Transistor models
Encyclopedia
Transistor
s are simple devices with complicated behavior. In order to ensure the reliable operation of circuits employing transistors, it is necessary to scientifically model
the physical phenomena observed in their operation using transistor models. There exists a variety of different models that range in complexity and in purpose. Transistor models divide into two major groups: models for device design and models for circuit design.
, impurity diffusion
, oxide growth
, annealing, and etching
affect device behavior. Process models
simulate the manufacturing steps and provide a microscopic description of device "geometry" to the device simulator
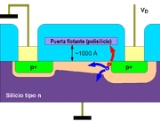
. By "geometry" is meant not only readily identified geometrical features such as whether the gate is planar or wrap-around, or whether the source and drain are raised or recessed (see Figure 1 for a memory device with some unusual modeling challenges related to charging the floating gate by an avalanche process), but also details inside the structure, such as the doping profiles after completion of device processing.
 With this information about what the device looks like, the device simulator models the physical processes taking place in the device to determine its electrical behavior in a variety of circumstances: DC current-voltage behavior, transient behavior (both large-signal and small-signal), dependence on device layout (long and narrow versus short and wide, or interdigitated versus rectangular, or isolated versus proximate to other devices). These simulations tell the device designer whether the device process will produce devices with the electrical behavior needed by the circuit designer, and is used to inform the process designer about any necessary process improvements. Once the process gets close to manufacture, the predicted device characteristics are compared with measurement on test devices to check that the process and device models are working adequately.
With this information about what the device looks like, the device simulator models the physical processes taking place in the device to determine its electrical behavior in a variety of circumstances: DC current-voltage behavior, transient behavior (both large-signal and small-signal), dependence on device layout (long and narrow versus short and wide, or interdigitated versus rectangular, or isolated versus proximate to other devices). These simulations tell the device designer whether the device process will produce devices with the electrical behavior needed by the circuit designer, and is used to inform the process designer about any necessary process improvements. Once the process gets close to manufacture, the predicted device characteristics are compared with measurement on test devices to check that the process and device models are working adequately.
Although long ago the device behavior modeled in this way was very simple - mainly drift plus diffusion in simple geometries - today many more processes must be modeled at a microscopic level; for example, leakage currents in junctions and oxides, complex transport of carriers including velocity saturation
and ballistic transport, quantum mechanical effects, use of multiple materials (for example, Si-SiGe devices, and stacks of different dielectrics) and even the statistical effects due to the probabilistic nature of ion placement and carrier transport inside the device. Several times a year the technology changes and simulations have to be repeated. The models may require change to reflect new physical effects, or to provide greater accuracy. The maintenance and improvement of these models is a business in itself.
These models are very computer intensive, involving detailed spatial and temporal solutions of coupled partial differential equations on three-dimensional grids inside the device.
Such models are slow to run and provide detail not needed for circuit design. Therefore, faster transistor models oriented toward circuit parameters are used for circuit design.
such as SPICE
use models to predict the behavior of a design. Most design work is related to integrated circuit design
s which have a very large tooling cost, primarily for the photomask
s used to create the devices, and there is a large economic incentive to get the design working without any iterations. Complete and accurate models allow a large percentage of designs to work the first time.
Modern circuits are usually very complex. The performance of such circuits is difficult to predict without accurate computer models, including but not limited to models of the devices used. The device models include effects of transistor layout: width, length, interdigitation, proximity to other devices; transient and DC current-voltage characteristic
s; parasitic device capacitance, resistance, and inductance; time delays; and temperature effects; to name a few items.
, or large signal transistor models fall into three main types:
The use of nonlinear models, which describe the entire operating area of a transistor, is required for digital designs, for circuits that operate in a large-signal regime such as power amplifiers and mixers
, and for the large-signal simulation of any circuit, for example, for stability or distortion analysis.
Nonlinear models are used with a computer simulation program, such as SPICE
. The models in SPICE are a hybrid of physical and empirical models, and such models are incomplete unless they include specification of how parameter values are to be extracted, especially as "unrealistic" (that is, unphysical) values can be made to fit the measured data without such a prescription. An incorrect set of fitting parameters results in wild predictions for devices that were not part of the originally fitted data set.
Large-signal computer models for devices continually evolve to keep up with changes in technology. To attempt standardization of model parameters used in different simulators, an industry working group was formed, the Compact Model Council
, to choose, maintain and promote the use of standard models. An elusive goal in such modeling is prediction of how circuits using the next generation of devices should work, to identify before the next step which direction the technology should take, and have models ready beforehand.
models are used to evaluate stability
, gain
, noise
and bandwidth, both in the conceptual stages of circuit design (to decide between alternative design ideas before computer simulation is warranted) and using computers. A small-signal model is generated by taking derivatives of the current-voltage curves about a bias point or Q-point. As long as the signal is small relative to the nonlinearity of the device, the derivatives do not vary significantly, and can be treated as standard linear circuit elements.
A big advantage of small signal models is they can be solved directly, while large signal nonlinear models are generally solved iteratively, with possible convergence or stability issues. By simplification to a linear model, the whole apparatus for solving linear equations becomes available, for example, simultaneous equations
, determinant
s, and matrix theory (often studied as part of linear algebra
), especially Cramer's rule
. Another advantage is that a linear model is easier to think about, and helps to organize thought.
, input impedance
, and output impedance
are components in its small-signal model.
Parameters used in small-signal circuits (two ports) adopt names related to the names of these circuits such as
These parameters all can be evaluated using measured scattering parameter
data. Scattering parameters, or S parameters, can be measured for a transistor at a given bias point with a vector network analyzer.
Transistor
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to amplify and switch electronic signals and power. It is composed of a semiconductor material with at least three terminals for connection to an external circuit. A voltage or current applied to one pair of the transistor's terminals changes the current...
s are simple devices with complicated behavior. In order to ensure the reliable operation of circuits employing transistors, it is necessary to scientifically model
Scientific modelling
Scientific modelling is the process of generating abstract, conceptual, graphical and/or mathematical models. Science offers a growing collection of methods, techniques and theory about all kinds of specialized scientific modelling...
the physical phenomena observed in their operation using transistor models. There exists a variety of different models that range in complexity and in purpose. Transistor models divide into two major groups: models for device design and models for circuit design.
Models for device design
The modern transistor has an internal structure that exploits complex physical mechanisms. Device design requires a detailed understanding of how device manufacturing processes such as ion implantationIon implantation
Ion implantation is a materials engineering process by which ions of a material are accelerated in an electrical field and impacted into another solid. This process is used to change the physical, chemical, or electrical properties of the solid...
, impurity diffusion
Atomic diffusion
Atomic diffusion is a diffusion process whereby the random thermally-activated movement of atoms in a solid results in the net transport of atoms. For example, helium atoms inside a balloon can diffuse through the wall of the balloon and escape, resulting in the balloon slowly deflating. Other air...
, oxide growth
Thermal oxidation
In microfabrication, thermal oxidation is a way to produce a thin layer of oxide on the surface of a wafer. The technique forces an oxidizing agent to diffuse into the wafer at high temperature and react with it. The rate of oxide growth is often predicted by the Deal-Grove model...
, annealing, and etching
Etching (microfabrication)
Etching is used in microfabrication to chemically remove layers from the surface of a wafer during manufacturing. Etching is a critically important process module, and every wafer undergoes many etching steps before it is complete....
affect device behavior. Process models
Semiconductor process simulation
Semiconductor process simulation is the modeling of the fabrication of semiconductor devices such as transistors. It is a branch of electronic design automation, and part of a sub-field known as technology CAD, or TCAD....
simulate the manufacturing steps and provide a microscopic description of device "geometry" to the device simulator
Semiconductor device modeling
Semiconductor device modeling creates models for the behavior of the electrical devices based on fundamental physics, such as the doping profiles of the devices. It may also include the creation of compact models , which try to capture the electrical behavior of such devices but do not generally...
. By "geometry" is meant not only readily identified geometrical features such as whether the gate is planar or wrap-around, or whether the source and drain are raised or recessed (see Figure 1 for a memory device with some unusual modeling challenges related to charging the floating gate by an avalanche process), but also details inside the structure, such as the doping profiles after completion of device processing.

Although long ago the device behavior modeled in this way was very simple - mainly drift plus diffusion in simple geometries - today many more processes must be modeled at a microscopic level; for example, leakage currents in junctions and oxides, complex transport of carriers including velocity saturation
Velocity saturation
In semiconductors, when a strong enough electric field is applied, the carrier velocity in the semiconductor reaches a maximum value, saturation velocity. When this happens, the semiconductor is said to be in a state of velocity saturation...
and ballistic transport, quantum mechanical effects, use of multiple materials (for example, Si-SiGe devices, and stacks of different dielectrics) and even the statistical effects due to the probabilistic nature of ion placement and carrier transport inside the device. Several times a year the technology changes and simulations have to be repeated. The models may require change to reflect new physical effects, or to provide greater accuracy. The maintenance and improvement of these models is a business in itself.
These models are very computer intensive, involving detailed spatial and temporal solutions of coupled partial differential equations on three-dimensional grids inside the device.
Such models are slow to run and provide detail not needed for circuit design. Therefore, faster transistor models oriented toward circuit parameters are used for circuit design.
Models for circuit design (compact models)
Transistor models are used for almost all modern electronic design work. Analog circuit simulatorsElectronic circuit simulation
Electronic circuit simulation uses mathematical models to replicate the behavior of an actual electronic device or circuit.Simulation software allows for modeling of circuit operation and is an invaluable analysis tool...
such as SPICE
SPICE
SPICE is a general-purpose, open source analog electronic circuit simulator.It is a powerful program that is used in integrated circuit and board-level design to check the integrity of circuit designs and to predict circuit behavior.- Introduction :Unlike board-level designs composed of discrete...
use models to predict the behavior of a design. Most design work is related to integrated circuit design
Integrated circuit design
Integrated circuit design, or IC design, is a subset of electrical engineering and computer engineering, encompassing the particular logic and circuit design techniques required to design integrated circuits, or ICs...
s which have a very large tooling cost, primarily for the photomask
Photomask
A photomask is an opaque plate with holes or transparencies that allow light to shine through in a defined pattern. They are commonly used in photolithography.-Overview:...
s used to create the devices, and there is a large economic incentive to get the design working without any iterations. Complete and accurate models allow a large percentage of designs to work the first time.
Modern circuits are usually very complex. The performance of such circuits is difficult to predict without accurate computer models, including but not limited to models of the devices used. The device models include effects of transistor layout: width, length, interdigitation, proximity to other devices; transient and DC current-voltage characteristic
Current-voltage characteristic
A current–voltage characteristic is a relationship, typically represented as a chart or graph, between an electric current and a corresponding voltage, or potential difference.-In electronics:...
s; parasitic device capacitance, resistance, and inductance; time delays; and temperature effects; to name a few items.
Large-signal nonlinear models
NonlinearNonlinearity
In mathematics, a nonlinear system is one that does not satisfy the superposition principle, or one whose output is not directly proportional to its input; a linear system fulfills these conditions. In other words, a nonlinear system is any problem where the variable to be solved for cannot be...
, or large signal transistor models fall into three main types:
Physical models
- These are models based upon device physicsSemiconductor device modelingSemiconductor device modeling creates models for the behavior of the electrical devices based on fundamental physics, such as the doping profiles of the devices. It may also include the creation of compact models , which try to capture the electrical behavior of such devices but do not generally...
, based upon approximate modeling of physical phenomena within a transistor. Parameters within these models are based upon physical properties such as oxide thicknesses, substrate doping concentrations, carrier mobility, etc. In the past these models were used extensively, but the complexity of modern devices makes them inadequate for quantitative design. Nonetheless, they find a place in hand analysis (that is, at the conceptual stage of circuit design), for example, for simplified estimates of signal-swing limitations.
Empirical models
- This type of model is entirely based upon curve fittingCurve fittingCurve fitting is the process of constructing a curve, or mathematical function, that has the best fit to a series of data points, possibly subject to constraints. Curve fitting can involve either interpolation, where an exact fit to the data is required, or smoothing, in which a "smooth" function...
, using whatever functions and parameter values most adequately fit measured data to enable simulation of transistor operation. Unlike a physical model, the parameters in an empirical model need have no fundamental basis, and will depend on the fitting procedure used to find them. The fitting procedure is key to success of these models if they are to be used to extrapolate to designs lying outside the range of data to which the models were originally fitted. Such extrapolation is a hope of such models, but is not fully realized so far.
Tabular models
- The third type of model is a form of look-up table containing a large number of values for common device parameters such as drain current and device parasitics. These values are indexed in reference to their corresponding bias voltage combinations. Thus, model accuracy is increased by inclusion of additional data points within the table. The chief advantage of this type of model is decreased simulation time (see article look-up table for discussion of the computational advantages of look-up tables). A limitation of these models is that they work best for designs that use devices within the table (interpolationInterpolationIn the mathematical field of numerical analysis, interpolation is a method of constructing new data points within the range of a discrete set of known data points....
) and are unreliable for devices outside the table (extrapolationExtrapolationIn mathematics, extrapolation is the process of constructing new data points. It is similar to the process of interpolation, which constructs new points between known points, but the results of extrapolations are often less meaningful, and are subject to greater uncertainty. It may also mean...
).
The use of nonlinear models, which describe the entire operating area of a transistor, is required for digital designs, for circuits that operate in a large-signal regime such as power amplifiers and mixers
Electronic mixer
An electronic mixer is a device that combines two or more electrical or electronic signals into one or two composite output signals. There are two basic circuits that both use the term mixer, but they are very different types of circuits: additive mixers and multiplying mixers...
, and for the large-signal simulation of any circuit, for example, for stability or distortion analysis.
Nonlinear models are used with a computer simulation program, such as SPICE
SPICE
SPICE is a general-purpose, open source analog electronic circuit simulator.It is a powerful program that is used in integrated circuit and board-level design to check the integrity of circuit designs and to predict circuit behavior.- Introduction :Unlike board-level designs composed of discrete...
. The models in SPICE are a hybrid of physical and empirical models, and such models are incomplete unless they include specification of how parameter values are to be extracted, especially as "unrealistic" (that is, unphysical) values can be made to fit the measured data without such a prescription. An incorrect set of fitting parameters results in wild predictions for devices that were not part of the originally fitted data set.
Large-signal computer models for devices continually evolve to keep up with changes in technology. To attempt standardization of model parameters used in different simulators, an industry working group was formed, the Compact Model Council
Compact Model Council
The Compact Model Council is a working group in the Electronic Design Automation industry formed to choose, maintain and promote the use of standard models. Commercial and industrial analog simulators need to add device models as technology advances and earlier models become inaccurate...
, to choose, maintain and promote the use of standard models. An elusive goal in such modeling is prediction of how circuits using the next generation of devices should work, to identify before the next step which direction the technology should take, and have models ready beforehand.
Small-signal linear models
Small-signal or linearLinear system
A linear system is a mathematical model of a system based on the use of a linear operator.Linear systems typically exhibit features and properties that are much simpler than the general, nonlinear case....
models are used to evaluate stability
BIBO stability
In electrical engineering, specifically signal processing and control theory, BIBO stability is a form of stability for linear signals and systems that take inputs. BIBO stands for Bounded-Input Bounded-Output...
, gain
Gain
In electronics, gain is a measure of the ability of a circuit to increase the power or amplitude of a signal from the input to the output. It is usually defined as the mean ratio of the signal output of a system to the signal input of the same system. It may also be defined on a logarithmic scale,...
, noise
Electronic noise
Electronic noise is a random fluctuation in an electrical signal, a characteristic of all electronic circuits. Noise generated by electronic devices varies greatly, as it can be produced by several different effects...
and bandwidth, both in the conceptual stages of circuit design (to decide between alternative design ideas before computer simulation is warranted) and using computers. A small-signal model is generated by taking derivatives of the current-voltage curves about a bias point or Q-point. As long as the signal is small relative to the nonlinearity of the device, the derivatives do not vary significantly, and can be treated as standard linear circuit elements.
A big advantage of small signal models is they can be solved directly, while large signal nonlinear models are generally solved iteratively, with possible convergence or stability issues. By simplification to a linear model, the whole apparatus for solving linear equations becomes available, for example, simultaneous equations
Simultaneous equations
In mathematics, simultaneous equations are a set of equations containing multiple variables. This set is often referred to as a system of equations. A solution to a system of equations is a particular specification of the values of all variables that simultaneously satisfies all of the equations...
, determinant
Determinant
In linear algebra, the determinant is a value associated with a square matrix. It can be computed from the entries of the matrix by a specific arithmetic expression, while other ways to determine its value exist as well...
s, and matrix theory (often studied as part of linear algebra
Linear algebra
Linear algebra is a branch of mathematics that studies vector spaces, also called linear spaces, along with linear functions that input one vector and output another. Such functions are called linear maps and can be represented by matrices if a basis is given. Thus matrix theory is often...
), especially Cramer's rule
Cramer's rule
In linear algebra, Cramer's rule is a theorem, which gives an expression for the solution of a system of linear equations with as many equations as unknowns, valid in those cases where there is a unique solution...
. Another advantage is that a linear model is easier to think about, and helps to organize thought.
Small-signal parameters
A transistor’s parameters represent its electrical properties. Engineers employ transistor parameters in production-line testing and in circuit design. A group of a transistor’s parameters sufficient to predict circuit gainGain
In electronics, gain is a measure of the ability of a circuit to increase the power or amplitude of a signal from the input to the output. It is usually defined as the mean ratio of the signal output of a system to the signal input of the same system. It may also be defined on a logarithmic scale,...
, input impedance
Electrical impedance
Electrical impedance, or simply impedance, is the measure of the opposition that an electrical circuit presents to the passage of a current when a voltage is applied. In quantitative terms, it is the complex ratio of the voltage to the current in an alternating current circuit...
, and output impedance
Electrical impedance
Electrical impedance, or simply impedance, is the measure of the opposition that an electrical circuit presents to the passage of a current when a voltage is applied. In quantitative terms, it is the complex ratio of the voltage to the current in an alternating current circuit...
are components in its small-signal model.
Parameters used in small-signal circuits (two ports) adopt names related to the names of these circuits such as
- Transmission parameters (T-parameters),
- Hybrid-parameters (h-parameters),
- Impedance parameters (z-parameters),
- Admittance parameters (y-parameters), and
- Scattering parameters (S-parameters).
These parameters all can be evaluated using measured scattering parameter
Scattering parameters
Scattering parameters or S-parameters describe the electrical behavior of linear electrical networks when undergoing various steady state stimuli by electrical signals....
data. Scattering parameters, or S parameters, can be measured for a transistor at a given bias point with a vector network analyzer.
Popular models
- Gummel–Poon modelGummel–Poon modelThe Gummel–Poon model is a model of the bipolar junction transistor. It was first described in a paper published by Hermann Gummel and H. C. Poon at Bell Labs in 1970....
- Ebers–Moll model
- BSIM3 (see BSIMBSIMBSIM refers to a family of MOSFET transistor models for integrated circuit design. Accurate transistor models are needed for electronic circuit simulation, which in turn is needed for integrated circuit design...
) - BSIM4
- BSIMSOI
- EKV MOSFET ModelEKV MOSFET ModelThe EKV Mosfet Model is a mathematical model of metal-oxide semiconductor field-effect transistors which is intended for circuit simulation and analog circuit design. It was developed by C. C. Enz, F. Krummenacher and E. A. Vittoz around 1995 based in part on work they had done in the 1980s...
(http://ekv.epfl.ch/its web site at EPFLÉcole polytechnique fédérale de LausanneThe École polytechnique fédérale de Lausanne is one of the two Swiss Federal Institutes of Technology and is located in Lausanne, Switzerland.The school was founded by the Swiss Federal Government with the stated mission to:...
]) - PSP
- HICUM
- MEXTRAM.
- Hybrid-pi modelHybrid-pi modelThe hybrid-pi model is a popular circuit model used for analyzing the small signal behavior of bipolar junction and field effect transistors. The model can be quite accurate for low-frequency circuits and can easily be adapted for higher frequency circuits with the addition of appropriate...
- H-parameter model
External links
- Agilent EEsof EDA, IC-CAP Parameter Extraction and Device Modeling Software http://eesof.tm.agilent.com/products/iccap_main.html
See also
- Bipolar junction transistor#Theory and modeling
- S-parameters
- Small-signal model
- SPICESPICESPICE is a general-purpose, open source analog electronic circuit simulator.It is a powerful program that is used in integrated circuit and board-level design to check the integrity of circuit designs and to predict circuit behavior.- Introduction :Unlike board-level designs composed of discrete...
- Two-port networkTwo-port networkA two-port network is an electrical circuit or device with two pairs of terminals connected together internally by an electrical network...
- Safe operating areaSafe operating areaFor power semiconductor devices , the safe operating area is defined as the voltage and current conditions over which the device can be expected to operate without self-damage....
- Electronic design automationElectronic design automationElectronic design automation is a category of software tools for designing electronic systems such as printed circuit boards and integrated circuits...
- Electronic circuit simulationElectronic circuit simulationElectronic circuit simulation uses mathematical models to replicate the behavior of an actual electronic device or circuit.Simulation software allows for modeling of circuit operation and is an invaluable analysis tool...
- Semiconductor device modelingSemiconductor device modelingSemiconductor device modeling creates models for the behavior of the electrical devices based on fundamental physics, such as the doping profiles of the devices. It may also include the creation of compact models , which try to capture the electrical behavior of such devices but do not generally...

