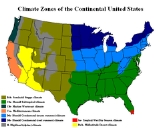
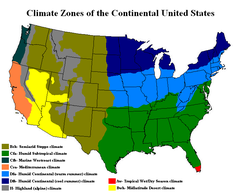
Climate of the United States
Encyclopedia
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
includes a wide variety of climate types due to its large size, range of geographic features, and non-contiguous arrangement. In the contiguous United States to the east of the 100th meridian
100th meridian west
The meridian 100° west of Greenwich is a line of longitude that extends from the North Pole across the Arctic Ocean, North America, the Pacific Ocean, the Southern Ocean, and Antarctica to the South Pole....
, the climate ranges from humid continental in the north to humid subtropical in the south. The southern tip of Florida
Florida
Florida is a state in the southeastern United States, located on the nation's Atlantic and Gulf coasts. It is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the north by Alabama and Georgia and to the east by the Atlantic Ocean. With a population of 18,801,310 as measured by the 2010 census, it...
is tropical. The Great Plains
Great Plains
The Great Plains are a broad expanse of flat land, much of it covered in prairie, steppe and grassland, which lies west of the Mississippi River and east of the Rocky Mountains in the United States and Canada. This area covers parts of the U.S...
west of the 100th meridian are semi-arid. Much of the Rocky Mountains
Rocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains are a major mountain range in western North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch more than from the northernmost part of British Columbia, in western Canada, to New Mexico, in the southwestern United States...
, the Sierra Nevada, and the Cascade Range
Cascade Range
The Cascade Range is a major mountain range of western North America, extending from southern British Columbia through Washington and Oregon to Northern California. It includes both non-volcanic mountains, such as the North Cascades, and the notable volcanoes known as the High Cascades...
are alpine. The climate is arid in the Great Basin
Great Basin
The Great Basin is the largest area of contiguous endorheic watersheds in North America and is noted for its arid conditions and Basin and Range topography that varies from the North American low point at Badwater Basin to the highest point of the contiguous United States, less than away at the...
, desert in the Southwest, Mediterranean
Mediterranean climate
A Mediterranean climate is the climate typical of most of the lands in the Mediterranean Basin, and is a particular variety of subtropical climate...
in coastal California
Coastal California
Coastal California refers to the coastal regions of the US state of California. The term is not primarily geographical as it also describes an area distinguished by sociological, economical and political attributes...
, and oceanic
Oceanic climate
An oceanic climate, also called marine west coast climate, maritime climate, Cascadian climate and British climate for Köppen climate classification Cfb and subtropical highland for Köppen Cfb or Cwb, is a type of climate typically found along the west coasts at the middle latitudes of some of the...
in coastal Oregon
Oregon
Oregon is a state in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States. It is located on the Pacific coast, with Washington to the north, California to the south, Nevada on the southeast and Idaho to the east. The Columbia and Snake rivers delineate much of Oregon's northern and eastern...
and Washington. The state of Alaska
Alaska
Alaska is the largest state in the United States by area. It is situated in the northwest extremity of the North American continent, with Canada to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the west and south, with Russia further west across the Bering Strait...
—on the northwestern corner of the North American continent—is largely subarctic, with an oceanic climate in its southern edge and a polar climate in the north. The archipelago state of Hawaii
Hawaii
Hawaii is the newest of the 50 U.S. states , and is the only U.S. state made up entirely of islands. It is the northernmost island group in Polynesia, occupying most of an archipelago in the central Pacific Ocean, southwest of the continental United States, southeast of Japan, and northeast of...
, in the middle of the Pacific Ocean, is tropical.
Extreme weather is not uncommon—the states bordering the Gulf of Mexico are prone to hurricanes, and tornado
Tornado
A tornado is a violent, dangerous, rotating column of air that is in contact with both the surface of the earth and a cumulonimbus cloud or, in rare cases, the base of a cumulus cloud. They are often referred to as a twister or a cyclone, although the word cyclone is used in meteorology in a wider...
es regularly occur in the area of the Midwest referred to as Tornado Alley
Tornado Alley
Tornado Alley is a colloquial and popular media term that most often refers to the area of the United States where tornadoes are most frequent. Although an official location is not defined, the area between the Rocky Mountains and Appalachian Mountains is usually associated with it.The areas...
. The United States has more tornadoes than the rest of the countries of the world combined.
Overview

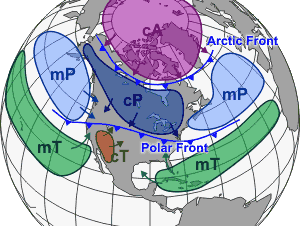
Weather
Weather is the state of the atmosphere, to the degree that it is hot or cold, wet or dry, calm or stormy, clear or cloudy. Most weather phenomena occur in the troposphere, just below the stratosphere. Weather refers, generally, to day-to-day temperature and precipitation activity, whereas climate...
in the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
is the polar jet stream
Jet stream
Jet streams are fast flowing, narrow air currents found in the atmospheres of some planets, including Earth. The main jet streams are located near the tropopause, the transition between the troposphere and the stratosphere . The major jet streams on Earth are westerly winds...
, which brings in large low pressure systems
Low pressure area
A low-pressure area, or "low", is a region where the atmospheric pressure at sea level is below that of surrounding locations. Low-pressure systems form under areas of wind divergence which occur in upper levels of the troposphere. The formation process of a low-pressure area is known as...
from the northern Pacific Ocean
Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest of the Earth's oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic in the north to the Southern Ocean in the south, bounded by Asia and Australia in the west, and the Americas in the east.At 165.2 million square kilometres in area, this largest division of the World...
. Once a Pacific cyclone moves over the Great Plains, uninterrupted flat land allows it to reorganize and can lead to major clashes of air masses. Sometimes during late winter
Winter
Winter is the coldest season of the year in temperate climates, between autumn and spring. At the winter solstice, the days are shortest and the nights are longest, with days lengthening as the season progresses after the solstice.-Meteorology:...
and spring these storms can combine with another low pressure system as they move up the East Coast
East Coast of the United States
The East Coast of the United States, also known as the Eastern Seaboard, refers to the easternmost coastal states in the United States, which touch the Atlantic Ocean and stretch up to Canada. The term includes the U.S...
and into the Atlantic Ocean
Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's oceanic divisions. With a total area of about , it covers approximately 20% of the Earth's surface and about 26% of its water surface area...
, where they intensify rapidly. These storms are known as Nor'easter
Nor'easter
A nor'easter is a type of macro-scale storm along the East Coast of the United States and Atlantic Canada, so named because the storm travels to the northeast from the south and the winds come from the northeast, especially in the coastal areas of the Northeastern United States and Atlantic Canada...
s and often bring widespread, heavy snow
Snow
Snow is a form of precipitation within the Earth's atmosphere in the form of crystalline water ice, consisting of a multitude of snowflakes that fall from clouds. Since snow is composed of small ice particles, it is a granular material. It has an open and therefore soft structure, unless packed by...
fall to the Mid-Atlantic
Mid-Atlantic States
The Mid-Atlantic states, also called middle Atlantic states or simply the mid Atlantic, form a region of the United States generally located between New England and the South...
and New England
New England
New England is a region in the northeastern corner of the United States consisting of the six states of Maine, New Hampshire, Vermont, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, and Connecticut...
. The uninterrupted flat grasslands of the Great Plains also leads to some of the most extreme climate swings in the world. Temperatures can rise or drop rapidly; winds can be extreme; and the flow of heat wave
Heat wave
A heat wave is a prolonged period of excessively hot weather, which may be accompanied by high humidity. There is no universal definition of a heat wave; the term is relative to the usual weather in the area...
s or Arctic air masses often advance uninterrupted through the plains.
The Great Basin
Great Basin
The Great Basin is the largest area of contiguous endorheic watersheds in North America and is noted for its arid conditions and Basin and Range topography that varies from the North American low point at Badwater Basin to the highest point of the contiguous United States, less than away at the...
and Columbia Plateau
Columbia Plateau
The Columbia Plateau is a geologic and geographic region that lies across parts of the U.S. states of Washington, Oregon, and Idaho. It is a wide flood basalt plateau between the Cascade Range and the Rocky Mountains, cut through by the Columbia River...
(the Intermontane Plateaus
Intermontane Plateaus
Physiographic regions of the U.S. InteriorSee:legendIn some places,high plateaus lie between the mountain ranges, for example,the plateau of Anatolia in Turkey and the plateau of Tibet.These are called "Intermontane plateaus"....
) are arid or semiarid regions that lie in the rain shadow of the Cascades and Sierra Nevada. Precipitation averages less than 15 inches (38 cm). The Southwest
Southwestern United States
The Southwestern United States is a region defined in different ways by different sources. Broad definitions include nearly a quarter of the United States, including Arizona, California, Colorado, Nevada, New Mexico, Oklahoma, Texas and Utah...
is a hot desert, with temperatures exceeding 100°F (38°C) for several weeks at a time in summer
Summer
Summer is the warmest of the four temperate seasons, between spring and autumn. At the summer solstice, the days are longest and the nights are shortest, with day-length decreasing as the season progresses after the solstice...
. The Southwest and the Great Basin are also affected by the monsoon
Monsoon
Monsoon is traditionally defined as a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation, but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with the asymmetric heating of land and sea...
from the Gulf of California
Gulf of California
The Gulf of California is a body of water that separates the Baja California Peninsula from the Mexican mainland...
from July-September, which brings localized but often severe thunderstorms to the region.
Precipitation
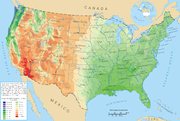
The characteristics of rainfall across the United States differ significantly across the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
and its possessions. Late summer and fall extratropical cyclone
Extratropical cyclone
Extratropical cyclones, sometimes called mid-latitude cyclones or wave cyclones, are a group of cyclones defined as synoptic scale low pressure weather systems that occur in the middle latitudes of the Earth having neither tropical nor polar characteristics, and are connected with fronts and...
s bring a majority of the precipitation which falls across western, southern, and southeast Alaska
Alaska
Alaska is the largest state in the United States by area. It is situated in the northwest extremity of the North American continent, with Canada to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the west and south, with Russia further west across the Bering Strait...
annually. During the fall, winter, and spring, Pacific storm systems bring most of Hawaii
Hawaii
Hawaii is the newest of the 50 U.S. states , and is the only U.S. state made up entirely of islands. It is the northernmost island group in Polynesia, occupying most of an archipelago in the central Pacific Ocean, southwest of the continental United States, southeast of Japan, and northeast of...
and the western United States much of their precipitation. Nor'easters moving up the East coast bring cold season precipitation to the Mid-Atlantic and New England states. Lake-effect snows add to precipitation potential downwind of the Great Lakes
Great Lakes
The Great Lakes are a collection of freshwater lakes located in northeastern North America, on the Canada – United States border. Consisting of Lakes Superior, Michigan, Huron, Erie, and Ontario, they form the largest group of freshwater lakes on Earth by total surface, coming in second by volume...
, as well as Great Salt Lake
Great Salt Lake
The Great Salt Lake, located in the northern part of the U.S. state of Utah, is the largest salt water lake in the western hemisphere, the fourth-largest terminal lake in the world. In an average year the lake covers an area of around , but the lake's size fluctuates substantially due to its...
and the Finger Lakes
Finger Lakes
The Finger Lakes are a pattern of lakes in the west-central section of Upstate New York in the United States. They are a popular tourist destination. The lakes are long and thin , each oriented roughly on a north-south axis. The two longest, Cayuga Lake and Seneca Lake, are among the deepest in...
during the cold season. The snow to liquid ratio across the contiguous United States is 13:1, meaning 13 inches (330.2 mm) of snow melts down to 1 inches (25.4 mm) of water. The El Niño-Southern Oscillation
El Niño-Southern Oscillation
El Niño/La Niña-Southern Oscillation, or ENSO, is a quasiperiodic climate pattern that occurs across the tropical Pacific Ocean roughly every five years...
affects the precipitation distribution, by altering rainfall patterns across the West, Midwest, the Southeast, and throughout the tropics.
During the summer, the Southwest monsoon
Monsoon
Monsoon is traditionally defined as a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation, but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with the asymmetric heating of land and sea...
combined with Gulf of California
Gulf of California
The Gulf of California is a body of water that separates the Baja California Peninsula from the Mexican mainland...
and Gulf of Mexico
Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico is a partially landlocked ocean basin largely surrounded by the North American continent and the island of Cuba. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United States, on the southwest and south by Mexico, and on the southeast by Cuba. In...
moisture moving around the subtropical ridge
Subtropical ridge
The subtropical ridge is a significant belt of high pressure situated around the latitudes of 30°N in the Northern Hemisphere and 30°S in the Southern Hemisphere. It is characterized by mostly calm winds, which acts to reduce air quality under its axis by causing fog overnight, and haze during...
in the Atlantic ocean bring the promise of afternoon and evening thunderstorms to the southern tier of the country as well as the Great Plains
Great Plains
The Great Plains are a broad expanse of flat land, much of it covered in prairie, steppe and grassland, which lies west of the Mississippi River and east of the Rocky Mountains in the United States and Canada. This area covers parts of the U.S...
. Equatorward of the subtropical ridge, tropical cyclone
Tropical cyclone
A tropical cyclone is a storm system characterized by a large low-pressure center and numerous thunderstorms that produce strong winds and heavy rain. Tropical cyclones strengthen when water evaporated from the ocean is released as the saturated air rises, resulting in condensation of water vapor...
s enhance precipitation across southern and eastern sections of the country, as well as Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico , officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico , is an unincorporated territory of the United States, located in the northeastern Caribbean, east of the Dominican Republic and west of both the United States Virgin Islands and the British Virgin Islands.Puerto Rico comprises an...
, the United States Virgin Islands
United States Virgin Islands
The Virgin Islands of the United States are a group of islands in the Caribbean that are an insular area of the United States. The islands are geographically part of the Virgin Islands archipelago and are located in the Leeward Islands of the Lesser Antilles.The U.S...
, the Northern Mariana Islands
Northern Mariana Islands
The Northern Mariana Islands, officially the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands , is a commonwealth in political union with the United States, occupying a strategic region of the western Pacific Ocean. It consists of 15 islands about three-quarters of the way from Hawaii to the Philippines...
, Guam
Guam
Guam is an organized, unincorporated territory of the United States located in the western Pacific Ocean. It is one of five U.S. territories with an established civilian government. Guam is listed as one of 16 Non-Self-Governing Territories by the Special Committee on Decolonization of the United...
, and American Samoa
American Samoa
American Samoa is an unincorporated territory of the United States located in the South Pacific Ocean, southeast of the sovereign state of Samoa...
. Over the top of the ridge, the jet stream brings a summer precipitation maximum to the Great Lakes
Great Lakes
The Great Lakes are a collection of freshwater lakes located in northeastern North America, on the Canada – United States border. Consisting of Lakes Superior, Michigan, Huron, Erie, and Ontario, they form the largest group of freshwater lakes on Earth by total surface, coming in second by volume...
. Large thunderstorm areas known as mesoscale convective complex
Mesoscale Convective Complex
A mesoscale convective complex is a unique kind of mesoscale convective system which is defined by characteristics observed in infrared satellite imagery. They are long-lived, nocturnal in formation and commonly contain heavy rainfall, wind, hail, lightning and possibly tornadoes.-Size:A...
es move through the Plains, Midwest, and Great Lakes during the warm season, contributing up to 10% of the annual precipitation to the region.
Extremes
Tundra
In physical geography, tundra is a biome where the tree growth is hindered by low temperatures and short growing seasons. The term tundra comes through Russian тундра from the Kildin Sami word tūndâr "uplands," "treeless mountain tract." There are three types of tundra: Arctic tundra, alpine...
and arctic
Arctic
The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost...
conditions predominate, and the temperature has fallen as low as -80 °F. On the other end of the spectrum, Death Valley, California
Death Valley National Park
Death Valley National Park is a national park in the U.S. states of California and Nevada located east of the Sierra Nevada in the arid Great Basin of the United States. The park protects the northwest corner of the Mojave Desert and contains a diverse desert environment of salt-flats, sand dunes,...
once reached 134 °F (56.7 °C), the second-highest temperature ever recorded on Earth.
On average, the mountains of the western states receive the highest levels of snowfall on Earth. The greatest annual snowfall level is at Mount Rainier
Mount Rainier
Mount Rainier is a massive stratovolcano located southeast of Seattle in the state of Washington, United States. It is the most topographically prominent mountain in the contiguous United States and the Cascade Volcanic Arc, with a summit elevation of . Mt. Rainier is considered one of the most...
in Washington, at 692 inches (1,758 cm); the record there was 1122 inches (2,850 cm) in the winter of 1971–72. This record was broken by the Mt. Baker Ski Area in northwestern Washington which reported 1140 inches (2,896 cm) of snowfall for the 1998-99 snowfall season. Other places with significant snowfall outside the Cascade Range are the Wasatch Mountains, near the Great Salt Lake and the Sierra Nevada, near Lake Tahoe
Lake Tahoe
Lake Tahoe is a large freshwater lake in the Sierra Nevada of the United States. At a surface elevation of , it is located along the border between California and Nevada, west of Carson City. Lake Tahoe is the largest alpine lake in North America. Its depth is , making it the USA's second-deepest...
.
Along the coastal mountain ranges in the Pacific Northwest
Pacific Northwest
The Pacific Northwest is a region in northwestern North America, bounded by the Pacific Ocean to the west and, loosely, by the Rocky Mountains on the east. Definitions of the region vary and there is no commonly agreed upon boundary, even among Pacific Northwesterners. A common concept of the...
, rainfall is greater than anywhere else in the continental U.S., with Quinault Ranger Station in Washington having an average of 137 inches (3,480 mm). Hawaii receives even more, with 460 inches (11,684 mm) measured annually, on average, on Mount Waialeale
Mount Waialeale
Mount Waialeale at an elevation of , is a shield volcano and the second highest point on the island of Kauai in the Hawaiian Islands. Averaging more than of rain a year since 1912, with a record in 1982, its summit is one of the rainiest spots on earth....
, in Kauai
Kauai
Kauai or Kauai, known as Tauai in the ancient Kaua'i dialect, is geologically the oldest of the main Hawaiian Islands. With an area of , it is the fourth largest of the main islands in the Hawaiian archipelago, and the 21st largest island in the United States. Known also as the "Garden Isle",...
. The Mojave Desert
Mojave Desert
The Mojave Desert occupies a significant portion of southeastern California and smaller parts of central California, southern Nevada, southwestern Utah and northwestern Arizona, in the United States...
in the southwest is home to the driest locale in the U.S. Yuma, Arizona
Yuma, Arizona
Yuma is a city in and the county seat of Yuma County, Arizona, United States. It is located in the southwestern corner of the state, and the population of the city was 77,515 at the 2000 census, with a 2008 Census Bureau estimated population of 90,041....
, has an average of 2.63 inches (66.8 mm) of precipitation each year.
Natural disasters

Hawaii
Hawaii
Hawaii is the newest of the 50 U.S. states , and is the only U.S. state made up entirely of islands. It is the northernmost island group in Polynesia, occupying most of an archipelago in the central Pacific Ocean, southwest of the continental United States, southeast of Japan, and northeast of...
in the Pacific Ocean
Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest of the Earth's oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic in the north to the Southern Ocean in the south, bounded by Asia and Australia in the west, and the Americas in the east.At 165.2 million square kilometres in area, this largest division of the World...
. Particularly at risk are the central and southern Texas
Texas
Texas is the second largest U.S. state by both area and population, and the largest state by area in the contiguous United States.The name, based on the Caddo word "Tejas" meaning "friends" or "allies", was applied by the Spanish to the Caddo themselves and to the region of their settlement in...
coasts, the area from southeastern Louisiana
Louisiana
Louisiana is a state located in the southern region of the United States of America. Its capital is Baton Rouge and largest city is New Orleans. Louisiana is the only state in the U.S. with political subdivisions termed parishes, which are local governments equivalent to counties...
east to the Florida Panhandle
Florida Panhandle
The Florida Panhandle, an informal, unofficial term for the northwestern part of Florida, is a strip of land roughly 200 miles long and 50 to 100 miles wide , lying between Alabama on the north and the west, Georgia also on the north, and the Gulf of Mexico to the south. Its eastern boundary is...
, the east coast of Florida
Florida
Florida is a state in the southeastern United States, located on the nation's Atlantic and Gulf coasts. It is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the north by Alabama and Georgia and to the east by the Atlantic Ocean. With a population of 18,801,310 as measured by the 2010 census, it...
, and the Outer Banks
Outer Banks
The Outer Banks is a 200-mile long string of narrow barrier islands off the coast of North Carolina, beginning in the southeastern corner of Virginia Beach on the east coast of the United States....
of North Carolina
North Carolina
North Carolina is a state located in the southeastern United States. The state borders South Carolina and Georgia to the south, Tennessee to the west and Virginia to the north. North Carolina contains 100 counties. Its capital is Raleigh, and its largest city is Charlotte...
. Hurricane season runs from June 1 to November 30, with a peak from mid-August through early October. Some of the more devastating hurricanes have included the Galveston Hurricane of 1900
Galveston Hurricane of 1900
The Hurricane of 1900 made landfall on the city of Galveston in the U.S. state of Texas, on September 8, 1900.It had estimated winds of at landfall, making it a Category 4 storm on the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Scale...
, Hurricane Andrew
Hurricane Andrew
Hurricane Andrew was the third Category 5 hurricane to make landfall in the United States, after the Labor Day Hurricane of 1935 and Hurricane Camille in 1969. Andrew was the first named storm and only major hurricane of the otherwise inactive 1992 Atlantic hurricane season...
in 1992, and Hurricane Katrina
Hurricane Katrina
Hurricane Katrina of the 2005 Atlantic hurricane season was a powerful Atlantic hurricane. It is the costliest natural disaster, as well as one of the five deadliest hurricanes, in the history of the United States. Among recorded Atlantic hurricanes, it was the sixth strongest overall...
in 2005. The remnants of tropical cyclones from the Eastern Pacific also occasionally impact the southwestern United States, bringing sometimes heavy rainfall.

Tornado
A tornado is a violent, dangerous, rotating column of air that is in contact with both the surface of the earth and a cumulonimbus cloud or, in rare cases, the base of a cumulus cloud. They are often referred to as a twister or a cyclone, although the word cyclone is used in meteorology in a wider...
es are more common than anywhere else on Earth and touch down most commonly in the spring and summer. The strip of land from north Texas
Texas
Texas is the second largest U.S. state by both area and population, and the largest state by area in the contiguous United States.The name, based on the Caddo word "Tejas" meaning "friends" or "allies", was applied by the Spanish to the Caddo themselves and to the region of their settlement in...
north to Nebraska
Nebraska
Nebraska is a state on the Great Plains of the Midwestern United States. The state's capital is Lincoln and its largest city is Omaha, on the Missouri River....
and east into Southern Michigan
Southern Michigan
Southern Michigan is a loosely defined geographic area of the Lower Peninsula of the U.S. state of Michigan. Southern Michigan may be referred to as a sub-region or component area to the larger geographic regions of Central Michigan, West Michigan, and Southeast Michigan.Southern Michigan is a...
is known as Tornado Alley
Tornado Alley
Tornado Alley is a colloquial and popular media term that most often refers to the area of the United States where tornadoes are most frequent. Although an official location is not defined, the area between the Rocky Mountains and Appalachian Mountains is usually associated with it.The areas...
, where many houses have tornado shelters and many towns have tornado sirens.
The Appalachian region and the Midwest experience the worst floods. Widespread severe flooding is rare. Some exceptions include the Great Mississippi Flood of 1927
Great Mississippi Flood of 1927
The Great Mississippi Flood of 1927 was the most destructive river flood in the history of the United States.-Events:The flood began when heavy rains pounded the central basin of the Mississippi in the summer of 1926. By September, the Mississippi's tributaries in Kansas and Iowa were swollen to...
, the Great Flood of 1993
Great Flood of 1993
The Great Mississippi and Missouri Rivers Flood of 1993 occurred in the American Midwest, along the Mississippi and Missouri rivers and their tributaries, from April to October 1993. The flood was among the most costly and devastating to ever occur in the United States, with $15 billion in damages...
, and widespread flooding and mudslides caused by the 1982-1983 El Niño
Enso
Ensō is a Japanese word meaning "circle" and a concept strongly associated with Zen. Ensō is one of the most common subjects of Japanese calligraphy even though it is a symbol and not a character. It symbolizes the Absolute enlightenment, strength, elegance, the Universe, and the void; it can...
event in the western United States. Localized flooding can, however, occur anywhere, and mudslides from heavy rain can cause problems in any mountainous area, particularly the Southwest. The narrow canyons of many mountain areas in the west and severe thunderstorm activity during the monsoon
Monsoon
Monsoon is traditionally defined as a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation, but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with the asymmetric heating of land and sea...
season in summer leads to sometimes devastating flash flood
Flash flood
A flash flood is a rapid flooding of geomorphic low-lying areas—washes, rivers, dry lakes and basins. It may be caused by heavy rain associated with a storm, hurricane, or tropical storm or meltwater from ice or snow flowing over ice sheets or snowfields...
s as well, while Nor'easter snowstorms can bring activity to a halt throughout the Northeast (although heavy snowstorms can occur almost anywhere).
The Southwest has the worst droughts; one is thought to have lasted over 500 years and to have decimated the Anasazi people. Large stretches of desert shrub in the west can fuel the spread of wildfire
Wildfire
A wildfire is any uncontrolled fire in combustible vegetation that occurs in the countryside or a wilderness area. Other names such as brush fire, bushfire, forest fire, desert fire, grass fire, hill fire, squirrel fire, vegetation fire, veldfire, and wilkjjofire may be used to describe the same...
s. Although severe drought is rare, it has occasionally caused major problems, such as during the Dust Bowl
Dust Bowl
The Dust Bowl, or the Dirty Thirties, was a period of severe dust storms causing major ecological and agricultural damage to American and Canadian prairie lands from 1930 to 1936...
(1931–1942), which coincided with the Great Depression
Great Depression
The Great Depression was a severe worldwide economic depression in the decade preceding World War II. The timing of the Great Depression varied across nations, but in most countries it started in about 1929 and lasted until the late 1930s or early 1940s...
. Farmland failed throughout the Plains, entire regions were virtually depopulated, and dust storms ravaged the land. More recently, the western U.S. experienced widespread drought from 1999-2004.
Hurricanes - Sunspot theory
A 2010 report correlates low sunspotSunspot
Sunspots are temporary phenomena on the photosphere of the Sun that appear visibly as dark spots compared to surrounding regions. They are caused by intense magnetic activity, which inhibits convection by an effect comparable to the eddy current brake, forming areas of reduced surface temperature....
activity with high hurricane
Cyclone
In meteorology, a cyclone is an area of closed, circular fluid motion rotating in the same direction as the Earth. This is usually characterized by inward spiraling winds that rotate anticlockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and clockwise in the Southern Hemisphere of the Earth. Most large-scale...
activity. Analyzing historical data, there was a 25% chance of at least one hurricane striking the continental US during a peak sunspot year; a 64% chance during a low sunspot year. In June 2010, the hurricanes predictors in the US were not using this information.
See also
- Geography of the United StatesGeography of the United StatesThe United States is a country in the Western Hemisphere. It consists of forty-eight contiguous states in North America, Alaska, a peninsula which forms the northwestern most part of North America, and Hawaii, an archipelago in the Pacific Ocean. There are several United States territories in the...
- United States tropical cyclone rainfall climatologyUnited States tropical cyclone rainfall climatologyThe United States tropical cyclone rainfall climatology concerns the amount of precipitation, primarily in the form of rain, which occurs during tropical cyclones and their extratropical cyclone remnants across the United States...
- MeteorologyMeteorologyMeteorology is the interdisciplinary scientific study of the atmosphere. Studies in the field stretch back millennia, though significant progress in meteorology did not occur until the 18th century. The 19th century saw breakthroughs occur after observing networks developed across several countries...

