
Leningrad Oblast
Encyclopedia
Leningrad Oblast is a federal subject
of Russia
(an oblast
). It was established on August 1, 1927, although it was not until 1946 that the oblast's borders had been mostly settled in their present position. The oblast was named after the city of Leningrad (now Saint Petersburg
).
The oblast is bordered by Finland
in the northwest, Estonia
in the west, as well as five federal subjects of Russia: the Republic of Karelia
in the northeast, Vologda Oblast
in the east, Novgorod Oblast
in the south, Pskov Oblast
in the southwest, and the federal city of Saint Petersburg in the west.
The first governor of Leningrad Oblast was Vadim Gustov (in 1996–1998). Since 1999 he has been succeeded by Valery Serdyukov.
The oblast has an area of 84500 square miles (218,854 km²) and a population of ; up from 1,669,205 recorded in the 2002 Census
. The most populous town of the oblast is Gatchina
, with 88,659 inhabitants (as of the 2002 Census). Leningrad Oblast is highly industrialized.
 The territory of present-day Leningrad Oblast was populated shortly after the end of the Weichsel glaciation and hosts numerous archaeological remnants. The Volga trade route
The territory of present-day Leningrad Oblast was populated shortly after the end of the Weichsel glaciation and hosts numerous archaeological remnants. The Volga trade route
and trade route from the Varangians to the Greeks
crossed the territory. Staraya Ladoga
, the first capital of legendary Rurik
, founded in the 8th-9th century, is situated in the east of the oblast, on the River Volkhov.
In the 12th-15th century, the territory was divided between the Kingdom of Sweden and Novgorod Republic
(see Swedish-Novgorodian Wars
) and mostly populated by Karelians
(northwest), Izhorians
and Votes
(west), Vepsians (east), and Novgorodians East Slavs
(south). During the Russo-Swedish Wars of the 15th-17th centuries, the border moved back and forth over the land.
The central part of the territory is known as the historical region of Ingria
and in the 17th century, after most of the present-day territory of Leningrad Oblast was captured by Sweden with the Treaty of Stolbovo
of 1617, became subject to substantial Finnish Lutheran population influx from Finnish Karelia
(which included Karelian Isthmus
, the northwestern part of present-day Leningrad Oblast) and Savonia
. Ingrian Finns
soon became the dominant ethnic group.
During the Great Northern War
(1700–1721) the territory of what is now Leningrad Oblast was returned from Sweden by Russia under Peter the Great, who founded Saint Petersburg
amidst the land in 1703, which soon became the capital of the Russian Empire
. In 1708, most of the territory was organized into Ingermanland Governorate
under Governor General Alexander Menshikov. It was renamed Saint Petersburg Governorate in 1710 (the borders of that governorate, however, differed very significantly from those of the present-day oblast). In 1721, the territorial concessions of Sweden were confirmed with the Treaty of Nystad
.
The life of the countryside was greatly influenced by the vicinity of the imperial capital, which became a growing market for its agricultural production as well as the main consumer of its mineral and forest resources. In 1719–1810, Ladoga Canal
was dug between the River Svir and the River Neva as part of the Volga-Baltic waterway to bypass stormy waters of Lake Ladoga
. Since the advent of the rail transport in the late 19th century, the areas in the vicinity of Saint Petersburg had been a popular summer resort destinations (dacha
s) for its residents. However, while Saint Petersburg itself from the very beginning was populated mostly by Russians, it was not until the 20th century that its surrounding population was Russified.
In 1914, with the beginning of World War I
, Saint Petersburg was renamed Petrograd and the governorate was accordingly renamed Petrograd Governorate. After the Russian Revolution, in 1918, the capital was transferred from Petrograd to Moscow
, farther from the borders of the country. In 1919, during the Russian Civil War
, the Northwestern White Army advancing from Estonia and led by Nikolai Yudenich tried to capture Petrograd and even managed to reach its southern outskirts, but the attack against the Red Army under Leon Trotsky
ultimately failed, and Yudenich retreated back. The border with Estonia was established in the Russian-Estonian Treaty of Tartu
of 1920. Ingrian Finns of North Ingria
attempted to secede in 1918–1920, but were incorporated back with the Russian-Finnish Treaty of Tartu
, which settled the border between Finland and Soviet Russia. In 1924, Petrograd was renamed Leningrad and Petrograd Governorate was again renamed accordingly (Leningrad Governorate).
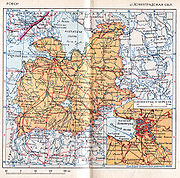
 Leningrad Oblast was established on August 1, 1927 by the resolutions of the All-Russian Central Executive Committee
Leningrad Oblast was established on August 1, 1927 by the resolutions of the All-Russian Central Executive Committee
"On the Establishment of Leningrad Oblast" and "On the Borders and Composition of the Okrugs of Leningrad Oblast" by merging Cherepovets
, Leningrad, Murmansk
, Novgorod
, and Pskov Governorates. The territory of the oblast corresponded to the modern territories of the present-day Leningrad Oblast (with the exception of the Karelian Isthmus
and the territories along the border with Estonia), Novgorod Oblast
, Pskov Oblast
, parts of Vologda Oblast
, most of Murmansk Oblast
, and the federal city of Saint Petersburg. The total area of the oblast was 360400 square kilometres (139,151.2 sq mi); more than four times larger than the modern entity. Administratively, the oblast was divided into nine okrug
s (Borovichi, Cherepovets, Leningrad, Lodeynoye Pole, Luga, Murmansk
, Novgorod, Pskov, and Velikiye Luki), each of which was in turn subdivided into district
s.
In 1929, Velikoluksky District
was transferred to newly formed Western Oblast
. Leningrad was administratively separated from Leningrad Oblast in December 1931. In 1935 five southernmost districts were made part of Kalinin Oblast. In 1936 some parts of the territory of Leningrad Suburban District of Leningrad was returned to Leningrad Oblast and divided into Vsevolozhsky District
, Krasnoselsky District
, Pargolovsky District and Slutsky District (renamed Pavlovsky District in 1944). Vologda Oblast
, which has included the easternmost districts of Leningrad Oblast (former Cherepovets Governorate), was created in 1937. Murmansk Oblast
was excluded from Leningrad Oblast in 1938.
In the fall of 1934, the Forbidden Border Zone
along the western border of the Soviet Union was established, where nobody could appear without special permission issued by NKVD
. It was officially only 7.5 km deep initially, but along the Estonian border it extended to as much as 90 km. The zone was to be free of Finnic and some other peoples, who were considered politically unreliable. Starting from the 1935, the Soviet authorities carried out mass forced transfer
of the Ingrian Finnish population of the oblast, which constituted majority in many rural localities as late as in the beginning of the century, to the east, replacing them with people from other parts of the Soviet Union.
On November 30, 1939, the Soviet Union waged the Winter War
against neighboring Finland and with the Moscow Peace Treaty in 1940 gained some territories, including Karelian Isthmus
. Their Karelian population was hastily evacuated
to inner Finland and later replaced with people from other parts of the Soviet Union. A small part of the territory (the districts of Kanneljärvi, Koivisto
and Rautu) was incorporated into Leningrad Oblast, the rest being included within the Karelo-Finnish SSR
.
In 1941, Nazi Germany
invaded the Soviet Union in the Operation Barbarossa
, and shortly thereafter the territory became place of the Battle of Leningrad. Wehrmacht captured the southwestern part of the oblast and reached Tikhvin
in the east, while Finnish troops quickly recaptured the ceded territories
in the Continuation War
, encircling Leningrad from the land. In 1944 Soviet offensives managed to expel Wehrmacht and put military pressure
on Finland, which ceded Karelian Isthmus
again with the Moscow Armistice
of September 19, 1944. This time the gained territories of the isthmus was incorporated within Leningrad Oblast (Vyborgsky
and Priozersky District
s). In 1947 the territorial gains were confirmed with the Paris Peace Treaty. Novgorod
and Pskov Oblast
s were formed out of the southern parts of Leningrad Oblast in 1944. In January 1945 a small part of the Estonian SSR to the east of the River Narva with the town of Jaanilinn (now Ivangorod) was transferred to the Russian SFSR and incorporated into Leningrad Oblast. Since then, the territory of Leningrad Oblast hasn't changed much, although some suburbs of Leningrad (now Saint Petersburg) have been excluded from the oblast and incorporated into the city. In October 1946 Leningrad gained from the oblast some former Finnish territories along the northern coast of the Gulf of Finland
divided into Sestroretsky District and Kurortny District
, including the town of Terijoki.
In 1953, Pavlovsky District
of the oblast was abolished, and parts of its territory including Pavlovsk were made subordinate to Leningrad. In 1954 the settlements Levashovo, Pargolovo and Pesochny
were also transferred to Leningrad. In 1956 Boksitogorsky District
of Leningrad Oblast gained a small territory of Novgorod Oblast
. Uritsk was transferred from the oblast to the city of Leningrad in 1963, Krasnoye Selo
and several settlements nearby—in 1973, Lomonosov
—in 1978.
After a referendum in 1991, the city of Leningrad was renamed back to Saint Petersburg, but Leningrad Oblast retained its name.
, Cyperaceae
, Poaceae
and Rosaceae
. By far the most diverse genus is Carex
(68 species). The diversity in genera Hieracium
(with Pilosella), Ranunculus
(with Batrachium), Alchemilla
, Galium
, Potamogeton
, Salix, Veronica
, Viola, Juncus
, Artemisia
, Potentilla
, Rumex
, Festuca, Epilobium
, Poa
, Trifolium, Campanula
, Vicia
, Lathyrus
, Geranium is also considerable. The territory has no endemic plant taxa. Vascular plant species of Leningrad Oblast listed in the red data book of Russia are Botrychium simplex, Cephalanthera rubra, Cypripedium calceolus
, Epipogium aphyllum
, Lobelia dortmanna
, Myrica gale
, Ophrys insectifera, Orchis militaris, Pulsatilla pratensis, Pulsatilla vernalis
. http://www.paslo.ru/newimg/111.doc
For the first half of 2007, the birth rate was 8.1 per 1000 http://demoscope.ru/weekly/2007/0301/barom04.php
Ethnic groups: According to the (2002 Census
) there were thirteen recognised ethnic groups of more than two thousand persons each; the 'national composition' was
and many other ethnic groups of less than eight hundred persons each. A further 2.34% of residents declined to state their nationality on the census questionnaire.
, Denmark
Chungcheongnam-do
, South Korea
Kyoto Prefecture
, Japan
Lombardy
, Italy
Lower Silesian Voivodeship
, Poland
Nordland
, Norway
from 1987
Federal subjects of Russia
Russia is a federation which, since March 1, 2008, consists of 83 federal subjects . In 1993, when the Constitution was adopted, there were 89 federal subjects listed...
of Russia
Russia
Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
(an oblast
Oblast
Oblast is a type of administrative division in Slavic countries, including some countries of the former Soviet Union. The word "oblast" is a loanword in English, but it is nevertheless often translated as "area", "zone", "province", or "region"...
). It was established on August 1, 1927, although it was not until 1946 that the oblast's borders had been mostly settled in their present position. The oblast was named after the city of Leningrad (now Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg is a city and a federal subject of Russia located on the Neva River at the head of the Gulf of Finland on the Baltic Sea...
).
The oblast is bordered by Finland
Finland
Finland , officially the Republic of Finland, is a Nordic country situated in the Fennoscandian region of Northern Europe. It is bordered by Sweden in the west, Norway in the north and Russia in the east, while Estonia lies to its south across the Gulf of Finland.Around 5.4 million people reside...
in the northwest, Estonia
Estonia
Estonia , officially the Republic of Estonia , is a state in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland, to the west by the Baltic Sea, to the south by Latvia , and to the east by Lake Peipsi and the Russian Federation . Across the Baltic Sea lies...
in the west, as well as five federal subjects of Russia: the Republic of Karelia
Republic of Karelia
The Republic of Karelia is a federal subject of Russia .-Geography:The republic is located in the northwestern part of Russia, taking intervening position between the basins of White and Baltic seas...
in the northeast, Vologda Oblast
Vologda Oblast
Vologda Oblast is a federal subject of Russia . Its administrative center is Vologda. The largest city is Cherepovets.Vologda Oblast is rich in historic monuments, such as the magnificent Kirillo-Belozersky Monastery, Ferapontov Convent , medieval towns of Velikiy Ustyug and Belozersk, baroque...
in the east, Novgorod Oblast
Novgorod Oblast
Novgorod Oblast is a federal subject of Russia , located between Moscow and Saint Petersburg. Its administrative center is the city of Veliky Novgorod. Some of the oldest Russian cities, including Veliky Novgorod and Staraya Russa, are located there...
in the south, Pskov Oblast
Pskov Oblast
Pskov Oblast is a federal subject of Russia . Pskov Oblast borders the countries of Estonia and Latvia, as well as Belarus. It is the westernmost federal subject of contiguous Russia . Its major cities are the administrative center Pskov and Velikiye Luki . Area: 55,300 km²...
in the southwest, and the federal city of Saint Petersburg in the west.
The first governor of Leningrad Oblast was Vadim Gustov (in 1996–1998). Since 1999 he has been succeeded by Valery Serdyukov.
The oblast has an area of 84500 square miles (218,854 km²) and a population of ; up from 1,669,205 recorded in the 2002 Census
Russian Census (2002)
Russian Census of 2002 was the first census of the Russian Federation carried out on October 9 through October 16, 2002. It was carried out by the Russian Federal Service of State Statistics .-Resident population:...
. The most populous town of the oblast is Gatchina
Gatchina
Gatchina is a town and the administrative center of Gatchinsky District of Leningrad Oblast, Russia, located south of St. Petersburg by the road leading to Pskov...
, with 88,659 inhabitants (as of the 2002 Census). Leningrad Oblast is highly industrialized.
Pre-Leningrad Oblast

Volga trade route
In the Middle Ages, the Volga trade route connected Northern Europe and Northwestern Russia with the Caspian Sea, via the Volga River. The Rus used this route to trade with Muslim countries on the southern shores of the Caspian Sea, sometimes penetrating as far as Baghdad...
and trade route from the Varangians to the Greeks
Trade route from the Varangians to the Greeks
The trade route from the Varangians to the Greeks was a trade route that connected Scandinavia, Kievan Rus' and the Byzantine Empire. The route allowed traders along the route to establish a direct prosperous trade with Byzantium, and prompted some of them to settle in the territories of...
crossed the territory. Staraya Ladoga
Staraya Ladoga
Staraya Ladoga , or the Aldeigjuborg of Norse sagas, is a village in the Volkhovsky District of Leningrad Oblast, Russia, located on the Volkhov River near Lake Ladoga, 8 km north of the town of Volkhov. The village used to be a prosperous trading outpost in the 8th and 9th centuries...
, the first capital of legendary Rurik
Rurik
Rurik, or Riurik , was a semilegendary 9th-century Varangian who founded the Rurik dynasty which ruled Kievan Rus and later some of its successor states, most notably the Tsardom of Russia, until 1598....
, founded in the 8th-9th century, is situated in the east of the oblast, on the River Volkhov.
In the 12th-15th century, the territory was divided between the Kingdom of Sweden and Novgorod Republic
Novgorod Republic
The Novgorod Republic was a large medieval Russian state which stretched from the Baltic Sea to the Ural Mountains between the 12th and 15th centuries, centred on the city of Novgorod...
(see Swedish-Novgorodian Wars
Swedish-Novgorodian Wars
Swedish–Novgorodian Wars were a series of conflicts in the 12th and 13th centuries between the Republic of Novgorod and medieval Sweden over control of the Gulf of Finland, an area vital to the Hanseatic League and part of the Varangian-Byzantine trade route...
) and mostly populated by Karelians
Karelians
The Karelians are a Baltic-Finnic ethnic group living mostly in the Republic of Karelia and in other north-western parts of the Russian Federation. The historic homeland of Karelians includes also parts of present-day Eastern Finland and the formerly Finnish territory of Ladoga Karelia...
(northwest), Izhorians
Izhorians
The Izhorians , along with the Votes are an indigenous people of Ingria. Small numbers can still be found in the Western part of Ingria, between the Narva and Neva rivers in northwestern Russia.- History :The history of the Izhorians is bound to the history of Ingria...
and Votes
Votes
Votes are a people of Votia in Ingria, the part of modern day northwestern Russia that is roughly southwest of Saint Petersburg and east of the Estonian border-town of Narva. Their own ethnic name is Vadjalain . The Finnic Votic language spoken by Votes is close to extinction. Votians were one of...
(west), Vepsians (east), and Novgorodians East Slavs
East Slavs
The East Slavs are Slavic peoples speaking East Slavic languages. Formerly the main population of the medieval state of Kievan Rus, by the seventeenth century they evolved into the Russian, Ukrainian, and Belarusian peoples.-Sources:...
(south). During the Russo-Swedish Wars of the 15th-17th centuries, the border moved back and forth over the land.
The central part of the territory is known as the historical region of Ingria
Ingria
Ingria is a historical region in the eastern Baltic, now part of Russia, comprising the southern bank of the river Neva, between the Gulf of Finland, the Narva River, Lake Peipus in the west, and Lake Ladoga and the western bank of the Volkhov river in the east...
and in the 17th century, after most of the present-day territory of Leningrad Oblast was captured by Sweden with the Treaty of Stolbovo
Treaty of Stolbovo
The Treaty of Stolbovo is a peace treaty of 1617 that ended the Ingrian War, fought between Sweden and Russia.After nearly two months of negotiations, representatives from Sweden and Russia met at the village of Stolbova, south of Lake Ladoga, on 27 February 1617.From the outset, Sweden had gone...
of 1617, became subject to substantial Finnish Lutheran population influx from Finnish Karelia
Finnish Karelia
Karelia is a historical province of Finland. It refers to the Western Karelia that during the second millennium has been under western dominance, religiously and politically. Western, i.e. Finnish Karelia is separate from Eastern, i.e...
(which included Karelian Isthmus
Karelian Isthmus
The Karelian Isthmus is the approximately 45–110 km wide stretch of land, situated between the Gulf of Finland and Lake Ladoga in northwestern Russia, to the north of the River Neva . Its northwestern boundary is the relatively narrow area between the Bay of Vyborg and Lake Ladoga...
, the northwestern part of present-day Leningrad Oblast) and Savonia
Savonia (historical province)
Savonia is a historical province in the east of Finland. It borders to Uusimaa, Tavastia, Ostrobothnia, and Karelia. Largest cities in Savo by population are Kuopio, Mikkeli, Savonlinna and Varkaus.-Administration:...
. Ingrian Finns
Ingrian Finns
The Ingrian Finns are the Finnish population of Ingria descending from Lutheran Finnish immigrants introduced to the area in the 17th century, when Finland and Ingria were both part of the Swedish Empire...
soon became the dominant ethnic group.
During the Great Northern War
Great Northern War
The Great Northern War was a conflict in which a coalition led by the Tsardom of Russia successfully contested the supremacy of the Swedish Empire in northern Central Europe and Eastern Europe. The initial leaders of the anti-Swedish alliance were Peter I the Great of Russia, Frederick IV of...
(1700–1721) the territory of what is now Leningrad Oblast was returned from Sweden by Russia under Peter the Great, who founded Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg is a city and a federal subject of Russia located on the Neva River at the head of the Gulf of Finland on the Baltic Sea...
amidst the land in 1703, which soon became the capital of the Russian Empire
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was a state that existed from 1721 until the Russian Revolution of 1917. It was the successor to the Tsardom of Russia and the predecessor of the Soviet Union...
. In 1708, most of the territory was organized into Ingermanland Governorate
Saint Petersburg Governorate
Saint Petersburg Governorate , or Government of Saint Petersburg, was an administrative division of the Russian Empire, which existed in 1708–1927....
under Governor General Alexander Menshikov. It was renamed Saint Petersburg Governorate in 1710 (the borders of that governorate, however, differed very significantly from those of the present-day oblast). In 1721, the territorial concessions of Sweden were confirmed with the Treaty of Nystad
Treaty of Nystad
The Treaty of Nystad was the last peace treaty of the Great Northern War. It was concluded between the Tsardom of Russia and Swedish Empire on 30 August / 10 September 1721 in the then Swedish town of Nystad , after Sweden had settled with the other parties in Stockholm and Frederiksborg.During...
.
The life of the countryside was greatly influenced by the vicinity of the imperial capital, which became a growing market for its agricultural production as well as the main consumer of its mineral and forest resources. In 1719–1810, Ladoga Canal
Ladoga Canal
Ladoga Canal is a historical water transport route, now situated in Leningrad Oblast, linking the Neva and the Svir River so as to bypass the stormy waters of Lake Ladoga which lies immediately to the north...
was dug between the River Svir and the River Neva as part of the Volga-Baltic waterway to bypass stormy waters of Lake Ladoga
Lake Ladoga
Lake Ladoga is a freshwater lake located in the Republic of Karelia and Leningrad Oblast in northwestern Russia, not far from Saint Petersburg. It is the largest lake in Europe, and the 14th largest lake by area in the world.-Geography:...
. Since the advent of the rail transport in the late 19th century, the areas in the vicinity of Saint Petersburg had been a popular summer resort destinations (dacha
Dacha
Dacha is a Russian word for seasonal or year-round second homes often located in the exurbs of Soviet and post-Soviet cities. Cottages or shacks serving as family's main or only home are not considered dachas, although many purpose-built dachas are recently being converted for year-round residence...
s) for its residents. However, while Saint Petersburg itself from the very beginning was populated mostly by Russians, it was not until the 20th century that its surrounding population was Russified.
In 1914, with the beginning of World War I
World War I
World War I , which was predominantly called the World War or the Great War from its occurrence until 1939, and the First World War or World War I thereafter, was a major war centred in Europe that began on 28 July 1914 and lasted until 11 November 1918...
, Saint Petersburg was renamed Petrograd and the governorate was accordingly renamed Petrograd Governorate. After the Russian Revolution, in 1918, the capital was transferred from Petrograd to Moscow
Moscow
Moscow is the capital, the most populous city, and the most populous federal subject of Russia. The city is a major political, economic, cultural, scientific, religious, financial, educational, and transportation centre of Russia and the continent...
, farther from the borders of the country. In 1919, during the Russian Civil War
Russian Civil War
The Russian Civil War was a multi-party war that occurred within the former Russian Empire after the Russian provisional government collapsed to the Soviets, under the domination of the Bolshevik party. Soviet forces first assumed power in Petrograd The Russian Civil War (1917–1923) was a...
, the Northwestern White Army advancing from Estonia and led by Nikolai Yudenich tried to capture Petrograd and even managed to reach its southern outskirts, but the attack against the Red Army under Leon Trotsky
Leon Trotsky
Leon Trotsky , born Lev Davidovich Bronshtein, was a Russian Marxist revolutionary and theorist, Soviet politician, and the founder and first leader of the Red Army....
ultimately failed, and Yudenich retreated back. The border with Estonia was established in the Russian-Estonian Treaty of Tartu
Treaty of Tartu (Russian–Estonian)
Tartu Peace Treaty or Treaty of Tartu was a peace treaty between Estonia and Russian SFSR signed on February 2, 1920 ending the Estonian War of Independence. The terms of the treaty stated that "Russia unreservedly recognises" the independence of Republic of Estonia de jure and renounced in...
of 1920. Ingrian Finns of North Ingria
North Ingria
The Republic of North Ingria or Republic of Kirjasalo was a short-lived state of Ingrian Finns in the southern part of the Karelian Isthmus, which seceded from Bolshevist Russia after the October Revolution. Its aim was to be incorporated into Finland. It ruled parts of Ingria from 1919 until...
attempted to secede in 1918–1920, but were incorporated back with the Russian-Finnish Treaty of Tartu
Treaty of Tartu (Russian–Finnish)
The Treaty of Tartu between Finland and Soviet Russia was signed on 14 October 1920 after negotiations that lasted for four months. The treaty confirmed the border between Finland and Soviet Russia after the Finnish civil war and Finnish volunteer expeditions in Russian East Karelia. Ratifications...
, which settled the border between Finland and Soviet Russia. In 1924, Petrograd was renamed Leningrad and Petrograd Governorate was again renamed accordingly (Leningrad Governorate).
Leningrad Oblast


All-Russian Central Executive Committee
All-Russian Central Executive Committee , was the highest legislative, administrative, and revising body of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic. Although the All-Russian Congress of Soviets had supreme authority, in periods between its sessions its powers were passed to VTsIK...
"On the Establishment of Leningrad Oblast" and "On the Borders and Composition of the Okrugs of Leningrad Oblast" by merging Cherepovets
Cherepovets Governorate
Cherepovets Governorate was a governorate of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic from 1918 to 1927. Its seat was in the city of Cherepovets...
, Leningrad, Murmansk
Murmansk Governorate
Murmansk Governorate was an administrative division of the early Russian SFSR which existed in 1921–1927. The governorate was established on the territory of former Alexandrovsky Uyezd of Arkhangelsk Governorate by the All-Russian Central Executive Committee Decree issued on June 13, 1921...
, Novgorod
Novgorod Governorate
Novgorod Governorate , or Government of Novgorod, was a governorate of the Russian Empire.The governorate was established in 1727 from Belozersk, Novgorod, Pskov, Tver, and Velikiye Luki Provinces of the St. Petersburg Governorate and existed until 1927, when its territory was included into...
, and Pskov Governorates. The territory of the oblast corresponded to the modern territories of the present-day Leningrad Oblast (with the exception of the Karelian Isthmus
Karelian Isthmus
The Karelian Isthmus is the approximately 45–110 km wide stretch of land, situated between the Gulf of Finland and Lake Ladoga in northwestern Russia, to the north of the River Neva . Its northwestern boundary is the relatively narrow area between the Bay of Vyborg and Lake Ladoga...
and the territories along the border with Estonia), Novgorod Oblast
Novgorod Oblast
Novgorod Oblast is a federal subject of Russia , located between Moscow and Saint Petersburg. Its administrative center is the city of Veliky Novgorod. Some of the oldest Russian cities, including Veliky Novgorod and Staraya Russa, are located there...
, Pskov Oblast
Pskov Oblast
Pskov Oblast is a federal subject of Russia . Pskov Oblast borders the countries of Estonia and Latvia, as well as Belarus. It is the westernmost federal subject of contiguous Russia . Its major cities are the administrative center Pskov and Velikiye Luki . Area: 55,300 km²...
, parts of Vologda Oblast
Vologda Oblast
Vologda Oblast is a federal subject of Russia . Its administrative center is Vologda. The largest city is Cherepovets.Vologda Oblast is rich in historic monuments, such as the magnificent Kirillo-Belozersky Monastery, Ferapontov Convent , medieval towns of Velikiy Ustyug and Belozersk, baroque...
, most of Murmansk Oblast
Murmansk Oblast
Murmansk Oblast is a federal subject of Russia , located in the northwestern part of Russia. Its administrative center is the city of Murmansk.-Geography:...
, and the federal city of Saint Petersburg. The total area of the oblast was 360400 square kilometres (139,151.2 sq mi); more than four times larger than the modern entity. Administratively, the oblast was divided into nine okrug
Okrug
Okrug is an administrative division of some Slavic states. The word "okrug" is a loanword in English, but it is nevertheless often translated as "area", "district", or "region"....
s (Borovichi, Cherepovets, Leningrad, Lodeynoye Pole, Luga, Murmansk
Murmansk Okrug
Murmansk Okrug was an administrative division of the Russian SFSR, Soviet Union, which existed in 1927–1938.-Creation:The okrug was established on August 1, 1927, when the All-Russian Central Executive Committee issued two Resolutions: "On the Establishment of Leningrad Oblast" and "On the...
, Novgorod, Pskov, and Velikiye Luki), each of which was in turn subdivided into district
Raion
A raion is a type of administrative unit of several post-Soviet countries. The term, which is from French rayon 'honeycomb, department,' describes both a type of a subnational entity and a division of a city, and is commonly translated in English as "district"...
s.
In 1929, Velikoluksky District
Velikoluksky District
Velikoluksky District is an administrative and municipal district , one of the 24 in Pskov Oblast, Russia....
was transferred to newly formed Western Oblast
Western Oblast
Western Oblast was an early oblast of Russian SFSR. It was established by VTsIK on October 1, 1929..By the 1937 All-Union Census, its population was 4,693,495 persons.It was dissolved on September 27, 1937....
. Leningrad was administratively separated from Leningrad Oblast in December 1931. In 1935 five southernmost districts were made part of Kalinin Oblast. In 1936 some parts of the territory of Leningrad Suburban District of Leningrad was returned to Leningrad Oblast and divided into Vsevolozhsky District
Vsevolozhsky District
Vsevolozhsky District is a district of Leningrad Oblast, Russia, located in the southeastern part of the Karelian Isthmus. The area of the district is . Its administrative center is the town of Vsevolozhsk. District's population:...
, Krasnoselsky District
Krasnoselsky District, Saint Petersburg
Krasnoselsky District, Saint Petersburg is an administrative and municipal district , one of the 18 in Saint Petersburg, Russia....
, Pargolovsky District and Slutsky District (renamed Pavlovsky District in 1944). Vologda Oblast
Vologda Oblast
Vologda Oblast is a federal subject of Russia . Its administrative center is Vologda. The largest city is Cherepovets.Vologda Oblast is rich in historic monuments, such as the magnificent Kirillo-Belozersky Monastery, Ferapontov Convent , medieval towns of Velikiy Ustyug and Belozersk, baroque...
, which has included the easternmost districts of Leningrad Oblast (former Cherepovets Governorate), was created in 1937. Murmansk Oblast
Murmansk Oblast
Murmansk Oblast is a federal subject of Russia , located in the northwestern part of Russia. Its administrative center is the city of Murmansk.-Geography:...
was excluded from Leningrad Oblast in 1938.
In the fall of 1934, the Forbidden Border Zone
Border Security Zone of Russia
The Border Security Zone in Russia is the designation of a strip of land where economic activity and access are restricted without permission of the FSB. In order to visit the zone, a permit issued by the local FSB department is required. The restricted access zone The Border Security Zone in...
along the western border of the Soviet Union was established, where nobody could appear without special permission issued by NKVD
NKVD
The People's Commissariat for Internal Affairs was the public and secret police organization of the Soviet Union that directly executed the rule of power of the Soviets, including political repression, during the era of Joseph Stalin....
. It was officially only 7.5 km deep initially, but along the Estonian border it extended to as much as 90 km. The zone was to be free of Finnic and some other peoples, who were considered politically unreliable. Starting from the 1935, the Soviet authorities carried out mass forced transfer
Population transfer in the Soviet Union
Population transfer in the Soviet Union may be classified into the following broad categories: deportations of "anti-Soviet" categories of population, often classified as "enemies of workers," deportations of entire nationalities, labor force transfer, and organized migrations in opposite...
of the Ingrian Finnish population of the oblast, which constituted majority in many rural localities as late as in the beginning of the century, to the east, replacing them with people from other parts of the Soviet Union.
On November 30, 1939, the Soviet Union waged the Winter War
Winter War
The Winter War was a military conflict between the Soviet Union and Finland. It began with a Soviet offensive on 30 November 1939 – three months after the start of World War II and the Soviet invasion of Poland – and ended on 13 March 1940 with the Moscow Peace Treaty...
against neighboring Finland and with the Moscow Peace Treaty in 1940 gained some territories, including Karelian Isthmus
Karelian Isthmus
The Karelian Isthmus is the approximately 45–110 km wide stretch of land, situated between the Gulf of Finland and Lake Ladoga in northwestern Russia, to the north of the River Neva . Its northwestern boundary is the relatively narrow area between the Bay of Vyborg and Lake Ladoga...
. Their Karelian population was hastily evacuated
Evacuation of Finnish Karelia
As a result of the 1940 Moscow Peace Treaty that concluded the Winter War, Finland ceded the area of Finnish Karelia and other territories to the Soviet Union...
to inner Finland and later replaced with people from other parts of the Soviet Union. A small part of the territory (the districts of Kanneljärvi, Koivisto
Primorsk, Leningrad Oblast
Primorsk is a coastal town in Vyborgsky District of Leningrad Oblast, Russia, and the largest Russian port on the Baltic. It is located on the Karelian Isthmus, west of St. Petersburg, at the northern coast of the Gulf of Finland, near Birch Islands, protected as a sea bird sanctuary...
and Rautu) was incorporated into Leningrad Oblast, the rest being included within the Karelo-Finnish SSR
Karelo-Finnish SSR
The Karelo-Finnish Soviet Socialist Republic was a short-lived republic that was a part of the former Soviet Union. The republic existed from 1940 until it was merged back into the Russian SFSR in 1956 ....
.
In 1941, Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany , also known as the Third Reich , but officially called German Reich from 1933 to 1943 and Greater German Reich from 26 June 1943 onward, is the name commonly used to refer to the state of Germany from 1933 to 1945, when it was a totalitarian dictatorship ruled by...
invaded the Soviet Union in the Operation Barbarossa
Operation Barbarossa
Operation Barbarossa was the code name for Germany's invasion of the Soviet Union during World War II that began on 22 June 1941. Over 4.5 million troops of the Axis powers invaded the USSR along a front., the largest invasion in the history of warfare...
, and shortly thereafter the territory became place of the Battle of Leningrad. Wehrmacht captured the southwestern part of the oblast and reached Tikhvin
Tikhvin
Tikhvin is a town and the administrative center of Tikhvinsky District of Leningrad Oblast, Russia, located on both banks of the Tikhvinka River in the east of the oblast, east of St. Petersburg. Tikhvin is also an industrial and cultural center of the district, as well as its transportation...
in the east, while Finnish troops quickly recaptured the ceded territories
Finnish reconquest of the Karelian Isthmus (1941)
The Finnish reconquest of the Karelian Isthmus refers to a military campaign carried out by Finland in 1941. It was part of what is commonly referred to as the Continuation War.Early in the war Finnish forces reconquered the Karelian Isthmus...
in the Continuation War
Continuation War
The Continuation War was the second of two wars fought between Finland and the Soviet Union during World War II.At the time of the war, the Finnish side used the name to make clear its perceived relationship to the preceding Winter War...
, encircling Leningrad from the land. In 1944 Soviet offensives managed to expel Wehrmacht and put military pressure
Fourth strategic offensive
The Vyborg–Petrozavodsk Offensive or Karelian offensive was a strategic operation by the Soviet Leningrad and Karelian Fronts against Finland on the Karelian Isthmus and East Karelia fronts of the Continuation War, on the Eastern Front of World War II. The Soviet forces captured East Karelia and...
on Finland, which ceded Karelian Isthmus
Karelian Isthmus
The Karelian Isthmus is the approximately 45–110 km wide stretch of land, situated between the Gulf of Finland and Lake Ladoga in northwestern Russia, to the north of the River Neva . Its northwestern boundary is the relatively narrow area between the Bay of Vyborg and Lake Ladoga...
again with the Moscow Armistice
Moscow Armistice
The Moscow Armistice was signed between Finland on one side and the Soviet Union and United Kingdom on the other side on September 19, 1944, ending the Continuation War...
of September 19, 1944. This time the gained territories of the isthmus was incorporated within Leningrad Oblast (Vyborgsky
Vyborgsky District, Leningrad Oblast
Vyborgsky District is a district of Leningrad Oblast, Russia, on the Karelian Isthmus, established in 1940 when the territory had been ceded by Finland to the Soviet Union by Moscow Peace Treaty as a result of the Winter War. The area of the district is . Its administrative center is the town of...
and Priozersky District
Priozersky District
Priozersky District is a district of Leningrad Oblast, Russia. The area of the district is . Its administrative center is the town of Priozersk. District's population: -History:...
s). In 1947 the territorial gains were confirmed with the Paris Peace Treaty. Novgorod
Novgorod Oblast
Novgorod Oblast is a federal subject of Russia , located between Moscow and Saint Petersburg. Its administrative center is the city of Veliky Novgorod. Some of the oldest Russian cities, including Veliky Novgorod and Staraya Russa, are located there...
and Pskov Oblast
Pskov Oblast
Pskov Oblast is a federal subject of Russia . Pskov Oblast borders the countries of Estonia and Latvia, as well as Belarus. It is the westernmost federal subject of contiguous Russia . Its major cities are the administrative center Pskov and Velikiye Luki . Area: 55,300 km²...
s were formed out of the southern parts of Leningrad Oblast in 1944. In January 1945 a small part of the Estonian SSR to the east of the River Narva with the town of Jaanilinn (now Ivangorod) was transferred to the Russian SFSR and incorporated into Leningrad Oblast. Since then, the territory of Leningrad Oblast hasn't changed much, although some suburbs of Leningrad (now Saint Petersburg) have been excluded from the oblast and incorporated into the city. In October 1946 Leningrad gained from the oblast some former Finnish territories along the northern coast of the Gulf of Finland
Gulf of Finland
The Gulf of Finland is the easternmost arm of the Baltic Sea. It extends between Finland and Estonia all the way to Saint Petersburg in Russia, where the river Neva drains into it. Other major cities around the gulf include Helsinki and Tallinn...
divided into Sestroretsky District and Kurortny District
Kurortny District
Kurortny District is a district of Saint Petersburg, Russia, located on the Karelian Isthmus along the northern shore of the Gulf of Finland. Population:...
, including the town of Terijoki.
In 1953, Pavlovsky District
Pavlovsky District
Pavlovsky District is the name of several administrative and municipal districts in Russia. The district names are generally related to or derived from the male first name Pavel.-Districts of the federal subjects:...
of the oblast was abolished, and parts of its territory including Pavlovsk were made subordinate to Leningrad. In 1954 the settlements Levashovo, Pargolovo and Pesochny
Pesochny
Pesochny is a municipal settlement in Kurortny District of the federal city of St. Petersurg, Russia, located on the Karelian Isthmus, on the northern shore of the Gulf of Finland. Population:...
were also transferred to Leningrad. In 1956 Boksitogorsky District
Boksitogorsky District
Boksitogorsky District is an administrative district , one of the 17 in Leningrad Oblast, Russia....
of Leningrad Oblast gained a small territory of Novgorod Oblast
Novgorod Oblast
Novgorod Oblast is a federal subject of Russia , located between Moscow and Saint Petersburg. Its administrative center is the city of Veliky Novgorod. Some of the oldest Russian cities, including Veliky Novgorod and Staraya Russa, are located there...
. Uritsk was transferred from the oblast to the city of Leningrad in 1963, Krasnoye Selo
Krasnoye Selo
Krasnoye Selo is a municipal town in Krasnoselsky District of the federal city of St. Petersburg, Russia. It is located south-southeast of the city center. Population:...
and several settlements nearby—in 1973, Lomonosov
Lomonosov, Russia
Lomonosov is a municipal town in Petrodvortsovy District of the federal city of St. Petersburg, Russia, situated on the southern coast of the Gulf of Finland, west of St. Petersburg proper. Population:...
—in 1978.
After a referendum in 1991, the city of Leningrad was renamed back to Saint Petersburg, but Leningrad Oblast retained its name.
Executive
The Leningrad Region Administration headed by the Governor exercises executive authority in the region. The head of the Administration is elected for a four-year term and represents the region both within Russia and abroad. In addition, he also independently forms various executive bodies and bears personal responsibility for the results of their activities. Under the powers granted to him by the region’s Statute, the Governor is authorized to:- present a draft of the regional budget to the Legislative Assembly for approval and ensure its implementation;
- appoint and dismiss the heads of non-municipal territorial administrative formations in Leningrad Region;
- suspend acts of the Leningrad Regional Government if they contradict existing legislation;
- decide questions of the formation, reorganization, and dissolution of territorial agencies of federal government executive bodies in the region and appoint the appropriate officials;
- settle disputes arising between the Government and the Legislative Assembly of the region.
Legislature
The Leningrad Regional Legislative Assembly is the standing government representative body. It autonomously exercises its function using the Constitution of the Russian Federation, federal legislation, the Statute of Leningrad Region, and regional laws as guides. The Legislative Assembly is a legal entity. Acts passed by it are binding on all bodies and officials of state authorities and local governments of Leningrad Region, organizations, and private citizens.Flora
The most taxonomically diverse vascular plant families are AsteraceaeAsteraceae
The Asteraceae or Compositae , is an exceedingly large and widespread family of vascular plants. The group has more than 22,750 currently accepted species, spread across 1620 genera and 12 subfamilies...
, Cyperaceae
Cyperaceae
Cyperaceae are a family of monocotyledonous graminoid flowering plants known as sedges, which superficially resemble grasses or rushes. The family is large, with some 5,500 species described in about 109 genera. These species are widely distributed, with the centers of diversity for the group...
, Poaceae
Poaceae
The Poaceae is a large and nearly ubiquitous family of flowering plants. Members of this family are commonly called grasses, although the term "grass" is also applied to plants that are not in the Poaceae lineage, including the rushes and sedges...
and Rosaceae
Rosaceae
Rosaceae are a medium-sized family of flowering plants, including about 2830 species in 95 genera. The name is derived from the type genus Rosa. Among the largest genera are Alchemilla , Sorbus , Crataegus , Cotoneaster , and Rubus...
. By far the most diverse genus is Carex
Carex
Carex is a genus of plants in the family Cyperaceae, commonly known as sedges. Other members of the Cyperaceae family are also called sedges, however those of genus Carex may be called "true" sedges, and it is the most species-rich genus in the family. The study of Carex is known as...
(68 species). The diversity in genera Hieracium
Hieracium
Hieracium known by its common name Hawkweed and long ago by its classical name hierakion which comes from the ancient Greek hierax, "a hawk"...
(with Pilosella), Ranunculus
Ranunculus
Ranunculus is a large genus of about 600 species of plants in the Ranunculaceae. Members of the genus include the buttercups, spearworts, water crowfoots and the lesser celandine....
(with Batrachium), Alchemilla
Alchemilla
Alchemilla is a genus of herbaceous perennial plants in the Rosaceae, and a popular garden herb with the common name Lady's mantle. There are about 300 species, the majority native to cool temperate and subarctic regions of Europe and Asia, with a few species native to the mountains of Africa,...
, Galium
Galium
Galium is a large genus of annual and perennial herbaceous plants in the family Rubiaceae, with 617 known species occurring in the temperate zones of both the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. Most species are known as bedstraw. G...
, Potamogeton
Potamogeton
Potamogeton is a genus of aquatic, mostly freshwater, plants of the family Potamogetonaceae. Most are known by the common name pondweed, although many unrelated plants may be called pondweed, such as Canadian pondweed...
, Salix, Veronica
Veronica (plant)
Veronica is the largest genus in the flowering plant family Plantaginaceae, with about 500 species; it was formerly classified in the family Scrophulariaceae...
, Viola, Juncus
Juncus
Juncus is a genus in the plant family Juncaceae. It consists of some 200 to 300 or more species of grassy plants commonly called rushes...
, Artemisia
Artemisia (plant)
Artemisia is a large, diverse genus of plants with between 200 to 400 species belonging to the daisy family Asteraceae. It comprises hardy herbs and shrubs known for their volatile oils. They grow in temperate climates of the Northern Hemisphere and Southern Hemisphere, usually in dry or semi-dry...
, Potentilla
Potentilla
Potentilla is the genus of typical cinquefoils, containing about 500 species of annual, biennial and perennial herbs in the rose family Rosaceae. They are generally Holarctic in distribution, though some may even be found in montane biomes of the New Guinea Highlands...
, Rumex
Rumex
The docks and sorrels, genus Rumex L., are a genus of about 200 species of annual, biennial and perennial herbs in the buckwheat family Polygonaceae....
, Festuca, Epilobium
Epilobium
Epilobium is a genus in the family Onagraceae, containing about 160-200 species of flowering plants with a worldwide distribution. They are generally abundant in the subarctic, temperate and subantarctic regions, whereas in the subtropics and tropics they are restricted to the cool montane biomes,...
, Poa
Poa
Poa is a genus of about 500 species of grasses, native to the temperate regions of both hemispheres. Common names include meadow-grass , bluegrass , tussock , and speargrass. "Poa" is Greek for fodder...
, Trifolium, Campanula
Campanula
Campanula is one of several genera in the family Campanulaceae with the common name bellflower. It takes its name from their bell-shaped flowers—campanula is Latin for "little bell"....
, Vicia
Vicia
Vicia is a genus of about 140 species of flowering plants commonly known as vetches. It is in the legume family . Member species are native to Europe, North America, South America, Asia and Africa. Some other genera of their subfamily Faboideae also have names containing "vetch", for example the...
, Lathyrus
Lathyrus
Lathyrus is a genus of flowering plant species known as sweet peas and vetchlings. Lathyrus is in the legume family Fabaceae and contains approximately 160 species. They are native to temperate areas, with a breakdown of 52 species in Europe, 30 species in North America, 78 in Asia, 24 in...
, Geranium is also considerable. The territory has no endemic plant taxa. Vascular plant species of Leningrad Oblast listed in the red data book of Russia are Botrychium simplex, Cephalanthera rubra, Cypripedium calceolus
Cypripedium calceolus
Cypripedium calceolus is a lady's-slipper orchid, and the type species of the genus Cypripedium.It is a widespread plant worldwide, found from Europe east through Asia to the Pacific Ocean. It is found in open woodland on moist calcareous soils. It is found in continental Europe growing in the...
, Epipogium aphyllum
Epipogium aphyllum
The Ghost Orchid - not to be confused with the American Ghost Orchid - is a myco-heterotrophic orchid lacking chlorophyll....
, Lobelia dortmanna
Lobelia dortmanna
Lobelia dortmanna is a species of Lobelia native to cool temperate regions of northern Europe and northern North America .It is a stoloniferous herbaceous...
, Myrica gale
Myrica gale
Myrica gale is a species of flowering plant in the genus Myrica, native to northern and western Europe and parts of northern North America. It is a deciduous shrub growing to 1–2 m tall. Common names include Bog Myrtle and Sweet Gale...
, Ophrys insectifera, Orchis militaris, Pulsatilla pratensis, Pulsatilla vernalis
Pulsatilla vernalis
Pulsatilla vernalis belongs to the Buttercup family , native to Europe.It grows to 5–15 cm high. The finely-dissected leaves appear in early spring....
. http://www.paslo.ru/newimg/111.doc
Administrative divisions
The Oblast consists of 29 municipal formations, including 17 districts, 16 regional cities, 10 district cities, and 41 worker-type settlements. St. Petersburg is its center.Demographics
Population: (2002) 1,669,205.For the first half of 2007, the birth rate was 8.1 per 1000 http://demoscope.ru/weekly/2007/0301/barom04.php
Ethnic groups: According to the (2002 Census
Russian Census (2002)
Russian Census of 2002 was the first census of the Russian Federation carried out on October 9 through October 16, 2002. It was carried out by the Russian Federal Service of State Statistics .-Resident population:...
) there were thirteen recognised ethnic groups of more than two thousand persons each; the 'national composition' was
- RussianRussiansThe Russian people are an East Slavic ethnic group native to Russia, speaking the Russian language and primarily living in Russia and neighboring countries....
89.58% - UkrainianUkrainiansUkrainians are an East Slavic ethnic group native to Ukraine, which is the sixth-largest nation in Europe. The Constitution of Ukraine applies the term 'Ukrainians' to all its citizens...
2.51% - BelarusiansBelarusiansBelarusians ; are an East Slavic ethnic group who populate the majority of the Republic of Belarus. Introduced to the world as a new state in the early 1990s, the Republic of Belarus brought with it the notion of a re-emerging Belarusian ethnicity, drawn upon the lines of the Old Belarusian...
1.70% - TatarTatarsTatars are a Turkic speaking ethnic group , numbering roughly 7 million.The majority of Tatars live in the Russian Federation, with a population of around 5.5 million, about 2 million of which in the republic of Tatarstan.Significant minority populations are found in Uzbekistan, Kazakhstan,...
0.57% - FinnishIngrian FinnsThe Ingrian Finns are the Finnish population of Ingria descending from Lutheran Finnish immigrants introduced to the area in the 17th century, when Finland and Ingria were both part of the Swedish Empire...
0.48% - ArmenianArmeniansArmenian people or Armenians are a nation and ethnic group native to the Armenian Highland.The largest concentration is in Armenia having a nearly-homogeneous population with 97.9% or 3,145,354 being ethnic Armenian....
0.33% - Roma 0.27
- AzeriAzeris in RussiaAside from the large Azeri community native to Russia's Dagestan Republic, the majority of Azeris in Russia are fairly recent immigrants. Azeris started settling in Russia around the late 19th century, but their migration became intensive after World War II. It rapidly increased with the collapse...
0.23% - ChuvashChuvash peopleThe Chuvash people are a Turkic ethnic group, native to an area stretching from the Volga Region to Siberia. Most of them live in Republic of Chuvashia and surrounding areas, although Chuvash communities may be found throughout all Russia.- Etymology :...
0.17% - GermanEthnic GermanEthnic Germans historically also ), also collectively referred to as the German diaspora, refers to people who are of German ethnicity. Many are not born in Europe or in the modern-day state of Germany or hold German citizenship...
0.14% - Mordvin 0.13%
- KarelianKareliansThe Karelians are a Baltic-Finnic ethnic group living mostly in the Republic of Karelia and in other north-western parts of the Russian Federation. The historic homeland of Karelians includes also parts of present-day Eastern Finland and the formerly Finnish territory of Ladoga Karelia...
0.12% - Veps 0.12%
- MoldovanMoldovansMoldovans or Moldavians are the largest population group of Moldova...
0.12% - JewishJewsThe Jews , also known as the Jewish people, are a nation and ethnoreligious group originating in the Israelites or Hebrews of the Ancient Near East. The Jewish ethnicity, nationality, and religion are strongly interrelated, as Judaism is the traditional faith of the Jewish nation...
0.10% - PolishPolesthumb|right|180px|The state flag of [[Poland]] as used by Polish government and diplomatic authoritiesThe Polish people, or Poles , are a nation indigenous to Poland. They are united by the Polish language, which belongs to the historical Lechitic subgroup of West Slavic languages of Central Europe...
0.10% - GeorgianGeorgian peopleThe Georgians are an ethnic group that have originated in Georgia, where they constitute a majority of the population. Large Georgian communities are also present throughout Russia, European Union, United States, and South America....
0.09% - EstonianEstoniansEstonians are a Finnic people closely related to the Finns and inhabiting, primarily, the country of Estonia. They speak a Finnic language known as Estonian...
0.08% - BashkirBashkirsThe Bashkirs are a Turkic people indigenous to Bashkortostan extending on both parts of the Ural mountains, on the place where Europe meets Asia. Groups of Bashkirs also live in the republic of Tatarstan, Perm Krai, Chelyabinsk, Orenburg, Tyumen, Sverdlovsk, Kurgan, Samara and Saratov Oblasts of...
0.07% - KoreanKoryo-saramKoryo-saram is the name which ethnic Koreans in the post-Soviet states use to refer to themselves. Approximately 500,000 ethnic Koreans reside in the former Soviet Union, primarily in the now-independent states of Central Asia. There are also large Korean communities in southern Russia , the...
0.06% - UzbekUzbeksThe Uzbeks are a Turkic ethnic group in Central Asia. They comprise the majority population of Uzbekistan, and large populations can also be found in Afghanistan, Tajikstan, Kyrgyzstan, Turkmenistan, Kazakhstan, Russia, Pakistan, Mongolia and the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region of China...
0.06% - Mari 0.06%
- Udmurt 0.06%
- Tajik 0.05%
- KazakhKazakhsThe Kazakhs are a Turkic people of the northern parts of Central Asia ....
0.05%
and many other ethnic groups of less than eight hundred persons each. A further 2.34% of residents declined to state their nationality on the census questionnaire.
Twin regions
Aarhus MunicipalityAarhus Municipality
Aarhus Municipality, also commonly known by its Danish spelling Århus Municipality, is a municipality on the east coast of the Jutland peninsula in central Denmark. The municipality covers an area of , and has a total population of 307.000...
, Denmark
Denmark
Denmark is a Scandinavian country in Northern Europe. The countries of Denmark and Greenland, as well as the Faroe Islands, constitute the Kingdom of Denmark . It is the southernmost of the Nordic countries, southwest of Sweden and south of Norway, and bordered to the south by Germany. Denmark...
Chungcheongnam-do
Chungcheongnam-do
Chungcheongnam-do or Chungnam is a province in the west of South Korea. The province was formed in 1896 from the south-western half of the former Chungcheong Province and remained a province of Korea until the country's division in 1945, thereafter becoming part of South Korea...
, South Korea
South Korea
The Republic of Korea , , is a sovereign state in East Asia, located on the southern portion of the Korean Peninsula. It is neighbored by the People's Republic of China to the west, Japan to the east, North Korea to the north, and the East China Sea and Republic of China to the south...
Kyoto Prefecture
Kyoto Prefecture
is a prefecture of Japan located in the Kansai region of the island of Honshu. The capital is the city of Kyoto.- History :Until the Meiji Restoration, the area of Kyoto prefecture was known as Yamashiro....
, Japan
Japan
Japan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south...
Lombardy
Lombardy
Lombardy is one of the 20 regions of Italy. The capital is Milan. One-sixth of Italy's population lives in Lombardy and about one fifth of Italy's GDP is produced in this region, making it the most populous and richest region in the country and one of the richest in the whole of Europe...
, Italy
Italy
Italy , officially the Italian Republic languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Italy's official name is as follows:;;;;;;;;), is a unitary parliamentary republic in South-Central Europe. To the north it borders France, Switzerland, Austria and...
Lower Silesian Voivodeship
Lower Silesian Voivodeship
Lower Silesian Voivodeship, or Lower Silesia Province , is one of the 16 voivodeships into which Poland is currently divided. It lies in southwestern Poland...
, Poland
Poland
Poland , officially the Republic of Poland , is a country in Central Europe bordered by Germany to the west; the Czech Republic and Slovakia to the south; Ukraine, Belarus and Lithuania to the east; and the Baltic Sea and Kaliningrad Oblast, a Russian exclave, to the north...
Nordland
Nordland
is a county in Norway in the North Norway region, bordering Troms in the north, Nord-Trøndelag in the south, Norrbottens län in Sweden to the east, Västerbottens län to the southeast, and the Atlantic Ocean to the west. The county was formerly known as Nordlandene amt. The county administration is...
, Norway
Norway
Norway , officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic unitary constitutional monarchy whose territory comprises the western portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula, Jan Mayen, and the Arctic archipelago of Svalbard and Bouvet Island. Norway has a total area of and a population of about 4.9 million...
from 1987
Nature
- Айрапетьянц А.Э., Стрелков П.П., Фокин И.М. Звери. [Природа Ленинградской области]. Leningrad: Лениздат, 1987.
- Балашова Н.Б., Никитина В.Н. Водоросли [Природа Ленинградской области]. Leningrad: Лениздат, 1989. ISBN 5289003444
- Биоразнообразие Ленинградской области (Водоросли. Грибы. Лишайники. Мохообразные. Беспозвоночные животные. Рыбы и рыбообразные) / Под. ред. Н.Б.Балашовой, А.А.Заварзина. - (Труды Санкт-Петербургского общества естествоиспытателей. Серия 6. Том 2.). – Saint Petersburg: Изд-во СПб. университета, 1999.
- Бобров Р.В. Леса Ленинградской области. Leningrad: Лениздат, 1979.
- Бродский А.К., Львовский А.Л. Пауки, насекомые [Природа Ленинградской области]. Leningrad: Лениздат, 1990. ISBN 528900610X
- Иллюстрированный определитель растений Ленинградской области / Под ред. А. Л. Буданцева, Г. П. Яковлева. Moscow: КМК, 2006. ISBN 5873172609
- Кириллова М.А., Распопов И.М. Озера Ленинградской области. Leningrad: Лениздат, 1971.
- Красная Книга природы Ленинградской области. Том 1. Особо охраняемые природные территории. Отв. ред. Г.А. Носков, М. С. Боч [Red Data Book of Nature of the Leningrad Region. Vol. 1. Protected Areas]. Saint Petersburg: Акционер и К, 1998. ISBN 5874010726
- Красная Книга природы Ленинградской области. Том 2. Растения и грибы. Отв. ред. Г.А. Носков [Red Data Book of Nature of the Leningrad Region. Vol. 2. Plants and Fungi]. Saint Petersburg: Мир и Семья, 2000. ISBN 5943650016
- Красная Книга природы Ленинградской области. Том 3. Животные. Отв. ред. Г.А. Носков [Red Data Book of Nature of the Leningrad Region. Vol. 3. Animals]. Saint Petersburg: Мир и Семья, 2002. ISBN 5943650210
- Леса Ленинградской области: современное состояние и пути их возможного развития. Saint Petersburg, 1998. ISBN 5230104570
- Мальчевский А. С., Пукинский Ю. Б. Птицы Ленинградской области и сопредельных территорий. История, биология, охрана. Т.1-2. Leningrad: Изд-во ЛГУ, 1983.
- Наумов Н.А. Флора грибов Ленинградской области. Том 1. Архимицеты и фикомицеты [The Fungus Flora of the Leningrad Region. Vol. 1. Archimycetes, Phycomycetes]. Moscow – Leningrad: Изд-во АН СССР, 1954.
- Наумов Н.А. Флора грибов Ленинградской области. Том 2 [The Fungus Flora of the Leningrad Region. Vol. 2]. Moscow – Leningrad: Наука, 1964.
- Неелов, А.В. Рыбы [Природа Ленинградской области]. Leningrad: Лениздат, 1987.
- Покровская Г.В., Бычкова А.Т. Климат Ленинграда и его окрестностей. Leningrad: Гидрометеоиздат, 1967.
- Природа Ленинградской области и ее охрана / Ред. Т.И. Миронова, Э.И. Слепян. - Leningrad: Лениздат, 1983.
- Пукинский Ю. Б. Птицы [Природа Ленинградской области]. Leningrad: Лениздат, 1988.
- Свидерская М.Д., Храбрый В.М. Сохраним для потомков: Особо охраняемые природные территории Ленинградской области. Leningrad: Лениздат, 1985.
- Старобогатов Я.И. Раки, моллюски [Природа Ленинградской области]. Leningrad: Лениздат, 1988. ISBN 5289001255
- Филимонов Р.В., Удалов С.Г. Жуки-усачи Ленинградской области. Атлас-определитель. [Longhorn Beetles of the St. Petersburg Region: An Identification Atlas]. Saint Petersburg: Петроглиф, 2001. ISBN 5902094054
- Флора Ленинградской области / Под ред. Б. К. Шишкина. Вып. 1-4. Leningrad: Изд. ЛГУ, 1955–1965.
- Хазанович К. К. Геологические памятники Ленинградской области. Leningrad: Лениздат, 1982.
- Черепанова Н.П., Пшедецкая Л.И. Грибы. [Природа Ленинградской области]. Leningrad: Лениздат, 1990.
History
- Лапшин В. А. Археологическая карта Ленинградской области. Часть 1: Западные районы. Leningrad, 1990.
- Лапшин В. А. Археологическая карта Ленинградской области. Часть 2: Восточные и северные районы. Saint Petersburg: Изд. СПбГУ, 1995. ISBN 5874030522
- Лебедев Г. С. Археологические памятники Ленинградской области. Leningrad: Лениздат, 1977.

