World language
Encyclopedia
A world language is a language
spoken internationally which is learned by many people as a second language
. A world language is not only characterized by the number of its speakers (native or second language speakers), but also by its geographical distribution, and its use in international organizations and in diplomatic relations. In this respect, major world languages are dominated by languages of Europe
an origin. The historical reason for this is the period of European colonialism
.
The international prominence of Arabic
has its historical reason in the medieval Islamic conquests and the subsequent Arabization
of the Middle East
and North Africa
, and also exists as a liturgical language amongst Muslim communities outside of the Arab World
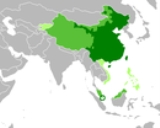
. Standard Chinese
is the direct replacement of Classical Chinese
which was an important historical lingua franca
in Far East Asia until the early 20th century, and today serves the function of providing a common spoken language between speakers of different and mutually unintelligible Chinese spoken languages not only within China proper
(between the Han Chinese
and other unrelated ethnic groups), but in overseas Chinese
communities as well as being widely taught as a second language internationally. Russian
was used in the Russian empire
and the Soviet Union
, and today is in use and widely understood in areas of Central
and Eastern Europe
, and Northern
and Central Asia
which were formerly part of the Soviet Union, or of the former Soviet bloc, and it remains the lingua franca in the Commonwealth of Independent States
. German
served as a lingua franca in large portions of Europe for centuries, mainly the Holy Roman Empire
and later the Austro-Hungarian Empire. It remains an important second language in much of Central
and Eastern Europe
, and in the international scientific community.
Other major languages are not widely used across several continents, but have had an international significance as the lingua franca
of a historical empire
. These include Greek
in the Hellenistic world after the conquests of Alexander the Great, and in the territories of the Byzantine Empire
; Latin
in the Roman Empire
and previously as the standard liturgical language for the Catholic faithful worldwide; Classical Chinese
in East Asia
during the Imperial era of Chinese history; Persian
(or Farsi, as it is known in the Persian language) during ancient and medieval incarnations of various succeeding Persian Empires, and once served as the second lingua franca of the Islamic World after Arabic; Sanskrit
during the ancient and medieval historical periods of various states in South Asia
, Southeast Asia
, and Central Asia
, and like Latin an important liturgical language of the Vedic religion
s.
The major languages of the Indian subcontinent
have numbers of speakers comparable to those of major world languages primarily due to the large population in the region rather than a supra-regional use of these languages, although Hindustani
(including all Hindi dialects and Urdu
) and to a lesser extent Tamil
may fulfill the criteria in terms of supra-regional usage and international recognition.
As an example, the native speaking population of Bengali
vastly outnumber those who speak French as a first language, and it is one of the most spoken languages (ranking fifth or sixth) in the world with nearly 230 million total speakers, and is known for its long and rich literary tradition. However, while French is spoken intercontinentally, is internationally recognized to be of high linguistic prestige and used in diplomacy and international commerce, as well as having a significant portion of second language speakers throughout the world, the overwhelming majority of Bengali speakers are native Bengali people
, with little to no influence outside of its regionally limited sprachraum
or language space.
, Akkadian
, Old Aramaic, Koine Greek
, Latin
, Arabic, Sanskrit
, Chinese
, Spanish
, Portuguese
, Dutch
, French
, Russian
and English
.
The Romance languages
bear testimony to the role of Latin
as the lingua franca of the Roman Empire
. Koine Greek
was the "world language" of the Hellenistic period
, but its distribution is not reflected in the distribution of Modern Greek
due to the linguistic impact of the Slavic, Arabic
and Turkic
expansions. The distribution of the Turkic languages
, in turn, are a legacy of the Turkic Khaganate.
Just as all the living world languages owe their status to historical imperialism
, the suggestion of a given language as a world language or "universal language
" has strong political implications. Thus, Russian was declared the "world language of internationalism
" in Soviet literature, which at the same time denounced French as the "language of fancy courtiers" and English as the "jargon of traders". A number of international auxiliary languages have been introduced as prospective world languages, the most successful of them being Esperanto
, but none of them can claim the status of a living world language. Many natural languages have been proffered as candidates for a global lingua franca, including Italian
, Dutch
, Hungarian
, German
and Malay
.
World languages in the strictest sense are:
Other sources denote the following languages as world languages, whilst stricter sources list them as supra-regional languages:
Two languages with a number of speakers in excess of 100 million, Japanese
and Bengali
, are not listed. Although considered to be some of the most internationally significant languages along with the listed world languages, they are not considered world languages per se - Japan for example is almost ethnically, culturally and linguistically homogeneous, thus Japanese does not have much history as a lingua franca amongst communities who do not share a mother tongue or first language; their overseas communities are strongly tied to ethnicity; Bengali is not as widely taught as a foreign language as Japanese, where international interest since the 1980s have prompted many major universities as well as a number of secondary and even primary schools worldwide to offer courses in the language; and at least in the present, these languages exert a regionally limited sphere of influence;).
Natural language
In the philosophy of language, a natural language is any language which arises in an unpremeditated fashion as the result of the innate facility for language possessed by the human intellect. A natural language is typically used for communication, and may be spoken, signed, or written...
spoken internationally which is learned by many people as a second language
Second language
A second language or L2 is any language learned after the first language or mother tongue. Some languages, often called auxiliary languages, are used primarily as second languages or lingua francas ....
. A world language is not only characterized by the number of its speakers (native or second language speakers), but also by its geographical distribution, and its use in international organizations and in diplomatic relations. In this respect, major world languages are dominated by languages of Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
an origin. The historical reason for this is the period of European colonialism
Colonialism
Colonialism is the establishment, maintenance, acquisition and expansion of colonies in one territory by people from another territory. It is a process whereby the metropole claims sovereignty over the colony and the social structure, government, and economics of the colony are changed by...
.
The international prominence of Arabic
Arabic language
Arabic is a name applied to the descendants of the Classical Arabic language of the 6th century AD, used most prominently in the Quran, the Islamic Holy Book...
has its historical reason in the medieval Islamic conquests and the subsequent Arabization
Arabization
Arabization or Arabisation describes a growing cultural influence on a non-Arab area that gradually changes into one that speaks Arabic and/or incorporates Arab culture...
of the Middle East
Middle East
The Middle East is a region that encompasses Western Asia and Northern Africa. It is often used as a synonym for Near East, in opposition to Far East...
and North Africa
North Africa
North Africa or Northern Africa is the northernmost region of the African continent, linked by the Sahara to Sub-Saharan Africa. Geopolitically, the United Nations definition of Northern Africa includes eight countries or territories; Algeria, Egypt, Libya, Morocco, South Sudan, Sudan, Tunisia, and...
, and also exists as a liturgical language amongst Muslim communities outside of the Arab World
Arab world
The Arab world refers to Arabic-speaking states, territories and populations in North Africa, Western Asia and elsewhere.The standard definition of the Arab world comprises the 22 states and territories of the Arab League stretching from the Atlantic Ocean in the west to the Arabian Sea in the...
. Standard Chinese
Standard Chinese
Standard Chinese, or Modern Standard Chinese, also known as Mandarin or Putonghua, is the official language of the People's Republic of China and Republic of China , and is one of the four official languages of Singapore....
is the direct replacement of Classical Chinese
Classical Chinese
Classical Chinese or Literary Chinese is a traditional style of written Chinese based on the grammar and vocabulary of ancient Chinese, making it different from any modern spoken form of Chinese...
which was an important historical lingua franca
Lingua franca
A lingua franca is a language systematically used to make communication possible between people not sharing a mother tongue, in particular when it is a third language, distinct from both mother tongues.-Characteristics:"Lingua franca" is a functionally defined term, independent of the linguistic...
in Far East Asia until the early 20th century, and today serves the function of providing a common spoken language between speakers of different and mutually unintelligible Chinese spoken languages not only within China proper
Greater China
Greater China is a term used to refer to mainland China, Hong Kong, Macau and Taiwan. As a "phrase of the moment", the precise meaning is not entirely clear, and people may use it for only the commercial ties, only the cultural actions, or even as a euphemism for the Two Chinas, while others may...
(between the Han Chinese
Han Chinese
Han Chinese are an ethnic group native to China and are the largest single ethnic group in the world.Han Chinese constitute about 92% of the population of the People's Republic of China , 98% of the population of the Republic of China , 78% of the population of Singapore, and about 20% of the...
and other unrelated ethnic groups), but in overseas Chinese
Overseas Chinese
Overseas Chinese are people of Chinese birth or descent who live outside the Greater China Area . People of partial Chinese ancestry living outside the Greater China Area may also consider themselves Overseas Chinese....
communities as well as being widely taught as a second language internationally. Russian
Russian language
Russian is a Slavic language used primarily in Russia, Belarus, Uzbekistan, Kazakhstan, Tajikistan and Kyrgyzstan. It is an unofficial but widely spoken language in Ukraine, Moldova, Latvia, Turkmenistan and Estonia and, to a lesser extent, the other countries that were once constituent republics...
was used in the Russian empire
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was a state that existed from 1721 until the Russian Revolution of 1917. It was the successor to the Tsardom of Russia and the predecessor of the Soviet Union...
and the Soviet Union
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991....
, and today is in use and widely understood in areas of Central
Central Europe
Central Europe or alternatively Middle Europe is a region of the European continent lying between the variously defined areas of Eastern and Western Europe...
and Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is the eastern part of Europe. The term has widely disparate geopolitical, geographical, cultural and socioeconomic readings, which makes it highly context-dependent and even volatile, and there are "almost as many definitions of Eastern Europe as there are scholars of the region"...
, and Northern
North Asia
North Asia or Northern Asia is a subregion of Asia, consisting of the Asian portion of Russia.The Phillips Illustrated Atlas of the World 1988 defines it as being most of the former USSR, the part that is to the east of the Ural Mountains...
and Central Asia
Central Asia
Central Asia is a core region of the Asian continent from the Caspian Sea in the west, China in the east, Afghanistan in the south, and Russia in the north...
which were formerly part of the Soviet Union, or of the former Soviet bloc, and it remains the lingua franca in the Commonwealth of Independent States
Commonwealth of Independent States
The Commonwealth of Independent States is a regional organization whose participating countries are former Soviet Republics, formed during the breakup of the Soviet Union....
. German
German language
German is a West Germanic language, related to and classified alongside English and Dutch. With an estimated 90 – 98 million native speakers, German is one of the world's major languages and is the most widely-spoken first language in the European Union....
served as a lingua franca in large portions of Europe for centuries, mainly the Holy Roman Empire
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a realm that existed from 962 to 1806 in Central Europe.It was ruled by the Holy Roman Emperor. Its character changed during the Middle Ages and the Early Modern period, when the power of the emperor gradually weakened in favour of the princes...
and later the Austro-Hungarian Empire. It remains an important second language in much of Central
Central Europe
Central Europe or alternatively Middle Europe is a region of the European continent lying between the variously defined areas of Eastern and Western Europe...
and Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is the eastern part of Europe. The term has widely disparate geopolitical, geographical, cultural and socioeconomic readings, which makes it highly context-dependent and even volatile, and there are "almost as many definitions of Eastern Europe as there are scholars of the region"...
, and in the international scientific community.
Other major languages are not widely used across several continents, but have had an international significance as the lingua franca
Lingua franca
A lingua franca is a language systematically used to make communication possible between people not sharing a mother tongue, in particular when it is a third language, distinct from both mother tongues.-Characteristics:"Lingua franca" is a functionally defined term, independent of the linguistic...
of a historical empire
Empire
The term empire derives from the Latin imperium . Politically, an empire is a geographically extensive group of states and peoples united and ruled either by a monarch or an oligarchy....
. These include Greek
Koine Greek
Koine Greek is the universal dialect of the Greek language spoken throughout post-Classical antiquity , developing from the Attic dialect, with admixture of elements especially from Ionic....
in the Hellenistic world after the conquests of Alexander the Great, and in the territories of the Byzantine Empire
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire was the Eastern Roman Empire during the periods of Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, centred on the capital of Constantinople. Known simply as the Roman Empire or Romania to its inhabitants and neighbours, the Empire was the direct continuation of the Ancient Roman State...
; Latin
Latin
Latin is an Italic language originally spoken in Latium and Ancient Rome. It, along with most European languages, is a descendant of the ancient Proto-Indo-European language. Although it is considered a dead language, a number of scholars and members of the Christian clergy speak it fluently, and...
in the Roman Empire
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire was the post-Republican period of the ancient Roman civilization, characterised by an autocratic form of government and large territorial holdings in Europe and around the Mediterranean....
and previously as the standard liturgical language for the Catholic faithful worldwide; Classical Chinese
Classical Chinese
Classical Chinese or Literary Chinese is a traditional style of written Chinese based on the grammar and vocabulary of ancient Chinese, making it different from any modern spoken form of Chinese...
in East Asia
East Asia
East Asia or Eastern Asia is a subregion of Asia that can be defined in either geographical or cultural terms...
during the Imperial era of Chinese history; Persian
Persian language
Persian is an Iranian language within the Indo-Iranian branch of the Indo-European languages. It is primarily spoken in Iran, Afghanistan, Tajikistan and countries which historically came under Persian influence...
(or Farsi, as it is known in the Persian language) during ancient and medieval incarnations of various succeeding Persian Empires, and once served as the second lingua franca of the Islamic World after Arabic; Sanskrit
Sanskrit
Sanskrit , is a historical Indo-Aryan language and the primary liturgical language of Hinduism, Jainism and Buddhism.Buddhism: besides Pali, see Buddhist Hybrid Sanskrit Today, it is listed as one of the 22 scheduled languages of India and is an official language of the state of Uttarakhand...
during the ancient and medieval historical periods of various states in South Asia
South Asia
South Asia, also known as Southern Asia, is the southern region of the Asian continent, which comprises the sub-Himalayan countries and, for some authorities , also includes the adjoining countries to the west and the east...
, Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, South-East Asia, South East Asia or Southeastern Asia is a subregion of Asia, consisting of the countries that are geographically south of China, east of India, west of New Guinea and north of Australia. The region lies on the intersection of geological plates, with heavy seismic...
, and Central Asia
Central Asia
Central Asia is a core region of the Asian continent from the Caspian Sea in the west, China in the east, Afghanistan in the south, and Russia in the north...
, and like Latin an important liturgical language of the Vedic religion
Vedic religion
Vedic religion may refer to:*the historical Vedic religion- Vedic Hinduism **Vedic mythology*Shrauta, surviving conservative traditions within HinduismIn wider meanings of the term "Vedic"*Vedanta*Hinduism in general...
s.
The major languages of the Indian subcontinent
Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent, also Indian Subcontinent, Indo-Pak Subcontinent or South Asian Subcontinent is a region of the Asian continent on the Indian tectonic plate from the Hindu Kush or Hindu Koh, Himalayas and including the Kuen Lun and Karakoram ranges, forming a land mass which extends...
have numbers of speakers comparable to those of major world languages primarily due to the large population in the region rather than a supra-regional use of these languages, although Hindustani
Hindustani language
Hindi-Urdu is an Indo-Aryan language and the lingua franca of North India and Pakistan. It is also known as Hindustani , and historically, as Hindavi or Rekhta...
(including all Hindi dialects and Urdu
Urdu
Urdu is a register of the Hindustani language that is identified with Muslims in South Asia. It belongs to the Indo-European family. Urdu is the national language and lingua franca of Pakistan. It is also widely spoken in some regions of India, where it is one of the 22 scheduled languages and an...
) and to a lesser extent Tamil
Tamil language
Tamil is a Dravidian language spoken predominantly by Tamil people of the Indian subcontinent. It has official status in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu and in the Indian union territory of Pondicherry. Tamil is also an official language of Sri Lanka and Singapore...
may fulfill the criteria in terms of supra-regional usage and international recognition.
As an example, the native speaking population of Bengali
Bengali language
Bengali or Bangla is an eastern Indo-Aryan language. It is native to the region of eastern South Asia known as Bengal, which comprises present day Bangladesh, the Indian state of West Bengal, and parts of the Indian states of Tripura and Assam. It is written with the Bengali script...
vastly outnumber those who speak French as a first language, and it is one of the most spoken languages (ranking fifth or sixth) in the world with nearly 230 million total speakers, and is known for its long and rich literary tradition. However, while French is spoken intercontinentally, is internationally recognized to be of high linguistic prestige and used in diplomacy and international commerce, as well as having a significant portion of second language speakers throughout the world, the overwhelming majority of Bengali speakers are native Bengali people
Bengali people
The Bengali people are an ethnic community native to the historic region of Bengal in South Asia. They speak Bengali , which is an Indo-Aryan language of the eastern Indian subcontinent, evolved from the Magadhi Prakrit and Sanskrit languages. In their native language, they are referred to as বাঙালী...
, with little to no influence outside of its regionally limited sprachraum
Sprachraum
Sprachraum is a linguistic term used to designate a geographical region/district where a language, dialect, group or family of languages is spoken. The German word Sprachraum literally means "language area"....
or language space.
History
Historical world languages include SumerianSumerian language
Sumerian is the language of ancient Sumer, which was spoken in southern Mesopotamia since at least the 4th millennium BC. During the 3rd millennium BC, there developed a very intimate cultural symbiosis between the Sumerians and the Akkadians, which included widespread bilingualism...
, Akkadian
Akkadian language
Akkadian is an extinct Semitic language that was spoken in ancient Mesopotamia. The earliest attested Semitic language, it used the cuneiform writing system derived ultimately from ancient Sumerian, an unrelated language isolate...
, Old Aramaic, Koine Greek
Koine Greek
Koine Greek is the universal dialect of the Greek language spoken throughout post-Classical antiquity , developing from the Attic dialect, with admixture of elements especially from Ionic....
, Latin
Latin
Latin is an Italic language originally spoken in Latium and Ancient Rome. It, along with most European languages, is a descendant of the ancient Proto-Indo-European language. Although it is considered a dead language, a number of scholars and members of the Christian clergy speak it fluently, and...
, Arabic, Sanskrit
Sanskrit
Sanskrit , is a historical Indo-Aryan language and the primary liturgical language of Hinduism, Jainism and Buddhism.Buddhism: besides Pali, see Buddhist Hybrid Sanskrit Today, it is listed as one of the 22 scheduled languages of India and is an official language of the state of Uttarakhand...
, Chinese
Chinese language
The Chinese language is a language or language family consisting of varieties which are mutually intelligible to varying degrees. Originally the indigenous languages spoken by the Han Chinese in China, it forms one of the branches of Sino-Tibetan family of languages...
, Spanish
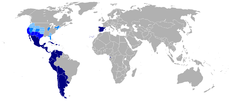
Spanish language
Spanish , also known as Castilian , is a Romance language in the Ibero-Romance group that evolved from several languages and dialects in central-northern Iberia around the 9th century and gradually spread with the expansion of the Kingdom of Castile into central and southern Iberia during the...
, Portuguese
Portuguese language
Portuguese is a Romance language that arose in the medieval Kingdom of Galicia, nowadays Galicia and Northern Portugal. The southern part of the Kingdom of Galicia became independent as the County of Portugal in 1095...
, Dutch
Dutch language
Dutch is a West Germanic language and the native language of the majority of the population of the Netherlands, Belgium, and Suriname, the three member states of the Dutch Language Union. Most speakers live in the European Union, where it is a first language for about 23 million and a second...
, French
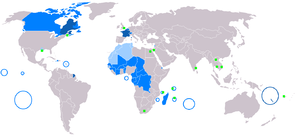
French language
French is a Romance language spoken as a first language in France, the Romandy region in Switzerland, Wallonia and Brussels in Belgium, Monaco, the regions of Quebec and Acadia in Canada, and by various communities elsewhere. Second-language speakers of French are distributed throughout many parts...
, Russian
Russian language
Russian is a Slavic language used primarily in Russia, Belarus, Uzbekistan, Kazakhstan, Tajikistan and Kyrgyzstan. It is an unofficial but widely spoken language in Ukraine, Moldova, Latvia, Turkmenistan and Estonia and, to a lesser extent, the other countries that were once constituent republics...
and English
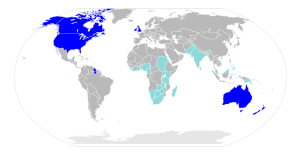
English language
English is a West Germanic language that arose in the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of England and spread into what was to become south-east Scotland under the influence of the Anglian medieval kingdom of Northumbria...
.
The Romance languages
Romance languages
The Romance languages are a branch of the Indo-European language family, more precisely of the Italic languages subfamily, comprising all the languages that descend from Vulgar Latin, the language of ancient Rome...
bear testimony to the role of Latin
Latin
Latin is an Italic language originally spoken in Latium and Ancient Rome. It, along with most European languages, is a descendant of the ancient Proto-Indo-European language. Although it is considered a dead language, a number of scholars and members of the Christian clergy speak it fluently, and...
as the lingua franca of the Roman Empire
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire was the post-Republican period of the ancient Roman civilization, characterised by an autocratic form of government and large territorial holdings in Europe and around the Mediterranean....
. Koine Greek
Koine Greek
Koine Greek is the universal dialect of the Greek language spoken throughout post-Classical antiquity , developing from the Attic dialect, with admixture of elements especially from Ionic....
was the "world language" of the Hellenistic period
Hellenistic period
The Hellenistic period or Hellenistic era describes the time which followed the conquests of Alexander the Great. It was so named by the historian J. G. Droysen. During this time, Greek cultural influence and power was at its zenith in Europe and Asia...
, but its distribution is not reflected in the distribution of Modern Greek
Modern Greek
Modern Greek refers to the varieties of the Greek language spoken in the modern era. The beginning of the "modern" period of the language is often symbolically assigned to the fall of the Byzantine Empire in 1453, even though that date marks no clear linguistic boundary and many characteristic...
due to the linguistic impact of the Slavic, Arabic
Muslim conquests
Muslim conquests also referred to as the Islamic conquests or Arab conquests, began with the Islamic prophet Muhammad. He established a new unified polity in the Arabian Peninsula which under the subsequent Rashidun and Umayyad Caliphates saw a century of rapid expansion of Muslim power.They...
and Turkic
Turkic migration
The Turkic migration as defined in this article was the expansion of the Turkic peoples across most of Central Asia into Europe and the Middle East between the 6th and 11th centuries AD . Tribes less certainly identified as Turkic began their expansion centuries earlier as the predominant element...
expansions. The distribution of the Turkic languages
Turkic languages
The Turkic languages constitute a language family of at least thirty five languages, spoken by Turkic peoples across a vast area from Eastern Europe and the Mediterranean to Siberia and Western China, and are considered to be part of the proposed Altaic language family.Turkic languages are spoken...
, in turn, are a legacy of the Turkic Khaganate.
Just as all the living world languages owe their status to historical imperialism
Imperialism
Imperialism, as defined by Dictionary of Human Geography, is "the creation and/or maintenance of an unequal economic, cultural, and territorial relationships, usually between states and often in the form of an empire, based on domination and subordination." The imperialism of the last 500 years,...
, the suggestion of a given language as a world language or "universal language
Universal language
Universal language may refer to a hypothetical or historical language spoken and understood by all or most of the world's population. In some circles, it is a language said to be understood by all living things, beings, and objects alike. It may be the ideal of an international auxiliary language...
" has strong political implications. Thus, Russian was declared the "world language of internationalism
Proletarian internationalism
Proletarian internationalism, sometimes referred to as international socialism, is a Marxist social class concept based on the view that capitalism is now a global system, and therefore the working class must act as a global class if it is to defeat it...
" in Soviet literature, which at the same time denounced French as the "language of fancy courtiers" and English as the "jargon of traders". A number of international auxiliary languages have been introduced as prospective world languages, the most successful of them being Esperanto
Esperanto
is the most widely spoken constructed international auxiliary language. Its name derives from Doktoro Esperanto , the pseudonym under which L. L. Zamenhof published the first book detailing Esperanto, the Unua Libro, in 1887...
, but none of them can claim the status of a living world language. Many natural languages have been proffered as candidates for a global lingua franca, including Italian
Italian language
Italian is a Romance language spoken mainly in Europe: Italy, Switzerland, San Marino, Vatican City, by minorities in Malta, Monaco, Croatia, Slovenia, France, Libya, Eritrea, and Somalia, and by immigrant communities in the Americas and Australia...
, Dutch
Dutch language
Dutch is a West Germanic language and the native language of the majority of the population of the Netherlands, Belgium, and Suriname, the three member states of the Dutch Language Union. Most speakers live in the European Union, where it is a first language for about 23 million and a second...
, Hungarian
Hungarian language
Hungarian is a Uralic language, part of the Ugric group. With some 14 million speakers, it is one of the most widely spoken non-Indo-European languages in Europe....
, German
German language
German is a West Germanic language, related to and classified alongside English and Dutch. With an estimated 90 – 98 million native speakers, German is one of the world's major languages and is the most widely-spoken first language in the European Union....
and Malay
Malay language
Malay is a major language of the Austronesian family. It is the official language of Malaysia , Indonesia , Brunei and Singapore...
.
Living world languages
Some sources define a living world language as having the following properties:- a large number of speakers
- a substantial fraction of non-native speakers (function as lingua francaLingua francaA lingua franca is a language systematically used to make communication possible between people not sharing a mother tongue, in particular when it is a third language, distinct from both mother tongues.-Characteristics:"Lingua franca" is a functionally defined term, independent of the linguistic...
) - officialOfficial languageAn official language is a language that is given a special legal status in a particular country, state, or other jurisdiction. Typically a nation's official language will be the one used in that nation's courts, parliament and administration. However, official status can also be used to give a...
status in several countries - a linguistic community not defined strictly along ethnic lines (multiethnic, pluricentric languagePluricentric languageA pluricentric language is a language with several standard versions, both in spoken and in written forms. This situation usually arises when language and the national identity of its native speakers do not, or did not, coincide.-English:...
) - one or more standard registersStandard languageA standard language is a language variety used by a group of people in their public discourse. Alternatively, varieties become standard by undergoing a process of standardization, during which it is organized for description in grammars and dictionaries and encoded in such reference works...
which are widely taughtLanguage educationLanguage education is the teaching and learning of a foreign or second language. Language education is a branch of applied linguistics.- Need for language education :...
as a foreign languageForeign languageA foreign language is a language indigenous to another country. It is also a language not spoken in the native country of the person referred to, i.e. an English speaker living in Japan can say that Japanese is a foreign language to him or her... - association with linguistic prestige
- use in international trade relations
- use in international organizations
- use in the academic community
- significant body of literatureLiteratureLiterature is the art of written works, and is not bound to published sources...
World languages in the strictest sense are:
| Language | Native speakers | Total speakers | Official Status Distribution | Official Status Maps |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| English English language English is a West Germanic language that arose in the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of England and spread into what was to become south-east Scotland under the influence of the Anglian medieval kingdom of Northumbria... |
328 M | 1800 M | Anglosphere English-speaking world The English-speaking world consists of those countries or regions that use the English language to one degree or another. For more information, please see:Lists:* List of countries by English-speaking population... |
 |
| Spanish (Castilian) Spanish language Spanish , also known as Castilian , is a Romance language in the Ibero-Romance group that evolved from several languages and dialects in central-northern Iberia around the 9th century and gradually spread with the expansion of the Kingdom of Castile into central and southern Iberia during the... |
329 M - 400 M | 500+ M | Hispanosphere Hispanophone Hispanophone or Hispanosphere denotes Spanish language speakers and the Spanish-speaking world. The word derives from the Latin political name of the Iberian Peninsula, Hispania, which comprised basically the territory of the modern states of Spain and Portugal.Hispanophones are estimated at... |
 |
| French French language French is a Romance language spoken as a first language in France, the Romandy region in Switzerland, Wallonia and Brussels in Belgium, Monaco, the regions of Quebec and Acadia in Canada, and by various communities elsewhere. Second-language speakers of French are distributed throughout many parts... |
67.8 - 110 M | 500 M | Francophone Francophone The adjective francophone means French-speaking, typically as primary language, whether referring to individuals, groups, or places. Often, the word is used as a noun to describe a natively French-speaking person.... |
 |
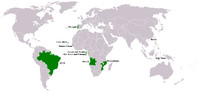
| Portuguese Portuguese language Portuguese is a Romance language that arose in the medieval Kingdom of Galicia, nowadays Galicia and Northern Portugal. The southern part of the Kingdom of Galicia became independent as the County of Portugal in 1095... |
178 M | 220 M | Lusophone Geographic distribution of Portuguese Portuguese is the official and first language of Angola, Brazil, Cape Verde, Guinea-Bissau, Mozambique, Portugal and São Tomé and Príncipe. It is also one of the official languages of East Timor , Macau and the Gabonese-Equatoguinean city of Cocobeach .Uruguay gave Portuguese an equal status to... |
 |
Other sources denote the following languages as world languages, whilst stricter sources list them as supra-regional languages:
| Language | Native speakers | Total speakers | Official Status Distribution | Official Status Maps |
|---|---|---|---|---|
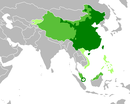
| Mandarin Mandarin -Officials:* Mandarin , a bureaucrat of Imperial China , Vietnam, and by analogy, any senior government bureaucrat-Language:... |
845 M | 1345 M | Sinosphere Sinosphere In areal linguistics, Sinosphere refers to a grouping of countries and regions that are currently inhabited with a majority of Chinese population or were historically under Chinese cultural influence... |
 |
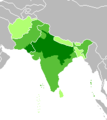
| Hindustani Hindustani language Hindi-Urdu is an Indo-Aryan language and the lingua franca of North India and Pakistan. It is also known as Hindustani , and historically, as Hindavi or Rekhta... |
460 M | 650 M | Indian subcontinent Indian subcontinent The Indian subcontinent, also Indian Subcontinent, Indo-Pak Subcontinent or South Asian Subcontinent is a region of the Asian continent on the Indian tectonic plate from the Hindu Kush or Hindu Koh, Himalayas and including the Kuen Lun and Karakoram ranges, forming a land mass which extends... |
 |
| Arabic Arabic language Arabic is a name applied to the descendants of the Classical Arabic language of the 6th century AD, used most prominently in the Quran, the Islamic Holy Book... |
221 M | 450 M | Arab world Arab world The Arab world refers to Arabic-speaking states, territories and populations in North Africa, Western Asia and elsewhere.The standard definition of the Arab world comprises the 22 states and territories of the Arab League stretching from the Atlantic Ocean in the west to the Arabian Sea in the... |
|
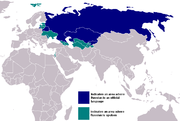
| Russian Russian language Russian is a Slavic language used primarily in Russia, Belarus, Uzbekistan, Kazakhstan, Tajikistan and Kyrgyzstan. It is an unofficial but widely spoken language in Ukraine, Moldova, Latvia, Turkmenistan and Estonia and, to a lesser extent, the other countries that were once constituent republics... |
144 M | 300 M | Russophone Russophone A Russophone is literally a speaker of the Russian language either natively or by preference. At the same time the term is used in a more specialized meaning to describe the category of people whose cultural background is associated with Russian language regardless of ethnic and territorial... |
 |
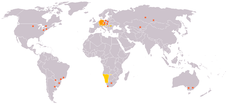
| German German language German is a West Germanic language, related to and classified alongside English and Dutch. With an estimated 90 – 98 million native speakers, German is one of the world's major languages and is the most widely-spoken first language in the European Union.... |
120 M | 200 M | German-speaking Europe German-speaking Europe The German language is spoken in a number of countries and territories in West, Central and Eastern Europe... |
 |
Other supra-regional languages
Other languages of supra-regional importance which fail some of the other criteria to be considered de facto world languages include:| Language | Native speakers | Total speakers | Official Status Distribution | Official Status Maps |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Malay Malay language Malay is a major language of the Austronesian family. It is the official language of Malaysia , Indonesia , Brunei and Singapore... and Indonesian Indonesian language Indonesian is the official language of Indonesia. Indonesian is a normative form of the Riau Islands dialect of Malay, an Austronesian language which has been used as a lingua franca in the Indonesian archipelago for centuries.... |
60 M | 176 M - 250 M | Malay Archipelago Malay Archipelago The Malay Archipelago refers to the archipelago between mainland Southeastern Asia and Australia. The name was derived from the anachronistic concept of a Malay race.... |
|
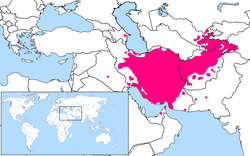
| Persian Persian language Persian is an Iranian language within the Indo-Iranian branch of the Indo-European languages. It is primarily spoken in Iran, Afghanistan, Tajikistan and countries which historically came under Persian influence... |
70 M | 144 M | Greater Iran Greater Iran Greater Iran refers to the regions that have significant Iranian cultural influence. It roughly corresponds to the territory on the Iranian plateau and its bordering plains, stretching from Iraq, the Caucasus, and Turkey in the west to the Indus River in the east... |
 |
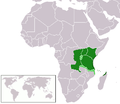
| Swahili Swahili language Swahili or Kiswahili is a Bantu language spoken by various ethnic groups that inhabit several large stretches of the Mozambique Channel coastline from northern Kenya to northern Mozambique, including the Comoro Islands. It is also spoken by ethnic minority groups in Somalia... |
5 - 10 M | 100 M | East Africa East Africa East Africa or Eastern Africa is the easterly region of the African continent, variably defined by geography or geopolitics. In the UN scheme of geographic regions, 19 territories constitute Eastern Africa:... |
 |
| Tamil Tamil language Tamil is a Dravidian language spoken predominantly by Tamil people of the Indian subcontinent. It has official status in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu and in the Indian union territory of Pondicherry. Tamil is also an official language of Sri Lanka and Singapore... |
68 M | 77 M | India India India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world... , Sri Lanka Sri Lanka Sri Lanka, officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka is a country off the southern coast of the Indian subcontinent. Known until 1972 as Ceylon , Sri Lanka is an island surrounded by the Indian Ocean, the Gulf of Mannar and the Palk Strait, and lies in the vicinity of India and the... , Singapore Singapore Singapore , officially the Republic of Singapore, is a Southeast Asian city-state off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, north of the equator. An island country made up of 63 islands, it is separated from Malaysia by the Straits of Johor to its north and from Indonesia's Riau Islands by the... |
|
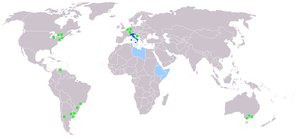
| Italian Italian language Italian is a Romance language spoken mainly in Europe: Italy, Switzerland, San Marino, Vatican City, by minorities in Malta, Monaco, Croatia, Slovenia, France, Libya, Eritrea, and Somalia, and by immigrant communities in the Americas and Australia... |
60 M | 70 M | Italy Italy Italy , officially the Italian Republic languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Italy's official name is as follows:;;;;;;;;), is a unitary parliamentary republic in South-Central Europe. To the north it borders France, Switzerland, Austria and... |
 |
| Dutch Dutch language Dutch is a West Germanic language and the native language of the majority of the population of the Netherlands, Belgium, and Suriname, the three member states of the Dutch Language Union. Most speakers live in the European Union, where it is a first language for about 23 million and a second... and Afrikaans Afrikaans Afrikaans is a West Germanic language, spoken natively in South Africa and Namibia. It is a daughter language of Dutch, originating in its 17th century dialects, collectively referred to as Cape Dutch .Afrikaans is a daughter language of Dutch; see , , , , , .Afrikaans was historically called Cape... |
28 M | 46 M | Dutch-speaking world | 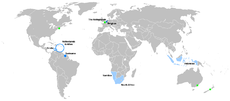 |
Two languages with a number of speakers in excess of 100 million, Japanese
Japanese language
is a language spoken by over 130 million people in Japan and in Japanese emigrant communities. It is a member of the Japonic language family, which has a number of proposed relationships with other languages, none of which has gained wide acceptance among historical linguists .Japanese is an...
and Bengali
Bengali language
Bengali or Bangla is an eastern Indo-Aryan language. It is native to the region of eastern South Asia known as Bengal, which comprises present day Bangladesh, the Indian state of West Bengal, and parts of the Indian states of Tripura and Assam. It is written with the Bengali script...
, are not listed. Although considered to be some of the most internationally significant languages along with the listed world languages, they are not considered world languages per se - Japan for example is almost ethnically, culturally and linguistically homogeneous, thus Japanese does not have much history as a lingua franca amongst communities who do not share a mother tongue or first language; their overseas communities are strongly tied to ethnicity; Bengali is not as widely taught as a foreign language as Japanese, where international interest since the 1980s have prompted many major universities as well as a number of secondary and even primary schools worldwide to offer courses in the language; and at least in the present, these languages exert a regionally limited sphere of influence;).
See also
- List of languages by number of speakers
- National languageNational languageA national language is a language which has some connection—de facto or de jure—with a people and perhaps by extension the territory they occupy. The term is used variously. A national language may for instance represent the national identity of a nation or country...
- Universal languageUniversal languageUniversal language may refer to a hypothetical or historical language spoken and understood by all or most of the world's population. In some circles, it is a language said to be understood by all living things, beings, and objects alike. It may be the ideal of an international auxiliary language...
- Lingua francaLingua francaA lingua franca is a language systematically used to make communication possible between people not sharing a mother tongue, in particular when it is a third language, distinct from both mother tongues.-Characteristics:"Lingua franca" is a functionally defined term, independent of the linguistic...
- International EnglishInternational EnglishInternational English is the concept of the English language as a global means of communication in numerous dialects, and also the movement towards an international standard for the language...
- World religion
- World populationWorld populationThe world population is the total number of living humans on the planet Earth. As of today, it is estimated to be billion by the United States Census Bureau...
- World economyWorld economyThe world economy, or global economy, generally refers to the economy, which is based on economies of all of the world's countries, national economies. Also global economy can be seen as the economy of global society and national economies – as economies of local societies, making the global one....
- World EnglishesWorld EnglishesWorld Englishes refers to the emergence of localised or indigenised varieties of English, especially varieties that have developed in nations colonised by Great Britain or influenced by the United States...
- IntercontinentalIntercontinentalIntercontinental may refer to:* anything spanning several continents* Intercontinental ballistic missile* the InterContinental hotel chain* InterContinental Hotels Group* Intercontinental Cup * Intercontinental Championship...
- International auxiliary languageInternational auxiliary languageAn international auxiliary language or interlanguage is a language meant for communication between people from different nations who do not share a common native language...

