
Carcinogenesis
Encyclopedia
Carcinogenesis or oncogenesis is literally the creation of cancer
. It is a process by which normal cells
are transformed into cancer cells. It is characterized by a progression of changes on cellular and genetic level that ultimately reprogram a cell to undergo uncontrolled cell division
, thus forming a malignant mass.
Cell division is a physiological process that occurs in almost all tissues and under many circumstances. Under normal circumstances, the balance between proliferation and programmed cell death, usually in the form of apoptosis
, is maintained by tightly regulating both processes to ensure the integrity of organs and tissues. Mutations in DNA that lead to cancer (only certain mutations can lead to cancer and the majority of potential mutations will have no bearing) disrupt these orderly processes by disrupting the programming regulating the processes.
Carcinogenesis is caused by this mutation of the genetic material of normal cells, which upsets the normal balance between proliferation and cell death. This results in uncontrolled cell division and the evolution of those cells
by natural selection
in the body. The uncontrolled and often rapid proliferation of cells can lead to benign tumors; some types of these may turn into malignant tumors (cancer). Benign tumors do not spread to other parts of the body or invade other tissues, and they are rarely a threat to life unless they compress vital structures or are physiologically active, for instance, producing a hormone. Malignant tumors can invade other organs, spread to distant locations (metastasis
) and become life-threatening.
More than one mutation is necessary for carcinogenesis. In fact, a series of several mutations to certain classes of genes is usually required before a normal cell will transform into a cancer cell. Only mutations in those certain types of genes that play vital roles in cell division, apoptosis (cell death), and DNA repair will cause a cell to lose control of its cell proliferation.
Oncovirinae
, retrovirus
es that contain an oncogene
, are categorized as oncogenic because they trigger the growth of tumorous tissues in the host
. This process is also referred to as viral transformation
.
Cancer is fundamentally a disease of regulation of tissue growth. In order for a normal cell to transform
into a cancer cell, genes
that regulate cell growth and differentiation must be altered. Genetic changes can occur at many levels, from gain or loss of entire chromosomes to a mutation affecting a single DNA nucleotide
. There are two broad categories of genes that are affected by these changes. Oncogene
s may be normal genes that are expressed at inappropriately high levels, or altered genes that have novel properties. In either case, expression of these genes promotes the malignant phenotype of cancer cells. Tumor suppressor gene
s are genes that inhibit cell division, survival, or other properties of cancer cells. Tumor suppressor genes are often disabled by cancer-promoting genetic changes. Typically, changes in many genes are required to transform a normal cell into a cancer cell.
There is a diverse classification scheme for the various genomic changes that may contribute to the generation of cancer cells. Most of these changes are mutation
s, or changes in the nucleotide
sequence of genomic DNA. Aneuploidy
, the presence of an abnormal number of chromosomes, is one genomic change that is not a mutation, and may involve either gain or loss of one or more chromosomes through errors in mitosis
.
Large-scale mutations involve the deletion or gain of a portion of a chromosome. Genomic amplification occurs when a cell gains many copies (often 20 or more) of a small chromosomal region, usually containing one or more oncogenes and adjacent genetic material. Translocation
occurs when two separate chromosomal regions become abnormally fused, often at a characteristic location. A well-known example of this is the Philadelphia chromosome
, or translocation of chromosomes 9 and 22, which occurs in chronic myelogenous leukemia
, and results in production of the BCR
-abl
fusion protein
, an oncogenic tyrosine kinase
.
Small-scale mutations include point mutations, deletions, and insertions, which may occur in the promoter of a gene and affect its expression
, or may occur in the gene's coding sequence and alter the function or stability of its protein
product. Disruption of a single gene may also result from integration of genomic material
from a DNA virus
or retrovirus
, and such an event may also result in the expression of viral oncogenes in the affected cell and its descendants.
s. However, with the help of cancer epidemiology techniques and information, it is possible to produce an estimate of a likely cause in many more situations. For example, lung cancer
has several causes, including tobacco use and radon gas. Men who currently smoke tobacco develop lung cancer at a rate 14 times that of men who have never smoked tobacco, so the chance of lung cancer in a current smoker being caused by smoking is about 93%; there is a 7% chance that the smoker's lung cancer was caused by radon gas or some other, non-tobacco cause. These statistical correlations have made it possible for researchers to infer that certain substances or behaviors are carcinogenic.
Using molecular biological
techniques, it is possible to characterize the mutations or chromosomal aberrations within a tumor, and rapid progress is being made in the field of predicting prognosis
based on the spectrum of mutations in some cases. For example, up to half of all tumors have a defective p53 gene. This mutation is associated with poor prognosis, since those tumor cells are less likely to go into apoptosis
or programmed cell death
when damaged by therapy. Telomerase
mutations remove additional barriers, extending the number of times a cell can divide. Other mutations enable the tumor to grow new blood vessels
to provide more nutrients, or to metastasize
, spreading to other parts of the body.
Several alternative theories of carcinogenesis, however, are based on scientific evidence and are increasingly being acknowledged. Some researchers believe that cancer may be caused by epigenetic alterations (heritable and reversible changes other than the DNA sequence) or aneuploidy
(numerical and structural abnormalities in chromosomes) rather than by mutations. Cancer has also been considered as a metabolic disease in which the cellular metabolism of oxygen is diverted from the pathway that generates energy (oxidative phosphorylation
) to the pathway that generates reactive oxygen species
(figure). This causes an energy switch from oxidative phosphorylation to aerobic glycolysis (Warburg's hypothesis) and the accumulation of reactive oxygen species
leading to oxidative stress
(oxidative stress theory of cancer). All these theories of carcinogenesis may be complementary rather than contradictory.
Another theory as to the origin of cancer was developed by astrobiologists
and suggests that cancer is an atavism
, an evolutionary throwback to an earlier form of multicellular life
. The genes responsible for uncontrolled cell growth and cooperation between cancer cells are very similar to those that enabled the first multicellular life forms to group together and flourish. These genes still exist within the genome of more complex metazoans
, such as humans, although more recently evolved genes keep them in check. When the newer controlling genes fail for whatever reason, the cell can revert to its more primitive programming and reproduce out of control. The theory is an alternative to the notion that cancers begin with rogue cells that undergo evolution within the body. Instead they possess a fixed number of primitive genes that are progressively activated, giving them finite variability.
. Among the distinguishing traits are an increased number of dividing cells, variation in nuclear
size and shape, variation in cell size and shape, loss of specialized cell features, and loss of normal tissue organization. Dysplasia
is an abnormal type of excessive cell proliferation characterized by loss of normal tissue arrangement and cell structure in pre-malignant cells. These early neoplastic changes must be distinguished from hyperplasia, a reversible increase in cell division caused by an external stimulus, such as a hormonal imbalance or chronic irritation.
The most severe cases of dysplasia are referred to as "carcinoma in situ
." In Latin, the term "in situ" means "in place", so carcinoma in situ refers to an uncontrolled growth of cells that remains in the original location and has not shown invasion into other tissues. Nevertheless, carcinoma in situ may develop into an invasive malignancy and is usually removed surgically, if possible.
, an unchecked population of cells also can undergo evolution. This undesirable process is called somatic evolution
, and is how cancer arises and becomes more malignant.
Most changes in cellular metabolism that allow cells to grow in a disorderly fashion lead to cell death. However once cancer begins, cancer cells undergo a process of natural selection
: the few cells with new genetic changes that enhance their survival or reproduction continue to multiply, and soon come to dominate the growing tumor, as cells with less favorable genetic change are out-competed. This is exactly how pathogens such as MRSA can become antibiotic-resistant
(or how HIV
can become drug-resistant
), and the same reason why crop blights and pests can become pesticide-resistant
. This evolution is why cancer recurrences will have cells that have acquired cancer-drug resistance (or in some cases, resistance to radiation from radiotherapy).
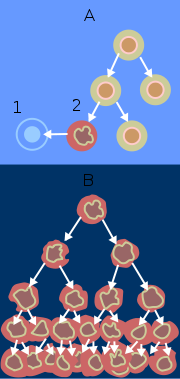 In a 2000 article by Hanahan and Weinberg
In a 2000 article by Hanahan and Weinberg
, the biological properties of malignant tumor cells were summarized as follows:
The completion of these multiple steps would be a very rare event without :
These biological changes are classical in carcinoma
s; other malignant tumors may not need to achieve them all. For example, tissue invasion and displacement to distant sites are normal properties of leukocytes; these steps are not needed in the development of leukemia
. The different steps do not necessarily represent individual mutations. For example, inactivation of a single gene, coding for the p53
protein, will cause genomic instability, evasion of apoptosis and increased angiogenesis. Not all the cancer cells are dividing. Rather, a subset of the cells in a tumor, called cancer stem cell
s, replicate themselves and generate differentiated cells.
, whereas tumor suppressor gene
s discourage cell growth, or temporarily halt cell division to carry out DNA repair
. Typically, a series of several mutation
s to these genes is required before a normal cell transforms into a cancer cell. This concept is sometimes termed "oncoevolution." Mutations to these genes provide the signals for tumor cells to start dividing uncontrollably. But the uncontrolled cell division that characterizes cancer also requires that the dividing cell duplicates all its cellular components to create two daughter cells. The activation of anaerobic glycolysis (the Warburg effect
), which is not necessarily induced by mutations in proto-oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes, provides most of the building blocks required to duplicate the cellular components of a dividing cell and, therefore, is also essential for carcinogenesis.
s promote cell growth through a variety of ways. Many can produce hormone
s, a "chemical messenger" between cells that encourage mitosis
, the effect of which depends on the signal transduction
of the receiving tissue or cells. In other words, when a hormone receptor on a recipient cell is stimulated, the signal is conducted from the surface of the cell to the cell nucleus
to affect some change in gene transcription regulation at the nuclear level. Some oncogenes are part of the signal transduction system itself, or the signal receptors
in cells and tissues themselves, thus controlling the sensitivity to such hormones. Oncogenes often produce mitogen
s, or are involved in transcription
of DNA in protein synthesis
, which creates the protein
s and enzyme
s responsible for producing the products and biochemicals
cells use and interact with.
Mutations in proto-oncogenes, which are the normally quiescent counterparts of oncogenes, can modify their expression
and function, increasing the amount or activity of the product protein. When this happens, the proto-oncogenes become oncogene
s, and this transition upsets the normal balance of cell cycle
regulation in the cell, making uncontrolled growth possible. The chance of cancer cannot be reduced by removing proto-oncogenes from the genome
, even if this were possible, as they are critical for growth, repair and homeostasis
of the organism. It is only when they become mutated that the signals for growth become excessive.
One of the first oncogenes to be defined in cancer research
is the ras oncogene. Mutations in the Ras family of proto-oncogenes (comprising H-Ras, N-Ras and K-Ras) are very common, being found in 20% to 30% of all human tumours. Ras was originally identified in the Harvey sarcoma virus genome, and researchers were surprised that not only is this gene present in the human genome but also, when ligated to a stimulating control element, it could induce cancers in cell line cultures.
s, "chemical messengers" between cells that encourage mitosis, the effect of which depends on the signal transduction
of the receiving tissue or cells. Some are responsible for the signal transduction system and signal receptors
in cells and tissues themselves, thus controlling the sensitivity to such hormones. They often produce mitogen
s, or are involved in transcription
of DNA in protein synthesis, which create the protein
s and enzyme
s is responsible for producing the products and biochemicals
cells use and interact with.
Mutations in proto-oncogenes can modify their expression
and function, increasing the amount or activity of the product protein. When this happens, they become oncogene
s, and, thus, cells have a higher chance to divide excessively and uncontrollably. The chance of cancer cannot be reduced by removing proto-oncogenes from the genome
, as they are critical for growth, repair and homeostasis
of the body. It is only when they become mutated that the signals for growth become excessive.
It is important to note that a gene possessing a growth-promoting role may increase carcinogenic potential of a cell, under the condition that all necessary cellular mechanisms that permit growth are activated. This condition includes also the inactivation of specific tumor suppressor genes (see below). If the condition is not fulfilled, the cell may cease to grow and can proceed to die. This makes knowledge of the stage and type of cancer cell that grows under the control of a given oncogene crucial for the development of treatment strategies.
 Tumor suppressor gene
Tumor suppressor gene
s code for anti-proliferation signals and proteins that suppress mitosis and cell growth. Generally, tumor suppressors are transcription factor
s that are activated by cellular stress
or DNA damage. Often DNA damage will cause the presence of free-floating genetic material as well as other signs, and will trigger enzymes and pathways that lead to the activation of tumor suppressor genes. The functions of such genes is to arrest the progression of the cell cycle in order to carry out DNA repair, preventing mutations from being passed on to daughter cells. The p53
protein, one of the most important studied tumor suppressor genes, is a transcription factor activated by many cellular stressors including hypoxia
and ultraviolet radiation damage.
Despite nearly half of all cancers possibly involving alterations in p53, its tumor suppressor function is poorly understood. p53 clearly has two functions: one a nuclear role as a transcription factor, and the other a cytoplasmic role in regulating the cell cycle, cell division, and apoptosis.
The Warburg hypothesis
is the preferential use of glycolysis for energy to sustain cancer growth. p53 has been shown to regulate the shift from the respiratory to the glycolytic pathway.
However, a mutation can damage the tumor suppressor gene itself, or the signal pathway that activates it, "switching it off". The invariable consequence of this is that DNA repair is hindered or inhibited: DNA damage accumulates without repair, inevitably leading to cancer.
Mutations of tumor suppressor genes that occur in germline
cells are passed along to offspring
, and increase the likelihood for cancer diagnoses in subsequent generations. Members of these families have increased incidence and decreased latency of multiple tumors. The tumor types are typical for each type of tumor suppressor gene mutation, with some mutations causing particular cancers, and other mutations causing others. The mode of inheritance of mutant tumor suppressors is that an affected member inherits a defective copy from one parent, and a normal copy from the other. For instance, individuals who inherit one mutant p53
allele (and are therefore heterozygous for mutated p53) can develop melanomas and pancreatic cancer
, known as Li-Fraumeni syndrome
. Other inherited tumor suppressor gene syndromes include Rb
mutations, linked to retinoblastoma
, and APC gene mutations, linked to adenopolyposis colon cancer
. Adenopolyposis colon cancer is associated with thousands of polyps in colon while young, leading to colon cancer
at a relatively early age. Finally, inherited mutations in BRCA1
and BRCA2
lead to early onset of breast cancer
.
Development of cancer was proposed in 1971 to depend on at least two mutational events. In what became known as the Knudson
two-hit hypothesis
, an inherited, germ-line mutation in a tumor suppressor gene
would cause cancer only if another mutation event occurred later in the organism's life, inactivating the other allele
of that tumor suppressor gene
.
Usually, oncogenes are dominant, as they contain gain-of-function mutations, while mutated tumor suppressors are recessive, as they contain loss-of-function mutations. Each cell has two copies of the same gene, one from each parent, and under most cases gain of function mutations in just one copy of a particular proto-oncogene is enough to make that gene a true oncogene. On the other hand, loss of function mutations need to happen in both copies of a tumor suppressor gene to render that gene completely non-functional. However, cases exist in which one mutated copy of a tumor suppressor gene
can render the other, wild-type copy non-functional. This phenomenon is called the dominant negative effect and is observed in many p53 mutations.
Knudson’s two hit model has recently been challenged by several investigators. Inactivation of one allele of some tumor suppressor genes is sufficient to cause tumors. This phenomenon is called haploinsufficiency
and has been demonstrated by a number of experimental approaches. Tumors caused by haploinsufficiency
usually have a later age of onset when compared with those by a two hit process.
ed by the Knudson hypothesis
. A mutation to only one tumor suppressor gene would not cause cancer either, due to the presence of many "backup
" genes that duplicate its functions. It is only when enough proto-oncogenes have mutated into oncogenes, and enough tumor suppressor genes deactivated or damaged, that the signals for cell growth overwhelm the signals to regulate it, that cell growth quickly spirals out of control. Often, because these genes regulate the processes that prevent most damage to genes themselves, the rate of mutations increases as one gets older, because DNA damage forms a feedback
loop.
Usually, oncogenes are dominant alleles, as they contain gain-of-function mutations, whereas mutated tumor suppressors are recessive alleles, as they contain loss-of-function mutations. Each cell has two copies of a same gene, one from each parent, and, under most cases, gain of function mutation in one copy of a particular proto-oncogene is enough to make that gene a true oncogene, while usually loss of function mutation must happen in both copies of a tumor suppressor gene to render that gene completely non-functional. However, cases exist in which one loss of function copy of a tumor suppressor gene can render the other copy non-functional, called the dominant negative effect. This is observed in many p53 mutations.
Mutation of tumor suppressor genes that are passed on to the next generation of not merely cells, but their offspring
, can cause increased likelihoods for cancers to be inherited. Members within these families have increased incidence and decreased latency of multiple tumors. The mode of inheritance of mutant tumor suppressors is that affected member inherits a defective copy from one parent, and a normal copy from another. Because mutations in tumor suppressors act in a recessive manner (note, however, there are exceptions), the loss of the normal copy creates the cancer phenotype
. For instance, individuals that are heterozygous for p53 mutations are often victims of Li-Fraumeni syndrome
, and that are heterozygous for Rb
mutations develop retinoblastoma
. In similar fashion, mutations in the adenomatous polyposis coli gene are linked to adenopolyposis colon cancer
, with thousands of polyps in the colon while young, whereas mutations in BRCA1
and BRCA2
lead to early onset of breast cancer
.
A new idea announced in 2011 is an extreme version of multiple mutations, called chromothripsis by its proponents. This idea, affecting only 2–3% of cases of cancer, although up to 25% of bone cancers, involves the catastrophic shattering of a chromosome into tens or hundreds of pieces and then being patched back together incorrectly. This shattering probably takes place when the chromosomes are compacted during normal cell division
, but the trigger for the shattering is unknown. Under this model, cancer arises as the result of a single, isolated event, rather than the slow accumulation of multiple mutations.
s are also carcinogen
s, but some carcinogens are not mutagens. Examples of carcinogens that are not mutagens include alcohol
and estrogen
. These are thought to promote cancers through their stimulating effect on the rate of cell mitosis
. Faster rates of mitosis increasingly leave fewer opportunities for repair enzymes to repair damaged DNA during DNA replication
, increasing the likelihood of a genetic mistake. A mistake made during mitosis can lead to the daughter cells' receiving the wrong number of chromosomes, which leads to aneuploidy
and may lead to cancer.
. Other types of bacteria have been implicated in other cancers.
infection
; this is especially true in animals such as bird
s, but less so in human
s. 12% of human cancers can be attributed to a viral infection. The mode of virally-induced tumors can be divided into two, acutely-transforming or slowly-transforming. In acutely-transforming viruses, the viral particles carry a gene that encodes for an overactive oncogene called viral-oncogene (v-onc), and the infected cell is transformed as soon as v-onc is expressed. In contrast, in slowly-transforming viruses, the virus genome is inserted, especially as viral genome insertion is obligatory part of retrovirus
es, near a proto-oncogene in the host genome. The viral promoter or other transcription regulation elements, in turn, cause over-expression of that proto-oncogene, which, in turn, induces uncontrolled cellular proliferation. Because viral genome insertion is not specific to proto-oncogenes and the chance of insertion near that proto-oncogene is low, slowly-transforming viruses have very long tumor latency compared to acutely-transforming virus, which already carries the viral-oncogene.
Viruses that are known to cause cancer such as HPV (cervical cancer
), Hepatitis B (liver cancer
), and EBV
(a type of lymphoma
), are all DNA viruses. It is thought that when the virus infects a cell, it inserts a part of its own DNA near the cell growth genes, causing cell division. The group of changed cells that are formed from the first cell dividing all have the same viral DNA near the cell growth genes. The group of changed cells are now special because one of the normal controls on growth has been lost.
Depending on their location, cells can be damaged through radiation from sunshine, chemicals from cigarette smoke, and inflammation from bacterial infection or other viruses. Each cell has a chance of damage, a step on a path toward cancer. Cells often die if they are damaged, through failure of a vital process or the immune system; however, sometimes damage will knock out a single cancer gene. In an old person, there are thousands, tens of thousands or hundreds of thousands of knocked-out cells. The chance that any one would form a cancer is very low.
When the damage occurs in any area of changed cells, something different occurs. Each of the cells has the potential for growth. The changed cells will divide quicker when the area is damaged by physical, chemical, or viral agents. A vicious circle
has been set up: Damaging the area will cause the changed cells to divide, causing a greater likelihood that they will suffer knock-outs.
This model of carcinogenesis is popular because it explains why cancers grow. It would be expected that cells that are damaged through radiation would die or at least be worse off because they have fewer genes working; viruses increase the number of genes working.
One concern is that we may end up with thousands of vaccines to prevent every virus that can change our cells. Viruses can have different effects on different parts of the body. It may be possible to prevent a number of different cancers by immunizing against one viral agent. It is likely that HPV, for instance, has a role in cancers of the mucous membranes of the mouth.
in cancer pathogenesis is that non-mutational changes to DNA can lead to alterations in gene expression. Normally, oncogenes are silent, for example, because of DNA methylation
. Loss of that methylation can induce the aberrant expression of oncogenes, leading to cancer pathogenesis. Known mechanisms of epigenetic change include DNA methylation
, and methylation or acetylation of histone
proteins bound to chromosomal DNA at specific locations. Classes of medications, known as HDAC inhibitors
and DNA methyltransferase
inhibitors, can re-regulate the epigenetic signaling in the cancer cell.
into oncology
. The cancer stem cell
hypothesis
proposes that the different kinds of cells in a heterogeneous tumor arise from a single cell, termed Cancer Stem Cell. Cancer stem cells may arise from transformation of adult stem cell
s or differentiated
cells within a body. These cells persist as a subcomponent of the tumor and retain key stem cell properties. They give rise to a variety of cells, are capable of self-renewal and homeostatic control. Furthermore, the relapse
of cancer and the emergence of metastasis
are also attributed to these cells. The cancer stem cell
hypothesis
does not contradict earlier concepts of carcinogenesis.
, known as somatic or clonal evolution
. Furthermore, in light of the Darwinistic mechanisms of carcinogenesis, it has been theorized that the various forms of cancer can be categorized as pubertarial and gerontological. Anthropological research is currently being conducted on cancer as a natural evolutionary process through which natural selection destroys environmentally inferior phenotypes while supporting others. According to this theory, cancer comes in two separate types: from birth to the end of puberty (approximately age 20) teleologically inclined toward supportive group dynamics, and from mid-life to death (approximately age 40+) teleologically inclined away from overpopulative group dynamics.
Cancer
Cancer , known medically as a malignant neoplasm, is a large group of different diseases, all involving unregulated cell growth. In cancer, cells divide and grow uncontrollably, forming malignant tumors, and invade nearby parts of the body. The cancer may also spread to more distant parts of the...
. It is a process by which normal cells
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all known living organisms. It is the smallest unit of life that is classified as a living thing, and is often called the building block of life. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos....
are transformed into cancer cells. It is characterized by a progression of changes on cellular and genetic level that ultimately reprogram a cell to undergo uncontrolled cell division
Cell division
Cell division is the process by which a parent cell divides into two or more daughter cells . Cell division is usually a small segment of a larger cell cycle. This type of cell division in eukaryotes is known as mitosis, and leaves the daughter cell capable of dividing again. The corresponding sort...
, thus forming a malignant mass.
Cell division is a physiological process that occurs in almost all tissues and under many circumstances. Under normal circumstances, the balance between proliferation and programmed cell death, usually in the form of apoptosis
Apoptosis
Apoptosis is the process of programmed cell death that may occur in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes and death. These changes include blebbing, cell shrinkage, nuclear fragmentation, chromatin condensation, and chromosomal DNA fragmentation...
, is maintained by tightly regulating both processes to ensure the integrity of organs and tissues. Mutations in DNA that lead to cancer (only certain mutations can lead to cancer and the majority of potential mutations will have no bearing) disrupt these orderly processes by disrupting the programming regulating the processes.
Carcinogenesis is caused by this mutation of the genetic material of normal cells, which upsets the normal balance between proliferation and cell death. This results in uncontrolled cell division and the evolution of those cells
Somatic evolution in cancer
Somatic evolution is the accumulation of mutations in the cells of a body during a lifetime, and the effects of those mutations on the fitness of those cells. Somatic evolution is important in the process of aging as well as the development of some diseases, including cancer.-Natural selection in...
by natural selection
Natural selection
Natural selection is the nonrandom process by which biologic traits become either more or less common in a population as a function of differential reproduction of their bearers. It is a key mechanism of evolution....
in the body. The uncontrolled and often rapid proliferation of cells can lead to benign tumors; some types of these may turn into malignant tumors (cancer). Benign tumors do not spread to other parts of the body or invade other tissues, and they are rarely a threat to life unless they compress vital structures or are physiologically active, for instance, producing a hormone. Malignant tumors can invade other organs, spread to distant locations (metastasis
Metastasis
Metastasis, or metastatic disease , is the spread of a disease from one organ or part to another non-adjacent organ or part. It was previously thought that only malignant tumor cells and infections have the capacity to metastasize; however, this is being reconsidered due to new research...
) and become life-threatening.
More than one mutation is necessary for carcinogenesis. In fact, a series of several mutations to certain classes of genes is usually required before a normal cell will transform into a cancer cell. Only mutations in those certain types of genes that play vital roles in cell division, apoptosis (cell death), and DNA repair will cause a cell to lose control of its cell proliferation.
Oncovirinae
Oncovirus
An oncovirus is a virus that can cause cancer. This term originated from studies of acutely-transforming retroviruses in the 1950–60s, often called oncornaviruses to denote their RNA virus origin. It now refers to any virus with a DNA or RNA genome causing cancer and is synonymous with "tumor...
, retrovirus
Retrovirus
A retrovirus is an RNA virus that is duplicated in a host cell using the reverse transcriptase enzyme to produce DNA from its RNA genome. The DNA is then incorporated into the host's genome by an integrase enzyme. The virus thereafter replicates as part of the host cell's DNA...
es that contain an oncogene
Oncogene
An oncogene is a gene that has the potential to cause cancer. In tumor cells, they are often mutated or expressed at high levels.An oncogene is a gene found in the chromosomes of tumor cells whose activation is associated with the initial and continuing conversion of normal cells into cancer...
, are categorized as oncogenic because they trigger the growth of tumorous tissues in the host
Host (biology)
In biology, a host is an organism that harbors a parasite, or a mutual or commensal symbiont, typically providing nourishment and shelter. In botany, a host plant is one that supplies food resources and substrate for certain insects or other fauna...
. This process is also referred to as viral transformation
Viral transformation
Viral transformation most commonly refers to the virus-induced malignant transformation of an animal cell in a body or cell culture. In molecular biology, the term may also refer to the transfection of DNA into a host cell using a viral vector....
.
Cancer is fundamentally a disease of regulation of tissue growth. In order for a normal cell to transform
Malignant transformation
Malignant transformation is the process by which cells acquire the properties of cancer. This may occur as a primary process in normal tissue, or secondarily as malignant degeneration of a previously existing benign tumor....
into a cancer cell, genes
Gênes
Gênes is the name of a département of the First French Empire in present Italy, named after the city of Genoa. It was formed in 1805, when Napoleon Bonaparte occupied the Republic of Genoa. Its capital was Genoa, and it was divided in the arrondissements of Genoa, Bobbio, Novi Ligure, Tortona and...
that regulate cell growth and differentiation must be altered. Genetic changes can occur at many levels, from gain or loss of entire chromosomes to a mutation affecting a single DNA nucleotide
Single nucleotide polymorphism
A single-nucleotide polymorphism is a DNA sequence variation occurring when a single nucleotide — A, T, C or G — in the genome differs between members of a biological species or paired chromosomes in an individual...
. There are two broad categories of genes that are affected by these changes. Oncogene
Oncogene
An oncogene is a gene that has the potential to cause cancer. In tumor cells, they are often mutated or expressed at high levels.An oncogene is a gene found in the chromosomes of tumor cells whose activation is associated with the initial and continuing conversion of normal cells into cancer...
s may be normal genes that are expressed at inappropriately high levels, or altered genes that have novel properties. In either case, expression of these genes promotes the malignant phenotype of cancer cells. Tumor suppressor gene
Tumor suppressor gene
A tumor suppressor gene, or anti-oncogene, is a gene that protects a cell from one step on the path to cancer. When this gene is mutated to cause a loss or reduction in its function, the cell can progress to cancer, usually in combination with other genetic changes.-Two-hit hypothesis:Unlike...
s are genes that inhibit cell division, survival, or other properties of cancer cells. Tumor suppressor genes are often disabled by cancer-promoting genetic changes. Typically, changes in many genes are required to transform a normal cell into a cancer cell.
There is a diverse classification scheme for the various genomic changes that may contribute to the generation of cancer cells. Most of these changes are mutation
Mutation
In molecular biology and genetics, mutations are changes in a genomic sequence: the DNA sequence of a cell's genome or the DNA or RNA sequence of a virus. They can be defined as sudden and spontaneous changes in the cell. Mutations are caused by radiation, viruses, transposons and mutagenic...
s, or changes in the nucleotide
Nucleotide
Nucleotides are molecules that, when joined together, make up the structural units of RNA and DNA. In addition, nucleotides participate in cellular signaling , and are incorporated into important cofactors of enzymatic reactions...
sequence of genomic DNA. Aneuploidy
Aneuploidy
Aneuploidy is an abnormal number of chromosomes, and is a type of chromosome abnormality. An extra or missing chromosome is a common cause of genetic disorders . Some cancer cells also have abnormal numbers of chromosomes. Aneuploidy occurs during cell division when the chromosomes do not separate...
, the presence of an abnormal number of chromosomes, is one genomic change that is not a mutation, and may involve either gain or loss of one or more chromosomes through errors in mitosis
Mitosis
Mitosis is the process by which a eukaryotic cell separates the chromosomes in its cell nucleus into two identical sets, in two separate nuclei. It is generally followed immediately by cytokinesis, which divides the nuclei, cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane into two cells containing roughly...
.
Large-scale mutations involve the deletion or gain of a portion of a chromosome. Genomic amplification occurs when a cell gains many copies (often 20 or more) of a small chromosomal region, usually containing one or more oncogenes and adjacent genetic material. Translocation
Chromosomal translocation
In genetics, a chromosome translocation is a chromosome abnormality caused by rearrangement of parts between nonhomologous chromosomes. A gene fusion may be created when the translocation joins two otherwise separated genes, the occurrence of which is common in cancer. It is detected on...
occurs when two separate chromosomal regions become abnormally fused, often at a characteristic location. A well-known example of this is the Philadelphia chromosome
Philadelphia chromosome
Philadelphia chromosome or Philadelphia translocation is a specific chromosomal abnormality that is associated with chronic myelogenous leukemia . It is the result of a reciprocal translocation between chromosome 9 and 22, and is specifically designated t...
, or translocation of chromosomes 9 and 22, which occurs in chronic myelogenous leukemia
Chronic myelogenous leukemia
Chronic myelogenous leukemia , also known as chronic granulocytic leukemia , is a cancer of the white blood cells. It is a form of leukemia characterized by the increased and unregulated growth of predominantly myeloid cells in the bone marrow and the accumulation of these cells in the blood...
, and results in production of the BCR
BCR gene
The BCR gene is one of the two genes in the bcr-abl complex, which is associated with the Philadelphia chromosome.-Pathology:...
-abl
Abl gene
V-abl Abelson murine leukemia viral oncogene homolog 1 also known as ABL1 is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the ABL1 gene located on chromosome 9.- Function :...
fusion protein
Fusion protein
Fusion proteins or chimeric proteins are proteins created through the joining of two or more genes which originally coded for separate proteins. Translation of this fusion gene results in a single polypeptide with functional properties derived from each of the original proteins...
, an oncogenic tyrosine kinase
Tyrosine kinase
A tyrosine kinase is an enzyme that can transfer a phosphate group from ATP to a protein in a cell. It functions as an "on" or "off" switch in many cellular functions....
.
Small-scale mutations include point mutations, deletions, and insertions, which may occur in the promoter of a gene and affect its expression
Gene expression
Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product. These products are often proteins, but in non-protein coding genes such as ribosomal RNA , transfer RNA or small nuclear RNA genes, the product is a functional RNA...
, or may occur in the gene's coding sequence and alter the function or stability of its protein
Protein
Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form, facilitating a biological function. A polypeptide is a single linear polymer chain of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of...
product. Disruption of a single gene may also result from integration of genomic material
Provirus
A provirus is a virus genome that is integrated into the DNA of a host cell.This state can be a stage of virus replication, or a state that persists over longer periods of time as either inactive viral infections or an endogenous retrovirus. In inactive viral infections the virus will not replicate...
from a DNA virus
DNA virus
A DNA virus is a virus that has DNA as its genetic material and replicates using a DNA-dependent DNA polymerase. The nucleic acid is usually double-stranded DNA but may also be single-stranded DNA . DNA viruses belong to either Group I or Group II of the Baltimore classification system for viruses...
or retrovirus
Retrovirus
A retrovirus is an RNA virus that is duplicated in a host cell using the reverse transcriptase enzyme to produce DNA from its RNA genome. The DNA is then incorporated into the host's genome by an integrase enzyme. The virus thereafter replicates as part of the host cell's DNA...
, and such an event may also result in the expression of viral oncogenes in the affected cell and its descendants.
Cause
It is impossible to determine the initial cause for most specific cancers. In a few cases, only one cause exists; for example, the virus HHV-8 causes all Kaposi's sarcomaKaposi's sarcoma
Kaposi's sarcoma is a tumor caused by Human herpesvirus 8 , also known as Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus . It was originally described by Moritz Kaposi , a Hungarian dermatologist practicing at the University of Vienna in 1872. It became more widely known as one of the AIDS defining...
s. However, with the help of cancer epidemiology techniques and information, it is possible to produce an estimate of a likely cause in many more situations. For example, lung cancer
Lung cancer
Lung cancer is a disease characterized by uncontrolled cell growth in tissues of the lung. If left untreated, this growth can spread beyond the lung in a process called metastasis into nearby tissue and, eventually, into other parts of the body. Most cancers that start in lung, known as primary...
has several causes, including tobacco use and radon gas. Men who currently smoke tobacco develop lung cancer at a rate 14 times that of men who have never smoked tobacco, so the chance of lung cancer in a current smoker being caused by smoking is about 93%; there is a 7% chance that the smoker's lung cancer was caused by radon gas or some other, non-tobacco cause. These statistical correlations have made it possible for researchers to infer that certain substances or behaviors are carcinogenic.
Using molecular biological
Molecular biology
Molecular biology is the branch of biology that deals with the molecular basis of biological activity. This field overlaps with other areas of biology and chemistry, particularly genetics and biochemistry...
techniques, it is possible to characterize the mutations or chromosomal aberrations within a tumor, and rapid progress is being made in the field of predicting prognosis
Prognosis
Prognosis is a medical term to describe the likely outcome of an illness.When applied to large statistical populations, prognostic estimates can be very accurate: for example the statement "45% of patients with severe septic shock will die within 28 days" can be made with some confidence, because...
based on the spectrum of mutations in some cases. For example, up to half of all tumors have a defective p53 gene. This mutation is associated with poor prognosis, since those tumor cells are less likely to go into apoptosis
Apoptosis
Apoptosis is the process of programmed cell death that may occur in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes and death. These changes include blebbing, cell shrinkage, nuclear fragmentation, chromatin condensation, and chromosomal DNA fragmentation...
or programmed cell death
Programmed cell death
Programmed cell-death is death of a cell in any form, mediated by an intracellular program. PCD is carried out in a regulated process which generally confers advantage during an organism's life-cycle...
when damaged by therapy. Telomerase
Telomerase
Telomerase is an enzyme that adds DNA sequence repeats to the 3' end of DNA strands in the telomere regions, which are found at the ends of eukaryotic chromosomes. This region of repeated nucleotide called telomeres contains non-coding DNA material and prevents constant loss of important DNA from...
mutations remove additional barriers, extending the number of times a cell can divide. Other mutations enable the tumor to grow new blood vessels
Angiogenesis
Angiogenesis is the physiological process involving the growth of new blood vessels from pre-existing vessels. Though there has been some debate over terminology, vasculogenesis is the term used for spontaneous blood-vessel formation, and intussusception is the term for the formation of new blood...
to provide more nutrients, or to metastasize
Metastasis
Metastasis, or metastatic disease , is the spread of a disease from one organ or part to another non-adjacent organ or part. It was previously thought that only malignant tumor cells and infections have the capacity to metastasize; however, this is being reconsidered due to new research...
, spreading to other parts of the body.
Non-mainstream theories
There are a number of theories of carcinogenesis and cancer treatment that fall outside the mainstream of scientific opinion, due to lack of scientific rationale, logic, or evidence base. These theories may be used to justify various alternative cancer treatments. They should be distinguished from those theories of carcinogenesis that have a logical basis within mainstream cancer biology, and from which conventionally-testable hypotheses can be made.Several alternative theories of carcinogenesis, however, are based on scientific evidence and are increasingly being acknowledged. Some researchers believe that cancer may be caused by epigenetic alterations (heritable and reversible changes other than the DNA sequence) or aneuploidy
Aneuploidy
Aneuploidy is an abnormal number of chromosomes, and is a type of chromosome abnormality. An extra or missing chromosome is a common cause of genetic disorders . Some cancer cells also have abnormal numbers of chromosomes. Aneuploidy occurs during cell division when the chromosomes do not separate...
(numerical and structural abnormalities in chromosomes) rather than by mutations. Cancer has also been considered as a metabolic disease in which the cellular metabolism of oxygen is diverted from the pathway that generates energy (oxidative phosphorylation
Oxidative phosphorylation
Oxidative phosphorylation is a metabolic pathway that uses energy released by the oxidation of nutrients to produce adenosine triphosphate . Although the many forms of life on earth use a range of different nutrients, almost all aerobic organisms carry out oxidative phosphorylation to produce ATP,...
) to the pathway that generates reactive oxygen species
Reactive oxygen species
Reactive oxygen species are chemically reactive molecules containing oxygen. Examples include oxygen ions and peroxides. Reactive oxygen species are highly reactive due to the presence of unpaired valence shell electrons....
(figure). This causes an energy switch from oxidative phosphorylation to aerobic glycolysis (Warburg's hypothesis) and the accumulation of reactive oxygen species
Reactive oxygen species
Reactive oxygen species are chemically reactive molecules containing oxygen. Examples include oxygen ions and peroxides. Reactive oxygen species are highly reactive due to the presence of unpaired valence shell electrons....
leading to oxidative stress
Oxidative stress
Oxidative stress represents an imbalance between the production and manifestation of reactive oxygen species and a biological system's ability to readily detoxify the reactive intermediates or to repair the resulting damage...
(oxidative stress theory of cancer). All these theories of carcinogenesis may be complementary rather than contradictory.
Another theory as to the origin of cancer was developed by astrobiologists
Astrobiology
Astrobiology is the study of the origin, evolution, distribution, and future of life in the universe. This interdisciplinary field encompasses the search for habitable environments in our Solar System and habitable planets outside our Solar System, the search for evidence of prebiotic chemistry,...
and suggests that cancer is an atavism
Atavism
Atavism is the tendency to revert to ancestral type. In biology, an atavism is an evolutionary throwback, such as traits reappearing which had disappeared generations before. Atavisms can occur in several ways...
, an evolutionary throwback to an earlier form of multicellular life
Multicellular organism
Multicellular organisms are organisms that consist of more than one cell, in contrast to single-celled organisms. Most life that can be seen with the the naked eye is multicellular, as are all animals and land plants.-Evolutionary history:Multicellularity has evolved independently dozens of times...
. The genes responsible for uncontrolled cell growth and cooperation between cancer cells are very similar to those that enabled the first multicellular life forms to group together and flourish. These genes still exist within the genome of more complex metazoans
Animal
Animals are a major group of multicellular, eukaryotic organisms of the kingdom Animalia or Metazoa. Their body plan eventually becomes fixed as they develop, although some undergo a process of metamorphosis later on in their life. Most animals are motile, meaning they can move spontaneously and...
, such as humans, although more recently evolved genes keep them in check. When the newer controlling genes fail for whatever reason, the cell can revert to its more primitive programming and reproduce out of control. The theory is an alternative to the notion that cancers begin with rogue cells that undergo evolution within the body. Instead they possess a fixed number of primitive genes that are progressively activated, giving them finite variability.
Cancer cell biology
Often, the multiple genetic changes that result in cancer may take many years to accumulate. During this time, the biological behavior of the pre-malignant cells slowly change from the properties of normal cells to cancer-like properties. Pre-malignant tissue can have a distinctive appearance under the microscopeMicroscope
A microscope is an instrument used to see objects that are too small for the naked eye. The science of investigating small objects using such an instrument is called microscopy...
. Among the distinguishing traits are an increased number of dividing cells, variation in nuclear
Cell nucleus
In cell biology, the nucleus is a membrane-enclosed organelle found in eukaryotic cells. It contains most of the cell's genetic material, organized as multiple long linear DNA molecules in complex with a large variety of proteins, such as histones, to form chromosomes. The genes within these...
size and shape, variation in cell size and shape, loss of specialized cell features, and loss of normal tissue organization. Dysplasia
Dysplasia
Dysplasia , is a term used in pathology to refer to an abnormality of development. This generally consists of an expansion of immature cells, with a corresponding decrease in the number and location of mature cells. Dysplasia is often indicative of an early neoplastic process...
is an abnormal type of excessive cell proliferation characterized by loss of normal tissue arrangement and cell structure in pre-malignant cells. These early neoplastic changes must be distinguished from hyperplasia, a reversible increase in cell division caused by an external stimulus, such as a hormonal imbalance or chronic irritation.
The most severe cases of dysplasia are referred to as "carcinoma in situ
Carcinoma in situ
Carcinoma in situ is an early form of cancer that is defined by the absence of invasion of tumor cells into the surrounding tissue, usually before penetration through the basement membrane. In other words, the neoplastic cells proliferate in their normal habitat, hence the name "in situ"...
." In Latin, the term "in situ" means "in place", so carcinoma in situ refers to an uncontrolled growth of cells that remains in the original location and has not shown invasion into other tissues. Nevertheless, carcinoma in situ may develop into an invasive malignancy and is usually removed surgically, if possible.
Clonal evolution
Just like a population of animals undergoes evolutionEvolution
Evolution is any change across successive generations in the heritable characteristics of biological populations. Evolutionary processes give rise to diversity at every level of biological organisation, including species, individual organisms and molecules such as DNA and proteins.Life on Earth...
, an unchecked population of cells also can undergo evolution. This undesirable process is called somatic evolution
Somatic evolution in cancer
Somatic evolution is the accumulation of mutations in the cells of a body during a lifetime, and the effects of those mutations on the fitness of those cells. Somatic evolution is important in the process of aging as well as the development of some diseases, including cancer.-Natural selection in...
, and is how cancer arises and becomes more malignant.
Most changes in cellular metabolism that allow cells to grow in a disorderly fashion lead to cell death. However once cancer begins, cancer cells undergo a process of natural selection
Natural selection
Natural selection is the nonrandom process by which biologic traits become either more or less common in a population as a function of differential reproduction of their bearers. It is a key mechanism of evolution....
: the few cells with new genetic changes that enhance their survival or reproduction continue to multiply, and soon come to dominate the growing tumor, as cells with less favorable genetic change are out-competed. This is exactly how pathogens such as MRSA can become antibiotic-resistant
Antibiotic resistance
Antibiotic resistance is a type of drug resistance where a microorganism is able to survive exposure to an antibiotic. While a spontaneous or induced genetic mutation in bacteria may confer resistance to antimicrobial drugs, genes that confer resistance can be transferred between bacteria in a...
(or how HIV
HIV
Human immunodeficiency virus is a lentivirus that causes acquired immunodeficiency syndrome , a condition in humans in which progressive failure of the immune system allows life-threatening opportunistic infections and cancers to thrive...
can become drug-resistant
Drug resistance
Drug resistance is the reduction in effectiveness of a drug such as an antimicrobial or an antineoplastic in curing a disease or condition. When the drug is not intended to kill or inhibit a pathogen, then the term is equivalent to dosage failure or drug tolerance. More commonly, the term is used...
), and the same reason why crop blights and pests can become pesticide-resistant
Pesticide resistance
Pesticide resistance is the adaptation of pest population targeted by a pesticide resulting in decreased susceptibility to that chemical. In other words, pests develop a resistance to a chemical through natural selection: the most resistant organisms are the ones to survive and pass on their...
. This evolution is why cancer recurrences will have cells that have acquired cancer-drug resistance (or in some cases, resistance to radiation from radiotherapy).
Biological properties of cancer cells

Robert Weinberg
Robert Allan Weinberg is a Daniel K. Ludwig Professor for Cancer Research at MIT and American Cancer Society Research Professor; his research is in the area of oncogenes and the genetic basis of human cancer. Weinberg is also affiliated with the Broad Institute and is a founding member of the...
, the biological properties of malignant tumor cells were summarized as follows:
- Acquisition of self-sufficiency in growth signalsGrowth factorA growth factor is a naturally occurring substance capable of stimulating cellular growth, proliferation and cellular differentiation. Usually it is a protein or a steroid hormone. Growth factors are important for regulating a variety of cellular processes....
, leading to unchecked growth. - Loss of sensitivity to anti-growth signals, also leading to unchecked growth.
- Loss of capacity for apoptosisApoptosisApoptosis is the process of programmed cell death that may occur in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes and death. These changes include blebbing, cell shrinkage, nuclear fragmentation, chromatin condensation, and chromosomal DNA fragmentation...
, in order to allow growth despite genetic errors and external anti-growth signals. - Loss of capacity for senescenceSenescenceSenescence or biological aging is the change in the biology of an organism as it ages after its maturity. Such changes range from those affecting its cells and their function to those affecting the whole organism...
, leading to limitless replicative potential (immortality) - Acquisition of sustained angiogenesisAngiogenesisAngiogenesis is the physiological process involving the growth of new blood vessels from pre-existing vessels. Though there has been some debate over terminology, vasculogenesis is the term used for spontaneous blood-vessel formation, and intussusception is the term for the formation of new blood...
, allowing the tumor to grow beyond the limitations of passive nutrient diffusion. - Acquisition of ability to invade neighbouring tissuesBiological tissueTissue is a cellular organizational level intermediate between cells and a complete organism. A tissue is an ensemble of cells, not necessarily identical, but from the same origin, that together carry out a specific function. These are called tissues because of their identical functioning...
, the defining property of invasive carcinoma. - Acquisition of ability to build metastasesMetastasisMetastasis, or metastatic disease , is the spread of a disease from one organ or part to another non-adjacent organ or part. It was previously thought that only malignant tumor cells and infections have the capacity to metastasize; however, this is being reconsidered due to new research...
at distant sites, the classical property of malignant tumors (carcinomas or others).
The completion of these multiple steps would be a very rare event without :
- Loss of capacity to repair genetic errors, leading to an increased mutationMutationIn molecular biology and genetics, mutations are changes in a genomic sequence: the DNA sequence of a cell's genome or the DNA or RNA sequence of a virus. They can be defined as sudden and spontaneous changes in the cell. Mutations are caused by radiation, viruses, transposons and mutagenic...
rate (genomic instability), thus accelerating all the other changes.
These biological changes are classical in carcinoma
Carcinoma
Carcinoma is the medical term for the most common type of cancer occurring in humans. Put simply, a carcinoma is a cancer that begins in a tissue that lines the inner or outer surfaces of the body, and that generally arises from cells originating in the endodermal or ectodermal germ layer during...
s; other malignant tumors may not need to achieve them all. For example, tissue invasion and displacement to distant sites are normal properties of leukocytes; these steps are not needed in the development of leukemia
Leukemia
Leukemia or leukaemia is a type of cancer of the blood or bone marrow characterized by an abnormal increase of immature white blood cells called "blasts". Leukemia is a broad term covering a spectrum of diseases...
. The different steps do not necessarily represent individual mutations. For example, inactivation of a single gene, coding for the p53
P53
p53 , is a tumor suppressor protein that in humans is encoded by the TP53 gene. p53 is crucial in multicellular organisms, where it regulates the cell cycle and, thus, functions as a tumor suppressor that is involved in preventing cancer...
protein, will cause genomic instability, evasion of apoptosis and increased angiogenesis. Not all the cancer cells are dividing. Rather, a subset of the cells in a tumor, called cancer stem cell
Cancer stem cell
Cancer stem cells are cancer cells that possess characteristics associated with normal stem cells, specifically the ability to give rise to all cell types found in a particular cancer sample. CSCs are therefore tumorigenic , perhaps in contrast to other non-tumorigenic cancer cells...
s, replicate themselves and generate differentiated cells.
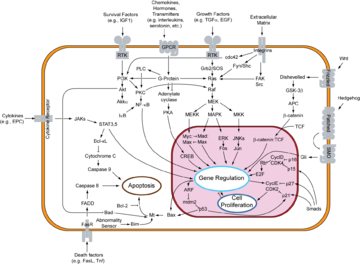
Mechanisms
Cancer is a genetic disease: In order for cells to start dividing uncontrollably, genes that regulate cell growth must be damaged. Proto-oncogenes are genes that promote cell growth and mitosisMitosis
Mitosis is the process by which a eukaryotic cell separates the chromosomes in its cell nucleus into two identical sets, in two separate nuclei. It is generally followed immediately by cytokinesis, which divides the nuclei, cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane into two cells containing roughly...
, whereas tumor suppressor gene
Tumor suppressor gene
A tumor suppressor gene, or anti-oncogene, is a gene that protects a cell from one step on the path to cancer. When this gene is mutated to cause a loss or reduction in its function, the cell can progress to cancer, usually in combination with other genetic changes.-Two-hit hypothesis:Unlike...
s discourage cell growth, or temporarily halt cell division to carry out DNA repair
DNA repair
DNA repair refers to a collection of processes by which a cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. In human cells, both normal metabolic activities and environmental factors such as UV light and radiation can cause DNA damage, resulting in as many as 1...
. Typically, a series of several mutation
Mutation
In molecular biology and genetics, mutations are changes in a genomic sequence: the DNA sequence of a cell's genome or the DNA or RNA sequence of a virus. They can be defined as sudden and spontaneous changes in the cell. Mutations are caused by radiation, viruses, transposons and mutagenic...
s to these genes is required before a normal cell transforms into a cancer cell. This concept is sometimes termed "oncoevolution." Mutations to these genes provide the signals for tumor cells to start dividing uncontrollably. But the uncontrolled cell division that characterizes cancer also requires that the dividing cell duplicates all its cellular components to create two daughter cells. The activation of anaerobic glycolysis (the Warburg effect
Warburg effect
The phrase "Warburg effect" is used for two unrelated observations in biochemistry, one in plant physiology and the other in oncology, both due to Nobel laureate Otto Heinrich Warburg.-Plant physiology:...
), which is not necessarily induced by mutations in proto-oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes, provides most of the building blocks required to duplicate the cellular components of a dividing cell and, therefore, is also essential for carcinogenesis.
Cell types involved in cancer growth
There are several different cell types that are critical to tumour growth. In particular endothelial progenitor cells are a very important cell population in tumour blood vessel growth. This importance of endothelial progenitor cells in tumour growth, angiogenesis and metastasis has been confirmed by a recent publication in Cancer Research (August 2010). This seminal paper has demonstrated that endothelial progenitor cells can be marked using the Inhibitor of DNA Binding 1 (ID1). This novel finding meant that investigators were able to track endothelial progenitor cells from the bone marrow to the blood to the tumour-stroma and even incorporated in tumour vasculature. This finding of endothelial progenitor cells incorporated in tumour vasculature proves the importance of this cell type in blood vessel development in a tumour setting and metastasis. Furthermore, ablation of the endothelial progenitor cells in the bone marrow lead to a significant decrease in tumour growth and vasculature development. Therefore endothelial progenitor cells are very important in tumour biology and present novel therapeutic targets.Oncogenes
OncogeneOncogene
An oncogene is a gene that has the potential to cause cancer. In tumor cells, they are often mutated or expressed at high levels.An oncogene is a gene found in the chromosomes of tumor cells whose activation is associated with the initial and continuing conversion of normal cells into cancer...
s promote cell growth through a variety of ways. Many can produce hormone
Hormone
A hormone is a chemical released by a cell or a gland in one part of the body that sends out messages that affect cells in other parts of the organism. Only a small amount of hormone is required to alter cell metabolism. In essence, it is a chemical messenger that transports a signal from one...
s, a "chemical messenger" between cells that encourage mitosis
Mitosis
Mitosis is the process by which a eukaryotic cell separates the chromosomes in its cell nucleus into two identical sets, in two separate nuclei. It is generally followed immediately by cytokinesis, which divides the nuclei, cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane into two cells containing roughly...
, the effect of which depends on the signal transduction
Signal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a cell surface receptor. In turn, this receptor alters intracellular molecules creating a response...
of the receiving tissue or cells. In other words, when a hormone receptor on a recipient cell is stimulated, the signal is conducted from the surface of the cell to the cell nucleus
Cell nucleus
In cell biology, the nucleus is a membrane-enclosed organelle found in eukaryotic cells. It contains most of the cell's genetic material, organized as multiple long linear DNA molecules in complex with a large variety of proteins, such as histones, to form chromosomes. The genes within these...
to affect some change in gene transcription regulation at the nuclear level. Some oncogenes are part of the signal transduction system itself, or the signal receptors
Receptor (biochemistry)
In biochemistry, a receptor is a molecule found on the surface of a cell, which receives specific chemical signals from neighbouring cells or the wider environment within an organism...
in cells and tissues themselves, thus controlling the sensitivity to such hormones. Oncogenes often produce mitogen
Mitogen
A mitogen is a chemical substance that encourages a cell to commence cell division, triggering mitosis. A mitogen is usually some form of a protein.Mitogenesis is the induction of mitosis, typically via a mitogen....
s, or are involved in transcription
Transcription (genetics)
Transcription is the process of creating a complementary RNA copy of a sequence of DNA. Both RNA and DNA are nucleic acids, which use base pairs of nucleotides as a complementary language that can be converted back and forth from DNA to RNA by the action of the correct enzymes...
of DNA in protein synthesis
Protein biosynthesis
Protein biosynthesis is the process in which cells build or manufacture proteins. The term is sometimes used to refer only to protein translation but more often it refers to a multi-step process, beginning with amino acid synthesis and transcription of nuclear DNA into messenger RNA, which is then...
, which creates the protein
Protein
Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form, facilitating a biological function. A polypeptide is a single linear polymer chain of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of...
s and enzyme
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
s responsible for producing the products and biochemicals
Biochemistry
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes in living organisms, including, but not limited to, living matter. Biochemistry governs all living organisms and living processes...
cells use and interact with.
Mutations in proto-oncogenes, which are the normally quiescent counterparts of oncogenes, can modify their expression
Gene expression
Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product. These products are often proteins, but in non-protein coding genes such as ribosomal RNA , transfer RNA or small nuclear RNA genes, the product is a functional RNA...
and function, increasing the amount or activity of the product protein. When this happens, the proto-oncogenes become oncogene
Oncogene
An oncogene is a gene that has the potential to cause cancer. In tumor cells, they are often mutated or expressed at high levels.An oncogene is a gene found in the chromosomes of tumor cells whose activation is associated with the initial and continuing conversion of normal cells into cancer...
s, and this transition upsets the normal balance of cell cycle
Cell cycle
The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that takes place in a cell leading to its division and duplication . In cells without a nucleus , the cell cycle occurs via a process termed binary fission...
regulation in the cell, making uncontrolled growth possible. The chance of cancer cannot be reduced by removing proto-oncogenes from the genome
Genome
In modern molecular biology and genetics, the genome is the entirety of an organism's hereditary information. It is encoded either in DNA or, for many types of virus, in RNA. The genome includes both the genes and the non-coding sequences of the DNA/RNA....
, even if this were possible, as they are critical for growth, repair and homeostasis
Homeostasis
Homeostasis is the property of a system that regulates its internal environment and tends to maintain a stable, constant condition of properties like temperature or pH...
of the organism. It is only when they become mutated that the signals for growth become excessive.
One of the first oncogenes to be defined in cancer research
Cancer research
Cancer research is basic research into cancer in order to identify causes and develop strategies for prevention, diagnosis, treatments and cure....
is the ras oncogene. Mutations in the Ras family of proto-oncogenes (comprising H-Ras, N-Ras and K-Ras) are very common, being found in 20% to 30% of all human tumours. Ras was originally identified in the Harvey sarcoma virus genome, and researchers were surprised that not only is this gene present in the human genome but also, when ligated to a stimulating control element, it could induce cancers in cell line cultures.
Proto-oncogenes
Proto-oncogenes promote cell growth in a variety of ways. Many can produce hormoneHormone
A hormone is a chemical released by a cell or a gland in one part of the body that sends out messages that affect cells in other parts of the organism. Only a small amount of hormone is required to alter cell metabolism. In essence, it is a chemical messenger that transports a signal from one...
s, "chemical messengers" between cells that encourage mitosis, the effect of which depends on the signal transduction
Signal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a cell surface receptor. In turn, this receptor alters intracellular molecules creating a response...
of the receiving tissue or cells. Some are responsible for the signal transduction system and signal receptors
Receptor (biochemistry)
In biochemistry, a receptor is a molecule found on the surface of a cell, which receives specific chemical signals from neighbouring cells or the wider environment within an organism...
in cells and tissues themselves, thus controlling the sensitivity to such hormones. They often produce mitogen
Mitogen
A mitogen is a chemical substance that encourages a cell to commence cell division, triggering mitosis. A mitogen is usually some form of a protein.Mitogenesis is the induction of mitosis, typically via a mitogen....
s, or are involved in transcription
Transcription (genetics)
Transcription is the process of creating a complementary RNA copy of a sequence of DNA. Both RNA and DNA are nucleic acids, which use base pairs of nucleotides as a complementary language that can be converted back and forth from DNA to RNA by the action of the correct enzymes...
of DNA in protein synthesis, which create the protein
Protein
Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form, facilitating a biological function. A polypeptide is a single linear polymer chain of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of...
s and enzyme
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
s is responsible for producing the products and biochemicals
Biochemistry
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes in living organisms, including, but not limited to, living matter. Biochemistry governs all living organisms and living processes...
cells use and interact with.
Mutations in proto-oncogenes can modify their expression
Gene expression
Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product. These products are often proteins, but in non-protein coding genes such as ribosomal RNA , transfer RNA or small nuclear RNA genes, the product is a functional RNA...
and function, increasing the amount or activity of the product protein. When this happens, they become oncogene
Oncogene
An oncogene is a gene that has the potential to cause cancer. In tumor cells, they are often mutated or expressed at high levels.An oncogene is a gene found in the chromosomes of tumor cells whose activation is associated with the initial and continuing conversion of normal cells into cancer...
s, and, thus, cells have a higher chance to divide excessively and uncontrollably. The chance of cancer cannot be reduced by removing proto-oncogenes from the genome
Genome
In modern molecular biology and genetics, the genome is the entirety of an organism's hereditary information. It is encoded either in DNA or, for many types of virus, in RNA. The genome includes both the genes and the non-coding sequences of the DNA/RNA....
, as they are critical for growth, repair and homeostasis
Homeostasis
Homeostasis is the property of a system that regulates its internal environment and tends to maintain a stable, constant condition of properties like temperature or pH...
of the body. It is only when they become mutated that the signals for growth become excessive.
It is important to note that a gene possessing a growth-promoting role may increase carcinogenic potential of a cell, under the condition that all necessary cellular mechanisms that permit growth are activated. This condition includes also the inactivation of specific tumor suppressor genes (see below). If the condition is not fulfilled, the cell may cease to grow and can proceed to die. This makes knowledge of the stage and type of cancer cell that grows under the control of a given oncogene crucial for the development of treatment strategies.
Tumor suppressor genes

Tumor suppressor gene
A tumor suppressor gene, or anti-oncogene, is a gene that protects a cell from one step on the path to cancer. When this gene is mutated to cause a loss or reduction in its function, the cell can progress to cancer, usually in combination with other genetic changes.-Two-hit hypothesis:Unlike...
s code for anti-proliferation signals and proteins that suppress mitosis and cell growth. Generally, tumor suppressors are transcription factor
Transcription factor
In molecular biology and genetics, a transcription factor is a protein that binds to specific DNA sequences, thereby controlling the flow of genetic information from DNA to mRNA...
s that are activated by cellular stress
Stress (medicine)
Stress is a term in psychology and biology, borrowed from physics and engineering and first used in the biological context in the 1930s, which has in more recent decades become commonly used in popular parlance...
or DNA damage. Often DNA damage will cause the presence of free-floating genetic material as well as other signs, and will trigger enzymes and pathways that lead to the activation of tumor suppressor genes. The functions of such genes is to arrest the progression of the cell cycle in order to carry out DNA repair, preventing mutations from being passed on to daughter cells. The p53
P53
p53 , is a tumor suppressor protein that in humans is encoded by the TP53 gene. p53 is crucial in multicellular organisms, where it regulates the cell cycle and, thus, functions as a tumor suppressor that is involved in preventing cancer...
protein, one of the most important studied tumor suppressor genes, is a transcription factor activated by many cellular stressors including hypoxia
Hypoxia (medical)
Hypoxia, or hypoxiation, is a pathological condition in which the body as a whole or a region of the body is deprived of adequate oxygen supply. Variations in arterial oxygen concentrations can be part of the normal physiology, for example, during strenuous physical exercise...
and ultraviolet radiation damage.
Despite nearly half of all cancers possibly involving alterations in p53, its tumor suppressor function is poorly understood. p53 clearly has two functions: one a nuclear role as a transcription factor, and the other a cytoplasmic role in regulating the cell cycle, cell division, and apoptosis.
The Warburg hypothesis
Warburg hypothesis
The Warburg effect is the observation that cancer cells exhibit glycolysis with lactate secretion and mitochondrial respiration even in the presence of oxygen....
is the preferential use of glycolysis for energy to sustain cancer growth. p53 has been shown to regulate the shift from the respiratory to the glycolytic pathway.
However, a mutation can damage the tumor suppressor gene itself, or the signal pathway that activates it, "switching it off". The invariable consequence of this is that DNA repair is hindered or inhibited: DNA damage accumulates without repair, inevitably leading to cancer.
Mutations of tumor suppressor genes that occur in germline
Germline
In biology and genetics, the germline of a mature or developing individual is the line of germ cells that have genetic material that may be passed to a child.For example, gametes such as the sperm or the egg, are part of the germline...
cells are passed along to offspring
Offspring
In biology, offspring is the product of reproduction, of a new organism produced by one or more parents.Collective offspring may be known as a brood or progeny in a more general way...
, and increase the likelihood for cancer diagnoses in subsequent generations. Members of these families have increased incidence and decreased latency of multiple tumors. The tumor types are typical for each type of tumor suppressor gene mutation, with some mutations causing particular cancers, and other mutations causing others. The mode of inheritance of mutant tumor suppressors is that an affected member inherits a defective copy from one parent, and a normal copy from the other. For instance, individuals who inherit one mutant p53
P53
p53 , is a tumor suppressor protein that in humans is encoded by the TP53 gene. p53 is crucial in multicellular organisms, where it regulates the cell cycle and, thus, functions as a tumor suppressor that is involved in preventing cancer...
allele (and are therefore heterozygous for mutated p53) can develop melanomas and pancreatic cancer
Pancreatic cancer
Pancreatic cancer refers to a malignant neoplasm of the pancreas. The most common type of pancreatic cancer, accounting for 95% of these tumors is adenocarcinoma, which arises within the exocrine component of the pancreas. A minority arises from the islet cells and is classified as a...
, known as Li-Fraumeni syndrome
Li-Fraumeni syndrome
Li-Fraumeni syndrome is an extremely rare autosomal dominant hereditary disorder. It is named after Frederick Pei Li and Joseph F. Fraumeni, Jr., the American physicians who first recognized and described the syndrome. Li-Fraumeni syndrome greatly increases susceptibility to cancer...
. Other inherited tumor suppressor gene syndromes include Rb
Retinoblastoma protein
The retinoblastoma protein is a tumor suppressor protein that is dysfunctional in the majority types of cancer. One highly studied function of pRb is to prevent excessive cell growth by inhibiting cell cycle progression until a cell is ready to divide...
mutations, linked to retinoblastoma
Retinoblastoma
Retinoblastoma is a rapidly developing cancer that develops in the cells of retina, the light-detecting tissue of the eye. In the developed world, Rb has one of the best cure rates of all childhood cancers , with more than nine out of every ten sufferers surviving into...
, and APC gene mutations, linked to adenopolyposis colon cancer
Familial adenomatous polyposis
Familial adenomatous polyposis is an inherited condition in which numerous polyps form mainly in the epithelium of the large intestine. While these polyps start out benign, malignant transformation into colon cancer occurs when not treated....
. Adenopolyposis colon cancer is associated with thousands of polyps in colon while young, leading to colon cancer
Colorectal cancer
Colorectal cancer, commonly known as bowel cancer, is a cancer caused by uncontrolled cell growth , in the colon, rectum, or vermiform appendix. Colorectal cancer is clinically distinct from anal cancer, which affects the anus....
at a relatively early age. Finally, inherited mutations in BRCA1
BRCA1
BRCA1 is a human caretaker gene that produces a protein called breast cancer type 1 susceptibility protein, responsible for repairing DNA. The first evidence for the existence of the gene was provided by the King laboratory at UC Berkeley in 1990...
and BRCA2
BRCA2
BRCA2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BRCA2 gene.BRCA2 orthologs have been identified in most mammals for which complete genome data are available....
lead to early onset of breast cancer
Breast cancer
Breast cancer is cancer originating from breast tissue, most commonly from the inner lining of milk ducts or the lobules that supply the ducts with milk. Cancers originating from ducts are known as ductal carcinomas; those originating from lobules are known as lobular carcinomas...
.
Development of cancer was proposed in 1971 to depend on at least two mutational events. In what became known as the Knudson
Alfred G. Knudson
Alfred George Knudson, Jr. M.D., Ph.D. is a geneticist specializing in cancer genetics. Among his many contributions to the field was the formulation of the Knudson hypothesis in 1971, which explains the effects of mutation on carcinogenesis .Born in Los Angeles in 1922, Knudson received his B.S...
two-hit hypothesis
Knudson hypothesis
The Knudson hypothesis is the hypothesis that cancer is the result of accumulated mutations to a cell's DNA. It was first proposed by Carl O. Nordling in 1953, and later formulated by Alfred G. Knudson in 1971. Knudson's work led indirectly to the identification of cancer-related genes...
, an inherited, germ-line mutation in a tumor suppressor gene
Tumor suppressor gene
A tumor suppressor gene, or anti-oncogene, is a gene that protects a cell from one step on the path to cancer. When this gene is mutated to cause a loss or reduction in its function, the cell can progress to cancer, usually in combination with other genetic changes.-Two-hit hypothesis:Unlike...
would cause cancer only if another mutation event occurred later in the organism's life, inactivating the other allele
Allele
An allele is one of two or more forms of a gene or a genetic locus . "Allel" is an abbreviation of allelomorph. Sometimes, different alleles can result in different observable phenotypic traits, such as different pigmentation...
of that tumor suppressor gene
Tumor suppressor gene
A tumor suppressor gene, or anti-oncogene, is a gene that protects a cell from one step on the path to cancer. When this gene is mutated to cause a loss or reduction in its function, the cell can progress to cancer, usually in combination with other genetic changes.-Two-hit hypothesis:Unlike...
.
Usually, oncogenes are dominant, as they contain gain-of-function mutations, while mutated tumor suppressors are recessive, as they contain loss-of-function mutations. Each cell has two copies of the same gene, one from each parent, and under most cases gain of function mutations in just one copy of a particular proto-oncogene is enough to make that gene a true oncogene. On the other hand, loss of function mutations need to happen in both copies of a tumor suppressor gene to render that gene completely non-functional. However, cases exist in which one mutated copy of a tumor suppressor gene
Tumor suppressor gene
A tumor suppressor gene, or anti-oncogene, is a gene that protects a cell from one step on the path to cancer. When this gene is mutated to cause a loss or reduction in its function, the cell can progress to cancer, usually in combination with other genetic changes.-Two-hit hypothesis:Unlike...
can render the other, wild-type copy non-functional. This phenomenon is called the dominant negative effect and is observed in many p53 mutations.
Knudson’s two hit model has recently been challenged by several investigators. Inactivation of one allele of some tumor suppressor genes is sufficient to cause tumors. This phenomenon is called haploinsufficiency
Haploinsufficiency
Haploinsufficiency occurs when a diploid organism only has a single functional copy of a gene and the single functional copy of the gene does not produce enough of a gene product to bring about a wild-type condition, leading to an abnormal or diseased state...
and has been demonstrated by a number of experimental approaches. Tumors caused by haploinsufficiency
Haploinsufficiency
Haploinsufficiency occurs when a diploid organism only has a single functional copy of a gene and the single functional copy of the gene does not produce enough of a gene product to bring about a wild-type condition, leading to an abnormal or diseased state...
usually have a later age of onset when compared with those by a two hit process.
Multiple mutations
In general, mutations in both types of genes are required for cancer to occur. For example, a mutation limited to one oncogene would be suppressed by normal mitosis control and tumor suppressor genes, first hypothesisHypothesis
A hypothesis is a proposed explanation for a phenomenon. The term derives from the Greek, ὑποτιθέναι – hypotithenai meaning "to put under" or "to suppose". For a hypothesis to be put forward as a scientific hypothesis, the scientific method requires that one can test it...
ed by the Knudson hypothesis
Knudson hypothesis
The Knudson hypothesis is the hypothesis that cancer is the result of accumulated mutations to a cell's DNA. It was first proposed by Carl O. Nordling in 1953, and later formulated by Alfred G. Knudson in 1971. Knudson's work led indirectly to the identification of cancer-related genes...
. A mutation to only one tumor suppressor gene would not cause cancer either, due to the presence of many "backup
Backup
In information technology, a backup or the process of backing up is making copies of data which may be used to restore the original after a data loss event. The verb form is back up in two words, whereas the noun is backup....
" genes that duplicate its functions. It is only when enough proto-oncogenes have mutated into oncogenes, and enough tumor suppressor genes deactivated or damaged, that the signals for cell growth overwhelm the signals to regulate it, that cell growth quickly spirals out of control. Often, because these genes regulate the processes that prevent most damage to genes themselves, the rate of mutations increases as one gets older, because DNA damage forms a feedback
Feedback
Feedback describes the situation when output from an event or phenomenon in the past will influence an occurrence or occurrences of the same Feedback describes the situation when output from (or information about the result of) an event or phenomenon in the past will influence an occurrence or...
loop.
Usually, oncogenes are dominant alleles, as they contain gain-of-function mutations, whereas mutated tumor suppressors are recessive alleles, as they contain loss-of-function mutations. Each cell has two copies of a same gene, one from each parent, and, under most cases, gain of function mutation in one copy of a particular proto-oncogene is enough to make that gene a true oncogene, while usually loss of function mutation must happen in both copies of a tumor suppressor gene to render that gene completely non-functional. However, cases exist in which one loss of function copy of a tumor suppressor gene can render the other copy non-functional, called the dominant negative effect. This is observed in many p53 mutations.
Mutation of tumor suppressor genes that are passed on to the next generation of not merely cells, but their offspring
Offspring
In biology, offspring is the product of reproduction, of a new organism produced by one or more parents.Collective offspring may be known as a brood or progeny in a more general way...
, can cause increased likelihoods for cancers to be inherited. Members within these families have increased incidence and decreased latency of multiple tumors. The mode of inheritance of mutant tumor suppressors is that affected member inherits a defective copy from one parent, and a normal copy from another. Because mutations in tumor suppressors act in a recessive manner (note, however, there are exceptions), the loss of the normal copy creates the cancer phenotype
Phenotype
A phenotype is an organism's observable characteristics or traits: such as its morphology, development, biochemical or physiological properties, behavior, and products of behavior...
. For instance, individuals that are heterozygous for p53 mutations are often victims of Li-Fraumeni syndrome
Li-Fraumeni syndrome
Li-Fraumeni syndrome is an extremely rare autosomal dominant hereditary disorder. It is named after Frederick Pei Li and Joseph F. Fraumeni, Jr., the American physicians who first recognized and described the syndrome. Li-Fraumeni syndrome greatly increases susceptibility to cancer...
, and that are heterozygous for Rb
Retinoblastoma protein
The retinoblastoma protein is a tumor suppressor protein that is dysfunctional in the majority types of cancer. One highly studied function of pRb is to prevent excessive cell growth by inhibiting cell cycle progression until a cell is ready to divide...
mutations develop retinoblastoma
Retinoblastoma
Retinoblastoma is a rapidly developing cancer that develops in the cells of retina, the light-detecting tissue of the eye. In the developed world, Rb has one of the best cure rates of all childhood cancers , with more than nine out of every ten sufferers surviving into...
. In similar fashion, mutations in the adenomatous polyposis coli gene are linked to adenopolyposis colon cancer
Familial adenomatous polyposis
Familial adenomatous polyposis is an inherited condition in which numerous polyps form mainly in the epithelium of the large intestine. While these polyps start out benign, malignant transformation into colon cancer occurs when not treated....
, with thousands of polyps in the colon while young, whereas mutations in BRCA1
BRCA1
BRCA1 is a human caretaker gene that produces a protein called breast cancer type 1 susceptibility protein, responsible for repairing DNA. The first evidence for the existence of the gene was provided by the King laboratory at UC Berkeley in 1990...
and BRCA2
BRCA2
BRCA2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BRCA2 gene.BRCA2 orthologs have been identified in most mammals for which complete genome data are available....
lead to early onset of breast cancer
Breast cancer
Breast cancer is cancer originating from breast tissue, most commonly from the inner lining of milk ducts or the lobules that supply the ducts with milk. Cancers originating from ducts are known as ductal carcinomas; those originating from lobules are known as lobular carcinomas...
.
A new idea announced in 2011 is an extreme version of multiple mutations, called chromothripsis by its proponents. This idea, affecting only 2–3% of cases of cancer, although up to 25% of bone cancers, involves the catastrophic shattering of a chromosome into tens or hundreds of pieces and then being patched back together incorrectly. This shattering probably takes place when the chromosomes are compacted during normal cell division
Mitosis
Mitosis is the process by which a eukaryotic cell separates the chromosomes in its cell nucleus into two identical sets, in two separate nuclei. It is generally followed immediately by cytokinesis, which divides the nuclei, cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane into two cells containing roughly...
, but the trigger for the shattering is unknown. Under this model, cancer arises as the result of a single, isolated event, rather than the slow accumulation of multiple mutations.
Non-mutagenic carcinogens
Many mutagenMutagen
In genetics, a mutagen is a physical or chemical agent that changes the genetic material, usually DNA, of an organism and thus increases the frequency of mutations above the natural background level. As many mutations cause cancer, mutagens are therefore also likely to be carcinogens...
s are also carcinogen
Carcinogen
A carcinogen is any substance, radionuclide, or radiation that is an agent directly involved in causing cancer. This may be due to the ability to damage the genome or to the disruption of cellular metabolic processes...
s, but some carcinogens are not mutagens. Examples of carcinogens that are not mutagens include alcohol
Alcohol
In chemistry, an alcohol is an organic compound in which the hydroxy functional group is bound to a carbon atom. In particular, this carbon center should be saturated, having single bonds to three other atoms....
and estrogen
Estrogen
Estrogens , oestrogens , or œstrogens, are a group of compounds named for their importance in the estrous cycle of humans and other animals. They are the primary female sex hormones. Natural estrogens are steroid hormones, while some synthetic ones are non-steroidal...
. These are thought to promote cancers through their stimulating effect on the rate of cell mitosis
Mitosis
Mitosis is the process by which a eukaryotic cell separates the chromosomes in its cell nucleus into two identical sets, in two separate nuclei. It is generally followed immediately by cytokinesis, which divides the nuclei, cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane into two cells containing roughly...
. Faster rates of mitosis increasingly leave fewer opportunities for repair enzymes to repair damaged DNA during DNA replication
DNA replication
DNA replication is a biological process that occurs in all living organisms and copies their DNA; it is the basis for biological inheritance. The process starts with one double-stranded DNA molecule and produces two identical copies of the molecule...
, increasing the likelihood of a genetic mistake. A mistake made during mitosis can lead to the daughter cells' receiving the wrong number of chromosomes, which leads to aneuploidy
Aneuploidy
Aneuploidy is an abnormal number of chromosomes, and is a type of chromosome abnormality. An extra or missing chromosome is a common cause of genetic disorders . Some cancer cells also have abnormal numbers of chromosomes. Aneuploidy occurs during cell division when the chromosomes do not separate...
and may lead to cancer.
Bacterial
Heliobacter pylori is known to cause MALT lymphomaMALT lymphoma
MALT lymphoma is a form of lymphoma involving the mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue , frequently of the stomach, but virtually any mucosal site can be afflicted...
. Other types of bacteria have been implicated in other cancers.
Viral
Furthermore, many cancers originate from a viralVirus
A virus is a small infectious agent that can replicate only inside the living cells of organisms. Viruses infect all types of organisms, from animals and plants to bacteria and archaea...
infection
Infection
An infection is the colonization of a host organism by parasite species. Infecting parasites seek to use the host's resources to reproduce, often resulting in disease...
; this is especially true in animals such as bird
Bird
Birds are feathered, winged, bipedal, endothermic , egg-laying, vertebrate animals. Around 10,000 living species and 188 families makes them the most speciose class of tetrapod vertebrates. They inhabit ecosystems across the globe, from the Arctic to the Antarctic. Extant birds range in size from...
s, but less so in human
Human
Humans are the only living species in the Homo genus...
s. 12% of human cancers can be attributed to a viral infection. The mode of virally-induced tumors can be divided into two, acutely-transforming or slowly-transforming. In acutely-transforming viruses, the viral particles carry a gene that encodes for an overactive oncogene called viral-oncogene (v-onc), and the infected cell is transformed as soon as v-onc is expressed. In contrast, in slowly-transforming viruses, the virus genome is inserted, especially as viral genome insertion is obligatory part of retrovirus
Retrovirus
A retrovirus is an RNA virus that is duplicated in a host cell using the reverse transcriptase enzyme to produce DNA from its RNA genome. The DNA is then incorporated into the host's genome by an integrase enzyme. The virus thereafter replicates as part of the host cell's DNA...
es, near a proto-oncogene in the host genome. The viral promoter or other transcription regulation elements, in turn, cause over-expression of that proto-oncogene, which, in turn, induces uncontrolled cellular proliferation. Because viral genome insertion is not specific to proto-oncogenes and the chance of insertion near that proto-oncogene is low, slowly-transforming viruses have very long tumor latency compared to acutely-transforming virus, which already carries the viral-oncogene.
Viruses that are known to cause cancer such as HPV (cervical cancer
Cervical cancer
Cervical cancer is malignant neoplasm of the cervix uteri or cervical area. One of the most common symptoms is abnormal vaginal bleeding, but in some cases there may be no obvious symptoms until the cancer is in its advanced stages...
), Hepatitis B (liver cancer
Liver cancer
Liver tumors or hepatic tumors are tumors or growths on or in the liver . Several distinct types of tumors can develop in the liver because the liver is made up of various cell types. These growths can be benign or malignant...
), and EBV
EBV
EBV may refer to:* Epstein-Barr virus, a virus of the herpes family* EBV infectious mononucleosis, mononucleosis caused by the Epstein-Barr virus* Escuela Bella Vista, an American school located in Maracaibo, Venezuela...
(a type of lymphoma
Lymphoma
Lymphoma is a cancer in the lymphatic cells of the immune system. Typically, lymphomas present as a solid tumor of lymphoid cells. Treatment might involve chemotherapy and in some cases radiotherapy and/or bone marrow transplantation, and can be curable depending on the histology, type, and stage...
), are all DNA viruses. It is thought that when the virus infects a cell, it inserts a part of its own DNA near the cell growth genes, causing cell division. The group of changed cells that are formed from the first cell dividing all have the same viral DNA near the cell growth genes. The group of changed cells are now special because one of the normal controls on growth has been lost.
Depending on their location, cells can be damaged through radiation from sunshine, chemicals from cigarette smoke, and inflammation from bacterial infection or other viruses. Each cell has a chance of damage, a step on a path toward cancer. Cells often die if they are damaged, through failure of a vital process or the immune system; however, sometimes damage will knock out a single cancer gene. In an old person, there are thousands, tens of thousands or hundreds of thousands of knocked-out cells. The chance that any one would form a cancer is very low.
When the damage occurs in any area of changed cells, something different occurs. Each of the cells has the potential for growth. The changed cells will divide quicker when the area is damaged by physical, chemical, or viral agents. A vicious circle
Vicious Circle
Vicious Circle is an album released in 1994 by L.A. Guns. Most of the songs have Phil Lewis on lead vocals, but the track "Nothing Better to Do" features Kelly Nickels on lead vocals, and "Tarantula" is instrumental. MC Bones drums on several songs. Lewis and Bones also played together in the band...
has been set up: Damaging the area will cause the changed cells to divide, causing a greater likelihood that they will suffer knock-outs.
This model of carcinogenesis is popular because it explains why cancers grow. It would be expected that cells that are damaged through radiation would die or at least be worse off because they have fewer genes working; viruses increase the number of genes working.
One concern is that we may end up with thousands of vaccines to prevent every virus that can change our cells. Viruses can have different effects on different parts of the body. It may be possible to prevent a number of different cancers by immunizing against one viral agent. It is likely that HPV, for instance, has a role in cancers of the mucous membranes of the mouth.
Helminthiasis
Certain parasitic worms are known to be carcinogenic. These include:- Clonorchis sinensisClonorchis sinensisClonorchis sinensis, the Chinese liver fluke, is a human liver fluke in the class Trematoda, Phylum Platyhelminthes. This parasite lives in the liver of humans, and is found mainly in the common bile duct and gall bladder, feeding on bile...
(the organism causing ClonorchiasisClonorchiasisClonorchiasis is an infectious disease caused by the Chinese liver fluke, Clonorchis sinensis.Clonorchiasis is a known risk factor for the development of cholangiocarcinoma, a neoplasm of the biliary system....
) and Opisthorchis viverriniOpisthorchis viverriniOpisthorchis viverrini, common name Southeast Asian liver fluke, is a trematode parasite from the family Opisthorchiidae that attacks the area of the bile duct. Infection is acquired when people ingest raw or undercooked fish. It causes the disease opisthorchiasis...
(causing OpisthorchiasisOpisthorchiasisOpisthorchiasis is an parasitic disease caused by species in the genus Opisthorchis ....
) are associated with cholangiocarcinomaCholangiocarcinomaCholangiocarcinoma is a cancer of the bile ducts which drain bile from the liver into the small intestine. Other biliary tract cancers include pancreatic cancer, gallbladder cancer, and cancer of the ampulla of Vater...
.
- SchistosomaSchistosomaA genus of trematodes, Schistosoma, commonly known as blood-flukes and bilharzia, includes flatworms which are responsible for a highly significant parasitic infection of humans by causing the disease schistosomiasis, and are considered by the World Health Organization as the second most...
species (the organisms causing SchistosomiasisSchistosomiasisSchistosomiasis is a parasitic disease caused by several species of trematodes , a parasitic worm of the genus Schistosoma. Snails often act as an intermediary agent for the infectious diseases until a new human host is found...
) is associated with bladder cancerBladder cancerBladder cancer is any of several types of malignant growths of the urinary bladder. It is a disease in which abnormal cells multiply without control in the bladder. The bladder is a hollow, muscular organ that stores urine; it is located in the pelvis...
.
Epigenetics
Epigenetics is the study of the regulation of gene expression through chemical, non-mutational changes in DNA structure. The theory of epigeneticsEpigenetics
In biology, and specifically genetics, epigenetics is the study of heritable changes in gene expression or cellular phenotype caused by mechanisms other than changes in the underlying DNA sequence – hence the name epi- -genetics...
in cancer pathogenesis is that non-mutational changes to DNA can lead to alterations in gene expression. Normally, oncogenes are silent, for example, because of DNA methylation
DNA methylation
DNA methylation is a biochemical process that is important for normal development in higher organisms. It involves the addition of a methyl group to the 5 position of the cytosine pyrimidine ring or the number 6 nitrogen of the adenine purine ring...
. Loss of that methylation can induce the aberrant expression of oncogenes, leading to cancer pathogenesis. Known mechanisms of epigenetic change include DNA methylation
DNA methylation
DNA methylation is a biochemical process that is important for normal development in higher organisms. It involves the addition of a methyl group to the 5 position of the cytosine pyrimidine ring or the number 6 nitrogen of the adenine purine ring...
, and methylation or acetylation of histone
Histone
In biology, histones are highly alkaline proteins found in eukaryotic cell nuclei that package and order the DNA into structural units called nucleosomes. They are the chief protein components of chromatin, acting as spools around which DNA winds, and play a role in gene regulation...
proteins bound to chromosomal DNA at specific locations. Classes of medications, known as HDAC inhibitors
Histone deacetylase inhibitor
Histone deacetylase inhibitors are a class of compounds that interfere with the function of histone deacetylase.HDIs have a long history of use in psychiatry and neurology as mood stabilzers and anti-epileptics...
and DNA methyltransferase
DNA methyltransferase
In biochemistry, the DNA methyltransferase family of enzymescatalyze the transfer of a methyl group to DNA. DNA methylation serves a wide variety of biological functions...
inhibitors, can re-regulate the epigenetic signaling in the cancer cell.
Cancer stem cells
A new way of looking at carcinogenesis comes from integrating the ideas of developmental biologyDevelopmental biology
Developmental biology is the study of the process by which organisms grow and develop. Modern developmental biology studies the genetic control of cell growth, differentiation and "morphogenesis", which is the process that gives rise to tissues, organs and anatomy.- Related fields of study...
into oncology
Oncology
Oncology is a branch of medicine that deals with cancer...
. The cancer stem cell
Cancer stem cell
Cancer stem cells are cancer cells that possess characteristics associated with normal stem cells, specifically the ability to give rise to all cell types found in a particular cancer sample. CSCs are therefore tumorigenic , perhaps in contrast to other non-tumorigenic cancer cells...
hypothesis
Hypothesis
A hypothesis is a proposed explanation for a phenomenon. The term derives from the Greek, ὑποτιθέναι – hypotithenai meaning "to put under" or "to suppose". For a hypothesis to be put forward as a scientific hypothesis, the scientific method requires that one can test it...
proposes that the different kinds of cells in a heterogeneous tumor arise from a single cell, termed Cancer Stem Cell. Cancer stem cells may arise from transformation of adult stem cell
Adult stem cell
Adult stem cells are undifferentiated cells, found throughout the body after embryonic development, that multiply by cell division to replenish dying cells and regenerate damaged tissues...
s or differentiated
Cellular differentiation
In developmental biology, cellular differentiation is the process by which a less specialized cell becomes a more specialized cell type. Differentiation occurs numerous times during the development of a multicellular organism as the organism changes from a simple zygote to a complex system of...
cells within a body. These cells persist as a subcomponent of the tumor and retain key stem cell properties. They give rise to a variety of cells, are capable of self-renewal and homeostatic control. Furthermore, the relapse
Relapse
Relapse, in relation to drug misuse, is resuming the use of a drug or a dependent substance after one or more periods of abstinence. The term is a landmark feature of both substance dependence and substance abuse, which are learned behaviors, and is maintained by neuronal adaptations that mediate...
of cancer and the emergence of metastasis
Metastasis
Metastasis, or metastatic disease , is the spread of a disease from one organ or part to another non-adjacent organ or part. It was previously thought that only malignant tumor cells and infections have the capacity to metastasize; however, this is being reconsidered due to new research...
are also attributed to these cells. The cancer stem cell
Cancer stem cell
Cancer stem cells are cancer cells that possess characteristics associated with normal stem cells, specifically the ability to give rise to all cell types found in a particular cancer sample. CSCs are therefore tumorigenic , perhaps in contrast to other non-tumorigenic cancer cells...
hypothesis
Hypothesis
A hypothesis is a proposed explanation for a phenomenon. The term derives from the Greek, ὑποτιθέναι – hypotithenai meaning "to put under" or "to suppose". For a hypothesis to be put forward as a scientific hypothesis, the scientific method requires that one can test it...
does not contradict earlier concepts of carcinogenesis.
Clonal evolution
While genetic and epigenetic alterations in tumor suppressor genes and oncogenes change the behavior of cells, those alterations, in the end, result in cancer through their effects on the population of neoplastic cells and their microenvironment. Mutant cells in neoplasms compete for space and resources. Thus, a clone with a mutation in a tumor suppressor gene or oncogene will expand only in a neoplasm if that mutation gives the clone a competitive advantage over the other clones and normal cells in its microenvironment. Thus, the process of carcinogenesis is formally a process of Darwinian evolutionEvolution
Evolution is any change across successive generations in the heritable characteristics of biological populations. Evolutionary processes give rise to diversity at every level of biological organisation, including species, individual organisms and molecules such as DNA and proteins.Life on Earth...
, known as somatic or clonal evolution
Somatic evolution in cancer
Somatic evolution is the accumulation of mutations in the cells of a body during a lifetime, and the effects of those mutations on the fitness of those cells. Somatic evolution is important in the process of aging as well as the development of some diseases, including cancer.-Natural selection in...
. Furthermore, in light of the Darwinistic mechanisms of carcinogenesis, it has been theorized that the various forms of cancer can be categorized as pubertarial and gerontological. Anthropological research is currently being conducted on cancer as a natural evolutionary process through which natural selection destroys environmentally inferior phenotypes while supporting others. According to this theory, cancer comes in two separate types: from birth to the end of puberty (approximately age 20) teleologically inclined toward supportive group dynamics, and from mid-life to death (approximately age 40+) teleologically inclined away from overpopulative group dynamics.

