
Barrel vault
Encyclopedia


Vault (architecture)
A Vault is an architectural term for an arched form used to provide a space with a ceiling or roof. The parts of a vault exert lateral thrust that require a counter resistance. When vaults are built underground, the ground gives all the resistance required...
: effectively a series of arch
Arch
An arch is a structure that spans a space and supports a load. Arches appeared as early as the 2nd millennium BC in Mesopotamian brick architecture and their systematic use started with the Ancient Romans who were the first to apply the technique to a wide range of structures.-Technical aspects:The...
es placed side by side, i.e., one after another. It is a form of barrel roof
Barrel roof
A barrel roof is a curved roof that, especially from below, is curved like a cut-away barrel. They have some advantages over dome roofs, especially being able to cover rectangular buildings., due to their uniform cross-section....
.
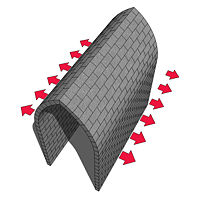
As with all arch-based constructions, there is an outward thrust generated against the walls underneath a barrel vault. There are several mechanisms for absorbing this thrust. One is, of course, to make the walls exceedingly thick and strong - this is a primitive and sometimes unacceptable method. A more elegant method is to build two or more vaults parallel to each other; the forces of their outward thrusts will thus negate each other. This method was most often used in construction of churches, where several vaulted nave
Nave
In Romanesque and Gothic Christian abbey, cathedral basilica and church architecture, the nave is the central approach to the high altar, the main body of the church. "Nave" was probably suggested by the keel shape of its vaulting...
s ran parallel down the length of the building. However, the outer walls of the outermost vault would still have to be quite strong or reinforced by buttress
Buttress
A buttress is an architectural structure built against or projecting from a wall which serves to support or reinforce the wall...
ing. The third and most elegant mechanism to resist the lateral thrust was to create an intersection of two barrel vaults at right angles, thus forming a groin vault
Groin vault
A groin vault or groined vault is produced by the intersection at right angles of two barrel vaults. The word groin refers to the edge between the intersecting vaults; cf. ribbed vault. Sometimes the arches of groin vaults are pointed instead of round...
.
Barrel vaults are known from Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt was an ancient civilization of Northeastern Africa, concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in what is now the modern country of Egypt. Egyptian civilization coalesced around 3150 BC with the political unification of Upper and Lower Egypt under the first pharaoh...
, and were used extensively in Roman architecture
Roman architecture
Ancient Roman architecture adopted certain aspects of Ancient Greek architecture, creating a new architectural style. The Romans were indebted to their Etruscan neighbors and forefathers who supplied them with a wealth of knowledge essential for future architectural solutions, such as hydraulics...
. They were also used to replace the Cloaca Maxima
Cloaca Maxima
The Cloaca Maxima is one of the world's earliest sewage systems. Constructed in Ancient Rome in order to drain local marshes and remove the waste of one of the world's most populous cities, it carried an effluent to the River Tiber, which ran beside the city....
with a system of underground sewers. Early barrel vault designs occur in northern Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
, Turkey
Turkey
Turkey , known officially as the Republic of Turkey , is a Eurasian country located in Western Asia and in East Thrace in Southeastern Europe...
, Morocco
Morocco
Morocco , officially the Kingdom of Morocco , is a country located in North Africa. It has a population of more than 32 million and an area of 710,850 km², and also primarily administers the disputed region of the Western Sahara...
and other regions. In medieval Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
the barrel vault was an important element of stone construction in monasteries
Monastery
Monastery denotes the building, or complex of buildings, that houses a room reserved for prayer as well as the domestic quarters and workplace of monastics, whether monks or nuns, and whether living in community or alone .Monasteries may vary greatly in size – a small dwelling accommodating only...
, castle
Castle
A castle is a type of fortified structure built in Europe and the Middle East during the Middle Ages by European nobility. Scholars debate the scope of the word castle, but usually consider it to be the private fortified residence of a lord or noble...
s, tower house
Tower house
A tower house is a particular type of stone structure, built for defensive purposes as well as habitation.-History:Tower houses began to appear in the Middle Ages, especially in mountain or limited access areas, in order to command and defend strategic points with reduced forces...
s and other structures. This form of design is observed in cellar
Basement
__FORCETOC__A basement is one or more floors of a building that are either completely or partially below the ground floor. Basements are typically used as a utility space for a building where such items as the furnace, water heater, breaker panel or fuse box, car park, and air-conditioning system...
s, crypt
Crypt
In architecture, a crypt is a stone chamber or vault beneath the floor of a burial vault possibly containing sarcophagi, coffins or relics....
s, long hallways, cloister
Cloister
A cloister is a rectangular open space surrounded by covered walks or open galleries, with open arcades on the inner side, running along the walls of buildings and forming a quadrangle or garth...
s and even great hall
Great hall
A great hall is the main room of a royal palace, nobleman's castle or a large manor house in the Middle Ages, and in the country houses of the 16th and early 17th centuries. At that time the word great simply meant big, and had not acquired its modern connotations of excellence...
s.
Theory and early history
Barrel vaulting was known and employed by early civilizations, including Ancient EgyptAncient Egypt
Ancient Egypt was an ancient civilization of Northeastern Africa, concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in what is now the modern country of Egypt. Egyptian civilization coalesced around 3150 BC with the political unification of Upper and Lower Egypt under the first pharaoh...
and Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a toponym for the area of the Tigris–Euphrates river system, largely corresponding to modern-day Iraq, northeastern Syria, southeastern Turkey and southwestern Iran.Widely considered to be the cradle of civilization, Bronze Age Mesopotamia included Sumer and the...
, but apparently it was not a very popular or very common method of construction. The technique probably evolved out of necessity to roof buildings with masonry elements such as bricks or stone blocks in areas where timber and wood were scarce. The earliest known example of a vault is a Tunnel vault found under the Sumer
Sumer
Sumer was a civilization and historical region in southern Mesopotamia, modern Iraq during the Chalcolithic and Early Bronze Age....
ian ziggurat
Ziggurat
Ziggurats were massive structures built in the ancient Mesopotamian valley and western Iranian plateau, having the form of a terraced step pyramid of successively receding stories or levels.Notable ziggurats include the Great Ziggurat of Ur near Nasiriyah, Iraq; the Ziggurat of Aqar Quf near...
at Nippur
Nippur
Nippur was one of the most ancient of all the Sumerian cities. It was the special seat of the worship of the Sumerian god Enlil, the "Lord Wind," ruler of the cosmos subject to An alone...
in Babylonia
Babylonia
Babylonia was an ancient cultural region in central-southern Mesopotamia , with Babylon as its capital. Babylonia emerged as a major power when Hammurabi Babylonia was an ancient cultural region in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq), with Babylon as its capital. Babylonia emerged as...
, ascribed to about 4000 BC, which was built of burnt bricks amalgamated with clay
Clay
Clay is a general term including many combinations of one or more clay minerals with traces of metal oxides and organic matter. Geologic clay deposits are mostly composed of phyllosilicate minerals containing variable amounts of water trapped in the mineral structure.- Formation :Clay minerals...
mortar
Mortar (masonry)
Mortar is a workable paste used to bind construction blocks together and fill the gaps between them. The blocks may be stone, brick, cinder blocks, etc. Mortar becomes hard when it sets, resulting in a rigid aggregate structure. Modern mortars are typically made from a mixture of sand, a binder...
. The earliest tunnel vaults in Egypt are found at Requagnah and Denderah, c. 3500 BC; these were built in sun-dried brick
Brick
A brick is a block of ceramic material used in masonry construction, usually laid using various kinds of mortar. It has been regarded as one of the longest lasting and strongest building materials used throughout history.-History:...
in three rings over passages descending to tomb
Tomb
A tomb is a repository for the remains of the dead. It is generally any structurally enclosed interment space or burial chamber, of varying sizes...
s: in these cases, as the span
Span (architecture)
Span is the distance between two intermediate supports for a structure, e.g. a beam or a bridge.A span can be closed by a solid beam or of a rope...
of the vault was only two meters. In these early instances, the barrel vault was chiefly used for underground structures such as drains and sewer
Sanitary sewer
A sanitary sewer is a separate underground carriage system specifically for transporting sewage from houses and commercial buildings to treatment or disposal. Sanitary sewers serving industrial areas also carry industrial wastewater...
s, though several buildings of the great Late Egyptian mortuary palace
Palace
A palace is a grand residence, especially a royal residence or the home of a head of state or some other high-ranking dignitary, such as a bishop or archbishop. The word itself is derived from the Latin name Palātium, for Palatine Hill, one of the seven hills in Rome. In many parts of Europe, the...
-temple
Temple
A temple is a structure reserved for religious or spiritual activities, such as prayer and sacrifice, or analogous rites. A templum constituted a sacred precinct as defined by a priest, or augur. It has the same root as the word "template," a plan in preparation of the building that was marked out...
of Ramesseum
Ramesseum
The Ramesseum is the memorial temple of Pharaoh Ramesses II . It is located in the Theban necropolis in Upper Egypt, across the River Nile from the modern city of Luxor...
were also vaulted in this way. Recent archaeological evidence discovered at the Morgantina
Morgantina
Morgantina is an archaeological site in east central Sicily, southern Italy. It is sixty kilometres from the coast of the Ionian Sea, in the province of Enna. The closest modern town is Aidone, two kilometres southwest of the site...
site (in the province of Enna
Enna
Enna is a city and comune located roughly at the center of Sicily, southern Italy, in the province of Enna, towering above the surrounding countryside...
) shows that the aboveground barrel vault was known and used in Hellenistic Sicily
Sicily
Sicily is a region of Italy, and is the largest island in the Mediterranean Sea. Along with the surrounding minor islands, it constitutes an autonomous region of Italy, the Regione Autonoma Siciliana Sicily has a rich and unique culture, especially with regard to the arts, music, literature,...
in 3rd century BC, indicating that the technique was also known to Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek is the stage of the Greek language in the periods spanning the times c. 9th–6th centuries BC, , c. 5th–4th centuries BC , and the c. 3rd century BC – 6th century AD of ancient Greece and the ancient world; being predated in the 2nd millennium BC by Mycenaean Greek...
s.
Ancient Romans most probably inherited their knowledge of barrel vaulting from Etruscans. Romans were the first to use this building method extensively on large-scale projects, and were probably the first to use scaffolding to aid them in construction of vaults spanning over widths greater than anything seen before. However, Roman builders gradually began to prefer the use of groin vault
Groin vault
A groin vault or groined vault is produced by the intersection at right angles of two barrel vaults. The word groin refers to the edge between the intersecting vaults; cf. ribbed vault. Sometimes the arches of groin vaults are pointed instead of round...
; though more complex to erect, this type of vault did not require heavy, thick walls for support (see bellow), and thus allowed for more spacious buildings with greater openings and much more light inside, such as thermae
Thermae
In ancient Rome, thermae and balnea were facilities for bathing...
.
After the fall of the Roman empire
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire was the post-Republican period of the ancient Roman civilization, characterised by an autocratic form of government and large territorial holdings in Europe and around the Mediterranean....
, few buildings large enough to require much in the way of vaulting were built for several centuries. In the early Romanesque
Romanesque architecture
Romanesque architecture is an architectural style of Medieval Europe characterised by semi-circular arches. There is no consensus for the beginning date of the Romanesque architecture, with proposals ranging from the 6th to the 10th century. It developed in the 12th century into the Gothic style,...
period, a return to stone barrel vaults was seen for the first great cathedrals; their interiors were fairly dark, due to thick, heavy walls needed to support the vault. One of the largest and most famous churches enclosed from above by a vast barrel vault was the church of Cluny Abbey
Cluny Abbey
Cluny Abbey is a Benedictine monastery in Cluny, Saône-et-Loire, France. It was built in the Romanesque style, with three churches built in succession from the 10th to the early 12th centuries....
, built between the 11th and 12th centuries.
In 13th and 14th century, with the advance of the new Gothic
Gothic architecture
Gothic architecture is a style of architecture that flourished during the high and late medieval period. It evolved from Romanesque architecture and was succeeded by Renaissance architecture....
style, barrel vaulting became almost extinct in constructions of great Gothic cathedrals; groin vault
Groin vault
A groin vault or groined vault is produced by the intersection at right angles of two barrel vaults. The word groin refers to the edge between the intersecting vaults; cf. ribbed vault. Sometimes the arches of groin vaults are pointed instead of round...
s reinforced by stone ribs were mostly used in the beginning, and later on various types of spectacular, ornate and complex medieval vaults were developed. However, with the coming of the Renaissance
Renaissance
The Renaissance was a cultural movement that spanned roughly the 14th to the 17th century, beginning in Italy in the Late Middle Ages and later spreading to the rest of Europe. The term is also used more loosely to refer to the historical era, but since the changes of the Renaissance were not...
and the Baroque
Baroque
The Baroque is a period and the style that used exaggerated motion and clear, easily interpreted detail to produce drama, tension, exuberance, and grandeur in sculpture, painting, literature, dance, and music...
style, and revived interest in art and architecture of antiquity, barrel vaulting was re-introduced on a truly grandiose scale, and employed in the construction of many famous buildings and churches, such as Basilica di Sant'Andrea di Mantova
Basilica di Sant'Andrea di Mantova
The Basilica concattedrale di Sant'Andrea is a Renaissance roman catholic church and minor basilica in Mantua, Lombardy .Commissioned by Ludovico II Gonzaga, the church was begun in 1462 according to designs by Leon Battista Alberti on a site occupied by a Benedictine monastery, of which the bell...
by Leone Battista Alberti
Leone Battista Alberti
Leon Battista Alberti was an Italian author, artist, architect, poet, priest, linguist, philosopher, cryptographer and general Renaissance humanist polymath...
, San Giorgio Maggiore
San Giorgio Maggiore
San Giorgio Maggiore is one of the islands of Venice, northern Italy, lying east of the Giudecca and south of the main island group. The isle is surrounded by Canale della Grazia, Canale della Giudecca, Saint Mark Basin, Canale di San Marco and the southern lagoon...
by Andrea Palladio
Andrea Palladio
Andrea Palladio was an architect active in the Republic of Venice. Palladio, influenced by Roman and Greek architecture, primarily by Vitruvius, is widely considered the most influential individual in the history of Western architecture...
, and perhaps most glorious of all, St. Peter's Basilica
St. Peter's Basilica
The Papal Basilica of Saint Peter , officially known in Italian as ' and commonly known as Saint Peter's Basilica, is a Late Renaissance church located within the Vatican City. Saint Peter's Basilica has the largest interior of any Christian church in the world...
in Rome, where a huge barrel vault spans the 27 meter wide nave.
Engineering issues
Muchalls Castle
Muchalls Castle stands overlooking the North Sea in the countryside of Kincardine and Mearns, Aberdeenshire, Scotland. The lower course is a well preserved double groined 13th century towerhouse structure, built by the Frasers of Muchalls. Upon this structure, the 17th century castle was begun by...
in Scotland
Scotland
Scotland is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Occupying the northern third of the island of Great Britain, it shares a border with England to the south and is bounded by the North Sea to the east, the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, and the North Channel and Irish Sea to the...
adjacent walls to the barrel vaulted chambers are up to 4,6 meters (15 feet) thick, adding the buttressing strength needed to secure the curved design. Well documented cases exist of the long term stress effects on inadequately laterally supported barrel vaults such as the 17th century church of Guimarei
Guimarei
Guimarei is a rural parish in Portugal with a population of 736 , and an area of 6.43km2. It is located 3km south of the center of the city of Santo Tirso in the Leça Valley.It is a residential place with some people working in agriculture....
.
The inherent difficulty of adequately lighting barrel vaulted structures has been widely acknowledged.
The intrinsic engineering issue is the need to avoid fenestration
Window
A window is a transparent or translucent opening in a wall or door that allows the passage of light and, if not closed or sealed, air and sound. Windows are usually glazed or covered in some other transparent or translucent material like float glass. Windows are held in place by frames, which...
punctures in stonework barrel vaults. Such openings could compromise the integrity of the entire arch system. Thus the Romanesque medieval builders had to resort to techniques of small windows, large buttresses, or other forms of interior wall cross-bracing to achieve the desired lighting outcomes. In many of the monasteries a natural solution was cloisters which could have high barrel-vaulted construction with an open courtyard to allow ample lighting.
Since 1996 structural engineer
Structural engineer
Structural engineers analyze, design, plan, and research structural components and structural systems to achieve design goals and ensure the safety and comfort of users or occupants...
s have applied Newton
Isaac Newton
Sir Isaac Newton PRS was an English physicist, mathematician, astronomer, natural philosopher, alchemist, and theologian, who has been "considered by many to be the greatest and most influential scientist who ever lived."...
ian mechanics to calculate numeric stress loads for ancient stonework barrel vaults. These analyses have typically used a finite element algorithm to calculate gravity induced stresses from the self weight of an arched system. In fact, for structural engineers, analysis of the barrel vault has become a benchmark test of a structural engineering computer model "because of the complex membrane and inextensional bending states of stress" involved.
In terms of comparison to other vaulting techniques the barrel vault is inherently a weaker design compared to the more complex groin vault
Groin vault
A groin vault or groined vault is produced by the intersection at right angles of two barrel vaults. The word groin refers to the edge between the intersecting vaults; cf. ribbed vault. Sometimes the arches of groin vaults are pointed instead of round...
. The barrel vault structure must rest on long walls creating less stable lateral stress, whereas the groin vault design can direct stresses almost purely vertically on the apexes.
Early occurrences
- Sistine ChapelSistine ChapelSistine Chapel is the best-known chapel in the Apostolic Palace, the official residence of the Pope in Vatican City. It is famous for its architecture and its decoration that was frescoed throughout by Renaissance artists including Michelangelo, Sandro Botticelli, Pietro Perugino, Pinturicchio...
, Vatican CityVatican CityVatican City , or Vatican City State, in Italian officially Stato della Città del Vaticano , which translates literally as State of the City of the Vatican, is a landlocked sovereign city-state whose territory consists of a walled enclave within the city of Rome, Italy. It has an area of... - Vatican grotto, Vatican CityVatican CityVatican City , or Vatican City State, in Italian officially Stato della Città del Vaticano , which translates literally as State of the City of the Vatican, is a landlocked sovereign city-state whose territory consists of a walled enclave within the city of Rome, Italy. It has an area of...
- Beverston CastleBeverston CastleBeverston Castle, also known as Beverstone Castle, was originally constructed as a medieval stone fortress and is situated in the village of Beverston, Gloucestershire, England. The castle was founded in 1229 by Maurice de Gaunt...
, EnglandEnglandEngland is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Scotland to the north and Wales to the west; the Irish Sea is to the north west, the Celtic Sea to the south west, with the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south separating it from continental...
, undercroftUndercroftAn undercroft is traditionally a cellar or storage room, often brick-lined and vaulted, and used for storage in buildings since medieval times. In modern usage, an undercroft is generally a ground area which is relatively open to the sides, but covered by the building above.- History :While some...
below south tower of west range - CathedralCathedralA cathedral is a Christian church that contains the seat of a bishop...
of CortonaCortonaCortona is a town and comune in the province of Arezzo, in Tuscany, Italy. It is the main cultural and artistic center of the Val di Chiana after Arezzo.-History:...
, Tuscany - Dunnottar CastleDunnottar CastleDunnottar Castle is a ruined medieval fortress located upon a rocky headland on the north-east coast of Scotland, about two miles south of Stonehaven. The surviving buildings are largely of the 15th–16th centuries, but the site is believed to have been an early fortress of the Dark Ages...
, ScotlandScotlandScotland is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Occupying the northern third of the island of Great Britain, it shares a border with England to the south and is bounded by the North Sea to the east, the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, and the North Channel and Irish Sea to the...
, Whigs VaultVault (architecture)A Vault is an architectural term for an arched form used to provide a space with a ceiling or roof. The parts of a vault exert lateral thrust that require a counter resistance. When vaults are built underground, the ground gives all the resistance required... - Hadrian's VillaHadrian's VillaThe Hadrian's Villa is a large Roman archaeological complex at Tivoli, Italy.- History :The villa was constructed at Tibur as a retreat from Rome for Roman Emperor Hadrian during the second and third decades of the 2nd century AD...
, Tivoli, ItalyTivoli, ItalyTivoli , the classical Tibur, is an ancient Italian town in Lazio, about 30 km east-north-east of Rome, at the falls of the Aniene river where it issues from the Sabine hills...
, numerous occurrences at this early 2nd century AD site - Mausoleum of Galla PlacidiaMausoleum of Galla PlacidiaThe Mausoleum of Galla Placidia is a Roman building in Ravenna, Italy. It was listed with seven other structures in Ravenna in the World Heritage List in 1996...
, RavennaRavennaRavenna is the capital city of the Province of Ravenna in the Emilia-Romagna region of Italy and the second largest comune in Italy by land area, although, at , it is little more than half the size of the largest comune, Rome...
, ItalyItalyItaly , officially the Italian Republic languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Italy's official name is as follows:;;;;;;;;), is a unitary parliamentary republic in South-Central Europe. To the north it borders France, Switzerland, Austria and...
(c. 500 AD) - Muchalls CastleMuchalls CastleMuchalls Castle stands overlooking the North Sea in the countryside of Kincardine and Mearns, Aberdeenshire, Scotland. The lower course is a well preserved double groined 13th century towerhouse structure, built by the Frasers of Muchalls. Upon this structure, the 17th century castle was begun by...
, ScotlandScotlandScotland is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Occupying the northern third of the island of Great Britain, it shares a border with England to the south and is bounded by the North Sea to the east, the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, and the North Channel and Irish Sea to the...
, cryptCryptIn architecture, a crypt is a stone chamber or vault beneath the floor of a burial vault possibly containing sarcophagi, coffins or relics....
and long hall - Myres CastleMyres CastleMyres Castle is a Scottish castle situated in Fife near the village of Auchtermuchty . Its history is interleaved with that of nearby Falkland Palace with present day castle construction dating to 1530...
, ScotlandScotlandScotland is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Occupying the northern third of the island of Great Britain, it shares a border with England to the south and is bounded by the North Sea to the east, the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, and the North Channel and Irish Sea to the...
, cellarBasement__FORCETOC__A basement is one or more floors of a building that are either completely or partially below the ground floor. Basements are typically used as a utility space for a building where such items as the furnace, water heater, breaker panel or fuse box, car park, and air-conditioning system...
s - Real Monasterio de Nuestra Senora de RuedaReal Monasterio de Nuestra Senora de RuedaRueda Abbey or Rueda de Ebro Abbey is a former Cistercian monastery in Sástago in the Ribera Baja del Ebro comarca, province of Zaragoza, Aragon, Spain, 74 kilometres to the south-east of Zaragoza on the left bank of the Ebro...
, SpainSpainSpain , officially the Kingdom of Spain languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Spain's official name is as follows:;;;;;;), is a country and member state of the European Union located in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula...
, cloisterCloisterA cloister is a rectangular open space surrounded by covered walks or open galleries, with open arcades on the inner side, running along the walls of buildings and forming a quadrangle or garth...
s of this 12th century monasteryMonasteryMonastery denotes the building, or complex of buildings, that houses a room reserved for prayer as well as the domestic quarters and workplace of monastics, whether monks or nuns, and whether living in community or alone .Monasteries may vary greatly in size – a small dwelling accommodating only... - Scrovegni Chapel also known as Cappella degli ScrovegniCappella degli ScrovegniThe Scrovegni Chapel, or Cappella degli Scrovegni, also known as the Arena Chapel, is a church in Padua, Veneto, Italy. It contains a fresco cycle by Giotto, completed about 1305, that is one of the most important masterpieces of Western art. The church was dedicated to Santa Maria della Carità at...
, PaduaPaduaPadua is a city and comune in the Veneto, northern Italy. It is the capital of the province of Padua and the economic and communications hub of the area. Padua's population is 212,500 . The city is sometimes included, with Venice and Treviso, in the Padua-Treviso-Venice Metropolitan Area, having...
, VenetoVenetoVeneto is one of the 20 regions of Italy. Its population is about 5 million, ranking 5th in Italy.Veneto had been for more than a millennium an independent state, the Republic of Venice, until it was eventually annexed by Italy in 1866 after brief Austrian and French rule...
, ItalyItalyItaly , officially the Italian Republic languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Italy's official name is as follows:;;;;;;;;), is a unitary parliamentary republic in South-Central Europe. To the north it borders France, Switzerland, Austria and...
(1303 AD) - Royal Granary, MeknesMeknesMeknes is a city in northern Morocco, located from the capital Rabat and from Fes. It is served by the A2 expressway between those two cities and by the corresponding railway. Meknes was the capital of Morocco under the reign of Moulay Ismail , before it was relocated to Marrakech. The...
, MoroccoMoroccoMorocco , officially the Kingdom of Morocco , is a country located in North Africa. It has a population of more than 32 million and an area of 710,850 km², and also primarily administers the disputed region of the Western Sahara...
(17th century) - Williamson Tunnels, LiverpoolLiverpoolLiverpool is a city and metropolitan borough of Merseyside, England, along the eastern side of the Mersey Estuary. It was founded as a borough in 1207 and was granted city status in 1880...
, EnglandEnglandEngland is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Scotland to the north and Wales to the west; the Irish Sea is to the north west, the Celtic Sea to the south west, with the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south separating it from continental...
(Early 19th century)
Modern examples
There are numerous contemporary examples of barrel vault design in VictorianVictorian architecture
The term Victorian architecture refers collectively to several architectural styles employed predominantly during the middle and late 19th century. The period that it indicates may slightly overlap the actual reign, 20 June 1837 – 22 January 1901, of Queen Victoria. This represents the British and...
and modern architecture
Modern architecture
Modern architecture is generally characterized by simplification of form and creation of ornament from the structure and theme of the building. It is a term applied to an overarching movement, with its exact definition and scope varying widely...
, including:
- BelfastBelfastBelfast is the capital of and largest city in Northern Ireland. By population, it is the 14th biggest city in the United Kingdom and second biggest on the island of Ireland . It is the seat of the devolved government and legislative Northern Ireland Assembly...
, Northern IrelandNorthern IrelandNorthern Ireland is one of the four countries of the United Kingdom. Situated in the north-east of the island of Ireland, it shares a border with the Republic of Ireland to the south and west...
, City Hall BanquetBanquetA banquet is a large meal or feast, complete with main courses and desserts. It usually serves a purpose such as a charitable gathering, a ceremony, or a celebration, and is often preceded or followed by speeches in honour of someone....
room with barrel vault ceiling 1896-1906, DonegalDonegalDonegal or Donegal Town is a town in County Donegal, Ireland. Its name, which was historically written in English as Dunnagall or Dunagall, translates from Irish as "stronghold of the foreigners" ....
Square - Huntington Bank BuildingHuntington Bank BuildingThe Huntington Bank Building is a high-rise office building on Euclid Avenue in downtown Cleveland, Ohio. When the building was completed in 1924, it was the second largest building in the world in terms of floor space, with more than 30 acres of floor space...
, Cleveland, OhioCleveland, OhioCleveland is a city in the U.S. state of Ohio and is the county seat of Cuyahoga County, the most populous county in the state. The city is located in northeastern Ohio on the southern shore of Lake Erie, approximately west of the Pennsylvania border...
, 1924 design - Kimbell Art MuseumKimbell Art MuseumThe Kimbell Art Museum in Fort Worth, Texas, hosts a small but excellent art collection as well as traveling art exhibitions, educational programs and an extensive research library. Its initial artwork came from the private collection of Kay and Velma Kimbell, who also provided funds for a new...
, Fort Worth, TexasFort Worth, TexasFort Worth is the 16th-largest city in the United States of America and the fifth-largest city in the state of Texas. Located in North Central Texas, just southeast of the Texas Panhandle, the city is a cultural gateway into the American West and covers nearly in Tarrant, Parker, Denton, and...
, USAUnited StatesThe United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
, spanning a width of 174 feet. - MelbourneMelbourneMelbourne is the capital and most populous city in the state of Victoria, and the second most populous city in Australia. The Melbourne City Centre is the hub of the greater metropolitan area and the Census statistical division—of which "Melbourne" is the common name. As of June 2009, the greater...
, AustraliaAustraliaAustralia , officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country in the Southern Hemisphere comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. It is the world's sixth-largest country by total area...
, Forest Hill Chase Shopping CentreForest Hill Chase Shopping CentreForest Hill Chase Shopping Centre is a major regional shopping centre located in the eastern suburb of Forest Hill in the city of Melbourne, Australia...
, made of polycarbonatePolycarbonatePolycarbonatePhysical PropertiesDensity 1.20–1.22 g/cm3Abbe number 34.0Refractive index 1.584–1.586FlammabilityV0-V2Limiting oxygen index25–27%Water absorption – Equilibrium0.16–0.35%Water absorption – over 24 hours0.1%... - The Indiana UniversityIndiana UniversityIndiana University is a multi-campus public university system in the state of Indiana, United States. Indiana University has a combined student body of more than 100,000 students, including approximately 42,000 students enrolled at the Indiana University Bloomington campus and approximately 37,000...
new libraryLibraryIn a traditional sense, a library is a large collection of books, and can refer to the place in which the collection is housed. Today, the term can refer to any collection, including digital sources, resources, and services...
In unconventional usage
Beyond the classical use of the barrel vault in macro-architectural design (e.g. as a major structural roofing element), there are a variety of derivative applications clearly based on the original concept and shape of the barrel vault. These applications arise in the fields of surgerySurgery
Surgery is an ancient medical specialty that uses operative manual and instrumental techniques on a patient to investigate and/or treat a pathological condition such as disease or injury, or to help improve bodily function or appearance.An act of performing surgery may be called a surgical...
, skylight design, children's toys and micro-structure design (such as bus shelters). While none of these applications rival the majesty of the ancient and Classical predecessors, they demonstrate the pervasiveness of the barrel vault as an architectural concept in contemporary times.
In the field of bone surgery the technique of a "barrel vault" shaped incision is not only a well-defined state-of-the-art surgical procedure, but the name barrel vault is given to this technique by orthopedic surgeon
Surgeon
In medicine, a surgeon is a specialist in surgery. Surgery is a broad category of invasive medical treatment that involves the cutting of a body, whether human or animal, for a specific reason such as the removal of diseased tissue or to repair a tear or breakage...
s. The Wohlfahrt study cited documents results of this surgical procedure on the human tibia
Tibia
The tibia , shinbone, or shankbone is the larger and stronger of the two bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates , and connects the knee with the ankle bones....
in 91 such operations.

