
Semi-syllabary
Encyclopedia
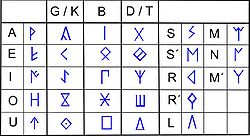
Writing system
A writing system is a symbolic system used to represent elements or statements expressible in language.-General properties:Writing systems are distinguished from other possible symbolic communication systems in that the reader must usually understand something of the associated spoken language to...
that behaves partly as an alphabet
Alphabet
An alphabet is a standard set of letters—basic written symbols or graphemes—each of which represents a phoneme in a spoken language, either as it exists now or as it was in the past. There are other systems, such as logographies, in which each character represents a word, morpheme, or semantic...
and partly as a syllabary
Syllabary
A syllabary is a set of written symbols that represent syllables, which make up words. In a syllabary, there is no systematic similarity between the symbols which represent syllables with the same consonant or vowel...
. The term has traditionally been extended to abugidas, but for the purposes of this article it will be restricted to scripts where some letters are alphabetic and others are syllabic.
Iberian semi-syllabaries
The Paleohispanic semi-syllabariesPaleohispanic scripts
The Paleohispanic scripts are the writing systems created in the Iberian peninsula before the Latin alphabet became the dominant script...
are a family of scripts developed in the Iberian Peninsula
Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula , sometimes called Iberia, is located in the extreme southwest of Europe and includes the modern-day sovereign states of Spain, Portugal and Andorra, as well as the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar...
at least from the 5th century BCE – possibly from the 7th century. Some researchers conclude that their origin lies solely with the Phoenician alphabet
Phoenician alphabet
The Phoenician alphabet, called by convention the Proto-Canaanite alphabet for inscriptions older than around 1050 BC, was a non-pictographic consonantal alphabet, or abjad. It was used for the writing of Phoenician, a Northern Semitic language, used by the civilization of Phoenicia...
, while others believe the Greek alphabet
Greek alphabet
The Greek alphabet is the script that has been used to write the Greek language since at least 730 BC . The alphabet in its classical and modern form consists of 24 letters ordered in sequence from alpha to omega...
also had a role. Paleohispanic semi-syllabaries
Paleohispanic scripts
The Paleohispanic scripts are the writing systems created in the Iberian peninsula before the Latin alphabet became the dominant script...
are typologically unusual because their syllabic and alphabetic components are equilibrated: they behave as a syllabary
Syllabary
A syllabary is a set of written symbols that represent syllables, which make up words. In a syllabary, there is no systematic similarity between the symbols which represent syllables with the same consonant or vowel...
for the stop consonant
Stop consonant
In phonetics, a plosive, also known as an occlusive or an oral stop, is a stop consonant in which the vocal tract is blocked so that all airflow ceases. The occlusion may be done with the tongue , lips , and &...
s and as an alphabet
Alphabet
An alphabet is a standard set of letters—basic written symbols or graphemes—each of which represents a phoneme in a spoken language, either as it exists now or as it was in the past. There are other systems, such as logographies, in which each character represents a word, morpheme, or semantic...
for other consonants and vowels. In the syllabic portions of the scripts, each stop-consonant sign stood for a different combination of consonant and vowel, so that the written form of ga displayed no resemblance to ge. In addition, the southern original format did not distinguish voicing
Voice (phonetics)
Voice or voicing is a term used in phonetics and phonology to characterize speech sounds, with sounds described as either voiceless or voiced. The term, however, is used to refer to two separate concepts. Voicing can refer to the articulatory process in which the vocal cords vibrate...
in these stops, so that ga stood for both /ga/ and /ka/, but one variant of the northeastern Iberian script
Northeastern Iberian script
The northeastern Iberian script is also known as Levantine Iberian or Iberian, because it is the Iberian script that was most frequently used, and was the main means of written expression of the Iberian language. The language is also expressed by the southeastern Iberian script and by the...
, the older one according the archaeological contexts, distinguished voicing
Voice (phonetics)
Voice or voicing is a term used in phonetics and phonology to characterize speech sounds, with sounds described as either voiceless or voiced. The term, however, is used to refer to two separate concepts. Voicing can refer to the articulatory process in which the vocal cords vibrate...
in the stop consonants by adding a stroke to the glyphs for the alveolar
Alveolar consonant
Alveolar consonants are articulated with the tongue against or close to the superior alveolar ridge, which is called that because it contains the alveoli of the superior teeth...
(/d/~/t/) and velar
Velar consonant
Velars are consonants articulated with the back part of the tongue against the soft palate, the back part of the roof of the mouth, known also as the velum)....
(/g/~/k/) syllables. The Tartessian or Southwestern script had a special behaviour: although the letter used to write a stop consonant was determined by the following vowel, the following vowel was also written. Some scholars treat Tartessian as a redundant semi-syllabary, others treat it as a redundant alphabet.
- Tartessian or Southwestern script – Tartessian or Southwestern languageTartessian languageThe Tartessian language is the extinct Paleohispanic language of inscriptions in the Southwestern script found in the southwest of the Iberian Peninsula: mainly in the south of Portugal , but also in Spain . There are 95 of these inscriptions with the longest having 82 readable signs...
- Southeastern Iberian scriptSoutheastern Iberian scriptThe southeastern Iberian script, also known as Meridional Iberian, was one of the means of written expression of the Iberian language, which was written mainly in the northeastern Iberian script and residually by the Greco-Iberian alphabet...
– Iberian languageIberian languageThe Iberian language was the language of a people identified by Greek and Roman sources who lived in the eastern and southeastern regions of the Iberian peninsula. The ancient Iberians can be identified as a rather nebulous local culture between the 7th and 1st century BC... - Northeastern Iberian scriptNortheastern Iberian scriptThe northeastern Iberian script is also known as Levantine Iberian or Iberian, because it is the Iberian script that was most frequently used, and was the main means of written expression of the Iberian language. The language is also expressed by the southeastern Iberian script and by the...
– Iberian languageIberian languageThe Iberian language was the language of a people identified by Greek and Roman sources who lived in the eastern and southeastern regions of the Iberian peninsula. The ancient Iberians can be identified as a rather nebulous local culture between the 7th and 1st century BC... - Celtiberian scriptCeltiberian scriptThe Celtiberian script is a paleohispanic script that was the main means of written expression of the Celtiberian language, an extinct Continental Celtic language, also expressed in Latin alphabet...
– Celtiberian languageCeltiberian languageCeltiberian is an extinct Indo-European language of the Celtic branch spoken by the Celtiberians in an area of the Iberian Peninsula lyingbetween the headwaters of the Duero, Tajo, Júcar and Turia rivers and the Ebro river...
Other semi-syllabaries
Other scripts combine attributes of alphabet and syllabary. One of these is zhuyin, a phonetic script devised for transcribing certain varieties of ChineseVarieties of Chinese
Chinese comprises many regional language varieties sometimes grouped together as the Chinese dialects, the primary ones being Mandarin, Wu, Cantonese, and Min. These are not mutually intelligible, and even many of the regional varieties are themselves composed of a number of...
. Zhuyin is not divided into consonants and vowels, but into onsets and rimes
Syllable rime
In the study of phonology in linguistics, the rime or rhyme of a syllable consists of a nucleus and an optional coda. It is the part of the syllable used in poetic rhyme, and the part that is lengthened or stressed when a person elongates or stresses a word in speech.The rime is usually the...
. Initial consonants and "medials" are alphabetic, but the nucleus and coda are combined as in syllabaries. That is, a syllable like kan is written k-an, and kwan is written k-w-an; the vowel is not written distinct from a final consonant. Pahawh Hmong
Pahawh Hmong
Pahawh Hmong is an indigenous semi-syllabic script, invented in 1959, to write the Hmong language.-Form:Pahawh is written left to right...
is somewhat similar, but the rime is written before the initial; there are two letters for each rime, depending on which tone diacritic is used; and the rime /āu/ and the initial /k/ are not written except in disambiguation.
Old Persian cuneiform was somewhat similar to the Tartessian script, in that some consonant letters were unique to a particular vowel, some were partially conflated, and some simple consonants, but all vowels were written regardless of whether or not they were redundant.
The modern Bamum script
Bamum script
The Bamum scripts are an evolutionary series of six scripts created for the Bamum language by King Njoya of Cameroon at the turn of the 20th century...
is essentially CV-syllabic, but doesn't have enough glyphs for all the CV syllables of the language. The rest are written by combining CV and V glyphs, making these effectively alphabetic.
Further reading
- Correa, José Antonio (2005): «Del alfabeto fenicio al semisilabario paleohispánico», Palaeohispanica 5, pp. 137–154.
- Ferrer i Jané, Joan (2005): «Novetats sobre el sistema dual de diferenciació gràfica de les oclusives sordes i sonores», Palaeohispanica 5, pp. 957–982.
- Rodríguez Ramos, Jesús (2000): «La lectura de las inscripciones sudlusitano-tartesias», Faventia 22/1, pp. 21–48.

