
Thermal ionization
Encyclopedia
In thermal ionization, also referred to as surface ionization, chemically-purified material loaded onto a filament which is then heated to cause some of the material to be ion
ized as it boils off the hot filament. Filaments are generally flat pieces of metal around 1-2mm wide, 0.1mm thick, bent into an upside-down U shape and welded to steel posts that supply a current.
of the filament substrate and the ionization energy
of the element
.
This is summarised in the Saha-Langmuir
equation:

, where the sample is ionized under vacuum. The ions being produced at the filament are focussed into an ion beam and then passed through a magnetic field to separate them by mass. The relative abundances of different isotopes can then be measured, yielding isotope ratios.
When these isotope ratios are measured by TIMS, mass-dependent fractionation occurs as species are emitted by the hot filament. Fractionation occurs due to the excitation of the sample and therefore must be corrected for accurate measurement of the isotope ratio.
There are several advantages of the TIMS method. It has a simple design, is less expensive than other mass spectrometers, and produces stable ion emissions. It requires a stable power supply, and is suitable for species with a low ionization energy, such as Strontium
(Sr), and Lead
(Pb).
The disadvantages of this method stem from the maximum temperature achieved in thermal ionization. The hot filament reaches a temperature of less than 2500 degrees Celsius, leading to the inability to create atomic ions of species with a high ionization energy, such as Osmium
(Os), and Tungsten
(Hf-W). Although the TIMS method can create molecular ions instead in this case, species with high ionization energy can be analyzed more effectively with MC-ICP-MS.
Ion
An ion is an atom or molecule in which the total number of electrons is not equal to the total number of protons, giving it a net positive or negative electrical charge. The name was given by physicist Michael Faraday for the substances that allow a current to pass between electrodes in a...
ized as it boils off the hot filament. Filaments are generally flat pieces of metal around 1-2mm wide, 0.1mm thick, bent into an upside-down U shape and welded to steel posts that supply a current.
Saha-Langmuir equation
The likelihood of ionisation is a function of the filament temperature, the work functionWork function
In solid-state physics, the work function is the minimum energy needed to remove an electron from a solid to a point immediately outside the solid surface...
of the filament substrate and the ionization energy
Ionization energy
The ionization energy of a chemical species, i.e. an atom or molecule, is the energy required to remove an electron from the species to a practically infinite distance. Large atoms or molecules have a low ionization energy, while small molecules tend to have higher ionization energies.The property...
of the element
Chemical element
A chemical element is a pure chemical substance consisting of one type of atom distinguished by its atomic number, which is the number of protons in its nucleus. Familiar examples of elements include carbon, oxygen, aluminum, iron, copper, gold, mercury, and lead.As of November 2011, 118 elements...
.
This is summarised in the Saha-Langmuir
Irving Langmuir
Irving Langmuir was an American chemist and physicist. His most noted publication was the famous 1919 article "The Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms and Molecules" in which, building on Gilbert N. Lewis's cubical atom theory and Walther Kossel's chemical bonding theory, he outlined his...
equation:

-
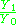 = ion to neutral ratio
= ion to neutral ratio
-
 = statistical weights of ion and neutral states
= statistical weights of ion and neutral states
-
 = surface work functionWork functionIn solid-state physics, the work function is the minimum energy needed to remove an electron from a solid to a point immediately outside the solid surface...
= surface work functionWork functionIn solid-state physics, the work function is the minimum energy needed to remove an electron from a solid to a point immediately outside the solid surface...
-
- IP = element ionization potentialIonization potentialThe ionization energy of a chemical species, i.e. an atom or molecule, is the energy required to remove an electron from the species to a practically infinite distance. Large atoms or molecules have a low ionization energy, while small molecules tend to have higher ionization energies.The property...
- IP = element ionization potential
-
- k = Boltzmann's constant
-
- T = surface temperature
Thermal ionization mass spectrometry
One application of thermal ionization is thermal ionization mass spectrometry (TIMS). This method is widely used in radiometric datingRadiometric dating
Radiometric dating is a technique used to date materials such as rocks, usually based on a comparison between the observed abundance of a naturally occurring radioactive isotope and its decay products, using known decay rates...
, where the sample is ionized under vacuum. The ions being produced at the filament are focussed into an ion beam and then passed through a magnetic field to separate them by mass. The relative abundances of different isotopes can then be measured, yielding isotope ratios.
When these isotope ratios are measured by TIMS, mass-dependent fractionation occurs as species are emitted by the hot filament. Fractionation occurs due to the excitation of the sample and therefore must be corrected for accurate measurement of the isotope ratio.
There are several advantages of the TIMS method. It has a simple design, is less expensive than other mass spectrometers, and produces stable ion emissions. It requires a stable power supply, and is suitable for species with a low ionization energy, such as Strontium
Strontium
Strontium is a chemical element with the symbol Sr and the atomic number 38. An alkaline earth metal, strontium is a soft silver-white or yellowish metallic element that is highly reactive chemically. The metal turns yellow when exposed to air. It occurs naturally in the minerals celestine and...
(Sr), and Lead
Lead
Lead is a main-group element in the carbon group with the symbol Pb and atomic number 82. Lead is a soft, malleable poor metal. It is also counted as one of the heavy metals. Metallic lead has a bluish-white color after being freshly cut, but it soon tarnishes to a dull grayish color when exposed...
(Pb).
The disadvantages of this method stem from the maximum temperature achieved in thermal ionization. The hot filament reaches a temperature of less than 2500 degrees Celsius, leading to the inability to create atomic ions of species with a high ionization energy, such as Osmium
Osmium
Osmium is a chemical element with the symbol Os and atomic number 76. Osmium is a hard, brittle, blue-gray or blue-blacktransition metal in the platinum family, and is the densest natural element. Osmium is twice as dense as lead. The density of osmium is , slightly greater than that of iridium,...
(Os), and Tungsten
Tungsten
Tungsten , also known as wolfram , is a chemical element with the chemical symbol W and atomic number 74.A hard, rare metal under standard conditions when uncombined, tungsten is found naturally on Earth only in chemical compounds. It was identified as a new element in 1781, and first isolated as...
(Hf-W). Although the TIMS method can create molecular ions instead in this case, species with high ionization energy can be analyzed more effectively with MC-ICP-MS.

