BRCA1
Encyclopedia
Caretaker gene
Changes in the genome that allow uncontrolled cell proliferation or cell immortality are responsible for cancer. It is believed that the major changes in the genome that lead to cancer arise from mutations in tumor suppressor genes. In 1997, Kinzler and Bert Vogelstein grouped these cancer...
that produces a protein
Protein
Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form, facilitating a biological function. A polypeptide is a single linear polymer chain of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of...
called breast cancer type 1 susceptibility protein, responsible for repairing DNA. The first evidence for the existence of the gene was provided by the King
Mary-Claire King
Mary-Claire King is an American human geneticist. She is a professor at the University of Washington, where she studies the genetics and interaction of genetics and environmental influences on human conditions such as HIV, lupus, inherited deafness, and also breast and ovarian cancer...
laboratory at UC Berkeley
University of California, Berkeley
The University of California, Berkeley , is a teaching and research university established in 1868 and located in Berkeley, California, USA...
in 1990. The gene was later cloned in 1994 by scientists at Myriad Genetics
Myriad Genetics
Myriad Genetics, Inc. is a molecular diagnostic company based in Salt Lake City, Utah. Myriad employs a number of proprietary technologies that permit doctors and patients to understand the genetic basis of human disease and the role that genes play in the onset, progression and treatment of disease...
.
BRCA1 is expressed in the cells of breast and other tissue, where it helps repair damaged DNA
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid is a nucleic acid that contains the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms . The DNA segments that carry this genetic information are called genes, but other DNA sequences have structural purposes, or are involved in...
, or destroy cells if DNA cannot be repaired. If BRCA1 itself is damaged, damaged DNA is not repaired properly and this increases risks for cancers.
The protein
Protein
Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form, facilitating a biological function. A polypeptide is a single linear polymer chain of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of...
encoded by the BRCA1 gene combines with other tumor suppressors, DNA damage sensors, and signal transducers to form a large multi-subunit protein complex known as the BRCA1-associated genome surveillance complex (BASC). The BRCA1 protein associates with RNA polymerase II
RNA polymerase II
RNA polymerase II is an enzyme found in eukaryotic cells. It catalyzes the transcription of DNA to synthesize precursors of mRNA and most snRNA and microRNA. A 550 kDa complex of 12 subunits, RNAP II is the most studied type of RNA polymerase...
, and through the C-terminal domain, also interacts with histone deacetylase
Histone deacetylase
Histone deacetylases are a class of enzymes that remove acetyl groups from an ε-N-acetyl lysine amino acid on a histone. This is important because DNA is wrapped around histones, and DNA expression is regulated by acetylation and de-acetylation. Its action is opposite to that of histone...
complexes. Thus, this protein plays a role in transcription, DNA repair
DNA repair
DNA repair refers to a collection of processes by which a cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. In human cells, both normal metabolic activities and environmental factors such as UV light and radiation can cause DNA damage, resulting in as many as 1...
of double-stranded breaks ubiquitin
Ubiquitin
Ubiquitin is a small regulatory protein that has been found in almost all tissues of eukaryotic organisms. Among other functions, it directs protein recycling.Ubiquitin can be attached to proteins and label them for destruction...
ation, transcriptional regulation
Transcriptional regulation
Transcriptional regulation is the change in gene expression levels by altering transcription rates. -Regulation of transcription:Regulation of transcription controls when transcription occurs and how much RNA is created...
as well as other functions.
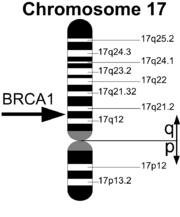
Gene location
The human BRCA1 gene is located on the long (q) arm of chromosome 17Chromosome 17 (human)
125px|rightChromosome 17 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 17 spans more than 81 million base pairs and represents between 2.5 and 3 % of the total DNA in cells.Identifying genes on each chromosome is an active area of...
at band 21, from base pair
Base pair
In molecular biology and genetics, the linking between two nitrogenous bases on opposite complementary DNA or certain types of RNA strands that are connected via hydrogen bonds is called a base pair...
38,429,551 to base pair 38,551,283 (Build GRCh37/hg19) (map). BRCA1 orthologs have been identified in most mammals for which complete genome data are available.
Protein structure
The BRCA1 proteinProtein
Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form, facilitating a biological function. A polypeptide is a single linear polymer chain of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of...
(breast cancer type 1 susceptibility protein also known as RING finger protein 53) contains the following domains:
- Zinc finger, C3HC4 type (RING fingerRING finger domainIn molecular biology, a RING finger domain is a protein structural domain of zinc finger type which contains a Cys3HisCys4 amino acid motif which binds two zinc cations. This protein domain contains from 40 to 60 amino acids...
) - BRCA1 C Terminus (BRCTBRCT domainBRCA1 C Terminus domain is a family of evolutionarily related proteins.The BRCT domain is found predominantly in proteins involved in cell cycle checkpoint functions responsive to DNA damage, for example as found in the breast cancer DNA-repair protein BRCA1...
) domain
This protein also contains nuclear localization signal
Nuclear localization signal
A nuclear localization signal or sequence is an amino acid sequence which 'tags' a protein for import into the cell nucleus by nuclear transport. Typically, this signal consists of one or more short sequences of positively charged lysines or arginines exposed on the protein surface. Different...
and nuclear export signal
Nuclear export signal
A nuclear export signal is a short amino acid sequence of 4 hydrophobic residues in a protein that targets it for export from the cell nucleus to the cytoplasm through the nuclear pore complex using nuclear transport. It has the opposite effect of a nuclear localization signal, which targets a...
motifs.
Function and mechanism
BRCA1 repairs double-strand breaks in DNA. The strands of the DNA double helix are continuously breaking from damage. Sometimes one strand is broken, and sometimes both strands are broken simultaneously. BRCA1 is part of a protein complex that repairs DNA when both strands are broken. When both strands are broken, it is difficult for the repair mechanism to "know" how to replace the correct DNA sequence, and there are multiple ways to attempt the repair. The double-stranded repair mechanism that BRCA1 participates in is homologous recombinationHomologous recombination
Homologous recombination is a type of genetic recombination in which nucleotide sequences are exchanged between two similar or identical molecules of DNA. It is most widely used by cells to accurately repair harmful breaks that occur on both strands of DNA, known as double-strand breaks...
, in which the repair proteins utilize homologous intact sequence from a sister chromatid, from a homologous chromosome
Homologous chromosome
Homologous chromosomes are chromosome pairs of approximately the same length, centromere position, and staining pattern, with genes for the same characteristics at corresponding loci. One homologous chromosome is inherited from the organism's mother; the other from the organism's father...
, or from the same chromosome (depending on cell cycle phase) as a template. This DNA repair takes place with the DNA in the cell nucleus, wrapped around the histone
Histone
In biology, histones are highly alkaline proteins found in eukaryotic cell nuclei that package and order the DNA into structural units called nucleosomes. They are the chief protein components of chromatin, acting as spools around which DNA winds, and play a role in gene regulation...
. Several proteins, including BRCA1, arrive at the histone-DNA complex for this repair. Regulatory aspect to BRCA1 nuclear ⁄ non-nuclear distribution was first shown by Dr Rao laboratory in 1997
In the nucleus of many types of normal cells, the BRCA1 protein interacts with RAD51
RAD51
RAD51 is a human gene. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the RAD51 protein family which assist in repair of DNA double strand breaks. RAD51 family members are homologous to the bacterial RecA and yeast Rad51...
during repair of DNA double-strand breaks. These breaks can be caused by natural radiation or other exposures, but also occur when chromosome
Chromosome
A chromosome is an organized structure of DNA and protein found in cells. It is a single piece of coiled DNA containing many genes, regulatory elements and other nucleotide sequences. Chromosomes also contain DNA-bound proteins, which serve to package the DNA and control its functions.Chromosomes...
s exchange genetic material (homologous recombination, e.g., "crossing over" during meiosis). The BRCA2
BRCA2
BRCA2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BRCA2 gene.BRCA2 orthologs have been identified in most mammals for which complete genome data are available....
protein, which has a function similar to that of BRCA1, also interacts with the RAD51 protein. By influencing DNA damage repair, these three proteins play a role in maintaining the stability of the human genome.
BRCA1 directly binds to DNA, with higher affinity for branched DNA structures. This ability to bind to DNA contributes to its ability to inhibit the nuclease activity of the MRN
Mre11-Rad50-Nbs1
The MRN complex is heterotrimeric protein complex consisting of Mre11, Rad50 and Nbs1. It is involved in DNA repair in mammals. Nbs1 is referred to as Nibrin. This complex recognizes DNA damage and rapidly relocates to DSB sites and forms nuclear foci. Its activity includes end-processing of...
complex as well as the nuclease activity of Mre11 alone. This may explain a role for BRCA1 to promote higher fidelity DNA repair by non-homologous end joining
Non-homologous end joining
Non-homologous end joining is a pathway that repairs double-strand breaks in DNA. NHEJ is referred to as "non-homologous" because the break ends are directly ligated without the need for a homologous template, in contrast to homologous recombination, which requires a homologous sequence to guide...
(NHEJ). BRCA1 also colocalizes with γ-H2AX (histone H2AX phosphorylated on serine-139) in DNA double-strand break repair foci, indicating it may play a role in recruiting repair factors.
Transcription
BRCA1 was shown to co-purify with the human RNA Polymerase II holoenzyme in HeLa extracts, implying it is a component of the holoenzyme. Later research, however, contradicted this assumption, instead showing that the predominant complex including BRCA1 in HeLa cells is a 2 megadalton complex containing SWI/SNF. SWI/SNF is a chromatin remodeling complex. Artificial tethering of BRCA1 to chromatin was shown to decondense heterochromatin, though the SWI/SNF interacting domain was not necessary for this role. BRCA1 interacts with the NELF-B (COBRA1Cofactor of BRCA1
Cofactor of BRCA1, also known as COBRA1, is a human gene that encodes NELF-B. NELF-B is a subunit of negative elongation factor , which also includes NELF-A , either NELF-C or NELF-D , and NELF-E...
) subunit of the NELF
Negative elongation factor
NELF is a four subunit protein that affects transcription by RNA polymerase II. Subunit NELF-E is also known as RDBP. The NELF-A subunit is encoded by the gene WHSC2, Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome candidate 2...
complex.
Other roles
Research suggests that both the BRCA1 and BRCA2 proteins regulate the activity of other genes and play a critical role in embryo development. The BRCA1 protein probably interacts with many other proteins, including tumor suppressors and regulators of the cell division cycle.Mutations and cancer risk
Certain variations of the BRCA1 gene lead to an increased risk for breast cancerBreast cancer
Breast cancer is cancer originating from breast tissue, most commonly from the inner lining of milk ducts or the lobules that supply the ducts with milk. Cancers originating from ducts are known as ductal carcinomas; those originating from lobules are known as lobular carcinomas...
as part of a hereditary breast-ovarian cancer syndrome. Researchers have identified hundreds of mutation
Mutation
In molecular biology and genetics, mutations are changes in a genomic sequence: the DNA sequence of a cell's genome or the DNA or RNA sequence of a virus. They can be defined as sudden and spontaneous changes in the cell. Mutations are caused by radiation, viruses, transposons and mutagenic...
s in the BRCA1 gene, many of which are associated with an increased risk of cancer. Women with an abnormal BRCA1 or BRCA2 gene have up to a 60% risk of developing breast cancer by age 90; increased risk of developing ovarian cancer is about 55% for women with BRCA1 mutations and about 25% for women with BRCA2 mutations.
These mutations can be changes in one or a small number of DNA base pair
Base pair
In molecular biology and genetics, the linking between two nitrogenous bases on opposite complementary DNA or certain types of RNA strands that are connected via hydrogen bonds is called a base pair...
s (the building-blocks of DNA). Those mutations can be identified with PCR and DNA sequencing.
In some cases, large segments of DNA are rearranged. Those large segments, also called large rearrangements, can be a deletion or a duplication of one or several exons in the gene. Classical methods for mutations detection (sequencing) are unable to reveal those mutations. Other methods are proposed: Q-PCR, Multiplex Ligation-dependent Probe Amplification
Multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification
Multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification is a variation of the polymerase chain reaction that permits multiple targets to be amplified with only a single primer pair. Each probe consists of a two oligonucleotides which recognise adjacent target sites on the DNA...
(MLPA), and Quantitative Multiplex PCR of Shorts Fluorescents Fragments (QMPSF). New methods have been recently proposed: heteroduplex analysis (HDA) by multi-capillary electrophoresis or also dedicated oligonucleotides array based on comparative genomic hybridization
Comparative genomic hybridization
Comparative genomic hybridization or Chromosomal Microarray Analysis is a molecular-cytogenetic method for the analysis of copy number changes in the DNA content of a given subject's DNA and often in tumor cells....
(array-CGH).
Some results suggest that hypermethylation
Methylation
In the chemical sciences, methylation denotes the addition of a methyl group to a substrate or the substitution of an atom or group by a methyl group. Methylation is a form of alkylation with, to be specific, a methyl group, rather than a larger carbon chain, replacing a hydrogen atom...
of the BRCA1 promoter, which has been reported in some cancers, could be considered as an inactivating mechanism for BRCA1 expression.
A mutated BRCA1 gene usually makes a protein
Protein
Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form, facilitating a biological function. A polypeptide is a single linear polymer chain of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of...
that does not function properly because it is abnormally short. Researchers believe that the defective BRCA1 protein is unable to help fix mutations that occur in other genes. These defects accumulate and may allow cells to grow and divide uncontrollably to form a tumor.
BRCA1 mRNA 3' UTR
Three prime untranslated region
In molecular genetics, the three prime untranslated region is a particular section of messenger RNA . It is preceeded by the coding region....
can be bound by an miRNA
Mirna
Mirna may refer to:geographical entities* Mirna , a river in Istria, Croatia* Mirna , a river in Slovenia, tributary of the river Sava* Mirna , a settlement in the municipality of Mirna in Southeastern Sloveniapeople...
, Mir-17 microRNA
Mir-17 microRNA precursor family
The miR-17 microRNA precursor family are a group of related small non-coding RNA genes called microRNAs that regulate gene expression. The microRNA precursor miR-17 family, includes miR-20, miR-91, and miR-103. miRNAs are transcribed as ~70 nucleotide precursors and subsequently processed by the...
. It has been suggested that variations in this miRNA along with Mir-30 microRNA
Mir-30 microRNA precursor
miR-30 microRNA precursor is a small non-coding RNA that regulates gene expression. Animal microRNAs are transcribed as ~70 nucleotide stem-loop precursor and subsequently processed by the Dicer enzyme to give a mature ~22 nucleotide product. In this case the mature sequence comes from both the 3' ...
could confer susceptibility to breast cancer.
In addition to breast cancer, mutations in the BRCA1 gene also increase the risk of ovarian
Ovarian cancer
Ovarian cancer is a cancerous growth arising from the ovary. Symptoms are frequently very subtle early on and may include: bloating, pelvic pain, difficulty eating and frequent urination, and are easily confused with other illnesses....
, fallopian tube
Fallopian tube
The Fallopian tubes, also known as oviducts, uterine tubes, and salpinges are two very fine tubes lined with ciliated epithelia, leading from the ovaries of female mammals into the uterus, via the utero-tubal junction...
, and prostate cancer
Prostate cancer
Prostate cancer is a form of cancer that develops in the prostate, a gland in the male reproductive system. Most prostate cancers are slow growing; however, there are cases of aggressive prostate cancers. The cancer cells may metastasize from the prostate to other parts of the body, particularly...
s. Moreover, precancerous lesions (dysplasia
Dysplasia
Dysplasia , is a term used in pathology to refer to an abnormality of development. This generally consists of an expansion of immature cells, with a corresponding decrease in the number and location of mature cells. Dysplasia is often indicative of an early neoplastic process...
) within the Fallopian tube have been linked to BRCA1 gene mutations. Pathogenic mutations anywhere in a model pathway containing BRCA1 and BRCA2 greatly increase risks for a subset of leukemias and lymphomas.
Women having inherited a defective BRCA1 or BRCA2 gene have risks for breast and ovarian cancer that are so high and seem so selective that many mutation carriers choose to have prophylactic surgery. There has been much conjecture to explain such apparently striking tissue specificity. Major determinants of where BRCA1/2 hereditary cancers occur are related to tissue specificity of the cancer pathogen, the agent that causes chronic inflammation or the carcinogen. The target tissue may have receptors for the pathogen, become selectively exposed to an inflammatory process or to a carcinogen. An innate genomic deficit in a tumor suppressor gene impairs normal responses and exacerbates the susceptibility to disease in organ targets. This theory also fits data for several tumor suppressors beyond BRCA1 or BRCA2. A major advantage of this model is that it suggests there may be some options in addition to prophylactic surgery.
Germ line mutations and founder effect
All germ-line BRCA1 mutations identified to date have been inherited, suggesting the possibility of a large “founder” effect in which a certain mutation is common to a well-defined population group and can, in theory, be traced back to a common ancestor. Given the complexity of mutation screening for BRCA1, these common mutations may simplify the methods required for mutation screening in certain populations. Analysis of mutations that occur with high frequency also permits the study of their clinical expression. Examples of manifestations of a founder effect are seen among Ashkenazi Jews. Three mutations in BRCA1 have been reported to account for the majority of Ashkenazi Jewish patients with inherited BRCA1-related breast and/or ovarian cancer: 185delAG, 188del11 and 5382insC in the BRCA1 gene. In fact, it has been shown that if a Jewish woman does not carry a BRCA1 185delAG, BRCA1 5382insC founder mutation, it is highly unlikely that a different BRCA1 mutation will be found. Additional examples of founder mutations in BRCA1 are given in Table 1 (mainly derived from ).| Population or subgroup | BRCA1 mutation(s) | Reference(s) |
|---|---|---|
| African-Americans | 943ins10, M1775R | |
| Ashkenazi Jewish | 185delAG, 188del11, 5382insC | |
| Austrians | 2795delA, C61G, 5382insC, Q1806stop | |
| Belgians | 2804delAA, IVS5+3A>G | |
| Dutch | Exon 2 deletion, exon 13 deletion, 2804delAA | |
| Finns | 3745delT, IVS11-2A>G | |
| French | 3600del11, G1710X | |
| French Canadians | C4446T | |
| Germans | 5382insC | 4184del4 Ref. http://mutview.dmb.med.keio.ac.jp/MutationView/jsp/mutview/html/brca1.html |
| Greeks | 5382insC | |
| Hungarians | 300T>G, 5382insC, 185delAG | |
| Italians | 5083del19 | |
| Japanese | L63X, Q934X | |
| Native North Americans | 1510insG, 1506A>G | |
| Northern Irish | 2800delAA | |
| Norwegians | 816delGT, 1135insA, 1675delA, 3347delAG | |
| Pakistanis | 2080insA, 3889delAG, 4184del4, 4284delAG, IVS14-1A>G | |
| Polish | 300T>G, 5382insC, C61G, 4153delA | |
| Russians | 5382insC, 4153delA | |
| Scottish | 2800delAA | |
| South Africans | E881X | |
| Spanish | R71G | |
| Swedish | Q563X, 3171ins5, 1201del11, 2594delC |
Patent
Methods to isolate and detect BRCA1 and BRCA2BRCA2
BRCA2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BRCA2 gene.BRCA2 orthologs have been identified in most mammals for which complete genome data are available....
were patented in the United States by Myriad Genetics
Myriad Genetics
Myriad Genetics, Inc. is a molecular diagnostic company based in Salt Lake City, Utah. Myriad employs a number of proprietary technologies that permit doctors and patients to understand the genetic basis of human disease and the role that genes play in the onset, progression and treatment of disease...
. This US patent has been challenged by the American Civil Liberties Union
American Civil Liberties Union
The American Civil Liberties Union is a U.S. non-profit organization whose stated mission is "to defend and preserve the individual rights and liberties guaranteed to every person in this country by the Constitution and laws of the United States." It works through litigation, legislation, and...
. On March 29, 2010, a coalition led by the American Civil Liberties Union (ACLU) successfully challenged the basis of Myriad’s patents in New York District Court. The patent was invalidated, but the decision was appealed. On July 29, 2011 the United States Court of Appeals for the Federal Circuit
United States courts of appeals
The United States courts of appeals are the intermediate appellate courts of the United States federal court system...
made their decision and ruled that Myriads patents are valid.
Interactions
BRCA1 has been shown to interactProtein-protein interaction
Protein–protein interactions occur when two or more proteins bind together, often to carry out their biological function. Many of the most important molecular processes in the cell such as DNA replication are carried out by large molecular machines that are built from a large number of protein...
with
- ABL1Abl geneV-abl Abelson murine leukemia viral oncogene homolog 1 also known as ABL1 is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the ABL1 gene located on chromosome 9.- Function :...
, - AKT1AKT1RAC-alpha serine/threonine-protein kinase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the AKT1 gene. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found for this gene.- Function :...
, - ARAndrogen receptorThe androgen receptor , also known as NR3C4 , is a type of nuclear receptor that is activated by binding of either of the androgenic hormones testosterone or dihydrotestosterone in the cytoplasm and then translocating into the nucleus...
, - ATRAtaxia telangiectasia and Rad3 relatedSerine/threonine-protein kinase ATR also known as ataxia telangiectasia and Rad3-related protein or FRAP-related protein 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ATR gene...
, - ATMAtaxia telangiectasia mutatedAtaxia telangiectasia mutated is a serine/threonine protein kinase that is recruited and activated by DNA double-strand breaks. It phosphorylates several key proteins that initiate activation of the DNA damage checkpoint, leading to cell cycle arrest, DNA repair or apoptosis...
, - ATF1ATF1Cyclic AMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ATF1 gene.-Interactions:ATF1 has been shown to interact with CSNK2A2, Casein kinase 2, alpha 1 and BRCA1. EWS,- External links :...
, - AURKAAurora A kinaseAurora A kinase also known as serine/threonine-protein kinase 6 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the AURKA gene.Aurora A is a member of a family of mitotic serine/threonine kinases. It is implicated with important processes during mitosis and meiosis whose proper function is integral for...
, - BACH1BACH1Transcription regulator protein BACH1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BACH1 gene.-Further reading:- External links :...
, - BARD1BARD1BRCA1-associated RING domain protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BARD1 gene.-Interactions:BARD1 has been shown to interact with BRE, UBE2D1, CSTF2, BRCC3, RAD51, BCL3, TACC1, Ewing sarcoma breakpoint region 1, FANCD2, H2AFX, CSTF1, NPM1, BRCA2, BRCA1, P53 and Aurora B...
, - BRCA2BRCA2BRCA2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BRCA2 gene.BRCA2 orthologs have been identified in most mammals for which complete genome data are available....
, - BRCC3BRCC3Lys-63-specific deubiquitinase BRCC36 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the BRCC3 gene.-Interactions:BRCC3 has been shown to interact with BRE, BRCA2, RAD51, BRCA1, P53 and BARD1.-Further reading:...
, - BREBRE (gene)BRCA1-A complex subunit BRE is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BRE gene.-Interactions:BRE has been shown to interact with BRCA2, RAD51, BRCC3, BRCA1, C19orf62, P53 and BARD1.-Further reading:...
, - BRIP1BRIP1Fanconi anemia group J protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BRCA1-interacting protein 1 gene.This protein also appears to be important in ovarian cancer where it seems to act as an antioncogene.-Further reading:...
, - C-junC-junc-Jun is the name of a gene and protein that, in combination with c-Fos, forms the AP-1 early response transcription factor. It was first identified as the Fos-binding protein p39 and only later rediscovered as the product of the c-jun gene. It is activated through double phosphorylation by the...
, - CHEK2CHEK2CHEK2 is the official symbol for the human gene CHK2 checkpoint homolog. It is located on the long arm of chromosome 22.-Function:The protein encoded by this gene, CHK2 a protein kinase that is activated in response to DNA damage and is involved in cell cycle arrest.In response to DNA damage and...
, - CLSPNCLSPNClaspin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CLSPN gene.-Interactions:CLSPN has been shown to interact with USP7, CHEK1 and BRCA1.-Further reading:...
, - COBRA1Cofactor of BRCA1Cofactor of BRCA1, also known as COBRA1, is a human gene that encodes NELF-B. NELF-B is a subunit of negative elongation factor , which also includes NELF-A , either NELF-C or NELF-D , and NELF-E...
, - CREBBP,
- CSNK2BCSNK2BCasein kinase, a ubiquitous, well-conserved protein kinase involved in cell metabolism and differentiation, is characterised by its preference for Serine or Threonine in acidic stretches of amino acids. The enzyme is a tetramer of 2 alpha- and 2 beta-subunits...
, - CSTF2CSTF2Cleavage stimulation factor 64 kDa subunit is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CSTF2 gene.-Interactions:CSTF2 has been shown to interact with CSTF3, SUB1, SYMPK, BARD1 and BRCA1.-Further reading:...
, - CDK2Cyclin-dependent kinase 2Cyclin-dependent kinase 2 also known as cell division protein kinase 2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CDK2 gene.-Function:...
, - DHX9DHX9ATP-dependent RNA helicase A is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the DHX9 gene.-Interactions:...
, - ELK4ELK4ETS domain-containing protein Elk-4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ELK4 gene.-Interactions:ELK4 has been shown to interact with Serum response factor and BRCA1.-Further reading:...
, - EP300EP300E1A binding protein p300 also known as EP300 or p300 is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the EP300 gene. This protein regulates the activity of many genes in tissues throughout the body...
, - ESR1Estrogen receptor alphaEstrogen receptor alpha , also known as NR3A1 , is a nuclear receptor that is activated by the sex hormone estrogen...
, - FANCAFANCAFanconi anemia, complementation group A, also known as FANCA, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the FANCA gene.- Function :...
, - FANCD2FANCD2Fanconi anemia group D2 protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FANCD2 gene. The Fanconi anemia complementation group currently includes FANCA, FANCB, FANCC, FANCD1 , FANCD2 , FANCE, FANCF, FANCG, and FANCL.- Function :Fanconi anemia is a genetically heterogeneous recessive disorder...
, - FHL2FHL2Four and a half LIM domains protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FHL2 gene.-Interactions:FHL2 has been shown to interact with Beta-catenin, Titin, Zinc finger and BTB domain-containing protein 16, Integrin, beta 6, Androgen receptor, ITGA7, CREB1, MAPK1, CD49c, ZNF638, BRCA1,...
, - H2AFXH2AFXH2AX is one of several genes coding for histone H2A. In humans and other eukaryotes, the DNA is wrapped around histone-groups, consisting of core histones H2A, H2B, H3 and H4. Thus, the H2AX contributes to the histone-formation and therefore the structure of DNA.H2AX becomes phosphorylated on...
, - JUNBJUNBTranscription factor jun-B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the JUNB gene. Transcription factor jun-B is a transcription factor involved in regulating gene activity following the primary growth factor response. It binds to the DNA sequence 5'-TGA[CG]TCA-3'.-Interactions:JUNB has been shown...
, - JunDJunDTranscription factor jun-D is a protein that in humans is encoded by the JUND gene.-Interactions:JunD has been shown to interact with ATF3, MEN1, DNA damage-inducible transcript 3 and BRCA1....
, - LMO4LMO4LIM domain transcription factor LMO4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LMO4 gene.-Interactions:LMO4 has been shown to interact with LDB1, RBBP8 and BRCA1.-Further reading:...
, - MAP3K3MAP3K3Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 3 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MAP3K3 gene.-Interactions:MAP3K3 has been shown to interact with [SQSTM1/p62], MAP2K5, YWHAE, GAB1 and BRCA1.-Further reading:...
, - MED1MED1Mediator of RNA polymerase II transcription subunit 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MED1 gene.- Function :The activation of gene transcription is a multistep process that is triggered by factors that recognize transcriptional enhancer sites in DNA. These factors work with...
, - MED17MED17Mediator of RNA polymerase II transcription subunit 17 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MED17 gene.-Interactions:MED17 has been shown to interact with PPARGC1A, Cyclin-dependent kinase 8 and BRCA1.-Further reading:...
, - MED21MED21Mediator of RNA polymerase II transcription subunit 21 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MED21 gene.-Interactions:MED21 has been shown to interact with Cyclin-dependent kinase 8, BRCA1, GTF2H4, MED6, POLR2A and GTF2F1.-Further reading:...
, - MED24MED24Mediator of RNA polymerase II transcription subunit 24 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MED24 gene.-Interactions:MED24 has been shown to interact with Estrogen receptor alpha, Cyclin-dependent kinase 8, Calcitriol receptor and BRCA1....
, - MRE11AMRE11ADouble-strand break repair protein MRE11A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MRE11A gene.-Interactions:MRE11A has been shown to interact with Ku70, Ataxia telangiectasia mutated, MDC1, Rad50, Nibrin, TERF2 and BRCA1.-Further reading:...
, - MSH2MSH2MSH2 is a gene commonly associated with Hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer.-Interactions:MSH2 has been shown to interact with Exonuclease 1, MSH3, MSH6, CHEK2, MAX, Ataxia telangiectasia and Rad3 related and BRCA1.-Further reading:...
, - MSH3MSH3DNA mismatch repair protein Msh3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MSH3 gene.-Interactions:MSH3 has been shown to interact with MSH2, PCNA and BRCA1.-Further reading:...
, - MSH6MSH6MSH6 is a gene commonly associated with hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer.-Function:MSH6 contributes to ADP and ATP binding. It also contributes to ATPase activity...
, - MycMycMyc is a regulator gene that codes for a transcription factor. In the human genome, Myc is located on chromosome 8 and is believed to regulate expression of 15% of all genes through binding on Enhancer Box sequences and recruiting histone acetyltransferases...
, - NBNNibrinNibrin, also known as NBN, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the NBN gene.- Function :Nibrin is a protein associated with the repair of double strand breaks which pose serious damage to a genome. It is a 754 amino acid protein identified as a member of the NBS1/hMre11/RAD50 double strand...
, - NMI,
- NPM1NPM1Nucleophosmin , also known as nucleolar phosphoprotein B23 or numatrin, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NPM1 gene.- Function :...
, - NCOA2Nuclear receptor coactivator 2The nuclear receptor coactivator 2 is a transcriptional coregulatory protein which contains several nuclear receptor interacting domains and an intrinsic histone acetyltransferase activity. NCOA2 is recruited to DNA promotion sites by ligand activated nuclear receptors. NCOA2 in turn acylates...
, - NUFIP1NUFIP1Nuclear fragile X mental retardation-interacting protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NUFIP1 gene.-Interactions:NUFIP1 has been shown to interact with FMR1, Cyclin T1 and BRCA1.-Further reading:...
, - P53P53p53 , is a tumor suppressor protein that in humans is encoded by the TP53 gene. p53 is crucial in multicellular organisms, where it regulates the cell cycle and, thus, functions as a tumor suppressor that is involved in preventing cancer...
, - PALB2PALB2Partner and localizer of BRCA2, also known as PALB2, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the PALB2 gene.- Function :This gene encodes a protein that functions in genome maintenance...
, - POLR2APOLR2ADNA-directed RNA polymerase II subunit RPB1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the POLR2A gene.-Interactions:POLR2A has been shown to interact with Transcription elongation regulator 1, CREB-binding protein, BRCA1, GTF2H4, TATA-binding protein, PCAF, GTF2F1, SUPT5H, Transcription Factor II...
, - PPP1CAPPP1CASerine/threonine-protein phosphatase PP1-alpha catalytic subunit is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PPP1CA gene.-Interactions:...
, - Rad50RAD50Rad50 may refer to:* RADIX-50, a character encoding scheme in computing* RAD50 , in biology, encodes a DNA repair protein involved in DNA double-strand break repair...
, - RAD51RAD51RAD51 is a human gene. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the RAD51 protein family which assist in repair of DNA double strand breaks. RAD51 family members are homologous to the bacterial RecA and yeast Rad51...
, - RBBP4RBBP4Histone-binding protein RBBP4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RBBP4 gene.-Interactions:RBBP4 has been shown to interact with HDAC1, Histone deacetylase 2, SIN3A, Retinoblastoma protein, SAP30, CREB-binding protein, GATAD2B, BRCA1, MTA2 and HDAC3.-Further reading:...
, - RBBP7RBBP7Histone-binding protein RBBP7 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RBBP7 gene.-Interactions:RBBP7 has been shown to interact with HDAC1, MTA2, SIN3A, Retinoblastoma protein, SAP30, GATAD2B and BRCA1.-Further reading:...
, - RBBP8RBBP8Retinoblastoma-binding protein 8 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RBBP8 gene.-Interactions:RBBP8 has been shown to interact with LMO4, Retinoblastoma-like protein 2, Retinoblastoma-like protein 1, Ataxia telangiectasia mutated, Retinoblastoma protein, CTBP1, SIAH1 and BRCA1.-Further...
, - RELARELATranscription factor p65 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RELA gene.-Interactions:RELA has been shown to interact with NFKBIB, ETHE1, NFKBIE, RFC1, TRIB3, CREB binding protein, Neutrophil cytosolic factor 1, Glucocorticoid receptor, MTPN, BRCA1, C-Fos, POU2F1, BTRC, TATA-binding...
, - RB1Retinoblastoma proteinThe retinoblastoma protein is a tumor suppressor protein that is dysfunctional in the majority types of cancer. One highly studied function of pRb is to prevent excessive cell growth by inhibiting cell cycle progression until a cell is ready to divide...
, - RBL1Retinoblastoma-like protein 1Retinoblastoma-like 1 , also known as RBL1, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RBL1 gene.- Function :The protein encoded by this gene is similar in sequence and possibly function to the product of the retinoblastoma 1 gene...
, - RBL2Retinoblastoma-like protein 2Retinoblastoma-like protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RBL2 gene.-Interactions:Retinoblastoma-like protein 2 has been shown to interact with HDAC1, C-Raf, RBBP8, Cyclin E1, Prohibitin, Cyclin-dependent kinase 2, BRF1 and BRCA1....
, - RPL31RPL3160S ribosomal protein L31 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RPL31 gene.-Further reading:...
, - SMARCA4SMARCA4Transcription activator BRG1 also known as ATP-dependent helicase SMARCA4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SMARCA4 gene.- Function :...
- SMARCB1SMARCB1SWI/SNF-related matrix-associated actin-dependent regulator of chromatin subfamily B member 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SMARCB1 gene.-Interactions:...
, - STAT1STAT1STAT1 is a member of the Signal Transducers and Activators of Transcription family of transcription factors. STAT1 is involved in upregulating genes due to a signal by either type I, type II or type III interferons...
, - UBE2D1UBE2D1Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 D1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the UBE2D1 gene.-Interactions:UBE2D1 has been shown to interact with BARD1, UBE3A and BRCA1.-Further reading:...
, - USF2USF2Upstream stimulatory factor 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the USF2 gene.-Interactions:USF2 has been shown to interact with USF1 , PPRC1 and BRCA1.- Regulation :The USF2 gene is repressed by the microRNA miR-10a....
, - VCPValosin-containing proteinTransitional endoplasmic reticulum ATPase also known as valosin-containing protein is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the VCP gene.- Function :...
, - XISTXIST (gene)Xist is an RNA gene on the X chromosome of the placental mammals that acts as major effector of the X inactivation process. It is a component of the Xic - X-chromosome inactivation centre - along with two other RNA genes and two protein genes...
, and - ZNF350ZNF350Zinc finger protein 350 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ZNF350 gene....
,
Browser view
View a graphical representation of all GenBankGenBank
The GenBank sequence database is an open access, annotated collection of all publicly available nucleotide sequences and their protein translations. This database is produced and maintained by the National Center for Biotechnology Information as part of the International Nucleotide Sequence...
isoforms at the UCSC Genome Browser
UCSC Gene details page

