population: -History:The oblast was formed on February 6, 1943, just when the Soviet Army decisively defeated Hitler's forces near Stalingrad... |
| 46 | Kursk Oblast Kursk Oblast Kursk Oblast is a federal subject of Russia . Its administrative center is the city of Kursk.-Geography:The oblast occupies the southern slopes of the middle-Russian plateau, and its average elevation is from 177 to 225 meters . The surface is hilly, and intersected by ravines... |
| 47 | Leningrad Oblast Leningrad Oblast Leningrad Oblast is a federal subject of Russia . It was established on August 1, 1927, although it was not until 1946 that the oblast's borders had been mostly settled in their present position... |
| 48 | Lipetsk Oblast Lipetsk Oblast Lipetsk Oblast is a federal subject of Russia which was formed on January 6, 1954. Its administrative center is the city of Lipetsk... |
| 49 | Magadan Oblast Magadan Oblast Magadan Oblast is a federal subject of Russia in the Far Eastern Federal District. Its administrative center is the city of Magadan.... |
| 50, 90, 150, 190 | Moscow Oblast Moscow Oblast Moscow Oblast , or Podmoskovye , is a federal subject of Russia . Its area, at , is relatively small compared to other federal subjects, but it is one of the most densely populated regions in the country and, with the 2010 population of 7,092,941, is the second most populous federal subject... |
| 51 | Murmansk Oblast Murmansk Oblast Murmansk Oblast is a federal subject of Russia , located in the northwestern part of Russia. Its administrative center is the city of Murmansk.-Geography:... |
| 52, 152 | Nizhny Novgorod Oblast Nizhny Novgorod Oblast Nizhny Novgorod Oblast is a federal subject of Russia . Its administrative center is the city of Nizhny Novgorod. Population: The oblast is crossed by the Volga River. Apart from Nizhny Novgorod's metropolitan area, the biggest city is Arzamas... |
| 53 | Novgorod Oblast Novgorod Oblast Novgorod Oblast is a federal subject of Russia , located between Moscow and Saint Petersburg. Its administrative center is the city of Veliky Novgorod. Some of the oldest Russian cities, including Veliky Novgorod and Staraya Russa, are located there... |
| 54, 154 | Novosibirsk Oblast Novosibirsk Oblast Novosibirsk Oblast is a federal subject of Russia located in southwestern Siberia. Its administrative and economic center is the city of Novosibirsk. Population: -Overview:... |
| 55 | Omsk Oblast Omsk Oblast Omsk Oblast is a federal subject of Russia , located in southwestern Siberia. The oblast has an area of and a population of with the majority, 1.15 million, living in Omsk, the administrative center.... |
| 56 | Orenburg Oblast Orenburg Oblast Orenburg Oblast is a federal subject of Russia . Its administrative center is the city of Orenburg. From 1938 to 1957, it bore the name Chkalov Oblast in honor of Valery Chkalov... |
| 57 | Oryol Oblast Oryol Oblast Oryol Oblast is a federal subject of Russia . Its administrative center is the city of Oryol. Population: -Geography:It is located in the southwestern part of the Central Federal District, in the Mid-Russian Highlands. Kaluga and Tula Oblasts border it in the north, Bryansk Oblast is located to... |
| 58 | Penza Oblast Penza Oblast -External links:* *... |
| 59, 81, 159 | Perm Krai Perm Krai Perm Krai is a federal subject of Russia that came into existence on December 1, 2005 as a result of the 2004 referendum on the merger of Perm Oblast and Komi-Permyak Autonomous Okrug. The city of Perm became the administrative center of the new federal subject... |
| 60 | Pskov Oblast Pskov Oblast Pskov Oblast is a federal subject of Russia . Pskov Oblast borders the countries of Estonia and Latvia, as well as Belarus. It is the westernmost federal subject of contiguous Russia . Its major cities are the administrative center Pskov and Velikiye Luki . Area: 55,300 km²... |
| 61, 161 | Rostov Oblast Rostov Oblast Rostov Oblast is a federal subject of Russia , located in the Southern Federal District. Rostov Oblast has an area of and a population of making it the sixth most populous federal subject in Russia... |
| 62 | Ryazan Oblast Ryazan Oblast Ryazan Oblast is a federal subject of Russia . Its administrative center is the city of Ryazan, which is the oblast's largest city. Population: -Geography:... |
| 63, 163 | Samara Oblast Samara Oblast Samara Oblast is a federal subject of Russia . Its administrative center is the city of Samara. Population: In 1936–1990, it was known as Kuybyshev Oblast , after the Soviet name of Samara .-Demographics:Population:... |
| 64, 164 | Saratov Oblast Saratov Oblast Saratov Oblast is a federal subject of Russia , located in the Volga Federal District. Its administrative center is the city of Saratov. Population: -Demographics:Population:... |
| 65 | Sakhalin Oblast Sakhalin Oblast Sakhalin Oblast is a federal subject of Russia comprising the island of Sakhalin and the Kuril Islands.The oblast has an area of 87,100 km² and a population of 546,695... |
| 66, 96 | Sverdlovsk Oblast Sverdlovsk Oblast Sverdlovsk Oblast is a federal subject of Russia located in the Urals Federal District. Its administrative center is the city of Yekaterinburg formerly known as Sverdlovsk. Population: -Geography:... |
| 67 | Smolensk Oblast Smolensk Oblast Smolensk Oblast is a federal subject of Russia . Its area is . Population: -Geography:The administrative center of Smolensk Oblast is the city of Smolensk. Other ancient towns include Vyazma and Dorogobuzh.... |
| 68 | Tambov Oblast Tambov Oblast Tambov Oblast is a federal subject of Russia . Its administrative center is the city of Tambov. Population: down from 1,178,443 recorded by the 2002 Census.Tambov Oblast is situated in forest steppe.-Birth rate:... |
| 69 | Tver Oblast Tver Oblast Tver Oblast is a federal subject of Russia . Its administrative center is the city of Tver. From 1935 to 1990, it was named Kalinin Oblast after Mikhail Kalinin. Population: Tver Oblast is an area of lakes, such as Seliger and Brosno... |
| 70 | Tomsk Oblast Tomsk Oblast Tomsk Oblast is a federal subject of Russia . It lies in the southeastern West Siberian Plain, in the southwest of the Siberian Federal District. Its administrative center is the city of Tomsk. Population:... |
| 71 | Tula Oblast Tula Oblast Tula Oblast is a federal subject of Russia with its present borders formed on September 26, 1937. Its administrative center is the city of Tula. The oblast has an area of and a population of 1,553,874... |
| 72 | Tyumen Oblast Tyumen Oblast Tyumen Oblast is a federal subject of Russia . Its administrative center is the city of Tyumen. The oblast has administrative jurisdiction over two autonomous okrugs—Khanty-Mansi Autonomous Okrug and Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug. Tyumen is the largest city, with over half a million inhabitants... |
| 73, 173 | Ulyanovsk Oblast Ulyanovsk Oblast Ulyanovsk Oblast is a federal subject of Russia . It is located in the Volga Federal District. Its administrative center is the city of Ulyanovsk... |
| 74, 174 | Chelyabinsk Oblast Chelyabinsk Oblast -External links:*... |
| 75, 80 | Zabaykalsky Krai |
| 76 | Yaroslavl Oblast Yaroslavl Oblast Yaroslavl Oblast is a federal subject of Russia , which is located in the Central Federal District, surrounded by Tver, Moscow, Ivanovo, Vladimir, Kostroma, and Vologda Oblasts. This geographic location affords the oblast the advantages of proximity to Moscow and St. Petersburg... |
| 77, 97, 99, 177, 197, 199 | Moscow Moscow Moscow is the capital, the most populous city, and the most populous federal subject of Russia. The city is a major political, economic, cultural, scientific, religious, financial, educational, and transportation centre of Russia and the continent... |
| 78, 98, 178 | Saint Petersburg Saint Petersburg Saint Petersburg is a city and a federal subject of Russia located on the Neva River at the head of the Gulf of Finland on the Baltic Sea... |
| 79 | Jewish Autonomous Oblast Jewish Autonomous Oblast The Jewish Autonomous Oblast is a federal subject of Russia situated in the Russian Far East, bordering Khabarovsk Krai and Amur Oblast of Russia and Heilongjiang province of China. Its administrative center is the town of Birobidzhan.... |
| 83 | Nenets Autonomous Okrug Nenets Autonomous Okrug Nenets Autonomous Okrug is a federal subject of Russia .It has an area of 176,700 km2 and population of 42,628 as of the preliminary results of the 2010 Census , 21,296 of whom live in Naryan-Mar, the administrative center.-Geography and ecology:The arctic ecology of this... |
| 86 | Khanty-Mansi Autonomous Okrug Khanty-Mansi Autonomous Okrug Khanty–Mansi Autonomous Okrug , also known as Yugra, is a federal subject of Russia . Population: The people native to the region are the Khanty and the Mansi, known collectively as Ob Ugric people... - Yugra |
| 87 | Chukotka Autonomous Okrug Chukotka Autonomous Okrug Chukotka Autonomous Okrug , or Chukotka , is a federal subject of Russia located in the Russian Far East.Chukotka has a population of 53,824 according to the 2002 Census, and a surface area of . The principal town and the administrative center is Anadyr... |
| 89 | Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug , is a federal subject of Russia . Its administrative center is the town of Salekhard. Population: -Geography and natural history:... |
| 94 | Baikonur Baikonur Baikonur , formerly known as Leninsk, is a city in Kyzylorda Province of Kazakhstan, rented and administered by the Russian Federation. It was constructed to service the Baikonur Cosmodrome and was officially renamed Baikonur by Russian president Boris Yeltsin on December 20, 1995.The shape of the... |
| 95 | Chechen Republic Chechnya The Chechen Republic , commonly referred to as Chechnya , also spelled Chechnia or Chechenia, sometimes referred to as Ichkeria , is a federal subject of Russia . It is located in the southeastern part of Europe in the Northern Caucasus mountains. The capital of the republic is the city of Grozny... |
Codes of diplomatic representative offices and the international organizations on diplomatic license plates
001 - Great Britain002 - Germany
003 - Canada
004 - USA
005 - Japan
006 - Spain
007 - France
008 - Belgium
009 - Greece
010 - Denmark
011 - Italy
012 - Luxembourg
013 - Netherlands
014 - Norway
015 - Turkey
016 - Australia
017 - Austria
018 - Algeria
019 - Egypt
020 - Rwanda*
021 - Argentina
022 - Afghanistan
023 - Myanmar (the former Burma)
024 - Bolivia
025 - Brazil
026 - Burundi
027 - Ghana
028 - Bangladesh
029 - Guinea
030 - Zambia
031 - Peru
032 - India
033 - Indonesia
034 - Jordan
035 - Iraq
036 - Iran
037 - Ireland
038 - Iceland
039 - Cambodia (the former Kampuchea)
040 - Kenya
041 - Cyprus
042 - Congo
043 - Costa Rica
044 - Kuwait
045 - Laos
047 - Lebanon
048 - Libya
049 - Mali
050 - Morocco
051 - Mexico
052 - Nepal
053 - Nigeria
054 - Venezuela
055 - New Zealand
056 - Pakistan
057 - Burkina Faso*
058 - Senegal*
059 - formerly Syria. Now code 133 is used.
060 - Somalia
061 - Sudan
062 - Sierra Leone
063 - Thailand
064 - Tanzania
065 - Tunisia
066 - Uganda
067 - Uruguay
068 - Philippines
069 - Finland
070 - Sri Lanka
071 - Chad
072 - Switzerland
073 - Sweden
074 - Ecuador
075 - Ethiopia
076 - Angola
077 - Democratic Republic Congo (the former Republic Zaire)
078 - Colombia
079 - Cameroon
080 - Guinea-Bissau
081 - Portugal
082 - Bulgaria
083 - Hungary
084 - Vietnam
086 - Poland
087 - Korean People's Democratic Republic (Northern Korea)
088 - Cuba
089 - Mongolia
090 - China
091 - Romania
092 - formerly Czechoslovakia (nowadays Czech Republic (148) and Slovakia (149))
093 - Yugoslavia
094 - Benin
095 - Gabon
096 - Guyana*
097 - Mauritania
098 - Madagaskar*
099 - Malaysia
100 - Niger*
101 - Singapore
102 - Togo*
103 - Central African Republic (code 106 used earlier)
104 - Jamaica*
105 - the Yemen Republic
106 - formerly Central African republic. Now code 103 is used.
107 - Palestine
108 - Nicaragua
109 - Mozambique
110 - Equatorial Guinea
111 - Sovereign Military Order of Malta (earlier code 111 belonged to Council for Mutual Economic Assistance (Comecon))
112 - Malta
113 - Cabo Verde
115 - Zimbabwe
116 - United Arab Emirates
117 - Côte d'Ivoire*
118 - Namibia
119 - formerly Republic of South Africa. Now code 137 is used.
120 - Oman
121 - Qatar
122 - formerly Arab League. Now code 503 is used
123 - formerly Liechtenstein
124 - Southern Korea
125 - Chile
126 - Panama (earlier code 126 belonged to UNESCO; see code 512)
127 - Israel
128 - Macedonia (earlier code 128 belonged to EU)
129 - Albania
130 - formerly international organizations
131 - Holy See (Vatican)
132 - Lithuania
133 - Syria (code 059 used earlier)
134 - Estonia
135 - Latvia
136 - Bahrain
137 - the republic of South Africa (code 119 used earlier)
138 - Armenia
139 - formerly Georgia. Now code 158 is used.
140 - Saudi Arabia
141 - Slovenia
142 - Uzbekistan
143 - Kyrgyzstan
144 - Croatia
145 - Azerbaijan
146 - Ukraine
147 - Moldova
148 - Czech Republic
149 - Slovakia
150 - Belarus
151 - Tajikistan
152 - Turkmenistan
153 - Kazakhstan
154 - Guatemala
155 - Bosnia and Herzegovina
156 - Eritrea
157 - Paraguay*
158 - Georgia (code 139 used earlier)
159 - Brunei-Darussalam
160 - Gambia
161 - Vietnam
162 - Mauritius
163 - Dominican Republic
164 - Montenegro
165 - South Ossetia
166 - Abkhazia
International organizations
499 - Eurocommission (code 502 used earlier)500 - European bank for Reconstruction and Development
501 - formerly UN Information Centre
502 - formerly Eurocommission. Now code 499 is used.
503 - Arab League (جامعة الدول العربية)
504 - International Bank for Reconstruction and Development
505 - International Monetary Fund (IMF)
506 - International Organization for Migration
507 - International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies
508 - International Committee of the Red Cross
509 - International Finance Corporation (IFC)
510 - United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO)
511 - United Nations (UN)
512 - United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO); code 126 used earlier.
514 - International Bank for Economic Complementation
515 - International Investment Bank
516 - The Intersputnik International Organization of Space Communications
517 - International Centre of Scientific and Technical Information
518 - International Scientific and Technical Centre
520 - International Labour Organization
521 - The Interelectro International Organization for Economic, Scientific and Technical Cooperation in Electrical Industry
522 - Coordination Centre of the Intergovernmental Commission for Cooperation in Computing Machinery
523 - Executive Committee of the Commonwealth of Independent States
524 - European Space Agency
525 - Eurasian Patent Organization
526 - earlier Taipei-Moscow Coordination Commission for Economic and Cultural Cooperation
527 - The Headquarters for Coordination of Military Cooperation of the state-participants of the Commonwealth of Independent States
528 - Interstate Bank
529 - Eurasian Economic Community (earlier - Integration Committee of the Eurasian Economic Community)
530 - International Research Institute of Management Problems
531 - Collective Security Treaty Organization (CSTA)
532 - Intergovernmental Statistical Committee of the CIS
533 - Secretary of Council of Interparliamentary Assembly of state-participants of the Commonwealth of Independent States
534 - Eurasian Development Bank (EDB)
535 - The Intergovernmental Foundation for Educational Cooperation of the CIS

