
VIX
Encyclopedia
Ticker symbol
A stock symbol or ticker symbol is a short abbreviation used to uniquely identify publicly traded shares of a particular stock on a particular stock market. A stock symbol may consist of letters, numbers or a combination of both. "Ticker symbol" refers to the symbols that were printed on the ticker...
for the Chicago Board Options Exchange Market Volatility Index, a popular measure of the implied volatility
Implied volatility
In financial mathematics, the implied volatility of an option contract is the volatility of the price of the underlying security that is implied by the market price of the option based on an option pricing model. In other words, it is the volatility that, when used in a particular pricing model,...
of S&P 500
S&P 500
The S&P 500 is a free-float capitalization-weighted index published since 1957 of the prices of 500 large-cap common stocks actively traded in the United States. The stocks included in the S&P 500 are those of large publicly held companies that trade on either of the two largest American stock...
index options
Option (finance)
In finance, an option is a derivative financial instrument that specifies a contract between two parties for a future transaction on an asset at a reference price. The buyer of the option gains the right, but not the obligation, to engage in that transaction, while the seller incurs the...
. Often referred to as the fear index or the fear gauge, it represents one measure of the market's expectation of stock market volatility
Volatility (finance)
In finance, volatility is a measure for variation of price of a financial instrument over time. Historic volatility is derived from time series of past market prices...
over the next 30 day period. The VIX is quoted in percentage points and translates, roughly, to the expected movement in the S&P 500 index over the next 30-day period, which is then annualized. The VIX Index was developed by Prof. Robert E. Whaley in 1993 and is a registered trademark of the CBOE.
Specifications
The VIX is calculated and disseminated in real-time by the Chicago Board Options ExchangeChicago Board Options Exchange
The Chicago Board Options Exchange , located at 400 South LaSalle Street in Chicago, is the largest U.S. options exchange with annual trading volume that hovered around one billion contracts at the end of 2007...
. It is a weighted blend of prices for a range of options on the S&P 500
S&P 500
The S&P 500 is a free-float capitalization-weighted index published since 1957 of the prices of 500 large-cap common stocks actively traded in the United States. The stocks included in the S&P 500 are those of large publicly held companies that trade on either of the two largest American stock...
index. On March 26, 2004, the first-ever trading in futures on the VIX Index began on CBOE Futures Exchange (CFE).
As of February 24, 2006, it became possible to trade VIX options contracts. A few Exchange Traded Funds seek to track its performance. The formula uses a kernel
Stochastic kernel
In statistics, a stochastic kernel estimate is an estimate of the transition function of a stochastic process. Often, this is an estimate of the conditional density function obtained using kernel density estimation...
-smoothed estimator
Estimator
In statistics, an estimator is a rule for calculating an estimate of a given quantity based on observed data: thus the rule and its result are distinguished....
that takes as inputs the current market prices for all out-of-the-money calls and puts for the front month and second month expirations. The goal is to estimate the implied volatility
Implied volatility
In financial mathematics, the implied volatility of an option contract is the volatility of the price of the underlying security that is implied by the market price of the option based on an option pricing model. In other words, it is the volatility that, when used in a particular pricing model,...
of the S&P 500 index over the next 30 days.
The VIX is the square root of the par variance swap rate for a 30 day term initiated today. Note that the VIX is the volatility of a variance swap
Variance swap
A variance swap is an over-the-counter financial derivative that allows one to speculate on or hedge risks associated with the magnitude of movement, i.e. volatility, of some underlying product, like an exchange rate, interest rate, or stock index....
and not that of a volatility swap
Volatility swap
In finance, a volatility swap is a forward contract on the future realised volatility of a given underlying asset. Volatility swaps allow investors to trade the volatility of an asset directly, much as they would trade a price index....
(volatility being the square root of variance). A variance swap
Variance swap
A variance swap is an over-the-counter financial derivative that allows one to speculate on or hedge risks associated with the magnitude of movement, i.e. volatility, of some underlying product, like an exchange rate, interest rate, or stock index....
can be perfectly statically replicated through vanilla puts and calls whereas a volatility swap requires dynamic hedging. The VIX is the square-root of the risk neutral expectation of the S&P 500 variance over the next 30 calendar days. The VIX is quoted as an annualized standard deviation.
The VIX has replaced the older VXO as the preferred volatility index used by the media. VXO was a measure of implied volatility calculated using 30-day S&P 100 index at-the-money options.
Interpretation
The VIX is quoted in percentage points and translates, roughly, to the expected movement in the S&P 500 index over the next 30-day period, which is then annualized. For example, if the VIX is 15, this represents an expected annualized change of 15% over the next 30 days; thus one can infer that the index option markets expect the S&P 500 to move up or down 15%/ = 4.33% over the next 30-day period. That is, index options are priced with the assumption of a 68% likelihood (one standard deviation) that the magnitude of the S&P 500's 30-day return will be less than 4.33% (up or down).The price of call options and put options can be used to calculate implied volatility, because volatility is one of the factors used to calculate the value of these options. Higher (or lower) volatility of the underlying security
Security
Security is the degree of protection against danger, damage, loss, and crime. Security as a form of protection are structures and processes that provide or improve security as a condition. The Institute for Security and Open Methodologies in the OSSTMM 3 defines security as "a form of protection...
makes an option more (or less) valuable, because there is a greater (or smaller) probability that the option will expire in the money (i.e., with a market value above zero). Thus, a higher option price implies greater volatility, other things being equal.
Even though the VIX is quoted as a percentage rather than a dollar amount there are a number of VIX-based derivative instruments in existence, including:
- VIX futures contracts, which began trading in 2004
- exchange-listed VIX options, which began trading in February 2006.
- VIX futures based exchange-traded notes and exchange-traded fundExchange-traded fundAn exchange-traded fund is an investment fund traded on stock exchanges, much like stocks. An ETF holds assets such as stocks, commodities, or bonds, and trades close to its net asset value over the course of the trading day. Most ETFs track an index, such as the S&P 500 or MSCI EAFE...
s, such as:- S&P 500 VIX Short-Term Futures ETN and S&P 500 VIX Mid-Term Futures ETN launched by Barclays iPath in February 2009.
- S&P 500 VIX ETF launched by Source UK Services in June 2010.
- VIX Short-Term Futures ETF and VIX Mid-Term Futures ETF launched by ProShares in January 2011.
Similar indices for bonds include the MOVE, LBPX indices.
Although the VIX is often called the "fear index", a high VIX is not necessarily bearish for stocks. Instead, the VIX is a measure of market perceived volatility in either direction, including to the upside. In practical terms, when investors anticipate large upside volatility, they are unwilling to sell upside call stock options unless they receive a large premium. Option buyers will be willing to pay such high premiums only if similarly anticipating a large upside move. The resulting aggregate of increases in upside stock option call prices raises the VIX just as does the aggregate growth in downside stock put option premiums that occurs when option buyers and sellers anticipate a likely sharp move to the downside. When the market is believed as likely to soar as to plummet, writing any option that will cost the writer in the event of a sudden large move in either direction may look equally risky. Hence high VIX readings mean investors see significant risk that the market will move sharply, whether downward or upward. The highest VIX readings occur when investors anticipate that huge moves in either direction are likely. Only when investors perceive neither significant downside risk nor significant upside potential will the VIX be low.
The Black–Scholes formula uses a model of stock price dynamics to estimate how an option’s value depends on the volatility of the underlying assets.
Criticism
VIX has received the same criticism as many other volatility forecasting models: Despite its sophisticated composition, the predictive power of VIX is similar to that of plain-vanilla measures, such as simple past volatility. The body of work dedicated to volatility forecasting models is overwhelming. Thousands of academics have devoted their entire careers to publishing models that supposedly are able to forecast volatility. Some authors have published well over 40 papers on this very topic, and yet none seems to deliver any improvement over the simple standard deviation. Prof. Torben Andersen has fiercely attacked skeptics in a number of papers. In Answering the Critics: Yes, ARCH models do provide good volatility forecasts, Profs. Andersen and Bollerslev attack the work of leading researchers such as Cumby, Figlewski, Hasbrouck, Jorion among many others, arguing that they do not know how to correctly implement their models. In Answering the Skeptics: Yes, Standard Volatility Models Do Provide Accurate Forecasts, Profs. Andersen and Bollerslev again repeat their attack on those who apply Occam's RazorOccam's razor
Occam's razor, also known as Ockham's razor, and sometimes expressed in Latin as lex parsimoniae , is a principle that generally recommends from among competing hypotheses selecting the one that makes the fewest new assumptions.-Overview:The principle is often summarized as "simpler explanations...
to dismiss volatility forecasting models. It is interesting to note that while critics are publishing their papers in top journals such as Journal of Finance
Journal of Finance
The Journal of Finance is a peer-reviewed academic journal published by Wiley-Blackwell on behalf of the American Finance Association. It was established in 1946. Its current editors are Campbell R. Harvey and John R. Graham...
, Journal of Derivatives, Journal of Portfolio Management
Journal of Portfolio Management
The Journal of Portfolio Management is a quarterly academic journal covering asset allocation, performance measurement, market trends, risk management, and portfolio optimization. The journal was established in 1974 by Peter L. Bernstein. The current editor-in-chief is Frank J...
, etc. those defending their volatility forecasting models or criticizing skeptics have been unable to publish their work in journals of similar prestige, in many cases opting for leaving them unpublished, as working paper
Working paper
A working paper or work paper or workpaper may refer to:*A preliminary scientific or technical paper. Often, authors will release working papers to share ideas about a topic or to elicit feedback before submitting to a peer reviewed conference or academic journal.* Sometimes the term working paper...
s.
Besides this controversy between believers in volatility forecasting models and the large majority of skeptics, there is a contentious battle among those same believers, one claiming that his model is superior to the rest. In August 2008, Prof. Torben Andersen and Prof. Oleg Bondarenko once again surprised the academic community by claiming not only that their volatility forecasting model was superior, but that they have mathematically demonstrated that future research was futile, since no future volatility forecasting model can beat theirs.
| In an interview regarding their CIV model, Andersen and Bondarenko go as far as to assert |
Removed from this controversy, practitioners and portfolio managers seem to completely ignore or dismiss volatility forecasting models. For example, Nassim Taleb
Nassim Taleb
Nassim Nicholas Taleb is a Lebanese American essayist whose work focuses on problems of randomness and probability. His 2007 book The Black Swan was described in a review by Sunday Times as one of the twelve most influential books since World War II....
famously titled one of his Journal of Portfolio Management
Journal of Portfolio Management
The Journal of Portfolio Management is a quarterly academic journal covering asset allocation, performance measurement, market trends, risk management, and portfolio optimization. The journal was established in 1974 by Peter L. Bernstein. The current editor-in-chief is Frank J...
papers We Don't Quite Know What We are Talking About When We Talk About Volatility. Nassim Taleb
Nassim Taleb
Nassim Nicholas Taleb is a Lebanese American essayist whose work focuses on problems of randomness and probability. His 2007 book The Black Swan was described in a review by Sunday Times as one of the twelve most influential books since World War II....
gained worldwide recognition though his Black swan theory
Black swan theory
The black swan theory or theory of black swan events is a metaphor that encapsulates the concept that The event is a surprise and has a major impact...
, which argues the silliness of trying to predict the unpredictable.
History
Here is a timeline of some key events in the history of the VIX Index:- 1993 - The VIX Index was introduced in a paper by Professor Robert E. Whaley at Vanderbilt University.
- 2003 - Revised, more robust methodology for the VIX Index was introduced. The underlying index is changed from the CBOE S&P 100 Index (OEX) to the CBOE S&P 500 Index (SPX).
- 2004 - On March 26, 2004, the first-ever trading in futures on the VIX Index began on the CBOE Futures Exchange (CFE).
- 2006 - VIX options were launched in February 2006.
- 2008 - On October 24, 2008, the VIX reached an intraday high of 89.53.
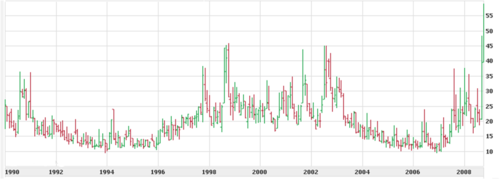
Between 1990 and October 2008, the average value of VIX was 19.04.
In 2004 and 2006, VIX Futures and VIX Options, respectively, were named Most Innovative Index Product at the Super Bowl of Indexing Conference.
See also
- VIX Charting - Implied and Historical Volatility
- Stock market bottom
- IVXIVXIVX is a volatility index providing an intraday, VIX-like measure for any of US securities and exchange traded instruments. IVX is the abbreviation of Implied Volatility Index and is a popular measure of the implied volatility of each individual stock...
- CBOE

