
SMS Ostfriesland
Encyclopedia
SMS Ostfriesland ("His Majesty's Ship East Frisia
")"SMS" stands for "Seiner Majestät Schiff
" was the second vessel of the of battleship
s of the German
Imperial Navy
. Named for the region of East Frisia
, Ostfrieslands keel was laid in October 1908 at the Kaiserliche Werft
dockyard in Wilhelmshaven
. She was launched on 30 September 1909 and was commissioned into the fleet on 1 August 1911. The ship was equipped with twelve 30.5 centimetres (12 in) guns in six twin turrets, and had a top speed of 21.2 knots (11.5 m/s). Ostfriesland was assigned to the I Battle Squadron of the High Seas Fleet
for the majority of her career, including World War I
.
Along with her three sister ships, , , and , Ostfriesland participated in all of the major fleet operations of World War I in the North Sea
against the British Grand Fleet. This included the Battle of Jutland
on 31 May – 1 June 1916, the largest naval battle of the war. The ship also saw action in the Baltic Sea
against the Russian Navy. She was present during the unsuccessful first incursion into the Gulf of Riga
in August 1915.
After the German collapse in November 1918, most of the High Seas Fleet was interned in Scapa Flow
during the peace negotiations. The four Helgoland-class ships were allowed to remain in Germany, however, and were therefore spared the destruction of the fleet in Scapa Flow
. Ostfriesland and her sisters were eventually ceded to the victorious Allied powers
as war reparations
; Ostfriesland was transferred to the United States Navy
. She was sunk during air power trials off the Virginia Capes in July 1921.
(Imperial Dockyard) in Wilhelmshaven
under construction number 31. Work began on 19 October 1908 with the laying of her keel, and the ship was launched less than a year later, on 30 September 1909. She was christened
by the Fürstin of Innhausen und Knyphausen, a representative of the oldest East Frisian nobility. Fitting-out
, including completion of the superstructure and the installation of armament, lasted until August 1911. Ostfriesland, named for the north-western coastal area of Germany, was commissioned into the High Seas Fleet on 1 August 1911, just under three years from when work commenced, at a cost of 43.579 million gold marks
.
The ship was 167.2 m (548.6 ft) long, had a beam
of 28.5 m (93.5 ft) and a draft of 8.94 m (29.3 ft), and displaced 24700 metric tons (24,309.8 LT) at full load. She was powered by three 4-cylinder vertical triple expansion steam engines with 15 boilers; each engine drove a four-bladed screw. The ship's engines produced a top speed of 21.2 knots. Ostfriesland stored up to 3200 metric tons (3,149.5 LT) of coal, which allowed her to steam for 5500 nautical miles (10,186 km) at a speed of 10 knots (5.4 m/s). After 1915 the boilers were modified to spray oil on the coal; the ship could carry up to 197 metric tons (193.9 LT) of fuel oil. She had a crew of 42 officers and 1,027 enlisted men.
Ostfriesland was armed with a main battery of twelve 30.5 cm SK L/50
In Imperial German Navy gun nomenclature, "SK" (Schnellfeuerkanone) denotes that the gun is quick firing, while the L/50 denotes the length of the gun. In this case, the L/50 gun is 50 calibers, meaning that the gun is 50 times as long as its diameter. guns in six twin gun turret
s, with one turret fore, one aft, and two on each flank of the ship. The ship's secondary armament consisted of fourteen 15 cm (5.9 in) SK L/45 guns and sixteen 8.8 cm (3.5 in) SK L/45 guns. After 1914, two of the 8.8 cm guns were removed and replaced by 8.8 cm anti-aircraft guns. Ostfriesland was also armed with six 50 cm (19.7 in) submerged torpedo tube
s. Her main armored belt
was 300 mm (11.8 in) thick in the central portion, and was composed of Krupp cemented armor
(KCA). Her main battery gun turrets were protected by the same thickness of KCA armor on the sides and faces. Ostfrieslands deck was 63.5 mm (2.5 in) thick.
(KzS) Walter Engelhardt served as the ship's first commanding officer. On the 22nd, the ship was formally assigned to the I Battle Squadron of the High Seas Fleet
. She then went on to conduct individual ship training exercises, which were followed by I Squadron and then fleet maneuvers in November. On 24 April 1912, Ostfriesland replaced as the squadron flagship
. The annual summer cruise in July–August, which typically went to Norway, was interrupted by the Agadir Crisis
. As a result, the cruise only went into the Baltic. Ostfriesland and the rest of the fleet then fell into a pattern of individual ship, squadron, and full fleet exercises over the next two years of peacetime. Ostfriesland won the 1912/1913 Kaiserschießpreis—the Kaiser's artillery shooting prize—for the I Squadron. Kapitänleutnant Friedrich Beesel was the ship's gunnery officer at the time, and as such, was responsible for the accuracy of the ship's shooting.
On 14 July 1914, the annual summer cruise to Norway began. During the last peacetime cruise of the Imperial Navy, the fleet conducted drills off Skagen
before proceeding to the Norwegian fjords on 25 July. The following day the fleet began to steam back to Germany, as a result of Austria-Hungary's ultimatum to Serbia
. On the 27th, the entire fleet assembled off Cape Skadenes before returning to port, where they remained at a heightened state of readiness. War between Austria-Hungary and Serbia broke out on the 28th, and in the span of a week all of the major European powers had joined the conflict. By 29 July Ostfriesland and the rest of I Squadron was back in Wilhelmshaven.
, received the order to join Ostfriesland and sail out of the harbor. At 05:00, the two battleships met the battered cruisers and . By 07:30, the ships had returned to port for the night. On the afternoon of 7 September, Ostfriesland and the rest of the High Seas Fleet conducted a training cruise to the island of Heligoland
. In October, Ostfriesland was equipped with a pair of 8.8 cm flak guns for anti-air defense.
Ostfriesland was present during the first sortie by the German fleet into the North Sea, which took place on 2–3 November 1914. No British forces were encountered during the operation. A second operation followed on 15–16 December. This sortie was the initiation of a strategy adopted by Admiral Friedrich von Ingenohl
, the commander of the High Seas Fleet. Admiral von Ingenohl intended to use the battlecruiser
s of Rear Admiral Franz von Hipper
's I Scouting Group
to raid British coastal towns to lure out portions of the Grand Fleet where they could be destroyed by the High Seas Fleet. Early on 15 December the fleet left port to raid the towns of Scarborough, Hartlepool, and Whitby
. That evening, the German battle fleet of some twelve dreadnoughts—including Ostfriesland and her three sisters
—and eight pre-dreadnoughts came to within 10 nmi (18.5 km) of an isolated squadron of six British battleships. However, skirmishes between the rival destroyer
screens in the darkness convinced von Ingenohl that he was faced with the entire Grand Fleet. Under orders from Kaiser Wilhelm II to avoid risking the fleet unnecessarily, von Ingenohl broke off the engagement and turned the battle fleet back toward Germany.
The Battle of Dogger Bank
, in which Vice Admiral David Beatty's
1st
and 2nd Battlecruiser Squadrons
ambushed the battlecruisers of Konteradmiral (Rear Admiral) Franz von Hipper
's I Scouting Group
, occurred on 24 January 1915. Ostfriesland and the rest of I Squadron were sortied to reinforce the outnumbered German battlecruisers; I Squadron left port at 12:33 CET
,The Germans were on Central European Time, which is one hour ahead of UTC
, the time zone commonly used in British works. along with the pre-dreadnought
s of II Squadron. They were too late, however, and they failed to locate any British forces. By 19:05, the fleet had returned to the Schillig Roads outside Wilhelmshaven. In the meantime, the armored cruiser
had been overwhelmed by concentrated British fire and sunk, while the battlecruiser was severely damaged by a fire in one of the ammunition magazines. As a result, Kaiser Wilhelm II removed von Ingenohl from his post and replaced him with Admiral Hugo von Pohl
on 2 February.
The eight I Squadron ships went into the Baltic on 22 February 1915 for unit training, which lasted until 13 March. Following their return to the North Sea, the ships participated in a series of uneventful fleet sorties on 29–30 March, 17–18 April, 21–22 April, 17–18 May, and 29–30 May. Ostfriesland and the rest of the fleet remained in port until 4 August, when the I Squadron returned to the Baltic for another round of training maneuvers. That month, KzS Ernst-Oldwig von Natzmer replaced Engelhardt as the ship's commanding officer. From the Baltic, the squadron was attached to the naval force that attempted to sweep the Gulf of Riga
of Russian naval forces in August 1915. The assault force included the eight I Squadron battleships, the battlecruisers , , and Seydlitz, several light cruiser
s, 32 destroyer
s and 13 minesweeper
s. The plan called for channels in Russian minefields to be swept so that the Russian naval presence, which included the pre-dreadnought battleship Slava
, could be eliminated. The Germans would then lay minefields of their own to prevent Russian ships from returning to the Gulf. Ostfriesland and the majority of the other big ships of the High Seas Fleet remained outside the Gulf for the entirety of the operation
. The dreadnoughts and were detached on 16 August to escort the minesweepers and to destroy Slava, though they failed to sink the old battleship. After three days, the Russian minefields had been cleared, and the flotilla entered the Gulf on 19 August, but reports of Allied submarines in the area prompted a German withdrawal from the Gulf the following day. By 26 August, the I Squadron had returned to Wilhelmshaven.
On 23–24 October, the High Seas Fleet undertook its last major offensive operation under the command of Admiral von Pohl, though it ended without contact with British forces. By January 1916 hepatic cancer had weakened von Pohl to the point where he was no longer able to carry out his duties, and he was replaced by Vice Admiral Reinhard Scheer
in January. Scheer proposed a more aggressive policy designed to force a confrontation with the British Grand Fleet; he received approval from the Kaiser in February. Scheer's first operation was a sweep into the North Sea on 5–7 March, followed by two more on 21–22 March and 25–26 March. During Scheer's next operation, Ostfriesland supported a raid on the English coast
on 24 April 1916 conducted by the German battlecruiser force. The battlecruisers left the Jade Estuary at 10:55 and the rest of the High Seas Fleet followed at 13:40. The battlecruiser struck a mine while en route to the target, and had to withdraw. The other battlecruisers bombarded the town of Lowestoft unopposed, but during the approach to Yarmouth, they encountered the British cruisers of the Harwich Force
. A short gun duel ensued before the Harwich Force withdrew. Reports of British submarines in the area prompted the retreat of the I Scouting Group. At this point, Scheer, who had been warned of the sortie of the Grand Fleet from its base in Scapa Flow, also withdrew to safer German waters.
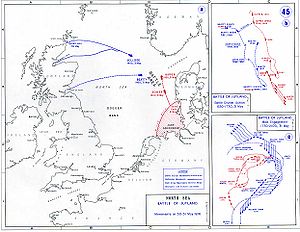 Ostfriesland was present during the fleet operation that resulted in the battle of Jutland
Ostfriesland was present during the fleet operation that resulted in the battle of Jutland
which took place on 31 May and 1 June 1916. The German fleet again sought to draw out and isolate a portion of the Grand Fleet and destroy it before the main British fleet could retaliate. During the operation, Ostfriesland was the lead ship in the I Division of I Squadron and the ninth ship in the line, directly astern of the fleet flagship and ahead of her sister Thüringen. The I Squadron was the center of the German line, behind the eight König- and Kaiser-class battleships of the III Squadron. The six elderly pre-dreadnought
s of the III and IV Divisions, II Battle Squadron, formed the rear of the formation. Ostfriesland flew the flag of Vizeadmiral (Vice Admiral) Erhardt Schmidt, the squadron commander during the battle and Scheer's deputy commander.
Shortly before 16:00, the battlecruisers of I Scouting Group
encountered the British 1st Battlecruiser Squadron under the command of David Beatty
. The opposing ships began an artillery duel that saw the destruction of , shortly after 17:00, and , less than half an hour later. By this time, the German battlecruisers were steaming south to draw the British ships toward the main body of the High Seas Fleet. At 17:30, the crew of the leading German battleship, König, spotted both the I Scouting Group and the 1st Battlecruiser Squadron approaching. The German battlecruisers were steaming to starboard, while the British ships steamed to port. At 17:45, Scheer ordered a two-point
turn to port to bring his ships closer to the British battlecruisers, and a minute later, the order to open fire was given.The compass can be divided into 32 points, each corresponding to 11.25 degrees. A two-point turn to port would alter the ships' course by 22.5 degrees.
While the leading battleships engaged the British battlecruiser squadron, Ostfriesland and ten other battleships fired on the British 2nd Light Cruiser Squadron. Ostfriesland, , and engaged the cruiser , though only Nassau scored a hit. After about 15 minutes, Ostfriesland shifted fire to and , though again failed to hit her targets. Shortly after 19:15, the British dreadnought came into range; Ostfriesland opened fire at 19:25 with her main battery guns, at ranges of 10800 to 15000 yd (9,875.5 to 13,716 m). Ostfriesland claimed hits from her third and fourth salvos. Warspite was hit by a total of thirteen heavy shells during this period.
By 20:15, the German battle line had faced the entire deployed Grand Fleet a second time. Scheer ordered a 180-degree turn at 20:17, which was covered by a charge by the battlecruiser squadron and a torpedo boat attack. In order to hasten the maneuver, Schmidt ordered Ostfriesland to turn immediately without waiting for Thüringen behind him. This move caused some difficulty for the III Squadron ships ahead, though the ships quickly returned to their stations. At around 23:30, the German fleet reorganized into the night cruising formation. Ostfriesland was the eighth ship, stationed toward the front of the 24-ship line. An hour later, the leading units of the German line encountered British light forces and a violent firefight at close range ensued. Sometime around 01:10, the armored cruiser stumbled into the German line. Thüringen illuminated the vessel with her spotlights and poured salvos of 30.5 cm rounds into the ship. Ostfriesland fired with her 15 cm guns and Kaiser fired both 30.5 cm and 15 cm guns. In the span of less than a minute, two massive explosions tore the cruiser apart and killed then entire 857-man crew.
Despite the ferocity of the night fighting, the High Seas Fleet punched through the British destroyer forces and reached Horns Reef
by 4:00 on 1 June. At 06:20, however, Ostfriesland struck a mine, previously laid by the destroyer on 4 May, on her starboard side. The ship hauled out of line, as the explosion was initially thought to have been a torpedo fired by a submarine. Ostfriesland fell behind the fleet and steamed at slow speed, screened by the destroyers , , and briefly by . By 10:40, the battleship had increased speed to 15 kn (8.2 m/s). Her anti-submarine escort was eventually reinforced by a floatplane, which spotted what it believed to be a British submarine at 12:20. Ostfriesland turned away, which caused the torpedo bulkhead
, which the mine explosion had damaged slightly, to tear open. More water entered the ship and caused a 4.75 degree list to starboard, which forced Ostfriesland to reduce speed again. The ship requested assistance from a pumping ship at 14:20, but by 14:45 the flooding was under control and the ship passed the Outer Jade Lightship. She was able to increase speed gradually to 10 kn (5.4 m/s), and at 18:15 she reached port in Wilhelmshaven. The mine tore a hole that measured 40 by 16 ft (12.2 by 4.9 m) and allowed 500 MT (492.1 LT) of water into the ship. Further flooding occurred after the torpedo bulkhead damage at 12:20, though the full damage report has not survived. Ostfriesland was drydocked in Wilhelmshaven for repairs, which lasted until 26 July. In the course of the battle, Ostfriesland fired 111 rounds from her main battery, 101 shells from her 15 cm guns, and a single 8.8 cm shell. The only damage sustained was the mine that was struck on the morning of 1 June, which killed one man and wounded ten.
about a British unit in the area. As a result, the bombardment was not carried out, and by 14:35, Scheer had been warned of the Grand Fleet's approach and so turned his forces around and retreated to German ports.
On 25–26 September, Ostfriesland and the rest of I Squadron covered an advance conducted by the II Führer der Torpedoboote (Leader of Torpedo Boats) to the Terschelling
Bank. Scheer conducted another fleet operation on 18–20 October in the direction of the Dogger Bank. For the majority of 1917, Ostfriesland was assigned to guard duty in the German Bight
. During Operation Albion
, the amphibious assault on the Russian-held islands in the Gulf of Riga, Ostfriesland and her three sisters were moved to the Danish straits
to block any possible British attempt to intervene. On 28 October the four ships arrived in Putzig Wiek
, and from there steamed to Arensburg
on the 29th. On 2 November the operation was completed and Ostfriesland and her sisters began the voyage back to the North Sea. In March 1918, Natzmer was replaced as the ship's commander by KzS Hans Herr. A final abortive fleet sortie took place on 23–24 April 1918. Ostfriesland, Thüringen, and Nassau were formed into a special unit for Operation Schlußstein, a planned occupation of St. Petersburg. The three ships reached the Baltic on 10 August, but the operation was postponed and eventually canceled. The special unit was dissolved on 21 August and the battleships were back in Wilhelmshaven on the 23rd.
(Großadmiral) of the fleet—intended to inflict as much damage as possible on the British navy, to improve Germany's bargaining position, despite the expected casualties. But many of the war-weary sailors felt that the operation would disrupt the peace process and prolong the war. On the morning of 29 October 1918, the order was given to sail from Wilhelmshaven the following day. Starting on the night of 29 October, sailors on Thüringen and then on several other battleships mutinied
. The unrest ultimately forced Hipper and Scheer to cancel the operation. Informed of the situation, the Kaiser stated "I no longer have a navy". On 6 November, Ostfriesland was decommissioned and used as a barracks ship.
Following the capitulation of Germany in November 1918, most of the High Seas Fleet, under the command of Rear Admiral Ludwig von Reuter
, was interned in the British naval base in Scapa Flow
. On the morning of 21 June, the British fleet left Scapa Flow to conduct training maneuvers, and at 11:20 Reuter transmitted the order to scuttle
his ships. In the span of a few hours, ten battleships and five battlecruisers sank in the shallow waters of Scapa Flow. KzS Karl Windmüller served as Ostfrieslands final commander, until she was stricken from the navy list on 5 November 1919. She was then surrendered to the Allies
as "H". The ship remained in Germany until 7 April 1920, when a German crew took the ship to Rosyth
. The ship was ceded to the United States as war reparations, and on 9 April an American crew arrived to bring the ship to the United States.
In July 1921, the Army Air Service
and the US Navy conducted a series of bombing tests off Cape Hatteras
, led by General Billy Mitchell. The targets included demobilized American and former German warships, including the old battleship , the cruiser , and finally Ostfriesland on 20 July. At 13:30 ET
, the first attack wave, armed with 230 lb (104.3 kg) bombs, struck the ship. Eight of thirty-three bombs found their mark, after which the ship was inspected. The second wave was also armed with 230 lb bombs, and the third and fourth carried 600 lb (272.2 kg) bombs. Five 600 lb bombs found their mark, but little damage was done to the ship's topside. The bombs that nearly missed the ship, however, had done significant underwater damage to the hull, which allowed some flooding and created a list of five degrees to port and three additional feet of draft at the stern. The bombing schedule was interrupted by a storm in the late afternoon.
 Early on the morning of 21 July, the fifth wave of bombers began their attack. At 08:52, the first Army bomber dropped a 1000 lb (453.6 kg) bomb which hit the ship; four more bombers followed and scored two further hits. Inspectors again went aboard the ship following the fifth attack and noted that the hits did not seriously damage the ship, though one had created a large hole on her starboard side that allowed further flooding. By noon, the ship was down five feet at the stern and one foot at the bow. At 12:19, the next attack wave, equipped with 2000 lb (907.2 kg) bombs, struck. Six bombs were dropped, none of which hit, though three detonated very close to the hull. At 12:30, Ostfriesland began to sink rapidly by the stern and the list to port increased dramatically. At 12:40, the ship rolled over and sank. The results of the tests were widely publicized and Mitchell became both a national hero and the "infallible prophet of aviation".
Early on the morning of 21 July, the fifth wave of bombers began their attack. At 08:52, the first Army bomber dropped a 1000 lb (453.6 kg) bomb which hit the ship; four more bombers followed and scored two further hits. Inspectors again went aboard the ship following the fifth attack and noted that the hits did not seriously damage the ship, though one had created a large hole on her starboard side that allowed further flooding. By noon, the ship was down five feet at the stern and one foot at the bow. At 12:19, the next attack wave, equipped with 2000 lb (907.2 kg) bombs, struck. Six bombs were dropped, none of which hit, though three detonated very close to the hull. At 12:30, Ostfriesland began to sink rapidly by the stern and the list to port increased dramatically. At 12:40, the ship rolled over and sank. The results of the tests were widely publicized and Mitchell became both a national hero and the "infallible prophet of aviation".
The leadership of the US Navy, however, was outraged by Mitchell's handling of the tests; the 2,000 lb bombs had not been sanctioned by the Navy, which had set the rules for the engagement. Mitchell's bombers had also not allowed inspectors aboard the ship between bombing runs as stipulated by the Navy. The joint Army–Navy report on the tests, issued a month later and signed by General John Pershing, stated that "the battleship is still the backbone of the fleet." Mitchell wrote his own, contradictory account of the tests, which was then leaked to the press. The sinking of the battleship sparked great controversy in the American public sphere; Mitchell's supporters exaggerated the significance of the tests by falsely claiming Ostfriesland to be an unsinkable "super-battleship" and that "old sea dogs ... wept aloud." Senator William Borah argued that the tests had rendered battleships obsolete. Mitchell was widely supported in the press, though his increasingly combative tactics eventually resulted in a court-martial for insubordination that forced him to retire from the military.
Citations
East Frisia
East Frisia or Eastern Friesland is a coastal region in the northwest of the German federal state of Lower Saxony....
")"SMS" stands for "Seiner Majestät Schiff
Seiner Majestät Schiff
Seiner Majestät Schiff was the ship prefix used by the Prussian Maritime Enterprise , the Prussian Navy, the Imperial German Navy and the Austro-Hungarian Navy...
" was the second vessel of the of battleship
Battleship
A battleship is a large armored warship with a main battery consisting of heavy caliber guns. Battleships were larger, better armed and armored than cruisers and destroyers. As the largest armed ships in a fleet, battleships were used to attain command of the sea and represented the apex of a...
s of the German
Germany
Germany , officially the Federal Republic of Germany , is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km2 and has a largely temperate seasonal climate...
Imperial Navy
Kaiserliche Marine
The Imperial German Navy was the German Navy created at the time of the formation of the German Empire. It existed between 1871 and 1919, growing out of the small Prussian Navy and Norddeutsche Bundesmarine, which primarily had the mission of coastal defense. Kaiser Wilhelm II greatly expanded...
. Named for the region of East Frisia
East Frisia
East Frisia or Eastern Friesland is a coastal region in the northwest of the German federal state of Lower Saxony....
, Ostfrieslands keel was laid in October 1908 at the Kaiserliche Werft
Kaiserliche Werft Wilhelmshaven
Kaiserliche Werft Wilhelmshaven was a German shipbuilding company in Wilhelmshaven, Prussian Hanover. It was founded in 1853, first as Königliche Werft Wilhelmshaven but renamed in 1871 with the proclamation of the German Empire...
dockyard in Wilhelmshaven
Wilhelmshaven
Wilhelmshaven is a coastal town in Lower Saxony, Germany. It is situated on the western side of the Jade Bight, a bay of the North Sea.-History:...
. She was launched on 30 September 1909 and was commissioned into the fleet on 1 August 1911. The ship was equipped with twelve 30.5 centimetres (12 in) guns in six twin turrets, and had a top speed of 21.2 knots (11.5 m/s). Ostfriesland was assigned to the I Battle Squadron of the High Seas Fleet
High Seas Fleet
The High Seas Fleet was the battle fleet of the German Empire and saw action during World War I. The formation was created in February 1907, when the Home Fleet was renamed as the High Seas Fleet. Admiral Alfred von Tirpitz was the architect of the fleet; he envisioned a force powerful enough to...
for the majority of her career, including World War I
World War I
World War I , which was predominantly called the World War or the Great War from its occurrence until 1939, and the First World War or World War I thereafter, was a major war centred in Europe that began on 28 July 1914 and lasted until 11 November 1918...
.
Along with her three sister ships, , , and , Ostfriesland participated in all of the major fleet operations of World War I in the North Sea
North Sea
In the southwest, beyond the Straits of Dover, the North Sea becomes the English Channel connecting to the Atlantic Ocean. In the east, it connects to the Baltic Sea via the Skagerrak and Kattegat, narrow straits that separate Denmark from Norway and Sweden respectively...
against the British Grand Fleet. This included the Battle of Jutland
Battle of Jutland
The Battle of Jutland was a naval battle between the British Royal Navy's Grand Fleet and the Imperial German Navy's High Seas Fleet during the First World War. The battle was fought on 31 May and 1 June 1916 in the North Sea near Jutland, Denmark. It was the largest naval battle and the only...
on 31 May – 1 June 1916, the largest naval battle of the war. The ship also saw action in the Baltic Sea
Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is a brackish mediterranean sea located in Northern Europe, from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from 20°E to 26°E longitude. It is bounded by the Scandinavian Peninsula, the mainland of Europe, and the Danish islands. It drains into the Kattegat by way of the Øresund, the Great Belt and...
against the Russian Navy. She was present during the unsuccessful first incursion into the Gulf of Riga
Battle of the Gulf of Riga
The Battle of the Gulf of Riga was a World War I naval operation of the German High Seas Fleet against the Russian Baltic Fleet in the Gulf of Riga in the Baltic Sea in August 1915...
in August 1915.
After the German collapse in November 1918, most of the High Seas Fleet was interned in Scapa Flow
Scapa Flow
right|thumb|Scapa Flow viewed from its eastern endScapa Flow is a body of water in the Orkney Islands, Scotland, United Kingdom, sheltered by the islands of Mainland, Graemsay, Burray, South Ronaldsay and Hoy. It is about...
during the peace negotiations. The four Helgoland-class ships were allowed to remain in Germany, however, and were therefore spared the destruction of the fleet in Scapa Flow
Scuttling of the German fleet in Scapa Flow
The scuttling of the German fleet took place at the Royal Navy's base at Scapa Flow, in Scotland, after the end of the First World War. The High Seas Fleet had been interned there under the terms of the Armistice whilst negotiations took place over the fate of the ships...
. Ostfriesland and her sisters were eventually ceded to the victorious Allied powers
Allies of World War I
The Entente Powers were the countries at war with the Central Powers during World War I. The members of the Triple Entente were the United Kingdom, France, and the Russian Empire; Italy entered the war on their side in 1915...
as war reparations
War reparations
War reparations are payments intended to cover damage or injury during a war. Generally, the term war reparations refers to money or goods changing hands, rather than such property transfers as the annexation of land.- History :...
; Ostfriesland was transferred to the United States Navy
United States Navy
The United States Navy is the naval warfare service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the seven uniformed services of the United States. The U.S. Navy is the largest in the world; its battle fleet tonnage is greater than that of the next 13 largest navies combined. The U.S...
. She was sunk during air power trials off the Virginia Capes in July 1921.
Construction
Ostfriesland was ordered by the German Imperial Navy (Kaiserliche Marine) under the provisional name Ersatz Oldenburg, as a replacement for the old coastal defense ship . The contract for the ship was awarded to the Kaiserliche WerftKaiserliche Werft Wilhelmshaven
Kaiserliche Werft Wilhelmshaven was a German shipbuilding company in Wilhelmshaven, Prussian Hanover. It was founded in 1853, first as Königliche Werft Wilhelmshaven but renamed in 1871 with the proclamation of the German Empire...
(Imperial Dockyard) in Wilhelmshaven
Wilhelmshaven
Wilhelmshaven is a coastal town in Lower Saxony, Germany. It is situated on the western side of the Jade Bight, a bay of the North Sea.-History:...
under construction number 31. Work began on 19 October 1908 with the laying of her keel, and the ship was launched less than a year later, on 30 September 1909. She was christened
Ship naming and launching
The ceremonies involved in naming and launching naval ships are based in traditions thousands of years old.-Methods of launch:There are three principal methods of conveying a new ship from building site to water, only two of which are called "launching." The oldest, most familiar, and most widely...
by the Fürstin of Innhausen und Knyphausen, a representative of the oldest East Frisian nobility. Fitting-out
Fitting-out
Fitting-out, or "outfitting”, is the process in modern shipbuilding that follows the float-out of a vessel and precedes sea trials. It is the period when all the remaining construction of the ship is completed and readied for delivery to her owners...
, including completion of the superstructure and the installation of armament, lasted until August 1911. Ostfriesland, named for the north-western coastal area of Germany, was commissioned into the High Seas Fleet on 1 August 1911, just under three years from when work commenced, at a cost of 43.579 million gold marks
German gold mark
The Goldmark was the currency used in the German Empire from 1873 to 1914.-History:Before unification, the different German states issued a variety of different currencies, though most were linked to the Vereinsthaler, a silver coin containing 16⅔ grams of pure silver...
.
The ship was 167.2 m (548.6 ft) long, had a beam
Beam (nautical)
The beam of a ship is its width at the widest point. Generally speaking, the wider the beam of a ship , the more initial stability it has, at expense of reserve stability in the event of a capsize, where more energy is required to right the vessel from its inverted position...
of 28.5 m (93.5 ft) and a draft of 8.94 m (29.3 ft), and displaced 24700 metric tons (24,309.8 LT) at full load. She was powered by three 4-cylinder vertical triple expansion steam engines with 15 boilers; each engine drove a four-bladed screw. The ship's engines produced a top speed of 21.2 knots. Ostfriesland stored up to 3200 metric tons (3,149.5 LT) of coal, which allowed her to steam for 5500 nautical miles (10,186 km) at a speed of 10 knots (5.4 m/s). After 1915 the boilers were modified to spray oil on the coal; the ship could carry up to 197 metric tons (193.9 LT) of fuel oil. She had a crew of 42 officers and 1,027 enlisted men.
Ostfriesland was armed with a main battery of twelve 30.5 cm SK L/50
30.5 cm SK L/50 gun
The 30.5 cm SK L/50 gunIn Imperial German Navy gun nomenclature, "SK" denotes that the gun is quick firing, while the L/50 denotes the length of the gun. In this case, the L/50 gun is 50 calibers, meaning that the gun is 50 times as long as it is in diameter. was a heavy gun mounted on 16 of...
In Imperial German Navy gun nomenclature, "SK" (Schnellfeuerkanone) denotes that the gun is quick firing, while the L/50 denotes the length of the gun. In this case, the L/50 gun is 50 calibers, meaning that the gun is 50 times as long as its diameter. guns in six twin gun turret
Gun turret
A gun turret is a weapon mount that protects the crew or mechanism of a projectile-firing weapon and at the same time lets the weapon be aimed and fired in many directions.The turret is also a rotating weapon platform...
s, with one turret fore, one aft, and two on each flank of the ship. The ship's secondary armament consisted of fourteen 15 cm (5.9 in) SK L/45 guns and sixteen 8.8 cm (3.5 in) SK L/45 guns. After 1914, two of the 8.8 cm guns were removed and replaced by 8.8 cm anti-aircraft guns. Ostfriesland was also armed with six 50 cm (19.7 in) submerged torpedo tube
Torpedo tube
A torpedo tube is a device for launching torpedoes. There are two main types of torpedo tube: underwater tubes fitted to submarines and some surface ships, and deck-mounted units installed aboard surface vessels...
s. Her main armored belt
Belt armor
Belt armor is a layer of heavy metal armor plated on to or within outer hulls of warships, typically on battleships, battlecruisers and cruisers, and on aircraft carriers converted from those types of ships....
was 300 mm (11.8 in) thick in the central portion, and was composed of Krupp cemented armor
Krupp cemented armour
Krupp Cemented Armour is a further evolved variant of Krupp Armour, developed during the early years of the 20th Century. The process is largely the same with slight changes in the alloy composition: in % of total – carbon 0.35, nickel 3.90, chromium 2.00, manganese .35, silicon .07, phosphorus...
(KCA). Her main battery gun turrets were protected by the same thickness of KCA armor on the sides and faces. Ostfrieslands deck was 63.5 mm (2.5 in) thick.
Service history
After commissioning, Ostfriesland conducted sea trials, which were completed by 15 September. Kapitän zur SeeCaptain at Sea
Captain at Sea, is a naval rank corresponding to command of a ship-of-the-line or capital ship....
(KzS) Walter Engelhardt served as the ship's first commanding officer. On the 22nd, the ship was formally assigned to the I Battle Squadron of the High Seas Fleet
High Seas Fleet
The High Seas Fleet was the battle fleet of the German Empire and saw action during World War I. The formation was created in February 1907, when the Home Fleet was renamed as the High Seas Fleet. Admiral Alfred von Tirpitz was the architect of the fleet; he envisioned a force powerful enough to...
. She then went on to conduct individual ship training exercises, which were followed by I Squadron and then fleet maneuvers in November. On 24 April 1912, Ostfriesland replaced as the squadron flagship
Flagship
A flagship is a vessel used by the commanding officer of a group of naval ships, reflecting the custom of its commander, characteristically a flag officer, flying a distinguishing flag...
. The annual summer cruise in July–August, which typically went to Norway, was interrupted by the Agadir Crisis
Agadir Crisis
The Agadir Crisis, also called the Second Moroccan Crisis, or the Panthersprung, was the international tension sparked by the deployment of the German gunboat Panther, to the Moroccan port of Agadir on July 1, 1911.-Background:...
. As a result, the cruise only went into the Baltic. Ostfriesland and the rest of the fleet then fell into a pattern of individual ship, squadron, and full fleet exercises over the next two years of peacetime. Ostfriesland won the 1912/1913 Kaiserschießpreis—the Kaiser's artillery shooting prize—for the I Squadron. Kapitänleutnant Friedrich Beesel was the ship's gunnery officer at the time, and as such, was responsible for the accuracy of the ship's shooting.
On 14 July 1914, the annual summer cruise to Norway began. During the last peacetime cruise of the Imperial Navy, the fleet conducted drills off Skagen
Skagen
Skagen is a projection of land and a town, with a population of 8,515 , in Region Nordjylland on the northernmost tip of Vendsyssel-Thy, a part of the Jutland peninsula in northern Denmark...
before proceeding to the Norwegian fjords on 25 July. The following day the fleet began to steam back to Germany, as a result of Austria-Hungary's ultimatum to Serbia
July Ultimatum
The July Crisis was a diplomatic crisis among the major powers of Europe in the summer of 1914 that led to the First World War...
. On the 27th, the entire fleet assembled off Cape Skadenes before returning to port, where they remained at a heightened state of readiness. War between Austria-Hungary and Serbia broke out on the 28th, and in the span of a week all of the major European powers had joined the conflict. By 29 July Ostfriesland and the rest of I Squadron was back in Wilhelmshaven.
World War I
The first major naval action in the North Sea, the Battle of Helgoland Bight, took place on 28 August 1914. At 04:30, Helgoland, which was stationed off the heavily fortified island of WangeroogeWangerooge
Wangerooge is one of the 32 Frisian Islands in the North Sea located close to the coasts of the Netherlands, Germany and Denmark. It is also a municipality in the district of Friesland in Lower Saxony in Germany.Wangerooge is one of the East Frisian Islands...
, received the order to join Ostfriesland and sail out of the harbor. At 05:00, the two battleships met the battered cruisers and . By 07:30, the ships had returned to port for the night. On the afternoon of 7 September, Ostfriesland and the rest of the High Seas Fleet conducted a training cruise to the island of Heligoland
Heligoland
Heligoland is a small German archipelago in the North Sea.Formerly Danish and British possessions, the islands are located in the Heligoland Bight in the south-eastern corner of the North Sea...
. In October, Ostfriesland was equipped with a pair of 8.8 cm flak guns for anti-air defense.
Ostfriesland was present during the first sortie by the German fleet into the North Sea, which took place on 2–3 November 1914. No British forces were encountered during the operation. A second operation followed on 15–16 December. This sortie was the initiation of a strategy adopted by Admiral Friedrich von Ingenohl
Friedrich von Ingenohl
Gustav Heinrich Ernst Friedrich von Ingenohl was a German admiral from Neuwied best known for his command of the German High Seas Fleet at the beginning of World War I....
, the commander of the High Seas Fleet. Admiral von Ingenohl intended to use the battlecruiser
Battlecruiser
Battlecruisers were large capital ships built in the first half of the 20th century. They were developed in the first decade of the century as the successor to the armoured cruiser, but their evolution was more closely linked to that of the dreadnought battleship...
s of Rear Admiral Franz von Hipper
Franz von Hipper
Franz Ritter von Hipper was an admiral in the German Imperial Navy . Franz von Hipper joined the German Navy in 1881 as an officer cadet. He commanded several torpedo boat units and served as watch officer aboard several warships, as well as Kaiser Wilhelm II's yacht Hohenzollern...
's I Scouting Group
I Scouting Group
The I Scouting Group was a special reconnaissance unit within the German Kaiserliche Marine. The unit was famously commanded by Admiral Franz von Hipper during World War I. The I Scouting Group was one of the most active formations in the High Seas Fleet during the war; the unit took part in every...
to raid British coastal towns to lure out portions of the Grand Fleet where they could be destroyed by the High Seas Fleet. Early on 15 December the fleet left port to raid the towns of Scarborough, Hartlepool, and Whitby
Raid on Scarborough, Hartlepool and Whitby
The raid on Scarborough, Hartlepool and Whitby, which took place on 16 December 1914, was an attack by the Imperial German Navy on the British seaport towns of Scarborough, Hartlepool, West Hartlepool, and Whitby. The attack resulted in 137 fatalities and 592 casualties, many of which were civilians...
. That evening, the German battle fleet of some twelve dreadnoughts—including Ostfriesland and her three sisters
Sister ship
A sister ship is a ship of the same class as, or of virtually identical design to, another ship. Such vessels share a near-identical hull and superstructure layout, similar displacement, and roughly comparable features and equipment...
—and eight pre-dreadnoughts came to within 10 nmi (18.5 km) of an isolated squadron of six British battleships. However, skirmishes between the rival destroyer
Destroyer
In naval terminology, a destroyer is a fast and maneuverable yet long-endurance warship intended to escort larger vessels in a fleet, convoy or battle group and defend them against smaller, powerful, short-range attackers. Destroyers, originally called torpedo-boat destroyers in 1892, evolved from...
screens in the darkness convinced von Ingenohl that he was faced with the entire Grand Fleet. Under orders from Kaiser Wilhelm II to avoid risking the fleet unnecessarily, von Ingenohl broke off the engagement and turned the battle fleet back toward Germany.
The Battle of Dogger Bank
Battle of Dogger Bank (1915)
The Battle of Dogger Bank was a naval battle fought near the Dogger Bank in the North Sea on 24 January 1915, during the First World War, between squadrons of the British Grand Fleet and the German High Seas Fleet....
, in which Vice Admiral David Beatty's
David Beatty, 1st Earl Beatty
Admiral of the Fleet David Richard Beatty, 1st Earl Beatty, GCB, OM, GCVO, DSO was an admiral in the Royal Navy...
1st
1st Battlecruiser Squadron (United Kingdom)
The First Battlecruiser Squadron was a Royal Navy squadron of battlecruisers that saw service as part of the Grand Fleet during the First World War. It was created in 1909 as the First Cruiser Squadron and was renamed in 1913 to First Battle Cruiser Squadron. It participated in the battles of...
and 2nd Battlecruiser Squadrons
2nd Battlecruiser Squadron (United Kingdom)
The 2nd Battlecruiser Squadron was a Royal Navy squadron of battlecruisers that saw service as part of the Grand Fleet during the First World War.-August 1914:In August 1914, the 2nd Battlecruiser Squadron was in the Mediterranean, and consisted of:-1915:...
ambushed the battlecruisers of Konteradmiral (Rear Admiral) Franz von Hipper
Franz von Hipper
Franz Ritter von Hipper was an admiral in the German Imperial Navy . Franz von Hipper joined the German Navy in 1881 as an officer cadet. He commanded several torpedo boat units and served as watch officer aboard several warships, as well as Kaiser Wilhelm II's yacht Hohenzollern...
's I Scouting Group
I Scouting Group
The I Scouting Group was a special reconnaissance unit within the German Kaiserliche Marine. The unit was famously commanded by Admiral Franz von Hipper during World War I. The I Scouting Group was one of the most active formations in the High Seas Fleet during the war; the unit took part in every...
, occurred on 24 January 1915. Ostfriesland and the rest of I Squadron were sortied to reinforce the outnumbered German battlecruisers; I Squadron left port at 12:33 CET
Central European Time
Central European Time , used in most parts of the European Union, is a standard time that is 1 hour ahead of Coordinated Universal Time . The time offset from UTC can be written as +01:00...
,The Germans were on Central European Time, which is one hour ahead of UTC
Coordinated Universal Time
Coordinated Universal Time is the primary time standard by which the world regulates clocks and time. It is one of several closely related successors to Greenwich Mean Time. Computer servers, online services and other entities that rely on having a universally accepted time use UTC for that purpose...
, the time zone commonly used in British works. along with the pre-dreadnought
Pre-dreadnought
Pre-dreadnought battleship is the general term for all of the types of sea-going battleships built between the mid-1890s and 1905. Pre-dreadnoughts replaced the ironclad warships of the 1870s and 1880s...
s of II Squadron. They were too late, however, and they failed to locate any British forces. By 19:05, the fleet had returned to the Schillig Roads outside Wilhelmshaven. In the meantime, the armored cruiser
Armored cruiser
The armored cruiser was a type of warship of the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Like other types of cruiser, the armored cruiser was a long-range, independent warship, capable of defeating any ship apart from a battleship, and fast enough to outrun any battleships it encountered.The first...
had been overwhelmed by concentrated British fire and sunk, while the battlecruiser was severely damaged by a fire in one of the ammunition magazines. As a result, Kaiser Wilhelm II removed von Ingenohl from his post and replaced him with Admiral Hugo von Pohl
Hugo von Pohl
Hugo von Pohl was a German admiral who during the First World War commanded the German High Seas Fleet from 1915 until shortly before his death from illness in 1916....
on 2 February.
The eight I Squadron ships went into the Baltic on 22 February 1915 for unit training, which lasted until 13 March. Following their return to the North Sea, the ships participated in a series of uneventful fleet sorties on 29–30 March, 17–18 April, 21–22 April, 17–18 May, and 29–30 May. Ostfriesland and the rest of the fleet remained in port until 4 August, when the I Squadron returned to the Baltic for another round of training maneuvers. That month, KzS Ernst-Oldwig von Natzmer replaced Engelhardt as the ship's commanding officer. From the Baltic, the squadron was attached to the naval force that attempted to sweep the Gulf of Riga
Gulf of Riga
The Gulf of Riga, or Bay of Riga, is a bay of the Baltic Sea between Latvia and Estonia. According to C.Michael Hogan, a saline stratification layer is found at a depth of approximately seventy metres....
of Russian naval forces in August 1915. The assault force included the eight I Squadron battleships, the battlecruisers , , and Seydlitz, several light cruiser
Light cruiser
A light cruiser is a type of small- or medium-sized warship. The term is a shortening of the phrase "light armored cruiser", describing a small ship that carried armor in the same way as an armored cruiser: a protective belt and deck...
s, 32 destroyer
Destroyer
In naval terminology, a destroyer is a fast and maneuverable yet long-endurance warship intended to escort larger vessels in a fleet, convoy or battle group and defend them against smaller, powerful, short-range attackers. Destroyers, originally called torpedo-boat destroyers in 1892, evolved from...
s and 13 minesweeper
Minesweeper (ship)
A minesweeper is a small naval warship designed to counter the threat posed by naval mines. Minesweepers generally detect then neutralize mines in advance of other naval operations.-History:...
s. The plan called for channels in Russian minefields to be swept so that the Russian naval presence, which included the pre-dreadnought battleship Slava
Russian battleship Slava
Slava was a pre-dreadnought battleship of the Imperial Russian Navy, the last of the five s. Commissioned too late to participate in the Battle of Tsushima during the Russo-Japanese War, she survived while all of her sister ships were either sunk during the battle or surrendered to the Imperial...
, could be eliminated. The Germans would then lay minefields of their own to prevent Russian ships from returning to the Gulf. Ostfriesland and the majority of the other big ships of the High Seas Fleet remained outside the Gulf for the entirety of the operation
Battle of the Gulf of Riga
The Battle of the Gulf of Riga was a World War I naval operation of the German High Seas Fleet against the Russian Baltic Fleet in the Gulf of Riga in the Baltic Sea in August 1915...
. The dreadnoughts and were detached on 16 August to escort the minesweepers and to destroy Slava, though they failed to sink the old battleship. After three days, the Russian minefields had been cleared, and the flotilla entered the Gulf on 19 August, but reports of Allied submarines in the area prompted a German withdrawal from the Gulf the following day. By 26 August, the I Squadron had returned to Wilhelmshaven.
On 23–24 October, the High Seas Fleet undertook its last major offensive operation under the command of Admiral von Pohl, though it ended without contact with British forces. By January 1916 hepatic cancer had weakened von Pohl to the point where he was no longer able to carry out his duties, and he was replaced by Vice Admiral Reinhard Scheer
Reinhard Scheer
Reinhard Scheer was an Admiral in the German Kaiserliche Marine. Scheer joined the navy in 1879 as an officer cadet; he progressed through the ranks, commanding cruisers and battleships, as well as major staff positions on land. At the outbreak of World War I, Scheer was the commander of the II...
in January. Scheer proposed a more aggressive policy designed to force a confrontation with the British Grand Fleet; he received approval from the Kaiser in February. Scheer's first operation was a sweep into the North Sea on 5–7 March, followed by two more on 21–22 March and 25–26 March. During Scheer's next operation, Ostfriesland supported a raid on the English coast
Bombardment of Yarmouth and Lowestoft
The Bombardment of Yarmouth and Lowestoft was a naval battle fought during the First World War between the German Empire and the British Empire in the North Sea....
on 24 April 1916 conducted by the German battlecruiser force. The battlecruisers left the Jade Estuary at 10:55 and the rest of the High Seas Fleet followed at 13:40. The battlecruiser struck a mine while en route to the target, and had to withdraw. The other battlecruisers bombarded the town of Lowestoft unopposed, but during the approach to Yarmouth, they encountered the British cruisers of the Harwich Force
Harwich Force
The Harwich Force was a squadron of the Royal Navy, formed during the First World War, that went on to play a significant role in the war.-History:...
. A short gun duel ensued before the Harwich Force withdrew. Reports of British submarines in the area prompted the retreat of the I Scouting Group. At this point, Scheer, who had been warned of the sortie of the Grand Fleet from its base in Scapa Flow, also withdrew to safer German waters.
Battle of Jutland

Jutland
Jutland , historically also called Cimbria, is the name of the peninsula that juts out in Northern Europe toward the rest of Scandinavia, forming the mainland part of Denmark. It has the North Sea to its west, Kattegat and Skagerrak to its north, the Baltic Sea to its east, and the Danish–German...
which took place on 31 May and 1 June 1916. The German fleet again sought to draw out and isolate a portion of the Grand Fleet and destroy it before the main British fleet could retaliate. During the operation, Ostfriesland was the lead ship in the I Division of I Squadron and the ninth ship in the line, directly astern of the fleet flagship and ahead of her sister Thüringen. The I Squadron was the center of the German line, behind the eight König- and Kaiser-class battleships of the III Squadron. The six elderly pre-dreadnought
Pre-dreadnought
Pre-dreadnought battleship is the general term for all of the types of sea-going battleships built between the mid-1890s and 1905. Pre-dreadnoughts replaced the ironclad warships of the 1870s and 1880s...
s of the III and IV Divisions, II Battle Squadron, formed the rear of the formation. Ostfriesland flew the flag of Vizeadmiral (Vice Admiral) Erhardt Schmidt, the squadron commander during the battle and Scheer's deputy commander.
Shortly before 16:00, the battlecruisers of I Scouting Group
I Scouting Group
The I Scouting Group was a special reconnaissance unit within the German Kaiserliche Marine. The unit was famously commanded by Admiral Franz von Hipper during World War I. The I Scouting Group was one of the most active formations in the High Seas Fleet during the war; the unit took part in every...
encountered the British 1st Battlecruiser Squadron under the command of David Beatty
David Beatty, 1st Earl Beatty
Admiral of the Fleet David Richard Beatty, 1st Earl Beatty, GCB, OM, GCVO, DSO was an admiral in the Royal Navy...
. The opposing ships began an artillery duel that saw the destruction of , shortly after 17:00, and , less than half an hour later. By this time, the German battlecruisers were steaming south to draw the British ships toward the main body of the High Seas Fleet. At 17:30, the crew of the leading German battleship, König, spotted both the I Scouting Group and the 1st Battlecruiser Squadron approaching. The German battlecruisers were steaming to starboard, while the British ships steamed to port. At 17:45, Scheer ordered a two-point
Boxing the compass
Boxing the compass is the action of naming all thirty-two points of the compass in clockwise order. Such names are formed by the initials of the cardinal directions and their intermediate ordinal directions, and are very handy to refer to a heading in a general or colloquial fashion, without...
turn to port to bring his ships closer to the British battlecruisers, and a minute later, the order to open fire was given.The compass can be divided into 32 points, each corresponding to 11.25 degrees. A two-point turn to port would alter the ships' course by 22.5 degrees.
While the leading battleships engaged the British battlecruiser squadron, Ostfriesland and ten other battleships fired on the British 2nd Light Cruiser Squadron. Ostfriesland, , and engaged the cruiser , though only Nassau scored a hit. After about 15 minutes, Ostfriesland shifted fire to and , though again failed to hit her targets. Shortly after 19:15, the British dreadnought came into range; Ostfriesland opened fire at 19:25 with her main battery guns, at ranges of 10800 to 15000 yd (9,875.5 to 13,716 m). Ostfriesland claimed hits from her third and fourth salvos. Warspite was hit by a total of thirteen heavy shells during this period.
By 20:15, the German battle line had faced the entire deployed Grand Fleet a second time. Scheer ordered a 180-degree turn at 20:17, which was covered by a charge by the battlecruiser squadron and a torpedo boat attack. In order to hasten the maneuver, Schmidt ordered Ostfriesland to turn immediately without waiting for Thüringen behind him. This move caused some difficulty for the III Squadron ships ahead, though the ships quickly returned to their stations. At around 23:30, the German fleet reorganized into the night cruising formation. Ostfriesland was the eighth ship, stationed toward the front of the 24-ship line. An hour later, the leading units of the German line encountered British light forces and a violent firefight at close range ensued. Sometime around 01:10, the armored cruiser stumbled into the German line. Thüringen illuminated the vessel with her spotlights and poured salvos of 30.5 cm rounds into the ship. Ostfriesland fired with her 15 cm guns and Kaiser fired both 30.5 cm and 15 cm guns. In the span of less than a minute, two massive explosions tore the cruiser apart and killed then entire 857-man crew.
Despite the ferocity of the night fighting, the High Seas Fleet punched through the British destroyer forces and reached Horns Reef
Horns Reef
Horns Rev is a shallow area in the eastern North Sea, about 15 km / 10 miles off the westernmost point of Denmark, Blåvands Huk...
by 4:00 on 1 June. At 06:20, however, Ostfriesland struck a mine, previously laid by the destroyer on 4 May, on her starboard side. The ship hauled out of line, as the explosion was initially thought to have been a torpedo fired by a submarine. Ostfriesland fell behind the fleet and steamed at slow speed, screened by the destroyers , , and briefly by . By 10:40, the battleship had increased speed to 15 kn (8.2 m/s). Her anti-submarine escort was eventually reinforced by a floatplane, which spotted what it believed to be a British submarine at 12:20. Ostfriesland turned away, which caused the torpedo bulkhead
Torpedo bulkhead
A torpedo bulkhead is a type of armor common on the more heavily armored warships, especially battleships and battlecruisers of the early 20th century. It is designed to keep the ship afloat even if the hull was struck underneath the belt armor by a shell or by a torpedo...
, which the mine explosion had damaged slightly, to tear open. More water entered the ship and caused a 4.75 degree list to starboard, which forced Ostfriesland to reduce speed again. The ship requested assistance from a pumping ship at 14:20, but by 14:45 the flooding was under control and the ship passed the Outer Jade Lightship. She was able to increase speed gradually to 10 kn (5.4 m/s), and at 18:15 she reached port in Wilhelmshaven. The mine tore a hole that measured 40 by 16 ft (12.2 by 4.9 m) and allowed 500 MT (492.1 LT) of water into the ship. Further flooding occurred after the torpedo bulkhead damage at 12:20, though the full damage report has not survived. Ostfriesland was drydocked in Wilhelmshaven for repairs, which lasted until 26 July. In the course of the battle, Ostfriesland fired 111 rounds from her main battery, 101 shells from her 15 cm guns, and a single 8.8 cm shell. The only damage sustained was the mine that was struck on the morning of 1 June, which killed one man and wounded ten.
Later operations
On 18 August, Admiral Scheer attempted a repeat of the 31 May operation. The two serviceable German battlecruisers, and , supported by three dreadnoughts, were to bombard the coastal town of Sunderland in an attempt to draw out and destroy Beatty's battlecruisers. The rest of the fleet, including Ostfriesland, would trail behind and provide cover. On the approach to the English coast, Scheer turned north after receiving a false report from a zeppelinZeppelin
A Zeppelin is a type of rigid airship pioneered by the German Count Ferdinand von Zeppelin in the early 20th century. It was based on designs he had outlined in 1874 and detailed in 1893. His plans were reviewed by committee in 1894 and patented in the United States on 14 March 1899...
about a British unit in the area. As a result, the bombardment was not carried out, and by 14:35, Scheer had been warned of the Grand Fleet's approach and so turned his forces around and retreated to German ports.
On 25–26 September, Ostfriesland and the rest of I Squadron covered an advance conducted by the II Führer der Torpedoboote (Leader of Torpedo Boats) to the Terschelling
Terschelling
Terschelling is a municipality and an island in the northern Netherlands, one of the West Frisian Islands.Waddenislanders are known for their resourcefulness in using anything and everything that washes ashore. With few trees to use for timber, most of the farms and barns are built with masts...
Bank. Scheer conducted another fleet operation on 18–20 October in the direction of the Dogger Bank. For the majority of 1917, Ostfriesland was assigned to guard duty in the German Bight
German Bight
German Bight is the southeastern bight of the North Sea bounded by the Netherlands and Germany to the south, and Denmark and Germany to the east . To the north and west it is limited by the Dogger Bank. The Bight contains the Frisian and Danish Islands. The Wadden Sea is approximately ten to...
. During Operation Albion
Operation Albion
Operation Albion was the German land and naval operation in September-October 1917 to invade and occupy the Estonian islands of Saaremaa , Hiiumaa and Muhu , then part of the Russian Republic...
, the amphibious assault on the Russian-held islands in the Gulf of Riga, Ostfriesland and her three sisters were moved to the Danish straits
Danish straits
The Danish straits are the three channels connecting the Baltic Sea to the North Sea through the Kattegat and Skagerrak. They transect Denmark, and are not to be confused with the Denmark Strait between Greenland and Iceland...
to block any possible British attempt to intervene. On 28 October the four ships arrived in Putzig Wiek
Bay of Puck
The Bay of Puck or Puck Bay , historically also known as the Bay of Putzig , is a shallow western branch of the Bay of Gdańsk in the southern Baltic Sea, off the shores of Gdańsk Pomerania, Poland. It is separated from the open sea by the Hel Peninsula.The bay has an average depth of 2-6 metres...
, and from there steamed to Arensburg
Kuressaare
Kuressaare is a town and a municipality on Saaremaa island in Estonia. It is the capital of Saare County. The current population is about 14,706 Kuressaare is a town and a municipality on Saaremaa island in Estonia. It is the capital of Saare County. The current population is about 14,706...
on the 29th. On 2 November the operation was completed and Ostfriesland and her sisters began the voyage back to the North Sea. In March 1918, Natzmer was replaced as the ship's commander by KzS Hans Herr. A final abortive fleet sortie took place on 23–24 April 1918. Ostfriesland, Thüringen, and Nassau were formed into a special unit for Operation Schlußstein, a planned occupation of St. Petersburg. The three ships reached the Baltic on 10 August, but the operation was postponed and eventually canceled. The special unit was dissolved on 21 August and the battleships were back in Wilhelmshaven on the 23rd.
Fate
Ostfriesland and her three sisters were to have taken part in a final fleet action at the end of October 1918, days before the Armistice was to take effect. The bulk of the High Seas Fleet was to have sortied from their base in Wilhelmshaven to engage the British Grand Fleet; Scheer—by now the Grand AdmiralGrand Admiral
Grand admiral is a historic naval rank, generally being the highest such rank present in any particular country. Its most notable use was in Germany — the German word is Großadmiral.-France:...
(Großadmiral) of the fleet—intended to inflict as much damage as possible on the British navy, to improve Germany's bargaining position, despite the expected casualties. But many of the war-weary sailors felt that the operation would disrupt the peace process and prolong the war. On the morning of 29 October 1918, the order was given to sail from Wilhelmshaven the following day. Starting on the night of 29 October, sailors on Thüringen and then on several other battleships mutinied
Wilhelmshaven mutiny
The Kiel mutiny was a major revolt by sailors of the German High Seas Fleet on 3 November 1918. The revolt triggered the German revolution which was to sweep aside the monarchy within a few days. It ultimately led to the end of the First World War and to the establishment of the Weimar Republic.-...
. The unrest ultimately forced Hipper and Scheer to cancel the operation. Informed of the situation, the Kaiser stated "I no longer have a navy". On 6 November, Ostfriesland was decommissioned and used as a barracks ship.
Following the capitulation of Germany in November 1918, most of the High Seas Fleet, under the command of Rear Admiral Ludwig von Reuter
Ludwig von Reuter
Ludwig von Reuter was a German admiral during World War I, who commanded the Imperial German Navy's High Seas Fleet when it was interned at Scapa Flow at the end of the war. On 21 June 1919 he ordered the scuttling of the fleet to prevent the British from seizing the ships.-Early life:Reuter was...
, was interned in the British naval base in Scapa Flow
Scapa Flow
right|thumb|Scapa Flow viewed from its eastern endScapa Flow is a body of water in the Orkney Islands, Scotland, United Kingdom, sheltered by the islands of Mainland, Graemsay, Burray, South Ronaldsay and Hoy. It is about...
. On the morning of 21 June, the British fleet left Scapa Flow to conduct training maneuvers, and at 11:20 Reuter transmitted the order to scuttle
Scuttling
Scuttling is the act of deliberately sinking a ship by allowing water to flow into the hull.This can be achieved in several ways—valves or hatches can be opened to the sea, or holes may be ripped into the hull with brute force or with explosives...
his ships. In the span of a few hours, ten battleships and five battlecruisers sank in the shallow waters of Scapa Flow. KzS Karl Windmüller served as Ostfrieslands final commander, until she was stricken from the navy list on 5 November 1919. She was then surrendered to the Allies
Allies of World War I
The Entente Powers were the countries at war with the Central Powers during World War I. The members of the Triple Entente were the United Kingdom, France, and the Russian Empire; Italy entered the war on their side in 1915...
as "H". The ship remained in Germany until 7 April 1920, when a German crew took the ship to Rosyth
Rosyth
Rosyth is a town located on the Firth of Forth, three miles south of the centre of Dunfermline. According to an estimate taken in 2008, the town has a population of 12,790....
. The ship was ceded to the United States as war reparations, and on 9 April an American crew arrived to bring the ship to the United States.
In July 1921, the Army Air Service
United States Army Air Service
The Air Service, United States Army was a forerunner of the United States Air Force during and after World War I. It was established as an independent but temporary wartime branch of the War Department by two executive orders of President Woodrow Wilson: on May 24, 1918, replacing the Aviation...
and the US Navy conducted a series of bombing tests off Cape Hatteras
Cape Hatteras
Cape Hatteras is a cape on the coast of North Carolina. It is the point that protrudes the farthest to the southeast along the northeast-to-southwest line of the Atlantic coast of North America...
, led by General Billy Mitchell. The targets included demobilized American and former German warships, including the old battleship , the cruiser , and finally Ostfriesland on 20 July. At 13:30 ET
Eastern Time Zone
The Eastern Time Zone of the United States and Canada is a time zone that falls mostly along the east coast of North America. Its UTC time offset is −5 hrs during standard time and −4 hrs during daylight saving time...
, the first attack wave, armed with 230 lb (104.3 kg) bombs, struck the ship. Eight of thirty-three bombs found their mark, after which the ship was inspected. The second wave was also armed with 230 lb bombs, and the third and fourth carried 600 lb (272.2 kg) bombs. Five 600 lb bombs found their mark, but little damage was done to the ship's topside. The bombs that nearly missed the ship, however, had done significant underwater damage to the hull, which allowed some flooding and created a list of five degrees to port and three additional feet of draft at the stern. The bombing schedule was interrupted by a storm in the late afternoon.

The leadership of the US Navy, however, was outraged by Mitchell's handling of the tests; the 2,000 lb bombs had not been sanctioned by the Navy, which had set the rules for the engagement. Mitchell's bombers had also not allowed inspectors aboard the ship between bombing runs as stipulated by the Navy. The joint Army–Navy report on the tests, issued a month later and signed by General John Pershing, stated that "the battleship is still the backbone of the fleet." Mitchell wrote his own, contradictory account of the tests, which was then leaked to the press. The sinking of the battleship sparked great controversy in the American public sphere; Mitchell's supporters exaggerated the significance of the tests by falsely claiming Ostfriesland to be an unsinkable "super-battleship" and that "old sea dogs ... wept aloud." Senator William Borah argued that the tests had rendered battleships obsolete. Mitchell was widely supported in the press, though his increasingly combative tactics eventually resulted in a court-martial for insubordination that forced him to retire from the military.
Footnotes
FootnotesCitations

