The Canadian
Encyclopedia
The Canadian is a Canadian
transcontinental passenger train originally operated by the Canadian Pacific Railway
between 1955 and 1978. It is currently operated as an Inter-city rail
service by Via Rail Canada (as the Canadian) with service between Union Station
in Toronto, Ontario
and Pacific Central Station
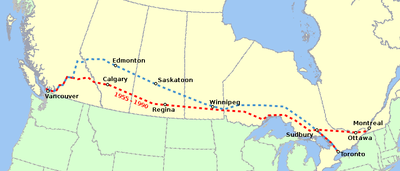
in Vancouver, British Columbia. Since 1990, the train has followed a completely different route from Canadian Pacific's Canadian, using Canadian National's more northerly main line, which goes through Saskatoon and Edmonton rather than through Regina and Calgary. It is also much slower than the Canadian Pacific version of the train, and no longer serves Montreal or Ottawa, as it did until 1990. Before 1955, the name "The Canadian" had been used on CPR's overnight Montreal / Chicago trains.
, passenger trains on the CPR consisted of a mixture of prewar heavyweight and pre- and post-war lightweight cars, even on their flagship
transcontinental The Dominion and its eastern extension, The Atlantic Limited. While these cars were serviceable, American
trains of the early 1950s, such as the California Zephyr
, had already adopted streamlined
all-stainless steel
consists featuring domed
observation car
s. Following an evaluation in 1949 of the dome cars featured on the General Motors
/ Pullman Standard
demonstrator Train of Tomorrow, CPR management, including then Vice President Norris Crump, resolved to upgrade their rolling stock. In 1953, CPR placed an order for 155 stainless steel
cars with the Budd Company
of Philadelphia that included 18 rear-end dome cars (Park series), 18 Skyline mid-train dome cars, 30 coaches, 18 dining car
s and 71 sleeping car
s (Manor and Chateau series). A subsequent order for 18 baggage-crew dormitory cars brought the final to total to 173 cars, sufficient for establishing an entirely new transcontinental service and partially re-equippiping The Dominion. The interior design
of these new cars was contracted to the Philadelphia architectural
firm Harbeson, Hough, Livingston & Larson (a company known for its industrial designs on other prominent passenger trains such as the Pioneer Zephyr
), and the resulting furnishings and pastel-shaded colour schemes were widely acclaimed. After deciding to name the Park series dome cars after famous Canadian parks, leading Canadian artist
s, including members of the Group of Seven
, were commissioned to paint suitable murals for these cars. When the decision was made to add budget sleeping cars, the Budd order was supplemented by 22 existing heavyweight sleepers that CPR refurbished in its own Angus Shops, each fitted out with Budd-style stainless steel cladding. To complement the new rolling stock, the CPR ordered General Motors Diesel
FP9
locomotives to supplement an existing fleet of FP7
s. Although these F-units
remained the preferred power for the train, it was occasionally pulled by a variety of motive power, including Montreal Locomotive Works
FPA-2s, and, as late as 1959, steam locomotive
s.
CPR christened their new flagship
train The Canadian and service began on April 24, 1955. Although CPR competitor Canadian National Railway
s began its own new transcontinental service, the Super Continental
, on the same day, CPR was able to boast honestly that The Canadian was "The first and only all-stainless steel 'dome' stream-liner in Canada" — it was not until 1964 that the CNR acquired dome cars.
CPR operated the train in two sections east of Sudbury, Ontario
. The section operating between Montreal and Vancouver (also serving Ottawa) was known as train 1 westbound and train 2 eastbound, with a connecting section to or from Toronto splitting or joining at Sudbury (this section was known as train 11 westbound, and train 12 eastbound). Matching its streamlined appearance, The Canadian's 71 hour westbound schedule was 16 hours faster than that of The Dominion.
Although initially successful, passenger train ridership began to decline in Canada during the 1960s. Facing competition from airlines and increased automobile usage following construction of the Trans-Canada Highway
, the CPR cancelled The Dominion in 1966, and petitioned the government
to discontinue The Canadian in 1970. Although this petition was denied, CPR during the 1970s attempted to remove itself from the passenger service market. The Canadian was operated at reduced levels, with the government subsidizing 80 percent of its losses.
In the aftermath of the deep budget
cuts made to Via Rail on January 15, 1990, the Super Continental service was abolished and the Canadian was moved from the CPR route to the Super Continental's CN route. This maintained transcontinental service and allowed Via to operate its government-mandated service to small communities along the line. Service was also reduced to 3 days per week. Today, Via Rail continues to operate the Canadian using the CN route with rebuilt ex-CPR Budd passenger equipment.
Canada
Canada is a North American country consisting of ten provinces and three territories. Located in the northern part of the continent, it extends from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west, and northward into the Arctic Ocean...
transcontinental passenger train originally operated by the Canadian Pacific Railway
Canadian Pacific Railway
The Canadian Pacific Railway , formerly also known as CP Rail between 1968 and 1996, is a historic Canadian Class I railway founded in 1881 and now operated by Canadian Pacific Railway Limited, which began operations as legal owner in a corporate restructuring in 2001...
between 1955 and 1978. It is currently operated as an Inter-city rail
Inter-city rail
Inter-city rail services are express passenger train services that cover longer distances than commuter or regional trains.There is no precise definition of inter-city rail. Its meaning may vary from country to country...
service by Via Rail Canada (as the Canadian) with service between Union Station
Union Station (Toronto)
Union Station is the major inter-city rail station and a major commuter rail hub in Toronto, located on Front Street West and occupying the south side of the block bounded by Bay Street and York Street in the central business district. The station building is owned by the City of Toronto, while the...
in Toronto, Ontario
Toronto
Toronto is the provincial capital of Ontario and the largest city in Canada. It is located in Southern Ontario on the northwestern shore of Lake Ontario. A relatively modern city, Toronto's history dates back to the late-18th century, when its land was first purchased by the British monarchy from...
and Pacific Central Station
Pacific Central Station (Vancouver)
Pacific Central Station in Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada is a railway station that acts as the western terminus of Via Rail's cross-country The Canadian to Toronto and the northern terminus of Amtrak’s Cascades to Seattle, Portland, and Eugene, Oregon...
in Vancouver, British Columbia. Since 1990, the train has followed a completely different route from Canadian Pacific's Canadian, using Canadian National's more northerly main line, which goes through Saskatoon and Edmonton rather than through Regina and Calgary. It is also much slower than the Canadian Pacific version of the train, and no longer serves Montreal or Ottawa, as it did until 1990. Before 1955, the name "The Canadian" had been used on CPR's overnight Montreal / Chicago trains.
Canadian Pacific
In the years following World War IIWorld War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
, passenger trains on the CPR consisted of a mixture of prewar heavyweight and pre- and post-war lightweight cars, even on their flagship
Flagship
A flagship is a vessel used by the commanding officer of a group of naval ships, reflecting the custom of its commander, characteristically a flag officer, flying a distinguishing flag...
transcontinental The Dominion and its eastern extension, The Atlantic Limited. While these cars were serviceable, American
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
trains of the early 1950s, such as the California Zephyr
California Zephyr
The California Zephyr is a long passenger train route operated by Amtrak in the midwestern and western United States.It runs from Chicago, Illinois, in the east to Emeryville, California, in the west, passing through the states of Illinois, Iowa, Nebraska, Colorado, Utah, Nevada, and California...
, had already adopted streamlined
Streamliner cars (rail)
The streamliners are a class of streamlined railway cars built in the forties and fifties of the twentieth century for long distance passenger railservices in North America.-Predecessors:...
all-stainless steel
Stainless steel
In metallurgy, stainless steel, also known as inox steel or inox from French "inoxydable", is defined as a steel alloy with a minimum of 10.5 or 11% chromium content by mass....
consists featuring domed
Dome car
A dome car is a type of railway passenger car that has a glass dome on the top of the car where passengers can ride and see in all directions around the train. It also can include features of a coach, lounge car, dining car or observation...
observation car
Observation car
An observation car/carriage/coach is a type of railroad passenger car, generally operated in a passenger train as the last carriage, with windows on the rear of the car for passengers' viewing pleasure...
s. Following an evaluation in 1949 of the dome cars featured on the General Motors
General Motors Diesel
General Motors Diesel was a Canadian railway diesel locomotive manufacturer.-History:General Motors Diesel, Limited, was created in 1949 as the Canadian subsidiary of the Electro Motive Division of General Motors located in the United States...
/ Pullman Standard
Pullman Company
The Pullman Palace Car Company, founded by George Pullman, manufactured railroad cars in the mid-to-late 19th century through the early decades of the 20th century, during the boom of railroads in the United States. Pullman developed the sleeping car which carried his name into the 1980s...
demonstrator Train of Tomorrow, CPR management, including then Vice President Norris Crump, resolved to upgrade their rolling stock. In 1953, CPR placed an order for 155 stainless steel
Stainless steel
In metallurgy, stainless steel, also known as inox steel or inox from French "inoxydable", is defined as a steel alloy with a minimum of 10.5 or 11% chromium content by mass....
cars with the Budd Company
Budd Company
The Budd Company is a metal fabricator and major supplier of body components to the automobile industry, and was formerly a manufacturer of stainless steel passenger rail cars during the 20th century....
of Philadelphia that included 18 rear-end dome cars (Park series), 18 Skyline mid-train dome cars, 30 coaches, 18 dining car
Dining car
A dining car or restaurant carriage , also diner, is a railroad passenger car that serves meals in the manner of a full-service, sit-down restaurant....
s and 71 sleeping car
Sleeping car
The sleeping car or sleeper is a railway/railroad passenger car that can accommodate all its passengers in beds of one kind or another, primarily for the purpose of making nighttime travel more restful. The first such cars saw sporadic use on American railroads in the 1830s and could be configured...
s (Manor and Chateau series). A subsequent order for 18 baggage-crew dormitory cars brought the final to total to 173 cars, sufficient for establishing an entirely new transcontinental service and partially re-equippiping The Dominion. The interior design
Interior design
Interior design describes a group of various yet related projects that involve turning an interior space into an effective setting for the range of human activities are to take place there. An interior designer is someone who conducts such projects...
of these new cars was contracted to the Philadelphia architectural
Architecture
Architecture is both the process and product of planning, designing and construction. Architectural works, in the material form of buildings, are often perceived as cultural and political symbols and as works of art...
firm Harbeson, Hough, Livingston & Larson (a company known for its industrial designs on other prominent passenger trains such as the Pioneer Zephyr
Pioneer Zephyr
The Pioneer Zephyr is a diesel-powered railroad train formed of railroad cars permanently articulated together with Jacobs bogies, built by the Budd Company in 1934 for the Chicago, Burlington and Quincy Railroad , commonly known as the Burlington...
), and the resulting furnishings and pastel-shaded colour schemes were widely acclaimed. After deciding to name the Park series dome cars after famous Canadian parks, leading Canadian artist
Artist
An artist is a person engaged in one or more of any of a broad spectrum of activities related to creating art, practicing the arts and/or demonstrating an art. The common usage in both everyday speech and academic discourse is a practitioner in the visual arts only...
s, including members of the Group of Seven
Group of Seven (artists)
The Group of Seven, sometimes known as the Algonquin school, were a group of Canadian landscape painters from 1920-1933, originally consisting of Franklin Carmichael , Lawren Harris , A. Y. Jackson , Franz Johnston , Arthur Lismer , J. E. H. MacDonald , and Frederick Varley...
, were commissioned to paint suitable murals for these cars. When the decision was made to add budget sleeping cars, the Budd order was supplemented by 22 existing heavyweight sleepers that CPR refurbished in its own Angus Shops, each fitted out with Budd-style stainless steel cladding. To complement the new rolling stock, the CPR ordered General Motors Diesel
General Motors Diesel
General Motors Diesel was a Canadian railway diesel locomotive manufacturer.-History:General Motors Diesel, Limited, was created in 1949 as the Canadian subsidiary of the Electro Motive Division of General Motors located in the United States...
FP9
EMD FP9
The EMD FP9 was a , B-B dual-service passenger and freight-hauling diesel locomotive produced between February 1954 and December 1959 by General Motors Electro-Motive Division, and General Motors Diesel. Final assembly was at GM-EMD's La Grange, Illinois plant, except for Canadian orders, which...
locomotives to supplement an existing fleet of FP7
EMD FP7
The EMD FP7 was a , B-B dual-service passenger and freight-hauling diesel locomotive produced between June 1949 and December 1953 by General Motors' Electro-Motive Division and General Motors Diesel. Final assembly was at GM-EMD's La Grange, Illinois plant, excepting locomotives destined for...
s. Although these F-units
EMD F-unit
EMD F-units were a line of Diesel-electric locomotives produced between November 1939 and November 1960 by General Motors Electro-Motive Division and General Motors-Diesel Division. Final assembly for all F-units was at the GM-EMD plant at La Grange, Illinois and the GMDD plant in London, Ontario...
remained the preferred power for the train, it was occasionally pulled by a variety of motive power, including Montreal Locomotive Works
Montreal Locomotive Works
Montreal Locomotive Works was a Canadian railway locomotive manufacturer which existed under several names from 1883–1985, producing both steam and diesel locomotives. For a number of years it was a subsidiary of the American Locomotive Company...
FPA-2s, and, as late as 1959, steam locomotive
Steam locomotive
A steam locomotive is a railway locomotive that produces its power through a steam engine. These locomotives are fueled by burning some combustible material, usually coal, wood or oil, to produce steam in a boiler, which drives the steam engine...
s.
CPR christened their new flagship
Flagship
A flagship is a vessel used by the commanding officer of a group of naval ships, reflecting the custom of its commander, characteristically a flag officer, flying a distinguishing flag...
train The Canadian and service began on April 24, 1955. Although CPR competitor Canadian National Railway
Canadian National Railway
The Canadian National Railway Company is a Canadian Class I railway headquartered in Montreal, Quebec. CN's slogan is "North America's Railroad"....
s began its own new transcontinental service, the Super Continental
Super Continental
The Super Continental was a transcontinental Canadian passenger train operated originally by the Canadian National Railway beginning in 1955 and subsequently by Via Rail from 1977 until its cancellation in 1981. Service was restored in 1985 but was again eliminated in 1990...
, on the same day, CPR was able to boast honestly that The Canadian was "The first and only all-stainless steel 'dome' stream-liner in Canada" — it was not until 1964 that the CNR acquired dome cars.
CPR operated the train in two sections east of Sudbury, Ontario
Ontario
Ontario is a province of Canada, located in east-central Canada. It is Canada's most populous province and second largest in total area. It is home to the nation's most populous city, Toronto, and the nation's capital, Ottawa....
. The section operating between Montreal and Vancouver (also serving Ottawa) was known as train 1 westbound and train 2 eastbound, with a connecting section to or from Toronto splitting or joining at Sudbury (this section was known as train 11 westbound, and train 12 eastbound). Matching its streamlined appearance, The Canadian's 71 hour westbound schedule was 16 hours faster than that of The Dominion.
Although initially successful, passenger train ridership began to decline in Canada during the 1960s. Facing competition from airlines and increased automobile usage following construction of the Trans-Canada Highway
Trans-Canada Highway
The Trans-Canada Highway is a federal-provincial highway system that joins the ten provinces of Canada. It is, along with the Trans-Siberian Highway and Australia's Highway 1, one of the world's longest national highways, with the main route spanning 8,030 km...
, the CPR cancelled The Dominion in 1966, and petitioned the government
Government of Canada
The Government of Canada, formally Her Majesty's Government, is the system whereby the federation of Canada is administered by a common authority; in Canadian English, the term can mean either the collective set of institutions or specifically the Queen-in-Council...
to discontinue The Canadian in 1970. Although this petition was denied, CPR during the 1970s attempted to remove itself from the passenger service market. The Canadian was operated at reduced levels, with the government subsidizing 80 percent of its losses.

Via Rail
The federal Crown corporation Via Rail Canada formally assumed responsibility for CPR's passenger services on October 29, 1978, although the Via identity was not assumed by the trains themselves until the following summer. Following the takeover by Via, the Canadian became the company's premier transcontinental train, and initially operated over its old CPR route. It was supplemented by the former CN Super Continental, which operated over the parallel, but more northerly, CN route. The Canadian continued to be operated in two sections east of Sudbury and provided daily service west to Vancouver and east to Toronto and Montreal.In the aftermath of the deep budget
Canadian federal budget
In Canada, federal budgets are presented annually by the Government of Canada to identify planned government spending, expected government revenue, and forecast economic conditions for the upcoming year....
cuts made to Via Rail on January 15, 1990, the Super Continental service was abolished and the Canadian was moved from the CPR route to the Super Continental's CN route. This maintained transcontinental service and allowed Via to operate its government-mandated service to small communities along the line. Service was also reduced to 3 days per week. Today, Via Rail continues to operate the Canadian using the CN route with rebuilt ex-CPR Budd passenger equipment.

