
Wind engineering
Encyclopedia
Wind engineering analyzes effects of wind
in the natural and the built environment
and studies the possible damage, inconvenience or benefits which may result from wind. In the field of structural engineering
it includes strong winds, which may cause discomfort, as well as extreme winds, such as in a tornado
, hurricane or heavy storm, which may cause widespread destruction. In the fields of wind energy
and air pollution
it also includes low and moderate winds as these are relevant to electricity production resp. dispersion of contaminants.
Wind engineering draws upon meteorology
, fluid dynamics
, mechanics
, Geographic Information System
s and a number of specialist engineering
disciplines including aerodynamics
, and structural dynamics
. The tools used include atmospheric model
s, atmospheric boundary layer wind tunnel
s and computational fluid dynamics
models.
Wind engineering involves, among other topics:
Wind engineering may be considered by structural engineers to be closely related to earthquake engineering
and explosion protection
.
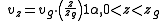
where:
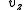 = speed of the wind at height
= speed of the wind at height 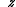
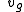 = gradient wind at gradient height
= gradient wind at gradient height 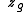
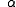 = exponential coefficient
= exponential coefficient
Typically, buildings are designed to resist a strong wind with a very long return period, such as 50 years or more. The design wind speed is determined from historical records using Extreme value theory
to predict future extreme wind speeds.
s are affected by wind shear. Vertical wind-speed profiles result in different wind speeds at the blades nearest to the ground level compared to those at the top of blade travel, and this in turn affects the turbine operation. The wind gradient can create a large bending moment in the shaft of a two bladed turbine when the blades are vertical. The reduced wind gradient over water means shorter and less expensive wind turbine towers can be used in shallow seas.
For wind turbine engineering, wind speed variation with height is often approximated using a power law:
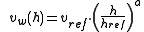
where:
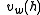 = velocity of the wind at height
= velocity of the wind at height 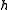
[m/s] 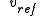 = velocity of the wind at some reference height
= velocity of the wind at some reference height 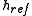
[m] 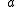 = Hellman exponent (aka power law exponent or shear exponent) (~= 1/7 in neutral flow, but can be >1)
= Hellman exponent (aka power law exponent or shear exponent) (~= 1/7 in neutral flow, but can be >1)
buildings, cable suspension bridge
s and cable-stayed bridge
s, electricity transmission towers and telecommunication towers and all other types of towers and chimneys. The wind load is the dominant load in the analysis of many tall buildings. So wind engineering is essential for the analysis and design of tall buildings. Again, wind load is a dominant load in the analysis and design of all long-span cable bridge
s.
Wind
Wind is the flow of gases on a large scale. On Earth, wind consists of the bulk movement of air. In outer space, solar wind is the movement of gases or charged particles from the sun through space, while planetary wind is the outgassing of light chemical elements from a planet's atmosphere into space...
in the natural and the built environment
Built environment
The term built environment refers to the human-made surroundings that provide the setting for human activity, ranging in scale from personal shelter and buildings to neighborhoods and cities that can often include their supporting infrastructure, such as water supply or energy networks.The built...
and studies the possible damage, inconvenience or benefits which may result from wind. In the field of structural engineering
Structural engineering
Structural engineering is a field of engineering dealing with the analysis and design of structures that support or resist loads. Structural engineering is usually considered a specialty within civil engineering, but it can also be studied in its own right....
it includes strong winds, which may cause discomfort, as well as extreme winds, such as in a tornado
Tornado
A tornado is a violent, dangerous, rotating column of air that is in contact with both the surface of the earth and a cumulonimbus cloud or, in rare cases, the base of a cumulus cloud. They are often referred to as a twister or a cyclone, although the word cyclone is used in meteorology in a wider...
, hurricane or heavy storm, which may cause widespread destruction. In the fields of wind energy
Wind energy
Wind energy is the kinetic energy of air in motion; see also wind power.Total wind energy flowing through an imaginary area A during the time t is:E = ½ m v2 = ½ v 2...
and air pollution
Air pollution
Air pollution is the introduction of chemicals, particulate matter, or biological materials that cause harm or discomfort to humans or other living organisms, or cause damage to the natural environment or built environment, into the atmosphere....
it also includes low and moderate winds as these are relevant to electricity production resp. dispersion of contaminants.
Wind engineering draws upon meteorology
Meteorology
Meteorology is the interdisciplinary scientific study of the atmosphere. Studies in the field stretch back millennia, though significant progress in meteorology did not occur until the 18th century. The 19th century saw breakthroughs occur after observing networks developed across several countries...
, fluid dynamics
Fluid dynamics
In physics, fluid dynamics is a sub-discipline of fluid mechanics that deals with fluid flow—the natural science of fluids in motion. It has several subdisciplines itself, including aerodynamics and hydrodynamics...
, mechanics
Mechanics
Mechanics is the branch of physics concerned with the behavior of physical bodies when subjected to forces or displacements, and the subsequent effects of the bodies on their environment....
, Geographic Information System
Geographic Information System
A geographic information system, geographical information science, or geospatial information studies is a system designed to capture, store, manipulate, analyze, manage, and present all types of geographically referenced data...
s and a number of specialist engineering
Engineering
Engineering is the discipline, art, skill and profession of acquiring and applying scientific, mathematical, economic, social, and practical knowledge, in order to design and build structures, machines, devices, systems, materials and processes that safely realize improvements to the lives of...
disciplines including aerodynamics
Aerodynamics
Aerodynamics is a branch of dynamics concerned with studying the motion of air, particularly when it interacts with a moving object. Aerodynamics is a subfield of fluid dynamics and gas dynamics, with much theory shared between them. Aerodynamics is often used synonymously with gas dynamics, with...
, and structural dynamics
Structural Dynamics
Structural dynamics is a subset of structural analysis which covers the behaviour of structures subjected to dynamic loading. Dynamic loads include people, wind, waves, traffic, earthquakes, and blasts. Any structure can be subject to dynamic loading. Dynamic analysis can be used to find dynamic...
. The tools used include atmospheric model
Atmospheric model
An atmospheric model is a mathematical model constructed around the full set of primitive dynamical equations which govern atmospheric motions. It can supplement these equations with parameterizations for turbulent diffusion, radiation, moist processes , heat exchange, soil, vegetation, surface...
s, atmospheric boundary layer wind tunnel
Wind tunnel
A wind tunnel is a research tool used in aerodynamic research to study the effects of air moving past solid objects.-Theory of operation:Wind tunnels were first proposed as a means of studying vehicles in free flight...
s and computational fluid dynamics
Computational fluid dynamics
Computational fluid dynamics, usually abbreviated as CFD, is a branch of fluid mechanics that uses numerical methods and algorithms to solve and analyze problems that involve fluid flows. Computers are used to perform the calculations required to simulate the interaction of liquids and gases with...
models.
Wind engineering involves, among other topics:
- Wind impact on structures (buildings, bridges, towers).
- Wind comfort near buildings.
- Effects of wind on the ventilation system in a building.
- Wind climate for wind energy.
- Air pollution near buildings.
Wind engineering may be considered by structural engineers to be closely related to earthquake engineering
Earthquake engineering
Earthquake engineering is the scientific field concerned with protecting society, the natural and the man-made environment from earthquakes by limiting the seismic risk to socio-economically acceptable levels...
and explosion protection
Explosion protection
Explosion protection is used to protect all sorts of buildings and civil engineering infrastructure against internal and external explosions or deflagrations. It was widely believed until recently that a building subject to an explosive attack had a chance to remain standing only if it possessed...
.
History
Wind Engineering as a separate discipline can be traced to the UK in the 1960s, when informal meetings were held at the [National Physical Laboratory (United Kingdom)|[National Physical Laboratory]], the Building Research Establishment and elsewhere.Wind loads on buildings
The design of buildings must account for wind loads, and these are affected by wind shear. For engineering purposes, a power law wind speed profile may be defined as follows: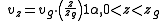
where:
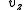 = speed of the wind at height
= speed of the wind at height 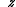
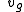 = gradient wind at gradient height
= gradient wind at gradient height 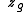
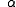 = exponential coefficient
= exponential coefficientTypically, buildings are designed to resist a strong wind with a very long return period, such as 50 years or more. The design wind speed is determined from historical records using Extreme value theory
Extreme value theory
Extreme value theory is a branch of statistics dealing with the extreme deviations from the median of probability distributions. The general theory sets out to assess the type of probability distributions generated by processes...
to predict future extreme wind speeds.
Wind turbines
Wind turbineWind turbine
A wind turbine is a device that converts kinetic energy from the wind into mechanical energy. If the mechanical energy is used to produce electricity, the device may be called a wind generator or wind charger. If the mechanical energy is used to drive machinery, such as for grinding grain or...
s are affected by wind shear. Vertical wind-speed profiles result in different wind speeds at the blades nearest to the ground level compared to those at the top of blade travel, and this in turn affects the turbine operation. The wind gradient can create a large bending moment in the shaft of a two bladed turbine when the blades are vertical. The reduced wind gradient over water means shorter and less expensive wind turbine towers can be used in shallow seas.
For wind turbine engineering, wind speed variation with height is often approximated using a power law:
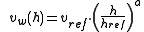
where:
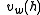 = velocity of the wind at height
= velocity of the wind at height 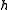
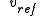 = velocity of the wind at some reference height
= velocity of the wind at some reference height 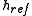
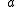 = Hellman exponent (aka power law exponent or shear exponent) (~= 1/7 in neutral flow, but can be >1)
= Hellman exponent (aka power law exponent or shear exponent) (~= 1/7 in neutral flow, but can be >1)Significance
The knowledge of wind engineering is used to analyze and design all high riseHigh Rise
High Rise is a 1975 novel by J. G. Ballard. It takes place in an ultra-modern, luxury high-rise building.-Plot summary:The building seems to give its well-established tenants all the conveniences and commodities that modern life has to offer: swimming pools, its own school, a supermarket,...
buildings, cable suspension bridge
Suspension bridge
A suspension bridge is a type of bridge in which the deck is hung below suspension cables on vertical suspenders. Outside Tibet and Bhutan, where the first examples of this type of bridge were built in the 15th century, this type of bridge dates from the early 19th century...
s and cable-stayed bridge
Cable-stayed bridge
A cable-stayed bridge is a bridge that consists of one or more columns , with cables supporting the bridge deck....
s, electricity transmission towers and telecommunication towers and all other types of towers and chimneys. The wind load is the dominant load in the analysis of many tall buildings. So wind engineering is essential for the analysis and design of tall buildings. Again, wind load is a dominant load in the analysis and design of all long-span cable bridge
Cable Bridge
The Cable Bridge, officially called the Ed Hendler Bridge and sometimes called the Intercity Bridge, spans the Columbia River between Pasco and Kennewick in southeastern Washington as State Route 397...
s.
See also
- Hurricane engineeringHurricane engineeringHurricane engineering is a specialist sub-discipline of civil engineering that encompasses planning, analysis, design, response, and recovery of civil engineering systems and infrastructure for hurricane hazards. Hurricane engineering is a relatively new and emerging discipline within the field of...
- Wind tunnelWind tunnelA wind tunnel is a research tool used in aerodynamic research to study the effects of air moving past solid objects.-Theory of operation:Wind tunnels were first proposed as a means of studying vehicles in free flight...
testing - Vibration controlVibration controlIn earthquake engineering, vibration control is a set of technical means aimed to mitigate seismic impacts in building and non-building structures.All seismic vibration control devices may be classified as passive, active or hybrid where:...
- John TwidellJohn TwidellJohn Twidell is Director of the AMSET Centre Ltd. and is a visiting lecturer at the Environmental Change Institute, University of Oxford, and the School of Aeronautics and Engineering, City University, London. He is Editor Emeritus of the academic journal Wind Engineering...

