
States of the German Confederation
Encyclopedia
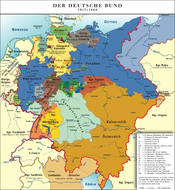
German Confederation
The German Confederation was the loose association of Central European states created by the Congress of Vienna in 1815 to coordinate the economies of separate German-speaking countries. It acted as a buffer between the powerful states of Austria and Prussia...
, which lasted, with some changes in the member states, until August 24, 1866, under the presidency of the Austrian imperial House of Habsburg, which was represented by an Austrian presidential envoy to the Federal diet
Diet (assembly)
In politics, a diet is a formal deliberative assembly. The term is mainly used historically for the Imperial Diet, the general assembly of the Imperial Estates of the Holy Roman Empire, and for the legislative bodies of certain countries.-Etymology:...
in Frankfurt
Free City of Frankfurt
For almost five centuries, the German city of Frankfurt am Main was a city-state within two major Germanic states:*The Holy Roman Empire as the Free Imperial City of Frankfurt...
.
Explanation
On the whole, its territory nearly coincided with that remaining in the Holy Roman EmpireHoly Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a realm that existed from 962 to 1806 in Central Europe.It was ruled by the Holy Roman Emperor. Its character changed during the Middle Ages and the Early Modern period, when the power of the emperor gradually weakened in favour of the princes...
at the outbreak of the French Revolution
French Revolution
The French Revolution , sometimes distinguished as the 'Great French Revolution' , was a period of radical social and political upheaval in France and Europe. The absolute monarchy that had ruled France for centuries collapsed in three years...
, with the notable exception of Belgium. Except for the two rival major powers, Habsburg
Habsburg Monarchy
The Habsburg Monarchy covered the territories ruled by the junior Austrian branch of the House of Habsburg , and then by the successor House of Habsburg-Lorraine , between 1526 and 1867/1918. The Imperial capital was Vienna, except from 1583 to 1611, when it was moved to Prague...
and Prussia
Kingdom of Prussia
The Kingdom of Prussia was a German kingdom from 1701 to 1918. Until the defeat of Germany in World War I, it comprised almost two-thirds of the area of the German Empire...
, and the western left bank of the Rhine (which France had annexed, with tiny Katzenelnbogen
County of Katzenelnbogen
The County of Katzenelnbogen was an immediate state of the Holy Roman Empire. It existed between 1095 and 1479, when it was inherited by the Landgraves of Hesse.The estate comprised two separate territories...
), the other member states or their precursors, making up most of present Germany
Germany
Germany , officially the Federal Republic of Germany , is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km2 and has a largely temperate seasonal climate...
, had been within Napoleon's Confederation of the Rhine
Confederation of the Rhine
The Confederation of the Rhine was a confederation of client states of the First French Empire. It was formed initially from 16 German states by Napoleon after he defeated Austria's Francis II and Russia's Alexander I in the Battle of Austerlitz. The Treaty of Pressburg, in effect, led to the...
.
- The Austrian EmpireAustrian EmpireThe Austrian Empire was a modern era successor empire, which was centered on what is today's Austria and which officially lasted from 1804 to 1867. It was followed by the Empire of Austria-Hungary, whose proclamation was a diplomatic move that elevated Hungary's status within the Austrian Empire...
, excluding the Kingdom of HungaryKingdom of HungaryThe Kingdom of Hungary comprised present-day Hungary, Slovakia and Croatia , Transylvania , Carpatho Ruthenia , Vojvodina , Burgenland , and other smaller territories surrounding present-day Hungary's borders...
, the Principality of TransylvaniaPrincipality of Transylvania (1711–1867)The Principality of Transylvania or Grand Principality of Transylvania was a province of the Habsburg Monarchy and Austrian Empire.-History:...
, and CroatiaKingdom of Croatia (Habsburg)The Kingdom of Croatia was an administrative division that existed between 1527 and 1868 within the Habsburg Monarchy . The Kingdom was a part of the Lands of the Crown of St. Stephen, but was subject to direct Imperial Austrian rule for significant periods of time, including its final years...
(all of which became parts of the apostolic kingdom of Hungary within the Danubian Dual MonarchyAustria-HungaryAustria-Hungary , more formally known as the Kingdoms and Lands Represented in the Imperial Council and the Lands of the Holy Hungarian Crown of Saint Stephen, was a constitutional monarchic union between the crowns of the Austrian Empire and the Kingdom of Hungary in...
), the Kingdom of Lombardy-Venetia (constituting parts lost to Italy in 1859- viz. 1866), Bukovina, the kingdoms of DalmatiaKingdom of DalmatiaThe Kingdom of Dalmatia was an administrative division of the Habsburg Monarchy from 1815 to 1918. Its capital was Zadar.-History:...
and GaliciaKingdom of Galicia and LodomeriaThe Kingdom of Galicia and Lodomeria was a crownland of the Habsburg Monarchy, the Austrian Empire, and Austria–Hungary from 1772 to 1918 .This historical region in eastern Central Europe is currently divided between Poland and Ukraine...
- Kingdom of BohemiaKingdom of BohemiaThe Kingdom of Bohemia was a country located in the region of Bohemia in Central Europe, most of whose territory is currently located in the modern-day Czech Republic. The King was Elector of Holy Roman Empire until its dissolution in 1806, whereupon it became part of the Austrian Empire, and...
- Archduchy of AustriaArchduchy of AustriaThe Archduchy of Austria , one of the most important states within the Holy Roman Empire, was the nucleus of the Habsburg Monarchy and the predecessor of the Austrian Empire...
(split into Upper AustriaUpper AustriaUpper Austria is one of the nine states or Bundesländer of Austria. Its capital is Linz. Upper Austria borders on Germany and the Czech Republic, as well as on the other Austrian states of Lower Austria, Styria, and Salzburg...
and Lower AustriaLower AustriaLower Austria is the northeasternmost state of the nine states in Austria. The capital of Lower Austria since 1986 is Sankt Pölten, the most recently designated capital town in Austria. The capital of Lower Austria had formerly been Vienna, even though Vienna is not officially part of Lower Austria...
in 1849) - Margraviate of Moravia
- Grand Duchy of Salzburg
- Duchy of CarinthiaDuchy of CarinthiaThe Duchy of Carinthia was a duchy located in southern Austria and parts of northern Slovenia. It was separated from the Duchy of Bavaria in 976, then the first newly created Imperial State beside the original German stem duchies....
- Duchy of CarniolaDuchy of CarniolaThe Duchy of Carniola was an administrative unit of the Holy Roman Empire and the Habsburg Monarchy from 1364 to 1918. Its capital was Ljubljana...
- Duchy of Upper and Lower Silesia
- Duchy of StyriaDuchy of StyriaThe history of Styria concerns the region roughly corresponding to the modern Austrian state of Styria and the Slovene region of Styria from its settlement by Germans and Slavs in the Dark Ages until the present...
- LittoralAustrian LittoralThe Austrian Littoral was established as a crown land of the Austrian Empire in 1849. In 1861 it was divided into the three crown lands of the Imperial Free City of Trieste and its suburbs, the Margraviate of Istria, and the Princely County of Gorizia and Gradisca, which each had separate...
(consisting of Gorizia and GradiscaGorizia and GradiscaThe County of Gorizia and Gradisca was a Habsburg county in Central Europe, in what is now a multilingual border area of Italy and Slovenia. It was named for its two major urban centers, Gorizia and Gradisca d'Isonzo.-Province of the Habsburg Empire:...
, IstriaIstriaIstria , formerly Histria , is the largest peninsula in the Adriatic Sea. The peninsula is located at the head of the Adriatic between the Gulf of Trieste and the Bay of Kvarner...
and TriesteTriesteTrieste is a city and seaport in northeastern Italy. It is situated towards the end of a narrow strip of land lying between the Adriatic Sea and Italy's border with Slovenia, which lies almost immediately south and east of the city...
) - County of TyrolCounty of TyrolThe County of Tyrol, Princely County from 1504, was a State of the Holy Roman Empire, from 1814 a province of the Austrian Empire and from 1867 a Cisleithanian crown land of Austria-Hungary...
- VorarlbergVorarlbergVorarlberg is the westernmost federal-state of Austria. Although it is the second smallest in terms of area and population , it borders three countries: Germany , Switzerland and Liechtenstein...
- Kingdom of Bohemia
- The Kingdom of PrussiaKingdom of PrussiaThe Kingdom of Prussia was a German kingdom from 1701 to 1918. Until the defeat of Germany in World War I, it comprised almost two-thirds of the area of the German Empire...
(without Posen, East PrussiaProvince of East PrussiaThe Province of East Prussia was a province of Prussia from 1773–1829 and 1878-1945. Composed of the historical region East Prussia, the province's capital was Königsberg ....
and West Prussia)- BrandenburgProvince of BrandenburgThe Province of Brandenburg was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia and the Free State of Prussia from 1815 to 1946.-History:The first people who are known to have inhabited Brandenburg were the Suevi. They were succeeded by the Slavonians, whom Henry II conquered and converted to Christianity in...
- Pomerania
- Rhine ProvinceRhine ProvinceThe Rhine Province , also known as Rhenish Prussia or synonymous to the Rhineland , was the westernmost province of the Kingdom of Prussia and the Free State of Prussia, within the German Reich, from 1822-1946. It was created from the provinces of the Lower Rhine and Jülich-Cleves-Berg...
(until 1822, Lower RhineGrand Duchy of the Lower RhineThe Grand Duchy of the Lower Rhine , or simply known as the Lower Rhine Province was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia and existed from 1815 to 1822....
and Jülich-Cleves-BergProvince of Jülich-Cleves-BergThe Province of Jülich-Cleves-Berg was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1815–22. The province was largely made up of the land held by the former United Duchies of Jülich-Cleves-Berg...
) - SaxonyProvince of SaxonyThe Province of Saxony was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia and later the Free State of Prussia from 1816 until 1945. Its capital was Magdeburg.-History:The province was created in 1816 out of the following territories:...
- SilesiaProvince of SilesiaThe Province of Silesia was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1815 to 1919.-Geography:The territory comprised the bulk of the former Bohemian crown land of Silesia and the County of Kladsko, which King Frederick the Great had conquered from the Austrian Habsburg Monarchy in the 18th...
- WestphaliaProvince of WestphaliaThe Province of Westphalia was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia and the Free State of Prussia from 1815 to 1946.-History:Napoleon Bonaparte founded the Kingdom of Westphalia, which was a client state of the First French Empire from 1807 to 1813...
- Brandenburg
- The Kingdom of BavariaKingdom of BavariaThe Kingdom of Bavaria was a German state that existed from 1806 to 1918. The Bavarian Elector Maximilian IV Joseph of the House of Wittelsbach became the first King of Bavaria in 1806 as Maximilian I Joseph. The monarchy would remain held by the Wittelsbachs until the kingdom's dissolution in 1918...
(the third largest member) - The Kingdom of SaxonyKingdom of SaxonyThe Kingdom of Saxony , lasting between 1806 and 1918, was an independent member of a number of historical confederacies in Napoleonic through post-Napoleonic Germany. From 1871 it was part of the German Empire. It became a Free state in the era of Weimar Republic in 1918 after the end of World War...
- The Kingdom of HanoverKingdom of HanoverThe Kingdom of Hanover was established in October 1814 by the Congress of Vienna, with the restoration of George III to his Hanoverian territories after the Napoleonic era. It succeeded the former Electorate of Brunswick-Lüneburg , and joined with 38 other sovereign states in the German...
- The Kingdom of WürttembergKingdom of WürttembergThe Kingdom of Württemberg was a state that existed from 1806 to 1918, located in present-day Baden-Württemberg, Germany. It was a continuation of the Duchy of Württemberg, which came into existence in 1495...
- The Electorate of Hesse
- The Grand Duchy of BadenGrand Duchy of BadenThe Grand Duchy of Baden was a historical state in the southwest of Germany, on the east bank of the Rhine. It existed between 1806 and 1918.-History:...
- The Grand Duchy of HesseGrand Duchy of HesseThe Grand Duchy of Hesse and by Rhine , or, between 1806 and 1816, Grand Duchy of Hesse —as it was also known after 1816—was a member state of the German Confederation from 1806, when the Landgraviate of Hesse-Darmstadt was elevated to a Grand Duchy, until 1918, when all the German...
- The Duchy of Holstein (in personal union with the Kingdom of DenmarkDenmarkDenmark is a Scandinavian country in Northern Europe. The countries of Denmark and Greenland, as well as the Faroe Islands, constitute the Kingdom of Denmark . It is the southernmost of the Nordic countries, southwest of Sweden and south of Norway, and bordered to the south by Germany. Denmark...
, was not a former member of the Confederation of the Rhine)- The Duchy of Schleswig (in personal union with the Kingdom of Denmark, was not a former member of either the Holy Roman EmpireHoly Roman EmpireThe Holy Roman Empire was a realm that existed from 962 to 1806 in Central Europe.It was ruled by the Holy Roman Emperor. Its character changed during the Middle Ages and the Early Modern period, when the power of the emperor gradually weakened in favour of the princes...
or the Confederation of the Rhine. The secessionist (pro-German) government of Schleswig-Holstein (1848–51) joined Schleswig to the Confederation. This was not recognized by the Danish government, and the peace settlement in 1851 specified that Schleswig was not a member.
- The Duchy of Schleswig (in personal union with the Kingdom of Denmark, was not a former member of either the Holy Roman Empire
- The Grand Duchy of Luxembourg (lost over half of its territory in the west to Belgium in the breakup of the United Kingdom of the NetherlandsUnited Kingdom of the NetherlandsUnited Kingdom of the Netherlands is the unofficial name used to refer to Kingdom of the Netherlands during the period after it was first created from part of the First French Empire and before the new kingdom of Belgium split out in 1830...
in 1839, and thereby causing Duchy of LimburgDuchy of Limburg (1839-1866)The Duchy of Limburg was created and formed from the eastern part of the Province of Limburg as a result of the Treaty of London in 1839. De jure it was a separate polity in personal union with the Kingdom of the Netherlands while at the same time a province of the Kingdom of the Netherlands. Until...
to become a member.) - The Duchy of LimburgDuchy of Limburg (1839-1866)The Duchy of Limburg was created and formed from the eastern part of the Province of Limburg as a result of the Treaty of London in 1839. De jure it was a separate polity in personal union with the Kingdom of the Netherlands while at the same time a province of the Kingdom of the Netherlands. Until...
(became a member in 1839 as a compensation for territorial losses in the Grand Duchy of Luxemburg that were caused by the breakup of the United Kingdom of the Netherlands.) - The Duchy of BrunswickDuchy of BrunswickBrunswick was a historical state in Germany. Originally the territory of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel in the Holy Roman Empire, it was established as an independent duchy by the Congress of Vienna in 1815...
(prior Brunswick-Lunenburgian Principality of Wolfenbüttel) - The Grand Duchy of Mecklenburg-Schwerin
- The Duchy of Nassau
- The Grand Duchy of Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach
- The Duchy of Saxe-Gotha-AltenburgSaxe-Gotha-AltenburgSaxe-Gotha-Altenburg was a duchy ruled by the Ernestine branch of the House of Wettin in today's Thuringia, Germany.It was nominally created in 1672 when Frederick William III, the last duke of Saxe-Altenburg, died and Ernest I, Duke of Saxe-Gotha , inherited the major part of his possessions...
(to 1825) - The Duchy of Saxe-Coburg-SaalfeldSaxe-Coburg-SaalfeldThe Duchy of Saxe-Coburg-Saalfeld was one of the Saxon Duchies held by the Ernestine line of the Wettin Dynasty. Established in the 17th century, the Saxe-Coburg-Saalfield line lasted until the reshuffle of Ernestine territories that occurred following the extinction of the Saxe-Gotha line in...
(to 1826) - The Duchy of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha (from 1826)
- The Duchy of Saxe-Meiningen
- The Duchy of Saxe-HildburghausenSaxe-HildburghausenSaxe-Hildburghausen was an Ernestine duchy in what is now southern Thuringia, Germany. Its territory was similar to that of the modern Hildburghausen district.-History:...
(Saxe-AltenburgSaxe-AltenburgSaxe-Altenburg was one of the Saxon duchies held by the Ernestine branch of the Wettin dynasty in present-day Thuringia.-History:The duchy originated from the medieval Burgraviate of Altenburg in the Imperial Pleissnerland , a possession of the Wettin Margraves of Meissen since 1243...
from 1826) - The Grand Duchy of Mecklenburg-Strelitz
- The Duchy of Oldenburg (Grand DuchyGrand DukeThe title grand duke is used in Western Europe and particularly in Germanic countries for provincial sovereigns. Grand duke is of a protocolary rank below a king but higher than a sovereign duke. Grand duke is also the usual and established translation of grand prince in languages which do not...
from 1829) - The Duchy of Anhalt-DessauAnhalt-DessauAnhalt-Dessau was a principality and later a duchy located in Germany. It was created in 1396 following the partition of the Principality of Anhalt-Zerbst. The capital of the state was Dessau. Anhalt-Dessau experienced a number of partitions throughout its existence with Anhalt-Köthen being...
(Duchy of Anhalt from 1863) - The Duchy of Anhalt-BernburgAnhalt-BernburgAnhalt-Bernburg was a principality of the Holy Roman Empire and a duchy of the German Confederation ruled by the House of Ascania with its residence at Bernburg in present-day Saxony-Anhalt...
(to 1863) - The Duchy of Anhalt-KöthenAnhalt-KöthenAnhalt-Köthen has existed on two separate occasions. The first state was created in 1396 when the Anhalt-Zerbst was partitioned between Anhalt-Dessau and Anhalt-Köthen. The first creation lasted until 1552 when it was inherited by Anhalt-Dessau....
(to 1847 - The Principality of Schwarzburg-Sondershausen
- The Principality of Schwarzburg-Rudolstadt
- The Principality of Hohenzollern-HechingenHohenzollern-HechingenHohenzollern-Hechingen was a county and principality in southwestern Germany. Its rulers belonged to a branch of the senior Swabian branch of the Hohenzollern dynasty.-History:...
(merged in Prussia in 1850) - The Principality of Liechtenstein
- The Principality of Hohenzollern-SigmaringenHohenzollern-Sigmaringen-Noble jurisdictions:Prince Karl Eitel of Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen, and descendants of his nephew Ferdinand ruled over the Kingdom of Romania, as Karl Eitel did not have children...
(merged in Prussia in 1850) - The Principality of Waldeck and Pyrmont
- The Principality of Reuss Senior Line
- The Principality of Reuss Junior Line
- The Principality of Schaumburg-Lippe
- The Principality of LippePrincipality of LippeLippe was a historical state in Germany. It was located between the Weser River and the southeast part of the Teutoburg forest.-History:...
- The Landgraviate of Hesse-Homburg (from 1817)
- The Duchy of Lauenburg
- The Free and Hanseatic City of Lübeck
- The Free City of Frankfurt upon MainFree City of FrankfurtFor almost five centuries, the German city of Frankfurt am Main was a city-state within two major Germanic states:*The Holy Roman Empire as the Free Imperial City of Frankfurt...
- The Free Hanseatic City of Bremen (still a constitutive state of federal Germany)
- The Free and Hanseatic City of Hamburg (still a constitutive state of federal Germany)
The four free cities were republic
Republic
A republic is a form of government in which the people, or some significant portion of them, have supreme control over the government and where offices of state are elected or chosen by elected people. In modern times, a common simplified definition of a republic is a government where the head of...
s by constitution, while all the others were monarchies, some constitutional
Constitutional monarchy
Constitutional monarchy is a form of government in which a monarch acts as head of state within the parameters of a constitution, whether it be a written, uncodified or blended constitution...
, some absolutist
Absolute monarchy
Absolute monarchy is a monarchical form of government in which the monarch exercises ultimate governing authority as head of state and head of government, his or her power not being limited by a constitution or by the law. An absolute monarch thus wields unrestricted political power over the...
.
Sources and references
- Westermann, Großer Atlas zur Weltgeschichte (in German, detailed maps)
- WorldStatesmen

