
Southeastern Iberian script
Encyclopedia
.jpg)
.jpg)
Iberian language
The Iberian language was the language of a people identified by Greek and Roman sources who lived in the eastern and southeastern regions of the Iberian peninsula. The ancient Iberians can be identified as a rather nebulous local culture between the 7th and 1st century BC...
, which was written mainly in the northeastern Iberian script
Northeastern Iberian script
The northeastern Iberian script is also known as Levantine Iberian or Iberian, because it is the Iberian script that was most frequently used, and was the main means of written expression of the Iberian language. The language is also expressed by the southeastern Iberian script and by the...
and residually by the Greco-Iberian alphabet
Greco-Iberian alphabet
The Greco-Iberian alphabet is a direct adaptation of an Ionic variant of a Greek alphabet to the specifics of the Iberian language, thus this script is an alphabet and lacks the distinctive characteristic of the rest of paleohispanic scripts that present signs with syllabic value, for the...
. About the relation between northeastern Iberian and southeastern Iberian scripts, it is necessary to point out that they are two different scripts with different values for the same signs; however it is clear that they had a common origin and the most accepted hypothesis is that northeastern Iberian script derives from southeastern Iberian script. In fact, the southeastern Iberian script is very similar, both considering the shape of the signs or their values, to the Southwestern script
Southwest script
The Southwest Script or Southwestern Script, also known as Tartessian or South Lusitanian, is a Paleohispanic script used to write an unknown language usually identified as Tartessian...
used to represent an unknown language usually named Tartessian
Tartessian
Tertessian may refer to:*an ancient civilization based in Tartessos in modern-day Andalusia*the Tartessian language*the Tartessian script...
. The main difference is that southeastern Iberian script doesn’t show the vocalic redundancy of the syllabic signs. Unlike the northeastern Iberian script
Northeastern Iberian script
The northeastern Iberian script is also known as Levantine Iberian or Iberian, because it is the Iberian script that was most frequently used, and was the main means of written expression of the Iberian language. The language is also expressed by the southeastern Iberian script and by the...
the decipherment of the southeastern Iberian script is not yet complete, because there are a significant number of signs on which scholars have not yet reached a consensus. Despite it is believed that unlike the northeastern Iberian script
Northeastern Iberian script
The northeastern Iberian script is also known as Levantine Iberian or Iberian, because it is the Iberian script that was most frequently used, and was the main means of written expression of the Iberian language. The language is also expressed by the southeastern Iberian script and by the...
the southeastern Iberian script doesn’t show any system to differentiate between voiced
Voice (phonetics)
Voice or voicing is a term used in phonetics and phonology to characterize speech sounds, with sounds described as either voiceless or voiced. The term, however, is used to refer to two separate concepts. Voicing can refer to the articulatory process in which the vocal cords vibrate...
and unvoiced occlusives, a recent paper (Ferrer i Jané 2010) defends the existence of a dual system also in the southeastern Iberian script.
All the paleohispanic scripts
Paleohispanic scripts
The Paleohispanic scripts are the writing systems created in the Iberian peninsula before the Latin alphabet became the dominant script...
, with the exception of the Greco-Iberian alphabet
Greco-Iberian alphabet
The Greco-Iberian alphabet is a direct adaptation of an Ionic variant of a Greek alphabet to the specifics of the Iberian language, thus this script is an alphabet and lacks the distinctive characteristic of the rest of paleohispanic scripts that present signs with syllabic value, for the...
, share a common distinctive typological characteristic: they represent syllabic value for the occlusives, and monophonemic value for the rest of the consonants and vowels. From the writing systems point of view they are neither alphabets nor syllabaries; rather, they are mixed scripts that normally are identified as semi-syllabaries. There is no agreement about how the paleohispanic semi-syllabaries
Paleohispanic scripts
The Paleohispanic scripts are the writing systems created in the Iberian peninsula before the Latin alphabet became the dominant script...
originated; some researchers conclude that their origin is linked only to the Phoenician alphabet
Phoenician alphabet
The Phoenician alphabet, called by convention the Proto-Canaanite alphabet for inscriptions older than around 1050 BC, was a non-pictographic consonantal alphabet, or abjad. It was used for the writing of Phoenician, a Northern Semitic language, used by the civilization of Phoenicia...
, while others believe the Greek alphabet
Greek alphabet
The Greek alphabet is the script that has been used to write the Greek language since at least 730 BC . The alphabet in its classical and modern form consists of 24 letters ordered in sequence from alpha to omega...
exercised some influence.
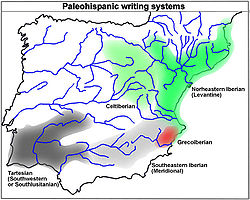
The inscriptions that use the southeastern Iberian script had been found mainly in the southeastern quadrant of the Iberian Peninsula
Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula , sometimes called Iberia, is located in the extreme southwest of Europe and includes the modern-day sovereign states of Spain, Portugal and Andorra, as well as the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar...
: eastern Andalusia
Andalusia
Andalusia is the most populous and the second largest in area of the autonomous communities of Spain. The Andalusian autonomous community is officially recognised as a nationality of Spain. The territory is divided into eight provinces: Huelva, Seville, Cádiz, Córdoba, Málaga, Jaén, Granada and...
, Murcia
Murcia
-History:It is widely believed that Murcia's name is derived from the Latin words of Myrtea or Murtea, meaning land of Myrtle , although it may also be a derivation of the word Murtia, which would mean Murtius Village...
, Albacete
Albacete
Albacete is a city and municipality in southeastern Spain, 258 km southeast of Madrid, the capital of the province of Albacete in the autonomous community of Castile-La Mancha. The municipality had a population of c. 169,700 in 2009....
, Alicante
Alicante
Alicante or Alacant is a city in Spain, the capital of the province of Alicante and of the comarca of Alacantí, in the south of the Valencian Community. It is also a historic Mediterranean port. The population of the city of Alicante proper was 334,418, estimated , ranking as the second-largest...
, and Valencia. The southeastern Iberian inscriptions were made on different object types (silver
Silver
Silver is a metallic chemical element with the chemical symbol Ag and atomic number 47. A soft, white, lustrous transition metal, it has the highest electrical conductivity of any element and the highest thermal conductivity of any metal...
and bronze
Bronze
Bronze is a metal alloy consisting primarily of copper, usually with tin as the main additive. It is hard and brittle, and it was particularly significant in antiquity, so much so that the Bronze Age was named after the metal...
coins
COinS
ContextObjects in Spans, commonly abbreviated COinS, is a method to embed bibliographic metadata in the HTML code of web pages. This allows bibliographic software to publish machine-readable bibliographic items and client reference management software to retrieve bibliographic metadata. The...
, silver and ceramic
Ceramic
A ceramic is an inorganic, nonmetallic solid prepared by the action of heat and subsequent cooling. Ceramic materials may have a crystalline or partly crystalline structure, or may be amorphous...
recipients, lead
Lead
Lead is a main-group element in the carbon group with the symbol Pb and atomic number 82. Lead is a soft, malleable poor metal. It is also counted as one of the heavy metals. Metallic lead has a bluish-white color after being freshly cut, but it soon tarnishes to a dull grayish color when exposed...
plaques, stones, etc.), but they number around 50 and represent more or less only 2% of the total found. Between them there are the lead plaque from Gador (Almeria
Almería
Almería is a city in Andalusia, Spain, on the Mediterranean Sea. It is the capital of the province of the same name.-Toponym:Tradition says that the name Almería stems from the Arabic المرية Al-Mariyya: "The Mirror", comparing it to "The Mirror of the Sea"...
) and the lead plaque from La Bastida de les Alcuses (Moixent, València
Valencia
-In Spain:* Valencia , Spain, capital of the Valencia Autonomous Community* Valencian Community, an autonomous community of Spain**Valencian people, an ethnic group or nationality whose homeland is the Valencian Community...
). The inscriptions that use this script almost always use the right to left direction of writing. The oldest inscriptions in southeastern Iberian script date to the 4th century BCE, and the modern ones date from the end of the 2nd century BCE.

