
Savoy
Encyclopedia
- For the two French départements of the region of Savoy, see SavoieSavoieSavoie is a French department located in the Rhône-Alpes region in the French Alps.Together with the Haute-Savoie, Savoie is one of the two departments of the historic region of Savoy that was annexed by France on June 14, 1860, following the signature of the Treaty of Turin on March 24, 1860...
and Haute-SavoieHaute-SavoieHaute-Savoie is a French department in the Rhône-Alpes region of eastern France. It borders both Switzerland and Italy. The capital is Annecy. To the north is Lake Geneva and Switzerland; to the south and southeast are the Mont Blanc and Aravis mountain ranges and the French entrance to the Mont...
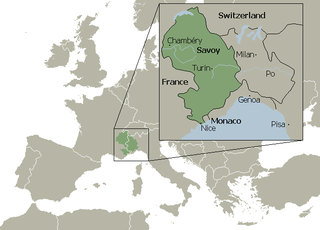
Savoy (ˈsævɔɪ; , saˈvwɛ; , savwa; ) is a region of France. It comprises roughly the territory of the Western Alps situated between Lake Geneva
Lake Geneva
Lake Geneva or Lake Léman is a lake in Switzerland and France. It is one of the largest lakes in Western Europe. 59.53 % of it comes under the jurisdiction of Switzerland , and 40.47 % under France...
in the north and Monaco
Monaco
Monaco , officially the Principality of Monaco , is a sovereign city state on the French Riviera. It is bordered on three sides by its neighbour, France, and its centre is about from Italy. Its area is with a population of 35,986 as of 2011 and is the most densely populated country in the...
and the Mediterranean coast in the south.
The historical land of Savoy emerged as the feudal territory of the house of Savoy
House of Savoy
The House of Savoy was formed in the early 11th century in the historical Savoy region. Through gradual expansion, it grew from ruling a small county in that region to eventually rule the Kingdom of Italy from 1861 until the end of World War II, king of Croatia and King of Armenia...
during the 11th to 14th centuries. The historical territory is shared between the modern republics of France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
and Italy
Italy
Italy , officially the Italian Republic languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Italy's official name is as follows:;;;;;;;;), is a unitary parliamentary republic in South-Central Europe. To the north it borders France, Switzerland, Austria and...
.
Installed by Rudolph III, King of Burgundy, officially in 1003, the House of Savoy
House of Savoy
The House of Savoy was formed in the early 11th century in the historical Savoy region. Through gradual expansion, it grew from ruling a small county in that region to eventually rule the Kingdom of Italy from 1861 until the end of World War II, king of Croatia and King of Armenia...
became the longest surviving royal house in Europe. It ruled the County of Savoy
County of Savoy
The Counts of Savoy emerged, along with the free communes of Switzerland, from the collapse of the Burgundian Kingdom of Arles in the 11th century....
to 1416 and then the Duchy of Savoy
Duchy of Savoy
From 1416 to 1847, the House of Savoy ruled the eponymous Duchy of Savoy . The Duchy was a state in the northern part of the Italian Peninsula, with some territories that are now in France. It was a continuation of the County of Savoy...
from 1416 to 1714.
The territory of Savoy was annexed to France in 1792 under the French First Republic
French First Republic
The French First Republic was founded on 22 September 1792, by the newly established National Convention. The First Republic lasted until the declaration of the First French Empire in 1804 under Napoleon I...
, before being returned to the Kingdom of Piedmont-Sardinia in 1815. Savoy was finally annexed to France, under the Second French Empire
Second French Empire
The Second French Empire or French Empire was the Imperial Bonapartist regime of Napoleon III from 1852 to 1870, between the Second Republic and the Third Republic, in France.-Rule of Napoleon III:...
in 1860, as part of a political agreement brokered between the French emperor Napoleon III and King Victor Emmanuel II of the Kingdom of Sardinia
Kingdom of Sardinia
The Kingdom of Sardinia consisted of the island of Sardinia first as a part of the Crown of Aragon and subsequently the Spanish Empire , and second as a part of the composite state of the House of Savoy . Its capital was originally Cagliari, in the south of the island, and later Turin, on the...
that began the process of unification of Italy
Italian unification
Italian unification was the political and social movement that agglomerated different states of the Italian peninsula into the single state of Italy in the 19th century...
. Victor Emmanuel's dynasty, the House of Savoy
House of Savoy
The House of Savoy was formed in the early 11th century in the historical Savoy region. Through gradual expansion, it grew from ruling a small county in that region to eventually rule the Kingdom of Italy from 1861 until the end of World War II, king of Croatia and King of Armenia...
, retained its Italian lands of Piedmont
Piedmont
Piedmont is one of the 20 regions of Italy. It has an area of 25,402 square kilometres and a population of about 4.4 million. The capital of Piedmont is Turin. The main local language is Piedmontese. Occitan is also spoken by a minority in the Occitan Valleys situated in the Provinces of...
and Liguria
Liguria
Liguria is a coastal region of north-western Italy, the third smallest of the Italian regions. Its capital is Genoa. It is a popular region with tourists for its beautiful beaches, picturesque little towns, and good food.-Geography:...
and became the ruling dynasty of Italy.
Geography
The County and Duchy of Savoy incorporated TurinTurin
Turin is a city and major business and cultural centre in northern Italy, capital of the Piedmont region, located mainly on the left bank of the Po River and surrounded by the Alpine arch. The population of the city proper is 909,193 while the population of the urban area is estimated by Eurostat...
and other territories in Piedmont
Piedmont
Piedmont is one of the 20 regions of Italy. It has an area of 25,402 square kilometres and a population of about 4.4 million. The capital of Piedmont is Turin. The main local language is Piedmontese. Occitan is also spoken by a minority in the Occitan Valleys situated in the Provinces of...
, a region in northwestern Italy that borders Savoy, which were also possessions of the House of Savoy. The capital of the Duchy remained at the traditional Savoyard capital of Chambéry
Chambéry
Chambéry is a city in the department of Savoie, located in the Rhône-Alpes region in southeastern France.It is the capital of the department and has been the historical capital of the Savoy region since the 13th century, when Amadeus V of Savoy made the city his seat of power.-Geography:Chambéry...
until 1563, when it was moved to Turin.
In modern France, Savoy is part of the Rhône-Alpes
Rhône-Alpes
Rhône-Alpes is one of the 27 regions of France, located on the eastern border of the country, towards the south. The region was named after the Rhône River and the Alps mountain range. Its capital, Lyon, is the second-largest metropolitan area in France after Paris...
region. Following its annexation to France in 1860, the territory of Savoy was divided administratively into two separate departments, Savoie
Savoie
Savoie is a French department located in the Rhône-Alpes region in the French Alps.Together with the Haute-Savoie, Savoie is one of the two departments of the historic region of Savoy that was annexed by France on June 14, 1860, following the signature of the Treaty of Turin on March 24, 1860...
and Haute-Savoie
Haute-Savoie
Haute-Savoie is a French department in the Rhône-Alpes region of eastern France. It borders both Switzerland and Italy. The capital is Annecy. To the north is Lake Geneva and Switzerland; to the south and southeast are the Mont Blanc and Aravis mountain ranges and the French entrance to the Mont...
.
The traditional capital remains Chambéry
Chambéry
Chambéry is a city in the department of Savoie, located in the Rhône-Alpes region in southeastern France.It is the capital of the department and has been the historical capital of the Savoy region since the 13th century, when Amadeus V of Savoy made the city his seat of power.-Geography:Chambéry...
(Ciamberì), on the rivers Leysse
Leysse
The Leysse is the river which crosses the city of Chambéry, Savoie, France. At its entrance into the city, it goes underground in a channel of about 1 km.-Characteristics:...
and Albane, hosting the castle
Castle
A castle is a type of fortified structure built in Europe and the Middle East during the Middle Ages by European nobility. Scholars debate the scope of the word castle, but usually consider it to be the private fortified residence of a lord or noble...
of the House of Savoy and the Savoyard senate
Senate
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a legislature or parliament. There have been many such bodies in history, since senate means the assembly of the eldest and wiser members of the society and ruling class...
. The state included six districts:
- Savoie Propre, sometimes known as Ducal Savoy (capital Chambéry)
- ChablaisChablaisChablais was a province of the Duchy of Savoy. Its capital was Thonon-les-Bains.This region is currently divided into three territories, the Chablais savoyard, the Chablais valaisan, and the Chablais vaudois, and is now split across two countries: France and Switzerland...
(capital Thonon-les-BainsThonon-les-BainsThonon-les-Bains is a town in the Haute-Savoie department in the Rhône-Alpes region in south-eastern France. It is a sub-prefecture of the department.-History:...
) - FaucignyFaucignyFaucigny is a commune in the Haute-Savoie department in the Rhône-Alpes region in south-eastern France.Historically, Faucigny was a region in Savoy which included the area of the modern département of Haute Savoie and the municipalities of Chamonix, Argentière, and Les Houches.-Geography:In the...
(capital BonnevilleBonneville-People:* Benjamin Louis Eulalie de Bonneville, a French-born officer in the United States Army, fur trapper, and explorer in the American West* Hugh Bonneville, an English stage, television, and film actor* Nicholas Bonneville, a French writer-Places in the USA:...
) - TarentaiseTarentaiseTarentaise can refer to the following:Places* Moûtiers, historically known as Tarentaise, in Savoy* Tarentaise Valley* Tarentaise, LoirePeople* Peter of TarentaiseOther*Tarentaise cattle...
(capital Moûtiers) - MaurienneMaurienneMaurienne is one of the provinces of Savoy, corresponding to the arrondissement of Saint-Jean-de-Maurienne in France. It is also the original name of the capital of the province, now Saint-Jean-de-Maurienne.-Location:...
(capital Saint-Jean-de-MaurienneSaint-Jean-de-MaurienneSaint-Jean-de-Maurienne is a commune in the Savoie department in the Rhône-Alpes region in south-eastern France. It is a sub-prefecture of the department....
) - GenevoisGenevois (province)The Genevois is a former province of the Duchy of Savoy. Its capital is Annecy and other centres include Faverges, Thônes, and La Clusaz. It was bordered by the provinces of Carouge to the north-west, Faucigny to the north-east, and Savoy proper to the south-east and south-west.Although the...
(capital AnnecyAnnecyAnnecy is a commune in the Haute-Savoie department in the Rhône-Alpes region in south-eastern France.It lies on the northern tip of Lake Annecy , 35 kilometres south of Geneva.-Administration:...
).
Early history
The region occupied by the Celtic AllobrogesAllobroges
The Allobroges were a Celtic tribe of ancient Gaul, located between the Rhône River and the Lake of Geneva in what later became Savoy, Dauphiné, and Vivarais. Their cities were in the areas of modern-day Annecy, Chambéry and Grenoble, the modern of Isère, and modern Switzerland...
people became part of the Roman Empire
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire was the post-Republican period of the ancient Roman civilization, characterised by an autocratic form of government and large territorial holdings in Europe and around the Mediterranean....
. The name Savoy stems from the Late Latin
Late Latin
Late Latin is the scholarly name for the written Latin of Late Antiquity. The English dictionary definition of Late Latin dates this period from the 3rd to the 6th centuries AD extending in Spain to the 7th. This somewhat ambiguously defined period fits between Classical Latin and Medieval Latin...
Sapaudia, referring to a fir forest
Fir
Firs are a genus of 48–55 species of evergreen conifers in the family Pinaceae. They are found through much of North and Central America, Europe, Asia, and North Africa, occurring in mountains over most of the range...
. It is first recorded in Ammianus Marcellinus
Ammianus Marcellinus
Ammianus Marcellinus was a fourth-century Roman historian. He wrote the penultimate major historical account surviving from Antiquity...
(354), to describe the southern part of Maxima Sequanorum
Sequani
Sequani, in ancient geography, were a Gallic people who occupied the upper river basin of the Arar , the valley of the Doubs and the Jura Mountains, their territory corresponding to Franche-Comté and part of Burgundy.-Etymology:...
According to the Gallic Chronicle of 452, it was separated from the rest of Burgundian territories in 443, after the Burgundian defeat by Flavius Aetius
Flavius Aëtius
Flavius Aëtius , dux et patricius, was a Roman general of the closing period of the Western Roman Empire. He was an able military commander and the most influential man in the Western Roman Empire for two decades . He managed policy in regard to the attacks of barbarian peoples pressing on the Empire...
.
Early and High Middle Ages
By the 8th century, the territory that would later become known as Savoy was part of the Kingdom of the Franks, and at the division of Francia at the Treaty of VerdunTreaty of Verdun
The Treaty of Verdun was a treaty between the three surviving sons of Louis the Pious, the son and successor of Charlemagne, which divided the Carolingian Empire into three kingdoms...
in 843, it became part of the short-lived kingdom of Middle Francia
Middle Francia
Middle Francia was an ephemeral Frankish kingdom created by the Treaty of Verdun in 843, which divided the Carolingian Empire among the sons of Louis the Pious...
. After only 12 years, at the death of Lothair I
Lothair I
Lothair I or Lothar I was the Emperor of the Romans , co-ruling with his father until 840, and the King of Bavaria , Italy and Middle Francia...
in 855,
Middle Francia was divided into Lotharingia
Lotharingia
Lotharingia was a region in northwest Europe, comprising the Low Countries, the western Rhineland, the lands today on the border between France and Germany, and what is now western Switzerland. It was born of the tripartite division in 855, of the kingdom of Middle Francia, itself formed of the...
north of the Alps, Italy
Kingdom of Italy (medieval)
The Kingdom of Italy was a political entity under control of Carolingian dynasty of Francia first, after the defeat of the Lombards in 774. It was finally incorporated as a part of the Holy Roman Empire in 962....
south of the Alps, and the parts of Burgundy in the Western Alps, inherited by Charles son of Lothair
Charles of Provence
Charles of Provence was the Carolingian King of Provence from 855 until his early death in 863.Charles was the youngest son of Holy Roman Emperor Lothair I and Ermengarde of Tours....
. This latter territory comprised what would become known as Savoy and Provence
Provence
Provence ; Provençal: Provença in classical norm or Prouvènço in Mistralian norm) is a region of south eastern France on the Mediterranean adjacent to Italy. It is part of the administrative région of Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur...
.
From the 10th to 14th century, parts of what would ultimately become Savoy remained within Kingdom of Arles
Kingdom of Arles
The Kingdom of Arles or Second Kingdom of Burgundy of the High Middle Ages was a Frankish dominion established in 933 from lands of the early medieval Kingdom of Burgundy at Arles...
). Beginning in the 11th century, the gradual rise to power of the house of Savoy
House of Savoy
The House of Savoy was formed in the early 11th century in the historical Savoy region. Through gradual expansion, it grew from ruling a small county in that region to eventually rule the Kingdom of Italy from 1861 until the end of World War II, king of Croatia and King of Armenia...
is reflected in the increasing territory of their County of Savoy
County of Savoy
The Counts of Savoy emerged, along with the free communes of Switzerland, from the collapse of the Burgundian Kingdom of Arles in the 11th century....
between 1003 and 1416.
The County of Savoy was detached de jure from the Kingdom of Arles by Charles IV
Charles IV, Holy Roman Emperor
Charles IV , born Wenceslaus , was the second king of Bohemia from the House of Luxembourg, and the first king of Bohemia to also become Holy Roman Emperor....
in 1361. It acquired the County of Nice
County of Nice
The County of Nice or Niçard Country is a historical region of France, located in the south-eastern part, around the city of Nice.-History:Its territory lies between the Mediterranean Sea , Var River and the southernmost crest of the...
in 1388, and in 1401 added the County of Genevois, the area of Geneva
Geneva
Geneva In the national languages of Switzerland the city is known as Genf , Ginevra and Genevra is the second-most-populous city in Switzerland and is the most populous city of Romandie, the French-speaking part of Switzerland...
except for the city proper, which was ruled by its prince-bishop
Prince-Bishop
A Prince-Bishop is a bishop who is a territorial Prince of the Church on account of one or more secular principalities, usually pre-existent titles of nobility held concurrently with their inherent clerical office...
, nominally under the duke's rule: the bishops of Geneva, by unspoken agreement, came from the house of Savoy
House of Savoy
The House of Savoy was formed in the early 11th century in the historical Savoy region. Through gradual expansion, it grew from ruling a small county in that region to eventually rule the Kingdom of Italy from 1861 until the end of World War II, king of Croatia and King of Armenia...
; this agreement came to an end in 1533.
Duchy of Savoy
Sigismund, Holy Roman Emperor
Sigismund of Luxemburg KG was King of Hungary, of Croatia from 1387 to 1437, of Bohemia from 1419, and Holy Roman Emperor for four years from 1433 until 1437, the last Emperor of the House of Luxemburg. He was also King of Italy from 1431, and of Germany from 1411...
, made the County of Savoy an independent duchy
Duchy of Savoy
From 1416 to 1847, the House of Savoy ruled the eponymous Duchy of Savoy . The Duchy was a state in the northern part of the Italian Peninsula, with some territories that are now in France. It was a continuation of the County of Savoy...
, with Amédée VIII as the first duke. Straddling the Alps, Savoy lay within two competing spheres of influence, a French sphere and a North Italian one. At the time of the Renaissance, Savoy showed only modest development. Its towns were few and small. Savoy derived its subsistence from agriculture. The geographic location of Savoy was also of military importance. During the interminable wars
Italian Wars
The Italian Wars, often referred to as the Great Italian Wars or the Great Wars of Italy and sometimes as the Habsburg–Valois Wars, were a series of conflicts from 1494 to 1559 that involved, at various times, most of the city-states of Italy, the Papal States, most of the major states of Western...
between France and Spain over the control of northern Italy, Savoy was important to France because it provided access to Italy. Savoy was important to Spain because it served as a buffer between France and the Spanish held lands in Italy. In 1563 Emmanuel Philibert
Emmanuel Philibert, Duke of Savoy
Emmanuel Philibert was Duke of Savoy from 1553 to 1580....
moved the capital from Chambéry
Chambéry
Chambéry is a city in the department of Savoie, located in the Rhône-Alpes region in southeastern France.It is the capital of the department and has been the historical capital of the Savoy region since the 13th century, when Amadeus V of Savoy made the city his seat of power.-Geography:Chambéry...
to Turin
Turin
Turin is a city and major business and cultural centre in northern Italy, capital of the Piedmont region, located mainly on the left bank of the Po River and surrounded by the Alpine arch. The population of the city proper is 909,193 while the population of the urban area is estimated by Eurostat...
, which was less vulnerable to French interference.
Vaud
Vaud
Vaud is one of the 26 cantons of Switzerland and is located in Romandy, the French-speaking southwestern part of the country. The capital is Lausanne. The name of the Canton in Switzerland's other languages are Vaud in Italian , Waadt in German , and Vad in Romansh.-History:Along the lakes,...
was annexed by Bern in 1536, and Savoy officially ceded Vaud to Bern in the treaty of Lausanne of 30 October 1564.
In 1714, as a consequence of the War of the Spanish Succession
War of the Spanish Succession
The War of the Spanish Succession was fought among several European powers, including a divided Spain, over the possible unification of the Kingdoms of Spain and France under one Bourbon monarch. As France and Spain were among the most powerful states of Europe, such a unification would have...
, Savoy was technically subsumed into the Kingdom of Sicily
Kingdom of Sicily
The Kingdom of Sicily was a state that existed in the south of Italy from its founding by Roger II in 1130 until 1816. It was a successor state of the County of Sicily, which had been founded in 1071 during the Norman conquest of southern Italy...
, then (after that island was traded to Austria
Austria
Austria , officially the Republic of Austria , is a landlocked country of roughly 8.4 million people in Central Europe. It is bordered by the Czech Republic and Germany to the north, Slovakia and Hungary to the east, Slovenia and Italy to the south, and Switzerland and Liechtenstein to the...
for Sardinia
Sardinia
Sardinia is the second-largest island in the Mediterranean Sea . It is an autonomous region of Italy, and the nearest land masses are the French island of Corsica, the Italian Peninsula, Sicily, Tunisia and the Spanish Balearic Islands.The name Sardinia is from the pre-Roman noun *sard[],...
) the Kingdom of Sardinia
Kingdom of Sardinia
The Kingdom of Sardinia consisted of the island of Sardinia first as a part of the Crown of Aragon and subsequently the Spanish Empire , and second as a part of the composite state of the House of Savoy . Its capital was originally Cagliari, in the south of the island, and later Turin, on the...
from 1720.
While the heads of the House of Savoy were known as the Kings of Sardinia, Turin remained their capital.
French Revolutionary Wars
Savoy was occupied by French revolutionary forcesFrench Revolutionary Army
The French Revolutionary Army is the term used to refer to the military of France during the period between the fall of the ancien regime under Louis XVI in 1792 and the formation of the First French Empire under Napoleon Bonaparte in 1804. These armies were characterised by their revolutionary...
between 1792 and 1815. The region was first added to the département of Mont-Blanc, then in 1798 was divided between the départements of Mont-Blanc and Léman (French name of Lake Geneva.) In 1801, Savoy officially left the Holy Roman Empire
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a realm that existed from 962 to 1806 in Central Europe.It was ruled by the Holy Roman Emperor. Its character changed during the Middle Ages and the Early Modern period, when the power of the emperor gradually weakened in favour of the princes...
.
- For the two French départements of the region of Savoy, see SavoieSavoieSavoie is a French department located in the Rhône-Alpes region in the French Alps.Together with the Haute-Savoie, Savoie is one of the two departments of the historic region of Savoy that was annexed by France on June 14, 1860, following the signature of the Treaty of Turin on March 24, 1860...
and Haute-SavoieHaute-SavoieHaute-Savoie is a French department in the Rhône-Alpes region of eastern France. It borders both Switzerland and Italy. The capital is Annecy. To the north is Lake Geneva and Switzerland; to the south and southeast are the Mont Blanc and Aravis mountain ranges and the French entrance to the Mont...
Savoy (ˈsævɔɪ; , saˈvwɛ; , savwa; ) is a region of France. It comprises roughly the territory of the Western Alps situated between Lake Geneva
Lake Geneva
Lake Geneva or Lake Léman is a lake in Switzerland and France. It is one of the largest lakes in Western Europe. 59.53 % of it comes under the jurisdiction of Switzerland , and 40.47 % under France...
in the north and Monaco
Monaco
Monaco , officially the Principality of Monaco , is a sovereign city state on the French Riviera. It is bordered on three sides by its neighbour, France, and its centre is about from Italy. Its area is with a population of 35,986 as of 2011 and is the most densely populated country in the...
and the Mediterranean coast in the south.
The historical land of Savoy emerged as the feudal territory of the house of Savoy
House of Savoy
The House of Savoy was formed in the early 11th century in the historical Savoy region. Through gradual expansion, it grew from ruling a small county in that region to eventually rule the Kingdom of Italy from 1861 until the end of World War II, king of Croatia and King of Armenia...
during the 11th to 14th centuries. The historical territory is shared between the modern republics of France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
and Italy
Italy
Italy , officially the Italian Republic languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Italy's official name is as follows:;;;;;;;;), is a unitary parliamentary republic in South-Central Europe. To the north it borders France, Switzerland, Austria and...
.
Installed by Rudolph III, King of Burgundy, officially in 1003, the House of Savoy
House of Savoy
The House of Savoy was formed in the early 11th century in the historical Savoy region. Through gradual expansion, it grew from ruling a small county in that region to eventually rule the Kingdom of Italy from 1861 until the end of World War II, king of Croatia and King of Armenia...
became the longest surviving royal house in Europe. It ruled the County of Savoy
County of Savoy
The Counts of Savoy emerged, along with the free communes of Switzerland, from the collapse of the Burgundian Kingdom of Arles in the 11th century....
to 1416 and then the Duchy of Savoy
Duchy of Savoy
From 1416 to 1847, the House of Savoy ruled the eponymous Duchy of Savoy . The Duchy was a state in the northern part of the Italian Peninsula, with some territories that are now in France. It was a continuation of the County of Savoy...
from 1416 to 1714.
The territory of Savoy was annexed to France in 1792 under the French First Republic
French First Republic
The French First Republic was founded on 22 September 1792, by the newly established National Convention. The First Republic lasted until the declaration of the First French Empire in 1804 under Napoleon I...
, before being returned to the Kingdom of Piedmont-Sardinia in 1815. Savoy was finally annexed to France, under the Second French Empire
Second French Empire
The Second French Empire or French Empire was the Imperial Bonapartist regime of Napoleon III from 1852 to 1870, between the Second Republic and the Third Republic, in France.-Rule of Napoleon III:...
in 1860, as part of a political agreement brokered between the French emperor Napoleon III and King Victor Emmanuel II of the Kingdom of Sardinia
Kingdom of Sardinia
The Kingdom of Sardinia consisted of the island of Sardinia first as a part of the Crown of Aragon and subsequently the Spanish Empire , and second as a part of the composite state of the House of Savoy . Its capital was originally Cagliari, in the south of the island, and later Turin, on the...
that began the process of unification of Italy
Italian unification
Italian unification was the political and social movement that agglomerated different states of the Italian peninsula into the single state of Italy in the 19th century...
. Victor Emmanuel's dynasty, the House of Savoy
House of Savoy
The House of Savoy was formed in the early 11th century in the historical Savoy region. Through gradual expansion, it grew from ruling a small county in that region to eventually rule the Kingdom of Italy from 1861 until the end of World War II, king of Croatia and King of Armenia...
, retained its Italian lands of Piedmont
Piedmont
Piedmont is one of the 20 regions of Italy. It has an area of 25,402 square kilometres and a population of about 4.4 million. The capital of Piedmont is Turin. The main local language is Piedmontese. Occitan is also spoken by a minority in the Occitan Valleys situated in the Provinces of...
and Liguria
Liguria
Liguria is a coastal region of north-western Italy, the third smallest of the Italian regions. Its capital is Genoa. It is a popular region with tourists for its beautiful beaches, picturesque little towns, and good food.-Geography:...
and became the ruling dynasty of Italy.
Geography
The County and Duchy of Savoy incorporated TurinTurin
Turin is a city and major business and cultural centre in northern Italy, capital of the Piedmont region, located mainly on the left bank of the Po River and surrounded by the Alpine arch. The population of the city proper is 909,193 while the population of the urban area is estimated by Eurostat...
and other territories in Piedmont
Piedmont
Piedmont is one of the 20 regions of Italy. It has an area of 25,402 square kilometres and a population of about 4.4 million. The capital of Piedmont is Turin. The main local language is Piedmontese. Occitan is also spoken by a minority in the Occitan Valleys situated in the Provinces of...
, a region in northwestern Italy that borders Savoy, which were also possessions of the House of Savoy. The capital of the Duchy remained at the traditional Savoyard capital of Chambéry
Chambéry
Chambéry is a city in the department of Savoie, located in the Rhône-Alpes region in southeastern France.It is the capital of the department and has been the historical capital of the Savoy region since the 13th century, when Amadeus V of Savoy made the city his seat of power.-Geography:Chambéry...
until 1563, when it was moved to Turin.
In modern France, Savoy is part of the Rhône-Alpes
Rhône-Alpes
Rhône-Alpes is one of the 27 regions of France, located on the eastern border of the country, towards the south. The region was named after the Rhône River and the Alps mountain range. Its capital, Lyon, is the second-largest metropolitan area in France after Paris...
region. Following its annexation to France in 1860, the territory of Savoy was divided administratively into two separate departments, Savoie
Savoie
Savoie is a French department located in the Rhône-Alpes region in the French Alps.Together with the Haute-Savoie, Savoie is one of the two departments of the historic region of Savoy that was annexed by France on June 14, 1860, following the signature of the Treaty of Turin on March 24, 1860...
and Haute-Savoie
Haute-Savoie
Haute-Savoie is a French department in the Rhône-Alpes region of eastern France. It borders both Switzerland and Italy. The capital is Annecy. To the north is Lake Geneva and Switzerland; to the south and southeast are the Mont Blanc and Aravis mountain ranges and the French entrance to the Mont...
.
The traditional capital remains Chambéry
Chambéry
Chambéry is a city in the department of Savoie, located in the Rhône-Alpes region in southeastern France.It is the capital of the department and has been the historical capital of the Savoy region since the 13th century, when Amadeus V of Savoy made the city his seat of power.-Geography:Chambéry...
(Ciamberì), on the rivers Leysse
Leysse
The Leysse is the river which crosses the city of Chambéry, Savoie, France. At its entrance into the city, it goes underground in a channel of about 1 km.-Characteristics:...
and Albane, hosting the castle
Castle
A castle is a type of fortified structure built in Europe and the Middle East during the Middle Ages by European nobility. Scholars debate the scope of the word castle, but usually consider it to be the private fortified residence of a lord or noble...
of the House of Savoy and the Savoyard senate
Senate
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a legislature or parliament. There have been many such bodies in history, since senate means the assembly of the eldest and wiser members of the society and ruling class...
. The state included six districts:
- Savoie Propre, sometimes known as Ducal Savoy (capital Chambéry)
- ChablaisChablaisChablais was a province of the Duchy of Savoy. Its capital was Thonon-les-Bains.This region is currently divided into three territories, the Chablais savoyard, the Chablais valaisan, and the Chablais vaudois, and is now split across two countries: France and Switzerland...
(capital Thonon-les-BainsThonon-les-BainsThonon-les-Bains is a town in the Haute-Savoie department in the Rhône-Alpes region in south-eastern France. It is a sub-prefecture of the department.-History:...
) - FaucignyFaucignyFaucigny is a commune in the Haute-Savoie department in the Rhône-Alpes region in south-eastern France.Historically, Faucigny was a region in Savoy which included the area of the modern département of Haute Savoie and the municipalities of Chamonix, Argentière, and Les Houches.-Geography:In the...
(capital BonnevilleBonneville-People:* Benjamin Louis Eulalie de Bonneville, a French-born officer in the United States Army, fur trapper, and explorer in the American West* Hugh Bonneville, an English stage, television, and film actor* Nicholas Bonneville, a French writer-Places in the USA:...
) - TarentaiseTarentaiseTarentaise can refer to the following:Places* Moûtiers, historically known as Tarentaise, in Savoy* Tarentaise Valley* Tarentaise, LoirePeople* Peter of TarentaiseOther*Tarentaise cattle...
(capital Moûtiers) - MaurienneMaurienneMaurienne is one of the provinces of Savoy, corresponding to the arrondissement of Saint-Jean-de-Maurienne in France. It is also the original name of the capital of the province, now Saint-Jean-de-Maurienne.-Location:...
(capital Saint-Jean-de-MaurienneSaint-Jean-de-MaurienneSaint-Jean-de-Maurienne is a commune in the Savoie department in the Rhône-Alpes region in south-eastern France. It is a sub-prefecture of the department....
) - GenevoisGenevois (province)The Genevois is a former province of the Duchy of Savoy. Its capital is Annecy and other centres include Faverges, Thônes, and La Clusaz. It was bordered by the provinces of Carouge to the north-west, Faucigny to the north-east, and Savoy proper to the south-east and south-west.Although the...
(capital AnnecyAnnecyAnnecy is a commune in the Haute-Savoie department in the Rhône-Alpes region in south-eastern France.It lies on the northern tip of Lake Annecy , 35 kilometres south of Geneva.-Administration:...
).
Early history
The region occupied by the Celtic AllobrogesAllobroges
The Allobroges were a Celtic tribe of ancient Gaul, located between the Rhône River and the Lake of Geneva in what later became Savoy, Dauphiné, and Vivarais. Their cities were in the areas of modern-day Annecy, Chambéry and Grenoble, the modern of Isère, and modern Switzerland...
people became part of the Roman Empire
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire was the post-Republican period of the ancient Roman civilization, characterised by an autocratic form of government and large territorial holdings in Europe and around the Mediterranean....
. The name Savoy stems from the Late Latin
Late Latin
Late Latin is the scholarly name for the written Latin of Late Antiquity. The English dictionary definition of Late Latin dates this period from the 3rd to the 6th centuries AD extending in Spain to the 7th. This somewhat ambiguously defined period fits between Classical Latin and Medieval Latin...
Sapaudia, referring to a fir forest
Fir
Firs are a genus of 48–55 species of evergreen conifers in the family Pinaceae. They are found through much of North and Central America, Europe, Asia, and North Africa, occurring in mountains over most of the range...
.Modern French sapin; sapinière signifies "fir forest". It is first recorded in Ammianus Marcellinus
Ammianus Marcellinus
Ammianus Marcellinus was a fourth-century Roman historian. He wrote the penultimate major historical account surviving from Antiquity...
(354), to describe the southern part of Maxima Sequanorum
Sequani
Sequani, in ancient geography, were a Gallic people who occupied the upper river basin of the Arar , the valley of the Doubs and the Jura Mountains, their territory corresponding to Franche-Comté and part of Burgundy.-Etymology:...
The territory, which has no modern counterpart, was perhaps bounded by the rivers Ain and Rhône, Lac Léman, the Jura and the Aar, though historians differ, and there seems to be insufficient evidence: see Norman H. Baynes, reviewing A. Coville, Recherches sur l'Histoire de Lyon du Ve au IXe Siècle (450-800) in The English Historical Review 45 No. 179 (July 1930:470-474) p 471.
According to the Gallic Chronicle of 452, it was separated from the rest of Burgundian territories in 443, after the Burgundian defeat by Flavius Aetius
Flavius Aëtius
Flavius Aëtius , dux et patricius, was a Roman general of the closing period of the Western Roman Empire. He was an able military commander and the most influential man in the Western Roman Empire for two decades . He managed policy in regard to the attacks of barbarian peoples pressing on the Empire...
.Sapaudia Burgundionum reliquiis datur cum indigenis dividenda. (in T. Mommsen, Chronica Minora II:660, 128.
Early and High Middle Ages
By the 8th century, the territory that would later become known as Savoy was part of the Kingdom of the Franks, and at the division of Francia at the Treaty of VerdunTreaty of Verdun
The Treaty of Verdun was a treaty between the three surviving sons of Louis the Pious, the son and successor of Charlemagne, which divided the Carolingian Empire into three kingdoms...
in 843, it became part of the short-lived kingdom of Middle Francia
Middle Francia
Middle Francia was an ephemeral Frankish kingdom created by the Treaty of Verdun in 843, which divided the Carolingian Empire among the sons of Louis the Pious...
. After only 12 years, at the death of Lothair I
Lothair I
Lothair I or Lothar I was the Emperor of the Romans , co-ruling with his father until 840, and the King of Bavaria , Italy and Middle Francia...
in 855,
Middle Francia was divided into Lotharingia
Lotharingia
Lotharingia was a region in northwest Europe, comprising the Low Countries, the western Rhineland, the lands today on the border between France and Germany, and what is now western Switzerland. It was born of the tripartite division in 855, of the kingdom of Middle Francia, itself formed of the...
north of the Alps, Italy
Kingdom of Italy (medieval)
The Kingdom of Italy was a political entity under control of Carolingian dynasty of Francia first, after the defeat of the Lombards in 774. It was finally incorporated as a part of the Holy Roman Empire in 962....
south of the Alps, and the parts of Burgundy in the Western Alps, inherited by Charles son of Lothair
Charles of Provence
Charles of Provence was the Carolingian King of Provence from 855 until his early death in 863.Charles was the youngest son of Holy Roman Emperor Lothair I and Ermengarde of Tours....
. This latter territory comprised what would become known as Savoy and Provence
Provence
Provence ; Provençal: Provença in classical norm or Prouvènço in Mistralian norm) is a region of south eastern France on the Mediterranean adjacent to Italy. It is part of the administrative région of Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur...
.
From the 10th to 14th century, parts of what would ultimately become Savoy remained within Kingdom of Arles
Kingdom of Arles
The Kingdom of Arles or Second Kingdom of Burgundy of the High Middle Ages was a Frankish dominion established in 933 from lands of the early medieval Kingdom of Burgundy at Arles...
). Beginning in the 11th century, the gradual rise to power of the house of Savoy
House of Savoy
The House of Savoy was formed in the early 11th century in the historical Savoy region. Through gradual expansion, it grew from ruling a small county in that region to eventually rule the Kingdom of Italy from 1861 until the end of World War II, king of Croatia and King of Armenia...
is reflected in the increasing territory of their County of Savoy
County of Savoy
The Counts of Savoy emerged, along with the free communes of Switzerland, from the collapse of the Burgundian Kingdom of Arles in the 11th century....
between 1003 and 1416.
The County of Savoy was detached de jure from the Kingdom of Arles by Charles IV
Charles IV, Holy Roman Emperor
Charles IV , born Wenceslaus , was the second king of Bohemia from the House of Luxembourg, and the first king of Bohemia to also become Holy Roman Emperor....
in 1361. It acquired the County of Nice
County of Nice
The County of Nice or Niçard Country is a historical region of France, located in the south-eastern part, around the city of Nice.-History:Its territory lies between the Mediterranean Sea , Var River and the southernmost crest of the...
in 1388, and in 1401 added the County of Genevois, the area of Geneva
Geneva
Geneva In the national languages of Switzerland the city is known as Genf , Ginevra and Genevra is the second-most-populous city in Switzerland and is the most populous city of Romandie, the French-speaking part of Switzerland...
except for the city proper, which was ruled by its prince-bishop
Prince-Bishop
A Prince-Bishop is a bishop who is a territorial Prince of the Church on account of one or more secular principalities, usually pre-existent titles of nobility held concurrently with their inherent clerical office...
, nominally under the duke's rule: the bishops of Geneva, by unspoken agreement, came from the house of Savoy
House of Savoy
The House of Savoy was formed in the early 11th century in the historical Savoy region. Through gradual expansion, it grew from ruling a small county in that region to eventually rule the Kingdom of Italy from 1861 until the end of World War II, king of Croatia and King of Armenia...
; this agreement came to an end in 1533.See the career of the last prince-bishop Pierre de La Baume
Pierre de La Baume
Pierre de La Baume was a grand seigneur of Savoy and a cardinal of the Roman Catholic Church. He was a councillor of Charles III, Duke of Savoy, whom he represented at the Fifth Lateran Council ....
.
Duchy of Savoy

Sigismund, Holy Roman Emperor
Sigismund of Luxemburg KG was King of Hungary, of Croatia from 1387 to 1437, of Bohemia from 1419, and Holy Roman Emperor for four years from 1433 until 1437, the last Emperor of the House of Luxemburg. He was also King of Italy from 1431, and of Germany from 1411...
, made the County of Savoy an independent duchy
Duchy of Savoy
From 1416 to 1847, the House of Savoy ruled the eponymous Duchy of Savoy . The Duchy was a state in the northern part of the Italian Peninsula, with some territories that are now in France. It was a continuation of the County of Savoy...
, with Amédée VIII as the first duke. Straddling the Alps, Savoy lay within two competing spheres of influence, a French sphere and a North Italian one. At the time of the Renaissance, Savoy showed only modest development.Henry S. Lucas, The Renaissance and the Reformation (Harper & Bros. Publishers: New York, 1960) p. 42. Its towns were few and small.Ibid. Savoy derived its subsistence from agriculture.Ibid. The geographic location of Savoy was also of military importance.Henry S. Lucas, The Renaissance and the Reformation (Harper & Bros. Publishers: New York, 1960) p. 42. During the interminable wars
Italian Wars
The Italian Wars, often referred to as the Great Italian Wars or the Great Wars of Italy and sometimes as the Habsburg–Valois Wars, were a series of conflicts from 1494 to 1559 that involved, at various times, most of the city-states of Italy, the Papal States, most of the major states of Western...
between France and Spain over the control of northern Italy, Savoy was important to France because it provided access to Italy.Henry S. Lucas, The Renaissance and the Reformation, p. 42. Savoy was important to Spain because it served as a buffer between France and the Spanish held lands in Italy.Ibid. In 1563 Emmanuel Philibert
Emmanuel Philibert, Duke of Savoy
Emmanuel Philibert was Duke of Savoy from 1553 to 1580....
moved the capital from Chambéry
Chambéry
Chambéry is a city in the department of Savoie, located in the Rhône-Alpes region in southeastern France.It is the capital of the department and has been the historical capital of the Savoy region since the 13th century, when Amadeus V of Savoy made the city his seat of power.-Geography:Chambéry...
to Turin
Turin
Turin is a city and major business and cultural centre in northern Italy, capital of the Piedmont region, located mainly on the left bank of the Po River and surrounded by the Alpine arch. The population of the city proper is 909,193 while the population of the urban area is estimated by Eurostat...
, which was less vulnerable to French interference.Robert Katz, The Fall of the House of Savoy (The MacMillan Company: New York, 1971) p. 18.
Vaud
Vaud
Vaud is one of the 26 cantons of Switzerland and is located in Romandy, the French-speaking southwestern part of the country. The capital is Lausanne. The name of the Canton in Switzerland's other languages are Vaud in Italian , Waadt in German , and Vad in Romansh.-History:Along the lakes,...
was annexed by Bern in 1536, and Savoy officially ceded Vaud to Bern in the treaty of Lausanne of 30 October 1564.
In 1714, as a consequence of the War of the Spanish Succession
War of the Spanish Succession
The War of the Spanish Succession was fought among several European powers, including a divided Spain, over the possible unification of the Kingdoms of Spain and France under one Bourbon monarch. As France and Spain were among the most powerful states of Europe, such a unification would have...
, Savoy was technically subsumed into the Kingdom of Sicily
Kingdom of Sicily
The Kingdom of Sicily was a state that existed in the south of Italy from its founding by Roger II in 1130 until 1816. It was a successor state of the County of Sicily, which had been founded in 1071 during the Norman conquest of southern Italy...
, then (after that island was traded to Austria
Austria
Austria , officially the Republic of Austria , is a landlocked country of roughly 8.4 million people in Central Europe. It is bordered by the Czech Republic and Germany to the north, Slovakia and Hungary to the east, Slovenia and Italy to the south, and Switzerland and Liechtenstein to the...
for Sardinia
Sardinia
Sardinia is the second-largest island in the Mediterranean Sea . It is an autonomous region of Italy, and the nearest land masses are the French island of Corsica, the Italian Peninsula, Sicily, Tunisia and the Spanish Balearic Islands.The name Sardinia is from the pre-Roman noun *sard[],...
) the Kingdom of Sardinia
Kingdom of Sardinia
The Kingdom of Sardinia consisted of the island of Sardinia first as a part of the Crown of Aragon and subsequently the Spanish Empire , and second as a part of the composite state of the House of Savoy . Its capital was originally Cagliari, in the south of the island, and later Turin, on the...
from 1720.
While the heads of the House of Savoy were known as the Kings of Sardinia, Turin remained their capital.
French Revolutionary Wars
Savoy was occupied by French revolutionary forcesFrench Revolutionary Army
The French Revolutionary Army is the term used to refer to the military of France during the period between the fall of the ancien regime under Louis XVI in 1792 and the formation of the First French Empire under Napoleon Bonaparte in 1804. These armies were characterised by their revolutionary...
between 1792 and 1815. The region was first added to the département of Mont-Blanc, then in 1798 was divided between the départements of Mont-Blanc and Léman (French name of Lake Geneva.) In 1801, Savoy officially left the Holy Roman Empire
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a realm that existed from 962 to 1806 in Central Europe.It was ruled by the Holy Roman Emperor. Its character changed during the Middle Ages and the Early Modern period, when the power of the emperor gradually weakened in favour of the princes...
.
- For the two French départements of the region of Savoy, see SavoieSavoieSavoie is a French department located in the Rhône-Alpes region in the French Alps.Together with the Haute-Savoie, Savoie is one of the two departments of the historic region of Savoy that was annexed by France on June 14, 1860, following the signature of the Treaty of Turin on March 24, 1860...
and Haute-SavoieHaute-SavoieHaute-Savoie is a French department in the Rhône-Alpes region of eastern France. It borders both Switzerland and Italy. The capital is Annecy. To the north is Lake Geneva and Switzerland; to the south and southeast are the Mont Blanc and Aravis mountain ranges and the French entrance to the Mont...
Savoy (ˈsævɔɪ; , saˈvwɛ; , savwa; ) is a region of France. It comprises roughly the territory of the Western Alps situated between Lake Geneva
Lake Geneva
Lake Geneva or Lake Léman is a lake in Switzerland and France. It is one of the largest lakes in Western Europe. 59.53 % of it comes under the jurisdiction of Switzerland , and 40.47 % under France...
in the north and Monaco
Monaco
Monaco , officially the Principality of Monaco , is a sovereign city state on the French Riviera. It is bordered on three sides by its neighbour, France, and its centre is about from Italy. Its area is with a population of 35,986 as of 2011 and is the most densely populated country in the...
and the Mediterranean coast in the south.
The historical land of Savoy emerged as the feudal territory of the house of Savoy
House of Savoy
The House of Savoy was formed in the early 11th century in the historical Savoy region. Through gradual expansion, it grew from ruling a small county in that region to eventually rule the Kingdom of Italy from 1861 until the end of World War II, king of Croatia and King of Armenia...
during the 11th to 14th centuries. The historical territory is shared between the modern republics of France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
and Italy
Italy
Italy , officially the Italian Republic languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Italy's official name is as follows:;;;;;;;;), is a unitary parliamentary republic in South-Central Europe. To the north it borders France, Switzerland, Austria and...
.
Installed by Rudolph III, King of Burgundy, officially in 1003, the House of Savoy
House of Savoy
The House of Savoy was formed in the early 11th century in the historical Savoy region. Through gradual expansion, it grew from ruling a small county in that region to eventually rule the Kingdom of Italy from 1861 until the end of World War II, king of Croatia and King of Armenia...
became the longest surviving royal house in Europe. It ruled the County of Savoy
County of Savoy
The Counts of Savoy emerged, along with the free communes of Switzerland, from the collapse of the Burgundian Kingdom of Arles in the 11th century....
to 1416 and then the Duchy of Savoy
Duchy of Savoy
From 1416 to 1847, the House of Savoy ruled the eponymous Duchy of Savoy . The Duchy was a state in the northern part of the Italian Peninsula, with some territories that are now in France. It was a continuation of the County of Savoy...
from 1416 to 1714.
The territory of Savoy was annexed to France in 1792 under the French First Republic
French First Republic
The French First Republic was founded on 22 September 1792, by the newly established National Convention. The First Republic lasted until the declaration of the First French Empire in 1804 under Napoleon I...
, before being returned to the Kingdom of Piedmont-Sardinia in 1815. Savoy was finally annexed to France, under the Second French Empire
Second French Empire
The Second French Empire or French Empire was the Imperial Bonapartist regime of Napoleon III from 1852 to 1870, between the Second Republic and the Third Republic, in France.-Rule of Napoleon III:...
in 1860, as part of a political agreement brokered between the French emperor Napoleon III and King Victor Emmanuel II of the Kingdom of Sardinia
Kingdom of Sardinia
The Kingdom of Sardinia consisted of the island of Sardinia first as a part of the Crown of Aragon and subsequently the Spanish Empire , and second as a part of the composite state of the House of Savoy . Its capital was originally Cagliari, in the south of the island, and later Turin, on the...
that began the process of unification of Italy
Italian unification
Italian unification was the political and social movement that agglomerated different states of the Italian peninsula into the single state of Italy in the 19th century...
. Victor Emmanuel's dynasty, the House of Savoy
House of Savoy
The House of Savoy was formed in the early 11th century in the historical Savoy region. Through gradual expansion, it grew from ruling a small county in that region to eventually rule the Kingdom of Italy from 1861 until the end of World War II, king of Croatia and King of Armenia...
, retained its Italian lands of Piedmont
Piedmont
Piedmont is one of the 20 regions of Italy. It has an area of 25,402 square kilometres and a population of about 4.4 million. The capital of Piedmont is Turin. The main local language is Piedmontese. Occitan is also spoken by a minority in the Occitan Valleys situated in the Provinces of...
and Liguria
Liguria
Liguria is a coastal region of north-western Italy, the third smallest of the Italian regions. Its capital is Genoa. It is a popular region with tourists for its beautiful beaches, picturesque little towns, and good food.-Geography:...
and became the ruling dynasty of Italy.
Geography
The County and Duchy of Savoy incorporated TurinTurin
Turin is a city and major business and cultural centre in northern Italy, capital of the Piedmont region, located mainly on the left bank of the Po River and surrounded by the Alpine arch. The population of the city proper is 909,193 while the population of the urban area is estimated by Eurostat...
and other territories in Piedmont
Piedmont
Piedmont is one of the 20 regions of Italy. It has an area of 25,402 square kilometres and a population of about 4.4 million. The capital of Piedmont is Turin. The main local language is Piedmontese. Occitan is also spoken by a minority in the Occitan Valleys situated in the Provinces of...
, a region in northwestern Italy that borders Savoy, which were also possessions of the House of Savoy. The capital of the Duchy remained at the traditional Savoyard capital of Chambéry
Chambéry
Chambéry is a city in the department of Savoie, located in the Rhône-Alpes region in southeastern France.It is the capital of the department and has been the historical capital of the Savoy region since the 13th century, when Amadeus V of Savoy made the city his seat of power.-Geography:Chambéry...
until 1563, when it was moved to Turin.
In modern France, Savoy is part of the Rhône-Alpes
Rhône-Alpes
Rhône-Alpes is one of the 27 regions of France, located on the eastern border of the country, towards the south. The region was named after the Rhône River and the Alps mountain range. Its capital, Lyon, is the second-largest metropolitan area in France after Paris...
region. Following its annexation to France in 1860, the territory of Savoy was divided administratively into two separate departments, Savoie
Savoie
Savoie is a French department located in the Rhône-Alpes region in the French Alps.Together with the Haute-Savoie, Savoie is one of the two departments of the historic region of Savoy that was annexed by France on June 14, 1860, following the signature of the Treaty of Turin on March 24, 1860...
and Haute-Savoie
Haute-Savoie
Haute-Savoie is a French department in the Rhône-Alpes region of eastern France. It borders both Switzerland and Italy. The capital is Annecy. To the north is Lake Geneva and Switzerland; to the south and southeast are the Mont Blanc and Aravis mountain ranges and the French entrance to the Mont...
.
The traditional capital remains Chambéry
Chambéry
Chambéry is a city in the department of Savoie, located in the Rhône-Alpes region in southeastern France.It is the capital of the department and has been the historical capital of the Savoy region since the 13th century, when Amadeus V of Savoy made the city his seat of power.-Geography:Chambéry...
(Ciamberì), on the rivers Leysse
Leysse
The Leysse is the river which crosses the city of Chambéry, Savoie, France. At its entrance into the city, it goes underground in a channel of about 1 km.-Characteristics:...
and Albane, hosting the castle
Castle
A castle is a type of fortified structure built in Europe and the Middle East during the Middle Ages by European nobility. Scholars debate the scope of the word castle, but usually consider it to be the private fortified residence of a lord or noble...
of the House of Savoy and the Savoyard senate
Senate
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a legislature or parliament. There have been many such bodies in history, since senate means the assembly of the eldest and wiser members of the society and ruling class...
. The state included six districts:
- Savoie Propre, sometimes known as Ducal Savoy (capital Chambéry)
- ChablaisChablaisChablais was a province of the Duchy of Savoy. Its capital was Thonon-les-Bains.This region is currently divided into three territories, the Chablais savoyard, the Chablais valaisan, and the Chablais vaudois, and is now split across two countries: France and Switzerland...
(capital Thonon-les-BainsThonon-les-BainsThonon-les-Bains is a town in the Haute-Savoie department in the Rhône-Alpes region in south-eastern France. It is a sub-prefecture of the department.-History:...
) - FaucignyFaucignyFaucigny is a commune in the Haute-Savoie department in the Rhône-Alpes region in south-eastern France.Historically, Faucigny was a region in Savoy which included the area of the modern département of Haute Savoie and the municipalities of Chamonix, Argentière, and Les Houches.-Geography:In the...
(capital BonnevilleBonneville-People:* Benjamin Louis Eulalie de Bonneville, a French-born officer in the United States Army, fur trapper, and explorer in the American West* Hugh Bonneville, an English stage, television, and film actor* Nicholas Bonneville, a French writer-Places in the USA:...
) - TarentaiseTarentaiseTarentaise can refer to the following:Places* Moûtiers, historically known as Tarentaise, in Savoy* Tarentaise Valley* Tarentaise, LoirePeople* Peter of TarentaiseOther*Tarentaise cattle...
(capital Moûtiers) - MaurienneMaurienneMaurienne is one of the provinces of Savoy, corresponding to the arrondissement of Saint-Jean-de-Maurienne in France. It is also the original name of the capital of the province, now Saint-Jean-de-Maurienne.-Location:...
(capital Saint-Jean-de-MaurienneSaint-Jean-de-MaurienneSaint-Jean-de-Maurienne is a commune in the Savoie department in the Rhône-Alpes region in south-eastern France. It is a sub-prefecture of the department....
) - GenevoisGenevois (province)The Genevois is a former province of the Duchy of Savoy. Its capital is Annecy and other centres include Faverges, Thônes, and La Clusaz. It was bordered by the provinces of Carouge to the north-west, Faucigny to the north-east, and Savoy proper to the south-east and south-west.Although the...
(capital AnnecyAnnecyAnnecy is a commune in the Haute-Savoie department in the Rhône-Alpes region in south-eastern France.It lies on the northern tip of Lake Annecy , 35 kilometres south of Geneva.-Administration:...
).
Early history
The region occupied by the Celtic AllobrogesAllobroges
The Allobroges were a Celtic tribe of ancient Gaul, located between the Rhône River and the Lake of Geneva in what later became Savoy, Dauphiné, and Vivarais. Their cities were in the areas of modern-day Annecy, Chambéry and Grenoble, the modern of Isère, and modern Switzerland...
people became part of the Roman Empire
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire was the post-Republican period of the ancient Roman civilization, characterised by an autocratic form of government and large territorial holdings in Europe and around the Mediterranean....
. The name Savoy stems from the Late Latin
Late Latin
Late Latin is the scholarly name for the written Latin of Late Antiquity. The English dictionary definition of Late Latin dates this period from the 3rd to the 6th centuries AD extending in Spain to the 7th. This somewhat ambiguously defined period fits between Classical Latin and Medieval Latin...
Sapaudia, referring to a fir forest
Fir
Firs are a genus of 48–55 species of evergreen conifers in the family Pinaceae. They are found through much of North and Central America, Europe, Asia, and North Africa, occurring in mountains over most of the range...
.Modern French sapin; sapinière signifies "fir forest". It is first recorded in Ammianus Marcellinus
Ammianus Marcellinus
Ammianus Marcellinus was a fourth-century Roman historian. He wrote the penultimate major historical account surviving from Antiquity...
(354), to describe the southern part of Maxima Sequanorum
Sequani
Sequani, in ancient geography, were a Gallic people who occupied the upper river basin of the Arar , the valley of the Doubs and the Jura Mountains, their territory corresponding to Franche-Comté and part of Burgundy.-Etymology:...
The territory, which has no modern counterpart, was perhaps bounded by the rivers Ain and Rhône, Lac Léman, the Jura and the Aar, though historians differ, and there seems to be insufficient evidence: see Norman H. Baynes, reviewing A. Coville, Recherches sur l'Histoire de Lyon du Ve au IXe Siècle (450-800) in The English Historical Review 45 No. 179 (July 1930:470-474) p 471.
According to the Gallic Chronicle of 452, it was separated from the rest of Burgundian territories in 443, after the Burgundian defeat by Flavius Aetius
Flavius Aëtius
Flavius Aëtius , dux et patricius, was a Roman general of the closing period of the Western Roman Empire. He was an able military commander and the most influential man in the Western Roman Empire for two decades . He managed policy in regard to the attacks of barbarian peoples pressing on the Empire...
.Sapaudia Burgundionum reliquiis datur cum indigenis dividenda. (in T. Mommsen, Chronica Minora II:660, 128.
Early and High Middle Ages
By the 8th century, the territory that would later become known as Savoy was part of the Kingdom of the Franks, and at the division of Francia at the Treaty of VerdunTreaty of Verdun
The Treaty of Verdun was a treaty between the three surviving sons of Louis the Pious, the son and successor of Charlemagne, which divided the Carolingian Empire into three kingdoms...
in 843, it became part of the short-lived kingdom of Middle Francia
Middle Francia
Middle Francia was an ephemeral Frankish kingdom created by the Treaty of Verdun in 843, which divided the Carolingian Empire among the sons of Louis the Pious...
. After only 12 years, at the death of Lothair I
Lothair I
Lothair I or Lothar I was the Emperor of the Romans , co-ruling with his father until 840, and the King of Bavaria , Italy and Middle Francia...
in 855,
Middle Francia was divided into Lotharingia
Lotharingia
Lotharingia was a region in northwest Europe, comprising the Low Countries, the western Rhineland, the lands today on the border between France and Germany, and what is now western Switzerland. It was born of the tripartite division in 855, of the kingdom of Middle Francia, itself formed of the...
north of the Alps, Italy
Kingdom of Italy (medieval)
The Kingdom of Italy was a political entity under control of Carolingian dynasty of Francia first, after the defeat of the Lombards in 774. It was finally incorporated as a part of the Holy Roman Empire in 962....
south of the Alps, and the parts of Burgundy in the Western Alps, inherited by Charles son of Lothair
Charles of Provence
Charles of Provence was the Carolingian King of Provence from 855 until his early death in 863.Charles was the youngest son of Holy Roman Emperor Lothair I and Ermengarde of Tours....
. This latter territory comprised what would become known as Savoy and Provence
Provence
Provence ; Provençal: Provença in classical norm or Prouvènço in Mistralian norm) is a region of south eastern France on the Mediterranean adjacent to Italy. It is part of the administrative région of Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur...
.
From the 10th to 14th century, parts of what would ultimately become Savoy remained within Kingdom of Arles
Kingdom of Arles
The Kingdom of Arles or Second Kingdom of Burgundy of the High Middle Ages was a Frankish dominion established in 933 from lands of the early medieval Kingdom of Burgundy at Arles...
). Beginning in the 11th century, the gradual rise to power of the house of Savoy
House of Savoy
The House of Savoy was formed in the early 11th century in the historical Savoy region. Through gradual expansion, it grew from ruling a small county in that region to eventually rule the Kingdom of Italy from 1861 until the end of World War II, king of Croatia and King of Armenia...
is reflected in the increasing territory of their County of Savoy
County of Savoy
The Counts of Savoy emerged, along with the free communes of Switzerland, from the collapse of the Burgundian Kingdom of Arles in the 11th century....
between 1003 and 1416.
The County of Savoy was detached de jure from the Kingdom of Arles by Charles IV
Charles IV, Holy Roman Emperor
Charles IV , born Wenceslaus , was the second king of Bohemia from the House of Luxembourg, and the first king of Bohemia to also become Holy Roman Emperor....
in 1361. It acquired the County of Nice
County of Nice
The County of Nice or Niçard Country is a historical region of France, located in the south-eastern part, around the city of Nice.-History:Its territory lies between the Mediterranean Sea , Var River and the southernmost crest of the...
in 1388, and in 1401 added the County of Genevois, the area of Geneva
Geneva
Geneva In the national languages of Switzerland the city is known as Genf , Ginevra and Genevra is the second-most-populous city in Switzerland and is the most populous city of Romandie, the French-speaking part of Switzerland...
except for the city proper, which was ruled by its prince-bishop
Prince-Bishop
A Prince-Bishop is a bishop who is a territorial Prince of the Church on account of one or more secular principalities, usually pre-existent titles of nobility held concurrently with their inherent clerical office...
, nominally under the duke's rule: the bishops of Geneva, by unspoken agreement, came from the house of Savoy
House of Savoy
The House of Savoy was formed in the early 11th century in the historical Savoy region. Through gradual expansion, it grew from ruling a small county in that region to eventually rule the Kingdom of Italy from 1861 until the end of World War II, king of Croatia and King of Armenia...
; this agreement came to an end in 1533.See the career of the last prince-bishop Pierre de La Baume
Pierre de La Baume
Pierre de La Baume was a grand seigneur of Savoy and a cardinal of the Roman Catholic Church. He was a councillor of Charles III, Duke of Savoy, whom he represented at the Fifth Lateran Council ....
.
Duchy of Savoy

Sigismund, Holy Roman Emperor
Sigismund of Luxemburg KG was King of Hungary, of Croatia from 1387 to 1437, of Bohemia from 1419, and Holy Roman Emperor for four years from 1433 until 1437, the last Emperor of the House of Luxemburg. He was also King of Italy from 1431, and of Germany from 1411...
, made the County of Savoy an independent duchy
Duchy of Savoy
From 1416 to 1847, the House of Savoy ruled the eponymous Duchy of Savoy . The Duchy was a state in the northern part of the Italian Peninsula, with some territories that are now in France. It was a continuation of the County of Savoy...
, with Amédée VIII as the first duke. Straddling the Alps, Savoy lay within two competing spheres of influence, a French sphere and a North Italian one. At the time of the Renaissance, Savoy showed only modest development.Henry S. Lucas, The Renaissance and the Reformation (Harper & Bros. Publishers: New York, 1960) p. 42. Its towns were few and small.Ibid. Savoy derived its subsistence from agriculture.Ibid. The geographic location of Savoy was also of military importance.Henry S. Lucas, The Renaissance and the Reformation (Harper & Bros. Publishers: New York, 1960) p. 42. During the interminable wars
Italian Wars
The Italian Wars, often referred to as the Great Italian Wars or the Great Wars of Italy and sometimes as the Habsburg–Valois Wars, were a series of conflicts from 1494 to 1559 that involved, at various times, most of the city-states of Italy, the Papal States, most of the major states of Western...
between France and Spain over the control of northern Italy, Savoy was important to France because it provided access to Italy.Henry S. Lucas, The Renaissance and the Reformation, p. 42. Savoy was important to Spain because it served as a buffer between France and the Spanish held lands in Italy.Ibid. In 1563 Emmanuel Philibert
Emmanuel Philibert, Duke of Savoy
Emmanuel Philibert was Duke of Savoy from 1553 to 1580....
moved the capital from Chambéry
Chambéry
Chambéry is a city in the department of Savoie, located in the Rhône-Alpes region in southeastern France.It is the capital of the department and has been the historical capital of the Savoy region since the 13th century, when Amadeus V of Savoy made the city his seat of power.-Geography:Chambéry...
to Turin
Turin
Turin is a city and major business and cultural centre in northern Italy, capital of the Piedmont region, located mainly on the left bank of the Po River and surrounded by the Alpine arch. The population of the city proper is 909,193 while the population of the urban area is estimated by Eurostat...
, which was less vulnerable to French interference.Robert Katz, The Fall of the House of Savoy (The MacMillan Company: New York, 1971) p. 18.
Vaud
Vaud
Vaud is one of the 26 cantons of Switzerland and is located in Romandy, the French-speaking southwestern part of the country. The capital is Lausanne. The name of the Canton in Switzerland's other languages are Vaud in Italian , Waadt in German , and Vad in Romansh.-History:Along the lakes,...
was annexed by Bern in 1536, and Savoy officially ceded Vaud to Bern in the treaty of Lausanne of 30 October 1564.
In 1714, as a consequence of the War of the Spanish Succession
War of the Spanish Succession
The War of the Spanish Succession was fought among several European powers, including a divided Spain, over the possible unification of the Kingdoms of Spain and France under one Bourbon monarch. As France and Spain were among the most powerful states of Europe, such a unification would have...
, Savoy was technically subsumed into the Kingdom of Sicily
Kingdom of Sicily
The Kingdom of Sicily was a state that existed in the south of Italy from its founding by Roger II in 1130 until 1816. It was a successor state of the County of Sicily, which had been founded in 1071 during the Norman conquest of southern Italy...
, then (after that island was traded to Austria
Austria
Austria , officially the Republic of Austria , is a landlocked country of roughly 8.4 million people in Central Europe. It is bordered by the Czech Republic and Germany to the north, Slovakia and Hungary to the east, Slovenia and Italy to the south, and Switzerland and Liechtenstein to the...
for Sardinia
Sardinia
Sardinia is the second-largest island in the Mediterranean Sea . It is an autonomous region of Italy, and the nearest land masses are the French island of Corsica, the Italian Peninsula, Sicily, Tunisia and the Spanish Balearic Islands.The name Sardinia is from the pre-Roman noun *sard[],...
) the Kingdom of Sardinia
Kingdom of Sardinia
The Kingdom of Sardinia consisted of the island of Sardinia first as a part of the Crown of Aragon and subsequently the Spanish Empire , and second as a part of the composite state of the House of Savoy . Its capital was originally Cagliari, in the south of the island, and later Turin, on the...
from 1720.
While the heads of the House of Savoy were known as the Kings of Sardinia, Turin remained their capital.
French Revolutionary Wars
Savoy was occupied by French revolutionary forcesFrench Revolutionary Army
The French Revolutionary Army is the term used to refer to the military of France during the period between the fall of the ancien regime under Louis XVI in 1792 and the formation of the First French Empire under Napoleon Bonaparte in 1804. These armies were characterised by their revolutionary...
between 1792 and 1815. The region was first added to the département of Mont-Blanc, then in 1798 was divided between the départements of Mont-Blanc and Léman (French name of Lake Geneva.) In 1801, Savoy officially left the Holy Roman Empire
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a realm that existed from 962 to 1806 in Central Europe.It was ruled by the Holy Roman Emperor. Its character changed during the Middle Ages and the Early Modern period, when the power of the emperor gradually weakened in favour of the princes...
.

