
Northeastern Iberian script
Encyclopedia

Iberian language
The Iberian language was the language of a people identified by Greek and Roman sources who lived in the eastern and southeastern regions of the Iberian peninsula. The ancient Iberians can be identified as a rather nebulous local culture between the 7th and 1st century BC...
. The language is also expressed by the southeastern Iberian script
Southeastern Iberian script
The southeastern Iberian script, also known as Meridional Iberian, was one of the means of written expression of the Iberian language, which was written mainly in the northeastern Iberian script and residually by the Greco-Iberian alphabet...
and by the Greco-Iberian alphabet
Greco-Iberian alphabet
The Greco-Iberian alphabet is a direct adaptation of an Ionic variant of a Greek alphabet to the specifics of the Iberian language, thus this script is an alphabet and lacks the distinctive characteristic of the rest of paleohispanic scripts that present signs with syllabic value, for the...
. To understand the relationship between northeastern Iberian and southeastern Iberian scripts, it is necessary to point out that they are two different scripts with different values for the same signs. However it is clear they have a common origin and the most accepted hypothesis is that northeastern Iberian script was derived from the southeastern Iberian script
Southeastern Iberian script
The southeastern Iberian script, also known as Meridional Iberian, was one of the means of written expression of the Iberian language, which was written mainly in the northeastern Iberian script and residually by the Greco-Iberian alphabet...
. There is no agreement on this, but some researchers conclude that it is linked to the Phoenician alphabet
Phoenician alphabet
The Phoenician alphabet, called by convention the Proto-Canaanite alphabet for inscriptions older than around 1050 BC, was a non-pictographic consonantal alphabet, or abjad. It was used for the writing of Phoenician, a Northern Semitic language, used by the civilization of Phoenicia...
alone, whilst others believe the Greek alphabet
Greek alphabet
The Greek alphabet is the script that has been used to write the Greek language since at least 730 BC . The alphabet in its classical and modern form consists of 24 letters ordered in sequence from alpha to omega...
also had a role.
All the paleohispanic scripts
Paleohispanic scripts
The Paleohispanic scripts are the writing systems created in the Iberian peninsula before the Latin alphabet became the dominant script...
, with the exception of the Greco-Iberian alphabet
Greco-Iberian alphabet
The Greco-Iberian alphabet is a direct adaptation of an Ionic variant of a Greek alphabet to the specifics of the Iberian language, thus this script is an alphabet and lacks the distinctive characteristic of the rest of paleohispanic scripts that present signs with syllabic value, for the...
, share a common distinctive typological characteristic: they represent syllabic value for the occlusives, and monophonemic value for the rest of the consonants and vowels. In a writing system
Writing system
A writing system is a symbolic system used to represent elements or statements expressible in language.-General properties:Writing systems are distinguished from other possible symbolic communication systems in that the reader must usually understand something of the associated spoken language to...
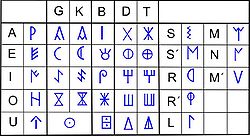
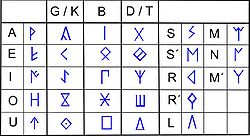
they are neither alphabets nor syllabaries, but are rather mixed scripts that are normally identified as semi-syllabaries. The basic signary contains 28 signs
Signs
Signs is the plural of sign. See sign .Signs may also refer to:*Signs , a 2002 film by M. Night Shyamalan*Signs , a journal of women's studies...
: 5 vowels, 15 syllabic and 8 consonantic (one lateral
Lateral consonant
A lateral is an el-like consonant, in which airstream proceeds along the sides of the tongue, but is blocked by the tongue from going through the middle of the mouth....
, two sibilants, two rhotic
Rhotic consonant
In phonetics, rhotic consonants, also called tremulants or "R-like" sounds, are liquid consonants that are traditionally represented orthographically by symbols derived from the Greek letter rho, including "R, r" from the Roman alphabet and "Р, p" from the Cyrillic alphabet...
and three nasals
Nasal consonant
A nasal consonant is a type of consonant produced with a lowered velum in the mouth, allowing air to escape freely through the nose. Examples of nasal consonants in English are and , in words such as nose and mouth.- Definition :...
). The northeastern script was very nearly deciphered in 1922 by Manuel Gómez-Moreno Martínez, who systematically linked the syllabic
Syllabic
Syllabic may refer to:*Canadian Aboriginal syllabics, a family of abugidas used to write a number of Aboriginal Canadian languages.*Syllabary, writing system using symbols for syllables...
signs with the occlusive values. The decipherment was based on the existence of a large number of coin
Coin
A coin is a piece of hard material that is standardized in weight, is produced in large quantities in order to facilitate trade, and primarily can be used as a legal tender token for commerce in the designated country, region, or territory....
legends (some of them bearing Latin
Latin
Latin is an Italic language originally spoken in Latium and Ancient Rome. It, along with most European languages, is a descendant of the ancient Proto-Indo-European language. Although it is considered a dead language, a number of scholars and members of the Christian clergy speak it fluently, and...
inscriptions) that could easily be linked to ancient place names known from Roman
Ancient Rome
Ancient Rome was a thriving civilization that grew on the Italian Peninsula as early as the 8th century BC. Located along the Mediterranean Sea and centered on the city of Rome, it expanded to one of the largest empires in the ancient world....
and Greek
Ancient Greece
Ancient Greece is a civilization belonging to a period of Greek history that lasted from the Archaic period of the 8th to 6th centuries BC to the end of antiquity. Immediately following this period was the beginning of the Early Middle Ages and the Byzantine era. Included in Ancient Greece is the...
sources. There are two variants of the northeastern Iberian script: the dual variant is almost exclusive to the ancient inscriptions from the 4th and 3rd centuries BCE and its distinctive characteristic is the use of the dual system. This system was discovered by Joan Maluquer de Motes in 1968 and allows differentiation of the occlusive signs (dentals and velars) between voiced
Voice (phonetics)
Voice or voicing is a term used in phonetics and phonology to characterize speech sounds, with sounds described as either voiceless or voiced. The term, however, is used to refer to two separate concepts. Voicing can refer to the articulatory process in which the vocal cords vibrate...
and unvoiced by the use of an additional stroke. The simple sign represents the voiced value whilst the complex sign represents the unvoiced value. The non-dual variant is almost exclusive of the modern inscriptions from the 2nd and 1st centuries BCE.
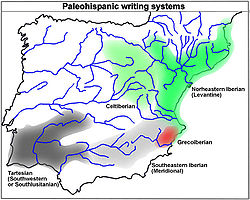
The inscriptions that use the northeastern Iberian script have been found mainly in the northeastern quadrant of the Iberian Peninsula
Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula , sometimes called Iberia, is located in the extreme southwest of Europe and includes the modern-day sovereign states of Spain, Portugal and Andorra, as well as the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar...
: largely along the coast from Languedoc-Roussillon
Languedoc-Roussillon
Languedoc-Roussillon is one of the 27 regions of France. It comprises five departments, and borders the other French regions of Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur, Rhône-Alpes, Auvergne, Midi-Pyrénées on the one side, and Spain, Andorra and the Mediterranean sea on the other side.-Geography:The region is...
to Alicante
Alicante
Alicante or Alacant is a city in Spain, the capital of the province of Alicante and of the comarca of Alacantí, in the south of the Valencian Community. It is also a historic Mediterranean port. The population of the city of Alicante proper was 334,418, estimated , ranking as the second-largest...
, but also with a deep penetration in the Ebre Valley. The northeastern Iberian inscriptions have been found on different object types (silver
Silver
Silver is a metallic chemical element with the chemical symbol Ag and atomic number 47. A soft, white, lustrous transition metal, it has the highest electrical conductivity of any element and the highest thermal conductivity of any metal...
and bronze
Bronze
Bronze is a metal alloy consisting primarily of copper, usually with tin as the main additive. It is hard and brittle, and it was particularly significant in antiquity, so much so that the Bronze Age was named after the metal...
coins
COinS
ContextObjects in Spans, commonly abbreviated COinS, is a method to embed bibliographic metadata in the HTML code of web pages. This allows bibliographic software to publish machine-readable bibliographic items and client reference management software to retrieve bibliographic metadata. The...
, silver and ceramic
Ceramic
A ceramic is an inorganic, nonmetallic solid prepared by the action of heat and subsequent cooling. Ceramic materials may have a crystalline or partly crystalline structure, or may be amorphous...
recipients, lead
Lead
Lead is a main-group element in the carbon group with the symbol Pb and atomic number 82. Lead is a soft, malleable poor metal. It is also counted as one of the heavy metals. Metallic lead has a bluish-white color after being freshly cut, but it soon tarnishes to a dull grayish color when exposed...
plaques, mosaics, amphores
Amphora
An amphora is a type of vase-shaped, usually ceramic container with two handles and a long neck narrower than the body...
, stones (stele
Stele
A stele , also stela , is a stone or wooden slab, generally taller than it is wide, erected for funerals or commemorative purposes, most usually decorated with the names and titles of the deceased or living — inscribed, carved in relief , or painted onto the slab...
s), spindle
Spindle (textiles)
A spindle is a wooden spike used for spinning wool, flax, hemp, cotton, and other fibres into thread. It is commonly weighted at either the bottom middle or top, most commonly by a circular or spherical object called a whorl, and may also have a hook, groove or notch, though spindles without...
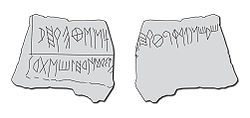
-whorls etc.), representing 95% of the total finds (over 2000 items), and nearly all the scripts were written from left to right. The oldest northeastern Iberian script date to the 4th or maybe the 5th century BCE. The modern ones date from the end of the 1st century BCE or maybe the beginning of the 1st century CE.

