Variance swap
Encyclopedia
A variance swap is an over-the-counter
financial derivative that allows one to speculate on or hedge
risks associated with the magnitude of movement, i.e. volatility
, of some underlying
product, like an exchange rate
, interest rate
, or stock index.
One leg of the swap will pay an amount based upon the realised variance
of the price changes of the underlying product. Conventionally, these price changes will be daily log
returns, based upon the most commonly used closing price. The other leg of the swap will pay a fixed amount, which is the strike, quoted at the deal's inception. Thus the net payoff to the counterparties
will be the difference between these two and will be settled in cash
at the expiration of the deal, though some cash payments will likely be made along the way by one or the other counterparty to maintain agreed upon margin
.
The payoff of a variance swap is given as follows:
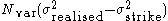
where:
The annualised realised variance is calculated based on a prespecified set of sampling points over the period. It does not always coincide with the classic statistical definition of variance as the contract terms may not subtract the mean. For example, suppose that there are n+1 sample points
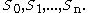
Define, for i=1 to n,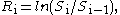 the natural log returns.
the natural log returns.
Then
where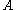 is an annualisation factor normally chosen to be approximately the number of sampling points in a year (commonly 252). It can be seen that subtracting the mean return will decrease the realised variance. If this is done, it is common to use
is an annualisation factor normally chosen to be approximately the number of sampling points in a year (commonly 252). It can be seen that subtracting the mean return will decrease the realised variance. If this is done, it is common to use  as the divisor rather than
as the divisor rather than  , corresponding to an unbiased estimate
, corresponding to an unbiased estimate
of the sample variance.
It is market practice to determine the number of contract units as follows:
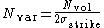
where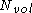 is the corresponding vega notional for a volatility swap
is the corresponding vega notional for a volatility swap
. This makes the payoff of a variance swap comparable to that of a volatility swap
, another less popular instrument used to trade volatility.
Any volatility smile
model which prices vanilla options can therefore be used to price the variance swap. For example, using the Heston model
, a closed-form solution can be derived for the fair variance swap rate. Care must be taken with the behaviour of the smile model in the wings as this can have a disproportionate effect on the price.
We can derive the payoff of a variance swap using Ito's Lemma
. We first assume that the underlying stock is described as follows:
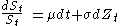
Applying Ito's formula, we get:
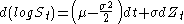
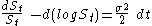
Taking integrals, the total variance is:
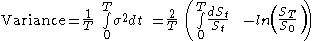
We can see that the total variance consists of a rebalanced hedge of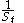 and short a log contract.
and short a log contract.
Using a static replication argument
, i.e., any twice continuously differentiable contract can be replicated using a bond, a future and infinitely many puts and calls, we can show that a short log contract position is equal to being short a futures contract and a collection of puts and calls:
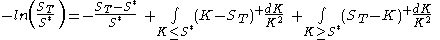
Taking expectations and setting the value of the variance swap equal to zero, we can rearrange the formula to solve for the fair variance swap strike:
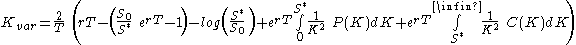
Where:
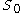 is the initial price of the underlying security,
is the initial price of the underlying security,
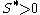 is an arbitrary cutoff,
is an arbitrary cutoff,
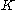 is the strike of the each option in the collection of options used.
is the strike of the each option in the collection of options used.
Often the cutoff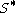 is chosen to be the current forward price
is chosen to be the current forward price 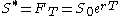 , in which case the fair variance swap strike can be written in the simpler form:
, in which case the fair variance swap strike can be written in the simpler form:
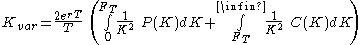
, but if one only has interest in volatility risk, this strategy will require constant delta hedging, so that direction risk of the underlying security is approximately removed. What is more, a replicating portfolio
of a variance swap would require an entire strip of options, which would be very costly to execute. Finally, one might often find the need to be regularly rolling this entire strip of options so that it remains centered around the current price of the underlying
security
.
The advantage of variance swaps is that they provide pure exposure to the volatility of the underlying price, as opposed to call and put options which may carry directional risk (delta). The profit and loss from a variance swap depends directly on the difference between realized and implied volatility.
Another aspect that some speculators may find interesting is that the quoted strike is determined by the implied volatility smile
in the options market, whereas the ultimate payout will be based upon actual realized variance. Historically, implied variance has been above realized variance, a phenomenon known as the Variance risk premium
, creating an opportunity for volatility arbitrage
, in this case known as the rolling short variance trade. For the same reason, these swaps can be used to hedge Options on Realized Variance.
, volatility swap
, correlation swap
, gamma swap, conditional variance swap
, corridor variance swap, forward-start variance swap, option on realized variance and correlation trading.
Over-the-counter (finance)
Within the derivatives markets, many products are traded through exchanges. An exchange has the benefit of facilitating liquidity and also mitigates all credit risk concerning the default of a member of the exchange. Products traded on the exchange must be well standardised to transparent trading....
financial derivative that allows one to speculate on or hedge
Hedge (finance)
A hedge is an investment position intended to offset potential losses that may be incurred by a companion investment.A hedge can be constructed from many types of financial instruments, including stocks, exchange-traded funds, insurance, forward contracts, swaps, options, many types of...
risks associated with the magnitude of movement, i.e. volatility
Volatility (finance)
In finance, volatility is a measure for variation of price of a financial instrument over time. Historic volatility is derived from time series of past market prices...
, of some underlying
Underlying
In finance, the underlying of a derivative is an asset, basket of assets, index, or even another derivative, such that the cash flows of the derivative depend on the value of this underlying...
product, like an exchange rate
Exchange rate
In finance, an exchange rate between two currencies is the rate at which one currency will be exchanged for another. It is also regarded as the value of one country’s currency in terms of another currency...
, interest rate
Interest rate
An interest rate is the rate at which interest is paid by a borrower for the use of money that they borrow from a lender. For example, a small company borrows capital from a bank to buy new assets for their business, and in return the lender receives interest at a predetermined interest rate for...
, or stock index.
One leg of the swap will pay an amount based upon the realised variance
Variance
In probability theory and statistics, the variance is a measure of how far a set of numbers is spread out. It is one of several descriptors of a probability distribution, describing how far the numbers lie from the mean . In particular, the variance is one of the moments of a distribution...
of the price changes of the underlying product. Conventionally, these price changes will be daily log
Logarithm
The logarithm of a number is the exponent by which another fixed value, the base, has to be raised to produce that number. For example, the logarithm of 1000 to base 10 is 3, because 1000 is 10 to the power 3: More generally, if x = by, then y is the logarithm of x to base b, and is written...
returns, based upon the most commonly used closing price. The other leg of the swap will pay a fixed amount, which is the strike, quoted at the deal's inception. Thus the net payoff to the counterparties
Counterparty
A counterparty is a legal and financial term. It means a party to a contract. A counterparty is usually the entity with whom one negotiates on a given agreement, and the term can refer to either party or both, depending on context....
will be the difference between these two and will be settled in cash
Cash
In common language cash refers to money in the physical form of currency, such as banknotes and coins.In bookkeeping and finance, cash refers to current assets comprising currency or currency equivalents that can be accessed immediately or near-immediately...
at the expiration of the deal, though some cash payments will likely be made along the way by one or the other counterparty to maintain agreed upon margin
Margin (finance)
In finance, a margin is collateral that the holder of a financial instrument has to deposit to cover some or all of the credit risk of their counterparty...
.
Structure and features
The features of a variance swap include:- the variance strike
- the realized variance
- the vega notional: Like other swapSwap (finance)In finance, a swap is a derivative in which counterparties exchange certain benefits of one party's financial instrument for those of the other party's financial instrument. The benefits in question depend on the type of financial instruments involved...
s, the payoff is determined based on a notional amountNotional amountThe notional amount on a financial instrument is the nominal or face amount that is used to calculate payments made on that instrument...
that is never exchanged. However, in the case of a variance swap, the notional amount is specified in terms of vega, to convert the payoff into dollar terms.
The payoff of a variance swap is given as follows:
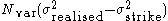
where:
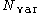 = variance notional (a.k.a. variance units),
= variance notional (a.k.a. variance units),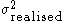 = annualised realised variance, and
= annualised realised variance, and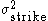 = variance strike.
= variance strike.
The annualised realised variance is calculated based on a prespecified set of sampling points over the period. It does not always coincide with the classic statistical definition of variance as the contract terms may not subtract the mean. For example, suppose that there are n+1 sample points
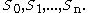
Define, for i=1 to n,
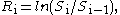 the natural log returns.
the natural log returns.Then
where
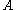 is an annualisation factor normally chosen to be approximately the number of sampling points in a year (commonly 252). It can be seen that subtracting the mean return will decrease the realised variance. If this is done, it is common to use
is an annualisation factor normally chosen to be approximately the number of sampling points in a year (commonly 252). It can be seen that subtracting the mean return will decrease the realised variance. If this is done, it is common to use  as the divisor rather than
as the divisor rather than  , corresponding to an unbiased estimate
, corresponding to an unbiased estimateEstimator
In statistics, an estimator is a rule for calculating an estimate of a given quantity based on observed data: thus the rule and its result are distinguished....
of the sample variance.
It is market practice to determine the number of contract units as follows:
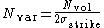
where
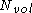 is the corresponding vega notional for a volatility swap
is the corresponding vega notional for a volatility swapVolatility swap
In finance, a volatility swap is a forward contract on the future realised volatility of a given underlying asset. Volatility swaps allow investors to trade the volatility of an asset directly, much as they would trade a price index....
. This makes the payoff of a variance swap comparable to that of a volatility swap
Volatility swap
In finance, a volatility swap is a forward contract on the future realised volatility of a given underlying asset. Volatility swaps allow investors to trade the volatility of an asset directly, much as they would trade a price index....
, another less popular instrument used to trade volatility.
Pricing and valuation
The variance swap may be hedged and hence priced using a portfolio of European call and put options with weights inversely proportional to the square of strike.Any volatility smile
Volatility Smile
In finance, the volatility smile is a long-observed pattern in which at-the-money options tend to have lower implied volatilities than in- or out-of-the-money options. The pattern displays different characteristics for different markets and results from the probability of extreme moves...
model which prices vanilla options can therefore be used to price the variance swap. For example, using the Heston model
Heston model
In finance, the Heston model, named after Steven Heston, is a mathematical model describing the evolution of the volatility of an underlying asset...
, a closed-form solution can be derived for the fair variance swap rate. Care must be taken with the behaviour of the smile model in the wings as this can have a disproportionate effect on the price.
We can derive the payoff of a variance swap using Ito's Lemma
Ito's lemma
In mathematics, Itō's lemma is used in Itō stochastic calculus to find the differential of a function of a particular type of stochastic process. It is named after its discoverer, Kiyoshi Itō...
. We first assume that the underlying stock is described as follows:
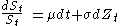
Applying Ito's formula, we get:
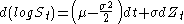
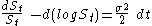
Taking integrals, the total variance is:
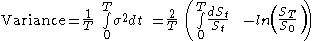
We can see that the total variance consists of a rebalanced hedge of
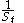 and short a log contract.
and short a log contract. Using a static replication argument
, i.e., any twice continuously differentiable contract can be replicated using a bond, a future and infinitely many puts and calls, we can show that a short log contract position is equal to being short a futures contract and a collection of puts and calls:
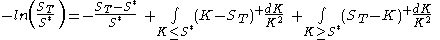
Taking expectations and setting the value of the variance swap equal to zero, we can rearrange the formula to solve for the fair variance swap strike:
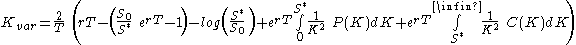
Where:
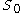 is the initial price of the underlying security,
is the initial price of the underlying security,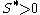 is an arbitrary cutoff,
is an arbitrary cutoff,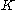 is the strike of the each option in the collection of options used.
is the strike of the each option in the collection of options used.Often the cutoff
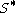 is chosen to be the current forward price
is chosen to be the current forward price 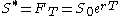 , in which case the fair variance swap strike can be written in the simpler form:
, in which case the fair variance swap strike can be written in the simpler form: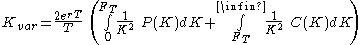
Uses
Many traders find variance swaps interesting or useful for their purity. An alternative way of speculating on volatility is with an optionOption (finance)
In finance, an option is a derivative financial instrument that specifies a contract between two parties for a future transaction on an asset at a reference price. The buyer of the option gains the right, but not the obligation, to engage in that transaction, while the seller incurs the...
, but if one only has interest in volatility risk, this strategy will require constant delta hedging, so that direction risk of the underlying security is approximately removed. What is more, a replicating portfolio
Replicating portfolio
In the valuation of a life insurance company, the actuary considers a series of future uncertain cashflows and attempts to put a value on these cashflows...
of a variance swap would require an entire strip of options, which would be very costly to execute. Finally, one might often find the need to be regularly rolling this entire strip of options so that it remains centered around the current price of the underlying
security
Security (finance)
A security is generally a fungible, negotiable financial instrument representing financial value. Securities are broadly categorized into:* debt securities ,* equity securities, e.g., common stocks; and,...
.
The advantage of variance swaps is that they provide pure exposure to the volatility of the underlying price, as opposed to call and put options which may carry directional risk (delta). The profit and loss from a variance swap depends directly on the difference between realized and implied volatility.
Another aspect that some speculators may find interesting is that the quoted strike is determined by the implied volatility smile
Volatility Smile
In finance, the volatility smile is a long-observed pattern in which at-the-money options tend to have lower implied volatilities than in- or out-of-the-money options. The pattern displays different characteristics for different markets and results from the probability of extreme moves...
in the options market, whereas the ultimate payout will be based upon actual realized variance. Historically, implied variance has been above realized variance, a phenomenon known as the Variance risk premium
Variance risk premium
Variance risk premium is a phenomenon on the Variance swap market, of the variance swap strike being greater than the realized variance on average. For most trades, the buyer of variance ends up with a loss on the trade, while the seller profits. The amount that the buyer of variance typically...
, creating an opportunity for volatility arbitrage
Volatility arbitrage
In finance, volatility arbitrage is a type of statistical arbitrage that is implemented by trading a delta neutral portfolio of an option and its underlier. The objective is to take advantage of differences between the implied volatility of the option, and a forecast of future realized volatility...
, in this case known as the rolling short variance trade. For the same reason, these swaps can be used to hedge Options on Realized Variance.
Related instruments
Closely related strategies include straddleStraddle
In finance, a straddle is an investment strategy involving the purchase or sale of particular option derivatives that allows the holder to profit based on how much the price of the underlying security moves, regardless of the direction of price movement...
, volatility swap
Volatility swap
In finance, a volatility swap is a forward contract on the future realised volatility of a given underlying asset. Volatility swaps allow investors to trade the volatility of an asset directly, much as they would trade a price index....
, correlation swap
Correlation swap
A correlation swap is an over-the-counter financial derivative that allows one to speculate on or hedge risks associated with the observed average correlation, of a collection of underlying products, where each product has periodically observable prices, as with a commodity, exchange rate,...
, gamma swap, conditional variance swap
Conditional variance swap
A conditional variance swap is a type of swap Derivative product that allows investors to take exposure to volatility in the price of an underlying security only while the underlying security is within a pre-specified price range...
, corridor variance swap, forward-start variance swap, option on realized variance and correlation trading.