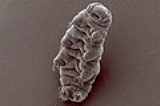
Tardigrade
Encyclopedia
Tardigrades form the phylum
Tardigrada, part of the superphylum Ecdysozoa
. They are microscopic, water-dwelling, segmented animal
s with eight legs. Tardigrades were first described by Johann August Ephraim Goeze
in 1773 (kleiner Wasserbär = little water bear). The name Tardigrada means "slow walker" and was given by Lazzaro Spallanzani
in 1777. The name water bear comes from the way they walk, reminiscent of a bear
's gait
. The biggest adults may reach a body length of 1.5 millimetre (0.0590551181102362 in), the smallest below 0.1 mm. Freshly hatched larva
e may be smaller than 0.05 mm.
More than 1,000 species of tardigrades have been described. Tardigrades occur over the entire world, from the high Himalayas
(above 6000 metres (19,685 ft)), to the deep sea
(below 4000 metres (13,123.4 ft)) and from the polar region
s to the equator
.
The most convenient place to find tardigrades is on lichen
s and moss
es. Other environments are dune
s, beach
es, soil
, and marine
or freshwater
sediments, where they may occur quite frequently (up to 25,000 animals per litre
). Tardigrades often can be found by soaking a piece of moss
in spring water.
Tardigrades are able to survive in extreme environments that would kill almost any other animal. Some can survive temperatures of close to absolute zero
(-273 C), temperatures as high as 151 °C (303.8 °F), 1,000 times more radiation than other animals, and almost a decade without water. Since 2007, tardigrades have also returned alive from studies in which they have been exposed to the vacuum of outer space in low earth orbit.
s each. The cuticle
contains chitin
and is moulted
periodically.
Tardigrades are eutelic, with all adult tardigrades of the same species having the same number of cells. Some species have as many as 40,000 cells in each adult, while others have far fewer.
The body cavity consists of a haemocoel, but the only place where a true coelom can be found is around the gonad. There are no respiratory organs, with gas exchange able to occur across the whole of the body. Some tardigrades have three tubular glands associated with the rectum; these may be excretory organs similar to the Malpighian tubules of arthropod
s, although the details remain unclear.
The tubular mouth is armed with stylets, which are used to pierce the plant cells, algae
, or small invertebrates on which the tardigrades feed, releasing the body fluids or cell contents. The mouth opens into a triradiate, muscular, sucking pharynx
. The stylets are lost when the animal moults, and a new pair is secreted from a pair of glands that lie on either side of the mouth. The pharynx connects to a short oesophagus, and then to an intestine that occupies much of the length of the body, which is the main site of digestion. The intestine opens, via a short rectum, to an anus
located at the terminal end of the body. Some species only defecate when they moult, leaving the faeces behind with the shed cuticle.
The brain includes multiple lobes, and is attached to a large ganglion
below the oesophagus, from which a double ventral nerve cord runs the length of the body. The cord possesses one ganglion per segment, each of which produces lateral nerve fibres that run into the limbs. Many species possess a pair of rhabdomeric pigment-cup eyes, and there are numerous sensory bristles on the head and body.
, both males and females are usually present, each with a single gonad
located above the intestine. Two ducts run from the testis in males, opening through a single pore in front of the anus. In contrast, females have a single duct opening either just above the anus or directly into the rectum, which thus forms a cloaca
.
Tardigrades are oviparous, and fertilisation is usually external. Mating occurs during the moult with the eggs being laid inside the shed cuticle of the female and then covered with sperm. A few species have internal fertilisation, with mating occurring before the female fully sheds her cuticle. In most cases, the eggs are left inside the shed cuticle to develop, but some attach them to the nearby substrate.
The eggs hatch after no more than fourteen days, with the young already possessing their full complement of adult cells. Growth to the adult size therefore occurs by enlargement of the individual cells (hypertrophy
), rather than by cell division. Tardigrades live for three to thirty months, and may moult up to twelve times.
s, on top of the Himalayas
, under layers of solid ice
and in ocean sediments. Many species can be found in a milder environment like lake
s, pond
s and meadow
s, while others can be found in stone walls and roofs. Tardigrades are most common in moist environments, but can stay active wherever they can retain at least some moisture.
 Tardigrades are one of the few groups of species that are capable of reversibly suspending their metabolism
Tardigrades are one of the few groups of species that are capable of reversibly suspending their metabolism
and going into a state of cryptobiosis
. Several species regularly survive in a dehydrated state for nearly ten years. Depending on the environment they may enter this state via anhydrobiosis, cryobiosis, osmobiosis or anoxybiosis. While in this state their metabolism lowers to less than 0.01% of normal and their water content can drop to 1% of normal. Their ability to remain desiccated for such a long period is largely dependent on the high levels of the non-reducing sugar
, trehalose
, which protects their membrane
s. In this cryptobiotic state the tardigrade is known as a tun.
Tardigrades have been known to withstand the following extremes while in this state:
and RNA
sequencing data indicate that tardigrades are the sister group to the arthropod
s and Onychophora
. These groups have been traditionally thought of as close relatives of the annelid
s, but newer schemes consider them Ecdysozoa
, together with the roundworms (Nematoda) and several smaller phyla. The Ecdysozoa
-concept resolves the problem of the nematode-like pharynx
as well as some data from 18S-rRNA and HOX (homeobox
) gene data, which indicate a relation to roundworms.
The minute sizes of tardigrades and their membranous integuments make their fossilization both difficult to detect and highly unlikely. The only known fossil specimens comprise some from mid-Cambrian
deposits in Siberia
and a few rare specimens from Cretaceous
amber
.
The Siberian tardigrades differ from living tardigrades in several ways. They have three pairs of legs rather than four; they have a simplified head morphology; and they have no posterior head appendages. It is considered that they probably represent a stem group of living tardigrades.
The rare specimens in Cretaceous amber comprise Milnesium swolenskyi, from New Jersey
, the oldest, whose claws and mouthparts are indistinguishable from the living M. tartigradum; and two specimens from western Canada
, some 15–20 million years younger than M. swolenskyi. Of the two latter, one has been given its own genus and family, Beorn leggi (the genus named by Cooper after the character Beorn
from The Hobbit
by J. R. R. Tolkien
and the species named after his student William M. Legg); however, it bears a strong resemblance to many living specimens in the family Hypsibiidae
.
Aysheaia
from the middle Cambrian
Burgess shale
has been proposed as a sister-taxon to an arthropod-tardigrade clade.
Tardigrades have sometimes been linked to the prehistoric oddity Opabinia
as a close living relative.
. Hypsibius dujardini has a compact genome and a generation time of about two weeks, and it can be cultured indefinitely and cryopreserved.
Phylum
In biology, a phylum The term was coined by Georges Cuvier from Greek φῦλον phylon, "race, stock," related to φυλή phyle, "tribe, clan." is a taxonomic rank below kingdom and above class. "Phylum" is equivalent to the botanical term division....
Tardigrada, part of the superphylum Ecdysozoa
Ecdysozoa
Ecdysozoa is a group of protostome animals, including Arthropoda , Nematoda, and several smaller phyla. They were first defined by Aguinaldo et al. in 1997, based mainly on trees constructed using 18S ribosomal RNA genes...
. They are microscopic, water-dwelling, segmented animal
Animal
Animals are a major group of multicellular, eukaryotic organisms of the kingdom Animalia or Metazoa. Their body plan eventually becomes fixed as they develop, although some undergo a process of metamorphosis later on in their life. Most animals are motile, meaning they can move spontaneously and...
s with eight legs. Tardigrades were first described by Johann August Ephraim Goeze
Johann August Ephraim Goeze
Johann August Ephraim Goeze was a German zoologist from Aschersleben.He was the son of Johann Heinrich and Catherine Margarete . He studied theology at University of Halle. He married Leopoldine Maria Keller in 1770, by whom he had four children. In 1751, he became a pastor at Aschersleben in...
in 1773 (kleiner Wasserbär = little water bear). The name Tardigrada means "slow walker" and was given by Lazzaro Spallanzani
Lazzaro Spallanzani
Lazzaro Spallanzani was an Italian Catholic priest, biologist and physiologist who made important contributions to the experimental study of bodily functions, animal reproduction, and essentially discovered echolocation...
in 1777. The name water bear comes from the way they walk, reminiscent of a bear
Bear
Bears are mammals of the family Ursidae. Bears are classified as caniforms, or doglike carnivorans, with the pinnipeds being their closest living relatives. Although there are only eight living species of bear, they are widespread, appearing in a wide variety of habitats throughout the Northern...
's gait
Gait
Gait is the pattern of movement of the limbs of animals, including humans, during locomotion over a solid substrate. Most animals use a variety of gaits, selecting gait based on speed, terrain, the need to maneuver, and energetic efficiency...
. The biggest adults may reach a body length of 1.5 millimetre (0.0590551181102362 in), the smallest below 0.1 mm. Freshly hatched larva
Larva
A larva is a distinct juvenile form many animals undergo before metamorphosis into adults. Animals with indirect development such as insects, amphibians, or cnidarians typically have a larval phase of their life cycle...
e may be smaller than 0.05 mm.
More than 1,000 species of tardigrades have been described. Tardigrades occur over the entire world, from the high Himalayas
Himalayas
The Himalaya Range or Himalaya Mountains Sanskrit: Devanagari: हिमालय, literally "abode of snow"), usually called the Himalayas or Himalaya for short, is a mountain range in Asia, separating the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau...
(above 6000 metres (19,685 ft)), to the deep sea
Deep sea
The deep sea, or deep layer, is the lowest layer in the ocean, existing below the thermocline and above the seabed, at a depth of 1000 fathoms or more. Little or no light penetrates this part of the ocean and most of the organisms that live there rely for subsistence on falling organic matter...
(below 4000 metres (13,123.4 ft)) and from the polar region
Polar region
Earth's polar regions are the areas of the globe surrounding the poles also known as frigid zones. The North Pole and South Pole being the centers, these regions are dominated by the polar ice caps, resting respectively on the Arctic Ocean and the continent of Antarctica...
s to the equator
Equator
An equator is the intersection of a sphere's surface with the plane perpendicular to the sphere's axis of rotation and containing the sphere's center of mass....
.
The most convenient place to find tardigrades is on lichen
Lichen
Lichens are composite organisms consisting of a symbiotic organism composed of a fungus with a photosynthetic partner , usually either a green alga or cyanobacterium...
s and moss
Moss
Mosses are small, soft plants that are typically 1–10 cm tall, though some species are much larger. They commonly grow close together in clumps or mats in damp or shady locations. They do not have flowers or seeds, and their simple leaves cover the thin wiry stems...
es. Other environments are dune
Dune
In physical geography, a dune is a hill of sand built by wind. Dunes occur in different forms and sizes, formed by interaction with the wind. Most kinds of dunes are longer on the windward side where the sand is pushed up the dune and have a shorter "slip face" in the lee of the wind...
s, beach
Beach
A beach is a geological landform along the shoreline of an ocean, sea, lake or river. It usually consists of loose particles which are often composed of rock, such as sand, gravel, shingle, pebbles or cobblestones...
es, soil
Soil
Soil is a natural body consisting of layers of mineral constituents of variable thicknesses, which differ from the parent materials in their morphological, physical, chemical, and mineralogical characteristics...
, and marine
Ocean
An ocean is a major body of saline water, and a principal component of the hydrosphere. Approximately 71% of the Earth's surface is covered by ocean, a continuous body of water that is customarily divided into several principal oceans and smaller seas.More than half of this area is over 3,000...
or freshwater
Freshwater
Fresh water is naturally occurring water on the Earth's surface in ice sheets, ice caps, glaciers, bogs, ponds, lakes, rivers and streams, and underground as groundwater in aquifers and underground streams. Fresh water is generally characterized by having low concentrations of dissolved salts and...
sediments, where they may occur quite frequently (up to 25,000 animals per litre
Litre
pic|200px|right|thumb|One litre is equivalent to this cubeEach side is 10 cm1 litre water = 1 kilogram water The litre is a metric system unit of volume equal to 1 cubic decimetre , to 1,000 cubic centimetres , and to 1/1,000 cubic metre...
). Tardigrades often can be found by soaking a piece of moss
Moss
Mosses are small, soft plants that are typically 1–10 cm tall, though some species are much larger. They commonly grow close together in clumps or mats in damp or shady locations. They do not have flowers or seeds, and their simple leaves cover the thin wiry stems...
in spring water.
Tardigrades are able to survive in extreme environments that would kill almost any other animal. Some can survive temperatures of close to absolute zero
Absolute zero
Absolute zero is the theoretical temperature at which entropy reaches its minimum value. The laws of thermodynamics state that absolute zero cannot be reached using only thermodynamic means....
(-273 C), temperatures as high as 151 °C (303.8 °F), 1,000 times more radiation than other animals, and almost a decade without water. Since 2007, tardigrades have also returned alive from studies in which they have been exposed to the vacuum of outer space in low earth orbit.
Anatomy and morphology
Tardigrades have barrel-shaped bodies with four pairs of stubby legs. Most range from 0.3 to 0.5 mm (0.0118110236220472 to 0.0196850393700787 in) in length, although the largest species may reach 1.2 millimetre (0.047244094488189 in). The body has four segments (not counting the head), four pairs of legs without joints, and feet with four to eight clawClaw
A claw is a curved, pointed appendage, found at the end of a toe or finger in most mammals, birds, and some reptiles. However, the word "claw" is also often used in reference to an invertebrate. Somewhat similar fine hooked structures are found in arthropods such as beetles and spiders, at the end...
s each. The cuticle
Cuticle
A cuticle , or cuticula, is a term used for any of a variety of tough but flexible, non-mineral outer coverings of an organism, or parts of an organism, that provide protection. Various types of "cuticles" are non-homologous; differing in their origin, structure, function, and chemical composition...
contains chitin
Chitin
Chitin n is a long-chain polymer of a N-acetylglucosamine, a derivative of glucose, and is found in many places throughout the natural world...
and is moulted
Ecdysis
Ecdysis is the moulting of the cuticula in many invertebrates. This process of moulting is the defining feature of the clade Ecdysozoa, comprising the arthropods, nematodes, velvet worms, horsehair worms, rotifers, tardigrades and Cephalorhyncha...
periodically.
Tardigrades are eutelic, with all adult tardigrades of the same species having the same number of cells. Some species have as many as 40,000 cells in each adult, while others have far fewer.
The body cavity consists of a haemocoel, but the only place where a true coelom can be found is around the gonad. There are no respiratory organs, with gas exchange able to occur across the whole of the body. Some tardigrades have three tubular glands associated with the rectum; these may be excretory organs similar to the Malpighian tubules of arthropod
Arthropod
An arthropod is an invertebrate animal having an exoskeleton , a segmented body, and jointed appendages. Arthropods are members of the phylum Arthropoda , and include the insects, arachnids, crustaceans, and others...
s, although the details remain unclear.
The tubular mouth is armed with stylets, which are used to pierce the plant cells, algae
Algae
Algae are a large and diverse group of simple, typically autotrophic organisms, ranging from unicellular to multicellular forms, such as the giant kelps that grow to 65 meters in length. They are photosynthetic like plants, and "simple" because their tissues are not organized into the many...
, or small invertebrates on which the tardigrades feed, releasing the body fluids or cell contents. The mouth opens into a triradiate, muscular, sucking pharynx
Pharynx
The human pharynx is the part of the throat situated immediately posterior to the mouth and nasal cavity, and anterior to the esophagus and larynx. The human pharynx is conventionally divided into three sections: the nasopharynx , the oropharynx , and the laryngopharynx...
. The stylets are lost when the animal moults, and a new pair is secreted from a pair of glands that lie on either side of the mouth. The pharynx connects to a short oesophagus, and then to an intestine that occupies much of the length of the body, which is the main site of digestion. The intestine opens, via a short rectum, to an anus
Anus
The anus is an opening at the opposite end of an animal's digestive tract from the mouth. Its function is to control the expulsion of feces, unwanted semi-solid matter produced during digestion, which, depending on the type of animal, may be one or more of: matter which the animal cannot digest,...
located at the terminal end of the body. Some species only defecate when they moult, leaving the faeces behind with the shed cuticle.
The brain includes multiple lobes, and is attached to a large ganglion
Ganglion
In anatomy, a ganglion is a biological tissue mass, most commonly a mass of nerve cell bodies. Cells found in a ganglion are called ganglion cells, though this term is also sometimes used to refer specifically to retinal ganglion cells....
below the oesophagus, from which a double ventral nerve cord runs the length of the body. The cord possesses one ganglion per segment, each of which produces lateral nerve fibres that run into the limbs. Many species possess a pair of rhabdomeric pigment-cup eyes, and there are numerous sensory bristles on the head and body.
Reproduction
Although some species are parthenogeneticParthenogenesis
Parthenogenesis is a form of asexual reproduction found in females, where growth and development of embryos occur without fertilization by a male...
, both males and females are usually present, each with a single gonad
Gonad
The gonad is the organ that makes gametes. The gonads in males are the testes and the gonads in females are the ovaries. The product, gametes, are haploid germ cells. For example, spermatozoon and egg cells are gametes...
located above the intestine. Two ducts run from the testis in males, opening through a single pore in front of the anus. In contrast, females have a single duct opening either just above the anus or directly into the rectum, which thus forms a cloaca
Cloaca
In zoological anatomy, a cloaca is the posterior opening that serves as the only such opening for the intestinal, reproductive, and urinary tracts of certain animal species...
.
Tardigrades are oviparous, and fertilisation is usually external. Mating occurs during the moult with the eggs being laid inside the shed cuticle of the female and then covered with sperm. A few species have internal fertilisation, with mating occurring before the female fully sheds her cuticle. In most cases, the eggs are left inside the shed cuticle to develop, but some attach them to the nearby substrate.
The eggs hatch after no more than fourteen days, with the young already possessing their full complement of adult cells. Growth to the adult size therefore occurs by enlargement of the individual cells (hypertrophy
Hypertrophy
Hypertrophy is the increase in the volume of an organ or tissue due to the enlargement of its component cells. It should be distinguished from hyperplasia, in which the cells remain approximately the same size but increase in number...
), rather than by cell division. Tardigrades live for three to thirty months, and may moult up to twelve times.
Ecology and life history
Most tardigrades are phytophagous (plant eaters) or bacteriophagous (bacteria eaters), but some are predatory (e.g., Milnesium tardigradum).Physiology
Scientists have reported tardigrades in hot springHot spring
A hot spring is a spring that is produced by the emergence of geothermally heated groundwater from the Earth's crust. There are geothermal hot springs in many locations all over the crust of the earth.-Definitions:...
s, on top of the Himalayas
Himalayas
The Himalaya Range or Himalaya Mountains Sanskrit: Devanagari: हिमालय, literally "abode of snow"), usually called the Himalayas or Himalaya for short, is a mountain range in Asia, separating the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau...
, under layers of solid ice
Ice
Ice is water frozen into the solid state. Usually ice is the phase known as ice Ih, which is the most abundant of the varying solid phases on the Earth's surface. It can appear transparent or opaque bluish-white color, depending on the presence of impurities or air inclusions...
and in ocean sediments. Many species can be found in a milder environment like lake
Lake
A lake is a body of relatively still fresh or salt water of considerable size, localized in a basin, that is surrounded by land. Lakes are inland and not part of the ocean and therefore are distinct from lagoons, and are larger and deeper than ponds. Lakes can be contrasted with rivers or streams,...
s, pond
Pond
A pond is a body of standing water, either natural or man-made, that is usually smaller than a lake. A wide variety of man-made bodies of water are classified as ponds, including water gardens, water features and koi ponds; all designed for aesthetic ornamentation as landscape or architectural...
s and meadow
Meadow
A meadow is a field vegetated primarily by grass and other non-woody plants . The term is from Old English mædwe. In agriculture a meadow is grassland which is not grazed by domestic livestock but rather allowed to grow unchecked in order to make hay...
s, while others can be found in stone walls and roofs. Tardigrades are most common in moist environments, but can stay active wherever they can retain at least some moisture.

Metabolism
Metabolism is the set of chemical reactions that happen in the cells of living organisms to sustain life. These processes allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. Metabolism is usually divided into two categories...
and going into a state of cryptobiosis
Cryptobiosis
Cryptobiosis is an ametabolic state of life entered by an organism in response to adverse environmental conditions such as desiccation, freezing, and oxygen deficiency. In the cryptobiotic state, all metabolic procedures stop, preventing reproduction, development, and repair...
. Several species regularly survive in a dehydrated state for nearly ten years. Depending on the environment they may enter this state via anhydrobiosis, cryobiosis, osmobiosis or anoxybiosis. While in this state their metabolism lowers to less than 0.01% of normal and their water content can drop to 1% of normal. Their ability to remain desiccated for such a long period is largely dependent on the high levels of the non-reducing sugar
Sugar
Sugar is a class of edible crystalline carbohydrates, mainly sucrose, lactose, and fructose, characterized by a sweet flavor.Sucrose in its refined form primarily comes from sugar cane and sugar beet...
, trehalose
Trehalose
Trehalose, also known as mycose or tremalose, is a natural alpha-linked disaccharide formed by an α,α-1,1-glucoside bond between two α-glucose units. In 1832, H.A.L. Wiggers discovered trehalose in an ergot of rye, and in 1859 Marcellin Berthelot isolated it from trehala manna, a substance made...
, which protects their membrane
Cell membrane
The cell membrane or plasma membrane is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. It basically protects the cell...
s. In this cryptobiotic state the tardigrade is known as a tun.
Tardigrades have been known to withstand the following extremes while in this state:
- TemperatureTemperatureTemperature is a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notions of hot and cold. Objects of low temperature are cold, while various degrees of higher temperatures are referred to as warm or hot...
– tardigrades can survive being heated for a few minutes to 151 °C (424 K), or being chilled for days at -200 °C (73 K), or for a few minutes at -272 °C (~1 degree above absolute zeroAbsolute zeroAbsolute zero is the theoretical temperature at which entropy reaches its minimum value. The laws of thermodynamics state that absolute zero cannot be reached using only thermodynamic means....
). - PressurePressurePressure is the force per unit area applied in a direction perpendicular to the surface of an object. Gauge pressure is the pressure relative to the local atmospheric or ambient pressure.- Definition :...
– they can withstand the extremely low pressure of a vacuumVacuumIn everyday usage, vacuum is a volume of space that is essentially empty of matter, such that its gaseous pressure is much less than atmospheric pressure. The word comes from the Latin term for "empty". A perfect vacuum would be one with no particles in it at all, which is impossible to achieve in...
and also very high pressures, more than 1,200 times atmospheric pressureAtmospheric pressureAtmospheric pressure is the force per unit area exerted into a surface by the weight of air above that surface in the atmosphere of Earth . In most circumstances atmospheric pressure is closely approximated by the hydrostatic pressure caused by the weight of air above the measurement point...
. Tardigrades can survive the vacuum of open space and solar radiation combined for at least 10 days. Some species can also withstand pressure of 6,000 atmospheres, which is nearly six times the pressure of water in the deepest ocean trench, the Mariana trenchMariana TrenchThe Mariana Trench or Marianas Trench is the deepest part of the world's oceans. It is located in the western Pacific Ocean, to the east of the Mariana Islands. The trench is about long but has a mean width of only...
. - DehydrationDehydrationIn physiology and medicine, dehydration is defined as the excessive loss of body fluid. It is literally the removal of water from an object; however, in physiological terms, it entails a deficiency of fluid within an organism...
– tardigrades have been shown to survive nearly 10 years in a dry state. When encountered by extremely low temperatures, their body composition goes from 85% water to only 3%. As water expands upon freezing, dehydration ensures the tardigrades do not get ripped apart by the freezing ice (as waterless tissues cannot freeze). - RadiationRadiationIn physics, radiation is a process in which energetic particles or energetic waves travel through a medium or space. There are two distinct types of radiation; ionizing and non-ionizing...
– tardigrades can withstand median lethal doses of 5,000 GyGray (unit)The gray is the SI unit of absorbed radiation dose of ionizing radiation , and is defined as the absorption of one joule of ionizing radiation by one kilogram of matter ....
(of gamma-rays) and 6,200 Gy (of heavy ions) in hydrated animals (5 to 10 Gy could be fatal to a human). The only explanation thus far for this ability is that their lowered water state provides fewer reactants for the ionizing radiationIonizing radiationIonizing radiation is radiation composed of particles that individually have sufficient energy to remove an electron from an atom or molecule. This ionization produces free radicals, which are atoms or molecules containing unpaired electrons...
. - Environmental toxinToxinA toxin is a poisonous substance produced within living cells or organisms; man-made substances created by artificial processes are thus excluded...
s – tardigrades can undergo chemobiosis—a cryptobioticCryptobiosisCryptobiosis is an ametabolic state of life entered by an organism in response to adverse environmental conditions such as desiccation, freezing, and oxygen deficiency. In the cryptobiotic state, all metabolic procedures stop, preventing reproduction, development, and repair...
response to high levels of environmental toxins. However, these laboratory results have yet to be verified. - Outer spaceOuter spaceOuter space is the void that exists between celestial bodies, including the Earth. It is not completely empty, but consists of a hard vacuum containing a low density of particles: predominantly a plasma of hydrogen and helium, as well as electromagnetic radiation, magnetic fields, and neutrinos....
– In September 2007, tardigrades were taken into low Earth orbit on the FOTON-M3Foton-MFoton-M is series of robotic spacecraft used by Russia and the European Space Agency for research conducted in the microgravity environment of Earth orbit. The Foton-M design is based on the design of the Foton, with several improvements including a new telemetry and telecommand unit for increased...
mission and for 10 days were exposed to the vacuum of space. After being rehydrated back on Earth, over 68% of the subjects protected from high-energy UV radiation survived and many of these produced viable embryos, and a handful had survived full exposure to solar radiation. In May 2011, tardigrades were sent into space along with other extremophiles on STS-134STS-134STS-134 was the penultimate mission of NASA's Space Shuttle program. The mission marked the 25th and final flight of . This flight delivered the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer and an ExPRESS Logistics Carrier to the International Space Station. Mark Kelly served as the mission commander...
, the final flight of . In November 2011, they were among the organisms sent by the US-based Planetary SocietyPlanetary SocietyThe Planetary Society is a large, publicly supported, non-government and non-profit organization that has many research projects related to astronomy...
on the Russian Phobos-GruntPhobos-GruntFobos-Grunt or Phobos-Grunt was an attempted Russian sample return mission to Phobos, one of the moons of Mars. It was launched on 9 November 2011 at 02:16 local time from the Baikonur Cosmodrome, but subsequent rocket burns intended to set the craft on a course for Mars failed, leaving it...
mission to PhobosPhobosPhobos may refer to:* an Ancient Greek word for fear* Phobos , the Greek god of fear* Phobos , a moon of Mars* Phobos , a 1997 album by Canadian heavy metal band Voivod...
.
Evolutionary relationships and history
Recent DNADNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid is a nucleic acid that contains the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms . The DNA segments that carry this genetic information are called genes, but other DNA sequences have structural purposes, or are involved in...
and RNA
RNA
Ribonucleic acid , or RNA, is one of the three major macromolecules that are essential for all known forms of life....
sequencing data indicate that tardigrades are the sister group to the arthropod
Arthropod
An arthropod is an invertebrate animal having an exoskeleton , a segmented body, and jointed appendages. Arthropods are members of the phylum Arthropoda , and include the insects, arachnids, crustaceans, and others...
s and Onychophora
Velvet worm
The velvet worms are a minor ecdysozoan phylum. These obscurely segmented organisms have tiny eyes, antennae, multiple pairs of legs and slime glands. They have variously been compared to worms with legs, caterpillars and slugs...
. These groups have been traditionally thought of as close relatives of the annelid
Annelid
The annelids , formally called Annelida , are a large phylum of segmented worms, with over 17,000 modern species including ragworms, earthworms and leeches...
s, but newer schemes consider them Ecdysozoa
Ecdysozoa
Ecdysozoa is a group of protostome animals, including Arthropoda , Nematoda, and several smaller phyla. They were first defined by Aguinaldo et al. in 1997, based mainly on trees constructed using 18S ribosomal RNA genes...
, together with the roundworms (Nematoda) and several smaller phyla. The Ecdysozoa
Ecdysozoa
Ecdysozoa is a group of protostome animals, including Arthropoda , Nematoda, and several smaller phyla. They were first defined by Aguinaldo et al. in 1997, based mainly on trees constructed using 18S ribosomal RNA genes...
-concept resolves the problem of the nematode-like pharynx
Pharynx
The human pharynx is the part of the throat situated immediately posterior to the mouth and nasal cavity, and anterior to the esophagus and larynx. The human pharynx is conventionally divided into three sections: the nasopharynx , the oropharynx , and the laryngopharynx...
as well as some data from 18S-rRNA and HOX (homeobox
Homeobox
A homeobox is a DNA sequence found within genes that are involved in the regulation of patterns of anatomical development in animals, fungi and plants.- Discovery :...
) gene data, which indicate a relation to roundworms.
The minute sizes of tardigrades and their membranous integuments make their fossilization both difficult to detect and highly unlikely. The only known fossil specimens comprise some from mid-Cambrian
Cambrian
The Cambrian is the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, lasting from Mya ; it is succeeded by the Ordovician. Its subdivisions, and indeed its base, are somewhat in flux. The period was established by Adam Sedgwick, who named it after Cambria, the Latin name for Wales, where Britain's...
deposits in Siberia
Siberia
Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th...
and a few rare specimens from Cretaceous
Cretaceous
The Cretaceous , derived from the Latin "creta" , usually abbreviated K for its German translation Kreide , is a geologic period and system from circa to million years ago. In the geologic timescale, the Cretaceous follows the Jurassic period and is followed by the Paleogene period of the...
amber
Amber
Amber is fossilized tree resin , which has been appreciated for its color and natural beauty since Neolithic times. Amber is used as an ingredient in perfumes, as a healing agent in folk medicine, and as jewelry. There are five classes of amber, defined on the basis of their chemical constituents...
.
The Siberian tardigrades differ from living tardigrades in several ways. They have three pairs of legs rather than four; they have a simplified head morphology; and they have no posterior head appendages. It is considered that they probably represent a stem group of living tardigrades.
The rare specimens in Cretaceous amber comprise Milnesium swolenskyi, from New Jersey
New Jersey
New Jersey is a state in the Northeastern and Middle Atlantic regions of the United States. , its population was 8,791,894. It is bordered on the north and east by the state of New York, on the southeast and south by the Atlantic Ocean, on the west by Pennsylvania and on the southwest by Delaware...
, the oldest, whose claws and mouthparts are indistinguishable from the living M. tartigradum; and two specimens from western Canada
Canada
Canada is a North American country consisting of ten provinces and three territories. Located in the northern part of the continent, it extends from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west, and northward into the Arctic Ocean...
, some 15–20 million years younger than M. swolenskyi. Of the two latter, one has been given its own genus and family, Beorn leggi (the genus named by Cooper after the character Beorn
Beorn
Beorn is a fictional character created by J. R. R. Tolkien. He appears in The Hobbit as a shape-shifter , a man who could assume the appearance of a great black bear.-Literature:...
from The Hobbit
The Hobbit
The Hobbit, or There and Back Again, better known by its abbreviated title The Hobbit, is a fantasy novel and children's book by J. R. R. Tolkien. It was published on 21 September 1937 to wide critical acclaim, being nominated for the Carnegie Medal and awarded a prize from the New York Herald...
by J. R. R. Tolkien
J. R. R. Tolkien
John Ronald Reuel Tolkien, CBE was an English writer, poet, philologist, and university professor, best known as the author of the classic high fantasy works The Hobbit, The Lord of the Rings, and The Silmarillion.Tolkien was Rawlinson and Bosworth Professor of Anglo-Saxon at Pembroke College,...
and the species named after his student William M. Legg); however, it bears a strong resemblance to many living specimens in the family Hypsibiidae
Hypsibiidae
Hypsibiidae is a family of water bear or moss piglet, a tardigrade in the class Eutardigrada.-Genera:* Acutuncus* Astatumen* Diphascon* Doryphoribius* Eremobiotus* Halobiotus* Hebesuncus* Hypsibius...
.
Aysheaia
Aysheaia
Aysheaia was a genus of soft-bodied, caterpillar-shaped organisms average body length of 1–6 cm. The genus name commemorates a mountain peak named "Ayesha" due north of the Wapta Glacier. This peak was originally named Aysha in the 1904 maps of the region, and was re-named Ayesha after the heroine...
from the middle Cambrian
Cambrian
The Cambrian is the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, lasting from Mya ; it is succeeded by the Ordovician. Its subdivisions, and indeed its base, are somewhat in flux. The period was established by Adam Sedgwick, who named it after Cambria, the Latin name for Wales, where Britain's...
Burgess shale
Burgess Shale
The Burgess Shale Formation, located in the Canadian Rockies of British Columbia, is one of the world's most celebrated fossil fields, and the best of its kind. It is famous for the exceptional preservation of the soft parts of its fossils...
has been proposed as a sister-taxon to an arthropod-tardigrade clade.
Tardigrades have sometimes been linked to the prehistoric oddity Opabinia
Opabinia
Opabinia is an animal genus found in Cambrian fossil deposits. Its sole species, Opabinia regalis, is known from the Middle Cambrian Burgess Shale of British Columbia, Canada. Fewer than twenty good specimens have been described; 3 specimens of Opabinia are known from the Greater Phyllopod bed,...
as a close living relative.
Genomes and genome sequencing
Tardigrade genomes vary in size, from about 75 to 800 megabase pairs of DNA. The genome of a tardigrade species, Hypsibius dujardini, is being sequenced at the Broad InstituteBroad Institute
The Broad Institute is a genomic medicine research center located in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States. Although it is independently governed and supported as a 501 nonprofit research organization, the institute is formally affiliated with the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Harvard...
. Hypsibius dujardini has a compact genome and a generation time of about two weeks, and it can be cultured indefinitely and cryopreserved.
External links
- Tardigrada Newsletter
- Tardigrades – Pictures and Movies
- The Edinburgh Tardigrade project
- NJ Tardigrade Survey
- Tardigrades (English/German)
- The incredible water bear!
- Tardigrade Reference Center
- Tardigrades in space
- Tardigrade data and analysis
- NASA's Tardigrade Research
- A short film about tardigrade research from NPR's Science Friday
- Tardigrada at the Tree of Life Web ProjectTree of Life Web ProjectThe Tree of Life Web Project is an ongoing Internet project providing information about the diversity and phylogeny of life on Earth. This collaborative peer reviewed project began in 1995, and is written by biologists from around the world....
- Swiss Center of Tardigrade Research – Ecology, Physiology and Evolutionary Biology of Tardigrades

