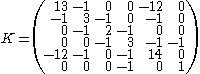Stiffness matrix
Encyclopedia
In the finite element method
and in analysis of spring system
s, a stiffness matrix, K, is a symmetric positive-semidefinite matrix that generalizes the stiffness of Hooke's law
to a matrix, describing the stiffness of between all of the degrees of freedom so that
where F and x are the force and the displacement vectors, and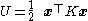
is the system's total potential energy.
For a simple spring network, the stiffness matrix is a Laplacian matrix
(in order to enforce Newton's third law) describing the connectivity graph
between degrees of freedom. Off-diagonal entries contain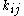 , the negative stiffness of the spring connecting degree-of-freedom i to j. For example,
, the negative stiffness of the spring connecting degree-of-freedom i to j. For example,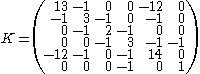
Finite element method
The finite element method is a numerical technique for finding approximate solutions of partial differential equations as well as integral equations...
and in analysis of spring system
Spring system
In engineering and physics, a spring system or spring network is a model of physics described as a graph with a position at each vertex and a spring of given stiffness and length along each edge. This generalizes Hooke's law to higher dimensions. This simple model can be used to solve the pose of...
s, a stiffness matrix, K, is a symmetric positive-semidefinite matrix that generalizes the stiffness of Hooke's law
Hooke's law
In mechanics, and physics, Hooke's law of elasticity is an approximation that states that the extension of a spring is in direct proportion with the load applied to it. Many materials obey this law as long as the load does not exceed the material's elastic limit. Materials for which Hooke's law...
to a matrix, describing the stiffness of between all of the degrees of freedom so that

where F and x are the force and the displacement vectors, and
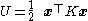
is the system's total potential energy.
For a simple spring network, the stiffness matrix is a Laplacian matrix
Laplacian matrix
In the mathematical field of graph theory the Laplacian matrix, sometimes called admittance matrix or Kirchhoff matrix, is a matrix representation of a graph. Together with Kirchhoff's theorem it can be used to calculate the number of spanning trees for a given graph. The Laplacian matrix can be...
(in order to enforce Newton's third law) describing the connectivity graph
Connectivity (graph theory)
In mathematics and computer science, connectivity is one of the basic concepts of graph theory: it asks for the minimum number of elements which need to be removed to disconnect the remaining nodes from each other. It is closely related to the theory of network flow problems...
between degrees of freedom. Off-diagonal entries contain
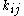 , the negative stiffness of the spring connecting degree-of-freedom i to j. For example,
, the negative stiffness of the spring connecting degree-of-freedom i to j. For example,