
Myc
Encyclopedia
Myc is a regulator gene
that codes
for a transcription factor
. In the human genome
, Myc is located on chromosome 8
and is believed to regulate expression of 15% of all genes through binding on Enhancer Box sequences (E-box
es) and recruiting histone acetyltransferase
s (HATs). This means that in addition to its role as a classical transcription factor, Myc also functions to regulate global chromatin structure by regulating histone acetylation both in gene-rich regions and at sites far from any known gene.
A mutated version of Myc is found in many cancers, which causes Myc to be constitutively
(persistently) expressed. This leads to the unregulated expression of many genes, some of which are involved in cell proliferation and results in the formation of cancer
. A common translocation
involving Myc is t(8;14) which is critical to the development of most cases of Burkitt's Lymphoma
. A recent study demonstrated that temporary inhibition of Myc selectively kills mouse lung cancer cells, making it a potential cancer drug target.
patients. In Burkitt's lymphoma, cancer cells show chromosomal translocation
s, in which Chromosome 8 is frequently involved. Cloning the break-point of the fusion chromosomes revealed a gene that was similar to myelocytomatosis viral oncogene (v-Myc). Thus, the newfound cellular gene was named c-Myc.
) domain. Myc protein, through its bHLH domain can bind to DNA
, while the leucine zipper domain allows the dimerization with its partner Max, another bHLH transcription factor.
Myc mRNA contains an IRES (internal ribosome entry site) that allows the RNA to be translated into protein when 5' cap
-dependent translation is inhibited, such as during viral infection.
that activates expression of a great number of genes through binding on consensus sequence
s (Enhancer Box sequences (E-boxes)) and recruiting histone acetyltransferase
s (HATs). It can also act as a transcriptional repressor. By binding Miz-1 transcription factor and displacing the p300
co-activator, it inhibits expression of Miz-1 target genes. In addition, myc has a direct role in the control of DNA replication.
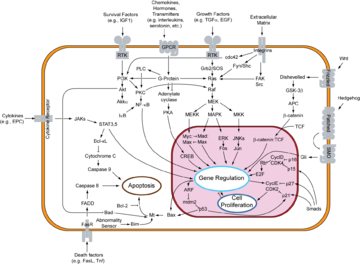
Myc is activated upon various mitogenic signal
s such as Wnt, Shh
and EGF
(via the MAPK/ERK pathway
).
By modifying the expression of its target genes, Myc activation results in numerous biological effects. The first to be discovered was its capability to drive cell proliferation (upregulates cyclins, downregulates p21), but it also plays a very important role in regulating cell growth
(upregulates ribosomal RNA and proteins), apoptosis
(downregulates Bcl-2
), differentiation and stem cell
self-renewal. Myc is a very strong proto-oncogene and it is very often found to be upregulated in many types of cancers. Myc overexpression stimulates gene amplification, presumably through DNA over-replication.
that normally drive expression of immunoglobin genes now lead to overexpression of Myc proto-oncogene in lymphoma cells. To study the mechanism of tumorigenesis in Burkitt's lymphoma by mimicking expression pattern of Myc in these cancer cells, transgenic mouse models were developed. Myc gene placed under the control of IgM
heavy chain enhancer in transgenic mice gives rise to mainly lymphomas. Later on, in order to study effects of Myc in other types of cancer, transgenic mice that overexpress Myc in different tissues (liver, breast) were also made. In all these mouse models overexpression of Myc causes tumorigenesis, illustrating the potency of Myc oncogene.
with NMI, NFYC
, NFYB
, Cyclin T1, RuvB-like 1
, GTF2I
, BRCA1
, T-cell lymphoma invasion and metastasis-inducing protein 1
, ACTL6A
, PCAF
, MYCBP2
, MAPK8
, Bcl-2
, Transcription initiation protein SPT3 homolog
, SAP130
, DNMT3A
, Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 3
, MAX
, Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 2
, MYCBP
, HTATIP
, ZBTB17
, Transformation/transcription domain-associated protein
, TADA2L
, PFDN5
, MAPK1
, TFAP2A
, P73
, TAF9
, YY1
, SMARCB1
, SMARCA4
, MLH1
, EP400
and let-7
.
proliferation.
c-Myc induces AEG-1 or MTDH gene expression and in turn itself requires AEG-1 oncogene for its expression.
Regulator gene
A regulator gene, regulator, or regulatory gene is a gene involved in controlling the expression of one or more other genes. A regulator gene may encode a protein, or it may work at the level of RNA, as in the case of genes encoding microRNAs....
that codes
Genetic code
The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded in genetic material is translated into proteins by living cells....
for a transcription factor
Transcription factor
In molecular biology and genetics, a transcription factor is a protein that binds to specific DNA sequences, thereby controlling the flow of genetic information from DNA to mRNA...
. In the human genome
Human genome
The human genome is the genome of Homo sapiens, which is stored on 23 chromosome pairs plus the small mitochondrial DNA. 22 of the 23 chromosomes are autosomal chromosome pairs, while the remaining pair is sex-determining...
, Myc is located on chromosome 8
Chromosome 8 (human)
Chromosome 8 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 8 spans about 145 million base pairs and represents between 4.5 and 5.0% of the total DNA in cells....
and is believed to regulate expression of 15% of all genes through binding on Enhancer Box sequences (E-box
E-box
An E-box is a DNA sequence which usually lies upstream of a gene in a promoter region. It is a transcription factor binding site where the specific sequence of DNA, CANNTG, is recognized by proteins that can bind to it to help initiate its transcription. Once transcription factors bind to...
es) and recruiting histone acetyltransferase
Histone acetyltransferase
Histone acetyltransferases are enzymes that acetylate conserved lysine amino acids on histone proteins by transferring an acetyl group from acetyl CoA to form ε-N-acetyl lysine....
s (HATs). This means that in addition to its role as a classical transcription factor, Myc also functions to regulate global chromatin structure by regulating histone acetylation both in gene-rich regions and at sites far from any known gene.
A mutated version of Myc is found in many cancers, which causes Myc to be constitutively
Glossary of gene expression terms
See also: gene expression, List of Glossaries, List of Natural Sciences Glossaries-A:*Activator - protein that binds to an enhancer and activates transcription from nearby promoter....
(persistently) expressed. This leads to the unregulated expression of many genes, some of which are involved in cell proliferation and results in the formation of cancer
Cancer
Cancer , known medically as a malignant neoplasm, is a large group of different diseases, all involving unregulated cell growth. In cancer, cells divide and grow uncontrollably, forming malignant tumors, and invade nearby parts of the body. The cancer may also spread to more distant parts of the...
. A common translocation
Translocation
Translocation may refer to:* Chromosomal translocation, in genetics* Translocation in plants, transport of food or pesticides through phloem or xylem* Protein translocation or protein targeting, a process in protein biosynthesis...
involving Myc is t(8;14) which is critical to the development of most cases of Burkitt's Lymphoma
Burkitt's lymphoma
Burkitt's lymphoma is a cancer of the lymphatic system...
. A recent study demonstrated that temporary inhibition of Myc selectively kills mouse lung cancer cells, making it a potential cancer drug target.
Discovery
Myc gene was first discovered in Burkitt's lymphomaBurkitt's lymphoma
Burkitt's lymphoma is a cancer of the lymphatic system...
patients. In Burkitt's lymphoma, cancer cells show chromosomal translocation
Chromosomal translocation
In genetics, a chromosome translocation is a chromosome abnormality caused by rearrangement of parts between nonhomologous chromosomes. A gene fusion may be created when the translocation joins two otherwise separated genes, the occurrence of which is common in cancer. It is detected on...
s, in which Chromosome 8 is frequently involved. Cloning the break-point of the fusion chromosomes revealed a gene that was similar to myelocytomatosis viral oncogene (v-Myc). Thus, the newfound cellular gene was named c-Myc.
Structure
Myc protein belongs to Myc family of transcription factors, which also includes N-Myc and L-Myc genes. Myc family of transcription factors contain bHLH/LZ (basic Helix-Loop-Helix Leucine ZipperLeucine zipper
A leucine zipper, aka leucine scissors, is a common three-dimensional structural motif in proteins. These motifs are usually found as part of a DNA-binding domain in various transcription factors, and are therefore involved in regulating gene expression...
) domain. Myc protein, through its bHLH domain can bind to DNA
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid is a nucleic acid that contains the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms . The DNA segments that carry this genetic information are called genes, but other DNA sequences have structural purposes, or are involved in...
, while the leucine zipper domain allows the dimerization with its partner Max, another bHLH transcription factor.
Myc mRNA contains an IRES (internal ribosome entry site) that allows the RNA to be translated into protein when 5' cap
5' cap
The 5' cap is a specially altered nucleotide on the 5' end of precursor messenger RNA and some other primary RNA transcripts as found in eukaryotes. The process of 5' capping is vital to creating mature messenger RNA, which is then able to undergo translation...
-dependent translation is inhibited, such as during viral infection.
Molecular Function
Myc protein is a transcription factorTranscription factor
In molecular biology and genetics, a transcription factor is a protein that binds to specific DNA sequences, thereby controlling the flow of genetic information from DNA to mRNA...
that activates expression of a great number of genes through binding on consensus sequence
Consensus sequence
In molecular biology and bioinformatics, consensus sequence refers to the most common nucleotide or amino acid at a particular position after multiple sequences are aligned. A consensus sequence is a way of representing the results of a multiple sequence alignment, where related sequences are...
s (Enhancer Box sequences (E-boxes)) and recruiting histone acetyltransferase
Histone acetyltransferase
Histone acetyltransferases are enzymes that acetylate conserved lysine amino acids on histone proteins by transferring an acetyl group from acetyl CoA to form ε-N-acetyl lysine....
s (HATs). It can also act as a transcriptional repressor. By binding Miz-1 transcription factor and displacing the p300
EP300
E1A binding protein p300 also known as EP300 or p300 is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the EP300 gene. This protein regulates the activity of many genes in tissues throughout the body...
co-activator, it inhibits expression of Miz-1 target genes. In addition, myc has a direct role in the control of DNA replication.
Myc is activated upon various mitogenic signal
Mitogen
A mitogen is a chemical substance that encourages a cell to commence cell division, triggering mitosis. A mitogen is usually some form of a protein.Mitogenesis is the induction of mitosis, typically via a mitogen....
s such as Wnt, Shh
Sonic hedgehog
Sonic hedgehog homolog is one of three proteins in the mammalian signaling pathway family called hedgehog, the others being desert hedgehog and Indian hedgehog . SHH is the best studied ligand of the hedgehog signaling pathway. It plays a key role in regulating vertebrate organogenesis, such as...
and EGF
Epidermal growth factor
Epidermal growth factor or EGF is a growth factor that plays an important role in the regulation of cell growth, proliferation, and differentiation by binding to its receptor EGFR...
(via the MAPK/ERK pathway
MAPK/ERK pathway
The MAPK/ERK pathway is a chain of proteins in the cell that communicates a signal from a receptor on the surface of the cell to the DNA in the nucleus of the cell. The signal starts when a growth factor binds to the receptor on the cell surface and ends when the DNA in the nucleus expresses a...
).
By modifying the expression of its target genes, Myc activation results in numerous biological effects. The first to be discovered was its capability to drive cell proliferation (upregulates cyclins, downregulates p21), but it also plays a very important role in regulating cell growth
Cell growth
The term cell growth is used in the contexts of cell development and cell division . When used in the context of cell division, it refers to growth of cell populations, where one cell grows and divides to produce two "daughter cells"...
(upregulates ribosomal RNA and proteins), apoptosis
Apoptosis
Apoptosis is the process of programmed cell death that may occur in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes and death. These changes include blebbing, cell shrinkage, nuclear fragmentation, chromatin condensation, and chromosomal DNA fragmentation...
(downregulates Bcl-2
Bcl-2
Bcl-2 is the founding member of the Bcl-2 family of apoptosis regulator proteins encoded by the BCL2 gene. Bcl-2 derives its name from B-cell lymphoma 2, as it is the second member of a range of proteins initially described in chromosomal translocations involving chromosomes 14 and 18 in...
), differentiation and stem cell
Stem cell
This article is about the cell type. For the medical therapy, see Stem Cell TreatmentsStem cells are biological cells found in all multicellular organisms, that can divide and differentiate into diverse specialized cell types and can self-renew to produce more stem cells...
self-renewal. Myc is a very strong proto-oncogene and it is very often found to be upregulated in many types of cancers. Myc overexpression stimulates gene amplification, presumably through DNA over-replication.
Animal Models
During the discovery of Myc gene, it was realized that chromosomes that translocate to Chromosome 8 contained immunoglobulin genes at the break-point. EnhancersEnhancer (genetics)
In genetics, an enhancer is a short region of DNA that can be bound with proteins to enhance transcription levels of genes in a gene cluster...
that normally drive expression of immunoglobin genes now lead to overexpression of Myc proto-oncogene in lymphoma cells. To study the mechanism of tumorigenesis in Burkitt's lymphoma by mimicking expression pattern of Myc in these cancer cells, transgenic mouse models were developed. Myc gene placed under the control of IgM
IGM
IGM as an acronym or abbreviation can refer to:* Immunoglobulin M , the primary antibody against A and B antigens on red blood cells* International Grandmaster, a chess ranking* intergalactic medium* Intragroup medium - see: Intracluster medium...
heavy chain enhancer in transgenic mice gives rise to mainly lymphomas. Later on, in order to study effects of Myc in other types of cancer, transgenic mice that overexpress Myc in different tissues (liver, breast) were also made. In all these mouse models overexpression of Myc causes tumorigenesis, illustrating the potency of Myc oncogene.
Interactions
Myc has been shown to interactProtein-protein interaction
Protein–protein interactions occur when two or more proteins bind together, often to carry out their biological function. Many of the most important molecular processes in the cell such as DNA replication are carried out by large molecular machines that are built from a large number of protein...
with NMI, NFYC
NFYC
Nuclear transcription factor Y subunit gamma is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NFYC gene.- Function :The protein encoded by this gene is one subunit of a trimeric complex, forming a highly conserved transcription factor that binds with high specificity to CCAAT motifs in the promoter...
, NFYB
NFYB
Nuclear transcription factor Y subunit beta is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NFYB gene.-Interactions:NFYB has been shown to interact with CCAAT/enhancer binding protein zeta, CNTN2, TATA binding protein and Myc.-Further reading:...
, Cyclin T1, RuvB-like 1
RuvB-like 1
RuvB-like 1 , also known as RUVBL1 and TIP49, is a human gene. RUVBL1 can form a hexamer. The hexamer can form a dodecamer with RUVBL2 protein.-Interactions:...
, GTF2I
GTF2I
General transcription factor II-I is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GTF2I gene.-Interactions:GTF2I has been shown to interact with USF1 , Histone deacetylase 2, PRKG1, Myc, MAPK3, HDAC3, Serum response factor and Bruton's tyrosine kinase.-Further reading:...
, BRCA1
BRCA1
BRCA1 is a human caretaker gene that produces a protein called breast cancer type 1 susceptibility protein, responsible for repairing DNA. The first evidence for the existence of the gene was provided by the King laboratory at UC Berkeley in 1990...
, T-cell lymphoma invasion and metastasis-inducing protein 1
T-cell lymphoma invasion and metastasis-inducing protein 1
T-cell lymphoma invasion and metastasis-inducing protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TIAM1 gene.- Structure :TIAM1 is tightly associate with BAIAP2 as a subunit...
, ACTL6A
ACTL6A
Actin-like protein 6A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ACTL6A gene.-Interactions:ACTL6A has been shown to interact with SMARCA2, Myc, Transformation/transcription domain-associated protein, RuvB-like 1 and SMARCA4.-Further reading:...
, PCAF
PCAF
P300/CBP-associated factor , also known as K acetyltransferase 2B , is a human gene and trancriptional coactivator associated with p53.-Structure:...
, MYCBP2
MYCBP2
Probable E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase MYCBP2 also known as myc-binding protein 2 or protein associates with myc is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MYCBP2 gene....
, MAPK8
MAPK8
Mitogen-activated protein kinase 8 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MAPK8 gene.-Interactions:MAPK8 has been shown to interact with SPIB, DUSP1, Activating transcription factor 2, SH3BP5, GSTP1, MAPK8IP1, MAP2K7, CRK, MAP2K4, DUSP22, Myc, MAP3K2, DUSP10, REL, MAPK8IP3, IRS1, MAP3K1 and...
, Bcl-2
Bcl-2
Bcl-2 is the founding member of the Bcl-2 family of apoptosis regulator proteins encoded by the BCL2 gene. Bcl-2 derives its name from B-cell lymphoma 2, as it is the second member of a range of proteins initially described in chromosomal translocations involving chromosomes 14 and 18 in...
, Transcription initiation protein SPT3 homolog
Transcription initiation protein SPT3 homolog
Transcription initiation protein SPT3 homolog is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SUPT3H gene.-Interactions:Transcription initiation protein SPT3 homolog has been shown to interact with GCN5L2, TAF6L, TADA3L, TAF5L, SF3B3, SUPT7L, Myc, TAF9, Transformation/transcription domain-associated...
, SAP130
SAP130
Histone deacetylase complex subunit SAP130 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the SAP130 gene.-Interactions:SAP130 has been shown to interact with CSN1S1, SIN3A, Myc, Von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor and CUL2.-Further reading:...
, DNMT3A
DNMT3A
DNA -methyltransferase 3A is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the DNMT3A gene.-Interactions:DNMT3A has been shown to interact with ZNF238, HDAC1, Myc, Protein inhibitor of activated STAT2, DNMT1, DNMT3B, PIAS1, UBE2I and SUV39H1....
, Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 3
Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 3
Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 3 also known as SMAD family member 3 or SMAD3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SMAD3 gene. SMAD3 is a member of the SMAD family of proteins.The human SMAD3 gene is located on chromosome 15...
, MAX
MAX (gene)
Protein max also known as myc-associated factor X is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MAX gene.- Function :Protein max is a member of the basic helix-loop-helix leucine zipper family of transcription factors. It is able to form homodimers and heterodimers with other family members, which...
, Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 2
Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 2
Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 2 also known as SMAD family member 2 or SMAD2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SMAD2 gene. MAD homolog 2 belongs to the SMAD, a family of proteins similar to the gene products of the Drosophila gene 'mothers against decapentaplegic' and the C....
, MYCBP
MYCBP
C-Myc-binding protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MYCBP gene.-Interactions:MYCBP has been shown to interact with AKAP1, C3orf15 and Myc.-Further reading:...
, HTATIP
HTATIP
Histone acetyltransferase KAT5 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the KAT5 gene.- Function :The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the MYST family of histone acetyl transferases and was originally isolated as an HIV-1 TAT-interactive protein...
, ZBTB17
ZBTB17
Zinc finger and BTB domain-containing protein 17 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ZBTB17 gene.-Interactions:ZBTB17 has been shown to interact with TOPBP1, Host cell factor C1 and Myc....
, Transformation/transcription domain-associated protein
Transformation/transcription domain-associated protein
Transformation/transcription domain-associated protein, also known asTRRAP, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TRRAP gene. TRRAP belongs to the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-related kinase protein family.- Function :...
, TADA2L
TADA2L
Transcriptional adapter 2-alpha is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TADA2A gene.-Interactions:TADA2L has been shown to interact with GCN5L2, TADA3L and Myc.-Further reading:...
, PFDN5
PFDN5
Prefoldin subunit 5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PFDN5 gene.-Further reading:...
, MAPK1
MAPK1
Mitogen-activated protein kinase 1, also known as MAPK1, p42MAPK, and ERK2, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MAPK1 gene.- Function :The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the MAP kinase family...
, TFAP2A
TFAP2A
Transcription factor AP-2 alpha , also known as TFAP2A, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TFAP2A gene.- Function :...
, P73
P73
p73 is a protein related to the p53 tumor protein. Because of its structural resemblance to p53, it has also been considered a tumor suppressor. It is involved in cell cycle regulation, and induction of apoptosis. Like p53, p73 is characterized by the presence of different isoforms of the protein...
, TAF9
TAF9
TAF9 RNA polymerase II, TATA box binding protein -associated factor, 32kDa, also known as TAF9, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the TAF9 gene.- Function :...
, YY1
YY1
Transcriptional repressor protein YY1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the YY1 gene.-Interactions:YY1 has been shown to interact with Histone deacetylase 2, FKBP3, ATF6, Myc, SAP30, EP300, HDAC3, NOTCH1 and RYBP....
, SMARCB1
SMARCB1
SWI/SNF-related matrix-associated actin-dependent regulator of chromatin subfamily B member 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SMARCB1 gene.-Interactions:...
, SMARCA4
SMARCA4
Transcription activator BRG1 also known as ATP-dependent helicase SMARCA4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SMARCA4 gene.- Function :...
, MLH1
MLH1
MutL homolog 1, colon cancer, nonpolyposis type 2 , also known as MLH1, is a human gene located on Chromosome 3. It is a gene commonly associated with hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer.It can also be associated with Turcot syndrome....
, EP400
EP400
E1A-binding protein p400 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EP400 gene.-Interactions:EP400 has been shown to interact with Transformation/transcription domain-associated protein, RuvB-like 1 and Myc.-Further reading:...
and let-7
Let-7 microRNA precursor
The Let-7 microRNA precursor was identified from a study of developmental timing in C. elegans, and was later shown to be part of a much larger class of non-coding RNAs termed microRNAs. miR-98 microRNA precursor from human is a let-7 family member. Let-7 miRNAs have now been predicted or...
.

Effects
A major effect of Myc is B cellB cell
B cells are lymphocytes that play a large role in the humoral immune response . The principal functions of B cells are to make antibodies against antigens, perform the role of antigen-presenting cells and eventually develop into memory B cells after activation by antigen interaction...
proliferation.
c-Myc induces AEG-1 or MTDH gene expression and in turn itself requires AEG-1 oncogene for its expression.

