
Saxony
Encyclopedia
The Free State of Saxony ( ˈfʁaɪʃtaːt ˈzaksən; ) is a landlocked state
of Germany
, contingent with Brandenburg
, Saxony Anhalt, Thuringia
, Bavaria
, the Czech Republic
and Poland
. It is the tenth-largest German state in area, with (18413 square kilometres (7,109 sq mi), and the sixth most-populous (4.3 million) of Germany's sixteen states.
Located in the middle of an erstwhile German-speaking part of Europe, the history of the state of Saxony spans more than a millennium. It has been a medieval duchy
, an electorate
of the Holy Roman Empire
, a kingdom
and from 1918 to 1952, and then again from 1990, a republic.
The area of the modern state of Saxony should not be confused with Old Saxony
, the area inhabited by Saxons
. Old Saxony corresponds approximately to the modern German states of Lower Saxony
, Saxony-Anhalt
and the Westphalian part of North Rhine-Westphalia
.
— Chemnitz
, Dresden
, Leipzig
— which are subdivided into 10 districts:
 1. Bautzen
1. Bautzen
(BZ)
2. Erzgebirgskreis
(ERZ)
3. Görlitz
(GR)
4. Leipzig
(L)
5. Meißen (MEI)(Meissen)
6. Mittelsachsen
(FG)
7. Nordsachsen
(TDO)
8. Sächsische Schweiz-Osterzgebirge
(PIR)
9. Vogtlandkreis
(V)
10. Zwickau
(Z)
The Erzgebirgskreis district covers the Ore Mountains, and the Schweiz-Osterzgebirge district is Saxon Switzerland and the Eastern Ore Mountains.
In addition there are three urban districts
, which also have district status:
, qualifies as an "Objective 1" development region within the European Union
, and is eligible to receive investment subsidies of up to 30% until 2013. FutureSAX
, a business plan competition and entrepreneurial support organization, has been in operation since 2002.
Microchip makers near Dresden have given the region a nickname of "Silicon Saxony". The publishing and porcelain industries of the region are well known, although their contributions to the regional economy are not significant.The state government is attempting to develop tourism, notably in the lake district of Lausitz
.
Saxony reported unemployment of 11.9% as average for 2010, by comparison the average for the former GDR was 12% and 7.7% for Germany overall.
, an electorate
of the Holy Roman Empire
(the Electorate of Saxony
), and eventually as a kingdom
(the Kingdom of Saxony
). In 1918, subsequent to Germany's defeat in World War I
, its monarchy was overthrown and a republican form of government was established under its current name. The state was broken up into smaller units during communist rule (1949–1989), but was re-established on 3 October 1990 on the reunification of East and West Germany
.
, dating from the 5th century BC. Notable archaeological sites have been discovered in Dresden
and the villages of Eythra and Zwenkau
near Leipzig
. The Slavic and Germanic
presence in the territory of today's Saxony is thought to have begun in the 1st century BC.
Parts of Saxony were possibly under the control of the Germanic King Marobod during the Roman era.
By the late Roman period, several tribes known as the Saxons emerged, from which the subsequent state(s) draw their name. For the origins of the Saxon tribes, see Saxons
.
 The first mediæval Duchy of Saxony was a late Early Middle Ages
The first mediæval Duchy of Saxony was a late Early Middle Ages
"Carolingian stem duchy
", which emerged about the year 700, and grew to cover the greater part of Northern Germany
. It covered the area of the modern German states of Lower Saxony
, North Rhine-Westphalia
, Schleswig-Holstein
and Saxony-Anhalt
. The Saxons converted to Christianity during this period.
While the Saxons were facing pressure from Charlemagne's Franks, they were also facing a westward push by Slavs to the east. The territory of the Free State of Saxony was occupied by Slavs before being reconquered by Germans. A legacy of this period is the Sorb
population in Saxony.
by the 10th century. In the 10th century, the dukes of Saxony were also kings (or emperors) of the Holy Roman Empire
, comprising the Ottonian, or Saxon, Dynasty. Around this time, the Billung
s, a Saxon
noble family, received extensive fiefs in Saxony. The Emperor eventually gave them the title of Duke of Saxony. After Duke Magnus
died in 1106, causing the extinction of the male line of Billungs, oversight of the duchy was given to Lothar of Supplinburg
, who also became Emperor for a short time.
In 1137, control of Saxony passed to the Guelph dynasty, descendants of Wulfhild Billung, eldest daughter of the last Billung duke, and the daughter of Lothar of Supplinburg. In 1180 large portions west of the Weser were ceded to the Bishops of Cologne, while some central parts between the Weser and the Elbe remained to the Guelphs, later forming the Duchy of Brunswick-Lüneburg
). The remaining eastern lands, together with the title of Duke of Saxony, passed to an Ascanian dynasty (descended from Eilika Billung
, Wulfhild's younger sister) and was divided in 1260 into the two small states of Saxe-Lauenburg and Saxe-Wittenberg
, the former also named Lower Saxony
, the latter Upper Saxony
, thence the later names of the two Imperial Circle
s. Saxe-Lauenburg and Saxe-Wittenberg both claimed the Saxon electoral privilege
for their part, but the Golden Bull of 1356
only accepted Wittenberg's claim, with Lauenburg nevertheless maintaining its claim. In 1422, when the Saxon electoral line of the Ascanians was extinct, the Ascanian Eric V of Saxe-Lauenburg tried to reunite the Saxon duchies.
However, Sigismund
, King of the Romans
, had already granted Margrave Frederick IV the Warlike of Meissen (House of Wettin) an expectancy on the Saxon electorate, in order to remunerate his military support. On 1 August 1425 Sigismund enfeoffed the Wettinian Frederick as Prince-Elector of Saxony, despite protestations of Eric V. Thus the Saxon territories remained separated in permanence. Electoral Saxony was then merged in the much bigger Wettinian Margraviate of Meissen, however using the higher ranking name Electorate of Saxony and even the Ascanian coat-of-arms for the entire monarchy. Thus the name Saxony was translated to areas as far as Dresden
and Meissen
. In the 18th and 19th centuries Saxe-Lauenburg became colloquially called the Duchy of Lauenburg, which in 1876 merged in Prussia
as Duchy of Lauenburg district.

 Saxony-Wittenberg, in modern Saxony-Anhalt
Saxony-Wittenberg, in modern Saxony-Anhalt
, became subject to the margravate
of Meissen
, ruled by the Wettin dynasty in 1423. This established a new and powerful state, occupying large portions of the present Free State of Saxony, Thuringia, and Saxony-Anhalt. Although the center of this state was far to the southeast of the former Saxony, it came to be referred to as Upper Saxony and then simply Saxony, while the former Saxon territories were now known as Lower Saxony.
In 1485, Saxony was split. A collateral line of the Wettin princes received what later became Thuringia
and founded several small states there (see Ernestine duchies
). The remaining Saxon state became still more powerful, becoming known in the 18th century for its cultural achievements, although it was politically inferior to Prussia
and Austria
, which pressed Saxony from either side.
Between the years 1697 and 1763, the Electors of Saxony were also elected Kings of Poland in personal union
.
In 1756, Saxony joined the coalition of Austria, France and Russia against Prussia. Frederick II of Prussia
chose to attack preemptively and invaded Saxony in August 1756, precipitating the Seven Years War. The Prussians quickly defeated Saxony and incorporated the Saxon army into the Prussian army. At the end of the Seven Years War, Saxony once again became an independent state.
Emperor Napoleon
abolished the Holy Roman Empire
and decreed the Electorate of Saxony
a kingdom in itself. Elector
Frederick Augustus III became King Frederick Augustus I
. Frederick Augustus remained loyal to Napoleon during the wars that swept Europe in the following years; he was taken prisoner and his territories declared forfeit by the allies in 1813, who intended the annexation of Saxony by Prussia. Ultimately, the opposition of Austria, France, and the United Kingdom
to this plan resulted in the restoration of Frederick Augustus to his throne at the Congress of Vienna
. At this time in 1815, Saxony was forced to cede the northern part of the kingdom to Prussia. These lands became the Prussian province of Saxony
, incorporated today in Saxony-Anhalt. The remnant of the Kingdom of Saxony
was roughly identical with the present federal state.
Meanwhile, in 1815, the southern part of Saxony, now called the "State of Saxony joined the German Confederation
. (The German Confederation should not be confused with the North German Confederation mentioned below.) In the politics of the Confederation, Saxony was overshadowed by Prussia. King Anthony of Saxony, came to the throne of Saxony in 1827. Shortly thereafter, liberal pressures in Saxony mounted and broke out in the revolt during 1830—a year of revolution in Europe. The revolution in Saxony resulted in a Constitution for the State of Saxony which served as a basis for the government in Saxony until 1918.
During the 1848–49 constitutionalist revolutions in Germany
, Saxony became a hotbed for revolutionaries, with anarchists such as Mikhail Bakunin
and democrats including Richard Wagner
and Gottfried Semper
taking part in the May Uprising in Dresden
in 1849. (Scenes of Richard Wagner's participation in the May 1849 Uprising in Dresden are pictured in the 1983 movie, Wagner starring Richard Burton as Richard Wagner.) The May Uprising in Dresden forced King Frederick Augustus II of Saxony
to concede further reforms in the Saxon government.
In 1854 Frederick Augustus II's brother, King John of Saxony, succeeded to the throne. A scholar, King John translated Dante. King John followed a federalistic and pro-Austrian policy throughout the early 1860s until the outbreak of the Austro-Prussian War
. During the war, Prussian troops overran Saxony without a fight and invaded then Austrian (today's Czech) Bohemia
. After the war, Saxony was forced to pay an indemnity and to join the North German Confederation
in 1867. Under the terms of the North German Confederation, Prussia took over control of the Saxon postal system, railroads, military and foreign affairs. In the Franco-Prussian War
of 1870, Saxon troops fought together with Prussian and other German troops against France. In 1871, Saxony joined the newly formed German Empire
.
After King Frederick Augustus III of Saxony
had abdicated on 13 November 1918, Saxony, remaining a constituent state of Germany (Weimar Republic
), became a republic renamed the Free State of Saxony following the new Saxon constitution of 1 November 1920. In 1923 Reichs's chancellor Gustav Stresemann
overthrew the SPD
-led Saxon government. The state maintained its name and borders during the National Socialist era as a Gau, but lost any quasi-autonomous status and its parliamentarian democracy.
By the by end of World War II
in April 1945, American troops under General George Patton conquered the western part of the Free State, while Soviet troops conquered the eastern part. That summer, the entire state was handed over to Soviet forces as agreed upon by the London Protocol of September 1944. Thereafter Britain, the USA, and the USSR negotiated at the Potsdam Conference
on Germany's future. By their trilateral Potsdam Agreement
all German territory east of the Oder-Neisse line
was to be annexed by Poland and the Soviet Union and, unlike the post-World War I secessions of German territory, this time the annexing powers were allowed to expel the inhabitants.
Through all the following three years, Poland forcibly expelled German-speaking people from its annexed territory. Since the three powers of Potsdam had further agreed to accept in their occupation zones more expellees from other countries, the government in Prague denaturalised and expropriated around three million Czechoslovaks due to their German native language. So also Saxons had to feed and house the destitute expellees, while their retained belongings became war booty shared by the profiteers of this exproprietary attitude. Only a small Saxon area, lying east of the Neisse
river and centered around the town of Reichenau (now called Bogatynia
), was annexed by Poland. The Soviet Military Administration in Germany
(SVAG) merged that tiny part of the Prussian
province of Lower Silesia
, which remained with Germany west of the Neisse, into Saxony.
On 20 October 1946, the SVAG organised elections for the Saxon state parliament (Landtag), which were unbalanced since many people were arbitrarily excluded from candidacy and suffrage and the Soviet support unilaterally preferring the communist Socialist Unity Party of Germany
(SED). The new Saxon minister-president (governor) Rudolf Friedrichs (SED, until April 1946 SPD
), who met with his Bavarian counterparts in the US zone of occupation in October 1946 and May 1947, suddenly died under unknown circumstances the month after. He was succeeded by Max Seydewitz
, a loyalist of Joseph Stalin
.
The Soviet Union set up the communist government of the German Democratic Republic in 1949, with Saxony a part of it, giving the USSR a satellite in the heart of Europe. The communist government officially dissolved the Free State in 1952, and divided it into the three smaller Bezirke of Leipzig
, Dresden
, and Karl-Marx-Stadt
. The Free State was reconstituted with slightly altered borders in 1990 upon German reunification
. Besides the formerly Silesian area of Saxony, which was mostly included in the territory of the new Saxon state, the free state gained further areas north of Leipzig
, which belonged to Saxony-Anhalt
until 1952.
 The most common patois
The most common patois
spoken in Saxony are combined in the group of "Thuringian and Upper Saxon dialects". Due to the incorrect usage of "Saxon dialects" in colloquial language, the Upper Saxon attribute has been added to distinguish it from Old Saxon
and Low Saxon
. Other German dialects spoken in Saxony are the dialects of the Erzgebirge (Ore Mountains), which have been affected by Upper Saxon dialects, and the dialects of the Vogtland, which are more affected by the East Franconian
languages.
Upper Sorbian (a Slavic language
) is still actively spoken in the parts of Upper Lusatia
that are occupied by the Sorbian
minority. The Germans in Upper Lusatia speak distinct dialects of their own (Lusatian dialects).
and perhaps Leipzig
, Saxony is not known as a primary destination for foreign tourists. Areas along the border with the Czech Republic
, such as the Lusatian Mountains
, Ore Mountains, Saxon Switzerland
, and Vogtland
, attract significant visitors, largely Germans. Saxony has well preserved historic towns such as Meissen
, Freiberg
, Pirna
, Bautzen
, and Görlitz
.

heads the government of Saxony. Since May 28, 2008 the minister-president of Saxony is Stanislaw Tillich
. See: List of Ministers-President of Saxony, for a full listing.
States of Germany
Germany is made up of sixteen which are partly sovereign constituent states of the Federal Republic of Germany. Land literally translates as "country", and constitutionally speaking, they are constituent countries...
of Germany
Germany
Germany , officially the Federal Republic of Germany , is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km2 and has a largely temperate seasonal climate...
, contingent with Brandenburg
Brandenburg
Brandenburg is one of the sixteen federal-states of Germany. It lies in the east of the country and is one of the new federal states that were re-created in 1990 upon the reunification of the former West Germany and East Germany. The capital is Potsdam...
, Saxony Anhalt, Thuringia
Thuringia
The Free State of Thuringia is a state of Germany, located in the central part of the country.It has an area of and 2.29 million inhabitants, making it the sixth smallest by area and the fifth smallest by population of Germany's sixteen states....
, Bavaria
Bavaria
Bavaria, formally the Free State of Bavaria is a state of Germany, located in the southeast of Germany. With an area of , it is the largest state by area, forming almost 20% of the total land area of Germany...
, the Czech Republic
Czech Republic
The Czech Republic is a landlocked country in Central Europe. The country is bordered by Poland to the northeast, Slovakia to the east, Austria to the south, and Germany to the west and northwest....
and Poland
Poland
Poland , officially the Republic of Poland , is a country in Central Europe bordered by Germany to the west; the Czech Republic and Slovakia to the south; Ukraine, Belarus and Lithuania to the east; and the Baltic Sea and Kaliningrad Oblast, a Russian exclave, to the north...
. It is the tenth-largest German state in area, with (18413 square kilometres (7,109 sq mi), and the sixth most-populous (4.3 million) of Germany's sixteen states.
Located in the middle of an erstwhile German-speaking part of Europe, the history of the state of Saxony spans more than a millennium. It has been a medieval duchy
Saxe-Wittenberg
The Duchy of Saxe-Wittenberg was a medieval duchy of the Holy Roman Empire centered at Wittenberg, which emerged after the dissolution of the stem duchy of Saxony. As the precursor of the Saxon Electorate, the Ascanian Wittenberg dukes prevailed in obtaining the Saxon electoral dignity.-Ascanian...
, an electorate
Electorate of Saxony
The Electorate of Saxony , sometimes referred to as Upper Saxony, was a State of the Holy Roman Empire. It was established when Emperor Charles IV raised the Ascanian duchy of Saxe-Wittenberg to the status of an Electorate by the Golden Bull of 1356...
of the Holy Roman Empire
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a realm that existed from 962 to 1806 in Central Europe.It was ruled by the Holy Roman Emperor. Its character changed during the Middle Ages and the Early Modern period, when the power of the emperor gradually weakened in favour of the princes...
, a kingdom
Kingdom of Saxony
The Kingdom of Saxony , lasting between 1806 and 1918, was an independent member of a number of historical confederacies in Napoleonic through post-Napoleonic Germany. From 1871 it was part of the German Empire. It became a Free state in the era of Weimar Republic in 1918 after the end of World War...
and from 1918 to 1952, and then again from 1990, a republic.
The area of the modern state of Saxony should not be confused with Old Saxony
Old Saxony
Old Saxony is the original homeland of the Saxons in the northwest corner of modern Germany and roughly corresponds today with the contemporary Lower Saxony, Westphalia and western Saxony-Anhalt....
, the area inhabited by Saxons
Saxons
The Saxons were a confederation of Germanic tribes originating on the North German plain. The Saxons earliest known area of settlement is Northern Albingia, an area approximately that of modern Holstein...
. Old Saxony corresponds approximately to the modern German states of Lower Saxony
Lower Saxony
Lower Saxony is a German state situated in north-western Germany and is second in area and fourth in population among the sixteen states of Germany...
, Saxony-Anhalt
Saxony-Anhalt
Saxony-Anhalt is a landlocked state of Germany. Its capital is Magdeburg and it is surrounded by the German states of Lower Saxony, Brandenburg, Saxony, and Thuringia.Saxony-Anhalt covers an area of...
and the Westphalian part of North Rhine-Westphalia
North Rhine-Westphalia
North Rhine-Westphalia is the most populous state of Germany, with four of the country's ten largest cities. The state was formed in 1946 as a merger of the northern Rhineland and Westphalia, both formerly part of Prussia. Its capital is Düsseldorf. The state is currently run by a coalition of the...
.
Administration
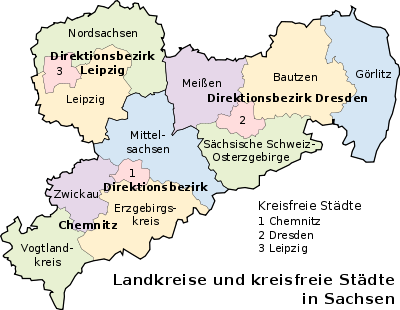
Sachsen is divided into three DirektionsbezirkeRegierungsbezirk
In Germany, a Government District, in German: Regierungsbezirk – is a subdivision of certain federal states .They are above the Kreise, Landkreise, and kreisfreie Städte...
— Chemnitz
Chemnitz (region)
thumb|right|200px|none|The [[:de:Regierungsbezirk Chemnitz|Regierungsbezirk Chemnitz]] before August 2008Chemnitz is one of the three Direktionsbezirke of the Free State of Saxony, Germany, located in the south-west of the state...
, Dresden
Dresden (region)
Dresden is one of the three Direktionsbezirke of the Free State of Saxony, Germany, located in the east of the state. It coincides with the Planungsregionen Oberlausitz-Niederschlesien and Oberes Elbtal/Osterzgebirge.-History:...
, Leipzig
Leipzig (region)
Leipzig is one of the three Direktionsbezirke of the Free State of Saxony, Germany, located in the north-west of the state. It coincides with the Planungsregion Westsachsen.-History:...
— which are subdivided into 10 districts:

Bautzen (district)
Bautzen is a district in the Free State of Saxony in Germany including the former districts of Bischofswerda and Kamenz. It is bounded by the Czech Republic, the district of Sächsische Schweiz-Osterzgebirge, the district-free city Dresden and the districts of Meißen and Görlitz...
(BZ)
2. Erzgebirgskreis
Erzgebirgskreis
Erzgebirgskreis is a district in the Free State of Saxony, Germany. It is named after the Erzgebirge , a mountain range in the southern part of the district which forms part of the Germany–Czech Republic border...
(ERZ)
3. Görlitz
Görlitz (district)
Görlitz is a district in the Free State of Saxony, Germany. It is named after its capital city Görlitz. It borders the district of Bautzen, the state Brandenburg, Poland and the Czech Republic.- History :...
(GR)
4. Leipzig
Leipzig (district)
Leipzig is a district in the Free State of Saxony, Germany. It is named after the city Leipzig, which is surrounded by the district, but not part of it...
(L)
5. Meißen (MEI)(Meissen)
6. Mittelsachsen
Mittelsachsen
Mittelsachsen is a district in the Free State of Saxony, Germany.- History :The district was established by merging the former districts of Döbeln, Freiberg and Mittweida as part of the district reform of August 2008.- Geography :...
(FG)
7. Nordsachsen
Nordsachsen
Nordsachsen is a district in the Free State of Saxony, Germany.- History :The district was established by merging the former districts of Delitzsch and Torgau-Oschatz as part of the district reform of August 2008....
(TDO)
8. Sächsische Schweiz-Osterzgebirge
Sächsische Schweiz-Osterzgebirge
Sächsische Schweiz-Osterzgebirge is a district in the Free State of Saxony, Germany. It is named after the mountain ranges Saxon Switzerland and Erzgebirge.- History :...
(PIR)
9. Vogtlandkreis
Vogtlandkreis
The Vogtlandkreis is a Landkreis in the southwest of the Free State of Saxony, Germany, at the borders to Thuringia, Bavaria, and the Czech Republic. Neighboring districts are Hof, Saale-Orla, Greiz, Zwickau and Erzgebirgskreis...
(V)
10. Zwickau
Zwickau (district)
Zwickau is a district in the Free State of Saxony, Germany.- History :The district was established by merging the former districts Zwickauer Land, Chemnitzer Land and the urban district Zwickau as part of the district reform of August 2008....
(Z)
The Erzgebirgskreis district covers the Ore Mountains, and the Schweiz-Osterzgebirge district is Saxon Switzerland and the Eastern Ore Mountains.
In addition there are three urban districts
Urban districts of Germany
This is a list of urban districts in Germany. Germany's sixteen states are further subdivided into 402 districts of which 107 are urban districts – cities which constitute a district in their own right. A similar concept is the Statutarstadt in Austria...
, which also have district status:
- ChemnitzChemnitzChemnitz is the third-largest city of the Free State of Saxony, Germany. Chemnitz is an independent city which is not part of any county and seat of the government region Direktionsbezirk Chemnitz. Located in the northern foothills of the Ore Mountains, it is a part of the Saxon triangle...
(C) - DresdenDresdenDresden is the capital city of the Free State of Saxony in Germany. It is situated in a valley on the River Elbe, near the Czech border. The Dresden conurbation is part of the Saxon Triangle metropolitan area....
(DD) - LeipzigLeipzigLeipzig Leipzig has always been a trade city, situated during the time of the Holy Roman Empire at the intersection of the Via Regia and Via Imperii, two important trade routes. At one time, Leipzig was one of the major European centres of learning and culture in fields such as music and publishing...
(L)
Economy
Saxony has, after Saxony Anhalt, the most vibrant economy among the federal states of the former GDR. Its economy grew by 1.9%% in 2010. Nonetheless, unemployment remains high, and investment is scarce. The eastern part of Germany, excluding BerlinBerlin
Berlin is the capital city of Germany and is one of the 16 states of Germany. With a population of 3.45 million people, Berlin is Germany's largest city. It is the second most populous city proper and the seventh most populous urban area in the European Union...
, qualifies as an "Objective 1" development region within the European Union
European Union
The European Union is an economic and political union of 27 independent member states which are located primarily in Europe. The EU traces its origins from the European Coal and Steel Community and the European Economic Community , formed by six countries in 1958...
, and is eligible to receive investment subsidies of up to 30% until 2013. FutureSAX
Futuresax
FutureSAX is the inner Saxony business plan competition of the Free State of Saxony in Germany that has an objective of lending support to start-up businesses and growing enterprises.-Business plan competition futureSAX:...
, a business plan competition and entrepreneurial support organization, has been in operation since 2002.
Microchip makers near Dresden have given the region a nickname of "Silicon Saxony". The publishing and porcelain industries of the region are well known, although their contributions to the regional economy are not significant.The state government is attempting to develop tourism, notably in the lake district of Lausitz
Lusatia
Lusatia is a historical region in Central Europe. It stretches from the Bóbr and Kwisa rivers in the east to the Elbe valley in the west, today located within the German states of Saxony and Brandenburg as well as in the Lower Silesian and Lubusz voivodeships of western Poland...
.
Saxony reported unemployment of 11.9% as average for 2010, by comparison the average for the former GDR was 12% and 7.7% for Germany overall.
History
Saxony has a long history as a duchyDuchy
A duchy is a territory, fief, or domain ruled by a duke or duchess.Some duchies were sovereign in areas that would become unified realms only during the Modern era . In contrast, others were subordinate districts of those kingdoms that unified either partially or completely during the Medieval era...
, an electorate
Prince-elector
The Prince-electors of the Holy Roman Empire were the members of the electoral college of the Holy Roman Empire, having the function of electing the Roman king or, from the middle of the 16th century onwards, directly the Holy Roman Emperor.The heir-apparent to a prince-elector was known as an...
of the Holy Roman Empire
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a realm that existed from 962 to 1806 in Central Europe.It was ruled by the Holy Roman Emperor. Its character changed during the Middle Ages and the Early Modern period, when the power of the emperor gradually weakened in favour of the princes...
(the Electorate of Saxony
Electorate of Saxony
The Electorate of Saxony , sometimes referred to as Upper Saxony, was a State of the Holy Roman Empire. It was established when Emperor Charles IV raised the Ascanian duchy of Saxe-Wittenberg to the status of an Electorate by the Golden Bull of 1356...
), and eventually as a kingdom
Monarchy
A monarchy is a form of government in which the office of head of state is usually held until death or abdication and is often hereditary and includes a royal house. In some cases, the monarch is elected...
(the Kingdom of Saxony
Kingdom of Saxony
The Kingdom of Saxony , lasting between 1806 and 1918, was an independent member of a number of historical confederacies in Napoleonic through post-Napoleonic Germany. From 1871 it was part of the German Empire. It became a Free state in the era of Weimar Republic in 1918 after the end of World War...
). In 1918, subsequent to Germany's defeat in World War I
World War I
World War I , which was predominantly called the World War or the Great War from its occurrence until 1939, and the First World War or World War I thereafter, was a major war centred in Europe that began on 28 July 1914 and lasted until 11 November 1918...
, its monarchy was overthrown and a republican form of government was established under its current name. The state was broken up into smaller units during communist rule (1949–1989), but was re-established on 3 October 1990 on the reunification of East and West Germany
West Germany
West Germany is the common English, but not official, name for the Federal Republic of Germany or FRG in the period between its creation in May 1949 to German reunification on 3 October 1990....
.
Prehistory
In prehistoric times, the territory of Saxony was the site of some of the largest of the ancient Central European monumental templesCircular ditches
About 150 arrangements of prehistoric circular ditches are known to archaeologists spread over Germany, Austria, Slovakia, and the Czech Republic. Their diameters range from ca. 20 to ca. 130 m, and they date to the 5th millennium BC. Tools, bones, and some artefacts were found in their context....
, dating from the 5th century BC. Notable archaeological sites have been discovered in Dresden
Dresden
Dresden is the capital city of the Free State of Saxony in Germany. It is situated in a valley on the River Elbe, near the Czech border. The Dresden conurbation is part of the Saxon Triangle metropolitan area....
and the villages of Eythra and Zwenkau
Zwenkau
Zwenkau is a city in the district of Leipzig, in the Free State of Saxony, Germany. Situated between the rivers Weiße Elster and Pleiße it unfolds to Leipzig lowlands and includes parts of the conservation area Elsteraue and Central Germany's Street of Lignite.- Geography :The city lies about...
near Leipzig
Leipzig
Leipzig Leipzig has always been a trade city, situated during the time of the Holy Roman Empire at the intersection of the Via Regia and Via Imperii, two important trade routes. At one time, Leipzig was one of the major European centres of learning and culture in fields such as music and publishing...
. The Slavic and Germanic
Germanic peoples
The Germanic peoples are an Indo-European ethno-linguistic group of Northern European origin, identified by their use of the Indo-European Germanic languages which diversified out of Proto-Germanic during the Pre-Roman Iron Age.Originating about 1800 BCE from the Corded Ware Culture on the North...
presence in the territory of today's Saxony is thought to have begun in the 1st century BC.
Parts of Saxony were possibly under the control of the Germanic King Marobod during the Roman era.
By the late Roman period, several tribes known as the Saxons emerged, from which the subsequent state(s) draw their name. For the origins of the Saxon tribes, see Saxons
Saxons
The Saxons were a confederation of Germanic tribes originating on the North German plain. The Saxons earliest known area of settlement is Northern Albingia, an area approximately that of modern Holstein...
.
Duchy of Saxony

Early Middle Ages
The Early Middle Ages was the period of European history lasting from the 5th century to approximately 1000. The Early Middle Ages followed the decline of the Western Roman Empire and preceded the High Middle Ages...
"Carolingian stem duchy
Stem duchy
Stem duchies were essentially the domains of the old German tribes of the area, associated with the Frankish Kingdom, especially the East, in the Early Middle Ages. These tribes were originally the Franks, the Saxons, the Alamanni, the Burgundians, the Thuringii, and the Rugii...
", which emerged about the year 700, and grew to cover the greater part of Northern Germany
Germany
Germany , officially the Federal Republic of Germany , is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km2 and has a largely temperate seasonal climate...
. It covered the area of the modern German states of Lower Saxony
Lower Saxony
Lower Saxony is a German state situated in north-western Germany and is second in area and fourth in population among the sixteen states of Germany...
, North Rhine-Westphalia
North Rhine-Westphalia
North Rhine-Westphalia is the most populous state of Germany, with four of the country's ten largest cities. The state was formed in 1946 as a merger of the northern Rhineland and Westphalia, both formerly part of Prussia. Its capital is Düsseldorf. The state is currently run by a coalition of the...
, Schleswig-Holstein
Schleswig-Holstein
Schleswig-Holstein is the northernmost of the sixteen states of Germany, comprising most of the historical duchy of Holstein and the southern part of the former Duchy of Schleswig...
and Saxony-Anhalt
Saxony-Anhalt
Saxony-Anhalt is a landlocked state of Germany. Its capital is Magdeburg and it is surrounded by the German states of Lower Saxony, Brandenburg, Saxony, and Thuringia.Saxony-Anhalt covers an area of...
. The Saxons converted to Christianity during this period.
While the Saxons were facing pressure from Charlemagne's Franks, they were also facing a westward push by Slavs to the east. The territory of the Free State of Saxony was occupied by Slavs before being reconquered by Germans. A legacy of this period is the Sorb
Sorbs
Sorbs are a Western Slavic people of Central Europe living predominantly in Lusatia, a region on the territory of Germany and Poland. In Germany they live in the states of Brandenburg and Saxony. They speak the Sorbian languages - closely related to Polish and Czech - officially recognized and...
population in Saxony.
Holy Roman Empire
The territory of the Free State of Saxony became part of the Holy Roman EmpireHoly Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a realm that existed from 962 to 1806 in Central Europe.It was ruled by the Holy Roman Emperor. Its character changed during the Middle Ages and the Early Modern period, when the power of the emperor gradually weakened in favour of the princes...
by the 10th century. In the 10th century, the dukes of Saxony were also kings (or emperors) of the Holy Roman Empire
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a realm that existed from 962 to 1806 in Central Europe.It was ruled by the Holy Roman Emperor. Its character changed during the Middle Ages and the Early Modern period, when the power of the emperor gradually weakened in favour of the princes...
, comprising the Ottonian, or Saxon, Dynasty. Around this time, the Billung
Billung
The House of Billung was a dynasty of Saxon noblemen in the 9th through 12th centuries.The first known member of the house was Count Wichmann, mentioned as a Billung in 811...
s, a Saxon
Saxons
The Saxons were a confederation of Germanic tribes originating on the North German plain. The Saxons earliest known area of settlement is Northern Albingia, an area approximately that of modern Holstein...
noble family, received extensive fiefs in Saxony. The Emperor eventually gave them the title of Duke of Saxony. After Duke Magnus
Magnus, Duke of Saxony
Magnus was the duke of Saxony from 1072 to 1106. Eldest son and successor of Ordulf and Wulfhild of Norway, he was the last member of the House of Billung.-Rebellion:...
died in 1106, causing the extinction of the male line of Billungs, oversight of the duchy was given to Lothar of Supplinburg
Lothair III, Holy Roman Emperor
Lothair III of Supplinburg , was Duke of Saxony , King of Germany , and Holy Roman Emperor from 1133 to 1137. The son of Count Gebhard of Supplinburg, his reign was troubled by the constant intriguing of Frederick I, Duke of Swabia and Duke Conrad of Franconia...
, who also became Emperor for a short time.
In 1137, control of Saxony passed to the Guelph dynasty, descendants of Wulfhild Billung, eldest daughter of the last Billung duke, and the daughter of Lothar of Supplinburg. In 1180 large portions west of the Weser were ceded to the Bishops of Cologne, while some central parts between the Weser and the Elbe remained to the Guelphs, later forming the Duchy of Brunswick-Lüneburg
Brunswick-Lüneburg
The Duchy of Brunswick-Lüneburg , or more properly Duchy of Brunswick and Lüneburg, was an historical ducal state from the late Middle Ages until the late Early Modern era within the North-Western domains of the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation, in what is now northern Germany...
). The remaining eastern lands, together with the title of Duke of Saxony, passed to an Ascanian dynasty (descended from Eilika Billung
Eilika of Saxony
Eilika of Saxony was the younger daughter of Magnus, Duke of Saxony and Sophia , daughter of Béla I of Hungary. After the death of her father, she became the heiress of Werben and Palatinate of Saxony. She was married Count Otto of Ballenstedt and was mother of Albrecht der Bär.-External links:*...
, Wulfhild's younger sister) and was divided in 1260 into the two small states of Saxe-Lauenburg and Saxe-Wittenberg
Saxe-Wittenberg
The Duchy of Saxe-Wittenberg was a medieval duchy of the Holy Roman Empire centered at Wittenberg, which emerged after the dissolution of the stem duchy of Saxony. As the precursor of the Saxon Electorate, the Ascanian Wittenberg dukes prevailed in obtaining the Saxon electoral dignity.-Ascanian...
, the former also named Lower Saxony
Lower Saxony
Lower Saxony is a German state situated in north-western Germany and is second in area and fourth in population among the sixteen states of Germany...
, the latter Upper Saxony
Upper Saxony
Upper Saxony was a name given to the majority of the German lands held by the House of Wettin, in what is now called Mitteldeutschland....
, thence the later names of the two Imperial Circle
Imperial Circle
An Imperial Circle comprised a regional grouping of territories of the Holy Roman Empire, primarily for the purpose of organizing a common defensive structure and of collecting the imperial taxes, but also as a means of organization within the Imperial Diet and the Imperial Chamber Court.Each...
s. Saxe-Lauenburg and Saxe-Wittenberg both claimed the Saxon electoral privilege
Prince-elector
The Prince-electors of the Holy Roman Empire were the members of the electoral college of the Holy Roman Empire, having the function of electing the Roman king or, from the middle of the 16th century onwards, directly the Holy Roman Emperor.The heir-apparent to a prince-elector was known as an...
for their part, but the Golden Bull of 1356
Golden Bull of 1356
The Golden Bull of 1356 was a decree issued by the Reichstag assembly in Nuremberg headed by the Luxembourg Emperor Charles IV that fixed, for a period of more than four hundred years, important aspects of the constitutional structure of the Holy Roman Empire...
only accepted Wittenberg's claim, with Lauenburg nevertheless maintaining its claim. In 1422, when the Saxon electoral line of the Ascanians was extinct, the Ascanian Eric V of Saxe-Lauenburg tried to reunite the Saxon duchies.
However, Sigismund
Sigismund, Holy Roman Emperor
Sigismund of Luxemburg KG was King of Hungary, of Croatia from 1387 to 1437, of Bohemia from 1419, and Holy Roman Emperor for four years from 1433 until 1437, the last Emperor of the House of Luxemburg. He was also King of Italy from 1431, and of Germany from 1411...
, King of the Romans
King of the Romans
King of the Romans was the title used by the ruler of the Holy Roman Empire following his election to the office by the princes of the Kingdom of Germany...
, had already granted Margrave Frederick IV the Warlike of Meissen (House of Wettin) an expectancy on the Saxon electorate, in order to remunerate his military support. On 1 August 1425 Sigismund enfeoffed the Wettinian Frederick as Prince-Elector of Saxony, despite protestations of Eric V. Thus the Saxon territories remained separated in permanence. Electoral Saxony was then merged in the much bigger Wettinian Margraviate of Meissen, however using the higher ranking name Electorate of Saxony and even the Ascanian coat-of-arms for the entire monarchy. Thus the name Saxony was translated to areas as far as Dresden
Dresden
Dresden is the capital city of the Free State of Saxony in Germany. It is situated in a valley on the River Elbe, near the Czech border. The Dresden conurbation is part of the Saxon Triangle metropolitan area....
and Meissen
Meissen
Meissen is a town of approximately 30,000 about northwest of Dresden on both banks of the Elbe river in the Free State of Saxony, in eastern Germany. Meissen is the home of Meissen porcelain, the Albrechtsburg castle, the Gothic Meissen Cathedral and the Meissen Frauenkirche...
. In the 18th and 19th centuries Saxe-Lauenburg became colloquially called the Duchy of Lauenburg, which in 1876 merged in Prussia
Kingdom of Prussia
The Kingdom of Prussia was a German kingdom from 1701 to 1918. Until the defeat of Germany in World War I, it comprised almost two-thirds of the area of the German Empire...
as Duchy of Lauenburg district.
Foundation of the second Saxon state


Saxony-Anhalt
Saxony-Anhalt is a landlocked state of Germany. Its capital is Magdeburg and it is surrounded by the German states of Lower Saxony, Brandenburg, Saxony, and Thuringia.Saxony-Anhalt covers an area of...
, became subject to the margravate
Margrave
A margrave or margravine was a medieval hereditary nobleman with military responsibilities in a border province of a kingdom. Border provinces usually had more exposure to military incursions from the outside, compared to interior provinces, and thus a margrave usually had larger and more active...
of Meissen
Meissen
Meissen is a town of approximately 30,000 about northwest of Dresden on both banks of the Elbe river in the Free State of Saxony, in eastern Germany. Meissen is the home of Meissen porcelain, the Albrechtsburg castle, the Gothic Meissen Cathedral and the Meissen Frauenkirche...
, ruled by the Wettin dynasty in 1423. This established a new and powerful state, occupying large portions of the present Free State of Saxony, Thuringia, and Saxony-Anhalt. Although the center of this state was far to the southeast of the former Saxony, it came to be referred to as Upper Saxony and then simply Saxony, while the former Saxon territories were now known as Lower Saxony.
In 1485, Saxony was split. A collateral line of the Wettin princes received what later became Thuringia
Thuringia
The Free State of Thuringia is a state of Germany, located in the central part of the country.It has an area of and 2.29 million inhabitants, making it the sixth smallest by area and the fifth smallest by population of Germany's sixteen states....
and founded several small states there (see Ernestine duchies
Ernestine duchies
The Ernestine duchies, also called the Saxon duchies , were a changing number of small states largely located in the present German state of Thuringia, governed by dukes of the Ernestine line of the House of Wettin.-Overview:The...
). The remaining Saxon state became still more powerful, becoming known in the 18th century for its cultural achievements, although it was politically inferior to Prussia
Prussia
Prussia was a German kingdom and historic state originating out of the Duchy of Prussia and the Margraviate of Brandenburg. For centuries, the House of Hohenzollern ruled Prussia, successfully expanding its size by way of an unusually well-organized and effective army. Prussia shaped the history...
and Austria
Austria
Austria , officially the Republic of Austria , is a landlocked country of roughly 8.4 million people in Central Europe. It is bordered by the Czech Republic and Germany to the north, Slovakia and Hungary to the east, Slovenia and Italy to the south, and Switzerland and Liechtenstein to the...
, which pressed Saxony from either side.
Between the years 1697 and 1763, the Electors of Saxony were also elected Kings of Poland in personal union
Personal union
A personal union is the combination by which two or more different states have the same monarch while their boundaries, their laws and their interests remain distinct. It should not be confused with a federation which is internationally considered a single state...
.
In 1756, Saxony joined the coalition of Austria, France and Russia against Prussia. Frederick II of Prussia
Frederick II of Prussia
Frederick II was a King in Prussia and a King of Prussia from the Hohenzollern dynasty. In his role as a prince-elector of the Holy Roman Empire, he was also Elector of Brandenburg. He was in personal union the sovereign prince of the Principality of Neuchâtel...
chose to attack preemptively and invaded Saxony in August 1756, precipitating the Seven Years War. The Prussians quickly defeated Saxony and incorporated the Saxon army into the Prussian army. At the end of the Seven Years War, Saxony once again became an independent state.
Saxony in the 19th and 20th centuries
In 1806, FrenchFrance
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
Emperor Napoleon
Napoleon I of France
Napoleon Bonaparte was a French military and political leader during the latter stages of the French Revolution.As Napoleon I, he was Emperor of the French from 1804 to 1815...
abolished the Holy Roman Empire
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a realm that existed from 962 to 1806 in Central Europe.It was ruled by the Holy Roman Emperor. Its character changed during the Middle Ages and the Early Modern period, when the power of the emperor gradually weakened in favour of the princes...
and decreed the Electorate of Saxony
Electorate of Saxony
The Electorate of Saxony , sometimes referred to as Upper Saxony, was a State of the Holy Roman Empire. It was established when Emperor Charles IV raised the Ascanian duchy of Saxe-Wittenberg to the status of an Electorate by the Golden Bull of 1356...
a kingdom in itself. Elector
Prince-elector
The Prince-electors of the Holy Roman Empire were the members of the electoral college of the Holy Roman Empire, having the function of electing the Roman king or, from the middle of the 16th century onwards, directly the Holy Roman Emperor.The heir-apparent to a prince-elector was known as an...
Frederick Augustus III became King Frederick Augustus I
Frederick Augustus I of Saxony
Frederick Augustus I was King of Saxony from the House of Wettin. He was also Elector Frederick Augustus III of Saxony and Duke Frederick Augustus I of Warsaw...
. Frederick Augustus remained loyal to Napoleon during the wars that swept Europe in the following years; he was taken prisoner and his territories declared forfeit by the allies in 1813, who intended the annexation of Saxony by Prussia. Ultimately, the opposition of Austria, France, and the United Kingdom
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
to this plan resulted in the restoration of Frederick Augustus to his throne at the Congress of Vienna
Congress of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna was a conference of ambassadors of European states chaired by Klemens Wenzel von Metternich, and held in Vienna from September, 1814 to June, 1815. The objective of the Congress was to settle the many issues arising from the French Revolutionary Wars, the Napoleonic Wars,...
. At this time in 1815, Saxony was forced to cede the northern part of the kingdom to Prussia. These lands became the Prussian province of Saxony
Province of Saxony
The Province of Saxony was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia and later the Free State of Prussia from 1816 until 1945. Its capital was Magdeburg.-History:The province was created in 1816 out of the following territories:...
, incorporated today in Saxony-Anhalt. The remnant of the Kingdom of Saxony
Kingdom of Saxony
The Kingdom of Saxony , lasting between 1806 and 1918, was an independent member of a number of historical confederacies in Napoleonic through post-Napoleonic Germany. From 1871 it was part of the German Empire. It became a Free state in the era of Weimar Republic in 1918 after the end of World War...
was roughly identical with the present federal state.
Meanwhile, in 1815, the southern part of Saxony, now called the "State of Saxony joined the German Confederation
German Confederation
The German Confederation was the loose association of Central European states created by the Congress of Vienna in 1815 to coordinate the economies of separate German-speaking countries. It acted as a buffer between the powerful states of Austria and Prussia...
. (The German Confederation should not be confused with the North German Confederation mentioned below.) In the politics of the Confederation, Saxony was overshadowed by Prussia. King Anthony of Saxony, came to the throne of Saxony in 1827. Shortly thereafter, liberal pressures in Saxony mounted and broke out in the revolt during 1830—a year of revolution in Europe. The revolution in Saxony resulted in a Constitution for the State of Saxony which served as a basis for the government in Saxony until 1918.
During the 1848–49 constitutionalist revolutions in Germany
Revolutions of 1848 in the German states
The Revolutions of 1848 in the German states, also called the March Revolution – part of the Revolutions of 1848 that broke out in many countries of Europe – were a series of loosely coordinated protests and rebellions in the states of the German Confederation, including the Austrian Empire...
, Saxony became a hotbed for revolutionaries, with anarchists such as Mikhail Bakunin
Mikhail Bakunin
Mikhail Alexandrovich Bakunin was a well-known Russian revolutionary and theorist of collectivist anarchism. He has also often been called the father of anarchist theory in general. Bakunin grew up near Moscow, where he moved to study philosophy and began to read the French Encyclopedists,...
and democrats including Richard Wagner
Richard Wagner
Wilhelm Richard Wagner was a German composer, conductor, theatre director, philosopher, music theorist, poet, essayist and writer primarily known for his operas...
and Gottfried Semper
Gottfried Semper
Gottfried Semper was a German architect, art critic, and professor of architecture, who designed and built the Semper Opera House in Dresden between 1838 and 1841. In 1849 he took part in the May Uprising in Dresden and was put on the government's wanted list. Semper fled first to Zürich and later...
taking part in the May Uprising in Dresden
May Uprising in Dresden
The May Uprising took place in Dresden, Germany in 1849; it was one of the last of the series of events known as the Revolutions of 1848.-Events leading to the May Uprising:...
in 1849. (Scenes of Richard Wagner's participation in the May 1849 Uprising in Dresden are pictured in the 1983 movie, Wagner starring Richard Burton as Richard Wagner.) The May Uprising in Dresden forced King Frederick Augustus II of Saxony
Frederick Augustus II of Saxony
Frederick Augustus II |Tyrol]], 9 August 1854) was King of Saxony and a member of the House of Wettin.He was the eldest son of Maximilian, Prince of Saxony --younger son of the Elector Frederick Christian of Saxony—by his...
to concede further reforms in the Saxon government.
In 1854 Frederick Augustus II's brother, King John of Saxony, succeeded to the throne. A scholar, King John translated Dante. King John followed a federalistic and pro-Austrian policy throughout the early 1860s until the outbreak of the Austro-Prussian War
Austro-Prussian War
The Austro-Prussian War was a war fought in 1866 between the German Confederation under the leadership of the Austrian Empire and its German allies on one side and the Kingdom of Prussia with its German allies and Italy on the...
. During the war, Prussian troops overran Saxony without a fight and invaded then Austrian (today's Czech) Bohemia
Bohemia
Bohemia is a historical region in central Europe, occupying the western two-thirds of the traditional Czech Lands. It is located in the contemporary Czech Republic with its capital in Prague...
. After the war, Saxony was forced to pay an indemnity and to join the North German Confederation
North German Confederation
The North German Confederation 1866–71, was a federation of 22 independent states of northern Germany. It was formed by a constitution accepted by the member states in 1867 and controlled military and foreign policy. It included the new Reichstag, a parliament elected by universal manhood...
in 1867. Under the terms of the North German Confederation, Prussia took over control of the Saxon postal system, railroads, military and foreign affairs. In the Franco-Prussian War
Franco-Prussian War
The Franco-Prussian War or Franco-German War, often referred to in France as the 1870 War was a conflict between the Second French Empire and the Kingdom of Prussia. Prussia was aided by the North German Confederation, of which it was a member, and the South German states of Baden, Württemberg and...
of 1870, Saxon troops fought together with Prussian and other German troops against France. In 1871, Saxony joined the newly formed German Empire
German Empire
The German Empire refers to Germany during the "Second Reich" period from the unification of Germany and proclamation of Wilhelm I as German Emperor on 18 January 1871, to 1918, when it became a federal republic after defeat in World War I and the abdication of the Emperor, Wilhelm II.The German...
.
After King Frederick Augustus III of Saxony
Frederick Augustus III of Saxony
This article is about King Frederick Augustus III of Saxony. For the elector Frederick Augustus III, see Frederick Augustus I of Saxony.Frederick Augustus III was the last King of Saxony and a member of the House of Wettin.Born in Dresden, Frederick Augustus was the son of King George of Saxony...
had abdicated on 13 November 1918, Saxony, remaining a constituent state of Germany (Weimar Republic
Weimar Republic
The Weimar Republic is the name given by historians to the parliamentary republic established in 1919 in Germany to replace the imperial form of government...
), became a republic renamed the Free State of Saxony following the new Saxon constitution of 1 November 1920. In 1923 Reichs's chancellor Gustav Stresemann
Gustav Stresemann
was a German politician and statesman who served as Chancellor and Foreign Minister during the Weimar Republic. He was co-laureate of the Nobel Peace Prize in 1926.Stresemann's politics defy easy categorization...
overthrew the SPD
Social Democratic Party of Germany
The Social Democratic Party of Germany is a social-democratic political party in Germany...
-led Saxon government. The state maintained its name and borders during the National Socialist era as a Gau, but lost any quasi-autonomous status and its parliamentarian democracy.
By the by end of World War II
World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
in April 1945, American troops under General George Patton conquered the western part of the Free State, while Soviet troops conquered the eastern part. That summer, the entire state was handed over to Soviet forces as agreed upon by the London Protocol of September 1944. Thereafter Britain, the USA, and the USSR negotiated at the Potsdam Conference
Potsdam Conference
The Potsdam Conference was held at Cecilienhof, the home of Crown Prince Wilhelm Hohenzollern, in Potsdam, occupied Germany, from 16 July to 2 August 1945. Participants were the Soviet Union, the United Kingdom, and the United States...
on Germany's future. By their trilateral Potsdam Agreement
Potsdam Agreement
The Potsdam Agreement was the Allied plan of tripartite military occupation and reconstruction of Germany—referring to the German Reich with its pre-war 1937 borders including the former eastern territories—and the entire European Theatre of War territory...
all German territory east of the Oder-Neisse line
Oder-Neisse line
The Oder–Neisse line is the border between Germany and Poland which was drawn in the aftermath of World War II. The line is formed primarily by the Oder and Lusatian Neisse rivers, and meets the Baltic Sea west of the seaport cities of Szczecin and Świnoujście...
was to be annexed by Poland and the Soviet Union and, unlike the post-World War I secessions of German territory, this time the annexing powers were allowed to expel the inhabitants.
Through all the following three years, Poland forcibly expelled German-speaking people from its annexed territory. Since the three powers of Potsdam had further agreed to accept in their occupation zones more expellees from other countries, the government in Prague denaturalised and expropriated around three million Czechoslovaks due to their German native language. So also Saxons had to feed and house the destitute expellees, while their retained belongings became war booty shared by the profiteers of this exproprietary attitude. Only a small Saxon area, lying east of the Neisse
Oder-Neisse line
The Oder–Neisse line is the border between Germany and Poland which was drawn in the aftermath of World War II. The line is formed primarily by the Oder and Lusatian Neisse rivers, and meets the Baltic Sea west of the seaport cities of Szczecin and Świnoujście...
river and centered around the town of Reichenau (now called Bogatynia
Bogatynia
Bogatynia is a town in Zgorzelec County, Lower Silesian Voivodeship, in south-western Poland, close to the tripoint of the Czech, German and Polish borders. The town lies approximately south of Zgorzelec, and west of the regional capital Wrocław. As of 2006 it had 19,068 inhabitants.The...
), was annexed by Poland. The Soviet Military Administration in Germany
Soviet Military Administration in Germany
The Soviet Military Administration in Germany was the Soviet military government, headquartered in Berlin-Karlshorst, that directly ruled the Soviet occupation zone of Germany from the German surrender in May 1945 until after the establishment of the German Democratic Republic in October...
(SVAG) merged that tiny part of the Prussian
Free State of Prussia (1918-1933)
The Free State of Prussia was a German state formed after the abolition of the Kingdom of Prussia in the aftermath of World War I. It was the major state of Germany during the time of the Weimar Republic, comprising almost 5/8 of its territory and population...
province of Lower Silesia
Province of Lower Silesia
The Province of Lower Silesia was a province of the Free State of Prussia from 1919 to 1945. Between 1938 and 1941 it was reunited with Upper Silesia as the Silesia Province. The capital of Lower Silesia was Breslau...
, which remained with Germany west of the Neisse, into Saxony.
On 20 October 1946, the SVAG organised elections for the Saxon state parliament (Landtag), which were unbalanced since many people were arbitrarily excluded from candidacy and suffrage and the Soviet support unilaterally preferring the communist Socialist Unity Party of Germany
Socialist Unity Party of Germany
The Socialist Unity Party of Germany was the governing party of the German Democratic Republic from its formation on 7 October 1949 until the elections of March 1990. The SED was a communist political party with a Marxist-Leninist ideology...
(SED). The new Saxon minister-president (governor) Rudolf Friedrichs (SED, until April 1946 SPD
Social Democratic Party of Germany
The Social Democratic Party of Germany is a social-democratic political party in Germany...
), who met with his Bavarian counterparts in the US zone of occupation in October 1946 and May 1947, suddenly died under unknown circumstances the month after. He was succeeded by Max Seydewitz
Max Seydewitz
Max Seydewitz was a German politician and Minister-President Saxony in East Germany)....
, a loyalist of Joseph Stalin
Joseph Stalin
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin was the Premier of the Soviet Union from 6 May 1941 to 5 March 1953. He was among the Bolshevik revolutionaries who brought about the October Revolution and had held the position of first General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union's Central Committee...
.
The Soviet Union set up the communist government of the German Democratic Republic in 1949, with Saxony a part of it, giving the USSR a satellite in the heart of Europe. The communist government officially dissolved the Free State in 1952, and divided it into the three smaller Bezirke of Leipzig
Leipzig (Bezirk)
The Bezirk Leipzig was a district of East Germany. The administrative seat and the main town was Leipzig.-History:The district was established, with the other 13, on July 25, 1952, substituting the old German states...
, Dresden
Dresden (Bezirk)
The Bezirk Dresden was a district of East Germany. The administrative seat and the main town was Dresden.-History:The district was established, with the other 13, on July 25, 1952, substituting the old German states...
, and Karl-Marx-Stadt
Karl-Marx-Stadt (Bezirk)
The Bezirk Karl-Marx-Stadt, also known as Bezirk Chemnitz, was a district of East Germany. The administrative seat and the main town was Karl-Marx-Stadt, renamed Chemnitz after the reunification of Germany.-History:...
. The Free State was reconstituted with slightly altered borders in 1990 upon German reunification
German reunification
German reunification was the process in 1990 in which the German Democratic Republic joined the Federal Republic of Germany , and when Berlin reunited into a single city, as provided by its then Grundgesetz constitution Article 23. The start of this process is commonly referred by Germans as die...
. Besides the formerly Silesian area of Saxony, which was mostly included in the territory of the new Saxon state, the free state gained further areas north of Leipzig
Leipzig
Leipzig Leipzig has always been a trade city, situated during the time of the Holy Roman Empire at the intersection of the Via Regia and Via Imperii, two important trade routes. At one time, Leipzig was one of the major European centres of learning and culture in fields such as music and publishing...
, which belonged to Saxony-Anhalt
Saxony-Anhalt
Saxony-Anhalt is a landlocked state of Germany. Its capital is Magdeburg and it is surrounded by the German states of Lower Saxony, Brandenburg, Saxony, and Thuringia.Saxony-Anhalt covers an area of...
until 1952.
Languages

Patois
Patois is any language that is considered nonstandard, although the term is not formally defined in linguistics. It can refer to pidgins, creoles, dialects, and other forms of native or local speech, but not commonly to jargon or slang, which are vocabulary-based forms of cant...
spoken in Saxony are combined in the group of "Thuringian and Upper Saxon dialects". Due to the incorrect usage of "Saxon dialects" in colloquial language, the Upper Saxon attribute has been added to distinguish it from Old Saxon
Old Saxon
Old Saxon, also known as Old Low German, is the earliest recorded form of Low German, documented from the 8th century until the 12th century, when it evolved into Middle Low German. It was spoken on the north-west coast of Germany and in the Netherlands by Saxon peoples...
and Low Saxon
Low German
Low German or Low Saxon is an Ingvaeonic West Germanic language spoken mainly in northern Germany and the eastern part of the Netherlands...
. Other German dialects spoken in Saxony are the dialects of the Erzgebirge (Ore Mountains), which have been affected by Upper Saxon dialects, and the dialects of the Vogtland, which are more affected by the East Franconian
East Franconian German
East Franconian is a dialect which is spoken in northern Bavaria and other areas in Germany around Nuremberg, Bamberg, Coburg, Würzburg, Hof, Bayreuth, Bad Mergentheim, Crailsheim and Suhl...
languages.
Upper Sorbian (a Slavic language
Slavic languages
The Slavic languages , a group of closely related languages of the Slavic peoples and a subgroup of Indo-European languages, have speakers in most of Eastern Europe, in much of the Balkans, in parts of Central Europe, and in the northern part of Asia.-Branches:Scholars traditionally divide Slavic...
) is still actively spoken in the parts of Upper Lusatia
Lusatia
Lusatia is a historical region in Central Europe. It stretches from the Bóbr and Kwisa rivers in the east to the Elbe valley in the west, today located within the German states of Saxony and Brandenburg as well as in the Lower Silesian and Lubusz voivodeships of western Poland...
that are occupied by the Sorbian
Sorbs
Sorbs are a Western Slavic people of Central Europe living predominantly in Lusatia, a region on the territory of Germany and Poland. In Germany they live in the states of Brandenburg and Saxony. They speak the Sorbian languages - closely related to Polish and Czech - officially recognized and...
minority. The Germans in Upper Lusatia speak distinct dialects of their own (Lusatian dialects).
Tourism
Except for DresdenDresden
Dresden is the capital city of the Free State of Saxony in Germany. It is situated in a valley on the River Elbe, near the Czech border. The Dresden conurbation is part of the Saxon Triangle metropolitan area....
and perhaps Leipzig
Leipzig
Leipzig Leipzig has always been a trade city, situated during the time of the Holy Roman Empire at the intersection of the Via Regia and Via Imperii, two important trade routes. At one time, Leipzig was one of the major European centres of learning and culture in fields such as music and publishing...
, Saxony is not known as a primary destination for foreign tourists. Areas along the border with the Czech Republic
Czech Republic
The Czech Republic is a landlocked country in Central Europe. The country is bordered by Poland to the northeast, Slovakia to the east, Austria to the south, and Germany to the west and northwest....
, such as the Lusatian Mountains
Lusatian Mountains
The Lusatian Mountains are a mountain range of the Western Sudetes, located on the southeastern border of Germany with the Czech Republic east of the Elbe river, a continuation of the Ore Mountains range west of the Elbe valley...
, Ore Mountains, Saxon Switzerland
Saxon Switzerland
Saxon Switzerland is a hilly climbing area and national park around the Elbe valley south-east of Dresden in Saxony, Germany. Together with the Bohemian Switzerland in the Czech Republic it forms the Elbe Sandstone Mountains....
, and Vogtland
Vogtland
The term Vogtland refers to a region reaching across the German free states of Bavaria, Saxony and Thuringia and into the Czech Republic . The name of the region contains a reference to the former leadership by the Vögte of Weida, Gera and Plauen, which translates approximately to advocates or lord...
, attract significant visitors, largely Germans. Saxony has well preserved historic towns such as Meissen
Meissen
Meissen is a town of approximately 30,000 about northwest of Dresden on both banks of the Elbe river in the Free State of Saxony, in eastern Germany. Meissen is the home of Meissen porcelain, the Albrechtsburg castle, the Gothic Meissen Cathedral and the Meissen Frauenkirche...
, Freiberg
Freiberg, Saxony
Freiberg is a city in the Free State of Saxony, Germany, administrative center of the Mittelsachsen district.-History:The city was founded in 1186, and has been a center of the mining industry in the Ore Mountains for centuries...
, Pirna
Pirna
Pirna is a town in the Free State of Saxony, Germany, capital of the administrative district Sächsische Schweiz-Osterzgebirge. The town's population is over 40,000. Pirna is located near Dresden and is an important district town as well as a Große Kreisstadt...
, Bautzen
Bautzen
Bautzen is a hill-top town in eastern Saxony, Germany, and administrative centre of the eponymous district. It is located on the Spree River. As of 2008, its population is 41,161...
, and Görlitz
Görlitz
Görlitz is a town in Germany. It is the easternmost town in the country, located on the Lusatian Neisse River in the Bundesland of Saxony. It is opposite the Polish town of Zgorzelec, which was a part of Görlitz until 1945. Historically, Görlitz was in the region of Upper Lusatia...
.

Politics
A minister-presidentMinister-President
A minister-president is the head of government in a number of European countries or subnational governments, in which a parliamentary or semi-presidential system of government prevails, who presides over the council of ministers...
heads the government of Saxony. Since May 28, 2008 the minister-president of Saxony is Stanislaw Tillich
Stanislaw Tillich
Stanislaw Tillich is a German CDU politician. He is the Minister-President of the Free State of Saxony...
. See: List of Ministers-President of Saxony, for a full listing.

