
Bernoulli trial
Encyclopedia
In the theory of probability
and statistics
, a Bernoulli trial is an experiment whose outcome is random and can be either of two possible outcomes, "success" and "failure".
In practice it refers to a single experiment
which can have one of two possible outcomes. These events can be phrased into "yes or no" questions:
Therefore success and failure are labels for outcomes, and should not be construed literally. Examples of Bernoulli trials include
Call one of the outcomes success and the other outcome failure.
Let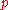 be the probability of success in a Bernoulli trial. Then the probability of failure
be the probability of success in a Bernoulli trial. Then the probability of failure 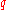 is given by
is given by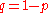 .
.
A binomial experiment consisting of a fixed number of trials, each with a probability of success
of trials, each with a probability of success 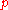 , is denoted by
, is denoted by 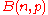 .
.
The probability of exactly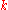 successes in the experiment
successes in the experiment 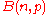 is given by:
is given by: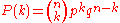 .
.
The function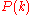 for
for 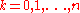 for
for 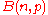 is called a binomial distribution.
is called a binomial distribution.
Bernoulli trials may also lead to negative binomial
, geometric, and other distributions as well.
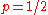 . Thus the probability of failure is given by
. Thus the probability of failure is given by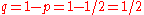 .
.
Using the equation above, the probability of exactly two tosses out of four total tosses resulting in a heads is given by: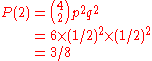 .
.
Probability
Probability is ordinarily used to describe an attitude of mind towards some proposition of whose truth we arenot certain. The proposition of interest is usually of the form "Will a specific event occur?" The attitude of mind is of the form "How certain are we that the event will occur?" The...
and statistics
Statistics
Statistics is the study of the collection, organization, analysis, and interpretation of data. It deals with all aspects of this, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of surveys and experiments....
, a Bernoulli trial is an experiment whose outcome is random and can be either of two possible outcomes, "success" and "failure".
In practice it refers to a single experiment
Experiment
An experiment is a methodical procedure carried out with the goal of verifying, falsifying, or establishing the validity of a hypothesis. Experiments vary greatly in their goal and scale, but always rely on repeatable procedure and logical analysis of the results...
which can have one of two possible outcomes. These events can be phrased into "yes or no" questions:
- Did the coin land heads?
- Was the newborn child a girl?
Therefore success and failure are labels for outcomes, and should not be construed literally. Examples of Bernoulli trials include
- Flipping a coin. In this context, obverse ("heads") conventionally denotes success and reverse ("tails") denotes failure. A fair coinFair coinIn probability theory and statistics, a sequence of independent Bernoulli trials with probability 1/2 of success on each trial is metaphorically called a fair coin. One for which the probability is not 1/2 is called a biased or unfair coin...
has the probability of success 0.5 by definition. - Rolling a dieDiceA die is a small throwable object with multiple resting positions, used for generating random numbers...
, where a six is "success" and everything else a "failure". - In conducting a political opinion pollOpinion pollAn opinion poll, sometimes simply referred to as a poll is a survey of public opinion from a particular sample. Opinion polls are usually designed to represent the opinions of a population by conducting a series of questions and then extrapolating generalities in ratio or within confidence...
, choosing a voter at random to ascertain whether that voter will vote "yes" in an upcoming referendum.
Definition
Independent repeated trials of an experiment with two outcomes only are called Bernoulli trials.Call one of the outcomes success and the other outcome failure.
Let
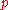 be the probability of success in a Bernoulli trial. Then the probability of failure
be the probability of success in a Bernoulli trial. Then the probability of failure 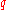 is given by
is given by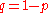 .
.A binomial experiment consisting of a fixed number
 of trials, each with a probability of success
of trials, each with a probability of success 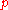 , is denoted by
, is denoted by 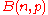 .
.The probability of exactly
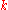 successes in the experiment
successes in the experiment 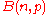 is given by:
is given by: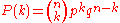 .
.The function
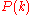 for
for 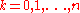 for
for 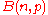 is called a binomial distribution.
is called a binomial distribution.Bernoulli trials may also lead to negative binomial
Negative binomial distribution
In probability theory and statistics, the negative binomial distribution is a discrete probability distribution of the number of successes in a sequence of Bernoulli trials before a specified number of failures occur...
, geometric, and other distributions as well.
Example: Tossing Coins
Consider the simple experiment where a fair coin is tossed four times. Find the probability that exactly two of the tosses result in heads.Solution
For this experiment, let a heads be defined as a success and a tails as a failure. Because the coin is assumed to be fair, the probability of success is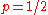 . Thus the probability of failure is given by
. Thus the probability of failure is given by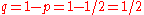 .
.Using the equation above, the probability of exactly two tosses out of four total tosses resulting in a heads is given by:
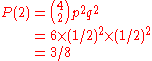 .
.See also
- Bernoulli schemeBernoulli schemeIn mathematics, the Bernoulli scheme or Bernoulli shift is a generalization of the Bernoulli process to more than two possible outcomes. Bernoulli schemes are important in the study of dynamical systems, as most such systems exhibit a repellor that is the product of the Cantor set and a smooth...
- Bernoulli samplingBernoulli samplingIn the theory of finite population sampling, Bernoulli sampling is a sampling process where each element of the population that is sampled is subjected to an independent Bernoulli trial which determines whether the element becomes part of the sample during the drawing of a single sample...
- Bernoulli distribution
- Binomial distribution
- Binomial proportion confidence intervalBinomial proportion confidence intervalIn statistics, a binomial proportion confidence interval is a confidence interval for a proportion in a statistical population. It uses the proportion estimated in a statistical sample and allows for sampling error. There are several formulas for a binomial confidence interval, but all of them rely...
- Poisson samplingPoisson samplingIn the theory of finite population sampling, Poisson sampling is a sampling process where each element of the population that is sampled is subjected to an independent Bernoulli trial which determines whether the element becomes part of the sample during the drawing of a single sample.Each element...
- Sampling designSampling designIn the theory of finite population sampling, a sampling design specifies for every possible sample its probability of being drawn.Mathematically, a sampling design is denoted by the function P which gives the probability of drawing a sample S....
- Coin flippingCoin flippingCoin flipping or coin tossing or heads or tails is the practice of throwing a coin in the air to choose between two alternatives, sometimes to resolve a dispute between two parties...
- Jacob Bernoulli

