
Ultima I
Encyclopedia
Ultima, later known as Ultima I: The First Age of Darkness or simply Ultima I, is the first game in the Ultima series of computer role-playing games. It was first published in the United States by California Pacific Computer Company
, which registered a copyright for the game on September 2, 1980 and officially released it in June 1981. Since its release, the game has been completely re-coded and ported
to many different platforms
. The 1986 re-code of Ultima is the most commonly known and available version of the game.
Ultima revolves around a quest to find and destroy the Gem of Immortality, which is being used by the evil wizard Mondain to enslave the lands of Sosaria. With the gem in his possession, he cannot be killed, and his minions roam and terrorize the countryside. The player takes on the role of 'The Stranger', an individual summoned from another world to end the rule of Mondain. The game follows the endeavors of the stranger in this task, which involves progressing through many aspects of game play, including dungeon crawling and space travel
.
The game was one of the first definitive commercial computer RPGs, and is considered an important and influential turning point for the development of the genre throughout years to come.
view, while dungeons are displayed in an isometric
, first person
design. In both scenarios the player character
is controlled with the keyboard directional arrows, and shortcut
keys are used for other commands, such as A for attack and B for board.
 Character creation
Character creation
at the start of Ultima is not unlike a simplified version of traditional pen and paper
roleplaying games. The player is presented with a number of points to distribute between various statistics
that will affect his competence in certain aspects of gameplay. For example, adding numerous points to the strength statistic will increase the potential amount of damage inflicted on a foe. Once this portion of creation has been completed satisfactorily, the player is given a choice of four races: Human, Elf
, Dwarf and Bobbit (a hobbit
-like creature). Depending on the race picked, points will be added to various statistics (e.g.: Elves are often seen as being lithe and agile, so points are added to the agility statistic). Once a race is chosen, the player is given a list of four classes to choose from, which also distribute more points to appropriate statistics. These classes are fighter
, cleric
, wizard
and thief
. The player is also asked to choose a gender
for their player character, though this is purely cosmetic.
Four other statistics are important and imperative to successful game completion. These are hit points, food
, experience point
s and coin
(gold
in the original release). Hit points determine the health of the character; the more HP the character has, the further away they are from death. They can be obtained in a variety of ways, including the acts of emerging alive from a dungeon
and of giving tribute payment to one of the eight lords of Sosaria. Food is consumed every tile that the character moves, and if the food supply drops to zero, the player will starve. Food can be bought in towns to prevent this situation occurring. Experience points are received by successfully doing battle with monsters. They determine when the character levels up; one thousand points are needed to progress to the next level. A vital item near the end of the game cannot be obtained until the player has reached the eighth level. Coin, or gold, is used to buy things in the game world, such as weapons, spells and food, and can be obtained by defeating monsters or rescuing princesses from castles.
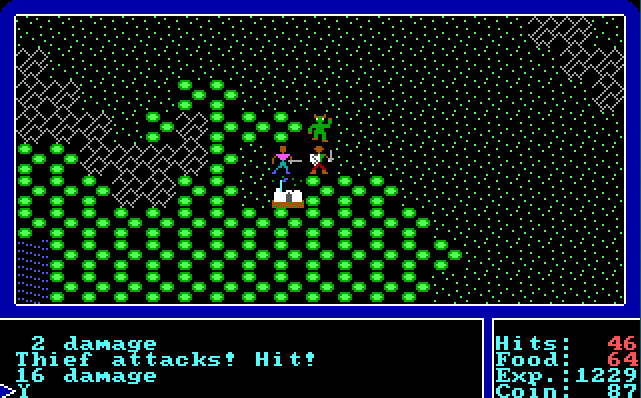
 The magic and combat systems in Ultima are simplistic. Spells are bought from shops and used as consumable items, each spell purchase having one use only. Combat is against randomly appearing enemies; it consists of each party attacking the other until one has fled or been defeated. In the original release of the game, enemies in the outdoor areas do not move around in any way but simply appear at the player's current location and immediately initiate attack; enemies in the dungeons are also random, but can move and follow the player. Buying more proficient weapons and armor improves the chances of succeeding in battle.
The magic and combat systems in Ultima are simplistic. Spells are bought from shops and used as consumable items, each spell purchase having one use only. Combat is against randomly appearing enemies; it consists of each party attacking the other until one has fled or been defeated. In the original release of the game, enemies in the outdoor areas do not move around in any way but simply appear at the player's current location and immediately initiate attack; enemies in the dungeons are also random, but can move and follow the player. Buying more proficient weapons and armor improves the chances of succeeding in battle.
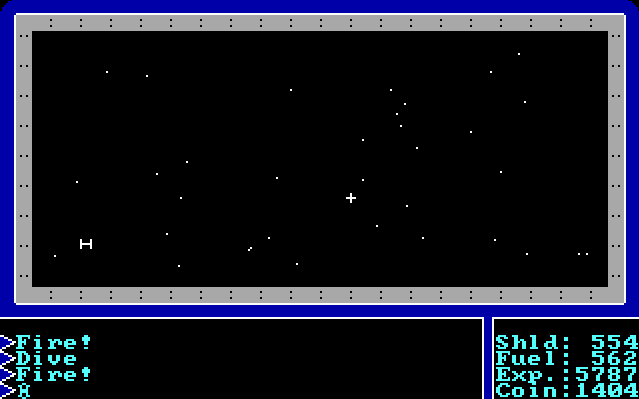
The game also sports an arcade
-like first-person space
shooter
section of gameplay, an element that only appeared in Ultima and not the subsequent games in the series. The player participates in a real-time space combat environment, confronted with enemy spaceships that they must shoot down in order to progress further along the story. Richard Garriott
says he added this just because he wanted to fill up every space there was on the disk, and do everything he possibly could.
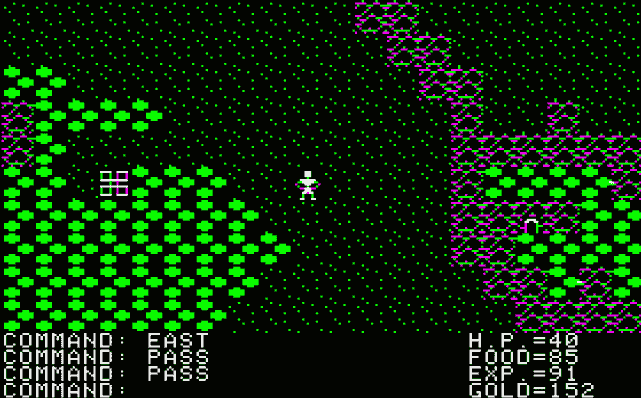
There are also a variety of towns where different goods and services can be purchased. The world map also houses many dungeons to be explored, and is populated by forests, mountain ranges, lakes and oceans. All towns are equivalent (and they all look exactly alike in the original release of the game), as are all dungeons (their maps are different, but are not designed but rather randomly created); castles differ only in the different quests that may be assigned. Due to the nature of the game's story, Sosaria is inhabited by numerous monsters and beasts that attack the player character on sight. There are also ruins and places of interest on each continent (usually in somewhat hard-to-reach places such as small islands) that the player can enter in order to receive rewards, usually in the form of a weapon or stat boost, or in order to solve quests.
The player is informed that the only way to defeat Mondain is to travel back in time and kill him before the gem of immortality is created. The majority of the game is spent searching for a time machine, and a way to activate it. Four of the lords in the game, one from each realm, hold a gem that will allow the time machine to work once all four gems have been found. In exchange for the gem, the lord will ask the player to complete a quest that involves travelling into a dungeon and killing a specific creature. Once this has been achieved, the lord will hand over his gem.
The time machine itself also needs to be found. Purchasing a space shuttle and travelling into outer space is a prerequisite of this —the PC must become a space ace, by destroying 20 enemy ships, in order to complete the game. Once this task has been completed, rescuing a princess will reveal the location of the time machine, which always appears to the north of the castle in which the princess was held prisoner. The main character will then travel back in time and face Mondain before he has completed the gem of immortality. Destroying the gem is a requirement for beating the game as well as killing the wizard himself. Once Mondain is dead, the player is transported one thousand years into the future and rewarded by Lord British.
 Richard Garriott started development on Ultima after the unexpected success of his previous game, Akalabeth
Richard Garriott started development on Ultima after the unexpected success of his previous game, Akalabeth
. Large sections of Akalabeth were used as subroutine
s within Ultima, to create the isometric dungeon sections of the game. Towns, quests, a plot and a user interface were all added to the original Akalabeth code before Ultima was completed. Development of Ultima was done during Garriott's freshman year at the University of Texas, with the help of a friend, Ken W. Arnold, he finishing it in less than a year. Ultima was coded in Applesoft BASIC
on an Apple II
computer, and used a tile-based graphics system, the first game in the genre to do so.
Unlike Akalabeth, however, the commercial sale of which was an afterthought to a hobbyist endeavour, Ultima was approached with a much more professional attitude right from the start of the project. The game was first planned to be called Ultimatum, but it was discovered that the name was already in use by a board game company, and so it was shortened to Ultima. The California Pacific Computer Company published Ultima in 1981 for the Apple II only. It sold 50,000 copies.
Sierra Online re-released Ultima for the Atari 8-bit
computers. In 1986 Origin Systems
completely re-coded the game in Assembly
and re-released it.
Because the 1986 remake was re-coded entirely in Assembly, it had significantly improved running speed and was able to handle superior graphics. Some small cosmetic changes to the content were also made, such as the addition of another castle map variant and three new city map
s, the introduction of traveling monsters in the outdoors section, and the division of the money the player has into separate "copper", "silver" and "gold" coins.
It was first released for the Apple II on December 23, 1986 as Ultima I: The First Age of Darkness. Ports for the Commodore 64
and DOS
/EGA
were also released. Many subsequent releases were made in later years, including the 1989 version for the MSX
, published only in Japan by Pony Canyon
, as well as an Apple IIGS
specific port in late 1994 by Vitesse. In 1997, the DOS/EGA version of Ultima was released by Electronic Arts
as part of the Ultima Collection.
California Pacific Computer Company
California Pacific Computer Company is a defunct software design company that published games and related software for the Apple II family of computers in the late 1970s and early 1980s...
, which registered a copyright for the game on September 2, 1980 and officially released it in June 1981. Since its release, the game has been completely re-coded and ported
Porting
In computer science, porting is the process of adapting software so that an executable program can be created for a computing environment that is different from the one for which it was originally designed...
to many different platforms
Platform (computing)
A computing platform includes some sort of hardware architecture and a software framework , where the combination allows software, particularly application software, to run...
. The 1986 re-code of Ultima is the most commonly known and available version of the game.
Ultima revolves around a quest to find and destroy the Gem of Immortality, which is being used by the evil wizard Mondain to enslave the lands of Sosaria. With the gem in his possession, he cannot be killed, and his minions roam and terrorize the countryside. The player takes on the role of 'The Stranger', an individual summoned from another world to end the rule of Mondain. The game follows the endeavors of the stranger in this task, which involves progressing through many aspects of game play, including dungeon crawling and space travel
Spaceflight
Spaceflight is the act of travelling into or through outer space. Spaceflight can occur with spacecraft which may, or may not, have humans on board. Examples of human spaceflight include the Russian Soyuz program, the U.S. Space shuttle program, as well as the ongoing International Space Station...
.
The game was one of the first definitive commercial computer RPGs, and is considered an important and influential turning point for the development of the genre throughout years to come.
Gameplay
The world of Ultima is presented in a variety of different ways. The overworld is projected in a topdown, third personThird-person shooter
Third-person shooter is a genre of 3D action games in which the player character is visible on-screen, and the gameplay consists primarily of shooting.-Definition:...
view, while dungeons are displayed in an isometric
Isometric projection
Isometric projection is a method for visually representing three-dimensional objects in two dimensions in technical and engineering drawings...
, first person
Perspective (visual)
Perspective, in context of vision and visual perception, is the way in which objects appear to the eye based on their spatial attributes; or their dimensions and the position of the eye relative to the objects...
design. In both scenarios the player character
Player character
A player character or playable character is a character in a video game or role playing game who is controlled or controllable by a player, and is typically a protagonist of the story told in the course of the game. A player character is a persona of the player who controls it. Player characters...
is controlled with the keyboard directional arrows, and shortcut
Keyboard shortcut
In computing, a keyboard shortcut is a finite set of one or more keys that invoke a software or operating system operation when triggered by the user. A meaning of term "keyboard shortcut" can vary depending on software manufacturer...
keys are used for other commands, such as A for attack and B for board.

Character creation
Character creation is the process of defining a game character or other character. Typically, a character's individual strengths and weaknesses are represented by a set of statistics. Games with a largely fictional setting may include traits such as race and class...
at the start of Ultima is not unlike a simplified version of traditional pen and paper
Role-playing game
A role-playing game is a game in which players assume the roles of characters in a fictional setting. Players take responsibility for acting out these roles within a narrative, either through literal acting, or through a process of structured decision-making or character development...
roleplaying games. The player is presented with a number of points to distribute between various statistics
Statistic (role-playing games)
A statistic in role-playing games is a piece of data which represents a particular aspect of a fictional character. That piece of data is usually a integer or, in some cases, a set of dice....
that will affect his competence in certain aspects of gameplay. For example, adding numerous points to the strength statistic will increase the potential amount of damage inflicted on a foe. Once this portion of creation has been completed satisfactorily, the player is given a choice of four races: Human, Elf
Elves in fantasy fiction and games
In many works of modern fantasy, elves are a race of semi-divine humanoid beings.-Characteristics and common features:Modern fantasy literature has revived the elves as a race of semi-divine beings of human stature who are friendly with animals. Fantasy elves are different from Norse elves and the...
, Dwarf and Bobbit (a hobbit
Hobbit
Hobbits are a fictional diminutive race who inhabit the lands of Middle-earth in J. R. R. Tolkien's fiction.Hobbits first appeared in the novel The Hobbit, in which the main protagonist, Bilbo Baggins, is the titular hobbit...
-like creature). Depending on the race picked, points will be added to various statistics (e.g.: Elves are often seen as being lithe and agile, so points are added to the agility statistic). Once a race is chosen, the player is given a list of four classes to choose from, which also distribute more points to appropriate statistics. These classes are fighter
Warrior (character class)
Warrior is a character class found in many role-playing games. This class may also be referred to as Fighter, as in Dungeons & Dragons. The class is sometimes also referred to as a Knight, although in some games this is a separate class with a more chivalric aspect...
, cleric
Cleric (character class)
The Cleric, Priest, or Bishop is a character class in Dungeons & Dragons and other fantasy role-playing games. The cleric is a healer, usually a priest and a holy warrior, originally modeled on or inspired by the Military Orders...
, wizard
Wizard (character class)
The Wizard is a type of magical character class in certain role-playing games and computer role-playing games. Wizards are considered to be spellcasters who wield powerful spells, but are often physically weak as a trade-off. Wizards are commonly confused with similar offensive spellcasting...
and thief
Thief (character class)
The Thief or Rogue is a character class in many role-playing games, including Dungeons & Dragons, Final Fantasy, World of Warcraft and many MMORPGs. Thieves are usually stealthy and dextrous characters able to disarm traps, pick locks, and perform backstabs from hiding...
. The player is also asked to choose a gender
Gender
Gender is a range of characteristics used to distinguish between males and females, particularly in the cases of men and women and the masculine and feminine attributes assigned to them. Depending on the context, the discriminating characteristics vary from sex to social role to gender identity...
for their player character, though this is purely cosmetic.
Four other statistics are important and imperative to successful game completion. These are hit points, food
Food
Food is any substance consumed to provide nutritional support for the body. It is usually of plant or animal origin, and contains essential nutrients, such as carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, or minerals...
, experience point
Experience point
An experience point is a unit of measurement used in many role-playing games and role-playing video games to quantify a player character's progression through the game...
s and coin
Coin
A coin is a piece of hard material that is standardized in weight, is produced in large quantities in order to facilitate trade, and primarily can be used as a legal tender token for commerce in the designated country, region, or territory....
(gold
Gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au and an atomic number of 79. Gold is a dense, soft, shiny, malleable and ductile metal. Pure gold has a bright yellow color and luster traditionally considered attractive, which it maintains without oxidizing in air or water. Chemically, gold is a...
in the original release). Hit points determine the health of the character; the more HP the character has, the further away they are from death. They can be obtained in a variety of ways, including the acts of emerging alive from a dungeon
Dungeon
A dungeon is a room or cell in which prisoners are held, especially underground. Dungeons are generally associated with medieval castles, though their association with torture probably belongs more to the Renaissance period...
and of giving tribute payment to one of the eight lords of Sosaria. Food is consumed every tile that the character moves, and if the food supply drops to zero, the player will starve. Food can be bought in towns to prevent this situation occurring. Experience points are received by successfully doing battle with monsters. They determine when the character levels up; one thousand points are needed to progress to the next level. A vital item near the end of the game cannot be obtained until the player has reached the eighth level. Coin, or gold, is used to buy things in the game world, such as weapons, spells and food, and can be obtained by defeating monsters or rescuing princesses from castles.

The game also sports an arcade
Arcade game
An arcade game is a coin-operated entertainment machine, usually installed in public businesses such as restaurants, bars, and amusement arcades. Most arcade games are video games, pinball machines, electro-mechanical games, redemption games, and merchandisers...
-like first-person space
Space
Space is the boundless, three-dimensional extent in which objects and events occur and have relative position and direction. Physical space is often conceived in three linear dimensions, although modern physicists usually consider it, with time, to be part of a boundless four-dimensional continuum...
shooter
Shooter game
Shooter games are a sub-genre of action game, which often test the player's speed and reaction time. It includes many subgenres that have the commonality of focusing "on the actions of the avatar using some sort of weapon. Usually this weapon is a gun, or some other long-range weapon". A common...
section of gameplay, an element that only appeared in Ultima and not the subsequent games in the series. The player participates in a real-time space combat environment, confronted with enemy spaceships that they must shoot down in order to progress further along the story. Richard Garriott
Richard Garriott
Richard Allen Garriott is a British-American video game developer and entrepreneur.He is also known as his alter egos Lord British in Ultima and General British in Tabula Rasa...
says he added this just because he wanted to fill up every space there was on the disk, and do everything he possibly could.
Setting
Ultima is set in the fictional world of Sosaria, a land broken into four different continents. The land is ruled by a total of eight different lords, two for each of the world's four land masses. The four continents contain two castles each, where quests can be obtained by the player. There are two types of quests given out in the castles—one entails visiting a certain location on the main map, the other killing a specific type of monster in the dungeons. Fulfilling the former type of quest gives stat boosts; the latter gains the player an important item needed to reach the endgame.There are also a variety of towns where different goods and services can be purchased. The world map also houses many dungeons to be explored, and is populated by forests, mountain ranges, lakes and oceans. All towns are equivalent (and they all look exactly alike in the original release of the game), as are all dungeons (their maps are different, but are not designed but rather randomly created); castles differ only in the different quests that may be assigned. Due to the nature of the game's story, Sosaria is inhabited by numerous monsters and beasts that attack the player character on sight. There are also ruins and places of interest on each continent (usually in somewhat hard-to-reach places such as small islands) that the player can enter in order to receive rewards, usually in the form of a weapon or stat boost, or in order to solve quests.
Characters
The two main characters featured in Ultima I are Mondain, the evil wizard antagonist who has induced a reign of terror over the world of Sosaria, and the protagonist, a character of the player's choosing. Character creation is open-ended and the protagonist could be anyone from an elf wizard to a human warrior. The game features the first introduction of characters such as Iolo, Shamino and Lord British, who become staples of nearly all future Ultima games.Story
The story of Ultima I revolves around the evil wizard Mondain and his rule over the kingdom of Sosaria. According to the game's back story, Mondain created an evil gem over 1000 years ago that granted him immortality. Since then, Mondain has released monsters and beasts upon the land that ravage the villages and towns of Sosaria and cause most of the nobles to bicker amongst themselves. In an effort to stop Mondain's dominion, Lord British searches for a person to bring about the wizard's end. This call is answered by the player.The player is informed that the only way to defeat Mondain is to travel back in time and kill him before the gem of immortality is created. The majority of the game is spent searching for a time machine, and a way to activate it. Four of the lords in the game, one from each realm, hold a gem that will allow the time machine to work once all four gems have been found. In exchange for the gem, the lord will ask the player to complete a quest that involves travelling into a dungeon and killing a specific creature. Once this has been achieved, the lord will hand over his gem.
The time machine itself also needs to be found. Purchasing a space shuttle and travelling into outer space is a prerequisite of this —the PC must become a space ace, by destroying 20 enemy ships, in order to complete the game. Once this task has been completed, rescuing a princess will reveal the location of the time machine, which always appears to the north of the castle in which the princess was held prisoner. The main character will then travel back in time and face Mondain before he has completed the gem of immortality. Destroying the gem is a requirement for beating the game as well as killing the wizard himself. Once Mondain is dead, the player is transported one thousand years into the future and rewarded by Lord British.
Development and release

Akalabeth
Akalabeth: World of Doom is a computer role-playing game, first released in 1979, and then published by California Pacific Computer Company for the Apple II in 1980...
. Large sections of Akalabeth were used as subroutine
Subroutine
In computer science, a subroutine is a portion of code within a larger program that performs a specific task and is relatively independent of the remaining code....
s within Ultima, to create the isometric dungeon sections of the game. Towns, quests, a plot and a user interface were all added to the original Akalabeth code before Ultima was completed. Development of Ultima was done during Garriott's freshman year at the University of Texas, with the help of a friend, Ken W. Arnold, he finishing it in less than a year. Ultima was coded in Applesoft BASIC
Applesoft BASIC
Applesoft BASIC was a dialect of Microsoft BASIC supplied with the Apple II series of computers. It superseded Integer BASIC and was the BASIC in ROM in all Apple II series computers after the original Apple II model. It was also referred to as FP because of the command used to invoke it instead...
on an Apple II
Apple II
The Apple II is an 8-bit home computer, one of the first highly successful mass-produced microcomputer products, designed primarily by Steve Wozniak, manufactured by Apple Computer and introduced in 1977...
computer, and used a tile-based graphics system, the first game in the genre to do so.
Unlike Akalabeth, however, the commercial sale of which was an afterthought to a hobbyist endeavour, Ultima was approached with a much more professional attitude right from the start of the project. The game was first planned to be called Ultimatum, but it was discovered that the name was already in use by a board game company, and so it was shortened to Ultima. The California Pacific Computer Company published Ultima in 1981 for the Apple II only. It sold 50,000 copies.
Sierra Online re-released Ultima for the Atari 8-bit
8-bit
The first widely adopted 8-bit microprocessor was the Intel 8080, being used in many hobbyist computers of the late 1970s and early 1980s, often running the CP/M operating system. The Zilog Z80 and the Motorola 6800 were also used in similar computers...
computers. In 1986 Origin Systems
Origin Systems
Origin Systems, Inc. was a computer game developer based in Austin, Texas that was active from 1983 to 2004...
completely re-coded the game in Assembly
Assembly language
An assembly language is a low-level programming language for computers, microprocessors, microcontrollers, and other programmable devices. It implements a symbolic representation of the machine codes and other constants needed to program a given CPU architecture...
and re-released it.
Because the 1986 remake was re-coded entirely in Assembly, it had significantly improved running speed and was able to handle superior graphics. Some small cosmetic changes to the content were also made, such as the addition of another castle map variant and three new city map
City map
A city map is a large-scale thematic map of a city created to enable the fastest possible orientation in an urban space. The graphic representation of objects on a city map is therefore usually greatly simplified, and reduced to generally understood symbology.Depending upon its target group or...
s, the introduction of traveling monsters in the outdoors section, and the division of the money the player has into separate "copper", "silver" and "gold" coins.
It was first released for the Apple II on December 23, 1986 as Ultima I: The First Age of Darkness. Ports for the Commodore 64
Commodore 64
The Commodore 64 is an 8-bit home computer introduced by Commodore International in January 1982.Volume production started in the spring of 1982, with machines being released on to the market in August at a price of US$595...
and DOS
DOS
DOS, short for "Disk Operating System", is an acronym for several closely related operating systems that dominated the IBM PC compatible market between 1981 and 1995, or until about 2000 if one includes the partially DOS-based Microsoft Windows versions 95, 98, and Millennium Edition.Related...
/EGA
Enhanced Graphics Adapter
The Enhanced Graphics Adapter is the IBM PC computer display standard specification which is between CGA and VGA in terms of color and space resolution. Introduced in October 1984 by IBM shortly after its new PC/AT, EGA produces a display of 16 simultaneous colors from a palette of 64 at a...
were also released. Many subsequent releases were made in later years, including the 1989 version for the MSX
MSX
MSX was the name of a standardized home computer architecture in the 1980s conceived by Kazuhiko Nishi, then Vice-president at Microsoft Japan and Director at ASCII Corporation...
, published only in Japan by Pony Canyon
Pony Canyon
is a Japanese company, established on October 1, 1966 , which publishes music, DVD and VHS videos, movies and video games. It is a subsidiary of Japanese Media Group, Fujisankei Communications Group.-History:...
, as well as an Apple IIGS
Apple IIGS
The Apple , the fifth and most powerful model in the Apple II series of personal computers produced by Apple Computer. The "GS" in the name stands for Graphics and Sound, referring to its enhanced graphics and sound capabilities, both of which greatly surpassed previous models of the line...
specific port in late 1994 by Vitesse. In 1997, the DOS/EGA version of Ultima was released by Electronic Arts
Electronic Arts
Electronic Arts, Inc. is a major American developer, marketer, publisher and distributor of video games. Founded and incorporated on May 28, 1982 by Trip Hawkins, the company was a pioneer of the early home computer games industry and was notable for promoting the designers and programmers...
as part of the Ultima Collection.

